Extramedullary Relapse of CBFA2T3::GLIS2-Positive Megakaryoblastic Leukemia Mimicking Secondary Ewing Sarcoma: An Exemplary Case for the Diagnostic Trap
Abstract
1. Introduction
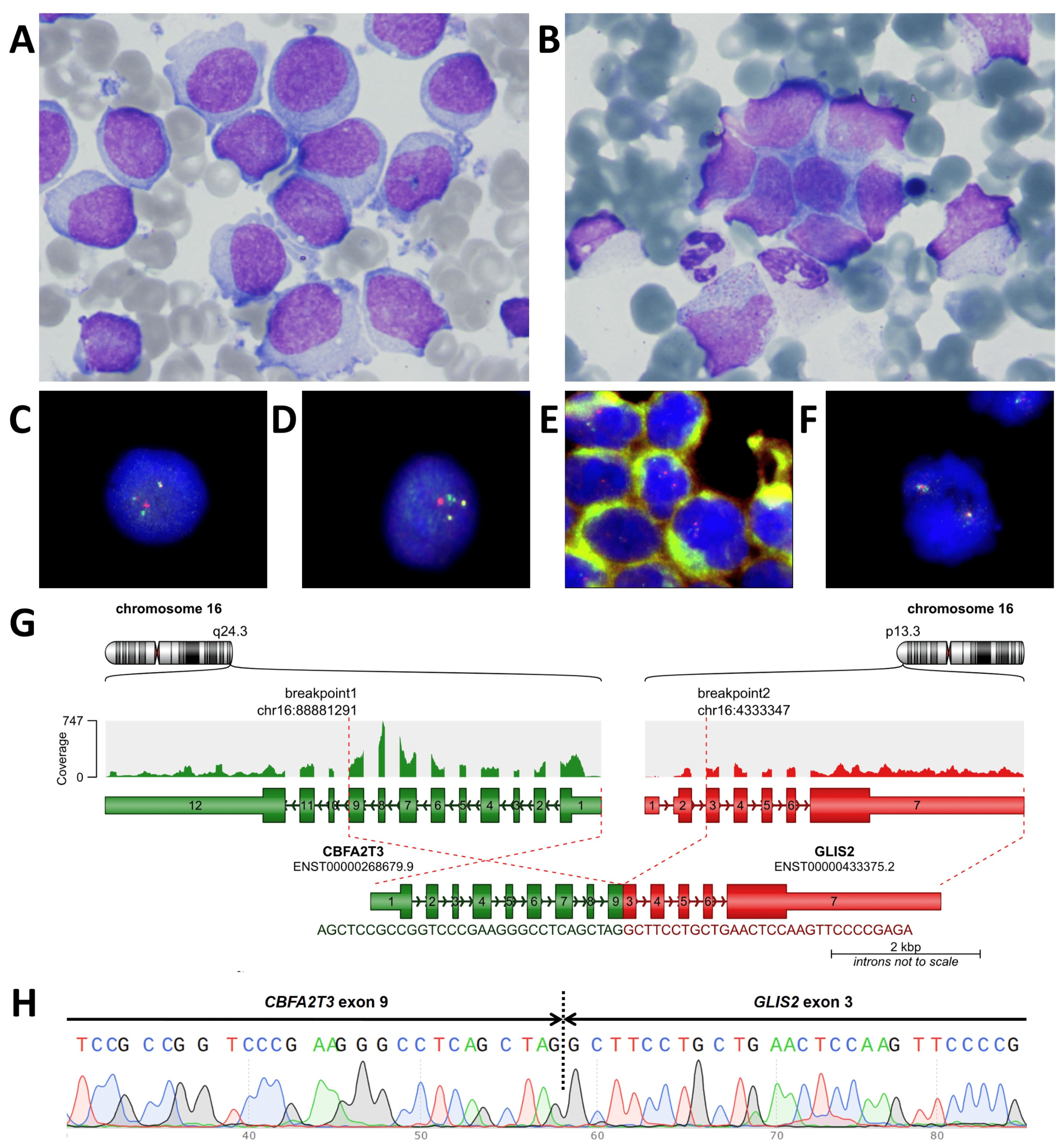
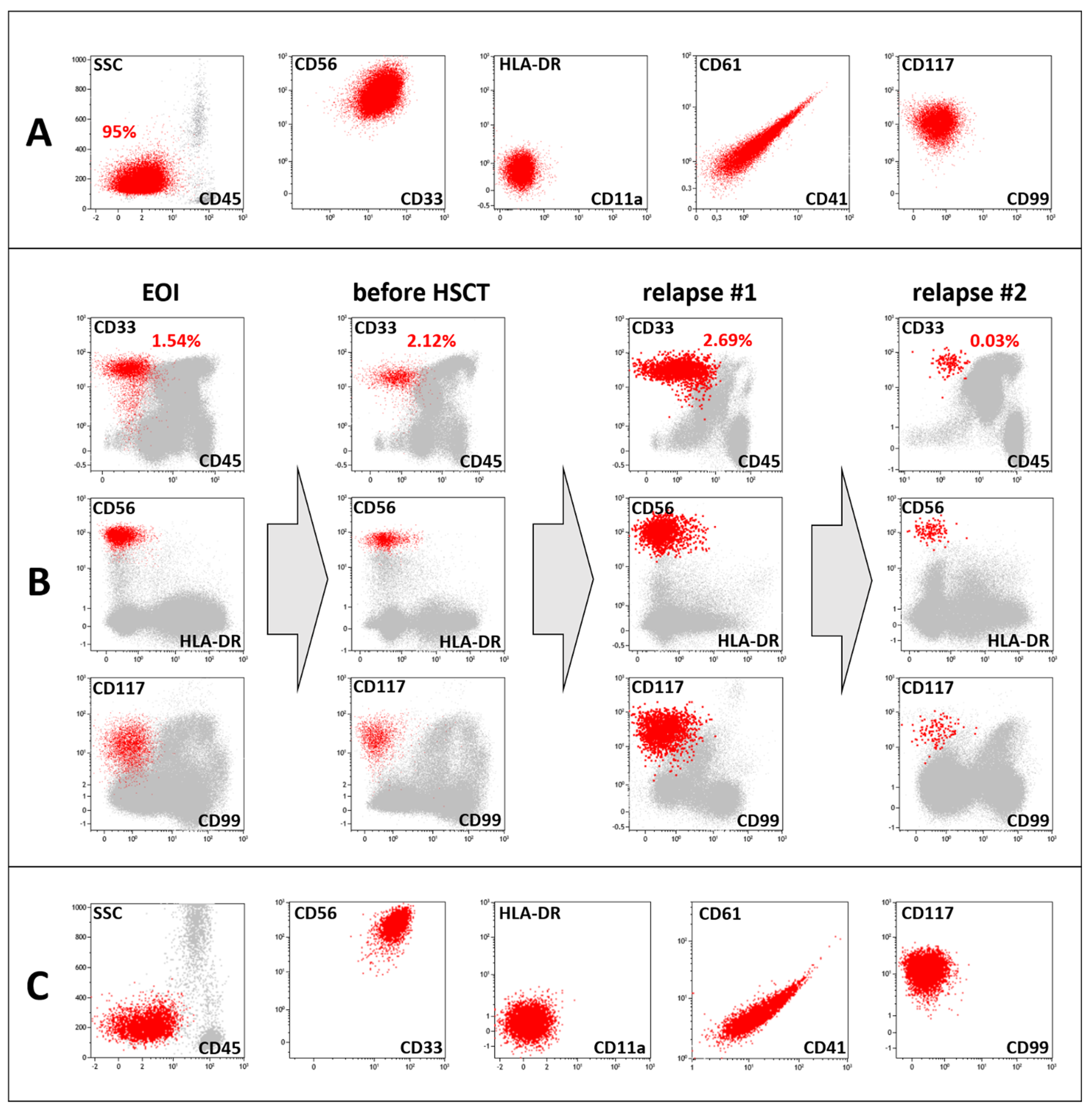
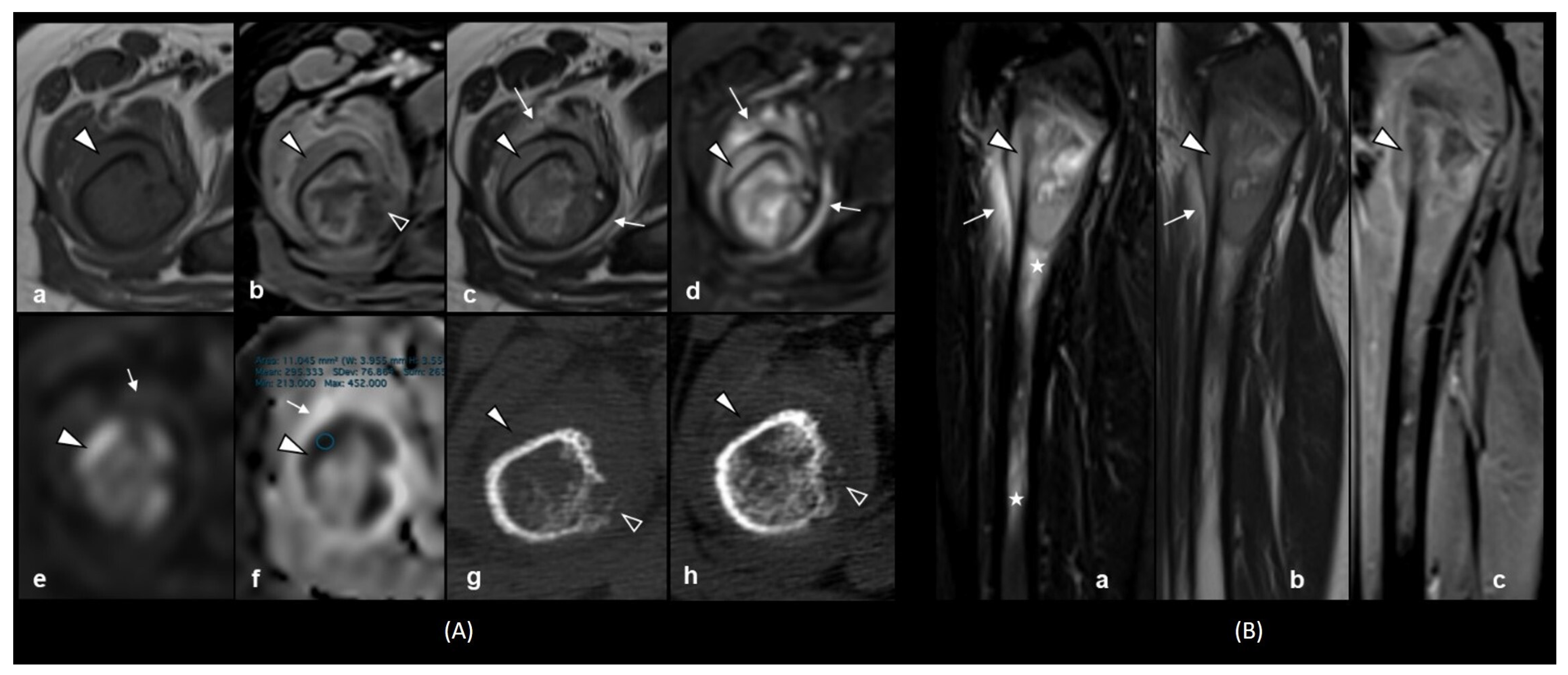
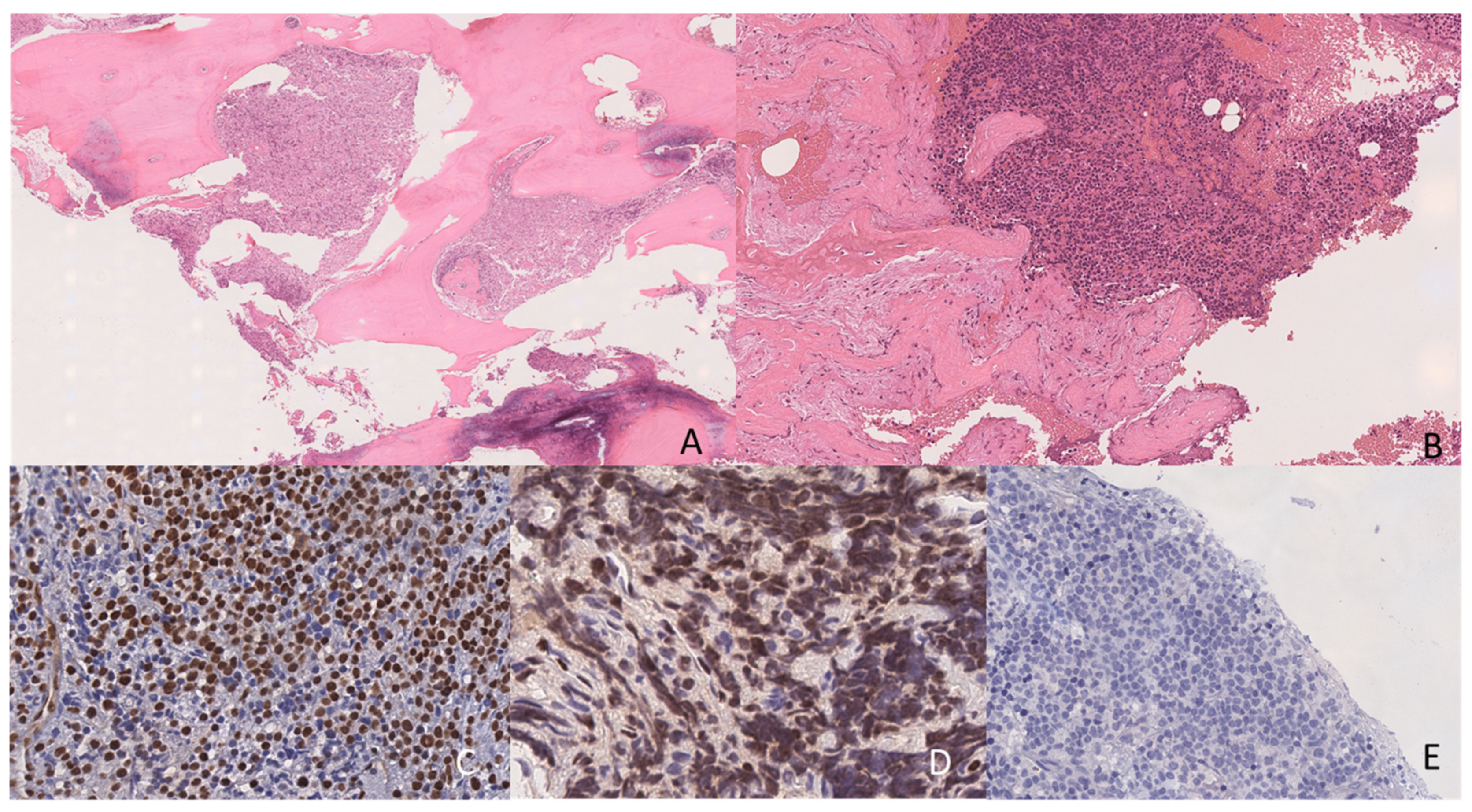
2. Case Presentation
3. Laboratory Studies at the Time of Suspected Relapse Diagnosis
4. Discussion
5. Methods
5.1. Immunophenotyping
5.2. Cytogenetic and Molecular Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Rooij, J.D.; Branstetter, C.; Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Walsh, M.P.; Cheng, J.; Obulkasim, A.; Dang, J.; Easton, J.; Verboon, L.J.; et al. Pediatric non-Down syndrome acute megakaryoblastic leukemia is characterized by distinct genomic subsets with varying outcomes. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.M.; Catovsky, D.; Daniel, M.T.; Flandrin, G.; Galton, D.A.; Gralnick, H.R.; Sultan, C. Criteria for the diagnosis of acute leukemia of megakaryocyte lineage (M7). A report of the French-American-British Cooperative Group. Ann. Intern. Med. 1985, 103, 460–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomfield, C.D.; Brunning, R.D. FAB M7: Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia--beyond morphology. Ann. Intern. Med. 1985, 103, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athale, U.H.; Razzouk, B.I.; Raimondi, S.C.; Long, X.; Behm, F.G.; Head, D.R.; Srivastava, D.K.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Bowman, L.; Pui, C.H.; et al. Biology and outcome of childhood acute megakaryoblastic leukemia: A single institution’s experience. Blood 2001, 97, 3727–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, D.R.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Lange, B.; Woods, W.G. Comparison of childhood myelodysplastic syndrome, AML FAB M6 or M7, CCG 2891: Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 49, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, L.; Pulsoni, A.; Vignetti, M.; Mele, L.; Fianchi, L.; Petti, M.C.; Mirto, S.; Falcucci, P.; Fazi, P.; Broccia, G.; et al. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia: Experience of GIMEMA trials. Leukemia 2002, 16, 1622–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.C.; Oliveira, M.S.P.; Fairclough, D.; Hurwitz, C.; Mirro, J.; Behm, F.G.; Head, D.; Silva, M.L.M.; Raimondi, S.C.; Crist, W.M.; et al. Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in Children and Adolescents: A Retrospective Analysis of 24 Cases. Leuk. Lymphoma 1993, 10, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallman, M.S.; Neuberg, D.; Bennett, J.M.; Francois, C.J.; Paietta, E.; Wiernik, P.H.; Dewald, G.; Cassileth, P.A.; Oken, M.M.; Rowe, J.M. Acute megakaryocytic leukemia: The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group experience. Blood 2000, 96, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Yang, L.; Qi, S.; Chen, Z.; Sun, M.; Wu, M.; Wu, B.; Tao, F.; Xiong, H. Clinical Analysis of Pediatric Acute Megakaryocytic Leukemia With CBFA2T3-GLIS2 Fusion Gene. