Allosteric Coupling in Full-Length Lyn Kinase Revealed by Molecular Dynamics and Network Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
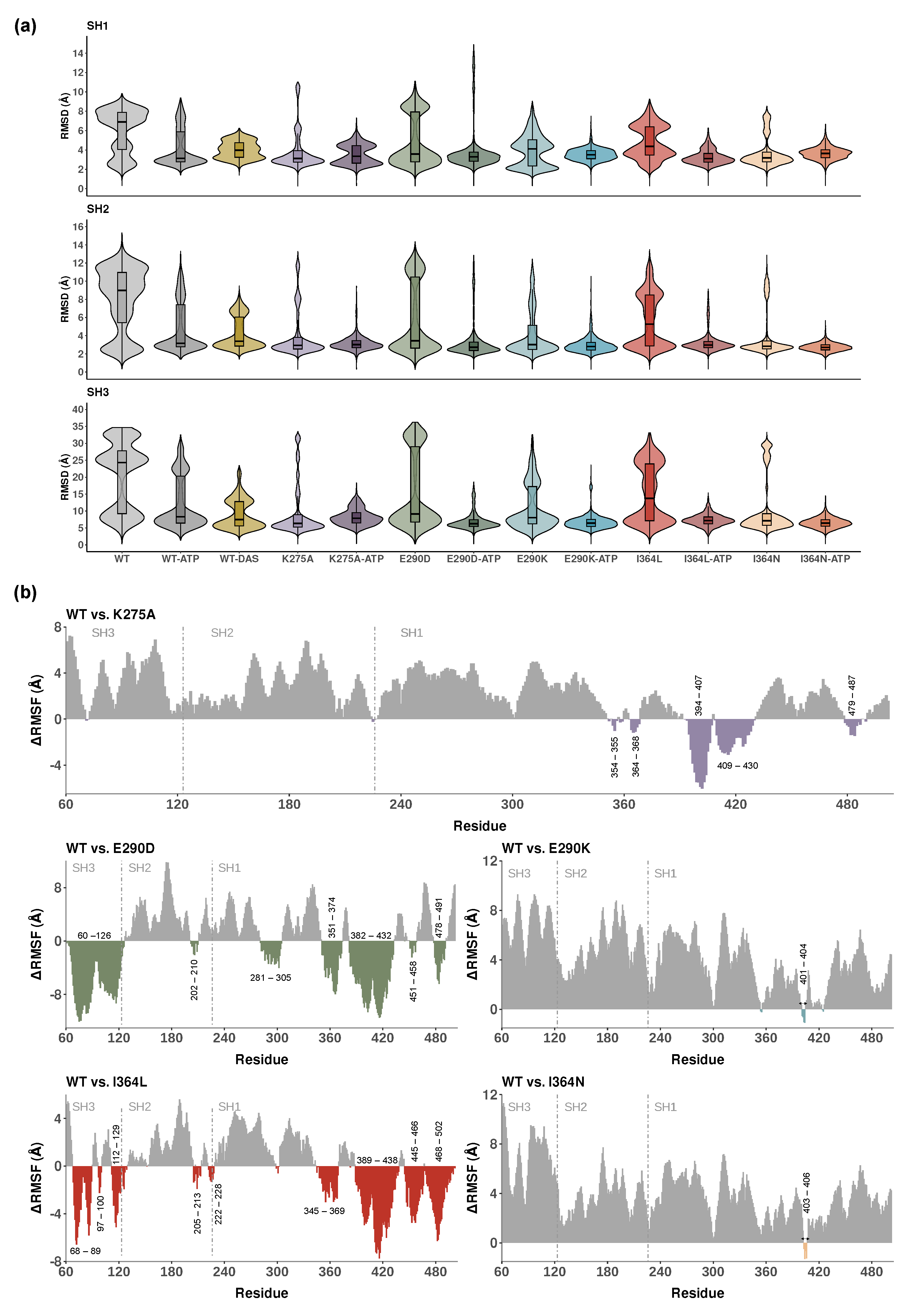
2.1. Global and Local Dynamics of Lyn Protein Across Domains
2.2. Ligand and Mutation Effects on Catalytic Site Architecture
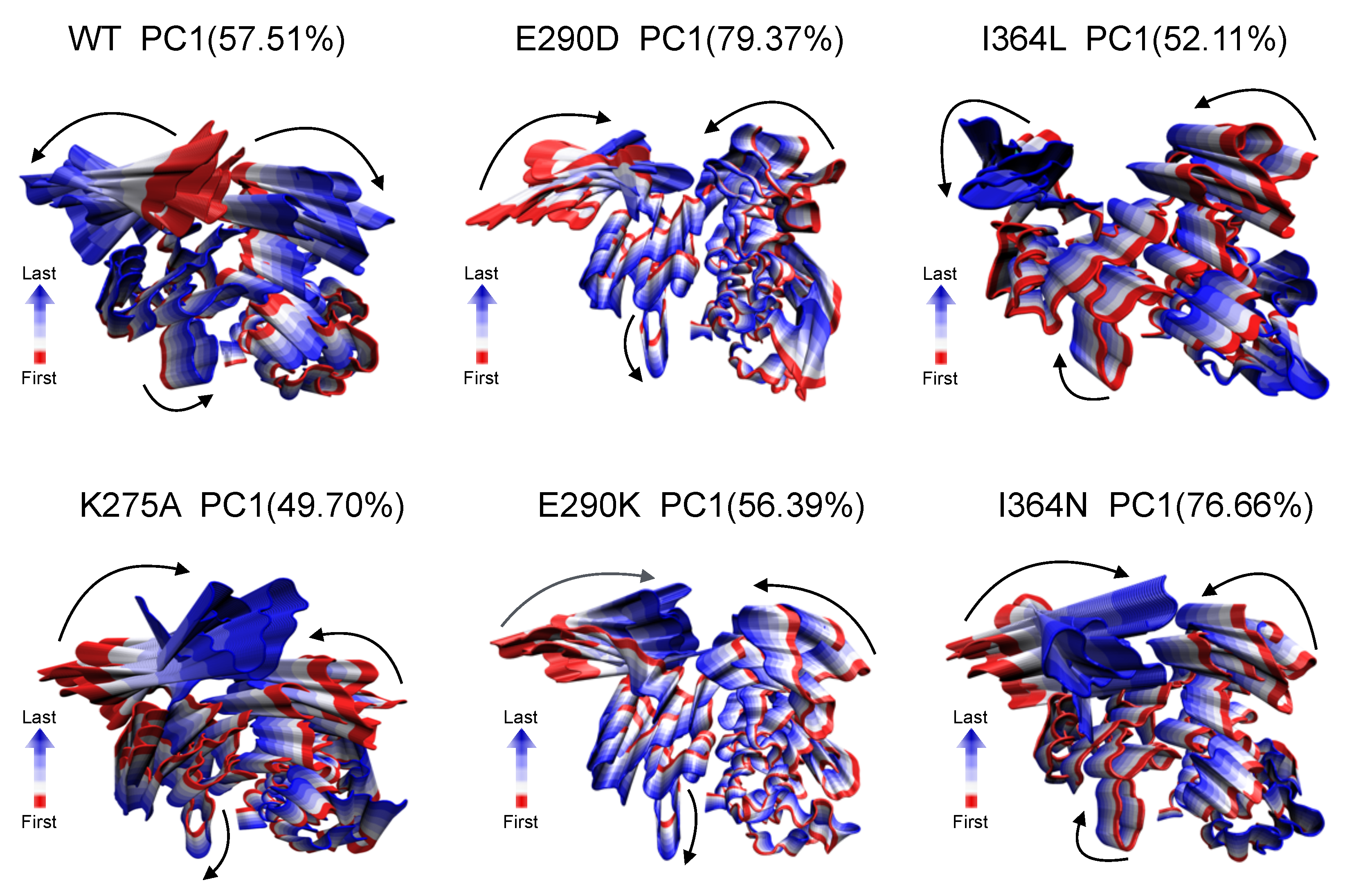
2.3. Dominant Global Motions Distinguish WT and Mutant Dynamics
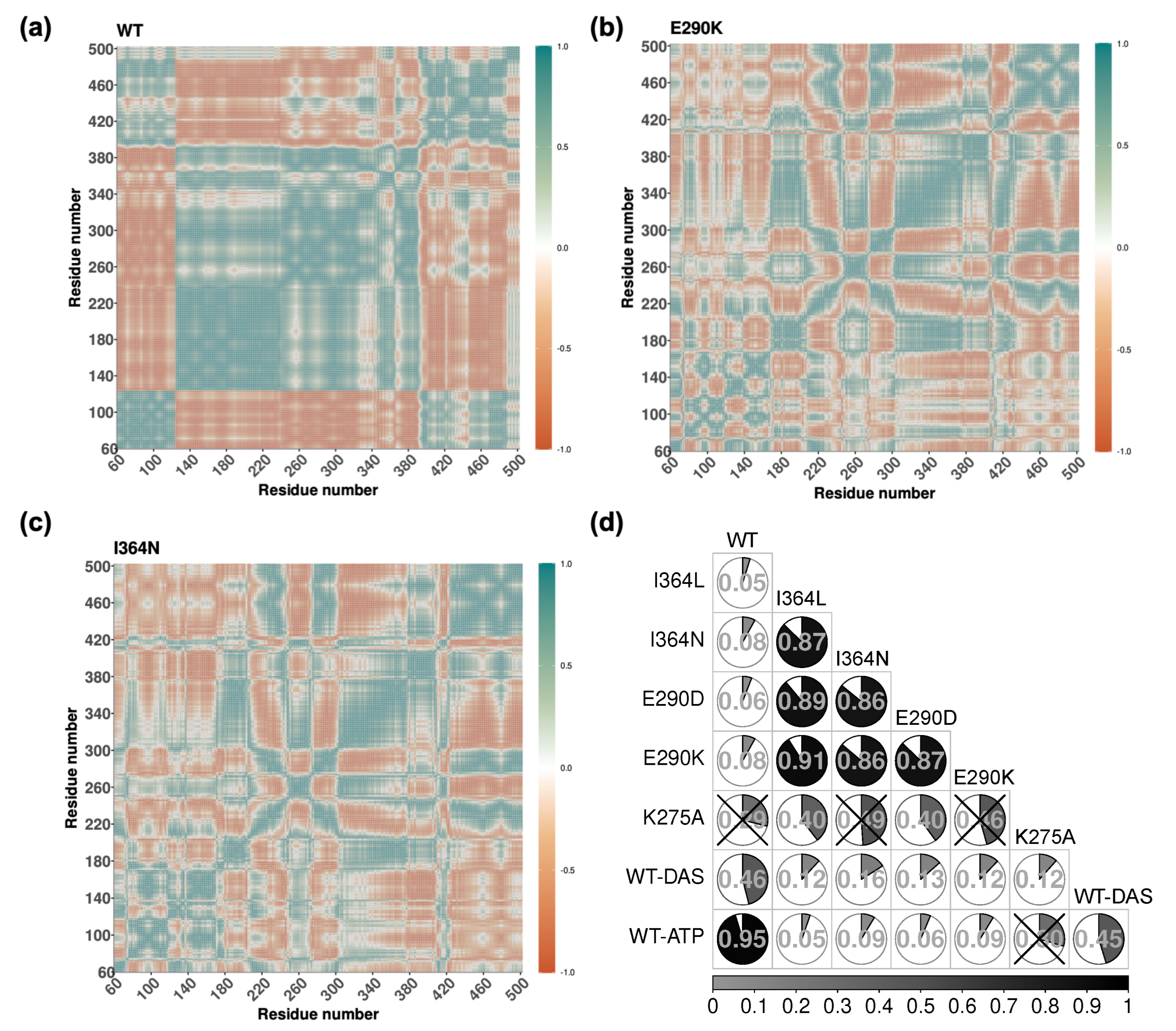
2.4. Mutation-Induced Perturbations in Allosteric Communication Revealed by DCCMs
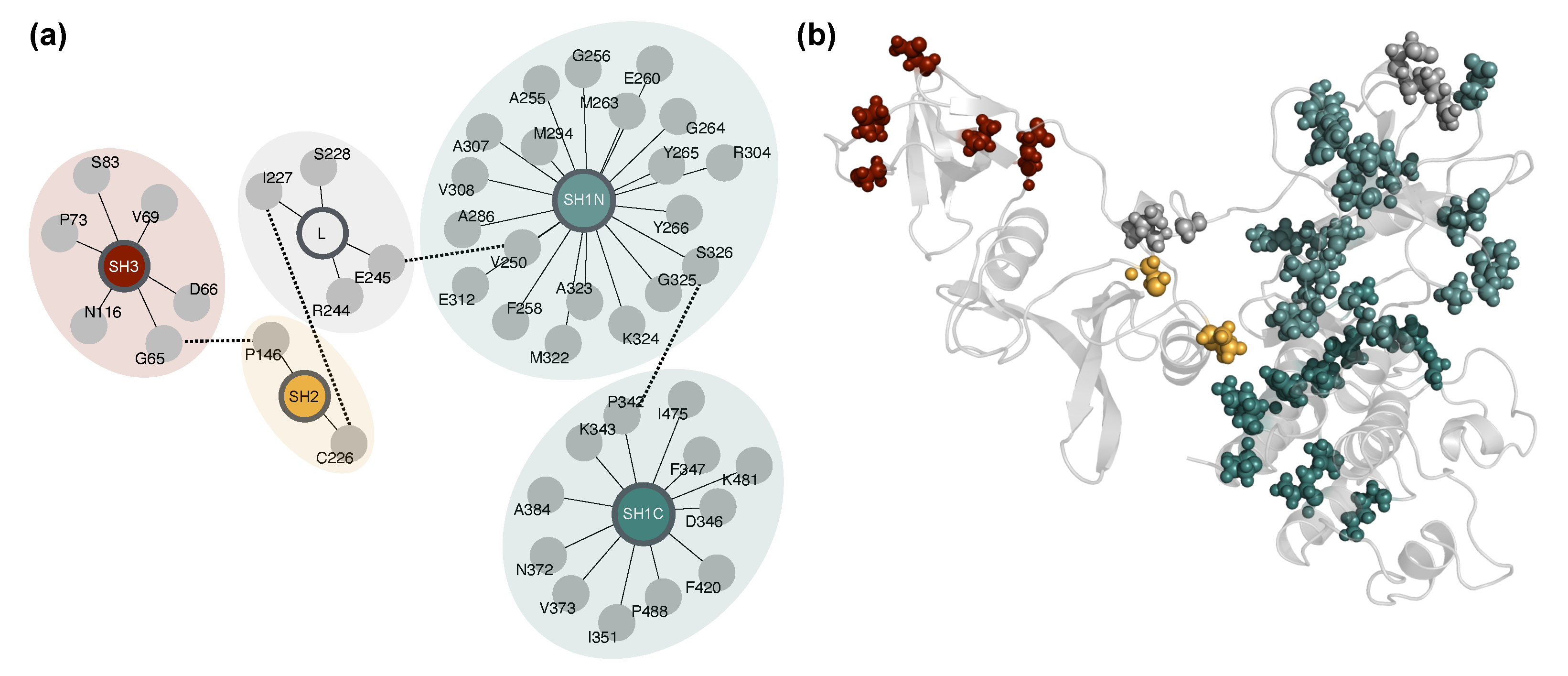
2.5. Network-Based Mapping of Allosteric Hubs
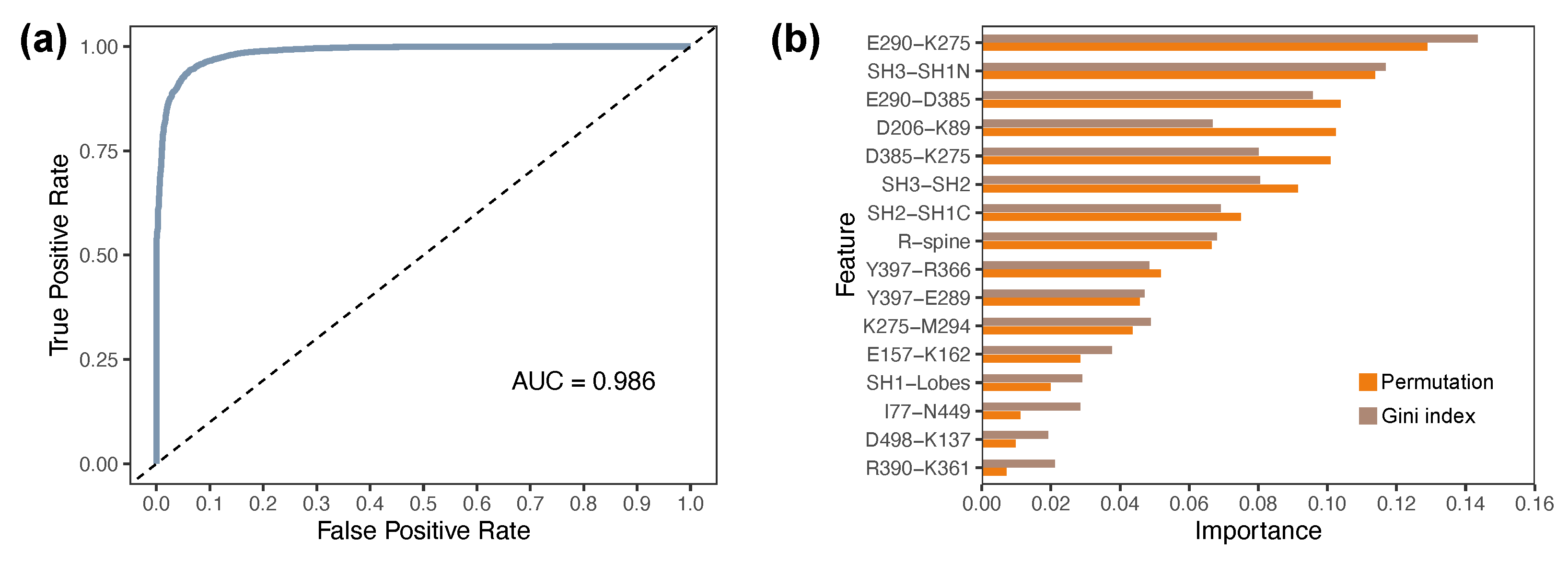
2.6. Discriminative Structural Features Define Domain-Level Determinants of Functional States
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Homology Modeling of Full-Length Lyn Protein
4.2. Mutant Generation and Small Molecule Incorporation
4.3. Quantum Mechanical Calculations
4.4. Classical MD Simulations
4.5. Trajectory Analyses
4.6. Interface Residues
4.7. Binding Pocket Surface Area Estimation
4.8. Projection of Dominant Motions Along Principal Components
4.9. Dynamical Cross-Correlation Analysis
4.10. Community Detection and Integration Module Identification
4.11. Identification of Allosteric Hubs from Networks and Interface Features
4.12. Random Forest Classification
4.13. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| DAS | Dasatinib |
| DCCM | Dynamical Cross-Correlation Matrix |
| MD | Molecular Dynamics |
| MM/PBSA | Molecular Mechanics/Poisson–Boltzmann Surface Area |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RMSD | Root Mean Square Deviation |
| RMSF | Root Mean Square Fluctuation |
| SASA | Solvent Accessible Surface Area |
| SFK | Src Family Kinase |
| SH1 | Src Homology 1 |
| SH2 | Src Homology 2 |
| SH3 | Src Homology 3 |
| WT | Wildtype |
References
