The Dual Role of TRADD in Liver Disease: From Cell Death Regulation to Inflammatory Microenvironment Remodeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Structure of TRADD
3. Functional Network of TRADD
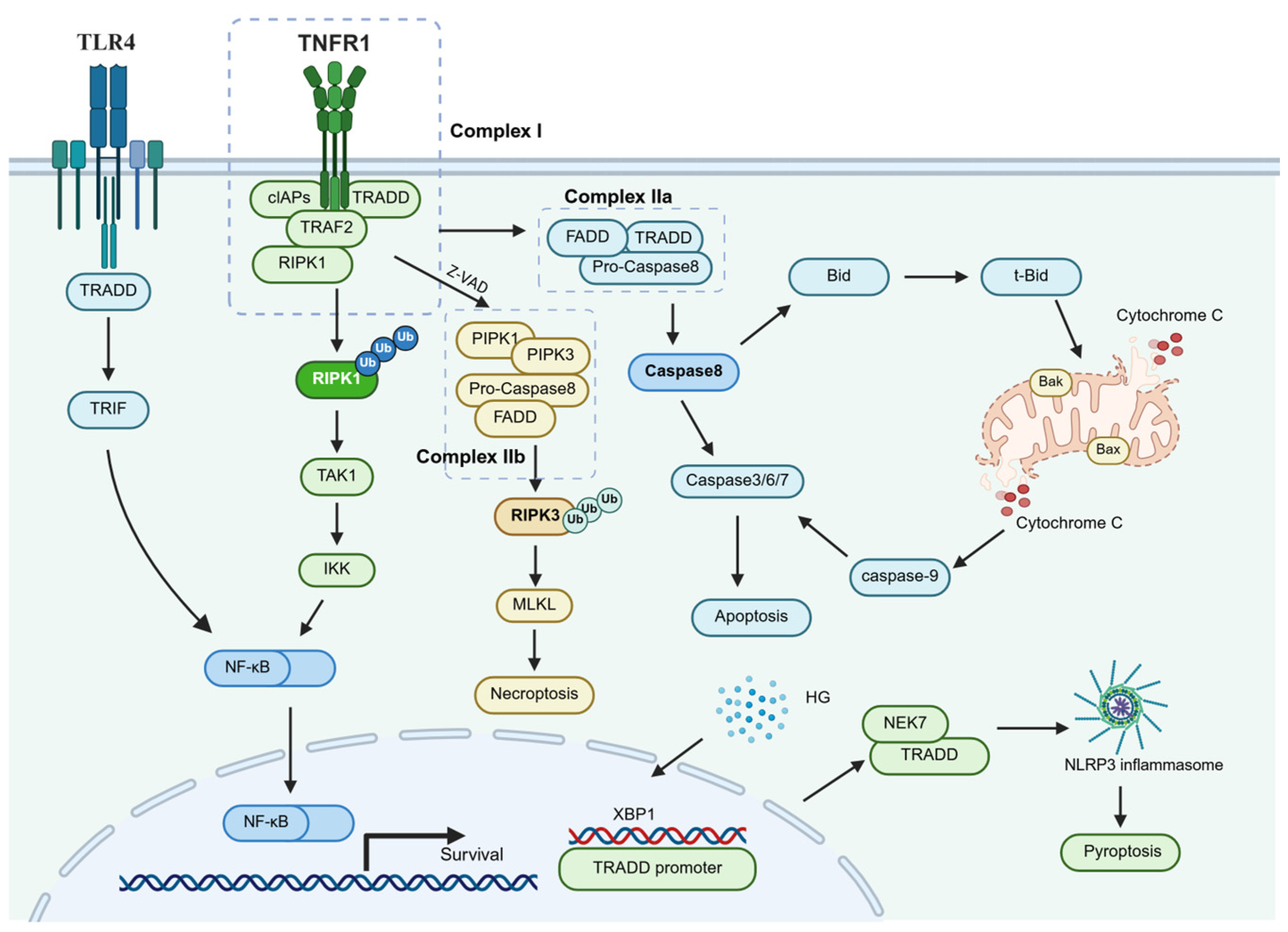
3.1. Dualistic Nature of TRADD-Mediated Signal Transduction
3.2. Non-Canonical Roles of TRADD in Cross-Receptor Signaling
4. Research Advances on TRADD in Various Liver Diseases
4.1. TRADD and HCC
4.2. TRADD and ALD
4.3. TRADD and MASLD
4.4. TRADD and ALI
4.5. TRADD and Viral Hepatitis/Liver Fibrosis
5. Therapeutic Potential of TRADD as a Drug Target
6. Summary and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TRADD | TNFR1-associated death domain protein |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TNFR1 | Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 |
| ALD | Alcohol-associated liver disease |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| RIPK1 | Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 |
| FADD | Fas-associated protein with death domain |
| TRAF2 | TNF receptor-associated factor 2 |
| cIAP1/2 | Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins 1 and 2 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HBx | Hepatitis B virus X protein |
| NS5A | Nonstructural protein 5A |
| HSCs | Hepatic stellate cells |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ALI | Acute liver injury |
| I/R | Ischemia–reperfusion |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| GA | Gallic acid |
| ASO | Antisense oligonucleotide |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TRAIL | TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| NTD | N-terminal domain |
| MLKL | Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein |
| HG | High-glucose |
| XBP1 | X-box binding protein 1 |
| NEK7 | NIMA related kinase 7 |
| NLRP3 | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 |
| GSDMD | Downstream target protein gasdermin D |
| DISC | Death-inducing signaling complex |
References
- Santos, A.A.; Delgado, T.C.; Marques, V.; Ramirez-Moncayo, C.; Alonso, C.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Hall, Z.; Martínez-Chantar, M.L.; Rodrigues, C.M.P. Spatial metabolomics and its application in the liver. Hepatology 2024, 79, 1158–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, S.K.; Arab, J.P.; Nartey, Y.A.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neshat, S.Y.; Quiroz, V.M.; Wang, Y.; Tamayo, S.; Doloff, J.C. Liver Disease: Induction, Progression, Immunological Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenwald, M.A.; Paul, S. Viral hepatitis: Past, present, and future. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1405–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Desert, R.; Das, S.; Song, Z.; Athavale, D.; Ge, X.; Nieto, N. Danger signals in liver injury and restoration of homeostasis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, H.; Annibaldi, A.; Kastner, D.L.; Aksentijevich, I. Genetic Regulation of Cell Death: Insights from Autoinflammatory Diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2025, 43, 313–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, F.; Shi, C.; Pei, M.; Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Gong, Z. TNF-α/HMGB1 inflammation signalling pathway regulates pyroptosis during liver failure and acute kidney injury. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Xie, H.B.; Huang, M.; Jiang, W.; Ding, B.W.; Zhu, Q.X. TNF-α/TNFR1 regulates the polarization of Kupffer cells to mediate trichloroethylene-induced liver injury. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 230, 113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Xu, Q.Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.H.; Zhu, Q.X.; Shen, T. Kupffer cell inactivation ameliorates immune liver injury via TNF-α/TNFR1 signal pathway in trichloroethylene sensitized mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2020, 42, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Hu, Y. TNFR1 and TNFR2, Which Link NF-κB Activation, Drive Lung Cancer Progression, Cell Dedifferentiation, and Metastasis. Cancers 2023, 15, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Wei, K.; Shan, Y. E3 ubiquitin ligase gene BIRC3 modulates TNF-induced cell death pathways and promotes aberrant proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1433898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ye, Q.; Xi, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Deng, T.; Deng, X.; Zhang, G.; et al. KW2449 ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting RIPK1-dependent necroptosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1135014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegmund, D.; Zaitseva, O.; Wajant, H. Fn14 and TNFR2 as regulators of cytotoxic TNFR1 signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1267837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummers, B.; Green, D.R. Caspase-8: Regulating life and death. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.; Xiong, J.; Goeddel, D.V. The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa B activation. Cell 1995, 81, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobezinskaya, Y.L.; Liu, Z. The role of TRADD in death receptor signaling. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, Y.; Xiong, X.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Meng, G. Roles of the adaptor protein tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated death domain protein (TRADD) in human diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Xie, G.; Geng, B.; Yang, R.; Tian, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, G. Modulation of TNFR 1-Triggered Inflammation and Apoptosis Signals by Jacaranone in Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.H.; Zhao, X.P.; Wang, B.J.; Yang, D.L.; Hao, L.J. FADD and TRADD expression and apoptosis in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 6, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Nie, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.D.; Wang, Y.D. miR-149* Suppresses Liver Cancer Progression by Down-Regulating Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1-Associated Death Domain Protein Expression. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, D.; Ghosh, S.; Dey, I.; Majumdar, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Das, S.; Banerjee, S.; Saha, M.; Ghosh, A.; Roy, N.; et al. Influence of polymorphisms in TNF-α and IL1β on susceptibility to alcohol induced liver diseases and therapeutic potential of miR-124-3p impeding TNF-α/IL1β mediated multi-cellular signaling in liver microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1241755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Eum, H.A.; Billiar, T.R.; Lee, S.M. Role of heme oxygenase 1 in TNF/TNF receptor-mediated apoptosis after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Shock. 2013, 39, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuña-Pilarte, K.; Reichert, E.C.; Green, Y.S.; Halberg, L.M.; Golkowski, M.; Maguire, K.M.; Mimche, P.N.; Kamdem, S.D.; Hu, P.A.; Wright, J.; et al. HAF prevents hepatocyte apoptosis and progression to MASH and HCC through transcriptional regulation of the NF-κB pathway. Hepatology 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hou, L.; Liang, S.; Lu, F.; Wang, G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; et al. Inhibition of TRADD ameliorates chondrocyte necroptosis and osteoarthritis by blocking RIPK1-TAK1 pathway and restoring autophagy. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhao, H.; Jin, M.; Zhu, H.; Shan, B.; Geng, J.; Dziedzic, S.A.; Amin, P.; Mifflin, L.; Naito, M.G.; et al. Modulating TRADD to restore cellular homeostasis and inhibit apoptosis. Nature 2020, 587, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Bao, L.; Liang, X. Strychni Semen and two alkaloidal components cause apoptosis in HK-2 cells through TRADD-MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Toxicon 2025, 256, 108224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Matos, A.F.; Silva Júnior, W.S.; Valerio, C.M. NAFLD as a continuum: From obesity to metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoff, G.; Trivieri, N.; Marsilio, S.; Crielesi, R.; Lalli, C.; Castellani, L.; Balog, E.M.; Ruberti, G. N-terminal and C-terminal domains of calmodulin mediate FADD and TRADD interaction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.H. Caspase recruitment domains for protein interactions in cellular signaling (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yuan, W.; Fan, J.S.; Lin, Z. Structure of the C-terminal domain of TRADD reveals a novel fold in the death domain superfamily. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.C.; Ye, H.; Hsia, C.; Segal, D.; Rich, R.L.; Liou, H.C.; Myszka, D.G.; Wu, H. A novel mechanism of TRAF signaling revealed by structural and functional analyses of the TRADD-TRAF2 interaction. Cell 2000, 101, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, D.H.; McDonagh, T.; Telliez, J.B.; Hsu, S.; Malakian, K.; Xu, G.Y.; Lin, L.L. Solution structure of N-TRADD and characterization of the interaction of N-TRADD and C-TRAF2, a key step in the TNFR1 signaling pathway. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idress, M.; Milne, B.F.; Thompson, G.S.; Trembleau, L.; Jaspars, M.; Houssen, W.E. Structure-Based Design, Synthesis and Bioactivity of a New Anti-TNFα Cyclopeptide. Molecules 2020, 25, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erusappan, T.; Paramasivam, S.; Ekambaram, S.P. Identification of galangin as the bioactive compound from Alpinia calcarata (Haw.) Roscoe rhizomes to inhibit IRAK-1/ MAPK/ NF-κB p65 and JAK-1 signaling in LPS stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 288, 114975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohandel, Z.; Farkhondeh, T.; Aschner, M.; Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M.; Samarghandian, S. Anti-inflammatory action of astaxanthin and its use in the treatment of various diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Markouli, M.; Orland, M.; Ogbue, O.; Dima, D.; Omar, N.; Mustafa Ali, M.K. Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia: Clinical Features, Molecular Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment. Cancers 2024, 16, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Ma, L.; Hu, W.; Xu, L.; Gao, J.S.; Chung, C.S.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.F.; et al. Phospho-SXXE/D motif mediated TNF receptor 1-TRADD death domain complex formation for T cell activation and migration. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, H.; Ren, X.; Li, H.; Feng, C. SNHG9, delivered by adipocyte-derived exosomes, alleviates inflammation and apoptosis of endothelial cells through suppressing TRADD expression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 872, 172977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feoktistova, M.; Makarov, R.; Yazdi, A.S.; Panayotova-Dimitrova, D. RIPK1 and TRADD Regulate TNF-Induced Signaling and Ripoptosome Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muendlein, H.I.; Connolly, W.M.; Cameron, J.; Jetton, D.; Magri, Z.; Smirnova, I.; Vannier, E.; Li, X.; Martinot, A.J.; Batorsky, R.; et al. Neutrophils and macrophages drive TNF-induced lethality via TRIF/CD14-mediated responses. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eadd0665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loo, G.; Bertrand, M.J.M. Death by TNF: A road to inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondelinger, Y.; Jouan-Lanhouet, S.; Divert, T.; Theatre, E.; Bertin, J.; Gough, P.J.; Giansanti, P.; Heck, A.J.; Dejardin, E.; Vandenabeele, P.; et al. NF-κB-Independent Role of IKKα/IKKβ in Preventing RIPK1 Kinase-Dependent Apoptotic and Necroptotic Cell Death during TNF Signaling. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, T.; Kumar, N.; Chawla, M.; Philpott, D.J.; Basak, S. The NF-κB signaling system in the immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Sci. Signal 2024, 17, eadh1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Tang, A.L.; Cheng, J.; Gao, N.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, C. RIPK1 in the inflammatory response and sepsis: Recent advances, drug discovery and beyond. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1114103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füllsack, S.; Rosenthal, A.; Wajant, H.; Siegmund, D. Redundant and receptor-specific activities of TRADD, RIPK1 and FADD in death receptor signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, O.; Takahashi, H.; Moriwaki, K.; Komazawa-Sakon, S.; Ohtake, F.; Murai, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Koyahara, Y.; Saeki, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; et al. MIND bomb 2 prevents RIPK1 kinase activity-dependent and -independent apoptosis through ubiquitylation of cFLIP(L). Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, G.; Samal, D.; Khandayataray, P.; Murthy, M.K. A Review on Caspases: Key Regulators of Biological Activities and Apoptosis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 5805–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, K.; Hertlein, V.; Jenner, A.; Dellmann, T.; Gojkovic, M.; Peña-Blanco, A.; Dadsena, S.; Wajngarten, N.; Danial, J.S.H.; Thevathasan, J.V.; et al. The interplay between BAX and BAK tunes apoptotic pore growth to control mitochondrial-DNA-mediated inflammation. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.; Schoeniger, A.; Edlich, F. Pro-apoptotic complexes of BAX and BAK on the outer mitochondrial membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2022, 1869, 119317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.S.; Pang, J.; Weir, A.; Kong, I.Y.; Fritsch, M.; Rashidi, M.; Cooney, J.P.; Davidson, K.C.; Speir, M.; Djajawi, T.M.; et al. Interferon-γ primes macrophages for pathogen ligand-induced killing via a caspase-8 and mitochondrial cell death pathway. Immunity 2022, 55, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korotkov, S.M. Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress Is the General Reason for Apoptosis Induced by Different-Valence Heavy Metals in Cells and Mitochondria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyovwi, M.O.; Oghenetega, O.B.; Victor, E.; Faith, F.Y.; Uchechukwu, J.G. Quercetin protects against levetiracetam induced gonadotoxicity in rats. Toxicology 2023, 491, 153518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, M.; Park, K.A.; Kim, S.; Ju, E.; Ko, Y.; Yoo, H.; Ro, H.; Lee, J.; Oh, J.; Lee, E.G.; et al. ANKRD13a controls early cell-death checkpoint by interacting with RIP1 independent of NF-κB. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, Q.; Yan, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, H.; et al. The Caspase Inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK Alleviates Endotoxic Shock via Inducing Macrophages Necroptosis and Promoting MDSCs-Mediated Inhibition of Macrophages Activation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Lei, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, L.H.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhu, H.W.; Han, D.; Huang, H.; Yu, X. Role of HMGB1 in TNF-α Combined with Z-VAD-fmk-Induced L929 Cells Necroptosis. Biochem. Genet. 2022, 60, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Y.; Shan, B.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C.; Yuan, J.; Xu, D. PARP5A and RNF146 phase separation restrains RIPK1-dependent necroptosis. Mol. Cell 2024, 84, 938–954.e938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chang, X.; Feng, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, G. TRADD Mediates RIPK1-Independent Necroptosis Induced by Tumor Necrosis Factor. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.L.; Yuan, L.S.; Wong, T.S.