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 46, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, T.A.; Larson Gedman, A.; Zhang, J.; Koss, C.S.; Marada, S.; Ta, H.Q.; Chen, S.C.; Su, X.; Ogden, S.K.; Dang, J.; et al. An inv(16)(p13.3q24.3)-encoded CBFA2T3-GLIS2 fusion protein defines an aggressive subtype of pediatric acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rørvik, S.D.; Torkildsen, S.; Bruserud, Ø.; Tvedt, T.H.A. Acute myeloid leukemia with rare recurring translocations—An overview of the entities included in the international consensus classification. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; LiuCui, Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, S.; et al. Genomic Landscape of Pediatric Non-Down’s Syndrome Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia in China. In Proceedings of the 65th ASH Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 29 November 2023; p. 4331. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.; Ries, R.E.; Hylkema, T.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Santaguida, M.T.; Brodersen, L.E.; Pardo, L.; Cummings, C.L.; Loeb, K.R.; et al. Comprehensive Transcriptome Profiling of Cryptic CBFA2T3-GLIS2 Fusion-positive AML Defines Novel Therapeutic Options–A COG and TARGET Pediatric AML Study. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masetti, R.; Pigazzi, M.; Togni, M.; Astolfi, A.; Indio, V.; Manara, E.; Casadio, R.; Pession, A.; Basso, G.; Locatelli, F. CBFA2T3-GLIS2 fusion transcript is a novel common feature in pediatric, cytogenetically normal AML, not restricted to FAB M7 subtype. Blood 2013, 121, 3469–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidenschink Brodersen, L.; Alonzo, T.A.; Menssen, A.J.; Gerbing, R.B.; Pardo, L.; Voigt, A.P.; Kahwash, S.B.; Hirsch, B.; Raimondi, S.; Gamis, A.S.; et al. A recurrent immunophenotype at diagnosis independently identifies high-risk pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: A report from Children’s Oncology Group. Leukemia 2016, 30, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangrando, A.; Cavagnero, F.; Scarparo, P.; Varotto, E.; Francescato, S.; Tregnago, C.; Cuccurullo, R.; Fagioli, F.; Nigro, L.L.; Masetti, R.; et al. CD56, HLA-DR, and CD45 recognize a subtype of childhood AML harboring CBFA2T3-GLIS2 fusion transcript. Cytom. A 2021, 99, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, K.; Hu, W.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, C.; Xie, Y.; Yu, L.; Huang, J.; et al. Immunophenotypic clustering in paediatric acute myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 204, 2275–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, L.M.; Voigt, A.P.; Alonzo, T.A.; Wilson, E.R.; Gerbing, R.B.; Paine, D.J.; Dai, F.; Menssen, A.J.