Effect on Different Glial Cell Types of S100B Modulation in Multiple Sclerosis Experimental Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
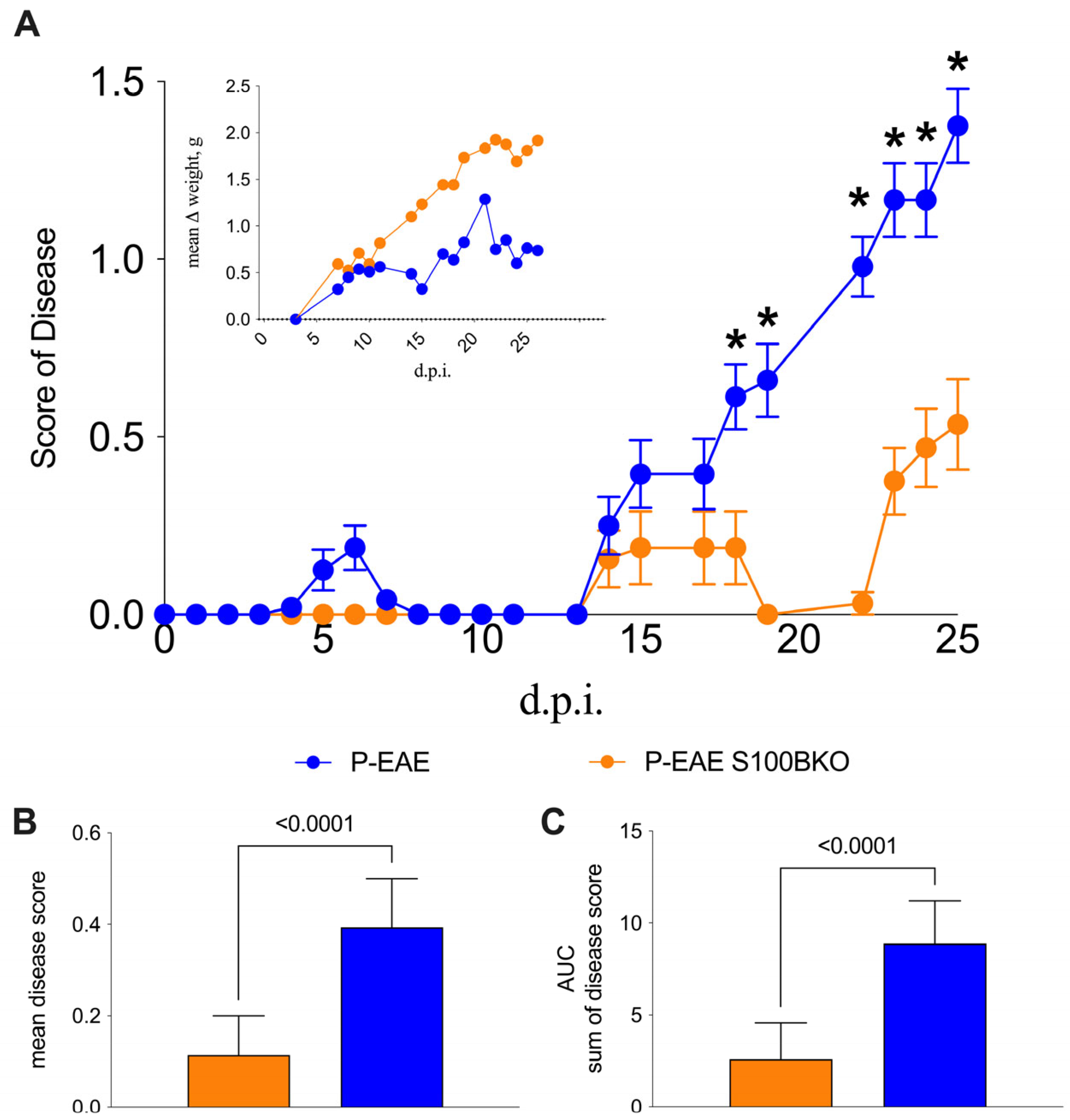
2.1. S100B Silencing Reduces Disease Severity
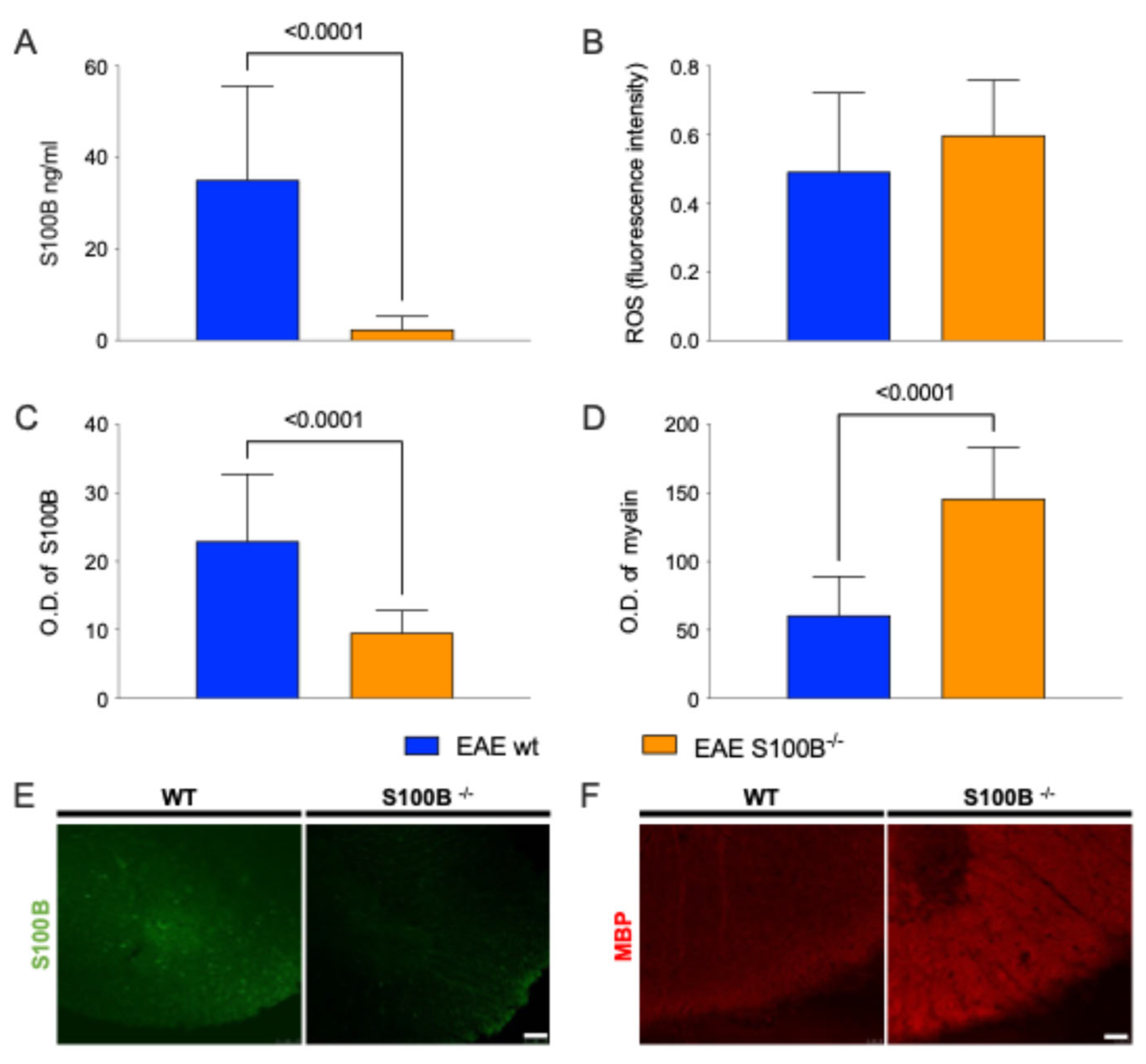
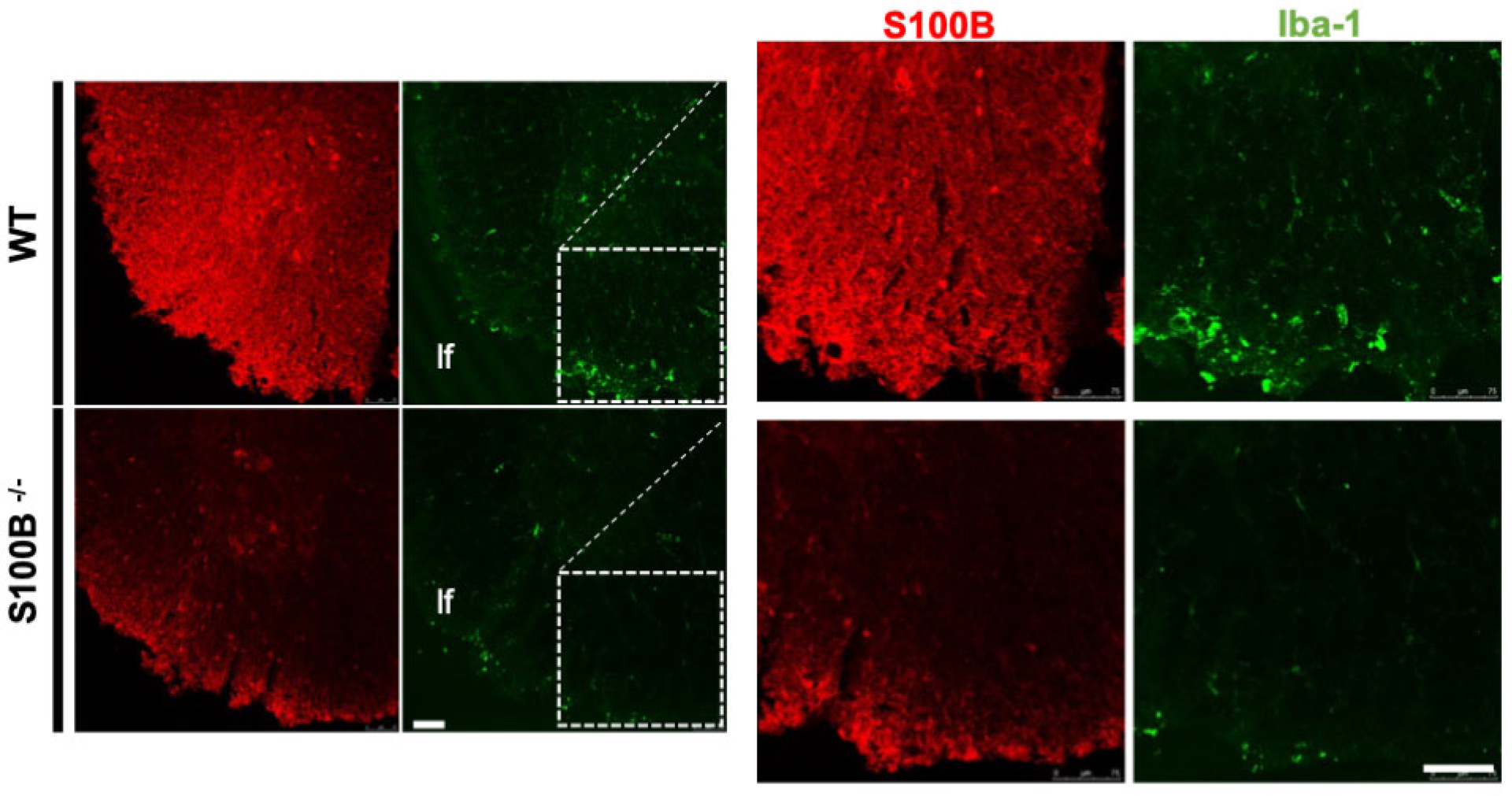
2.2. S100B Silencing Impacts on Astrocytosis, Demyelination, and Microglia Activation
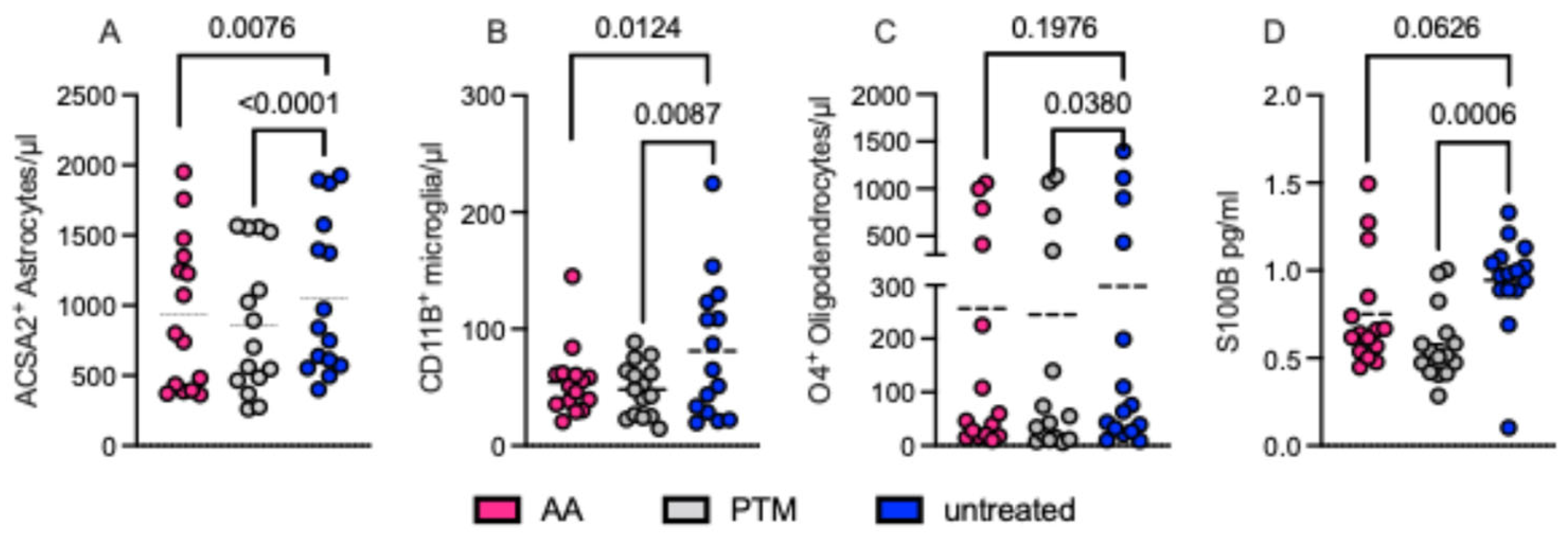
2.3. Pharmacological S100B Modulation Affects Definite Glial Cell Populations
3. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Procedure
4.2. Astrocytes’ Primary Isolation
4.3. Cell Cultures
4.4. Flow Cytometry Assay
4.5. RT-qPCR Assay
4.6. S100B ELISA Assay
4.7. Assessment of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
4.8. Immunofluorescence and Data Analysis
4.9. Quantification and Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ponath, G.; Park, C.; Pitt, D. The Role of Astrocytes in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, R.; Eilam, R.; Arnon, R. Astrocytes in Multiple Sclerosis—Essential Constituents with Diverse Multifaceted Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.-S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocytes Are Induced by Activated Microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.J.M.; Ffrench-Constant, C. Regenerating CNS Myelin—From Mechanisms to Experimental Medicines. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäkel, S.; Agirre, E.; Mendanha Falcão, A.; Van Bruggen, D.; Lee, K.W.; Knuesel, I.; Malhotra, D.; Ffrench-Constant, C.; Williams, A.; Castelo-Branco, G. Altered Human Oligodendrocyte Heterogeneity in Multiple Sclerosis. Nature 2019, 566, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, L.; Velmeshev, D.; Holmqvist, S.; Kaufmann, M.; Werneburg, S.; Jung, D.; Vistnes, S.; Stockley, J.H.; Young, A.; Steindel, M.; et al. Neuronal Vulnerability and Multilineage Diversity in Multiple Sclerosis. Nature 2019, 573, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michetti, F.; Lauriola, L.; Rende, M.; Stolfi, V.M.; Battaglia, F.; Cocchia, D. S-100 Protein in the Testis: An Immunochemical and Immunohistochemical Study. Cell Tissue Res. 1985, 240, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, M.M.; Bosisio, F.M.; Manzoni, M.; Schapiro, D.; Tagliabue, R.; Faretta, M.; Parravicini, C.; Haberman, A.M.; Cattoretti, G. The Landscape of S100B+ and HLA-DR+ Dendritic Cell Subsets in Tonsils at the Single Cell Level via High-Parameter Mapping. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michetti, F.; D’Ambrosi, N.; Toesca, A.; Puglisi, M.A.; Serrano, A.; Marchese, E.; Corvino, V.; Geloso, M.C. The S100B Story: From Biomarker to Active Factor in Neural Injury. J. Neurochem. 2019, 148, 168–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michetti, F.; Di Sante, G.; Clementi, M.E.; Sampaolese, B.; Casalbore, P.; Volonté, C.; Romano Spica, V.; Parnigotto, P.P.; Di Liddo, R.; Amadio, S.; et al. Growing Role of S100B Protein as a Putative Therapeutic Target for Neurological- and Nonneurological-Disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 127, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Porel, P.; Kosey, S.; Aran, K.R. Diverse Role of S100 Calcium-Binding Protein B in Alzheimer’s Disease: Pathological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Inflammopharmacology 2025, 33, 1803–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristóvão, J.S.; Morris, V.K.; Cardoso, I.; Leal, S.S.; Martínez, J.; Botelho, H.M.; Göbl, C.; David, R.; Kierdorf, K.; Alemi, M.; et al. The Neuronal S100B Protein Is a Calcium-Tuned Suppressor of Amyloid-β Aggregation. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Piperi, C. Emerging Role of S100B Protein Implication in Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 78, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Du, R. miR-135b-Dependent Downregulation of S100B Promotes Neural Stem Cell Differentiation in a Hypoxia/Ischemia-Induced Cerebral Palsy Rat Model. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 319, C955–C966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michetti, F.; Clementi, M.E.; Di Liddo, R.; Valeriani, F.; Ria, F.; Rende, M.; Di Sante, G.; Romano Spica, V. The S100B Protein: A Multifaceted Pathogenic Factor More Than a Biomarker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttunen, H.J.; Kuja-Panula, J.; Sorci, G.; Agneletti, A.L.; Donato, R.; Rauvala, H. Coregulation