Therapeutic Potential of CHCHD2 in Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: Mechanistic Insights into Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Defense in HK2 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
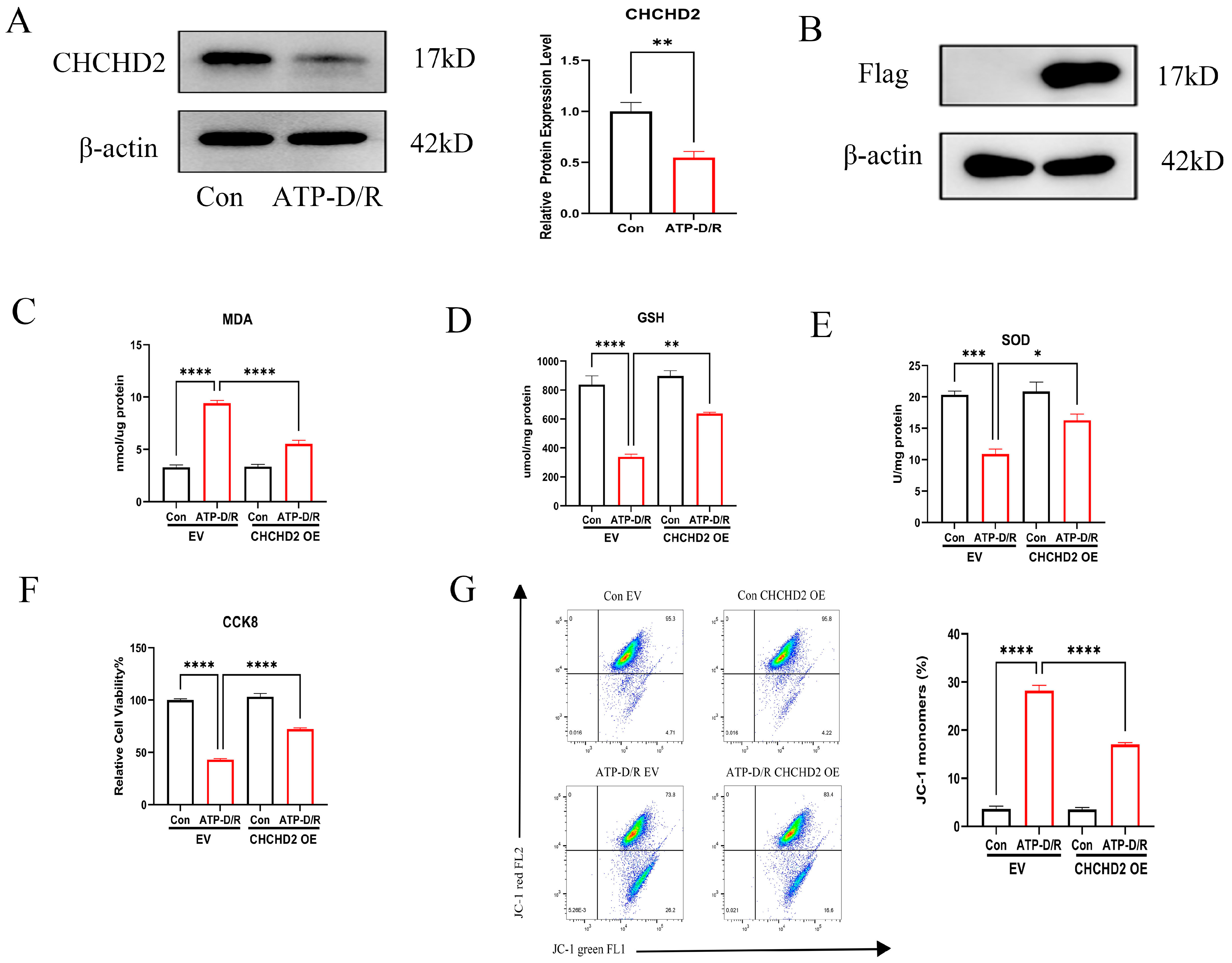
2.1. CCCP Toxicity Experiment and ATP-D/R Oxidative Stress Assessment
2.2. Effects of CHCHD2 Overexpression on Cellular Oxidative Stress Markers
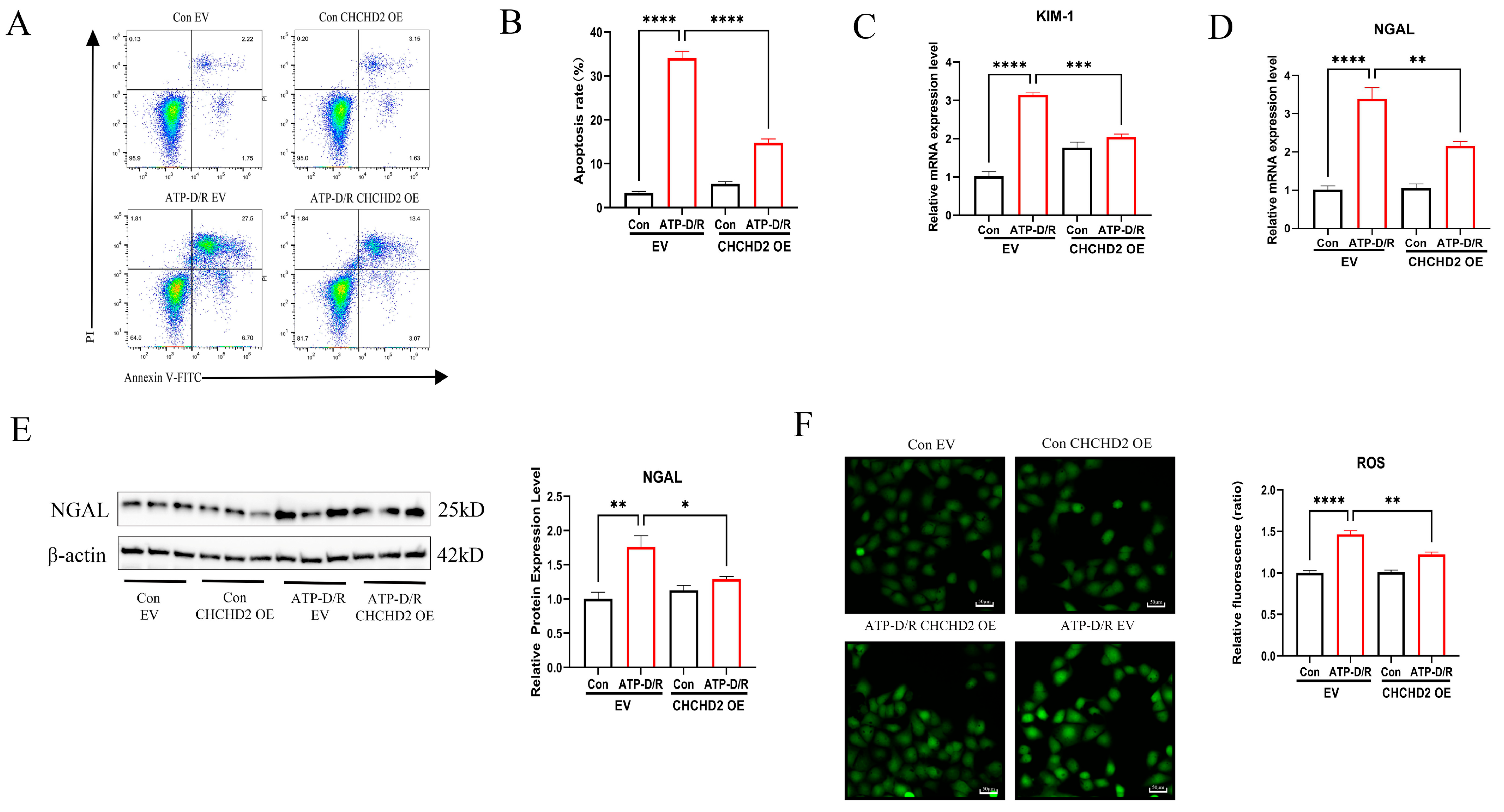
2.3. CHCHD2 Overexpression Mitigated Apoptosis and Cellular Injury
2.4. CHCHD2 Knockdown Exacerbated Cellular Injury
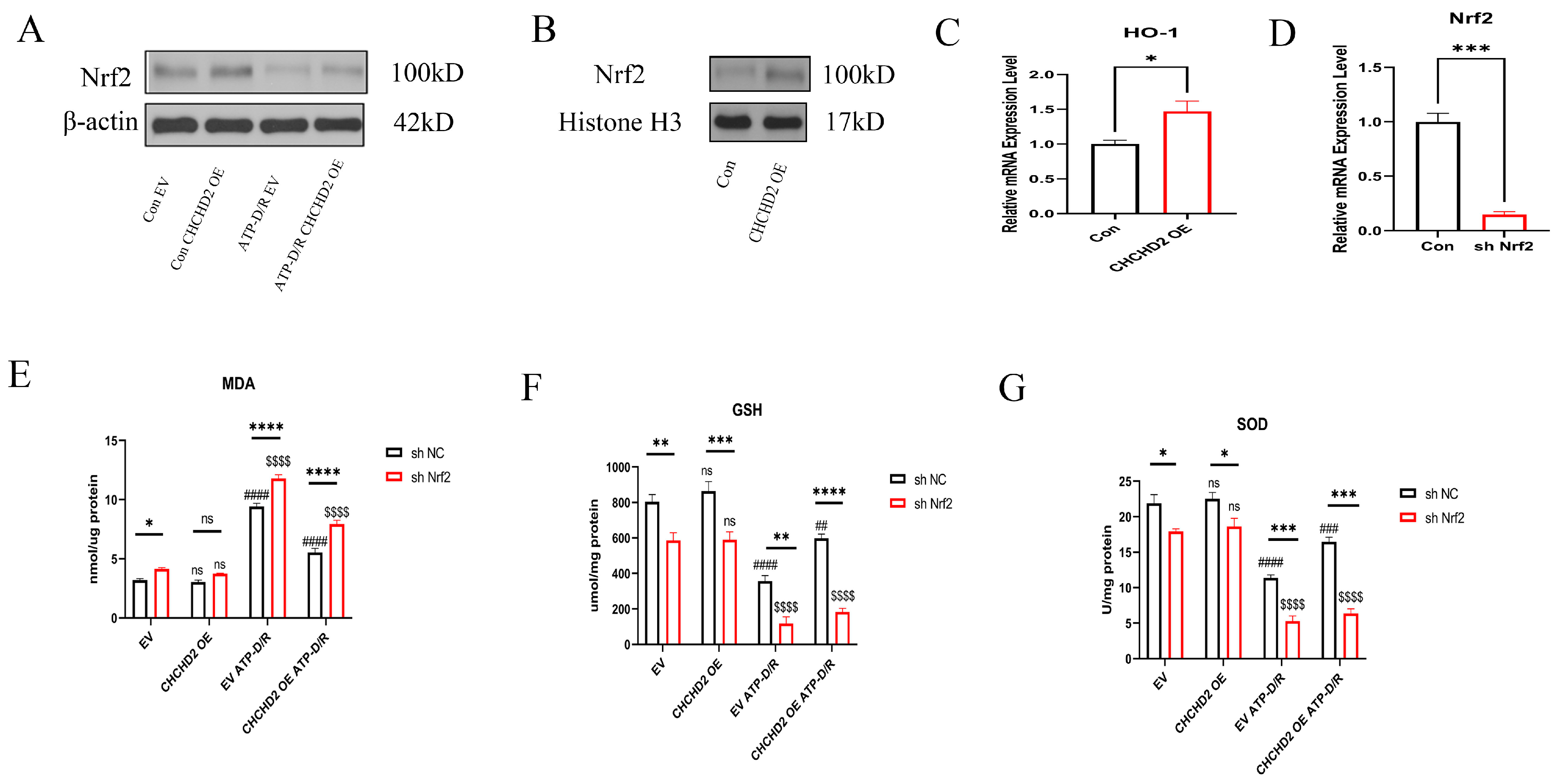
2.5. Mechanistic Investigation of CHCHD2 Regulation of the Nrf2 Axis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.3. Analysis of Cell Viability
4.4. Reactive Oxygen Assays
4.5. GSH Assay
4.6. SOD Assay
4.7. MDA Assay
4.8. Nuclear Protein Extraction
4.9. WB
4.10. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| I/R | Ischemia/Reperfusion |
| CCCP | Carbonyl Cyanide m-Chlorophenyl Hydrazone |
| ATP-D/R | ATP depletion and recovery |
| HK2 | Human Kidney-2 |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| KIM-1 | Kidney Injury Molecule-1 |
| NGAL | Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 |
| HO-1 | Heme Oxygenase-1 |
| NQO1 | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (Phosphate) Dehydrogenase Quinone 1 |
| shRNA | Short Hairpin RNA |
| ARE | Antioxidant Response Elements |
| CCK8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| OE | Overexpression |
| KD | Knockdown |
| EV | Empty Vector |
| WB | Western Blot |
| shNC | Non-Targeting Short Hairpin RNA |
| Tert-butyl hydroperoxide | TBHP |
| Hydrogen peroxide | H2O2 |
| 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal | 4HNE |
| 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine | 8-OHdG |
References
- Jonker, S.J.; Menting, T.P.; Warlé, M.C.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M.; Wever, K.E. Preclinical evidence for the efficacy of ischemic postconditioning against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury, a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Akker, E.K.; Manintveld, O.C.; Hesselink, D.A.; De Bruin, R.W.; Ijzermans, J.N.; Dor, F.J. Protection against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by ischemic postconditioning. Transplantation 2013, 95, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pefanis, A.; Ierino, F.L.; Murphy, J.M.; Cowan, P.J. Regulated necrosis in kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasorsa, F.; Rutigliano, M.; Milella, M.; d’Amati, A.; Crocetto, F.