Efficacy of Expanded Hemodialysis and Comparison with Standard Hemodialysis and Online Hemodiafiltration
Abstract
1. Introduction
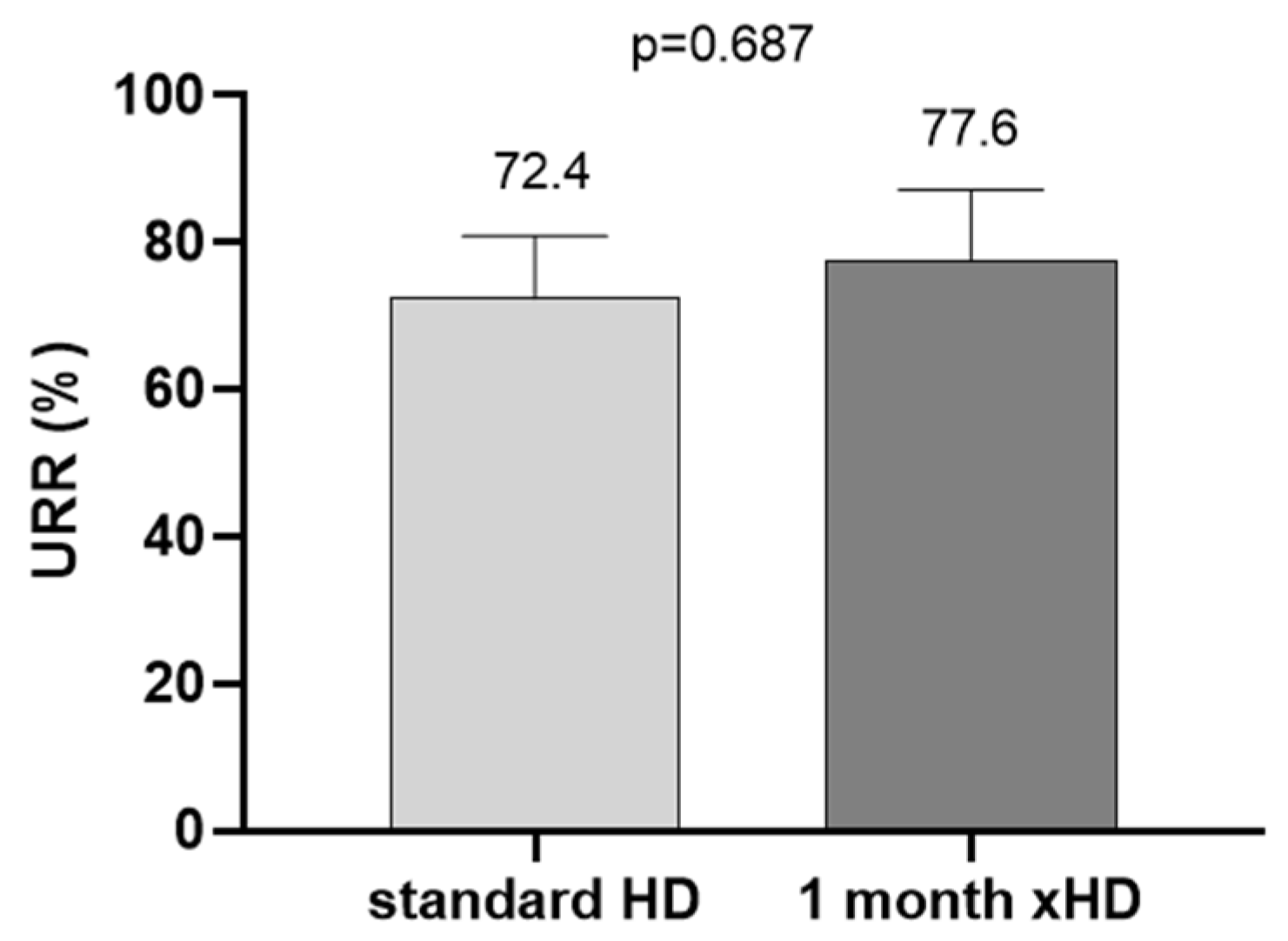
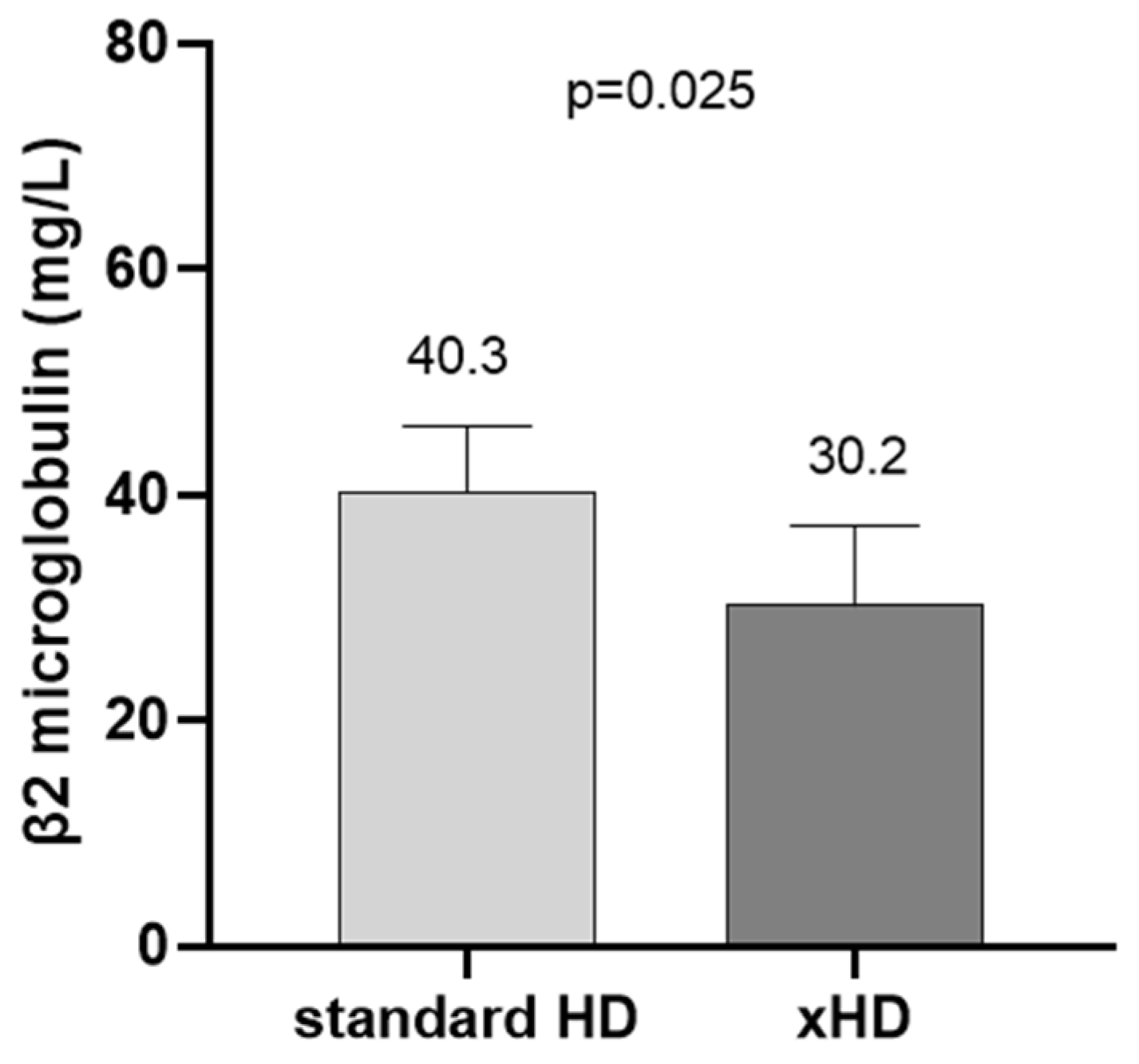
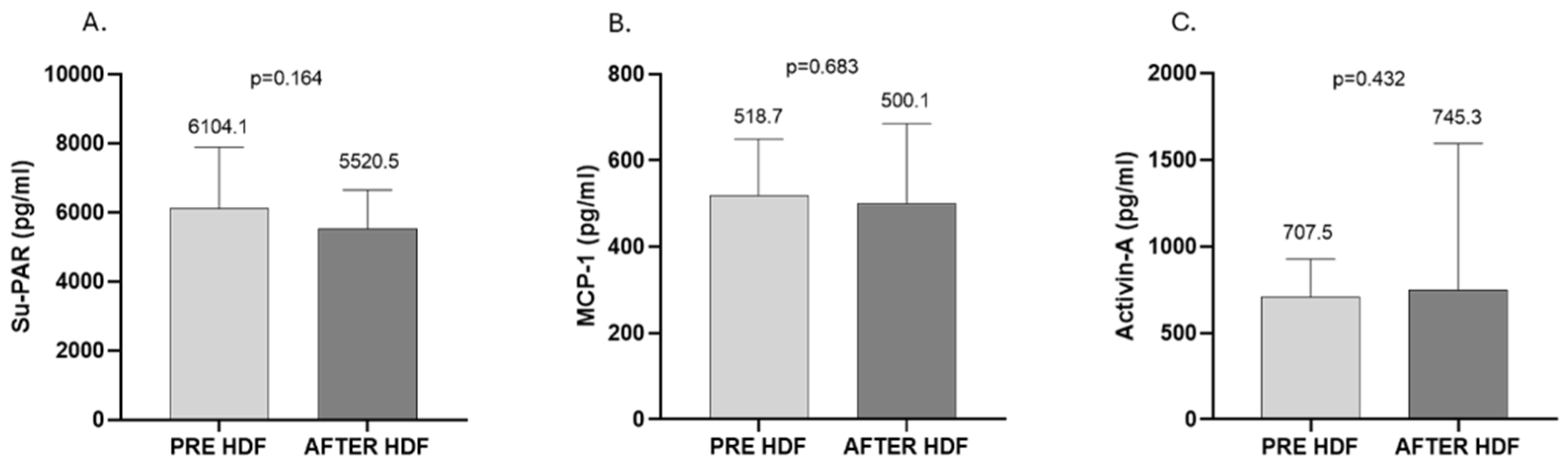
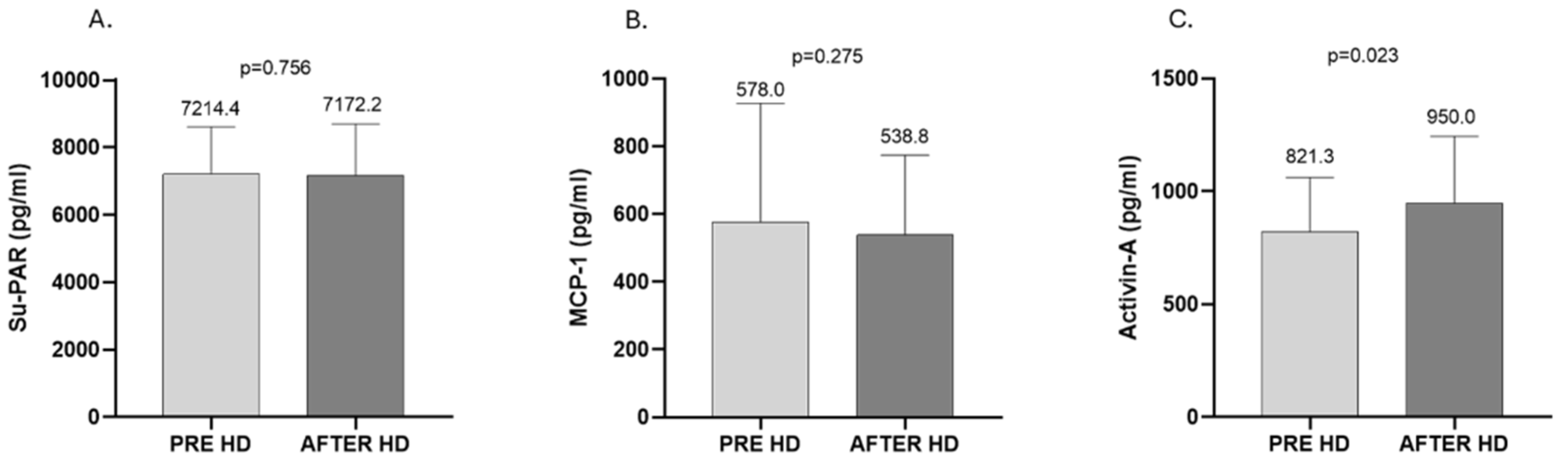
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Study Procedures and Data Collection
4.3. Serum Su-PAR, Activin-A, MCP-1, and Standard Biochemical Measurements
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ronco, C. The Rise of Expanded Hemodialysis. Blood Purif. 2017, 44, I–VIII. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzoni, P.; Del Vecchio, L.; Pontoriero, G.; Di Filippo, S.; Locatelli, F. Long-term outcome in hemodialysis: Morbidity and mortality. J. Nephrol. 2004, 17 (Suppl. 8), S87–S95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, M.; Mangano, M.; Stucchi, A.; Ciceri, P.; Conte, F.; Galassi, A. Cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018, 33 (Suppl. 3), iii28–iii34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longenecker, J.C.; Coresh, J.; Powe, N.R.; Levey, A.S.; Fink, N.E.; Martin, A.; Klag, M.J. Traditional cardiovascular disease risk factors in dialysis patients compared with the general population: The CHOICE Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Salim, S.; Masoud, A.T.; Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Soliman, K.M.; Garla, V.; Sofy, A.A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Abdelsattar, A.T.; Zsom, L.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Antibiotic and Antimicrobial Lock Solutions for Prevention of Hemodialysis Catheter-Related Infections. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.T.; Lin, S.H. Uremic Toxins and Frailty in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Molecular Insight. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argiles, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, M.H.; Reis, T.; Husain-Syed, F.; Vanholder, R.; Hutchison, C.; Stenvinkel, P.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Cozzolino, M.; Juillard, L.; Kashani, K.; et al. Classification of Uremic Toxins and Their Role in Kidney Failure. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduell, F.; Moreso, F.; Pons, M.; Ramos, R.; Mora-Macia, J.; Carreras, J.; Soler, J.; Torres, F.; Campistol, J.M.; Martinez-Castelao, A. High-efficiency postdilution online hemodiafiltration reduces all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lornoy, W.; Becaus, I.; Billiouw, J.M.; Sierens, L.; Van Malderen, P.; D’Haenens, P. Online haemodiafiltration. Remarkable removal of beta2-microglobulin. Long-term clinical observations. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15 (Suppl. 1), 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, R.; Marcelli, D.; Cardinal, H.; Caron, M.L.; Grooteman, M.P.; Bots, M.L.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Nubé, M.J.; Grassmann, A.; Canaud, B.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of High-Efficiency Hemodiafiltration Versus Low-Flux Hemodialysis Based on the Canadian Arm of the CONTRAST Study. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy. 2015, 13, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combarnous, F.; Tetta, C.; Cellier, C.C.; Wratten, M.L.; Custaud De Catheu, T.; Fouque, D.; David, S.; Carraro, G.; Laville, M. Albumin loss in online hemodiafiltration. Int. J. Artif. Organs. 