Distinct Biomarker Profiles of B-Cell Activation in Metabolic and Viral Hepatic Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Differential Expression of B-Cell Activation Markers in Metabolic and Viral Fibrosis: Univariate and Adjusted Findings
2.2. Correlation Patterns and Insights into the Role of BAFF
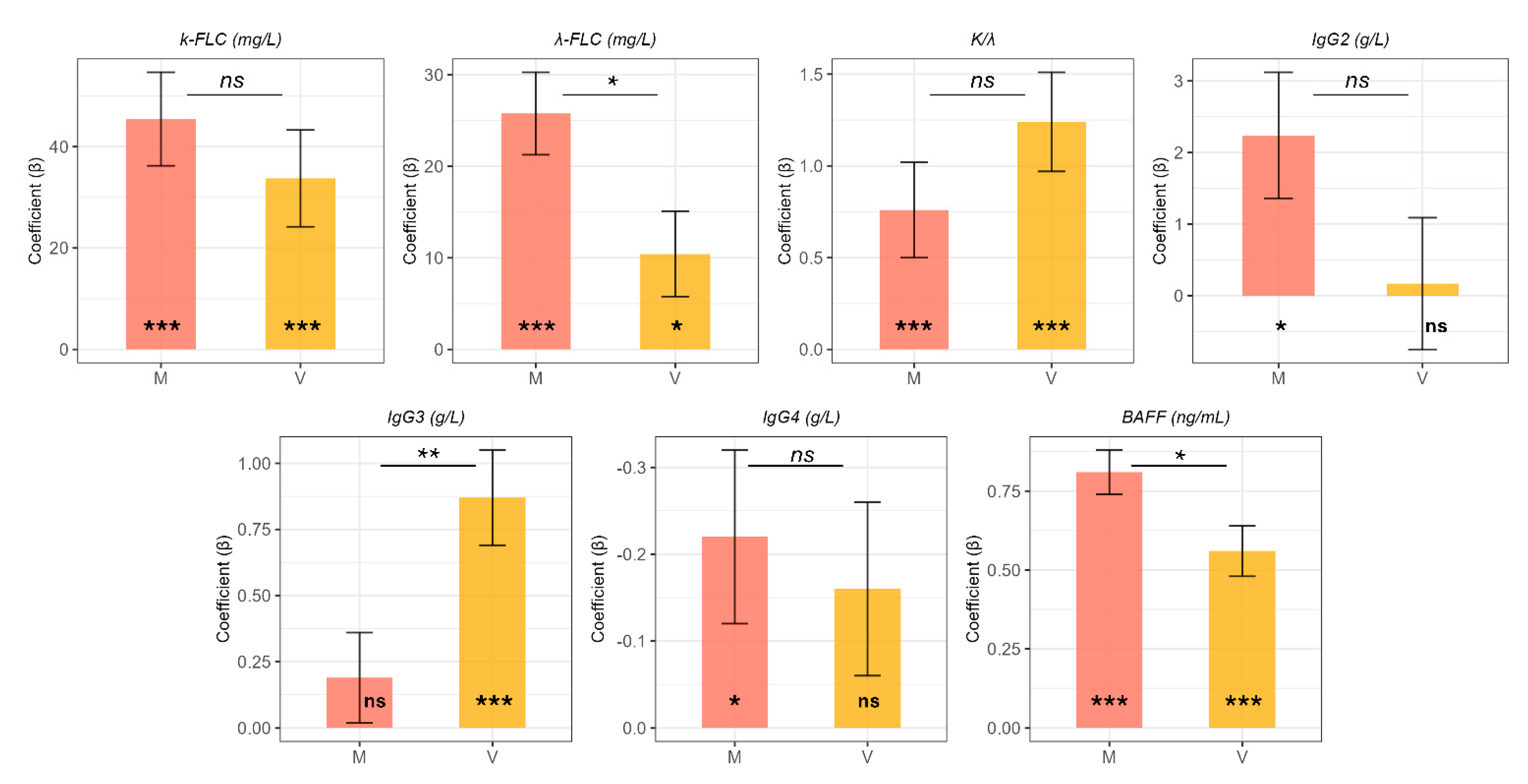
2.3. Multivariate Analysis of Circulating Markers for Hepatic Fibrosis: A Molecular Fingerprint of Viral and Metabolic Etiology
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Patients and Methods
4.2. Laboratory Testing
4.3. Statistical Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Lackner, C.; Tiniakos, D. Fibrosis and alcohol-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuppan, D.; Surabattula, R.; Wang, X.Y. Determinants of fibrosis progression and regression in NASH. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnazzo, V.; Pignalosa, S.; Tagliaferro, M.; Gragnani, L.; Zignego, A.L.; Racco, C.; Di Biase, L.; Basile, V.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Di Santo, R.; et al. Exploratory study of extracellular matrix biomarkers for non-invasive liver fibrosis staging: A machine learning approach with XGBoost and explainable AI. Clin. Biochem. 2025, 135, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, W.K.; Lo, Y.R.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Yuen, M.F. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2018, 392, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, A.; Winkler, M.; Silva Afonso, M.; Aggarwal, A.; Lopez, D.; Berger, H.; Kohlhepp, M.S.; Liu, H.; Özdirik, B.; Eschrich, J.; et al. Mapping the hepatic immune landscape identifies monocytic macrophages as key drivers of steatohepatitis and cholangiopathy progression. Hepatology 2023, 78, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Cui, H.; Racanelli, A.C.; Zhang, L.; Ye, T.; Ding, B.; et al. Targeting fibrosis: Mechanisms and clinical trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghany, M.G.; Strader, D.B.; Thomas, D.L.; Seeff, L.B. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: An update. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1335–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, U.; Miele, L.; Napodano, C.; Ciasca, G.; Gulli, F.; Pocino, K.; De Matthaeis, N.; Liguori, A.; De Magistris, A.; Marrone, G.; et al. The diagnostic performance of PIVKA-II in metabolic and viral hepatocellular carcinoma: A pilot study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 12675–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierantonelli, I.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Basic pathogenetic mechanisms in the progression from NAFLD to NASH. Transplantation 2019, 103, e1–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiha, G.; Alswat, K.; Al Khatry, M.; ISharara, A.; Örmeci, N.; Waked, I.; Benazzouz, M.; Al-Ali, F.; Hamed, A.E.; Hamoudi, W.; et al. Nomenclature and definition of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A consensus from the Middle East and north Africa. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver fibrosis, but no other histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentini, M.; Conti, V.; Cristofoletti, C.; Lazzeri, C.; Marrapodi, R.; Russo, G.; Casato, M.; Fiorilli, M. Clonal expansion and functional exhaustion of monoclonal marginal zone B cells in mixed cryoglobulinemia: The yin and yang of HCV-driven lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napodano, C.; Gulli, F.