L-3-[18F]-Fluoro-α-Methyl Tyrosine as a PET Tracer for Tumor Diagnosis: A Systematic Review from Mechanisms to Clinical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Radiosynthesis of [18F]FAMT
3.2. Structural Characteristics of [18F]FAMT
3.3. Molecular Mechanism: [18F]FAMT and LAT1 Interaction
3.4. Pharmacokinetics of [18F]FAMT
3.5. Clinical Value of [18F]FAMT PET in Differential Diagnosis
3.5.1. Lung Cancer
Diagnostic Performance
Prognostic Significance in NSCLC
Methodological Challenges and Optimization Strategies in NSCLC
3.5.2. Esophageal Cancer
Diagnostic Accuracy and Staging Utility
Lymph Node Assessment
Predictive Value for Treatment Outcomes
Critical Analysis of Methodological Challenges in ESCC
3.5.3. Oral Cancer
Diagnostic Efficacy in Oral Cancer
Correlation with LAT1 and Prognosis
Methodological Challenges and Optimization Strategies in OSCC
3.5.4. Glioma
Diagnostic Performance
Comparative Advantages
Biological and Methodological Challenges in Glioma Imaging
3.5.5. Applications in Other Tumors and Sarcoidosis
Multiple Myeloma
Diagnostic Specificity and Imaging Challenges in MM
Bone Metastases
Diagnostic Specificity and Phenotype-Related Variation in Bone Metastases
Breast Cancer
Critical Appraisal of Specificity and Prognostic Imaging in Breast Cancer
Sarcoidosis
Critical Analysis of Diagnostic Imaging in Sarcoidosis
3.6. Limitations and Challenges
3.6.1. Technical Challenges
3.6.2. Biological and Imaging Limitations
3.6.3. Clinical Implementation and Standardization Issues
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| [18F]FAMT | L-3-[18F]-fluoro-α-methyltyrosine |
| [18F]FDG | 2-[18F]Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| 11C-MET | I-methyl-11C-methionine |
| [18F]FET | O-(2-[18F]-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine |
| [123I]IMT | 3-[123I]-L-α-methyl-tyrosine |
| LAT1 | L-type amino acid transporter 1 |
| CH3COO18F | 18F-acetylhypofluorite |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| SCC | squamous cell carcinoma |
| AC | adenocarcinoma |
| LCC | large cell carcinoma |
| SUVmax | maximum standardized uptake value |
| LN | lymph nodes |
| CT | computerized tomography |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| HGG | high-grade gliomas |
| LGG | low-grade gliomas |
| MM | multiple myeloma |
| OAT | organic anion transporter |
References
- Plathow, C.; Weber, W.A. Tumor Cell Metabolism Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 43S–63S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kang, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J. Recent Advances in Radiotracers Targeting Novel Cancer-Specific Biomarkers in China: A Brief Overview. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 38S–45S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crișan, G.; Moldovean-Cioroianu, N.S.; Timaru, D.G.; Andrieș, G.; Căinap, C.; Chiș, V. Radiopharmaceuticals for PET and SPECT Im-aging: A Literature Review over the Last Decade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avril, N. GLUT1 expression in tissue and (18)F-FDG uptake. J. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 930–932. [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler, M.; Thorens, B. The SLC2 (GLUT) family of membrane transporters. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Koyama, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Alyafei, S.; Yuan, Z.; Suzuki, H.; Takeuchi, K.; Tomaru, Y.; Tomiyoshi, K.; Aoki, J.; et al. Detection of Malignant Tumors: Whole-Body PET with Fluorine 18 α-Methyl Tyrosine versus FDG—Preliminary Study. Radiology 2001, 220, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Shim, H. Current Molecular Imaging Positron Emitting Radiotracers in Oncology. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; McConathy, J. Radiolabeled Amino Acids for Oncologic Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloar, H.M.; Fujiwara, T.; Nakamura, T.; Itoh, M.; Imai, D.; Miyake, M.; Watanuki, S. Estimation of internal absorbed dose of l-[methyl-11C]methionine using whole-body positron emission tomography. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 25, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, L.; Bonatto, E.; Nieri, A.; Castello, A.; Maffione, A.M.; Marzola, M.C.; Cittanti, C.; Bartolomei, M.; Panareo, S.; Mansi, L.; et al. The Role of Molecular Imaging in Patients with Brain Metastases: A Literature Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.M.; Smith, C.S. Causes and imaging features of false positives and false negatives on 18F-PET/CT in oncologic imaging. Insights Into Imaging 2011, 2, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jager, P.L.; Vaalburg, W.; Pruim, J.; De Vries, E.G.; Langen, K.J.; A Piers, D. Radiolabeled amino acids: Basic aspects and clinical applications in oncology. J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 42, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomiyoshi, K.; Amed, K.; Muhammad, S.; Higuchi, T.; Inoue, T.; Endo, K.; Yang, D. Synthesis of isomers of 18F-labelled amino acid radiopharmaceutical: Position 2- and 3-L-18F-alpha-methyltyrosine using a separation and purification system. Nucl. Med. Commun. 1997, 18, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiriyasermkul, P.; Nagamori, S.; Tominaga, H.; Oriuchi, N.; Kaira, K.; Nakao, H.; Kitashoji, T.; Ohgaki, R.; Tanaka, H.; Endou, H.; et al. Transport of 3-Fluoro-l-α-Methyl-Tyrosine by Tumor-Upregulated L-Type Amino Acid Transporter 1: A Cause of the Tumor Uptake in PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Tominaga, H.; Ohgaki, R.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Hagiwara, K.; Okuda, S.; Kaira, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Nagamori, S.; Kanai, Y. Specific transport of 3-fluoro-l-alpha-methyl-tyrosine by LAT1 explains its specificity to malignant tumors in imaging. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, Y. Amino acid transporter LAT1 (SLC7A5) as a molecular target for cancer diagnosis and therapeutics. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 230, 107964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, Y.; Fukasawa, Y.; Cha, S.H.; Segawa, H.; Chairoungdua, A.; Kim, D.K.; Matsuo, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Miyamoto, K.