LC-MS/MS-Based Determination of Ambroxol in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid: Validation and Applicability in a Phase II Study on GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
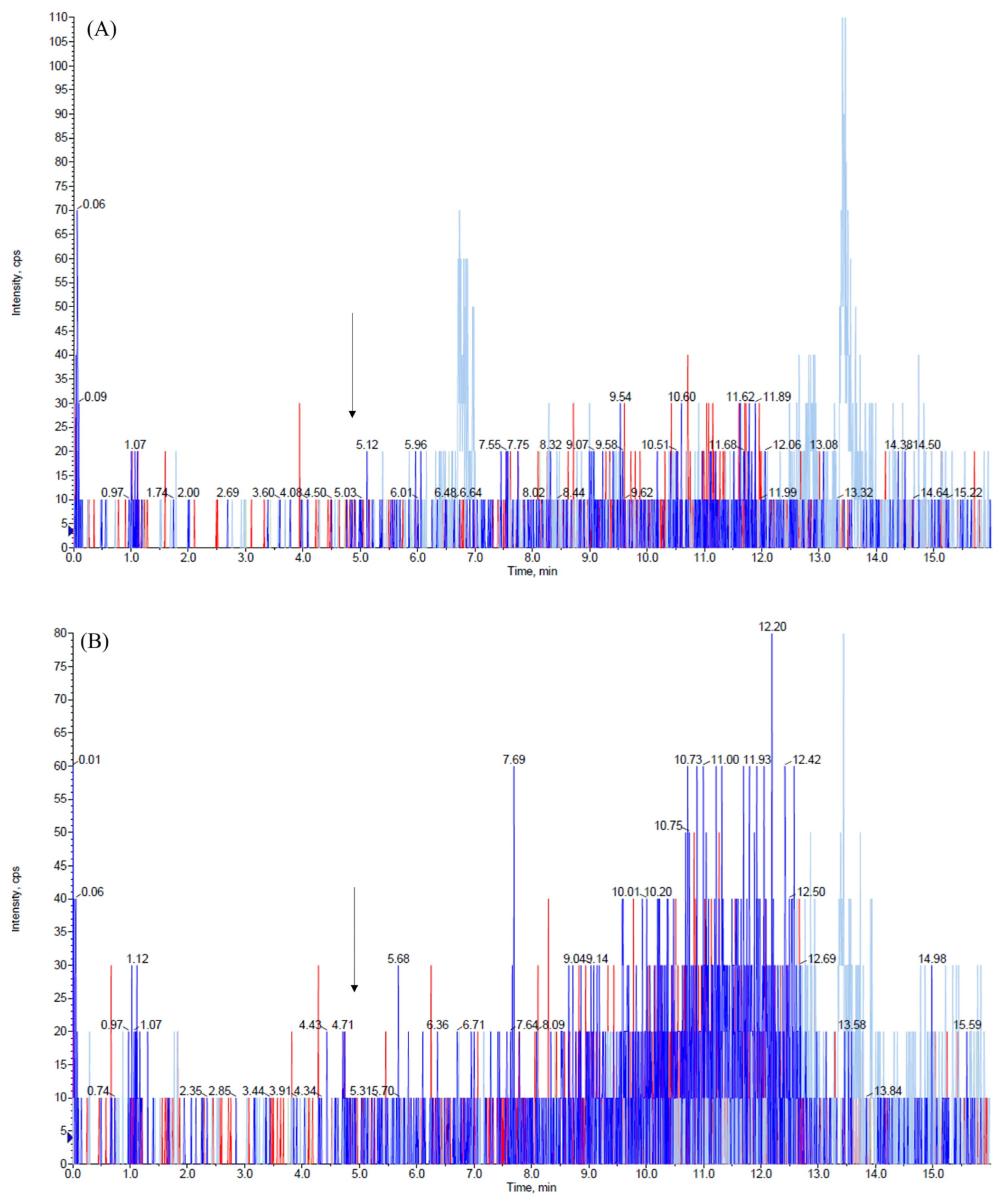
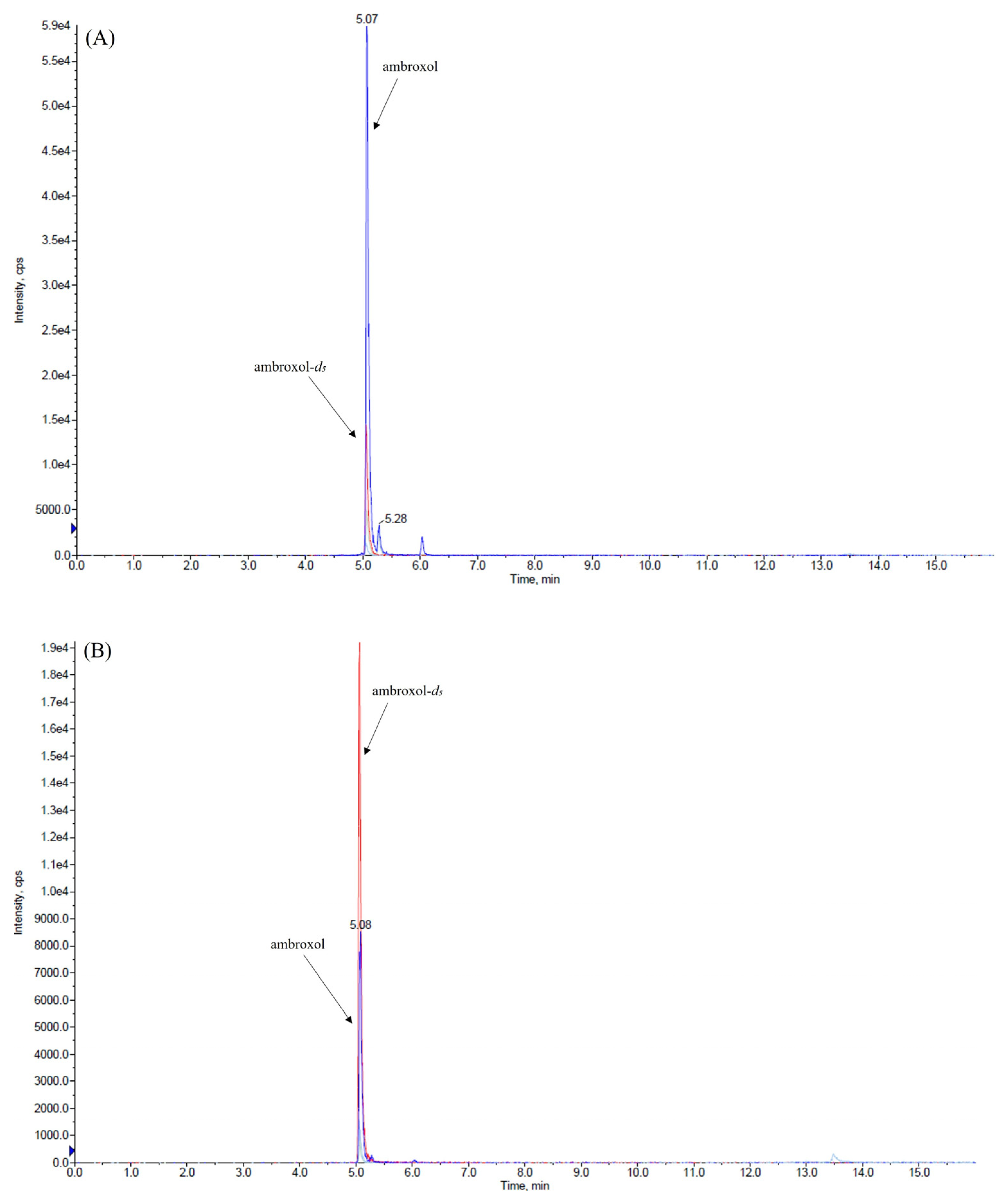
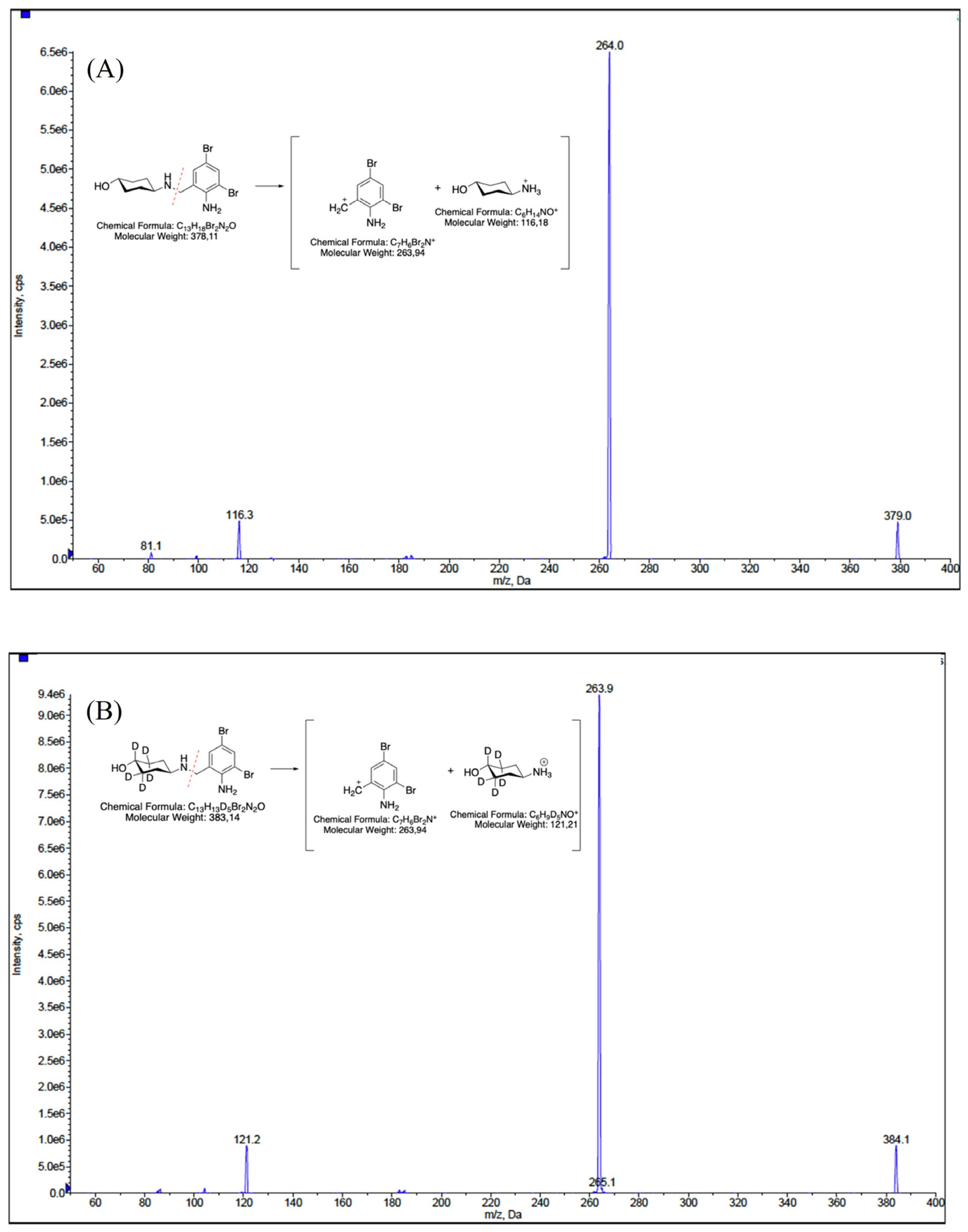
2.1. HPLC-MS/MS Parameters Optimization
2.2. Optimization of the Extraction Procedure
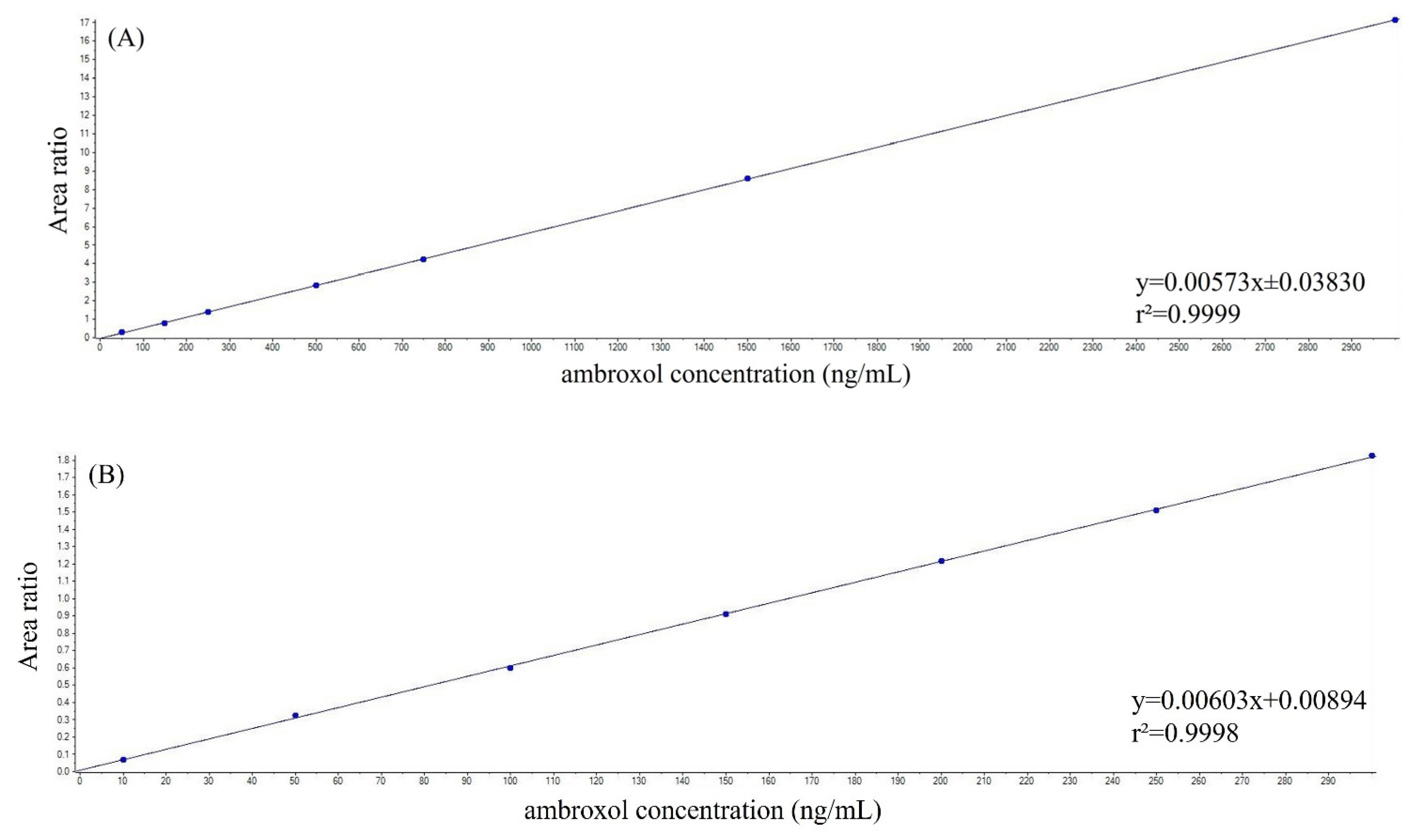
2.3. Assay Performance
2.4. Analysis of Patient Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Plasma and CSF Sample Preparation
4.3. LC-MS/MS System
4.4. HPLC and Mass Spectrometer Conditions
4.5. Calibration Standards, Quality Control and Unknown Samples
4.6. Method Validation
4.7. Statistical Analysis
4.8. Clinical Applicability in a Phase II Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| CV% | Coefficient of variation |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EMA | European Medicine Agency |
| ESI | Electrospray ionization |
| GD | Gaucher’s Disease |
| GCase | Glucocerebrosidase |
| IS | Internal standard |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LLOQ | Lower limit of quantitation |
| MDS | Parkinson and Movement Disorders Society |
| MRM | Multiple reaction monitoring |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| QC | Quality control |