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The Protein Kinase Complement of the Human Genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, M.E.M.; Endicott, J.A.; Johnson, L.N. Protein kinase inhibitors: Insights into drug design from structure. Science 2004, 303, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingley, E. Functions of the Lyn tyrosine kinase in health and disease. Cell Commun. Signal. 2012, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brian, B.F., 4th; Freedman, T.S. The Src-family Kinase Lyn in Immunoreceptor Signaling. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roginskaya, V.; Zuo, S.; Caudell, E.; Nambudiri, G.; Kraker, A.; Corey, S. Therapeutic targeting of Src-kinase Lyn in myeloid leukemic cell growth. Leukemia 1999, 13, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Harder, K.; Huntington, N.; Hibbs, M.; Tarlinton, D. Lyn Tyrosine Kinase. Immunity 2005, 22, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerawarna, P.; Richardson, T. Lyn Kinase Structure, Regulation, and Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Mini Review. Kinases Phosphatases 2023, 1, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Estrange-Stranieri, E.; Gottschalk, T.A.; Wright, M.D.; Hibbs, M.L. The dualistic role of Lyn tyrosine kinase in immune cell signaling: Implications for systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1395427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Malecka, K.; Fink, L.; Jordan, E.; Duffy, E.; Kolander, S.; Peterson, J.; Dunbrack, R. Identifying three-dimensional structures of autophosphorylation complexes in crystals of protein kinases. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, rs13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.H.; Fedorchenko, O.; Rosen, N.; Koch, M.; Barthel, R.; Winarski, T.; Florin, A.; Wunderlich, F.; Reinart, N.; Hallek, M. LYN Kinase in the Tumor Microenvironment Is Essential for the Progression of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohal, R.; Bhavana; Kumari, P.; Sharma, A.K.; Gupta, G.D.; Verma, S.K. Fyn, Blk, and Lyn kinase inhibitors: A mini-review on medicinal attributes, research progress, and future insights. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2024, 102, 129674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellucci, S.; Clementi, L.; Sabetta, S.; Mattei, V.; Botta, L.; Angelucci, A. Src Family Kinases as Therapeutic Targets in Advanced Solid Tumors: What We Have Learned So Far. Cancers 2020, 12, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsantikos, E.; Maxwell, M.J.; Kountouri, N.; Harder, K.W.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Hibbs, M.L. Genetic interdependence of Lyn and negative regulators of B cell receptor signaling in autoimmune disease development. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1726–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, N.K.; Lucet, I.S.; Klinken, S.P.; Ingley, E.; Rossjohn, J. Crystal structures of the Lyn protein tyrosine kinase domain in its Apo- and inhibitor-bound state. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contri, A.; Brunati, A.; Trentin, L.; Cabrelle, A.; Miorin, M.; Cesaro, L.; Pinna, L.; Zambello, R.; Semenzato, G.; Donella-Deana, A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells contain anomalous Lyn tyrosine kinase, a putative contribution to defective apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingione, V.; Paung, Y.; Outhwaite, I.; Seeliger, M. Allosteric regulation and inhibition of protein kinases. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowerman, S.; Wereszczynski, J. Detecting Allosteric Networks Using Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Methods Enzymol. 2016, 578, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Song, K.; Zhang, J.; Lu, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Dynamic Network Analysis Reveal the Allosteric Unbinding of Monobody to H-Ras Triggered by R135K Mutation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, P.; Paul, D.; Chakravorty, D. The natural way forward: Molecular dynamics simulation analysis of phytochemicals from Indian medicinal plants as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 targets. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 3420–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abram, C.L.; Lowell, C.A. The diverse functions of Src family kinases in macrophages. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 4426–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, M.; Kuriyan, J. The conformational plasticity of protein kinases. Cell 2002, 109, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getahun, A. Role of inhibitory signaling in peripheral B cell tolerance. Immunol. Rev. 2022, 307, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getlik, M.; Grütter, C.; Simard, J.R.; Klüter, S.; Rabiller, M.; Rode, H.B.; Robubi, A.; Rauh, D. Hybrid compound design to overcome the gatekeeper T338M mutation in cSrc. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3915–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M. Regulation of the SRC family kinases by Csk. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.; Meng, Y.; Roux, B.; Pande, V.S. Activation pathway of Src kinase reveals intermediate states as targets for drug design. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucheta-Martínez, E.; Saladino, G.; Morando, M.A.; Martinez-Torrecuadrada, J.; Lelli, M.; Sutto, L.; D’Amelio, N.; Gervasio, F.L. An Allosteric Cross-Talk Between the Activation Loop and the ATP Binding Site Regulates the Activation of Src Kinase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbaky, I.; Tayara, H.; Chong, K.T. Prediction of kinase inhibitors binding modes with machine learning and reduced descriptor sets. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, M.; Keskin, O.; Gursoy, A. DeepAllo: Allosteric Site Prediction using Protein Language Model (pLM) with Multitask Learning. Bioinformatics 2025, 41, btaf294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.H.; Amacher, J.F.; Nocka, L.M.; Kuriyan, J. The Src module: An ancient scaffold in the evolution of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 53, 535–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, V.; Dunbrack, R.L., Jr. Defining a new nomenclature for the structures of active and inactive kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6818–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, V.; Dunbrack, R.L. Kincore: A web resource for structural classification of protein kinases and their inhibitors. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2022, 50, D654–D664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foda, Z.H.; Shan, Y.; Kim, E.T.; Shaw, D.E.; Seeliger, M.A. A dynamically coupled allosteric network underlies binding cooperativity in Src kinase. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, S.H.; Oshima, H.; Sugita, Y. Allosteric changes in the conformational landscape of Src kinase upon substrate binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2024, 168871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelkova, M.A.; Tolstova, A.P.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Petrushanko, I.Y.; Makarov, A.A. Structure of Full-Length Src Kinase and Its Key Phosphorylated States: Molecular Dynamics Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakaash, D.; Fagnen, C.; Cook, G.P.; Acuto, O.; Kalli, A.C. Molecular dynamics simulations reveal membrane lipid interactions of the full-length lymphocyte specific kinase (Lck). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, M.P.; Eells, R.; Treece, B.W.; Heinrich, F.; Lösche, M.; Roux, B. Membrane Anchoring of Hck Kinase via the Intrinsically Disordered SH4-U and Length Scale Associated with Subcellular Localization. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 2985–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.A.; Gonfloni, S.; Superti-Furga, G.; Roux, B.; Kuriyan, J. Dynamic coupling between the SH2 and SH3 domains of c-Src and Hck underlies their inactivation by C-terminal tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell 2001, 105, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, J.R.; Wales, T.E.; Hochrein, J.M.; Meyn, M.A., 3rd; Banu Ozkan, S.; Bahar, I.; Smithgall, T.E. Structure and dynamic regulation of Src-family kinases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3058–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.K.; Park, H.S.; Lee, Y.B.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, J.I.; Park, J.B. Cross-Talk between Wnt Signaling and Src Tyrosine Kinase. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.A. The modular logic of signaling proteins: Building allosteric switches from simple binding domains. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2002, 12, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroco, J.A.; Craigo, J.K.; Iacob, R.E.; Wales, T.E.; Engen, J.R.; Smithgall, T.E. Differential sensitivity of Src-family kinases to activation by SH3 domain displacement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L.; Wang, W.; Wu, M.; Yuan, T.; Yang, W.; Tian, C.; Miao, Z.; Wang, T.; et al. Small molecules in targeted cancer therapy: Advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selzer, A.M.; Gerlach, G.; Gonzalez-Areizaga, G.; Wales, T.E.; Cui, S.Y.; Iyer, P.; Engen, J.R.; Camacho, C.; Ishima, R.; Smithgall, T.E. An SH3-binding allosteric modulator stabilizes the global conformation of the AML-associated Src-family kinase, Hck. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Limsakul, P.; Meng, X.; Huang, Y.; Harrison, R.E.S.; Huang, T.S.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Charupanit, K.; Zhong, S.; et al. Integration of FRET and sequencing to engineer kinase biosensors from mammalian cell libraries. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiser, A.; Šali, A. Modeller: Generation and Refinement of Homology-Based Protein Structure Models. Methods Enzymol. 2003, 374, 461–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colovos, C.; Yeates, T.O. Verification of protein structures: Patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS 2022.4 Manual. Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.; Jacobs, D. Principal Component Analysis: A Method for Determining the Essential Dynamics of Proteins. In Protein Dynamics; Livesay, D., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 193–226. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian∼16 Revision A.03; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; MacKerell, A. CHARMM36 all-atom additive protein force field: Validation based on comparison to NMR data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allnér, O.; Nilsson, L.; Villa, A. Magnesium Ion–Water Coordination and Exchange in Biomolecular Simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.; Impey, R.; Klein, M. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An Nlog(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021.
- Hennig, C. fpc: Flexible Procedures for Clustering, R Package Version 2.2-13; 2024. Available online: https://rdocumentation.org/packages/fpc/versions/2.2-13 (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Maechler, M.; Rousseeuw, P.; Struyf, A.; Hubert, M.; Hornik, K. cluster: Cluster Analysis Basics and Extensions, R Package Version 2.1.8.1—For New Features, See the ‘NEWS’ and the ‘Changelog’ File in the Package Source. 