-I.; Takeda, E.; et al. Transport Properties of a System y+L Neutral and Basic Amino Acid Transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 20787–20793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Bren-nan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermert, J. 18F-Labelled Intermediates for Radiosynthesis by Modular Build-Up Reactions: Newer Developments. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermert, J.; Coenen, H.H. Nucleophilic 18F-Fluorination of Complex Molecules in Activated Carbocyclic Aromatic Position. Curr. Radiopharm. 2010, 3, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrota, A.; Comar, D.; Cerf, M.; Plummer, D.; Maziere, M.; Kellershohn, C. (C-11) methionine pancreatic scanning with positron emission computed-tomography. J. Nucl. Med. 1979, 20, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wester, H.J.; Herz, M.; Weber, W.; Heiss, P.; Senekowitsch-Schmidtke, R.; Schwaiger, M.; Stöcklin, G. Synthesis and radiopharmacology of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine for tumor imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 40, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaira, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Imai, H.; Shimizu, K.; Yanagitani, N.; Sunaga, N.; Hisada, T.; Tanaka, S.; Ishizuka, T.; Kanai, Y.; et al. Prognostic significance of L-type amino acid transporter 1 expression in resectable stage I–III nonsmall cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, Y.; Hanaoka, H.; Tominaga, H.; Kanai, Y.; Kaira, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Nagamori, S.; Oriuchi, N.; Tsushima, Y.; Endo, K.; et al. Biological evaluation of 3-[18F]fluoro-α-methyl-d-tyrosine (d-[18F]FAMT) as a novel amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2013, 27, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleán, J.C.; Humpert, S.; Ermert, J.; Coenen, H.H. Stereoselective radiosynthesis of l- and d-3-[18F]fluoro-α-methyltyrosine. J. Fluor. Chem. 2015, 178, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, Y.; Segawa, H.; Miyamoto, K.-I.; Uchino, H.; Takeda, E.; Endou, H. Expression Cloning and Characterization of a Transporter for Large Neutral Amino Acids Activated by the Heavy Chain of 4F2 Antigen (CD98). J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 23629–23632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yan, R.; Song, S.; Swansiger, A.K.; Li, Y.; Prell, J.S.; Zhou, Q.; Robinson, C.V. The complete assembly of human LAT1-4F2hc complex provides insights into its regulation, function and localisation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Jin, C.; Quan, L.; Ohgaki, R.; Okuda, S.; Kusakizako, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Oda, K.; Ishitani, R.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human L-type amino acid transporter 1 in complex with glycoprotein CD98hc. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, O.; Kanai, Y.; Chairoungdua, A.; Kim, D.K.; Segawa, H.; Nii, T.; Cha, S.H.; Matsuo, H.; Fukushima, J.