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.A.; et al. Deciphering the Significance of CD56 Expression in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2020, 98, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Facio, C.S.; Botafogo, V.; Ferrao, P.M.; Canellas, M.C.; Milito, C.B.; Romano, S.; Lopes, D.V.; Teixeira, L.C.; Oliveira, E.; Bruno-Riscarolli, E.; et al. Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping for Diagnostic Orientation and Classification of Pediatric Cancer Based on the EuroFlow Solid Tumor Orientation Tube (STOT). Cancers 2021, 13, 4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajendra, S.; Anupurba, S.; Gupta, R.; Mallick, S.; Panda, D.; Thakral, D.; Gupta, S.K.; Bakhshi, S.; Seth, R.; Rai, S.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia with RAM immunophenotype: A new underdiagnosed entity. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2023, 45, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, D.; Chatterjee, G.; Sardana, R.; Khanka, T.; Ghogale, S.; Deshpande, N.; Badrinath, Y.; Shetty, D.; Narula, G.; Banavali, S.; et al. Utility of CD36 as a novel addition to the immunophenotypic signature of RAM-phenotype acute myeloid leukemia and study of its clinicopathological characteristics. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2021, 100, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, K.M.; Smith, J.; Heerema-McKenney, A.E.; Choi, J.K.; Ries, R.E.; Hirsch, B.A.; Raimondi, S.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Dang, A.; Alonzo, T.A.; et al. Pathologic, cytogenetic, and molecular features of acute myeloid leukemia with megakaryocytic differentiation: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, N.; Matarraz, S.; Nierkens, S.; Hofmans, M.; Novakova, M.; da Costa, E.S.; Fernandez, P.; Bras, A.E.; de Mello, F.V.; Mejstrikova, E.; et al. Immunophenotypic Analysis of Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia: A EuroFlow Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisschop, M.M.; Revesz, T.; Bierings, M.; van Weerden, J.F.; van Wering, E.R.; Hahlen, K.; van der Does-van den Berg, A. Extramedullary infiltrates at diagnosis have no prognostic significance in children with acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2001, 15, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinikina, Y.V.; Maschan, A.A. Extramedullary involvement in pediatric myeloid leukemia: Challenges of diagnosis and treatment. Clinical cases and a literature review (In Russ.). Pediatr. Hematol./Oncol. Immunopathol. 2023, 22, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samborska, M.; Derwich, K.; Skalska-Sadowska, J.; Kurzawa, P.; Wachowiak, J. Myeloid sarcoma in children–diagnostic and therapeutic difficulties. Contemp. Oncol. 2016, 20, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Støve, H.K.; Sandahl, J.D.; Abrahamsson, J.; Asdahl, P.H.; Forestier, E.; Ha, S.Y.; Jahnukainen, K.; Jónsson, Ó.G.; Lausen, B.; Palle, J.; et al. Extramedullary leukemia in children with acute myeloid leukemia: A population-based cohort study from the Nordic Society of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology (NOPHO). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.J.; Beimler, M.; Borte, G.; Pönisch, W.; Surov, A. Radiological and Clinical Patterns of Myeloid Sarcoma. Radiology and Oncology 2019, 53, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.S.; Shetty, A.S.; Mellnick, V.M.; Pickhardt, P.J.; Bhalla, S.; Menias, C.O. Extramedullary haematopoiesis: Radiological imaging features. Clin. Radiol. 2016, 71, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, M.S.; Kalinina, I.I.; Venyov, D.A.; Lebedeva, S.A.; Bankole, V.A.; Abashidze, Z.A.; Aleinikova, O.V.; Zerkalenkova, E.A.; Gaskova, M.V.; Itov, A.B.; et al. Preliminary results of treatment of intermediate-risk patients according to the AML-MRD-2018 protocol. Pediatr. Hematol./Oncol. Immunopathol. 2025, 24, 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lebedeva, S.A.; Kalinina, I.I.; Kazakova, A.N.; Bankole, V.A.; Vasileva, M.S.; Venyov, D.A.; Baydildina, D.D.; Aleinikova, O.V.; Popa, A.V.; Maschan, A.A.; et al. The prognostic significance of partner genes and breakpoint locations in children with KMT2A-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. Pediatr. Hematol./Oncol. Immunopathol. 2025, 24, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Surov, A.; Meyer, H.J.; Wienke, A. Correlation between apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and cellularity is different in several tumors: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wu, X.; Cui, Y.; Chu, C.; Ren, G.; Li, W. Role of apparent diffusion coefficients with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating between benign and malignant bone tumors. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, H.; Evangelista, L.; Hassold, N.; Winkler, B.; Schlegel, P.G.; Köstler, H.; Hahn, D.; Beer, M. Diffusion-weighted MRI for detection and differentiation of musculoskeletal tumorous and tumor-like lesions in pediatric patients. World J. Pediatr. 2012, 8, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.Y.K.; Gardner, J.M.; Lucas, D.R.; McHugh, J.B.; Patel, R.M. Ewing sarcoma. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 31, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Tian, W.; Liang, X.; Yao, W.; Zhang, P. Ewing’s sarcoma of proximal femur: Case report of extreme osteotomy with 3D-printed prosthesis for the reconstruction. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1248330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Careri, S.; Attala, D.; Florio, M.; Milano, G.M.; Giordano, M. A new proximal femur reconstruction technique after bone tumor resection in a very small patient: An exemplificative case. Children 2021, 8, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, Y.A.; Elsadawy, M.E.; El Naggar, T. Role of quantitative diffusion-weighted imaging in differentiation between red and infiltrated marrow in pediatric patients with hematologic malignancy. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2019, 50, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexenko, M.; Illarionova, O.; Verzhbitskaya, T.; Zerkalenkova, E.; Novikova, I.; Panferova, A.; Fechina, L.; Tsaur, G.; Olshanskaya, J.; Popov, A. Immunophenotypic characterization of acute megakaryoblastic leukaemia in children. Pediatr. Hematol./Oncol. Immunopathol. 2019, 18, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, J.; Zimmermann, M.; Rasche, M.; von Neuhoff, C.; Creutzig, U.; Dworzak, M.; Reinhardt, D.; Klusmann, J.H. Improved outcome of pediatric patients with acute megakaryoblastic leukemia in the AML-BFM 04 trial. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y.; Shiba, N.; Ohki, K.; Tabuchi, K.; Yamato, G.; Park, M.J.; Tomizawa, D.; Kinoshita, A.; Shimada, A.; Arakawa, H.; et al. Prognostic impact of specific molecular profiles in pediatric acute megakaryoblastic leukemia in non-Down syndrome. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017, 56, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiollier, C.; Lopez, C.K.; Gerby, B.; Ignacimouttou, C.; Poglio, S.; Duffourd, Y.; Guegan, J.; Rivera-Munoz, P.; Bluteau, O.; Mabialah, V.; et al. Characterization of novel genomic alterations and therapeutic approaches using acute megakaryoblastic leukemia xenograft models. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2017–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakos, I.; Paterakis, G.; Papadakis, V.; Vicha, A.; Topakas, G.; Jencova, P.; Karchilaki, E.; Taparkou, A.; Tsagarakis, N.J.; Polychronopoulou, S. Interference of bone marrow CD56(+) mesenchymal stromal cells in minimal residual disease investigation of neuroblastoma and other CD45(−) /CD56(+) pediatric malignancies using flow cytometry. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masetti, R.; Bertuccio, S.N.; Pession, A.; Locatelli, F. CBFA2T3-GLIS2-positive acute myeloid leukaemia. A peculiar paediatric entity. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pession, A.; Masetti, R.; Rizzari, C.; Putti, M.C.; Casale, F.; Fagioli, F.; Luciani, M.; Lo Nigro, L.; Menna, G.; Micalizzi, C.; et al. Results of the AIEOP AML 2002/01 multicenter prospective trial for the treatment of children with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013, 122, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollner, S.K.; Kauertz, K.L.; Kaiser, I.; Kerkhoff, M.; Schaefer, C.; Tassius, M.; Jabar, S.; Jurgens, H.; Ladenstein, R.; Kuhne, T.; et al. Ewing Sarcoma as Secondary Malignant Neoplasm-Epidemiological and Clinical Analysis of an International Trial Registry. Cancers 2022, 14, 5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loning, L.; Zimmermann, M.; Reiter, A.; Kaatsch, P.; Henze, G.; Riehm, H.; Schrappe, M. Secondary neoplasms subsequent to Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood: Significantly lower risk without cranial radiotherapy. Blood 2000, 95, 2770–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applebaum, M.A.; Goldsby, R.; Neuhaus, J.; DuBois, S.G. Clinical features and outcomes in patients with secondary Ewing sarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.E.; Beach, B.