| SPE | Solid-phase extraction |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Hruska, K.S.; LaMarca, M.E.; Scott, C.R.; Sidransky, E. Gaucher disease: Mutation and polymorphism spectrum in the glucocerebrosidase gene (GBA). Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan-Or, Z.; Liong, C.; Alcalay, R.N. GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease and Other Synucleinopathies. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalay, R.N.; Levy, O.A.; Waters, C.H.; Fahn, S.; Ford, B.; Kuo, S.H.; Mazzoni, P.; Pauciulo, M.W.; Nichols, W.C.; Gan-Or, Z.; et al. Glucocerebrosidase activity in Parkinson’s disease with and without GBA mutations. Brain 2015, 138, 2648–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, Y.V.; Liu, J.; Ruan, J.; Pacheco, J.; Zhang, X.; Abbasi, J.; Keutzer, J.; Mistry, P.K.; Chandra, S.S. Glucosylsphingosine Promotes alpha-Synuclein Pathology in Mutant GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 9617–9631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, N.; van Dussen, L.; Hollak, C.E.; Overkleeft, H.; Scheij, S.; Ghauharali, K.; van Breemen, M.J.; Ferraz, M.J.; Groener, J.E.; Maas, M.; et al. Elevated plasma glucosylsphingosine in Gaucher disease: Relation to phenotype, storage cell markers, and therapeutic response. Blood 2011, 118, e118–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, G.; Ghezzi, C.; Zangaglia, R.; Levandis, G.; Pacchetti, C.; Blandini, F. Ambroxol-induced rescue of defective glucocerebrosidase is associated with increased LIMP-2 and saposin C levels in GBA1 mutant Parkinson’s disease cells. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 82, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, S.; Smith, L.; Lee, K.; D’Souza, G.; Woodgate, P.; Elflein, J.; Hallqvist, J.; Toffoli, M.; Streeter, A.; Hosking, J.; et al. Ambroxol for the Treatment of Patients with Parkinson Disease with and Without Glucocerebrosidase Gene Mutations: A Nonrandomized, Noncontrolled Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Wang, X.; Di, X.; Liu, Y.; Zang, Y.; Ma, D.; Liu, Y.; Di, X. Quantitative Detection of Ambroxol in Human Plasma Using HPLC-APCI-MS/MS: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study. Anal. Sci. 2017, 33, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, G.; Zhong, D. Quantification of the major metabolites of bromhexine in human plasma using RRLC-MS/MS and its application to pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Xu, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, A.; Guo, Q. Rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of ambroxol in human plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, T.; Zhao, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, L.; Shi, X.; Michael, M.; Ding, L. Pharmacokinetics and safety of salbutamol/ambroxol fixed-dose combination granules in healthy Chinese subjects. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 56, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, T.; Zhao, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, L.; Shi, X.; Ding, L. Investigation of a potential drug-drug interaction between salbutamol and ambroxol and bioequivalence of a new fixed-dose combination containing these two drugs in healthy Chinese subjects. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 56, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Hou, L.; Chen, L.; Fan, J. Bioequivalence assessment of ambroxol orally-disintegrating tablet after a single oral-dose administration to healthy volunteers. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 54, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Song, L.X.; Jiang, N.; Xu, X.T.; Di, X.H.; Zhang, M. Pharmacokinetics of ambroxol and clenbuterol tablets in healthy Chinese volunteers. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 18744–18750. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ding, X.; Huang, C.; Miao, L. Simultaneous determination of ambroxol and salbutamol in human plasma by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, A.; Hang, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Ding, L.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, X. Simultaneous determination of amoxicillin and ambroxol in human plasma by LC-MS/MS: Validation and application to pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, T.J.; Zhang, M.; Song, M.; Shen, J.P.; Zhang, Y.D. Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of roxithromycin and ambroxol hydrochloride in human plasma by LC-MS/MS. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 382, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yoo, J.Y.; Han, S.B.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.R. Determination of ambroxol in human plasma using LC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 32, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Ding, L.; Cao, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhong, S. A sensitive LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of amoxicillin and ambroxol in human plasma with segmental monitoring. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, M.; Sun, L.; Li, W.; Liu, Q. A simple LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of cilostazol and ambroxol in Sprague-Dawley rat plasma and its application to drug-drug pharmacokinetic interaction study following oral delivery in rats. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1179, 122766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Wang, F.; Gao, W.; Li, H. Determination of ambroxol in human plasma by high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/ESI). J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 853, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci, F.; Avenali, M.; De Micco, R.; Fusar Poli, M.; Cerri, S.; Stanziano, M.; Bacila, A.; Cuconato, G.; Franco, V.; Franciotta, D.; et al. Ambroxol as a disease-modifying treatment to reduce the risk of cognitive impairment in GBA-associated Parkinson’s disease: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial. The AMBITIOUS study protocol. BMJ Neurol. Open 2023, 5, e000535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA. ICH Guideline M10 on Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-guideline-m10-bioanalytical-method-validation-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2024).