of Neurite Outgrowth and Cell Survival by Amphoterin and S100 Proteins through Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40096–40105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, C.; Lattanzi, W.; Businaro, R.; Leone, S.; Corvino, V.; Sorci, G.; Lauro, G.; Fumagalli, L.; Donato, F.R.; Michetti, F. Transcritpional Effects of S100B on Neuroblastoma Cells: Perturbation of Cholesterol Homeostasis and Interference on the Cell Cycle. Gene Expr. 2010, 14, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Cirillo, C.; Sarnelli, G.; De Filippis, D.; D’Armiento, F.P.; Rocco, A.; Nardone, G.; Petruzzelli, R.; Grosso, M.; Izzo, P.; et al. Enteric Glial-Derived S100B Protein Stimulates Nitric Oxide Production in Celiac Disease. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Castets, F.; Guevara, J.L.; Van Eldik, L.J. S100 Beta Stimulates Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity and mRNA Levels in Rat Cortical Astrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 2543–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, T.V.; Hu, J.; Van Eldik, L.J. Modulation of Glial Activation by Astrocyte-Derived Protein S100B: Differential Responses of Astrocyte and Microglial Cultures. Brain Res. 2000, 853, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, N.; Reddy, M.A.; Natarajan, R. Distinct Roles of Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonuclear Protein K and microRNA-16 in Cyclooxygenase-2 RNA Stability Induced by S100b, a Ligand of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 36221–36233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tully, M.; Shi, R. New Insights in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis—Role of Acrolein in Neuronal and Myelin Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20037–20047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal, A.; Aviles Reyes, R.X.; Angelo, M.F.; Reines, A.G.; Ramos, A.J. S100B Alters Neuronal Survival and Dendrite Extension via RAGE-Mediated NF-κB Signaling. J. Neurochem. 2011, 117, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, A.; Seoane, R.; González Torres, A.; Rosciszewski, G.; Angelo, M.F.; Rossi, A.; Barker, P.A.; Ramos, A.J. S100B Protein Activates a RAGE-Dependent Autocrine Loop in Astrocytes: Implications for Its Role in the Propagation of Reactive Gliosis. J. Neurochem. 