Flame Retardant from Eugenol as Green Modifier for Epoxy Resins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
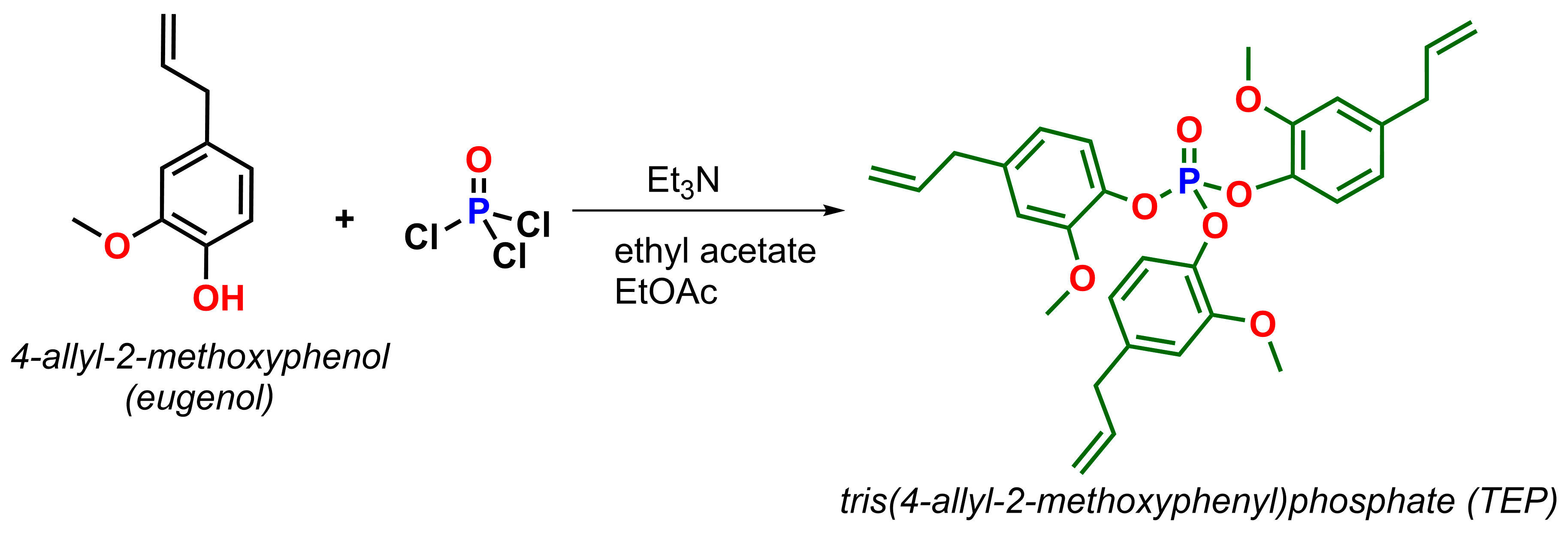
2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.2. UL-94 Vertical and Horizontal Burning Test
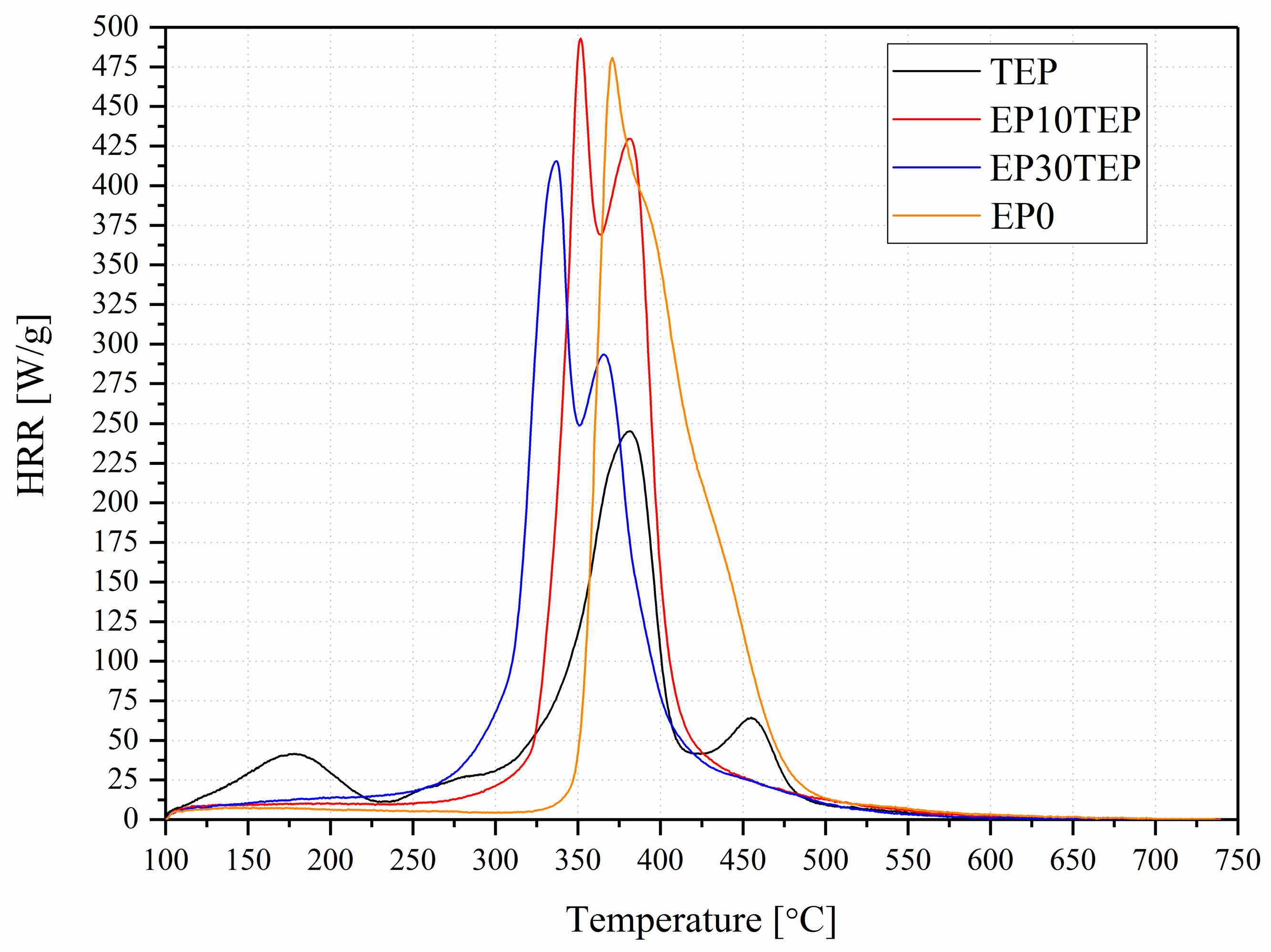
2.3. Microcalorimetry
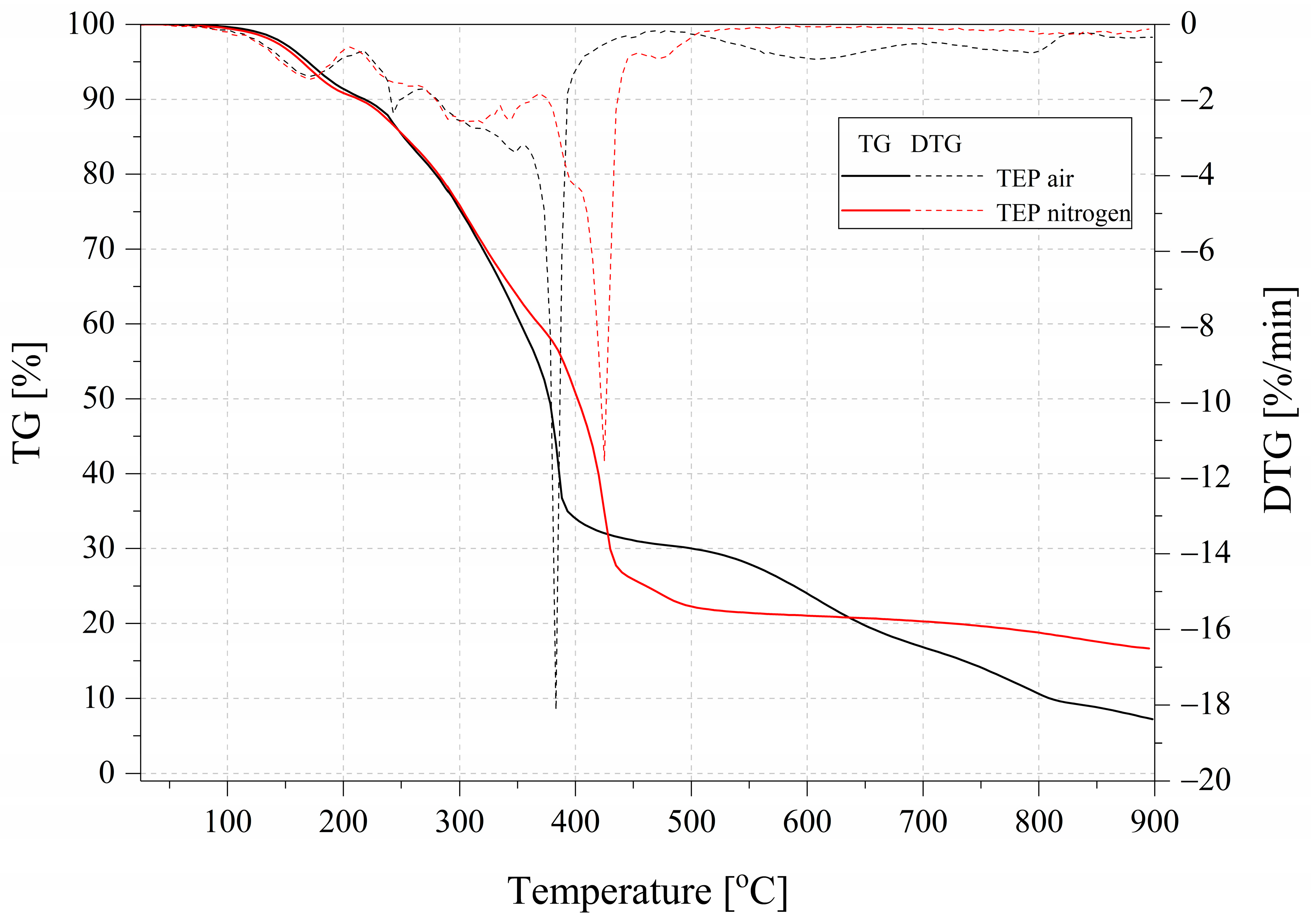
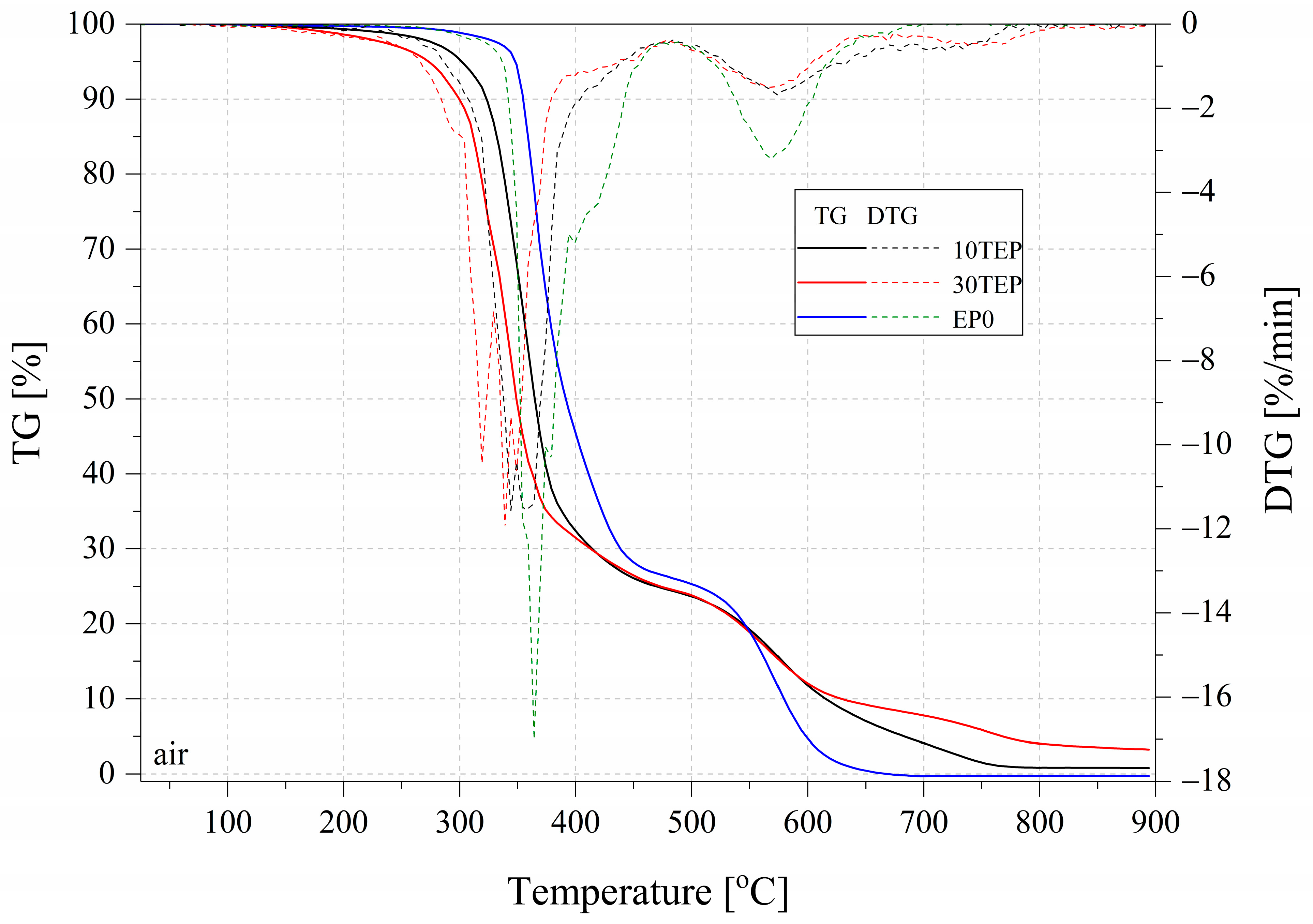
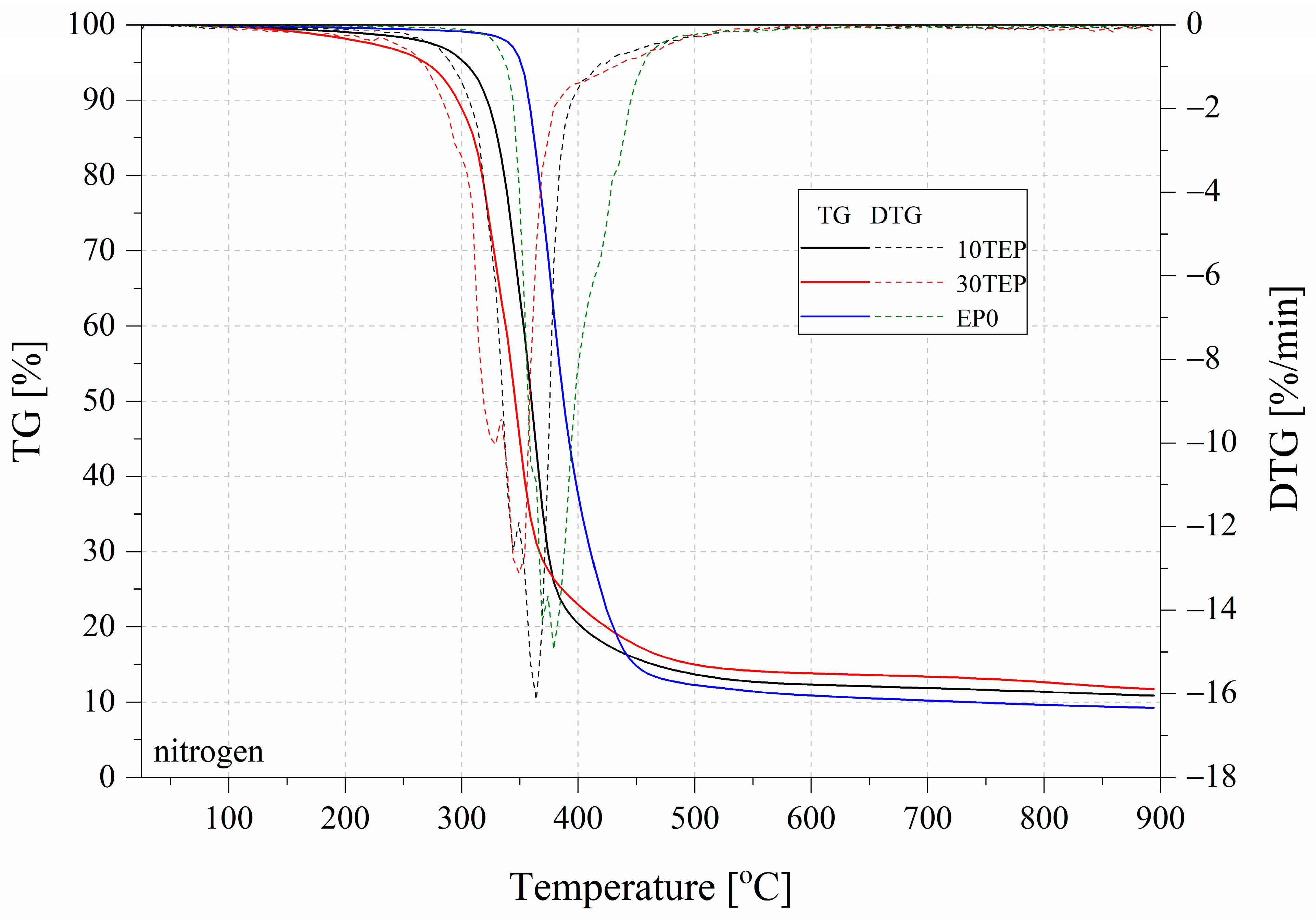
2.4. Thermogravimetry
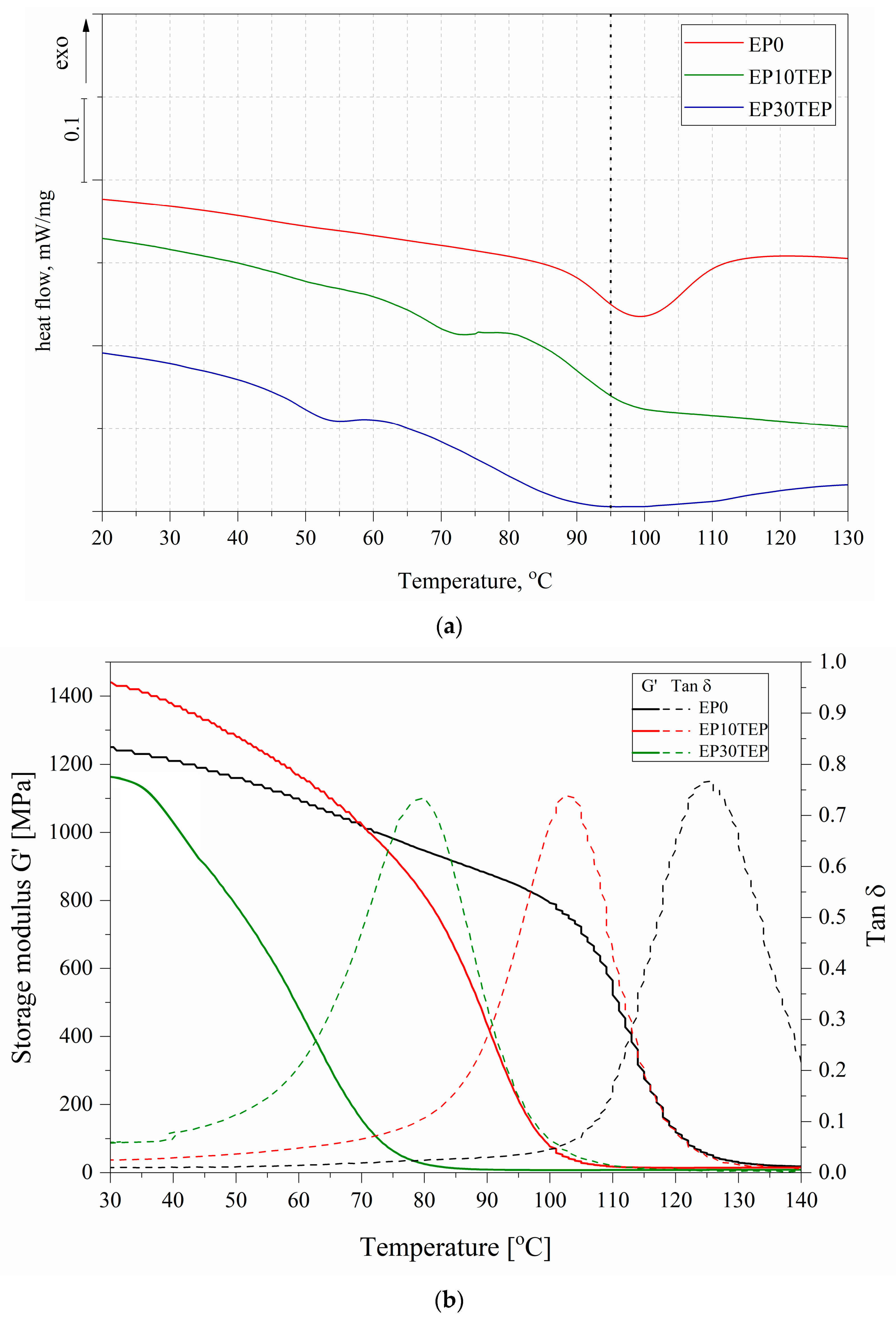
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.6. Dynamic Mechanical Thermal Analysis (DMTA)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. Characterization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nisar, M.F.; Khadim, M.; Rafiq, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Wan, C.C. Pharmacological Properties and Health Benefits of Eugenol: A Comprehensive Review. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 2497354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Cerrada, R.; Molina-Gutierrez, S.; Lacroix-Desmazes, P.; Caillol, S. Eugenol, a Promising Building Block for Biobased Polymers with Cutting-Edge Properties. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 3625–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerosenewala, J.; Vaidya, P.; Ozarkar, V.; Shirapure, Y.; More, A.P. Eugenol: Extraction, Properties and Its Applications on Incorporation with Polymers and Resins—A Review. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 7047–7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, M.; Yang, X.; Fan, R.; Yue, S.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Q.; He, Y. A Comprehensive Review of Reactive Flame-Retardant Epoxy Resin: Fundamentals, Recent Developments, and Perspectives. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 201, 109976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T. Polymer Combustion and Flammability—Role of the Condensed Phase. Symp. Combust. 1994, 25, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Sabee, M.M.S.; Itam, Z.; Beddu, S.; Zahari, N.M.; Mohd Kamal, N.L.; Mohamad, D.; Zulkepli, N.A.; Shafiq, M.D.; Abdul Hamid, Z.A. Flame Retardant Coatings: Additives, Binders, and Fillers. Polymers 2022, 14, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Peng, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, P. Recent Developments in the Flame-Retardant System of Epoxy Resin. Materials 2020, 13, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, T.; Wang, C. Synergistic Effect of a Phosphorus–Nitrogen Flame Retardant on Engineering Plastics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.A. Thermal Degradation of Organophosphorus Flame Retardants. Polymers 2022, 14, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passauer, L. Thermal Characterization of Ammonium Starch Phosphate Carbamates for Potential Applications as Bio-Based Flame-Retardants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Guo, W.-W.; Wang, P.-L.; Xing, W.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Renewable Cardanol-Based Phosphate as a Flame Retardant Toughening Agent for Epoxy Resins. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3409–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shen, L.; Cui, Z.; Kou, L.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J. A Renewable Resveratrol-Based Epoxy Resin with High Tg, Excellent Mechanical Properties and Low Flammability. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Gu, X. A Review on Lignin-Based Epoxy Resins: Lignin Effects on Their Synthesis and Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 229, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Ding, H.; Hu, Y. Synthesis of a Vanillin-Derived BisDOPO Co-Curing Agent Rendering Epoxy Thermosets Simultaneously Improved Flame Retardancy, Mechanical Strength and Transparency. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 211, 110333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, C.; Cao, J.; He, S.; Huang, Z.; Shen, N.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, H.-B.; Rao, W. Efficient Hyperbranched Flame Retardant Derived from Quercetin for Use in Epoxy Resin with Well-Balanced Comprehensive Performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huo, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Chen, K.; Li, C.; Fang, D.; Fang, Z.; Song, P.; Wang, H. Green and Facile Synthesis of Bio-Based, Flame-Retardant, Latent Imidazole Curing Agent for Single-Component Epoxy Resin. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 3564–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lin, W.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, W. Flame-Retardant Epoxy Thermosets Derived from Renewable Resources: Research Development and Future Perspectives. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 195, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, H.; Guo, W.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Cardanol as a Versatile Platform for Fabrication of Bio-Based Flame-Retardant Epoxy Thermosets as DGEBA Substitutes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.A. Flame Retardants of the Future: Biobased, Organophosphorus, Reactive or Oligomeric. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1500782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebke, S.; Thümmler, K.; Sonnier, R.; Tech, S.; Wagenführ, A.; Fischer, S. Suitability and Modification of Different Renewable Materials as Feedstock for Sustainable Flame Retardants. Molecules 2020, 25, 5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, Q.; Lin, J.; Huang, J.; Xie, K.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wei, W. A Phosphorus/Silicon-containing Flame Retardant Based on Eugenol for Improving Flame Retardancy and Smoke Suppression of Epoxy Resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Senanayake, R.B.; Nunna, S.; Zhang, J.; Basnayake, A.P.; Heitzmann, M.T.; Varley, R.J. A DOPO-Eugenol Linear Siloxane as a Highly Effective Liquid Flame Retardant Also Imparting Improved Mechanical Properties to an Epoxy Amine Network. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecochard, Y.; Decostanzi, M.; Negrell, C.; Sonnier, R.; Caillol, S. Cardanol and Eugenol Based Flame Retardant Epoxy Monomers for Thermostable Networks. Molecules 2019, 24, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamil Watson, D.A.; Schiraldi, D.A. Biomolecules as Flame Retardant Additives for Polymers: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Chen, G.; Yao, Y. Two Novel Phosphorus–Nitrogen-Containing Halogen-Free Flame Retardants of High Performance for Epoxy Resin. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, K.