Aligned Electrospun PCL/PLA Nanofibers Containing Green-Synthesized CeO2 Nanoparticles for Enhanced Wound Healing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
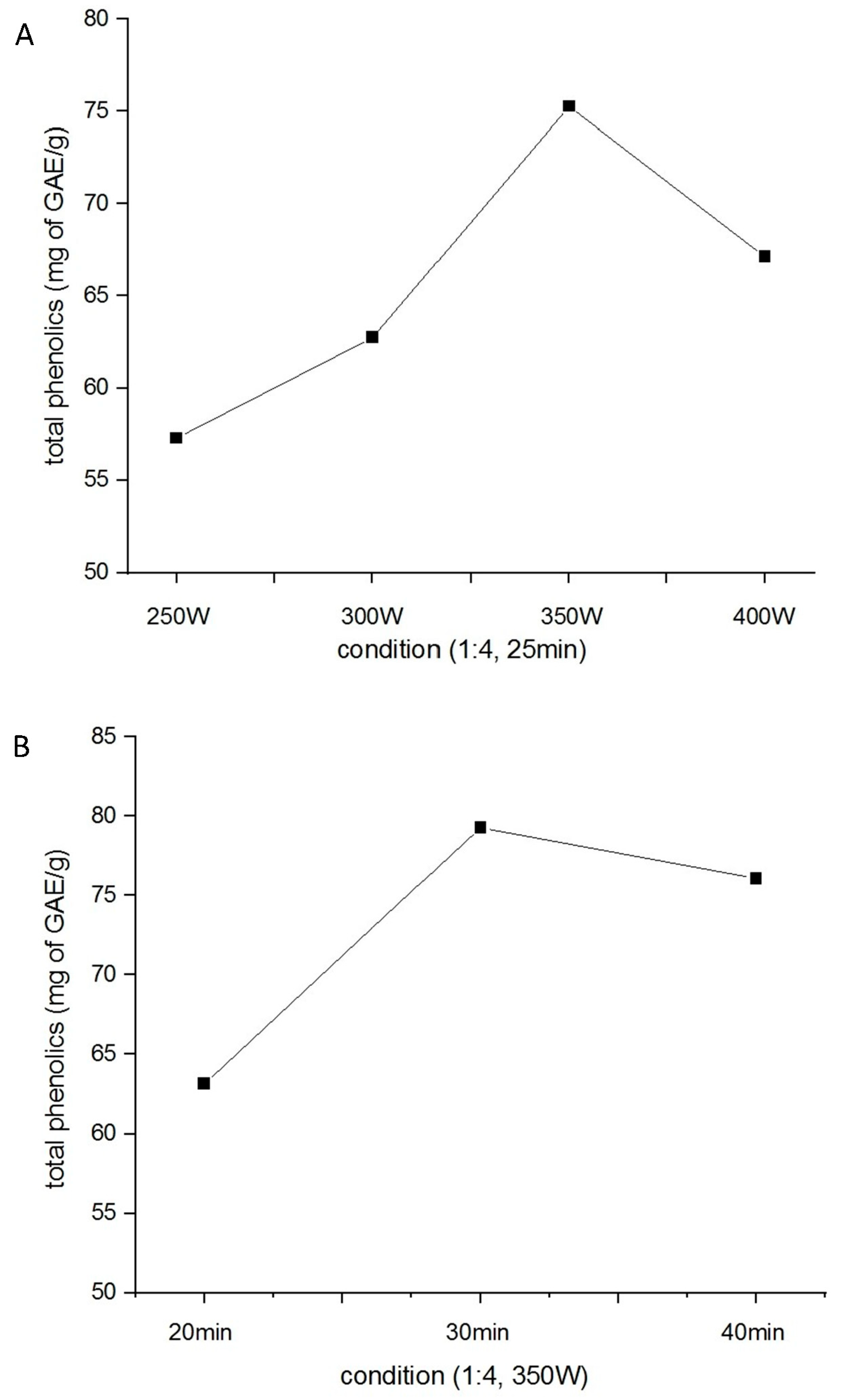
2.1. Optimization of H. citrina Extract Yield
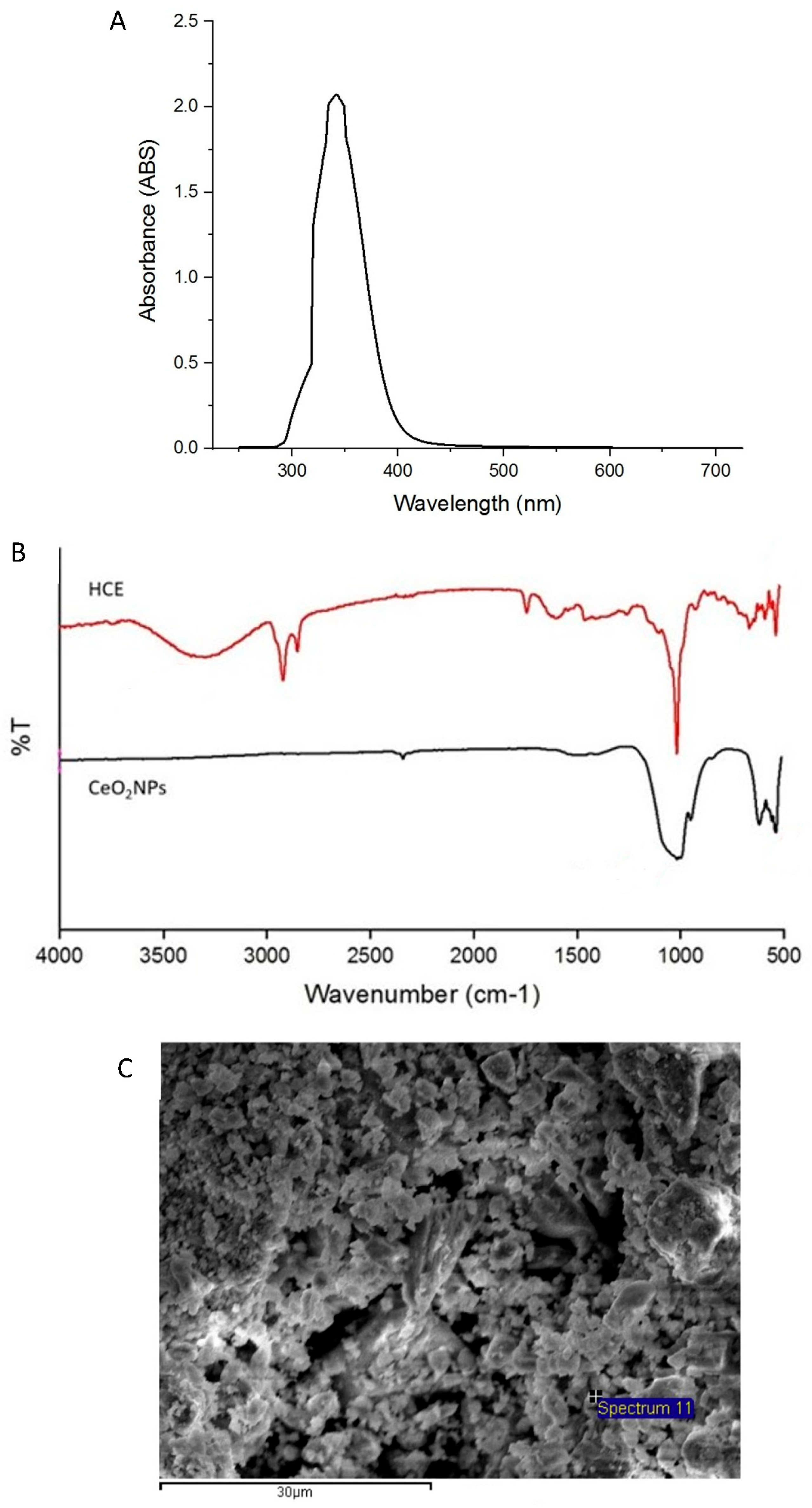
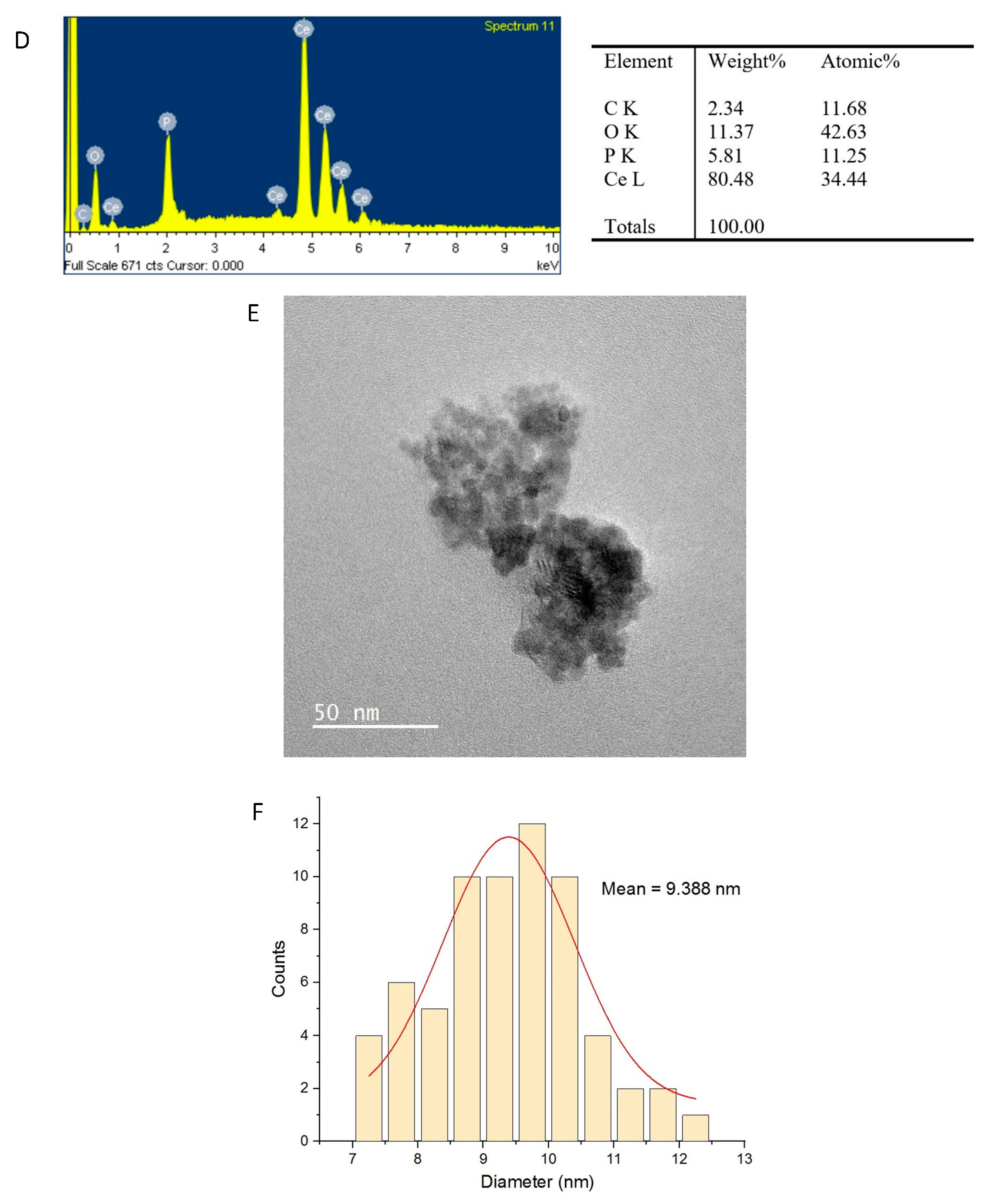
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of CeO2NPs
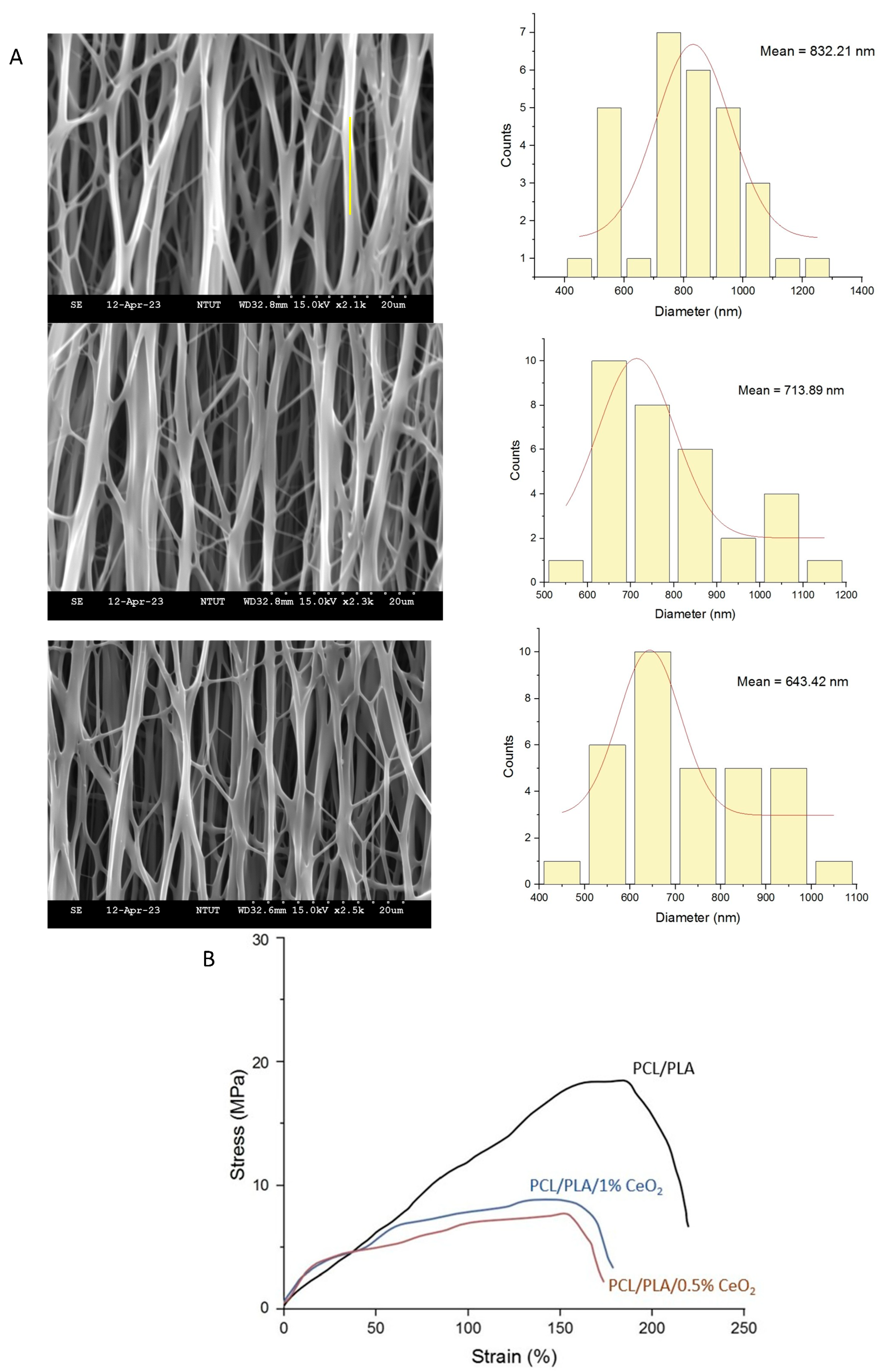
2.3. Characterization of PCL/PLA/CeO2NP Nanofibers
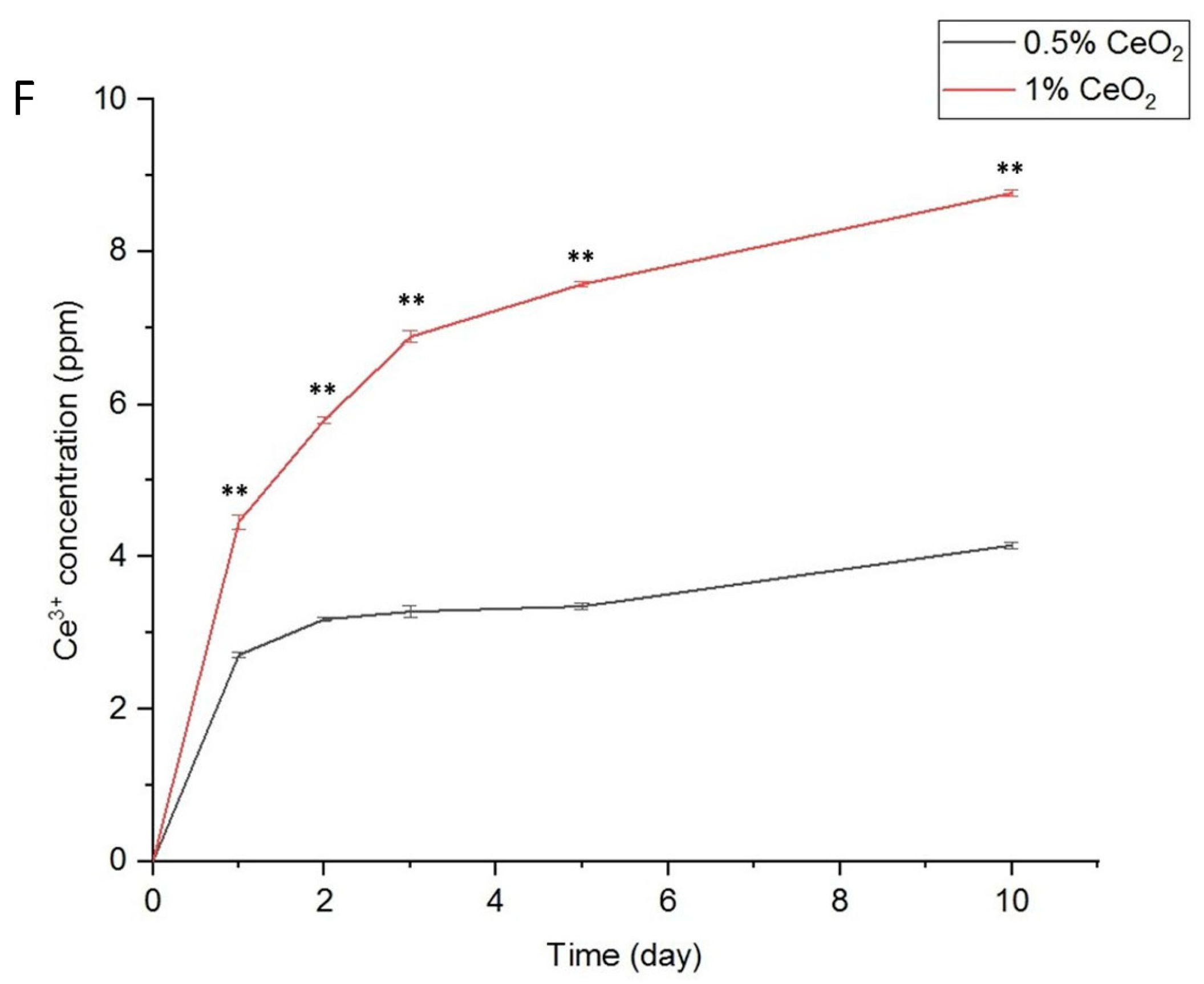
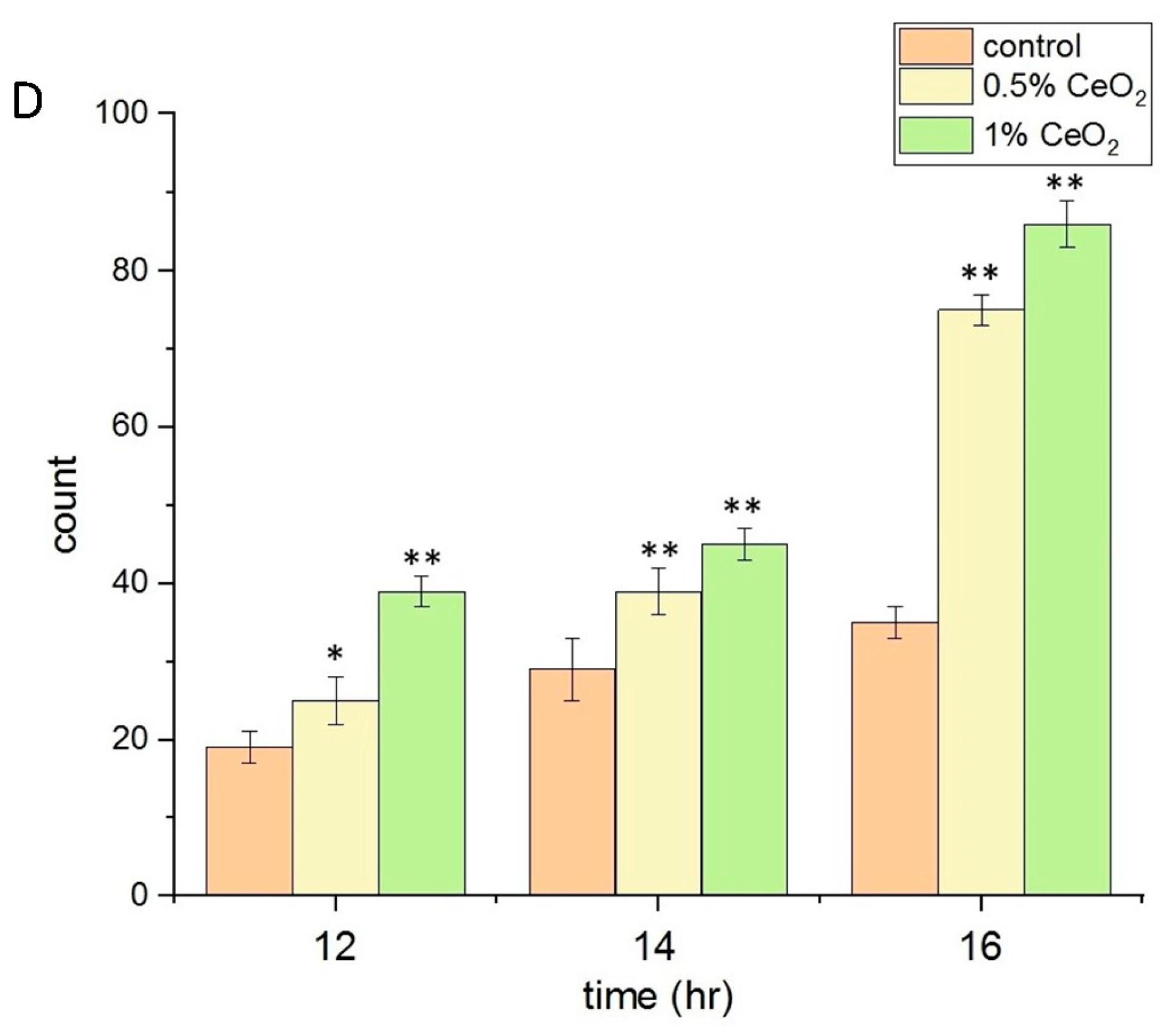
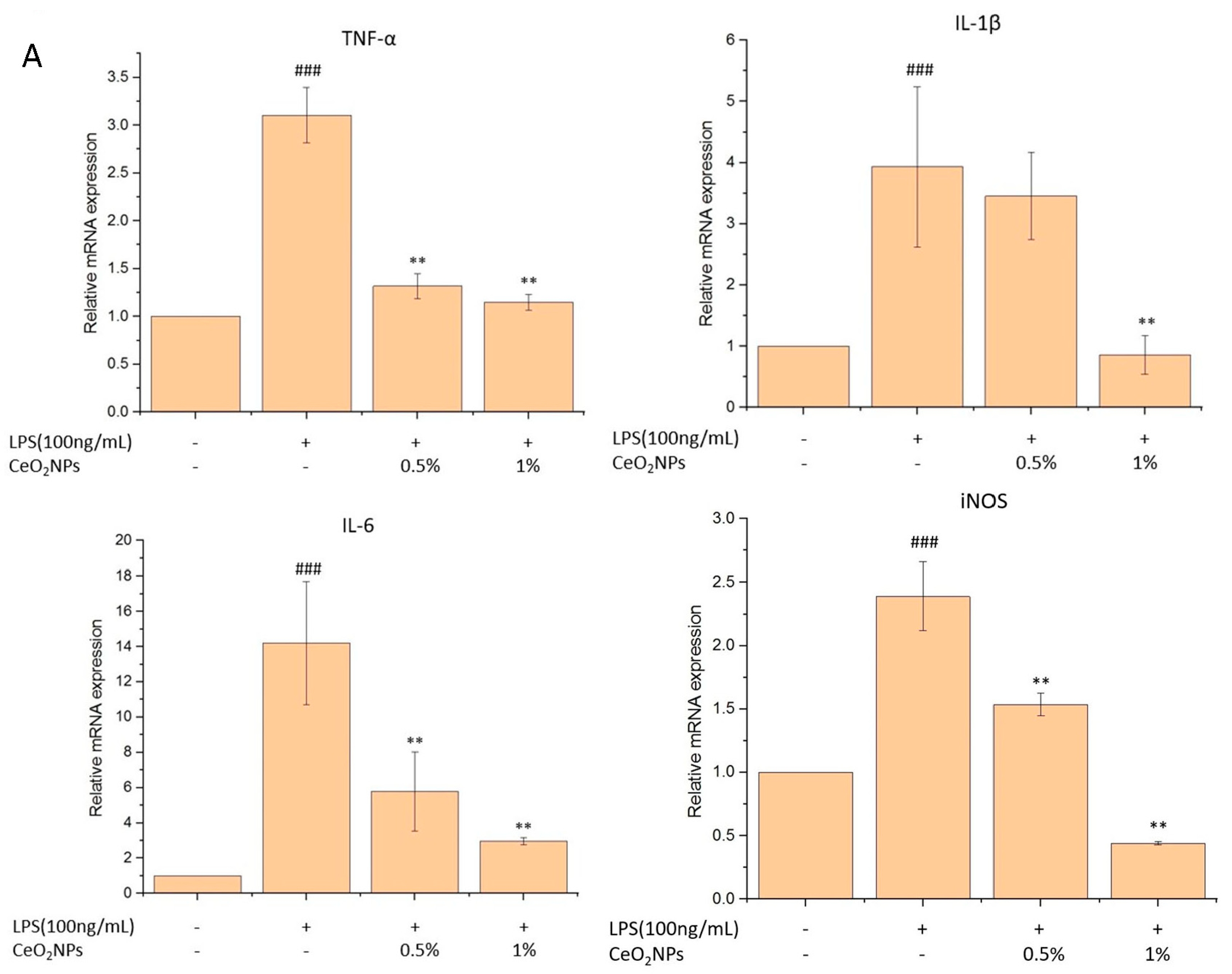
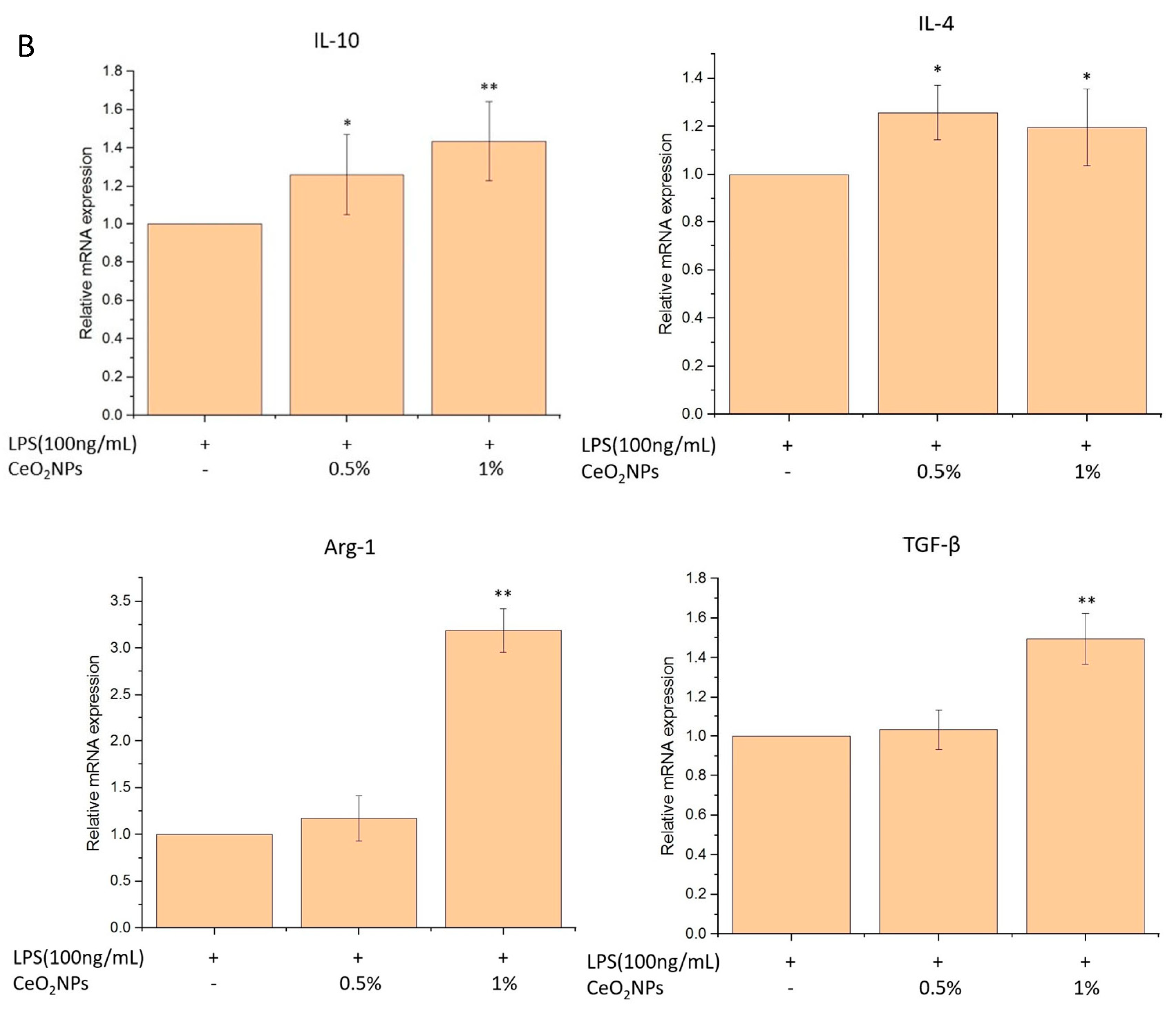
2.4. Biocompatibility, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antioxidant Properties of CeO2NPs
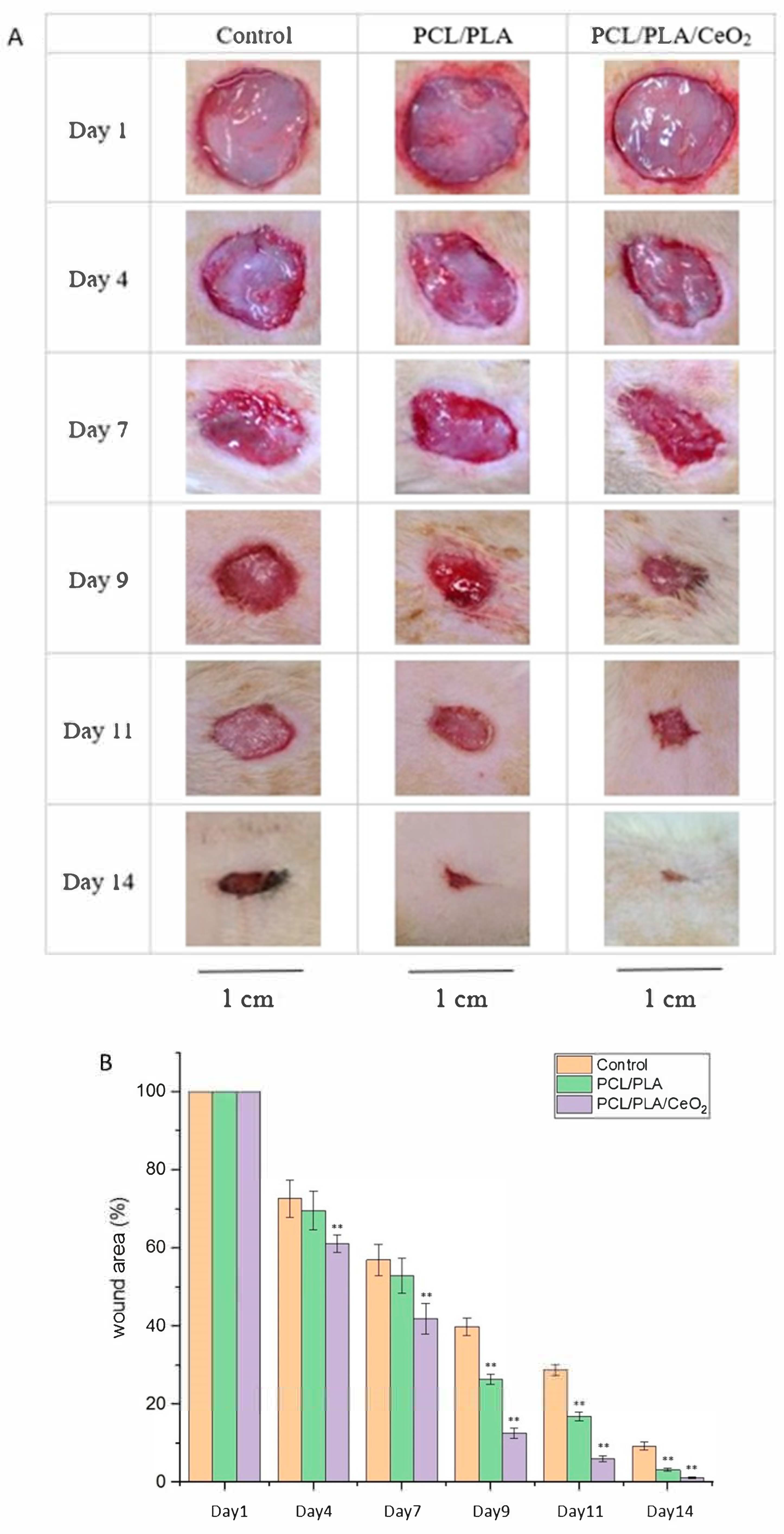
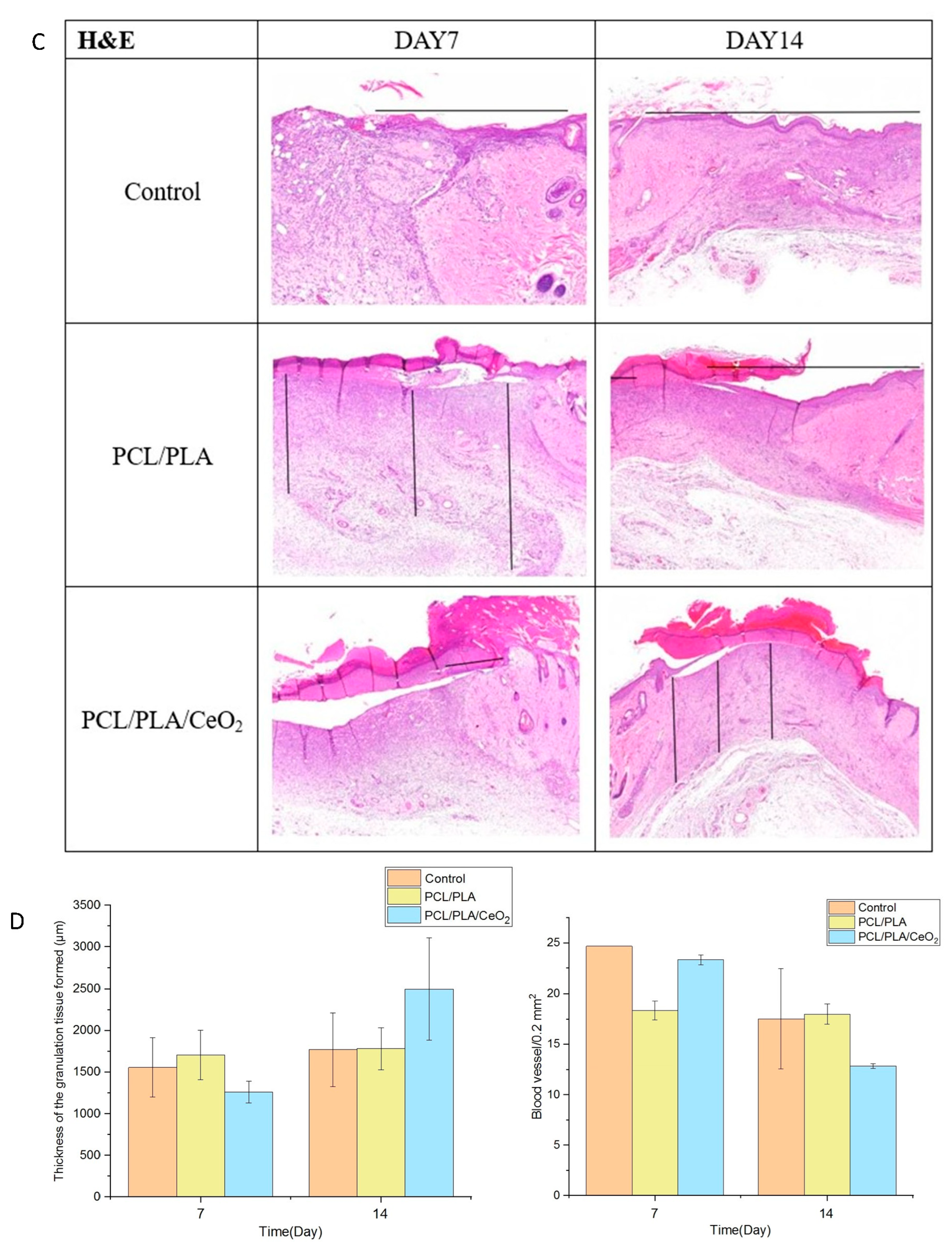
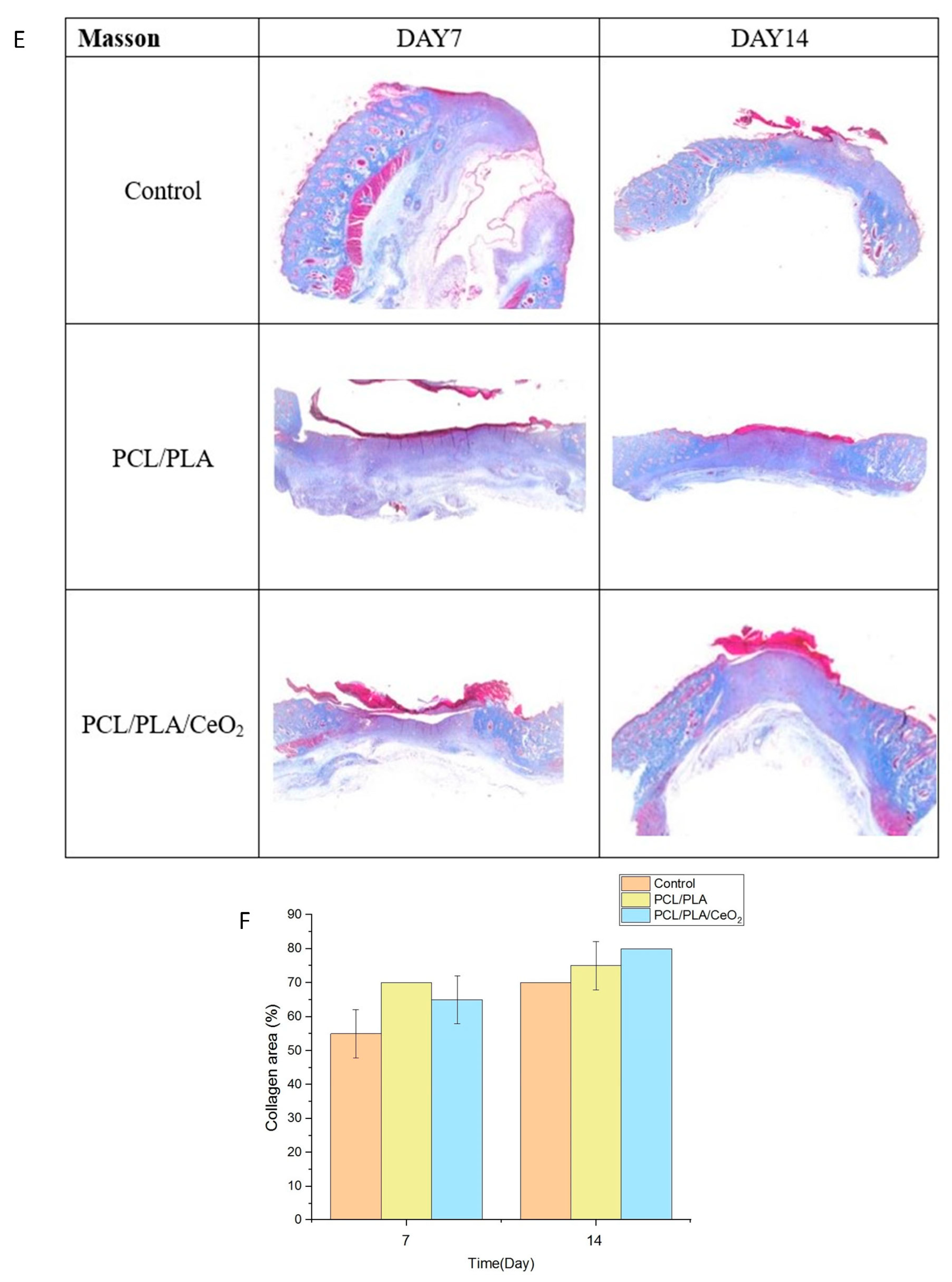
2.5. In Vivo Wound Healing Assessment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Optimization of H. citrina Extraction Via Microwave-Assisted Extraction
4.2. Green Synthesis and Characterization of CeO2 Nanoparticles
4.3. Fabrication and Characterization of Aligned Electrospun Nanofibers
4.4. Cytotoxicity and Cell Migration Assays of CeO2NPs
4.5. Anti-Inflammatory Activity and ROS Quantification
4.6. Gene Expression Analysis via RT-PCR
4.7. In Vivo Burn Wound Healing Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desjardins-Park, H.E.; Mascharak, S.; Chinta, M.S.; Wan, D.C.; Longaker, M.T. The spectrum of scarring in craniofacial wound repair. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkefli, N.; Che Zahari, C.N.M.; Sayuti, N.H.; Kamarudin, A.A.; Saad, N.; Hamezah, H.S.; Bunawan, H.; Baharum, S.N.; Mediani, A.; Ahmed, Q.U.; et al. Flavonoids as potential wound-healing molecules: Emphasis on pathways perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.M.; Le, T.T.N.; Nguyen, A.T.; Le, H.N.T.; Pham, T.T. Biomedical materials for wound dressing: Recent advances and applications. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 5509–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, E.R.; Khosravi, F.; Neisiany, R.E.; Singh, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Future of additive manufacturing in healthcare. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 17, 100255. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.-Y.; Lin, J.-Y.; Su, W.