-I.; Fukasawa, Y.; et al. Human L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): Characterization of function and expression in tumor cell lines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2001, 1514, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawashiro, H.; Otani, N.; Shinomiya, N.; Fukui, S.; Ooigawa, H.; Shima, K.; Matsuo, H.; Kanai, Y.; Endou, H. L-type amino acid transporter 1 as a potential molecular target in human astrocytic tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaira, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Shimizu, K.; Imai, H.; Tominaga, H.; Yanagitani, N.; Sunaga, N.; Hisada, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Kanai, Y.; et al. Comparison of l-type amino acid transporter 1 expression and l-[3-18F]-α-methyl tyrosine uptake in outcome of non-small cell lung cancer. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2010, 37, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobusawa, A.; Kim, M.; Kaira, K.; Miyashita, G.; Negishi, A.; Oriuchi, N.; Higuchi, T.; Tsushima, Y.; Kanai, Y.; Yokoo, S.; et al. Diagnostic usefulness of 18F-FAMT PET and L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 40, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, M.; Watabe, T.; Nagamori, S.; Naka, S.; Ikeda, H.; Kongpracha, P.; Horitsugi, G.; Kanai, Y.; Shimosegawa, E.; Kanai, Y.; et al. Distribution of LAT1-targeting PET tracer was independent of the tumor blood flow in rat xenograft models of C6 glioma and MIA PaCa-2. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2019, 33, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaira, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Shimizu, K.; Tominaga, H.; Yanagitani, N.; Sunaga, N.; Ishizuka, T.; Kanai, Y.; Mori, M.; Endo, K. 18F-FMT Uptake Seen Within Primary Cancer on PET Helps Predict Outcome of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaira, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Shimizu, K.; Ishikita, T.; Higuchi, T.; Imai, H.; Yanagitani, N.; Sunaga, N.; Hisada, T.; Ishizuka, T.; et al. Evaluation of thoracic tumors with (18)F-FMT and (18)F-FDG PET-CT: A clinicopathological study. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segawa, H.; Fukasawa, Y.; Miyamoto, K.-I.; Takeda, E.; Endou, H.; Kanai, Y. Identification and Functional Characterization of a Na+-independent Neutral Amino Acid Transporter with Broad Substrate Selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19745–19751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Tomiyoshi, K.; Higuichi, T.; Ahmed, K.; Sarwar, M.; Aoyagi, K.; Amano, S.; Alyafei, S.; Zhang, H.; Endo, K. Biodistribution studies on L-3-[fluorine-18]fluoro-alpha-methyl tyrosine: A potential tumor-detecting agent. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 39, 663–667. [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita, G.; Higuchi, T.; Oriuchi, N.; Arisaka, Y.; Hanaoka, H.; Tominaga, H.; Morita, S.; Miyakubo, M.; Ishikita, T.; Nakasone, Y.; et al. 18F-FAMT uptake correlates with tumor proliferative activity in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Comparative study with 18F-FDG PET and immunohistochemistry. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2010, 24, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Kaira, K.; Ohshima, Y.; Ishioka, N.S.; Sohda, M.; Yokobori, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Oriuchi, N.; Tominaga, H.; Kanai, Y.; et al. Biological significance of fluorine-18-α-methyltyrosine (FAMT) uptake on PET in patients with oesophageal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Shibasaki, T.; Oriuchi, N.; Aoyagi, K.; Tomiyoshi, K.; Amano, S.; Mikuni, M.; Ida, I.; Aoki, J.; Endo, K. 18F alpha-methyl tyrosine PET studies in patients with brain tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 1999, 40, 399–405. [Google Scholar]
- Meikle, S.R.; Bailey, D.L.; Hooper, P.K.; Eberl, S.; Hutton, B.F.; Jones, W.F.; Fulton, R.R.; Fulham, M.J. Simultaneous emission and transmission measurements for attenuation correction in whole-body PET. J. Nucl. Med. 1995, 36, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Amano, S.; Inoue, T.; Tomiyoshi, K.; Ando, T.; Endo, K. In vivo comparison of PET and SPECT radiopharmaceuticals in detecting breast cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 39, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Tominaga, H.; Ohgaki, R.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Hagiwara, K.; Okuda, S.; Kaira, K.; Kato, Y.; Oriuchi, N.; Nagamori, S.; et al. Transport of 3-fluoro-l-α-methyl-tyrosine (FAMT) by organic ion transporters explains renal background in [18F]FAMT positron emission tomography. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 130, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Wei, L.; Ohgaki, R.; Tominaga, H.; Xu, M.; Okuda, S.; Okanishi, H.; Kawamoto, Y.; He, X.; Nagamori, S.; et al. Interaction of Halogenated Tyrosine/Phenylalanine Derivatives with Organic Anion Transporter 1 in the Renal Handling of Tumor Imaging Probes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 375, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaira, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Otani, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Tanaka, S.; Imai, H.; Yanagitani, N.; Sunaga, N.; Hisada, T.; Ishizuka, T.; et al. Fluorine-18-α-Methyltyrosine Positron Emission Tomography for Diagnosis and Staging of Lung Cancer: A Clinicopathologic Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 6369–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaira, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Shimizu, K.; Ishikita, T.; Higuchi, T.; Imai, H.; Yanagitani, N.; Sunaga, N.; Hisada, T.; Ishizuka, T.; et al. Correlation of angiogenesis with 18F-FMT and 18F-FDG uptake in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohda, M.; Kato, H.; Suzuki, S.; Tanaka, N.; Sano, A.; Sakai, M.; Inose, T.; Nakajima, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Fukuchi, M.; et al. 18F-FAMT-PET Is Useful for the Diagnosis of Lymph Node Metastasis in Operable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 3181–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Higuchi, T.; Arisaka, Y.; Achmad, A.; Tokue, A.; Tominaga, H.; Miyashita, G.; Miyazaki, H.; Negishi, A.; Yokoo, S.; et al. Clinical significance of 18F-α-methyl tyrosine PET/CT for the detection of bone marrow invasion in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma: Comparison with 18F-FDG PET/CT and MRI. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2013, 27, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, K.; Tosaka, M.; Higuchi, T.; Arisaka, Y.; Sugawara, K.; Hirato, J.; Yokoo, H.; Tsushima, Y.; Yoshimoto, Y. Clinical value of fluorine-18α-methyltyrosine PET in patients with gliomas: Comparison with fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose PET. EJNMMI Res. 2017, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Higuchi, T.; Achmad, A.; Tokue, A.; Arisaka, Y.; Tsushima, Y. Complementary roles of tumour specific PET tracer 18F-FAMT to 18F-FDG PET/CT for the assessment of bone metastasis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 40, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoda, A.; Higuchi, T.; Nakano, S.; Arisaka, Y.; Kaira, K.; Kamio, T.; Mawatari, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Sawamura, M.; Tsushima, Y. 18F-FAMT in patients with multiple myeloma: Clinical utility compared to 18F-FDG. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2012, 26, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Achmad, A.; Higuchi, T.; Arisaka, Y.; Yokoo, H.; Yokoo, S.; Tsushima, Y. Effects of Intratumoral Inflammatory Process on 18F-FDG Uptake: Pathologic and Comparative Study with 18F-Fluoro-α-Methyltyrosine PET/CT in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 56, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumasaka, S.; Nakajima, T.; Arisaka, Y.; Tokue, A.; Achmad, A.; Fukushima, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Kaira, K.; Higuchi, T.; Tsushima, Y. Prognostic value of metabolic tumor volume of pretreatment 18F-FAMT PET/CT in non-small cell lung Cancer. BMC Med. Imaging 2018, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaira, K.; Higuchi, T.; Sunaga, N.; Arisaka, Y.; Hisada, T.; Tominaga, H.; Oriuchi, N.; Asao, T.; Tsushima, Y.; Yamada, M. Usefulness of 18F-α-Methyltyrosine PET for Therapeutic Monitoring of Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 6481–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaira, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Yanagitani, N.; Sunaga, N.; Ishizuka, T.; Mori, M.; Endo, K. Assessment of therapy response in lung cancer with 18F-α-methyl tyrosine PET. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohda, M.; Honjyo, H.; Hara, K.; Ozawa, D.; Suzuki, S.; Tanaka, N.; Sano, A.; Sakai, M.; Yokobori, T.; Inose, T.; et al. L-[3-18F]-α-methyltyrosine accumulation as a definitive chemoradiotherapy response predictor in patients with esophageal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 909–913. [Google Scholar]