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Barone, B.; Ferro, M.; Spilotros, M.; Battaglia, M.; et al. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezić, A.; Stajic, N.; Thaiss, F. Innate immune response in kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury: Potential target for therapy. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 6305439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, J.L.; Xu, H.Z.; Zhou, C.; Han, B.C.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Z.Z.; Ma, Z.M.; Ming, Z.Y.; Yao, Y.; et al. XJB-5-131 inhibited ferroptosis in tubular epithelial cells after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Martínez, S.M.; López-Novoa, J.M.; López-Hernández, F.J. Pathophysiological role of different tubular epithelial cell death modes in acute kidney injury. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.M.; Parikh, C.R. Current concepts and advances in biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2021, 58, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiva, N.; Sharma, N.; Kulkarni, Y.A.; Mulay, S.R.; Gaikwad, A.B. Renal ischemia/reperfusion injury: An insight on in vitro and in vivo models. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, N.K.; Singh, P.; Koch, B. CoCl2 simulated hypoxia induce cell proliferation and alter the expression pattern of hypoxia associated genes involved in angiogenesis and apoptosis. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Miglioranza Scavuzzi, B.; Abcouwer, S.F.; Zacks, D.N. A simplified protocol to induce hypoxia in a standard incubator: A focus on retinal cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2023, 236, 109653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, R.P.; Penketh, P.G.; Seow, H.A.; Shyam, K.; Sartorelli, A.C. Generation of oxygen deficiency in cell culture using a two-enzyme system to evaluate agents targeting hypoxic tumor cells. Radiat. Res. 2008, 170, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreucci, M.; Michael, A.; Kramers, C.; Park, K.M.; Chen, A.; Matthaeus, T.; Alessandrini, A.; Haq, S.; Force, T.; Bonventre, J.V. Renal ischemia/reperfusion and ATP depletion/repletion in LLC-PK1 cells result in phosphorylation of FKHR and FKHRL1. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenpaa, C.J.; Shames, B.D.; Van Why, S.K.; Johnson, C.P.; Nilakantan, V. Oxidant-mediated apoptosis in proximal tubular epithelial cells following ATP depletion and recovery. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaubasarova, I.R.; Khailova, L.S.; Firsov, A.M.; Grivennikova, V.G.; Kirsanov, R.S.; Korshunova, G.A.; Kotova, E.A.; Antonenko, Y.N. The mitochondria-targeted derivative of the classical uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone is an effective mitochondrial recoupler. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.J.; Lv, X.Q.; Leng, J.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Song, L.S. LC3-mediated mitophagy after CCCP or Vibrio splendidus exposure in the pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 885478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, A.O.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; Dijkman, H.B.; De Abreu, R.A.; Birkenkamp, K.U.; De Witte, T.; van der Reijden, B.A.; Smeitink, J.A.M.; Jansen, J.H. Bcl-2 prevents loss of mitochondria in CCCP-induced apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 299, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.J.; Guo, X.Z.; Cui, S.C.; Wu, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Shen, X.Y.; Xie, C.; Li, J.Y. Dephosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase exacerbates ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury via mitochondrial dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, M.J.; Wang, J.H.; Zhou, J.L.; Wu, G.Y.; Ganley, I.G.; Hill, J.A.; Yin, X.M.; Dong, Z. Clearance of damaged mitochondria via mitophagy is important to the protective effect of ischemic preconditioning in kidneys. Autophagy 2019, 15, 2142–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Hu, J.Q.; Che, Y.P.; Liu, Y.Y.; Luo, Z.H.; Cheng, J.; Han, Q.; He, H.; Zhou, Q.H. CHCHD2 and CHCHD10 regulate mitochondrial dynamics and integrated stress response. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumibao, J.C.; Haak, P.L.; Kolossov, V.L.; Chen, J.W.E.; Stutchman, J.; Ruiz, A.; Sivaguru, M.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Harley, B.A.C.; Steelman, A.J.; et al. CHCHD2 mediates glioblastoma cell proliferation, mitochondrial metabolism, hypoxia-induced invasion and therapeutic resistance. Int. J. Oncol. 