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.P.; Xu, R.; You, Y.P.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, H.R.; Shi, Z.J.; et al. Dimethyl fumarate inhibits necroptosis and alleviates systemic inflammatory response syndrome by blocking the RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL axis. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 189, 106697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, L.; Wachsmuth, L.; Kumari, S.; Schwarzer, R.; Wagner, T.; Jiao, H.; Pasparakis, M. ZBP1 causes inflammation by inducing RIPK3-mediated necroptosis and RIPK1 kinase activity-independent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2024, 31, 938–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Y.; Shen, D.N.; Peng, X.L.; San, W.Q.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Yang, S.J.; Meng, G.L.; Shi, J.H.; Chen, Y. TRADD-mediated pyroptosis contributes to diabetic cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2025, 46, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaro, F.; Luciano-Mateo, F.; Moreno-Caceres, J.; Hernández-Madrigal, M.; Both, D.; Montironi, C.; Püschel, F.; Nadal, E.; Eldering, E.; Muñoz-Pinedo, C. TRAIL receptors promote constitutive and inducible IL-8 secretion in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, T.; Lin, J.; Kaya, G.G.; Ju, E.; Kondylis, V.; Kelepouras, K.; Liccardi, G.; Kim, C.; Pasparakis, M. The RIPK1 death domain restrains ZBP1- and TRIF-mediated cell death and inflammation. Immunity 2024, 57, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chang, R.; Song, L. The origin and evolution of necroptosis signaling pathway in metazoa. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2025, 165, 105339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, J.M.; Zhou, J.Y.; Wu, G.S. The Role of TRAIL in Apoptosis and Immunosurveillance in Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, B.; Kc, R.; Uludağ, H. TRAIL therapy and prospective developments for cancer treatment. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffoli, B.; Tonon, F.; Tisato, V.; Zauli, G.; Secchiero, P.; Fabris, B.; Bernardi, S. TRAIL/DR5 pathway promotes AKT phosphorylation, skeletal muscle differentiation, and glucose uptake. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Hu, Z.; Pan, B.; Lu, X. Targeting of keloid with TRAIL and TRAIL-R2/DR5. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2021, 32, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Lin, L. Biological Functions and Clinical Implications of CFLAR: From Cell Death Mechanisms to Therapeutic Targeting in Immune Regulation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 4911–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, D.G.; Koo, G.B.; Yu, J.W.; Kim, Y.S. TRADD is critical for resistance to TRAIL-induced cell death through NF-κB activation. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2144–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witort, E.; Lulli, M.; Carloni, V.; Capaccioli, S. Anticancer activity of an antisense oligonucleotide targeting TRADD combined with proteasome inhibitors in chemoresistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Chemother. 2013, 25, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, B.K.; Hsieh, M.J.; Lin, C.C.; Ho, H.Y.; Hsieh, M.C. Dehydrocrenatidine Induces Liver Cancer Cell Apoptosis by Suppressing JNK-Mediated Signaling. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ye, B.; Wei, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, C.; Yu, G. MiR-199a-5p regulates rat liver regeneration and hepatocyte proliferation by targeting TNF-α TNFR1/TRADD/CASPASE8/CASPASE3 signalling pathway. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 4110–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaciuc, I.V.; D’Souza, N.B.; Burikhanov, R.; Lee, E.Y.; Tarba, C.N.; McClain, C.J.; de Villiers, W.J. Epidermal growth factor protects the liver against alcohol-induced injury and sensitization to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Cui, H.; Deng, H.; Kuang, P.; Liu, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Sodium fluoride causes oxidative stress and apoptosis in the mouse liver. Aging 2017, 9, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Jian, Z.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Copper Induces Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in the Mouse Liver. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 1359164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Gu, L.L.; Hou, B.Y.; Du, G.H. Oxymatrine Induces Liver Injury through JNK Signalling Pathway Mediated by TNF-α In Vivo. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 119, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Duan, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, G.; Gao, L.; Niu, C.; Xu, J.; Li, S. Lactobacillus plantarum C88 protects against aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury in mice via inhibition of NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses and excessive apoptosis. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, K.; Li, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, F.; Xia, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, C. Pretreatment with Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Protected against ConA-Induced Acute Liver Injury by Inhibiting Both Intrinsic and Extrinsic Apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, F.; Qiu, G.; Xie, K. Integration of the hepatitis B virus X fragment in hepatocellular carcinoma and its effects on the expression of multiple molecules: A key to the cell cycle and apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Steele, R.; Zhou, X.Y.; Phillips, N.J.; Ray, R.; Ray, R.B. Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein impairs TNF-mediated hepatic apoptosis, but not by an anti-FAS antibody, in transgenic mice. Virology 2002, 294, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J.; Hsu, S.L.; Liu, Y.T.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, M.H.; Huang, S.J.; Ho, J.A.; Wu, L.C. Gallic acid induces necroptosis via TNF-α signaling pathway in activated hepatic stellate cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, A. Evolving Global Etiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Insights and Trends for 2024. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2025, 15, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, G.P.; Dariya, B.; Kasa, P.; Peela, S.; El-Rayes, B.F. Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Mathurin, P. Diagnosis and Treatment of Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jophlin, L.L.; Singal, A.K.; Bataller, R.; Wong, R.J.; Sauer, B.G.; Terrault, N.A.; Shah, V.H. ACG Clinical Guideline: Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 119, 30–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dukić, M.; Radonjić, T.; Jovanović, I.; Zdravković, M.; Todorović, Z.; Kraišnik, N.; Aranđelović, B.; Mandić, O.; Popadić, V.; Nikolić, N.; et al. Alcohol, Inflammation, and Microbiota in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Deng, S.; Xiong, L. Role of Kynurenine and Its Derivatives in Liver Diseases: Recent Advances and Future Clinical Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, A.; Kwo, P. Viral Hepatitis Other than A, B, and C: Evaluation and Management. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 24, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, R.; Plunkett, J.; Cieply, L.; Ijaz, S.; Desai, M.; Mandal, S. Blood-borne virus testing in emergency departments—A systematic review of seroprevalence, feasibility, acceptability and linkage to care. HIV Med. 2023, 24, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuda, D.; Kaneoka, Y.; Ono, R.; Kato, M.; Sugawara, Y.; Shimizu, R.; Inami, T.; Nakajima, E.; Tsuge, S.; Sakurai, R.; et al. Current perspectives of viral hepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2402–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirino, A.; Marascio, N.; Branda, F.; Ciccozzi, A.; Romano, C.; Locci, C.; Azzena, I.; Pascale, N.; Pavia, G.; Matera, G.; et al. Viral Hepatitis: Host Immune Interaction, Pathogenesis and New Therapeutic Strategies. Pathogens 2024, 13, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, E.; Perumal, E.; Subramaniyan, R.; Mustapha, N. Liver fibrosis: Extracellular vesicles mediated intercellular communication in perisinusoidal space. Hepatology 2022, 76, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Cabrera, D.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Jalan-Sakrikar, N.; Verma, V.K.; Simonetto, D.; Cao, S.; Yaqoob, U.; Leon, J.; Freire, M.; et al. Hepatic stellate cell activation promotes alcohol-induced steatohepatitis through Igfbp3 and SerpinA12. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, A.; Jeevitha, S.; Vusa, L. Peptidomimetics for CVD screened via TRADD-TRAF2 complex interface assessments. In Silico Pharmacol. 2023, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cebotaru, L.; Lee, H.W.; Yang, Q.; Pollard, B.S.; Pollard, H.B.; Guggino, W.B. CFTR Controls the Activity of NF-κB by Enhancing the Degradation of TRADD. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Geng, Z.; Deng, T.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Type 1-Associated Death Domain Protein Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 357, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Li, L.; Tang, H.; Xie, Y.; Puliyappadamba, V.T.; Raisanen, J.; Burma, S.; Boothman, D.A.; Cochran, B.; Wu, J.; et al. Cytoplasmic TRADD confers a worse prognosis in glioblastoma. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wu, X.; Ma, L.; Xue, H. Apoptosis-Associated Gene Expression Profiling Is One New Prognosis Risk Predictor of Human Rectal Cancer. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 4596810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Xue, R.; Ueki, H.; Huang, P. The Necroptotic Process-related Signature Predicts Immune Infiltration and Drug Sensitivity in Kidney Renal Papillary Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2025, 25, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururaja, T.L.; Yung, S.; Ding, R.; Huang, J.; Zhou, X.; McLaughlin, J.; Daniel-Issakani, S.; Singh, R.; Cooper, R.D.; Payan, D.G.; et al. A class of small molecules that inhibit TNFalpha-induced survival and death pathways via prevention of interactions between TNFalphaRI, TRADD, and RIP1. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu El-Asrar, A.M.; Dralands, L.; Missotten, L.; Geboes, K. Expression of antiapoptotic and proapoptotic molecules in diabetic retinas. Eye 2007, 21, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Boonmars, T.; Nagano, I.; Boonjaraspinyo, S.; Srinontong, P.; Ratasuwan, P.; Narong, K.; Nielsen, P.S.; Maekawa, Y. Significance of S100P as a biomarker in diagnosis, prognosis and therapy of opisthorchiasis-associated cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ye, R.; Dai, H.; Lin, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, Y. Exploring TNFR1: From discovery to targeted therapy development. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayir, M.; Wang, Y.W.; Chu, T.; Wang, X.L.; Fan, Y.Q.; Cao, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Wu, D.D. The function of necroptosis in liver cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Meng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zeng, F.; Deng, G.; Chen, X. Targeting regulated cell death: Apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis in anticancer immunity. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2025, 13, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Vredevoogd, D.; Yu, X.; Lu, D.; Peeper, D.S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Wang, J.; Wajant, H.; Siegmund, D. TRAF2 and RIPK1 redundantly mediate classical NFκB signaling by TNFR1 and CD95-type death receptors. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Liang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y. Interpretable Machine Learning reveals the Role of PANoptosis in the Diagnosis and Subtyping of NAFLD. Immunobiology 2025, 230, 152909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Liver Diseases | Role of TRADD | Related Regulatory Factors |