- Sohda, M.; Sakai, M.; Honjyo, H.; Hara, K.; Ozawa, D.; Suzuki, S.; Tanaka, N.; Yokobori, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Fukuchi, M.; et al. Use of pre-treatment 18F-FAMT PET to predict patient survival in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus treated by curative surgery. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 3623–3628. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Higuchi, T.; Nakajima, T.; Andriana, P.; Hirasawa, H.; Tokue, A.; Kurihara, J.; Yokoo, S.; Tsushima, Y. 18F-FDG and 18F-FAMT PET-derived metabolic parameters predict outcome of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Radiol. 2019, 35, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, D.G.; Ang, K.K.; Brizel, D.M.; Burtness, B.A.; Cmelak, A.J.; Colevas, A.D.; Dunphy, F.; Eisele, D.W.; Gilbert, J.; Gillison, M.L.; et al. Head and neck cancers. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2011, 9, 596–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, J.; Zuo, X.; Li, C. Comparison of whole body positron emission tomography (PET)/PET-computed tomography and conventional anatomic imaging for detecting distant malignancies in patients with head and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1974–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Inoue, T.; Tomiyoshi, K.; Aoki, J.; Oriuchi, N.; Takahashi, A.; Otani, T.; Kurihara, H.; Sasaki, T.; Endo, K. Gliomatosis cerebri evaluated by 18F?-methyl tyrosine positron-emission tomography. Neuroradiology 2003, 45, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudistiro, R.; Arisaka, Y.; Tokue, A.; Nakajima, T. Differentiation of sarcoidosis-lymphoma syndrome lesions: A case report on the use of two different positron emission tomography tracers. BMC Med. Imaging 2016, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, Y.; Hanaoka, H.; Watanabe, S.; Sugo, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Tominaga, H.; Oriuchi, N.; Endo, K.; Ishioka, N.S. Prepara-tion and biological evaluation of 3-[(76)Br]bromo-alpha-methyl-L-tyrosine, a novel tyrosine analog for positron emission to-mography imaging of tumors. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2011, 38, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achmad, A.; Hanaoka, H.; Holik, H.A.; Endo, K.; Tsushima, Y.; Kartamihardja, A.H.S. LAT1-specific PET radiotracers: Development and clinical experiences of a new class of cancer-specific radiopharmaceuticals. Theranostics 2025, 15, 1864–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda-Nakashima, K.; Zhang, Z.; Manabe, Y.; Shimoyama, A.; Kabayama, K.; Watabe, T.; Kanai, Y.; Ooe, K.; Toyoshima, A.; Shirakami, Y.; et al. alpha-Emitting cancer therapy using (211) At-AAMT targeting LAT1. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watabe, T.; Kaneda-Nakashima, K.; Shirakami, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ooe, K.; Teramoto, T.; Toyoshima, A.; Shimosegawa, E.; Nakano, T.; Kanai, Y.; et al. Targeted alpha therapy using astatine (211At)-labeled phenylalanine: A preclinical study in glioma bearing mice. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, H.; Ohshima, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yamaguchi, A.; Watanabe, S.; Uehara, T.; Nagamori, S.; Kanai, Y.; Ishioka, N.S.; Tsu-shima, Y.; et al. Development of a Widely Usable Amino Acid Tracer: (7)(6)Br-alpha-Methyl-Phenylalanine for Tumor PET Im-aging. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