2014, 131, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.; Donno, C.; Giannetti, S.; Perić, M.; Andjus, P.; D’Ambrosi, N.; Michetti, F. The Astrocytic S100B Protein with Its Receptor RAGE Is Aberrantly Expressed in SOD1G93A Models, and Its Inhibition Decreases the Expression of Proinflammatory Genes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 1626204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclerc, E.; Fritz, G.; Vetter, S.W.; Heizmann, C.W. Binding of S100 Proteins to RAGE: An Update. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2009, 1793, 993–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Ali, S.A. Multifunctional Role of S100 Protein Family in the Immune System: An Update. Cells 2022, 11, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.C.; Cristóvão, J.S.; Pardon, E.; Steyaert, J.; Fritz, G.; Gomes, C.M. Functional Modulation of RAGE Activation by Multimeric S100B Using Single-Domain Antibodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sante, G.; Amadio, S.; Sampaolese, B.; Valentini, M.; Volonté, C.; Casalbore, P.; Ria, F.; Michetti, F. The S100B Inhibitor Pentamidine Ameliorates Clinical Score and Neuropathology of Relapsing—Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Mouse Model. Cells 2020, 9, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camponeschi, C.; De Carluccio, M.; Amadio, S.; Clementi, M.E.; Sampaolese, B.; Volonté, C.; Tredicine, M.; Romano Spica, V.; Di Liddo, R.; Ria, F.; et al. S100B Protein as a Therapeutic Target in Multiple Sclerosis: The S100B Inhibitor Arundic Acid Protects from Chronic Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barateiro, A.; Afonso, V.; Santos, G.; Cerqueira, J.J.; Brites, D.; van Horssen, J.; Fernandes, A. S100B as a Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Multiple Sclerosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 3976–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, C.; Barateiro, A.; Neto, A.; Soromenho, B.; Basto, A.P.; Mateus, J.M.; Xapelli, S.; Sebastião, A.M.; Brites, D.; Graça, L.; et al. S100B Inhibition Protects from Chronic Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Verkhratsky, A.; Shi, F.-D. Astrocytes and Microglia in Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; Volume 210, pp. 133–145. ISBN 978-0-443-19102-2. [Google Scholar]