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Murata-Collins, J.L.; Rowland, J.M.; O’Donnell, R.J.; Goldsby, R.E. Ewing sarcoma as a second malignant neoplasm after acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2005, 45, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Ni, H.; Guo, S.; Shen, Y.Q.; Chen, Q. Bone complications of cancer treatment. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2024, 130, 102828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, L.M.; Charalampakis, M.; Ford, S.J.; Gourevitch, D.; Desai, A. Myeloid Sarcoma: Presentation, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Sharma, C.; Parampalli, R. Role of diffusion-weighted MRI in differentiating benign from malignant bone tumors. BJR Open 2019, 1, 20180048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekcevik, Y.; Kahya, M.; Kaya, A. Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Diagnosis of Bone Tumors: Preliminary Results. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2013, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlSemari, M.A.; Perrotta, M.; Russo, C.; Alkatan, H.M.; Maktabi, A.; Elkhamary, S.; Crescenzo, R.M.D.; Mascolo, M.; Elefante, A.; Rombetto, L.; et al. Orbital myeloid sarcoma (chloroma): Report of 2 cases and literature review. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2020, 19, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semchenkova, A.; Mikhailova, E.; Komkov, A.; Gaskova, M.; Abasov, R.; Matveev, E.; Kazanov, M.; Mamedov, I.; Shmitko, A.; Belova, V.; et al. Lineage Conversion in Pediatric B-Cell Precursor Acute Leukemia under Blinatumomab Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Acosta, E.; Pelayo, R. Lineage switching in acute leukemias: A consequence of stem cell plasticity? Bone Marrow Res. 2012, 2012, 406796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbert, S.K.; Rankin, A.W.; Hoang, C.N.; Semchenkova, A.; Myers, R.M.; Zerkalenkova PhD, E.; Wang, H.-W.; Kovach, A.E.; Yuan, C.M.; Delgado Colon, D.; et al. Project EVOLVE: An international analysis of postimmunotherapy lineage switch, an emergent form of relapse in leukemia. Blood 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permikin, Z.; Popov, A.; Verzhbitskaya, T.; Riger, T.; Plekhanova, O.; Makarova, O.; Fronkova, E.; Trka, J.; Meyer, C.; Marschalek, R.; et al. Lineage switch to acute myeloid leukemia during induction chemotherapy for early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the translocation t(6;11)(q27;q23)/KMT2A-AFDN: A case report. Leuk. Res. 2022, 112, 