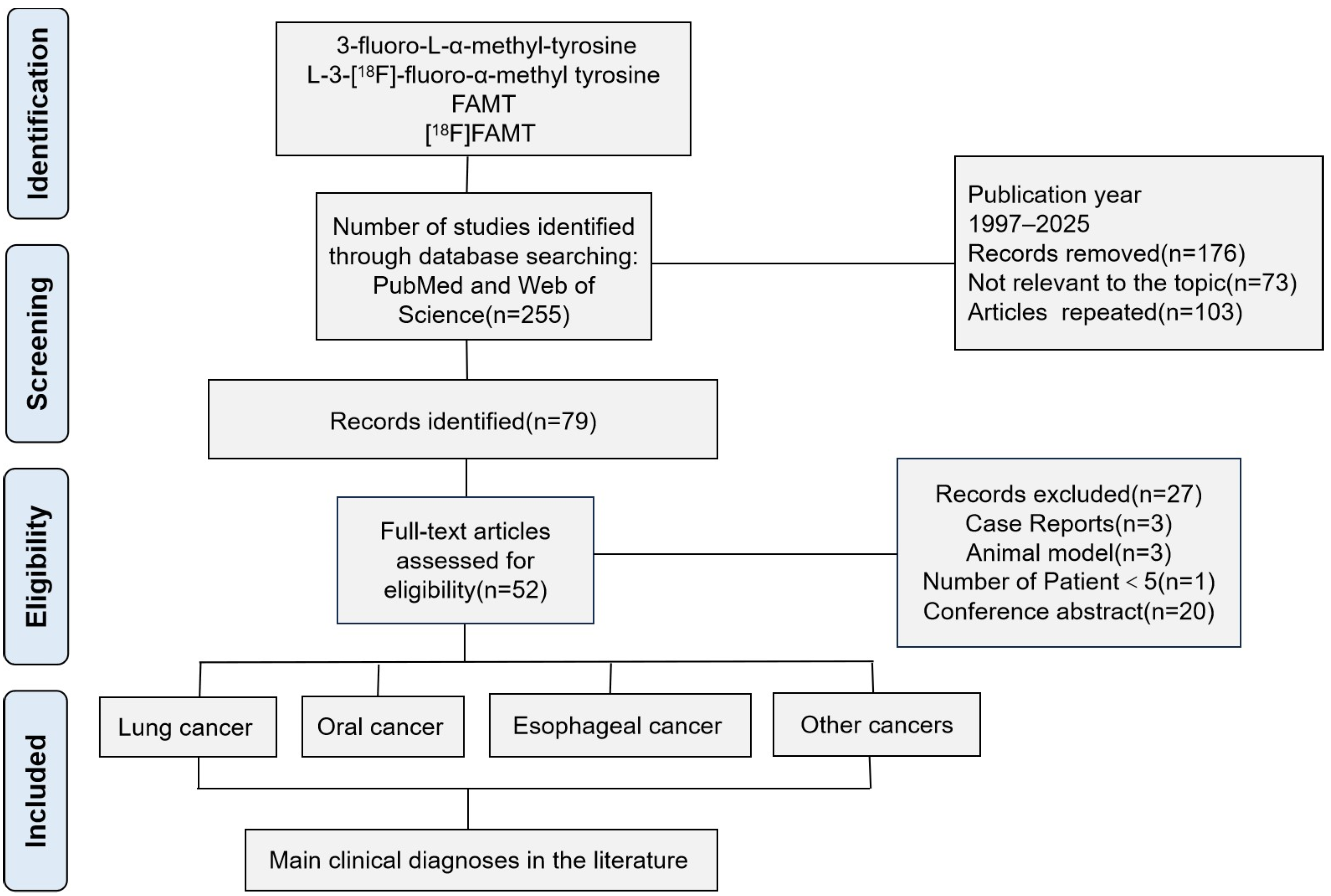
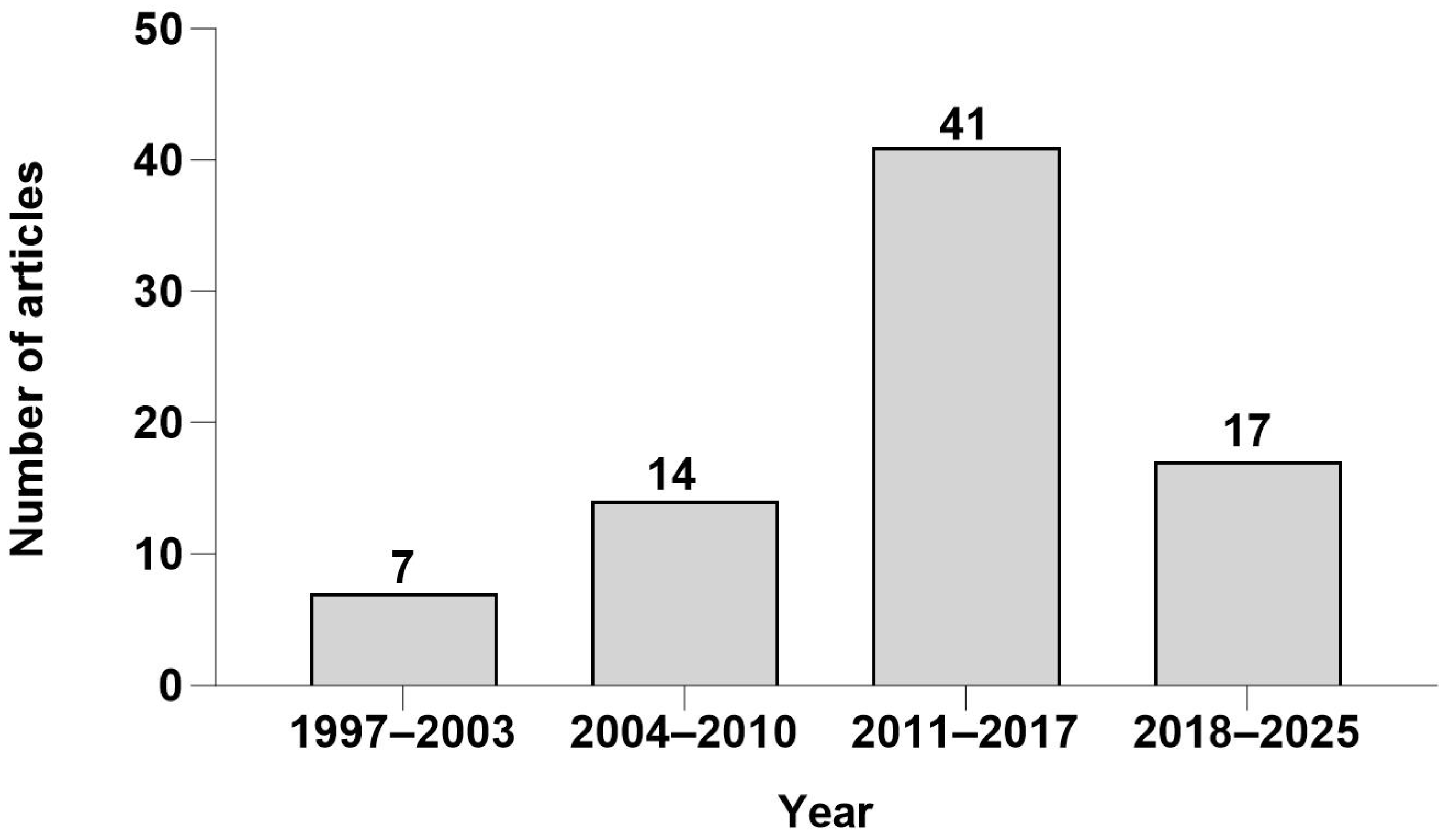

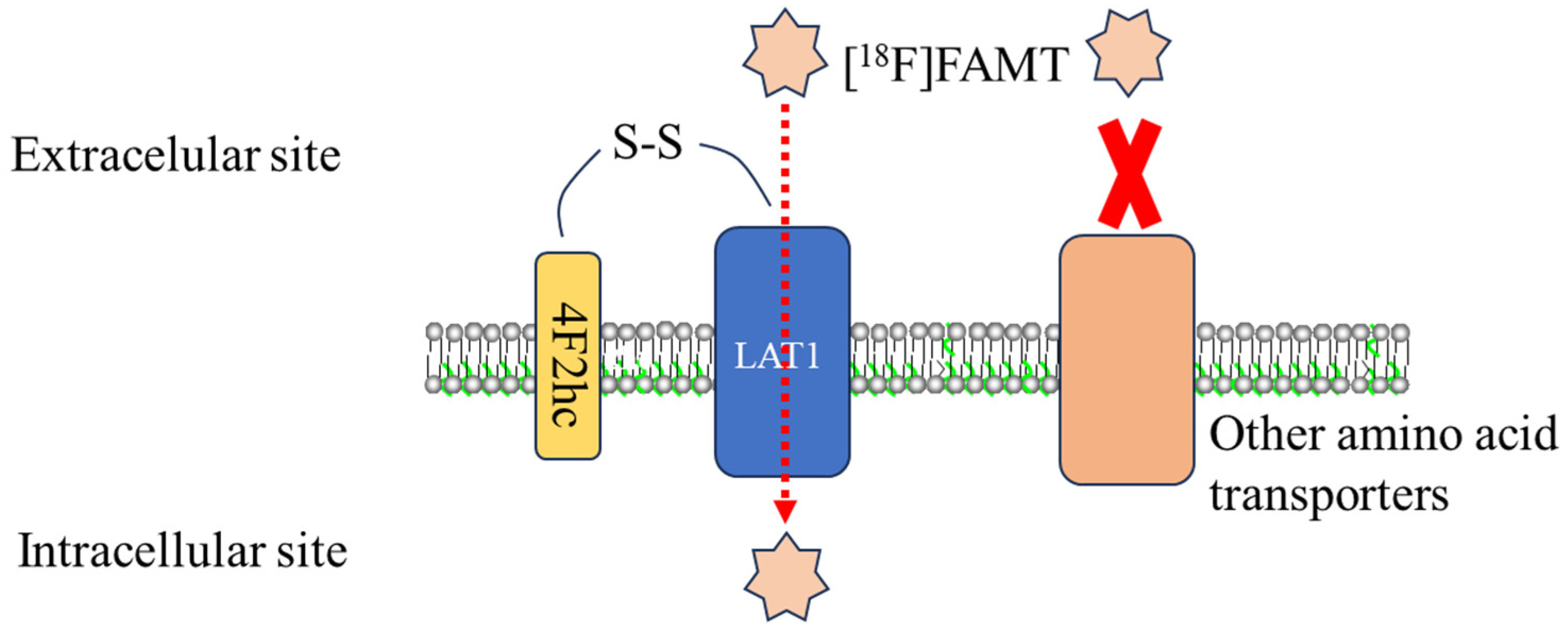
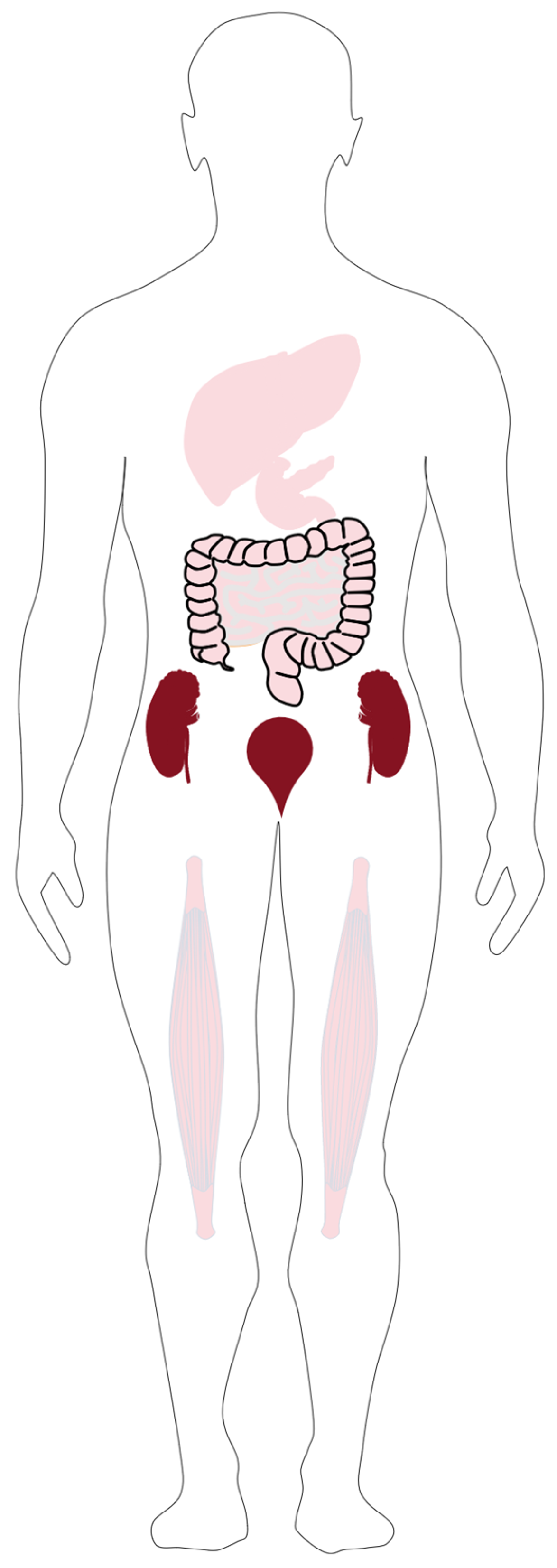
| Indication | Tumor | Tracer | Refs. | Year | Methodology Ref. | No. of Patients | Sens. | Spec. | SUV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The primary tumor detection | NSCLC | [18F]FAMT | [45] | 2007 | 1 | 50 | 90% | NR | NR |
| [46] | 2009 | 2 | 37 | NR | NR | 2.65 | |||
| [34] | 2009 | 3 | 98 | NR | NR | 0.6–5.8, median of 1.6 | |||
| [18F]FDG | [45] | 2007 | 1 | 50 | 94% | NR | NR | ||
| [46] | 2009 | 2 | 37 | NR | NR | 11.5 | |||
| [34] | 2009 | 3 | 98 | NR | NR | 0.9–29.6, median of 6.8 | |||
| ESCC | [18F]FAMT | [47] | 2010 | 4 | 21 | 76.2% | NR | NR | |
| [18F]FDG | [47] | 2010 | 4 | 21 | 90.5% | NR | NR | ||
| OSCC | [18F]FAMT | [38] | 2010 | 5 | 25 | 84% | NR | 1.3–8.5, median of 3.5 | |
| [32] | 2013 | 6 | 68 | 98% | NR | NR | |||
| [48] | 2013 | 7 | 27 | 90% | 85.7% | NR | |||
| [18F]FDG | [38] | 2010 | 5 | 25 | 88% | NR | 4.2–15.9, median of 9.7 | ||
| [32] | 2013 | 6 | 68 | 100% | NR | NR | |||
| [48] | 2013 | 7 | 27 | 100% | 14.3% | NR | |||
| LN Staging | NSCLC | [18F]FAMT | [45] | 2007 | 1 | 50 | 57.8% | 100% | NR |
| [18F]FDG | [45] | 2007 | 1 | 50 | 65.7% | 91% | NR | ||
| ESCC | [18F]FAMT | [47] | 2010 | 4 | 21 | 18.2% | 100% | NR | |
| [18F]FDG | [47] | 2010 | 4 | 21 | 24.2% | 93.7% | NR | ||
| OSCC | [18F]FAMT | [32] | 2013 | 6 | 68 | 68% | 99% | NR | |
| [18F]FDG | [32] | 2013 | 6 | 68 | 84% | 94% | NR | ||
| Glioma | [18F]FAMT | [49] | 2017 | 8 | 38 | 61.5% | 75% | 0.94 | |
| [18F]FDG | [49] | 2017 | 8 | 38 | 89% | 67% | 5.91 | ||
| BM | [18F]FAMT | [50] | 2013 | 9 | 21 | NR | 97.4% | 2.88–4.20, median of 3.6 | |
| [18F]FDG | [50] | 2013 | 9 | 21 | NR | NR | 5.40–9.15, median of 6.55 | ||
| MM | [18F]FAMT | [51] | 2012 | 10 | 11 | NR | NR | 0.80–4.90, median of 1.5 | |
| [18F]FDG | [51] | 2012 | 10 | 11 | NR | NR | 1.50–7.20, median of 2.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, M.; Gu, X.; Tong, K.; Chu, F.; Ye, P.; Kaneda-Nakashima, K.; Hou, W.; Li, Y.; Wei, L. L-3-[18F]-Fluoro-α-Methyl Tyrosine as a PET Tracer for Tumor Diagnosis: A Systematic Review from Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125848
Bao M, Gu X, Tong K, Chu F, Ye P, Kaneda-Nakashima K, Hou W, Li Y, Wei L. L-3-[18F]-Fluoro-α-Methyl Tyrosine as a PET Tracer for Tumor Diagnosis: A Systematic Review from Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125848
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Mei, Xiang Gu, Kai Tong, Fei Chu, Pinmao Ye, Kazuko Kaneda-Nakashima, Wenbin Hou, Yiliang Li, and Ling Wei. 2025. "L-3-[18F]-Fluoro-α-Methyl Tyrosine as a PET Tracer for Tumor Diagnosis: A Systematic Review from Mechanisms to Clinical Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125848
APA StyleBao, M., Gu, X., Tong, K., Chu, F., Ye, P., Kaneda-Nakashima, K., Hou, W., Li, Y., & Wei, L. (2025). L-3-[18F]-Fluoro-α-Methyl Tyrosine as a PET Tracer for Tumor Diagnosis: A Systematic Review from Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125848