- Burrows, D.J.; McGown, A.; Jain, S.A.; De Felice, M.; Ramesh, T.M.; Sharrack, B.; Majid, A. Animal Models of Multiple Sclerosis: From Rodents to Zebrafish. Mult. Scler. J. 2019, 25, 306–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantzer, C.G.; Parmigiani, E.; Cerrato, V.; Tomiuk, S.; Knauel, M.; Jungblut, M.; Buffo, A.; Bosio, A. ACSA-2 and GLAST Classify Subpopulations of Multipotent and Glial-Restricted Cerebellar Precursors. J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 2228–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, U.C.; Bhol, N.K.; Swain, S.K.; Samal, R.R.; Nayak, P.K.; Raina, V.; Panda, S.K.; Kerry, R.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Neurological Disorders: Mechanisms and Implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clementi, M.E.; Sampaolese, B.; Di Sante, G.; Ria, F.; Di Liddo, R.; Romano Spica, V.; Michetti, F. S100B Expression Plays a Crucial Role in Cytotoxicity, Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Nitric Oxide Synthase Activation Induced by Amyloid β-Protein in an Astrocytoma Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, F.; Tsoporis, J.N.; Izhar, S.; Desjardins, J.-F.; Parker, T.G. Deficiency of S100B Confers Resistance to Experimental Diabetes in Mice. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 365, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, G.A.; Geßner, C.; Osterhof, C.; Hankeln, T.; Burmester, T. Transcriptomes of Clusterin- and S100B-Transfected Neuronal Cells Elucidate Protective Mechanisms against Hypoxia and Oxidative Stress in the Hooded Seal (Cystophora Cristata) Brain. BMC Neurosci. 2022, 23, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeh, U.; Singh, S. Targeting S100B Protein as a Surrogate Biomarker and Its Role in Various Neurological Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyck, R.H.; Bogoch, I.I.; Marks, A.; Melvin, N.R.; Teskey, G.C. Enhanced Epileptogenesis in S100B Knockout Mice. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2002, 106, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmitia, E.C.; Dolan, K.; Whitaker-Azmitia, P.M. S-100B but Not NGF, EGF, Insulin or Calmodulin Is a CNS Serotonergic Growth Factor. Brain Res. 1990, 516, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.; Zhou, W.; Ye, P.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Tian, L.; Peng, B.; Hu, M.; Xu, B. LncRNA 4933431K23Rik Modulate Microglial Phenotype via Inhibiting miR-10a-5p in Spinal Cord Injury Induced Neuropathic Pain. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotegut, P.; Kuehn, S.; Meißner, W.; Dick, H.B.; Joachim, S.C. Intravitreal S100B Injection Triggers a Time-Dependent Microglia Response in a Pro-Inflammatory Manner in Retina and Optic Nerve. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1186–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Ortega, K.; Canul-Euan, A.A.; Solis-Paredes, J.M.; Borboa-Olivares, H.; Reyes-Muñoz, E.; Estrada-Gutierrez, G.; Camacho-Arroyo, I. S100B Actions on Glial and Neuronal Cells in the Developing Brain: An Overview. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1425525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.; Bernstein, H.-G.; Bielau, H.; Berndt, A.; Brisch, R.; Mawrin, C.; Keilhoff, G.; Bogerts, B. Evidence for a Wide Extra-Astrocytic Distribution of S100B in Human Brain. BMC Neurosci. 2007, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, J.L.; Neves, J.D.; Vizuete, A.F.; Aristimunha, D.; Pedroso, T.A.; Sanches, E.F.; Gonçalves, C.A.; Netto, C.A. Arundic Acid (ONO-2506), an Inhibitor of S100B Protein Synthesis, Prevents Neurological Deficits and Brain Tissue Damage Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Male Wistar Rats. Neuroscience 2020, 440, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakov, A.S.; Sofin, A.D.; Avkhacheva, N.V.; Deryusheva, E.I.; Rastrygina, V.A.; Permyakova, M.E.; Uversky, V.N.; Permyakov, E.A.; Permyakov, S.E. Interferon-β Activity Is Affected by S100B Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, A.-M.; Neațu, M.; Luca, D.-G.; Davidescu, E.I.; Popescu, B.