2002, 25, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ke, G.; Liao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Gao, X. Efficacy of medium cut-off dialyzers and comparison with high-flux dialyzers in patients on maintenance hemodialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2022, 26, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gan, L.; Niu, Q.; Ni, M.; Zuo, L. Efficacy and safety of expanded hemodialysis in hemodialysis patients: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankestijn, P.J.; Bots, M.L. Effect of Hemodiafiltration or Hemodialysis on Mortality in Kidney Failure. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zickler, D.; Schindler, R.; Willy, K.; Martus, P.; Pawlak, M.; Storr, M.; Hulko, M.; Boehler, T.; Glomb, M.A.; Liehr, K.; et al. Medium Cut-Off (MCO) Membranes Reduce Inflammation in Chronic Dialysis Patients-A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiamcharoenying, J.; Takkavatakarn, K.; Chariyavilaskul, P.; Susantitaphong, P.; Eiam-Ong, S.; Tiranathanagul, K. Comparative Effectiveness between Expanded Hemodialysis (Hemodialysis Using a Medium Cut-Off Dialyzer) and Mixed-Dilution Online Hemodiafiltration Using a High-Flux Dialyzer in Removing Middle-Molecule Uremic Toxins. Blood Purif. 2022, 51, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansrivijit, P.; Chen, Y.J.; Lnu, K.; Trongtorsak, A.; Puthenpura, M.M.; Thongprayoon, C.; Bathini, T.; A Mao, M.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Prediction of mortality among patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. World J. Nephrol. 