2023, 63, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Z.; Wang, F.; Fan, X.M.; Chen, M.Y.; Xu, X.X.; Xu, Q.H.; Zhu, H.L.; Xu, A.D.; Pouladi, M.A.; Xu, X.H. CHCHD2 up-regulation in Huntington disease mediates a compensatory protective response against oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, X.Z.; Chen, M.Y.; Xu, X.X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q.H.; Zhu, H.L.; Xu, A.D.; Pouladi, M.A.; Xu, X.H. Neuroprotective role of CHCHD2 in Parkinson’s disease: Insights into the GPX4-related ferroptosis pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 226, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.R.; Yamashita, C.; Shiba-Fukushima, K.; Inoshita, T.; Funayama, M.; Sato, S.; Hatta, T.; Natsume, T.; Umitsu, M.; Takagi, J.; et al. Loss of Parkinson’s disease-associated protein CHCHD2 affects mitochondrial crista structure and destabilizes cytochrome c. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Qu, J.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, P.P.; Zhou, W.C.; Cui, W.H.; Mo, X.T.; Li, L.C.; Xu, L.; Gao, J. Nrf2 antioxidant pathway suppresses Numb-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition during pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.Y.; Wang, R.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.L. ALDOA protects cardiomyocytes against H/R-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress by regulating the VEGF/Notch 1/Jagged 1 pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhai, Y.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Xiang, Z.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Liu, L.; Li, W.Q.; Wang, W.; et al. RP105 attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in the myocardium via activation of the Lyn/Syk/STAT3 signaling pathway. Inflammation 2024, 47, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotova, E.A.; Antonenko, Y.N. Fifty years of research on protonophores: Mitochondrial uncoupling as a basis for therapeutic action. Acta Naturae 2022, 14, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khailova, L.S.; Firsov, A.M.; Kotova, E.A.; Antonenko, Y.N. Interaction of potent mitochondrial uncouplers with thiol-containing antioxidants. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aras, S.; Purandare, N.; Gladyck, S.; Somayajulu-Nitu, M.; Zhang, K.; Wallace, D.C.; Grossman, L.I. Mitochondrial Nuclear Retrograde Regulator 1 (MNRR1) rescues the cellular phenotype of MELAS by inducing homeostatic mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 32056–32065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purandare, N.; Somayajulu, M.; Hüttemann, M.; Grossman, L.I.; Aras, S. The cellular stress proteins CHCHD10 and MNRR1 (CHCHD2): Partners in mitochondrial and nuclear function and dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6517–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granger, D.N.; Kvietys, P.R. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 524–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, F.; Khori, V.; Alizadeh, A.M.; Khalighfard, S.; Khodayari, S.; Khodayari, H. Reactive oxygen species-mediated cardiac-reperfusion injury: Mechanisms and therapies. Life Sci. 2016, 165, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Genes | Accession Number | Primer (5′→3′) Sequences |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | NM_001101.5 | Forward: CAGGATGCAGAAGGAGATCACT Reverse: CGATCCACACGGAGTACTTGC |
| Kim-1 | NM_024446023.2 | Forward: CCGTGACAGAGTCTTCAGATGG Reverse: AGCAAGAAGCACCAAGACAGA |
| NGAL | NM_005564.5 | Forward: GAGCACCAACTACAACCAGCA Reverse: TCCTTTAGTTCCGAAGTCAGCT |
| CHCHD2 | NM_001320327.2 | Forward: AGGAAGTAATGCTGAGCCTG Reverse: ACCCTCACAGAGCTTGATGTC |
| HO-1 | NM_002133.3 | Forward: CTGCTGACCCATGACACCAAG Reverse: CTGTCGCCACCAGAAAGCTGA |
| Nrf2 | NM_001145412.3 | Forward: TGTGGCATCACCAGAACACT Reverse: TCCAGGGGCACTATCTAGCTC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, Y.; Zhou, X. Therapeutic Potential of CHCHD2 in Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: Mechanistic Insights into Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Defense in HK2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136089
Hao Y, Zhou X. Therapeutic Potential of CHCHD2 in Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: Mechanistic Insights into Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Defense in HK2 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136089
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Yajie, and Xiaoshuang Zhou. 2025. "Therapeutic Potential of CHCHD2 in Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: Mechanistic Insights into Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Defense in HK2 Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136089
APA StyleHao, Y., & Zhou, X. (2025). Therapeutic Potential of CHCHD2 in Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: Mechanistic Insights into Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Defense in HK2 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6089. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136089