-O. Fluid Biomarkers in Demyelinating Spectrum Disorders: Past, Present, and Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.A.; Drury, S.; Fu, C.; Qu, W.; Taguchi, A.; Lu, Y.; Avila, C.; Kambham, N.; Bierhaus, A.; Nawroth, P.; et al. RAGE Mediates a Novel Proinflammatory Axis: A Central Cell Surface Receptor for S100/Calgranulin Polypeptides. Cell 1999, 97, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponath, G.; Schettler, C.; Kaestner, F.; Voigt, B.; Wentker, D.; Arolt, V.; Rothermundt, M. Autocrine S100B Effects on Astrocytes Are Mediated via RAGE. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 184, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srakočić, S.; Josić, P.; Trifunović, S.; Gajović, S.; Grčević, D.; Glasnović, A. Proposed Practical Protocol for Flow Cytometry Analysis of Microglia from the Healthy Adult Mouse Brain: Systematic Review and Isolation Methods’ Evaluation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1017976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tredicine, M.; Camponeschi, C.; Pirolli, D.; Lucchini, M.; Valentini, M.; Geloso, M.C.; Mirabella, M.; Fidaleo, M.; Righino, B.; Moliterni, C.; et al. A TLR/CD44 Axis Regulates T Cell Trafficking in Experimental and Human Multiple Sclerosis. iScience 2022, 25, 103763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penitente, R.; Nicolò, C.; Van den Elzen, P.; Di Sante, G.; Agrati, C.; Aloisi, F.; Sercarz, E.E.; Ria, F. Administration of PLP 139–151 Primes T Cells Distinct from Those Spontaneously Responsive In Vitro to This Antigen. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 6611–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stromnes, I.M.; Goverman, J.M. Active Induction of Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolò, C.; Di Sante, G.; Orsini, M.; Rolla, S.; Columba-Cabezas, S.; Romano Spica, V.; Ricciardi, G.; Chan, B.M.C.; Ria, F. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in the Adjuvant Modulates the Balance of Th Immune Response to Self-Antigen of the CNS without Influencing a “Core” Repertoire of Specific T Cells. Int. Immunol. 