2021, 10, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayek, S.S.; Sever, S.; Ko, Y.A.; Trachtman, H.; Awad, M.; Wadhwani, S.; Altintas, M.M.; Wei, C.; Hotton, A.L.; French, A.L.; et al. Soluble Urokinase Receptor and Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, L.P.; Tio, M.C.; Li, X.; Adams-Huet, B.; de Lemos, J.A.; Hedayati, S.S. Association of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 with Death and Atherosclerotic Events in Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 47, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reque, J.; Perez Alba, A.; Panizo, N.; Sanchez-Canel, J.J.; Pascual, M.J.; Pons Prades, R. Is Expanded Hemodialysis an Option to Online Hemodiafiltration for Small- and Middle-Sized Molecules Clearance? Blood Purif. 2019, 47, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Prieto, A.; de la Flor, J.C.; Coll, E.; Iglesias, E.; Reque, J.; Valga, F. Expanded hemodialysis: What’s up, Doc? Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| (A) | |||
| n | 7 | ||
| Male (n, %) | 4, 57% | ||
| Age (y) | 64.2 ± 10.8 | ||
| Hemodialysis vintage (y) | 10.8 ± 4.6 | ||
| Baseline Renal Disease | |||
| Diabetic Nephropathy (n, %) | 2, 28.6% | ||
| Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis (n, %) | 3, 43% | ||
| Glomerulonephritis (n, %) | 2, 28.6% | ||
| Vascular access | |||
| AVF (arteriovenus fistula) (n, %) | 4, 57% | ||
| AVG (arteriovenus graft) (n, %) | 1, 14.3% | ||
| Central catheter (n, %) | 2, 28.6% | ||
| Comorbidities | |||
| Diabetes mellitus (n, %) | 2, 28.6% | ||
| Hypertension (n, %) | 7, 100% | ||
| Coronary artery disease (n, %) | 2, 28.6% | ||
| Heart failure (n, %) | 1, 14.3% | ||