106758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, I.; Dagestani, A.; Borkovskaia, A.; Semchenkova, A.; Soldatkina, O.; Kashpor, S.; Olshanskaya, Y.; Roumiantseva, J.; Karachunskiy, A.; Novichkova, G.; et al. Immunophenotypic but Not Genetic Changes Reclassify the Majority of Relapsed/Refractory Pediatric Cases of Early T-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.; Verzhbitskaya, T.; Movchan, L.; Demina, I.; Mikhailova, E.; Semchenkova, A.; Permikin, Z.; Shman, T.; Karachunskiy, A.; Novichkova, G.A. Flow cytometry in acute leukemia diagnostics. Guidelines of Russian-Belarusian multicenter group for pediatric leukemia studies. Pediatr. Hematol./Oncol. Immunopathol. 2023, 22, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novello, M.; Coli, A.; Della Pepa, G.M.; Martini, M.; Doglietto, F.; De Stefano, V.; Bellesi, S.; Pescarmona, E.; Lauriola, L. Myeloid sarcoma with megakaryoblastic differentiation mimicking a sellar tumor. Neuropathol. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Neuropathol. 2014, 34, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannatella, J.; Ganapathi, K.; Horvai, A. Hematolymphoid Neoplasms Rarely Mimic Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma of Soft Tissue. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buldini, B.; Maurer-Granofszky, M.; Varotto, E.; Dworzak, M.N. Flow-Cytometric Monitoring of Minimal Residual Disease in Pediatric Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Recent Advances and Future Strategies. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer-Granofszky, M.; Kohrer, S.; Fischer, S.; Schumich, A.; Nebral, K.; Larghero, P.; Meyer, C.; Mecklenbrauker, A.; Muhlegger, N.; Marschalek, R.; et al. Genomic breakpoint-specific monitoring of measurable residual disease in pediatric non-standard-risk acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2024, 109, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, T.; Flores-Montero, J.; Lecrevisse, Q.; Pedreira, C.E.; van der Velden, V.H.; Novakova, M.; Mejstrikova, E.; Hrusak, O.; Bottcher, S.; Karsch, D.; et al. Quality assessment program for EuroFlow protocols: Summary results of four-year (2010–2013) quality assurance rounds. Cytom. A 2015, 87, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boztug, H.; Schumich, A.; Potschger, U.; Muhlegger, N.; Kolenova, A.; Reinhardt, K.; Dworzak, M. Blast cell deficiency of CD11a as a marker of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia and transient myeloproliferative disease in children with and without Down syndrome. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2013, 84, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semchenkova, A.; Zerkalenkova, E.; Demina, I.; Kashpor, S.; Volchkov, E.; Zakharova, E.; Larin, S.; Olshanskaya, Y.; Novichkova, G.; Maschan, A.; et al. Recognizing Minor Leukemic Populations with Monocytic Features in Mixed-Phenotype Acute Leukemia by Flow Cell Sorting Followed by Cytogenetic and Molecular Studies: Report of Five Exemplary Cases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Nijs, J.I.; Gonggrijp, H.S.; Augustinus, E.; Leeksma, C.H. Hot bands: A simple G-banding method for leukemic metaphases. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1985, 15, 373–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISCN 2020: An International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (2020); ISCN 2020; S Karger Ag: Basel, Switzerland, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Uhrig, S.; Ellermann, J.; Walther, T.; Burkhardt, P.; Frohlich, M.; Hutter, B.; Toprak, U.H.; Neumann, O.; Stenzinger, A.; Scholl, C.; et al. Accurate and efficient detection of gene fusions from RNA sequencing data. Genome. Res. 2021, 31, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tube | FITC | PE | ECD | PC5.5 | PC7 | APC | APC-Alexa700 | APC-Alexa750 | PB | KrO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CD66b | CD19 | CD56 | CD117 | CD33 | CD34 | CD14 | CD45 | CD7 | CD3 |
| 2 | iLZ | iMPO | iCD22 | iCD79a | iCD3 | CD45 | ||||
| 3 | CD61 | CD11a | CD34 | CD117 | CD33 | CD2 | CD5 | CD41a | CD235a | CD45 |
| 4 | CD64 | NG2 | CD34 | CD117 | CD33 | CD11c | CD4 | CD303 | CD13 | CD45 |
| 5 | CD38 | CD371 | CD34 | CD117 | CD33 | CD99 | CD123 | CD45RA | HLA-DR | CD45 |
| 6 | CD15 | CD11a | CD34 | CD117 | CD33 | CD56 | CD14 | CD11b | HLA-DR | CD45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lebedeva, S.; Mikhailova, E.; Bogacheva, S.; Abramov, D.; Kashpor, S.; Druy, A.; Semchenkova, A.; Gaskova, M.; Lotonina, O.; Sidorov, I.; et al. Extramedullary Relapse of CBFA2T3::GLIS2-Positive Megakaryoblastic Leukemia Mimicking Secondary Ewing Sarcoma: An Exemplary Case for the Diagnostic Trap. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125895
Lebedeva S, Mikhailova E, Bogacheva S, Abramov D, Kashpor S, Druy A, Semchenkova A, Gaskova M, Lotonina O, Sidorov I, et al. Extramedullary Relapse of CBFA2T3::GLIS2-Positive Megakaryoblastic Leukemia Mimicking Secondary Ewing Sarcoma: An Exemplary Case for the Diagnostic Trap. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125895
Chicago/Turabian StyleLebedeva, Svetlana, Ekaterina Mikhailova, Sophia Bogacheva, Dmitry Abramov, Svetlana Kashpor, Alexander Druy, Alexandra Semchenkova, Marina Gaskova, Olga Lotonina, Ilya Sidorov, and et al. 2025. "Extramedullary Relapse of CBFA2T3::GLIS2-Positive Megakaryoblastic Leukemia Mimicking Secondary Ewing Sarcoma: An Exemplary Case for the Diagnostic Trap" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125895
APA StyleLebedeva, S., Mikhailova, E., Bogacheva, S., Abramov, D., Kashpor, S., Druy, A., Semchenkova, A., Gaskova, M., Lotonina, O., Sidorov, I., Tereschenko, G., Olshanskaya, Y., Novichkova, G., Maschan, A., Zerkalenkova, E., & Popov, A. (2025). Extramedullary Relapse of CBFA2T3::GLIS2-Positive Megakaryoblastic Leukemia Mimicking Secondary Ewing Sarcoma: An Exemplary Case for the Diagnostic Trap. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125895