2006, 18, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolò, C.; Sali, M.; Di Sante, G.; Geloso, M.C.; Signori, E.; Penitente, R.; Uniyal, S.; Rinaldi, M.; Ingrosso, L.; Fazio, V.M.; et al. Mycobacterium Smegmatis Expressing a Chimeric Protein MPT64-Proteolipid Protein (PLP) 139-151 Reorganizes the PLP-Specific T Cell Repertoire Favoring a CD8-Mediated Response and Induces a Relapsing Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piermattei, A.; Migliara, G.; Di Sante, G.; Foti, M.; Hayrabedyan, S.B.; Papagna, A.; Geloso, M.C.; Corbi, M.; Valentini, M.; Sgambato, A.; et al. Toll-Like Receptor 2 Mediates In Vivo Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Modulates Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zhu, X.; Xu, P.; Li, Y. Pharmacological Inhibition of USP7 Promotes Antitumor Immunity and Contributes to Colon Cancer Therapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Carluccio, M.; Di Sante, G.; Clementi, M.E.; Ruggirello, M.; Stabile, A.M.; Pistilli, A.; Marini, S.; Romano Spica, V.; Rende, M.; Ria, F.; et al. Effect on Different Glial Cell Types of S100B Modulation in Multiple Sclerosis Experimental Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135948
De Carluccio M, Di Sante G, Clementi ME, Ruggirello M, Stabile AM, Pistilli A, Marini S, Romano Spica V, Rende M, Ria F, et al. Effect on Different Glial Cell Types of S100B Modulation in Multiple Sclerosis Experimental Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):5948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135948
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Carluccio, Maria, Gabriele Di Sante, Maria Elisabetta Clementi, Mariangela Ruggirello, Anna Maria Stabile, Alessandra Pistilli, Stefano Marini, Vincenzo Romano Spica, Mario Rende, Francesco Ria, and et al. 2025. "Effect on Different Glial Cell Types of S100B Modulation in Multiple Sclerosis Experimental Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 5948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135948
APA StyleDe Carluccio, M., Di Sante, G., Clementi, M. E., Ruggirello, M., Stabile, A. M., Pistilli, A., Marini, S., Romano Spica, V., Rende, M., Ria, F., & Michetti, F. (2025). Effect on Different Glial Cell Types of S100B Modulation in Multiple Sclerosis Experimental Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 5948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135948