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Marino, M.; Basile, U. Cryoglobulins: Identification, classification, and novel biomarkers of mysterious proteins. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 104, 299–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragnani, L.; Piluso, A.; Giannini, C.; Caini, P.; Fognani, E.; Monti, M.; Petrarca, A.; Ranieri, J.; Razzolini, G.; Froio, V.; et al. Genetic determinants in hepatitis C virus-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia: Role of polymorphic variants of BAFF promoter and Fcγ receptors. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanova, S.Y.; Lysenko Kozlovskaya, L.V.; Milovanova, L.Y.; Mrykhin, N.N.; Russkih, A.V.; Muchin, N.A. HCV-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia and b-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma—pathogenetically related problems. Ter. Arkhiv 2018, 90, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napodano, C.; Ciasca, G.; Chiusolo, P.; Pocino, K.; Gragnani, L.; Stefanile, A.; Gulli, F.; Lorini, S.; Minnella, G.; Fosso, F.; et al. Serological and Molecular Characterization of Hepatitis C Virus-Related Cryoglobulinemic Vasculitis in Patients without Cryoprecipitate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferro, M.; Marino, M.; Basile, V.; Pocino, K.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Ciasca, G.; Basile, U.; Carnazzo, V. New Biomarkers in Liver Fibrosis: A Pass through the Quicksand? J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, Y.; Cai, J.; Sun, M.; Zeng, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M. Serum biomarkers for liver fibrosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 537, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, M.; Pinzani, M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 65, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toubi, E.; Gordon, S.; Kessel, A.; Rosner, I.; Rozenbaum, M.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Zuckerman, E. Elevated serum B-Lymphocyte activating factor (BAFF) in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: Association with autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2006, 27, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, F.; Khan, S.; Wang, H.; Revelo, X.S. The emerging role of B cells in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, M.; Chinnadurai, R.; Velazquez, V.M.; Tedesco, D.; Elrod, E.; Han, J.; Sharma, P.; Ibegbu, C.; Gewirtz, A.; Anania, F.; et al. Liver fibrosis occurs through dysregulation of MyD88-dependent innate B-cell activity. Hepatology 2015, 61, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, F.E. Cytokine-producing B lymphocytes—Key regulators of immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; Schwabe, R.F. Hepatic inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.A.; Belvedere, O.; Orr, A.; Pieri, K.; LaFleur, D.W.; Feng, P.; Soppet, D.; Charters, M.; Gentz, R.; Parmelee, D.; et al. BLyS: Member of the tumor necrosis factor family and B lymphocyte stimulator. Science 1999, 285, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, P.; Sanyal, A.J. The BAFFling problem of B cell-activating factor in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2013, 7, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Napodano, C.; Marino, M.; Stefanile, A.; Pocino, K.; Scatena, R.; Gulli, F.; Rapaccini, G.L.; Delli Noci, S.; Capozio, G.; Rigante, D.; et al. Immunological role of IgG subclasses. Immunol. Investig. 