-S.; Kim, N. Synergistic Improvement of Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/Benzoxazine/Aluminum Trihydrate Adhesive Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Lin, F.; Yang, M.; Fan, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, Z. Flame Retardant Strategies and Applications of Organic Phase Change Materials: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2412492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yu, Q.; Yu, B.; Zhou, F. New Progress in the Application of Flame-Retardant Modified Epoxy Resins and Fire-Retardant Coatings. Coatings 2023, 13, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, R.; Nayak, L.; Rahaman, M. Flame and Fire Retardancy of Polymer-Based Composites. Mater. Res. Innov. 2021, 25, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babrauskas, V.; Peacock, R.D. Heat Release Rate: The Single Most Important Variable in Fire Hazard. Fire Saf. J. 1992, 18, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biteau, H.; Steinhaus, T.; Schemel, C.; Simeoni, A.; Marlair, G.; Bal, N.; Torero, J. Calculation Methods for the Heat Release Rate of Materials of Unknown Composition. Fire Saf. Sci. 2008, 9, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hu, W. Effect of Additive Phosphorus-Nitrogen Containing Flame Retardant on Char Formation and Flame Retardancy of Epoxy Resin. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 214, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, X. Synthesis, Characterization, Thermal Properties and Flame Retardancy of a Novel Nonflammable Phosphazene-Based Epoxy Resin. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouritz, A.P.; Mathys, Z.; Gibson, A.G. Heat Release of Polymer Composites in Fire. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1040–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, M.H.; Dashtizadeh, A.; Motamedoshariati, H.; Soury, H. A Simple Model for Reliable Prediction of the Specific Heat Release Capacity of Polymers as an Important Characteristic of Their Flammability. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 128, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ye, X.; Huan, X.; Xu, Q.; Ma, S.; Bao, D.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Du, H. P/N/S Flame Retardant Based on DOPS-Triazine Groups for Improving the Flame Retardancy, Char Formation Properties and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin. Eur. Polym. J. 2024, 202, 112634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Kandola, B.K.; Horrocks, A.R.; Price, D. A Quantitative Study of Carbon Monoxide and Carbon Dioxide Evolution during Thermal Degradation of Flame Retarded Epoxy Resins. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.; Kim, J.; Jang, B.N. Synthesis and Performance of Cyclic Phosphorus-Containing Flame Retardants. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilias, D.S.; Karabela, M.M.; Varkopoulou, E.A.; Sideridou, I.D. Cure Kinetics Study of Two Epoxy Systems with Fourier Tranform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC). J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2012, 49, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-O.; Cho, J.; Yeo, H.; Lee, B.W.; Moon, B.J.; Ha, Y.-M.; Jo, Y.R.; Jung, Y.C. Flame Retardant Epoxy Derived from Tannic Acid as Biobased Hardener. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3858–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Xue, X. Preparation and Properties of UV-Cured Epoxy Acrylate/Glycidyl-POSS Coatings. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Kang, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W. Well-Designed Flame Retardants for Epoxy Resin Composites That Simultaneously Improve Heat Resistance, Mechanical Properties and Fire Safety. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auvergne, R.; Caillol, S.; David, G.; Boutevin, B.; Pascault, J.-P. Biobased Thermosetting Epoxy: Present and Future. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1082–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faye, I.; Decostanzi, M.; Ecochard, Y.; Caillol, S. Eugenol Bio-Based Epoxy Thermosets: From Cloves to Applied Materials. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 5236–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matykiewicz, D.; Dudziec, B. Curing and Degradation Kinetics of Phosphorus-Modified Eugenol-Based Epoxy Resin. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 4353–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
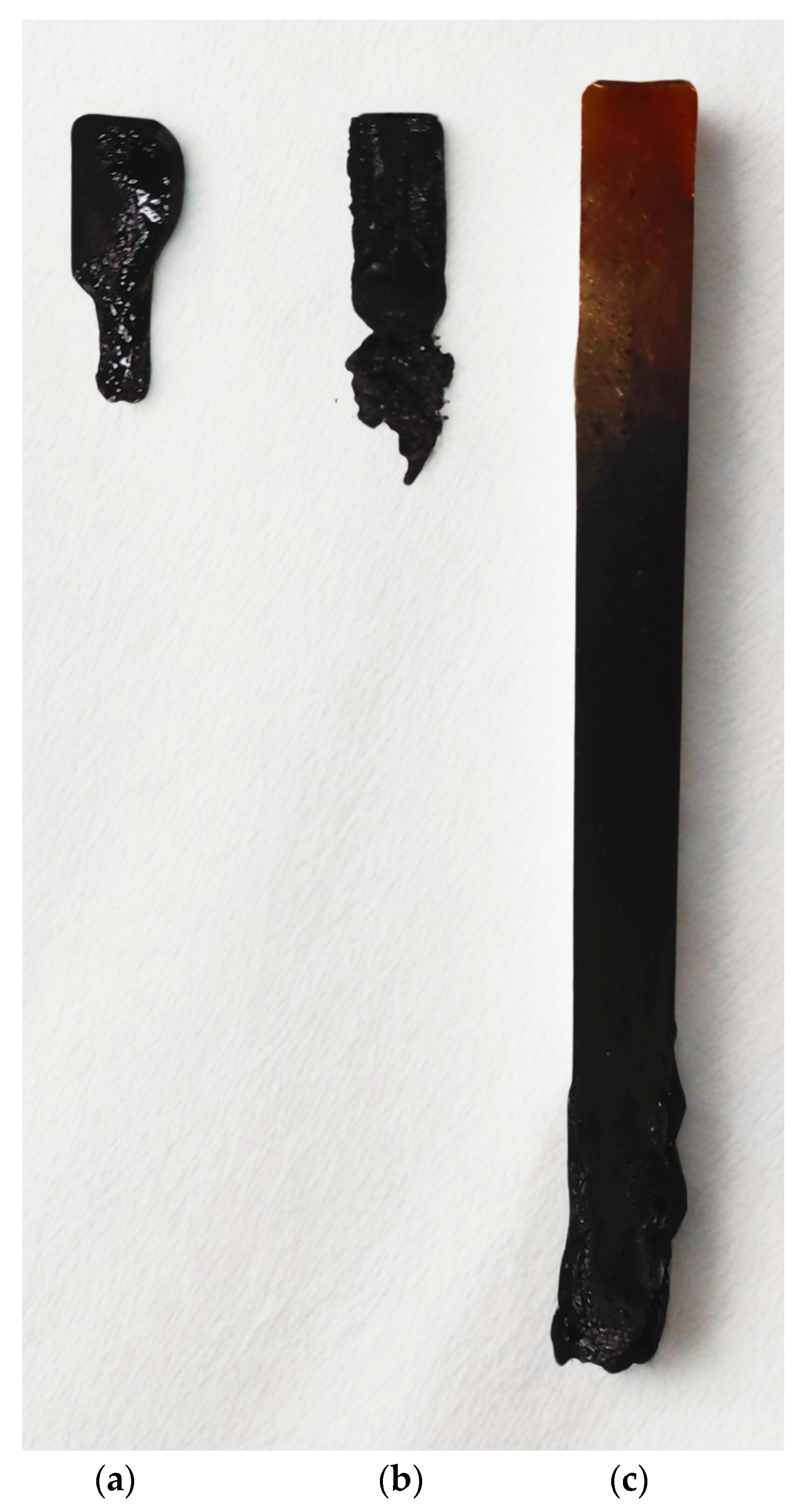


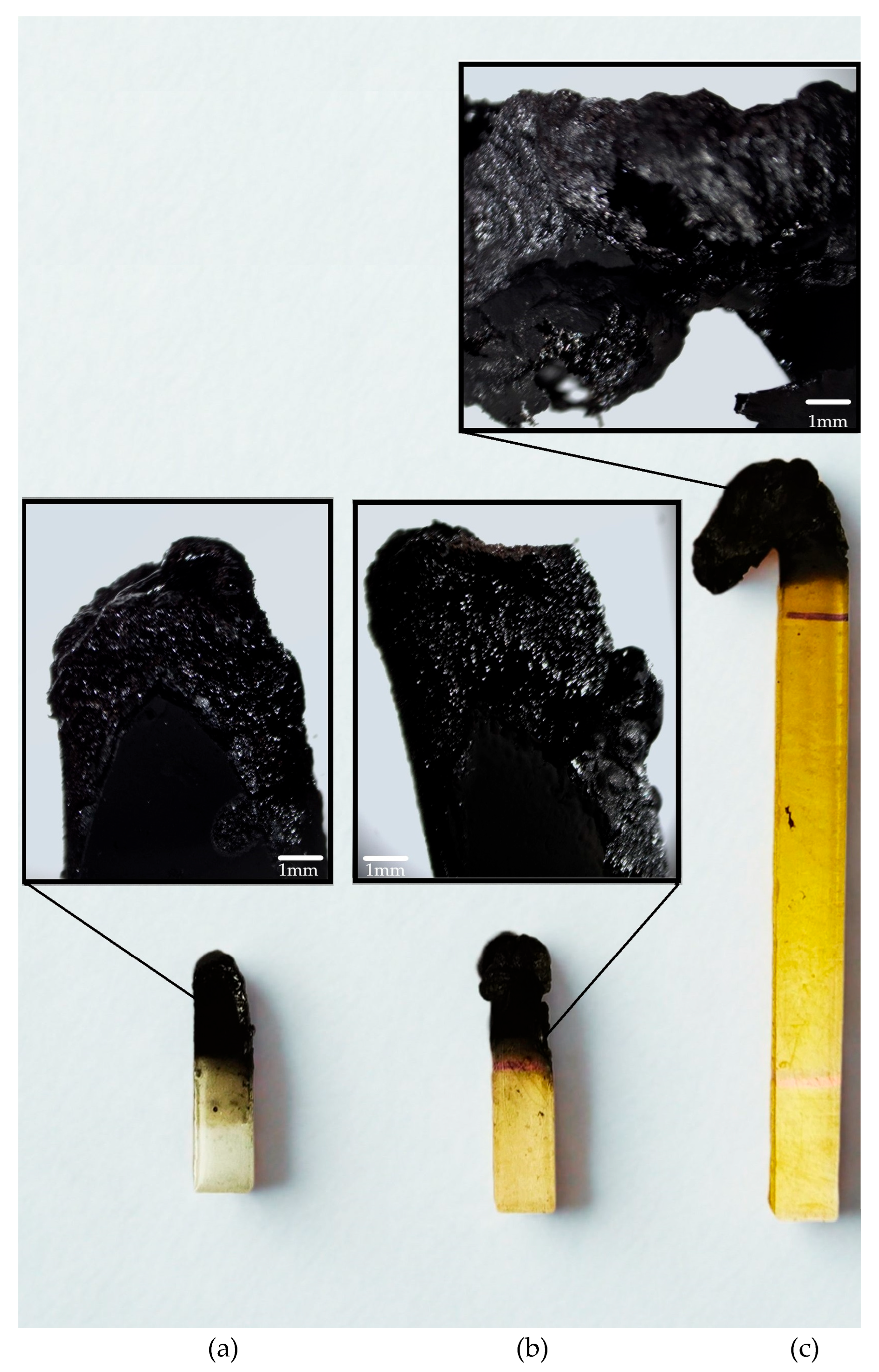
| Name | t * [s] | Classification UL94V | Falling Drops |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP | 70 | No Rating | yes |
| EP10TEP | 60 | No Rating | no |
| EP30TEP | 30 | V-1 | no |
| Name | V [mm/min] | Classification UL 94HB | Falling Drops |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP | 35 | HB40 | yes |
| EP10TEP | 20 | HB40 | no |
| EP30TEP | self-extinguish before measurement | HB | no |
| Name | pcHRR (W/g) | TpcHRR (℃) | THR (kJ/g) | HRC (J/g·K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEP | 262.4 ± 30.0 | 374 ± 2 | 24.8 ± 2.1 | 283 ± 35 |
| EP10TEP | 505.2 ± 30.0 | 351 ± 1 | 30.9 ± 0.5 | 546 ± 35 |
| EP30TEP | 414.4 ± 5.5 | 336 ± 5 | 29.1 ± 0.6 | 446 ± 7 |