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, B.; Grabli, D.; Bernard, B.; Czernecki, V.; Goldman, J.G.; Stebbins, G.; Dubois, B.; Goetz, C.G. Clinical validation of Movement Disorder Society-recommended diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease with dementia. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, M.; Aarsland, D.; Brown, R.; Burn, D.J.; Duyckaerts, C.; Mizuno, Y.; Broe, G.A.; Cummings, J.; Dickson, D.W.; Gauthier, S.; et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia associated with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1689–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | LLOQ 50 ng/mL | Low QC 100 ng/mL | Medium QC 950 ng/mL | High QC 2500 ng/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-day precision and accuracy (n = 5) | ||||
| Measured concentration (ng/mL) | 48.3 ± 5.4 | 96.5 ± 9.0 | 915.0 ± 107.8 | 2246.4 ± 106.5 |
| Precision (CV%) | 11.2 | 9.4 | 11.8 | 4.7 |
| Accuracy (%) | 96.6 | 96.5 | 96.3 | 89.9 |
| Inter-day precision and accuracy (n = 15) | ||||
| Measured concentration (ng/mL) | 51.5 ± 4.5 | 100.6 ± 7.4 | 943.4 ± 72.5 | 2363.9 ± 128.6 |
| Precision (CV%) | 8.8 | 7.4 | 7.7 | 5.4 |
| Accuracy (%) | 103.1 | 100.6 | 99.3 | 94.6 |
| Parameter | LLOQ 10 ng/mL | Low QC 25 ng/mL | Medium QC 125 ng/mL | High QC 275 ng/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-day precision and accuracy (n = 5) | ||||
| Measured concentration (ng/mL) | 10.8 ± 1.1 | 25.3 ± 1.1 | 123.0 ± 13.9 | 265.0 ± 26.4 |
| Precision (CV%) | 10.1 | 4.2 | 11.3 | 10.0 |
| Accuracy (%) | 107.8 | 101.4 | 98.4 | 96.3 |
| Inter-day precision and accuracy (n = 15) | ||||
| Measured concentration (ng/mL) | 9.7 ± 1.1 | 24.4 ± 1.3 | 129.2 ± 9.4 | 278.4 ± 19.0 |
| Precision (CV%) | 11.0 | 5.3 | 7.3 | 6.8 |
| Accuracy (%) | 97.1 | 97.5 | 103.3 | 101.2 |
| Stability Condition | Low QC 100 ng/mL | High QC 2500 ng/mL |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh samples (ng/mL) | 102.9 ± 6.5 | 2452.0 ± 70.3 |
| Precision (CV%) | 6.4 | 2.9 |
| Accuracy (%) | 102.9 | 98.1 |
| 24 h at room temperature (ng/mL) | 100.7 ± 2.7 | 2403.8 ± 84.2 |
| Precision (CV%) | 2.7 | 3.5 |
| Accuracy (%) | 100.7 | 96.2 |
| Three freeze–thaw cycles (ng/mL) | 99.3 ± 6.5 | 2407.9 ± 44.5 |
| Precision (CV%) | 6.6 | 1.8 |
| Accuracy (%) | 99.3 | 96.3 |
| 48 h at room temperature in autosampler | 102.1 ± 6.5 | 2471.3 ± 75.6 |
| Precision (CV%) | 6.4 | 3.1 |
| Accuracy (%) | 102.1 | 98.9 |
| Stability Condition | Low QC 25 ng/mL | High QC 275 ng/mL |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh samples (ng/mL) | 26.6 ± 1.1 | 268.6 ± 12.0 |
| Precision (CV%) | 4.3 | 4.5 |
| Accuracy (%) | 106.4 | 97.7 |
| 24 h at room temperature (ng/mL) | 26.0 ± 1.3 | 254.8 ± 5.6 |
| Precision (CV%) | 4.8 | 2.2 |
| Accuracy (%) | 104.2 | 92.7 |
| Three freeze–thaw cycles (ng/mL) | 25.3 ± 0.3 | 270.1 ± 7.6 |
| Precision (CV%) | 1.3 | 2.8 |
| Accuracy (%) | 101.3 | 98.2 |
| 48 h at room temperature in autosampler | 27.1 ± 0.5 | 270.3 ± 4.9 |
| Precision (CV%) | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| Accuracy (%) | 108.3 | 98.3 |