-T. Coaxial nanofibers encapsulated with Ampelopsis brevipedunculata extract and green synthesized AgNPs for wound repair. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 235, 113771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subeshan, B.; Atayo, A.; Asmatulu, E. Machine learning applications for electrospun nanofibers: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 14095–14140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chu, C.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Hu, C.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Qu, Y.; Man, Y. The diameter factor of aligned membranes facilitates wound healing by promoting epithelialization in an immune way. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 11, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; John, J.V.; McCarthy, A.; Wong, S.L.; Xie, J. Mesenchymal stem cell-laden. personalized 3D scaffolds with controlled structure and fiber alignment promote diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Xu, H.; Ke, Q. An aligned porous electrospun fibrous membrane with controlled drug delivery-An efficient strategy to accelerate diabetic wound healing with improved angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2018, 70, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessy, J.; Robin, A.; Nandakumar, K.; Sabu, Y.; Bastien, S.; Yves, G. Recent advances in electrospun polycaprolactone based scaffolds for wound healing and skin bioengineering applications. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 19, 319–335. [Google Scholar]
- Homa, M.; Bahareh, A.; Saeed, I.; Serena, D. Poly(lactic acid)-based electrospun fibrous structures for biomedical applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3192. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q.; Cosme, J.G.; Xu, T.; Miszuk, J.M.; Picciani, P.H.; Fong, H.; Sun, H. Three dimensional electrospun PCL/PLA blend nanofibrous scaffolds with significantly improved stem cells osteogenic differentiation and cranial bone formation. Biomaterials 2017, 115, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.R.; Nayak, V.; Sarkar, T.; Singh, R.P. Cerium oxide nanoparticles: Properties. biosynthesis and biomedical application. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 27194–27214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Renick, P.; Senkowsky, J.; Nair, A.; Tang, L. Diagnostics for wound infections. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangha, M.S.; Deroide, F.; Meys, R. Wound healing. scarring and management. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 49, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Bao, S.; Yao, L.; Fu, X.; Yu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Pang, H.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles in wound care: A review of mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1404651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Yu, H.; Huang, J.; Yuan, H.; Chen, C. Effects of different extraction methods on phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in Hemerocallis flower. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 303–312. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S. Study on Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoids from Hemerocallis fulva (Daylily) Leaves. Molecules 2022, 27, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. Green’ synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rónavári, A.; Igaz, N.; Adamecz, D.I.; Szerencsés, B.; Molnar, C.; Kónya, Z.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kiricsi, M. Green silver and gold nanoparticles: Biological synthesis approaches and potentials for biomedical applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, O.L.; Mesaros, A.; Vodnar, D.C.; Suharoschi, R.; Tăbăran, F.; Magerușan, L.; Tódor, I.S.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Balint, A.; Ciontea, L.; et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles and their efficient antibacterial application in vitro against gram-positive and gram-negative pathogens. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Siddique, M.A.R.; Sajid, M.; Karim, S.; Ali, M.U.; Abid, R.; Bokhari, S.A.I. A comparative study of green and chemical cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2-NPs): From synthesis. characterization, and electrochemical analysis to multifaceted biomedical applications. BioNanoScience 2023, 13, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsefidi, F.S.; Nejati, M.; Verdi, J.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Green synthesis and characterization of cerium oxide nanostructures in the presence carbohydrate sugars as a capping agent and investigation of their cytotoxicity on the mesenchymal stem cell. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamizhdurai, P.; Sakthinathan, S.; Chen, S.M.; Shanthi, K.; Sivasanker, S.; Sangeetha, P. Environmentally friendly synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles for the catalytic oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde and selective detection of nitrite. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, N.; Xu, L.; Hou, S. Synthesis and conductivity of cerium oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1254–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Liao, H.X.; Su, W.T. A sprayable hydroxypropyl chitin/collagen/extract of Ampelopsis brevipedunculata hydrogel accelerated wound healing. J. Wound Care 2024, 33, S10–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, L.A.; Downes, S. Physicochemical characterization of degrading polycaprolactone scaffolds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, D.; Sanchez, A.; Tward, J.D. Successful salvage brachytherapy after infusion of gold auroshell nanoshells for localized prostate cancer in a human patient. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 8, 101202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motelica, L.; Vasile, B.S.; Ficai, A.; Surdu, A.V.; Ficai, D.; Oprea, O.C.; Andronescu, E.; Mustățea, G.; Ungureanu, E.L.; Dobre, A.A. Antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles loaded with essential oils. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, K.P.; Naruphontjirakul, P.; Chen, J.H.; Ko, C.S.; Lin, C.W.; Su, W.T. Incorporation of zinc oxide nanoparticles biosynthesized from Epimedium brevicornum Maxim. into PCL nanofibers to enhance osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Materials 2025, 18, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, K.; Vimala, K.; Gopi, D.; Kannan, S. Fabrication of a pH responsive DOX conjugated PEGylated palladium nanoparticle mediated drug delivery system: An in vitro and in vivo evaluation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 44998–45014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminzai, M.T.; Yildirim, M.; Yabalak, E. Metallic nanoparticles unveiled: Synthesis. characterization, and their environmental, medicinal, and agricultural applications. Talanta 2024, 280, 126790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Zhang, Y.; Farghali, M.; Rashwan, A.K.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Mohamed, I.M.; Badr, M.M.; Ihara, I.; Rooney, D.W.; et al. Synthesis of green nanoparticles for energy. biomedical, environmental, agricultural, and food applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 841–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, X.; Ye, H.; Sheng, X. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles from the extract of Crocus sativus to study the effect of antidepressant in adolescence and to observe its aggressive and impulsive behavior in rat models. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 165, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerdtoob, S.; Chanthasena, P.; Rosyidah, A.L.; Limphirat, W.; Penkhrue, W.; Ganta, P.; Srisakvarangkool, W.; Yasawong, M.; Nantapong, N. Streptomyces monashensis MSK03-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Characterization and antibacterial activity. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 4778–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Elshafie, H.S.; Pohl, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) by Lallemantia royleana leaf Extract: Their Bio-Pharmaceutical and catalytic properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 2024, 448, 115318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hong, G.; Mazaleuskaya, L.; Hsu, J.C.; Rosario-Berrios, D.N.; Grosser, T.; Cho-Park, P.F.; Cormode, D.P. Ultrasmall antioxidant cerium oxide nanoparticles for regulation of acute inflammation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 60852–60864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Kumari, S.; Manohar Aeshala, L.; Singh, S. Investigating temperature variability on antioxidative behavior of synthesized cerium oxide nanoparticle for potential biomedical application. J. Biomater. Appl. 2024, 38, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serebrovska, Z.; Swanson, R.J.; Portnichenko, V.; Shysh, A.; Pavlovich, S.; Tumanovska, L.; Dorovskych, A.; Lysenko, V.; Tertykh, V.; Bolbukh, Y.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect of cerium dioxide nanoparticles immobilized on the surface of silica nanoparticles in rat experimental pneumonia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Yu, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, D.; Yang, C.; Deng, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wen, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. The regulatory mechanisms of cerium oxide nanoparticles in oxidative stress and emerging applications in refractory wound care. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1439960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribera, J.; Rodriguez-Vita, J.; Cordoba, B.; Portoles, I.; Casals, G.; Casals, E.; Jimenez, W.; Puntes, V.; Morales-Ruiz, M. Functionalized cerium oxide nanoparticles mitigate the oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory activity associated to the portal vein endothelium of cirrhotic rats. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Shi, Z.; Yue, K.; Huang, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, C.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, Y.S.; Wang, J. Sprayable hydrogel dressing accelerates wound healing with combined reactive oxygen species-scavenging and antibacterial abilities. Acta Biomater. 2021, 124, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Hasan, A.; Patan, N.K.; Dalvi, Y.B.; Varghese, R.; Antony, A.; Unni, R.N.; Sandhyarani, N.; Moustafa, A.E.A. Cerium oxide nanoparticle incorporated electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) membranes for diabetic wound healing applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Javed, M.S.; Khan, S.; Almutairi, T.M.; Mohammed, A.A.; Luque, R. Green synthesized Ag decorated CeO2 nanoparticles: Efficient photocatalysts and potential antibacterial agents. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 13684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Tian, L. Advanced biological applications of cerium oxide nanozymes in disease related to oxidative damage. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 8601–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Baker, A.B. Biomaterials and nanotherapeutics for enhancing skin wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Duan, X.P.; Li, Y.M.; Yang, D.P.; Long, Y.Z. Electrospun nanofibers for wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 76, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, R.; Kaushik, M.; Prakash, J.; Venkataprasanna, K.S.; Arpana, C.; Balashanmugam, P.; Venkatasubbu, G.D. Enhanced wound healing by PVA/chitosan/curcumin patches: In vitro and in vivo study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 182, 110339. [Google Scholar]