|---|---|---|
| HCC | TRADD expression correlates with tumor differentiation levels [20]. Targeting TRADD significantly inhibits HCC proliferation. Modulation of TRADD-mediated death receptor pathways suppresses HCC progression. | ASO-TRADD [71], miR-149* [21], dehydrocrenatidine [72], miR-199a-5p [73]. |
| ALD | Inhibition of TRADD and other pro-apoptotic genes alleviates alcohol-induced liver injury and fibrosis. | miR-124-3p [22], EGF [74]. |
| MASLD | Regulation of TRADD/RIPK1 transcription affects the NF-κB pathway. | HAF [24]. |
| I/R Injury | Inhibition of TRADD-related complex formation reduces hepatocyte apoptosis. | HO-1 [23]. |
| Drug-Induced Liver Injury | Activation of TRADD-dependent apoptotic pathways leads to liver damage. | Oxymatrine, sodium fluoride, and copper [75,76,77]. |
| Aflatoxin B1-Induced Liver Injury | Downregulation of TRADD and FADD expression inhibits hepatocyte apoptosis and inflammation. | Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum C88 [78]. |
| ConA-Induced Liver Injury | Modulation of TRADD-mediated death receptor pathways alleviates liver injury. | Fucoidan [79]. |
| Viral hepatitis | Significant correlation between HBx integration and TRADD expression levels. NS5A binds TRADD, block-ing its interaction with FADD and inhibiting NF-κB activation. | HBx [80], NS5A [81]. |
| Liver Fibrosis | Induction of necroptosis in activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) via the TNF-α/TRADD/RIP3 pathway. | GA [82]. |
| Targeting Strategy | Mechanism | Associated Diseases |
|---|---|---|
| Small-Molecule Inhibitors | Binds to the N-terminal TRAF2-binding domain of TRADD, inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation. Restores cellular autophagy by inhibiting TRADD activity. Blocks TNFα receptor binding to TRADD, suppressing NF-κB signaling. | Neurodegenerative diseases [26], diabetic cardiomyopathy [61]. |
| ASO-TRADD | Silences TRADD expression, inhibiting its pro-apoptotic effects. Synergistic effect with proteasome inhibitors (e.g., MG132 or ALLN) enhances antitumor activity. | HCC [71]. |
| Peptide Mimetics | Disrupts TRADD-TRAF2 complex formation. | Cardiovascular diseases [99]. |
| Bioactive Compounds | Promotes lysosomal degradation of TRADD, inhibiting NF-κB signaling. | Chronic lung infections [100]. |
| Biomarker Potential | TRADD expression levels correlate with disease prognosis. | Various cancers (AML [101], GBM [102], RC [103], KIRP [104], CCA [100]). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, D.; Cao, H.; Deng, S.; Zhang, Y. The Dual Role of TRADD in Liver Disease: From Cell Death Regulation to Inflammatory Microenvironment Remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125860
Wang X, Tan Q, Zhang D, Cao H, Deng S, Zhang Y. The Dual Role of TRADD in Liver Disease: From Cell Death Regulation to Inflammatory Microenvironment Remodeling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125860
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xueling, Qiwen Tan, Di Zhang, Huan Cao, Shenghe Deng, and Yu Zhang. 2025. "The Dual Role of TRADD in Liver Disease: From Cell Death Regulation to Inflammatory Microenvironment Remodeling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125860
APA StyleWang, X., Tan, Q., Zhang, D., Cao, H., Deng, S., & Zhang, Y. (2025). The Dual Role of TRADD in Liver Disease: From Cell Death Regulation to Inflammatory Microenvironment Remodeling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5860. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125860