2021, 50, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, U.; Gulli, F.; Gragnani, L.; Fognani, E.; Napodano, C.; Pocino, K.; Zignego, A.L.; Rapaccini, G.L. IgG3 subclass: A possible trigger of mixed cryoglobulin cascade in hepatitis C virus chronic infection. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, A.; Han, H.; Yuan, L.; Donovan, J.; Kaplowitz, N.; Kanel, G.; Kahn, J.; Dara, L. IgG: IgM ratios of liver plasma cells reveal similar phenotypes of primary biliary cholangitis with and without features of autoimmune hepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 19, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, N. The multifaceted roles of B lymphocytes in metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1447391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, T.V.; Succurro, E.; Arturi, F.; Giancotti, A.; Peronace, C.; Quirino, A.; Sesti, F.; Andreozzi, F.; Hribal, M.L.; Perticone, F.; et al. Serum IgG2 levels are specifically associated with whole-body insulin-mediated glucose disposal in non-diabetic offspring of type 2 diabetic individuals: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomp, R.; Ruhaak, L.R.; Uh, H.W.; Reiding, K.R.; Selman, M.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Slagboom, P.E.; Beekman, M.; Wuhrer, M. Subclass-specific IgG glycosylation is associated with markers of inflammation and metabolic health. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulli, F.; Napodano, C.; Marino, M.; Ciasca, G.; Pocino, K.; Basile, V.; Visentini, M.; Stefanile, A.; Todi, L.; De Spirito, M.; et al. Serum immunoglobulin free light chain levels in systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 199, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot Kormelink, T.; Askenase, P.W.; Redegeld, F.A. Immunobiology of antigen-specific immunoglobulin free light chains in chronic inflammatory diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, U.; Marino, M.; Napodano, C.; Pocino, K.; Alboini, P.E.; Gulli, F.; Evoli, A.; Provenzano, C.; Bartoccioni, E. Serological Immunoglobulin-Free Light Chain Profile in Myasthenia Gravis Patients. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 25, 9646209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napodano, C.; Callà, C.; Fiorita, A.; Marino, M.; Taddei, E.; Di Cesare, T.; Passali, G.C.; Di Santo, R.; Stefanile, A.; Fantoni, M.; et al. Salivary Biomarkers in COVID-19 Patients: Towards a Wide-Scale Test for Monitoring Disease Activity. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, C.; Ciasca, G.; Baglivo, I.; Di Santo, R.; Gasbarrini, A.; Firinu, D.; Bagnasco, D.; Passalacqua, G.; Schiappoli, M.; Caminati, M.; et al. Immunoglobulin free light chains in severe asthma patient: Could they be a new biomarker? Allergy 2024, 79, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandireddy, R.; Sakthivel, S.; Gupta, P.; Behari, J.; Tripathi, M.; Singh, B.K. Systemic impacts of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) on heart, muscle, and kidney related diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1433857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, F.; Kite, C.; Lagojda, L.; Dallaway, A.; Chatha, K.K.; Chaggar, S.S.; Dalamaga, M.; Kassi, E.; Kyrou, I.; Randeva, H.S. Non-invasive Scores and Serum Biomarkers for Fatty Liver in the Era of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Comprehensive Review From NAFLD to MAFLD and MASLD. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 510–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Kubota, N.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Role of Insulin Resistance in MAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Cuevas, J.; Santos, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Pathophysiological Molecular Mechanisms of Obesity: A Link between MAFLD and NASH with Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, H.; Armutcu, F.; Akyol, O.; Weiskirchen, R. The potential pathophysiological role of altered lipid metabolism and electronegative low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 523, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accacha, S.; Barillas-Cerritos, J.; Srivastava, A.; Ross, F.; Drewes, W.; Gulkarov, S.; De Leon, J.; Reiss, A.B. From Childhood Obesity to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Hyperlipidemia Through Oxidative Stress During Childhood. Metabolites 2025, 15, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocino, K.; Stefanile, A.; Basile, V.; Napodano, C.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Di Santo, R.; Callà, C.A.M.; Gulli, F.; Saporito, R.; Ciasca, G.; et al. Cytokines and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Biomarkers of a Deadly Embrace. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratim Das, P.; Medhi, S. Role of inflammasomes and cytokines in immune dysfunction of liver cirrhosis. Cytokine 2023, 170, 156347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; Lario, M.; Álvarez-Mon, M. Cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction: Distinctive features and clinical relevance. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napodano, C.; Carnazzo, V.; Basile, V.; Pocino, K.; Stefanile, A.; Gallucci, S.; Natali, P.; Basile, U.; Marino, M. NLRP3 inflammasome involvement in heart, liver, and lung diseases—A lesson from cytokine storm syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Tilg, H. MASLD: A systemic metabolic disorder with cardiovascular and malignant complications. Gut 2024, 73, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, C.M. NAFLD (MASLD)/NASH (MASH): Does It Bother to Label at All? A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khlaiphuengsin, A.; Chuaypen, N.; Pinjaroen, N.; Sirichindakul, B.; Hirankarn, N.; Tangkijvanich, P. Plasma B-cell activating factor levels and polymorphisms in hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical correlation and prognosis. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 39, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Yang, C.; Li, N.; Li, F.; Sang, J.