- Memic, A.; Abdullah, T.; Mohammed, H.S.; Joshi Navare, K.; Colombani, T.; Bencherif, S.A. Latest Progress in electrospun nanofibers for wound healing applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 952–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, R.; Kumar, V.; Ranjan, N.; Gupta, J.; Bhura, N. On 3D printed thermoresponsive PCL-PLA nanofibers based architected smart nanoporous scaffolds for tissue reconstruction. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 119, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, H.M.; Motawea, A.; Kamel, A.H.; Bary, E.M.A.; Hassan, S.S.M. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun nanofibers using biocompatible polymers for the sustained release of venlafaxine. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Plavec, T.V.; Zupančič, Š.; Berlec, A. Modified vaginal lactobacilli expressing fluorescent and luminescent proteins for more effective monitoring of their release from nanofibers. safety and cell adhesion. Microb. Cell Fact. 2024, 23, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.I.; Araujo-Rodríguez, D.G.; Valencia-Llano, C.H.; Tenorio, D.L.; Saavedra, M.; Zapata, P.A.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. Biocompatibility assessment of Polycaprolactone/Polylactic Acid/Zinc Oxide nanoparticle composites under in vivo conditions for biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 25, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Ren, G.; Sun, Q.; Liang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, W.; Yu, H.D. Autonomous moisture-driven flexible electrogenerative dressing for enhanced wound healing. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2418074. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, A.; Tudorache, D.I.; Niculescu, A.G.; Grumezescu, A.M. Advancements in wound dressing materials: Highlighting recent progress in hydrogels. foams, and antimicrobial dressings. Gels 2025, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Sun, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y. Wireless bioelectronic devices for next-generation electrotherapy. Cell Biomater. 2025, 1, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Q.; Yang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, K.; Hou, R.; Zhu, Y. Smart wound dressing for advanced wound management: Real-time monitoring and on-demand treatment. Mater. Des. 2023, 229, 111917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Yao, Z.; Yuan, F.; Liu, H.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, G.; Yao, X.; Cui, H.; et al. NLRP3-Dependent crosstalk between pyroptotic macrophage and senescent cell orchestrates trauma-induced heterotopic ossification during aberrant wound healing. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2207383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Zhao, C.; Wan, Y.; Majid, M.; Abbas, S.Q.; Wang, Y. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of alginate hydrogel-based wound dressing loaded with green chemistry cerium oxide nanoparticles. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1298808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, N.; Rostom, D.M.; Mashal, M. The use of cerium oxide nanoparticles in liver disorders: A double-sided coin? Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 130, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Oligo Name | Oligo Seq (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| IL-6 forward | TACCACTTCACAAGTCGGAGGC |
| IL-6 reverse | CTGCAAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTC |
| IL-1β forward | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG |
| IL-1β reverse | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG |
| TNF-α forward | CCTGTAGCCCACGTCGTAG |
| TNF-α reverse | GGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCC |
| iNOS forward | GTTCTCAGCCCAACAATACAAGA |
| iNOS reverse | GTGGACGGGTCGATGTCAC |
| Arg-1 forward | CTCCAAGCCAAAGTCCTTAGAG |
| Arg-1 reverse | AGGAGCTGTCATTAGGGACATC |
| IL-4 forward | GGTCTCAACCCCCAGCTAGT |
| IL-4 reverse | GGTCTCAACCCCCAGCTAGT |
| IL-10 forward | TACAGCCGGGAAGACAATAA |
| IL-10 reverse | AAGGAGTCGGTTAGCAGTAT |
| TGF-β forward | GTCCTTGCCCTCTACAACCA |
| TGF-β reverse | GTTGGACAACTGCTCCACCT |
| GAPDH forward | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG |
| GAPDH reverse | GGGGTCGTTGATGGCAACA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, Y.-C.; Su, W.-T. Aligned Electrospun PCL/PLA Nanofibers Containing Green-Synthesized CeO2 Nanoparticles for Enhanced Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136087
Le Y-C, Su W-T. Aligned Electrospun PCL/PLA Nanofibers Containing Green-Synthesized CeO2 Nanoparticles for Enhanced Wound Healing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136087
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Yen-Chen, and Wen-Ta Su. 2025. "Aligned Electrospun PCL/PLA Nanofibers Containing Green-Synthesized CeO2 Nanoparticles for Enhanced Wound Healing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136087
APA StyleLe, Y.-C., & Su, W.-T. (2025). Aligned Electrospun PCL/PLA Nanofibers Containing Green-Synthesized CeO2 Nanoparticles for Enhanced Wound Healing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136087