| EP0 | 481.5 ± 1.1 | 373 ± 3 | 32.3 ± 0.3 | 520 ± 3 |
| Name | T5% (°C) | T10% (°C) | Residual Mass (%) | DTG Peak (°C)/max.rate (%/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | ||||
| TEP | 164.5 | 213.7 | 16.60 | 424.4/11.61 |
| EP10TEP | 302.6 | 322.1 | 10.82 | 364.1/16.15 |
| EP30TEP | 268.9 | 296.4 | 11.71 | 346.9/13.43 |
| EP0 | 351.0 | 357.8 | 9.21 | 376.9/16.78 |
| Air | ||||
| TEP | 169.5 | 218.2 | 7.17 | 384.6/21.69 |
| EP10TEP | 301.9 | 323.3 | 0.82 | 362.0/12.97 |
| EP30TEP | 273.3 | 299.7 | 3.25 | 340.7/15.53 |
| EP0 | 348.2 | 354.7 | 0.10 | 364.7/17.75 |
| Name | G’ at 25 °C [MPa] | tan δ | Tg [°C] from DMTA | Tg [°C] from DSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0 | 1250 | 0.767 | 125 | 96 |
| EP10TEP | 1440 | 0.738 | 103 | 89 |
| EP30TEP | 1160 | 0.733 | 80 | 79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matykiewicz, D.; Dudziec, B.; Michałowski, S. Flame Retardant from Eugenol as Green Modifier for Epoxy Resins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125861
Matykiewicz D, Dudziec B, Michałowski S. Flame Retardant from Eugenol as Green Modifier for Epoxy Resins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125861
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatykiewicz, Danuta, Beata Dudziec, and Sławomir Michałowski. 2025. "Flame Retardant from Eugenol as Green Modifier for Epoxy Resins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125861
APA StyleMatykiewicz, D., Dudziec, B., & Michałowski, S. (2025). Flame Retardant from Eugenol as Green Modifier for Epoxy Resins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5861. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125861