| Stability Condition | Low QC 100 ng/mL | High QC 2500 ng/mL |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh samples (ng/mL) | 110.9 ± 4.2 | 2341.8 ± 31.9 |
| Precision (CV%) | 3.8 | 1.4 |
| Accuracy (%) | 110.9 | 93.7 |
| 15 days at −20 °C (ng/mL) | 109.5 ± 4.3 | 2206.7 ± 112.6 |
| Precision (CV%) | 4.0 | 5.1 |
| Accuracy (%) | 109.5 | 88.3 |
| Stability Condition | Low QC 25 ng/mL | High QC 275 ng/mL |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh samples (ng/mL) | 23.8 ± 1.5 | 262.6 ± 22.9 |
| Precision (CV%) | 6.2 | 8.7 |
| Accuracy (%) | 95.3 | 95.5 |
| 15 days at −20 °C (ng/mL) | 22.5 ± 1.2 | 246.2 ± 6.7 |
| Precision (CV%) | 5.4 | 2.7 |
| Accuracy (%) | 89.9 | 89.5 |
| Stability Condition | Low QC 25 ng/mL | High QC 275 ng/mL |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh samples (ng/mL) | 23.9 ± 1.7 | 254.9 ± 4.4 |
| Precision (CV%) | 7.1 | 1.7 |
| Accuracy (%) | 95.4 | 92.7 |
| 42 days at −20 °C (ng/mL) | 22.2 ± 0.6 | 244.7 ± 6.7 |
| Precision (CV%) | 2.9 | 2.7 |
| Accuracy (%) | 88.8 | 89.0 |
| Stability Condition | Low QC 100 ng/mL | High QC 2500 ng/mL |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh samples (ng/mL) | 96.6 ± 2.5 | 2393.4 ± 60.3 |
| Precision (CV%) | 2.6 | 2.5 |
| Accuracy (%) | 96.6 | 95.7 |
| 42 days at −80 °C (ng/mL) | 93.5 ± 5.4 | 2354.5 ± 34.9 |
| Precision (CV%) | 5.8 | 1.5 |
| Accuracy (%) | 93.5 | 94.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco, V.; Palmisani, M.; Colucci, F.; De Micco, R.; Aloisio, S.; Cazzaniga, F.; Cerri, S.; Crema, F.; Dattrino, F.; Garavaglia, B.; et al. LC-MS/MS-Based Determination of Ambroxol in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid: Validation and Applicability in a Phase II Study on GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136094
Franco V, Palmisani M, Colucci F, De Micco R, Aloisio S, Cazzaniga F, Cerri S, Crema F, Dattrino F, Garavaglia B, et al. LC-MS/MS-Based Determination of Ambroxol in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid: Validation and Applicability in a Phase II Study on GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136094
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco, Valentina, Michela Palmisani, Fabiana Colucci, Rosa De Micco, Simone Aloisio, Federico Cazzaniga, Silvia Cerri, Francesca Crema, Francesca Dattrino, Barbara Garavaglia, and et al. 2025. "LC-MS/MS-Based Determination of Ambroxol in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid: Validation and Applicability in a Phase II Study on GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136094
APA StyleFranco, V., Palmisani, M., Colucci, F., De Micco, R., Aloisio, S., Cazzaniga, F., Cerri, S., Crema, F., Dattrino, F., Garavaglia, B., Gastaldi, M., Mitrotti, P., Moda, F., Rota, P., Stiuso, R., Tassorelli, C., Eleopra, R., Tessitore, A., Valente, E. M., ... Cilia, R. (2025). LC-MS/MS-Based Determination of Ambroxol in Human Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid: Validation and Applicability in a Phase II Study on GBA-Associated Parkinson’s Disease Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136094