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Liu, Z. Association of genetic variation in B-cell activating factor with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 188, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, M.; Pinzani, M. Liver fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH: From pathophysiology towards diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Asp. Med. 2024, 95, 101231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.U.; Cusi, K. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Causes, diagnosis, cardiometabolic consequences, and treatment strategies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemitsu-Okada, K.; Abe, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Miyake, T.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshida, O.; Koizumi, Y.; Hirooka, M.; Tokumoto, Y.; Matsuura, B.; et al. Role of B cell-activating factor in fibrosis progression in a murine model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, D.C.V.; Castellanos, S.G.; Sandoval, M.E.V.; García, A.G. B-Cell Activating Factor Increases Related to Adiposity, Insulin Resistance, and Endothelial Dysfunction in Overweight and Obese Subjects. Life 2022, 12, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Abe, M.; Miyake, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Tada, F.; Furukawa, S.; Matsuura, B.; Hiasa, Y.; Onji, M. B cell-activating factor controls the production of adipokines and induces insulin resistance. Obesity 2011, 19, 1915–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestri, S.; Nascimbeni, F.; Romagnoli, D.; Baldelli, E.; Targher, G.; Lonardo, A. Type 2 Diabetes in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hepatitis C Virus Infection--Liver: The “Musketeer” in the Spotlight. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Guaraldi, G.; Nascimbeni, F.; Romagnoli, D.; Zona, S.; Targher, G. Fatty liver is associated with an increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease—Evidence from three different disease models: NAFLD, HCV and HIV. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9674–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Metabolomics Data Analysis, Interpretation, and Integration with Other Omics Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2104, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Li, S.; Xia, J. Network-Based Approaches for Multi-omics Integration. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2104, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnovsky, A.; Li, S. Pathway Analysis for Targeted and Untargeted Metabolomics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2104, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoberg, D.D.; Whiting, K.; Curry, M.; Lavery, J.A.; Larmarange, J. Reproducible Summary Tables with the gtsummary Package. R J. 2021, 13, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Psychogios, N.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.S. MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W652–W660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
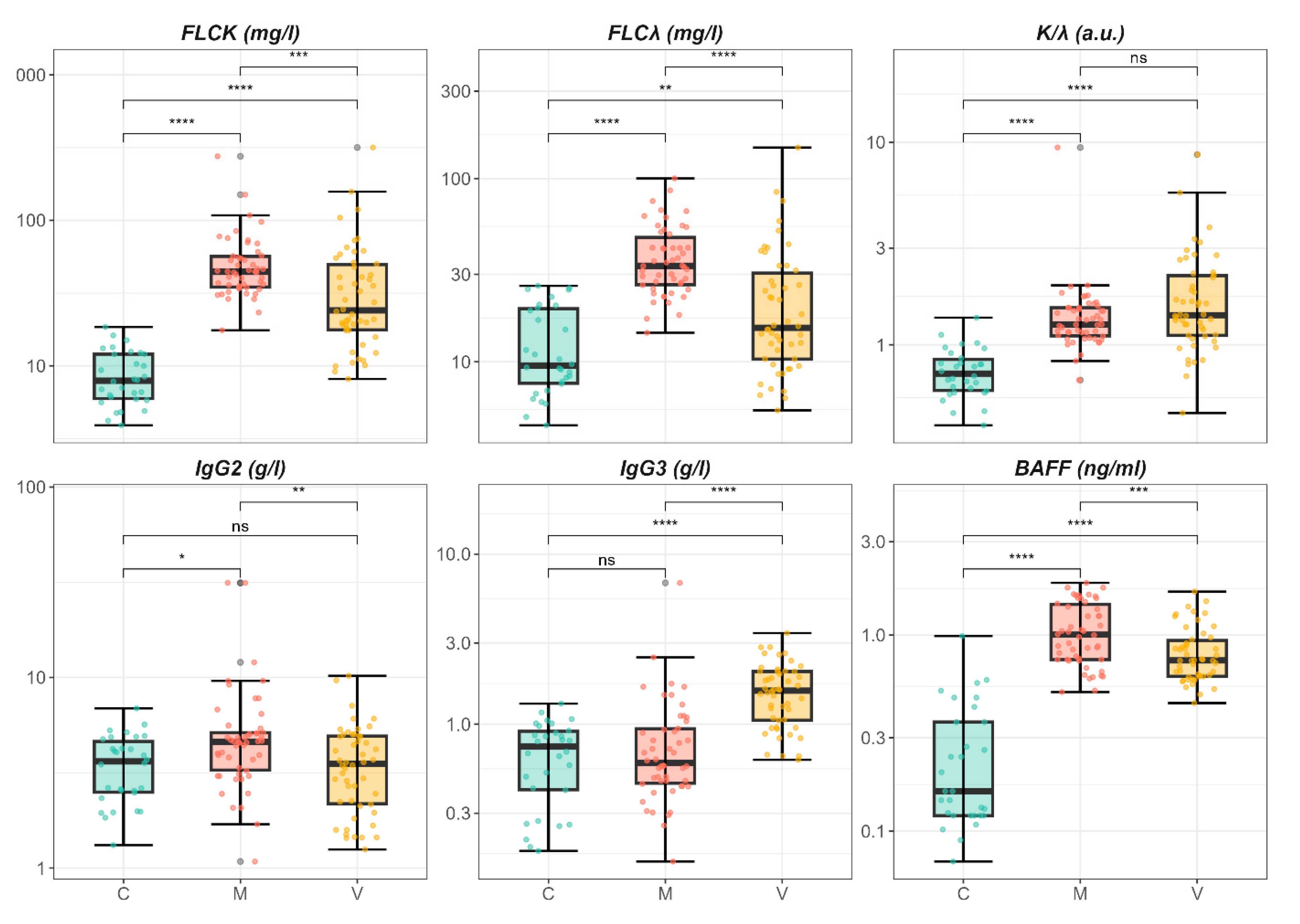


| Characteristic | C, N = 30 1 | M, N = 50 1 | V, N = 50 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 60.0 (54.3, 64.0) | 58.0 (53.3, 66.8) | 52.0 (46.3, 58.8) | 0.002 |
| Sex | 16.0 (53.3%) | 28.0 (56.0%) | 19.0 (38.0%) | 0.2 |
| FLC-k | 7.9 (6.0, 12.0) | 44.3 (34.8, 56.5) | 24.1 (17.7, 49.7) | <0.001 |