2025. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=cluster (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, B.; Rodrigues, A.; ElSawy, K.; McCammon, J.; Caves, L. Bio3d: An R package for the comparative analysis of protein structures. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2695–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active-like | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.87 |
| Inactive-like | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| Accuracy | 0.96 | ||
| Macro average | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.92 |
| Weighted average | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabipour, M.; Hassenrück, F.; Pallaske, E.; Röhrig, F.; Hallek, M.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R.; Kramer, O.; Rebollido-Rios, R. Allosteric Coupling in Full-Length Lyn Kinase Revealed by Molecular Dynamics and Network Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125835
Rabipour M, Hassenrück F, Pallaske E, Röhrig F, Hallek M, Alvarez-Idaboy JR, Kramer O, Rebollido-Rios R. Allosteric Coupling in Full-Length Lyn Kinase Revealed by Molecular Dynamics and Network Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125835
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabipour, Mina, Floyd Hassenrück, Elena Pallaske, Fernanda Röhrig, Michael Hallek, Juan Raul Alvarez-Idaboy, Oliver Kramer, and Rocio Rebollido-Rios. 2025. "Allosteric Coupling in Full-Length Lyn Kinase Revealed by Molecular Dynamics and Network Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125835
APA StyleRabipour, M., Hassenrück, F., Pallaske, E., Röhrig, F., Hallek, M., Alvarez-Idaboy, J. R., Kramer, O., & Rebollido-Rios, R. (2025). Allosteric Coupling in Full-Length Lyn Kinase Revealed by Molecular Dynamics and Network Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125835