| FLC-λ | 9.5 (7.6, 19.5) | 33.4 (26.4, 47.8) | 15.3 (10.3, 30.5) | <0.001 |
| K/λ | 0.7 (0.6, 0.8) | 1.3 (1.1, 1.5) | 1.4 (1.1, 2.2) | <0.001 |
| IgG1 | 8.0 (5.9, 8.5) | 5.7 (4.3, 7.1) | 6.8 (4.8, 9.9) | 0.061 |
| IgG2 | 3.6 (2.5, 4.6) | 4.6 (3.3, 5.1) | 3.5 (2.2, 4.9) | 0.01 |
| IgG3 | 0.7 (0.4, 0.9) | 0.6 (0.5, 0.9) | 1.6 (1.1, 2.0) | <0.001 |
| IgG4 | 0.3 (0.2, 0.8) | 0.3 (0.2, 0.5) | 0.3 (0.2, 0.7) | 0.5 |
| METAVIR-SCORE | 0.3 | |||
| F2 | 22.0 (44.0%) | 28.0 (56.0%) | ||
| F3 | 28.0 (56.0%) | 22.0 (44.0%) | ||
| BAFF | 0.2 (0.1, 0.4) | 1.0 (0.8, 1.4) | 0.7 (0.6, 0.9) | <0.001 |
| Group V | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Adjusted Differences | Std. Error | p-Value |
| k-FLC (mg/L) | 33.73 | 9.54 | <0.001 |
| λ-FLC (mg/L) | 10.43 | 4.66 | 0.027 |
| k/λ | 1.24 | 0.27 | <0.001 |
| IgG2 (g/L) | 0.17 | 0.92 | 0.85 |
| IgG3 (g/L) | 0.87 | 0.18 | <0.001 |
| IgG4 (g/L) | −0.16 | 0.10 | 0.11 |
| BAFF (ng/mL) | 0.56 | 0.08 | <0.001 |
| Group M | |||
| Model | Adjusted Differences | Std. Error | p-Value |
| k-FLC (mg/L) | 45.42 | 9.21 | <0.001 |
| λ-FLC (mg/L) | 25.75 | 4.5 | <0.001 |
| k/λ | 0.76 | 0.26 | <0.001 |
| IgG2 (g/L) | 2.24 | 0.88 | 0.012 |
| IgG3 (g/L) | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.28 |
| IgG4 (g/L) | −0.22 | 0.10 | 0.023 |
| BAFF (ng/mL) | 0.81 | 0.07 | <0.001 |
| Model Outcome | BAFF (Estimate ± SE, p) | State V (Estimate ± SE, p) | State M (Estimate ± SE, p) | Model p-Value | Adj. R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| κ-FLC | –5.41 ± 11.25 p = 0.63 | 35.80 ± 11.14 p = 0.0017 | 49.61 ± 12.89 p < 0.0001 | 4.15 × 10⁻⁵ | 0.146 |
| λ-FLC | –1.12 ± 5.55 p = 0.84 | 12.76 ± 5.49, p = 0.0218 | 26.87 ± 6.36 p < 0.0001 | 1.03 × 10⁻⁶ | 0.196 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basile, U.; Carnazzo, V.; Basile, V.; Pignalosa, S.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Vinante, I.; Tagliaferro, M.; Niccolini, B.; Di Santo, R.; Rapaccini, G.L.; et al. Distinct Biomarker Profiles of B-Cell Activation in Metabolic and Viral Hepatic Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135942
Basile U, Carnazzo V, Basile V, Pignalosa S, D’Ambrosio F, Vinante I, Tagliaferro M, Niccolini B, Di Santo R, Rapaccini GL, et al. Distinct Biomarker Profiles of B-Cell Activation in Metabolic and Viral Hepatic Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):5942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135942
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasile, Umberto, Valeria Carnazzo, Valerio Basile, Stefano Pignalosa, Francesca D’Ambrosio, Ilaria Vinante, Marzia Tagliaferro, Benedetta Niccolini, Riccardo Di Santo, Gian Ludovico Rapaccini, and et al. 2025. "Distinct Biomarker Profiles of B-Cell Activation in Metabolic and Viral Hepatic Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 5942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135942
APA StyleBasile, U., Carnazzo, V., Basile, V., Pignalosa, S., D’Ambrosio, F., Vinante, I., Tagliaferro, M., Niccolini, B., Di Santo, R., Rapaccini, G. L., Rosa, E., De Spirito, M., Marino, M., & Ciasca, G. (2025). Distinct Biomarker Profiles of B-Cell Activation in Metabolic and Viral Hepatic Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 5942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26135942