| (B) | |||
| Standard HD | Online HDF | xHD | |
| n | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Male (n, %) | 7, 70% | 7, 70% | 7, 70% |
| Age (y) | 61.7 ± 5.3 | 61.7 ± 4.9 | 61.9 ± 6.0 |
| Hemodialysis vintage (y) | 6.1 ± 1.4 | 5.8 ± 1.3 | 5.8 ± 1.3 |
| Baseline Renal Disease | |||
| Diabetic nephropathy (n, %) | 3, 30% | 4, 40% | 3, 30% |
| Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis (n, %) | 4, 40% | 3, 30% | 30, 30% |
| Glomerulonephritis (n, %) | 3, 30% | 3, 30% | 4, 40% |
| Vascular access | |||
| AVF (arteriovenus fistula) (n, %) | 6, 60% | 7, 70% | 6, 60% |
| AVG (arteriovenus graft) (n, %) | 2, 20% | 2, 20% | 2, 20% |
| Central catheter (n, %) | 2, 20% | 1, 10% | 2, 20% |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Diabetes mellitus (n, %) | 4, 40% | 4, 40% | 4, 40% |
| Hypertension (n, %) | 10, 100% | 9, 90% | 10, 100% |
| Coronary artery disease (n, %) | 2, 20% | 2, 20% | 1, 10% |
| Heart failure (n, %) | 1, 10% | 0, 0% | 1, 10% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bratsiakou, A.; Papasotiriou, M.; Davoulou, P.; Georgopoulou, G.A.; Papachristou, E.; Goumenos, D.S. Efficacy of Expanded Hemodialysis and Comparison with Standard Hemodialysis and Online Hemodiafiltration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125747
Bratsiakou A, Papasotiriou M, Davoulou P, Georgopoulou GA, Papachristou E, Goumenos DS. Efficacy of Expanded Hemodialysis and Comparison with Standard Hemodialysis and Online Hemodiafiltration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125747
Chicago/Turabian StyleBratsiakou, Adamantia, Marios Papasotiriou, Panagiota Davoulou, Georgia Andriana Georgopoulou, Evangelos Papachristou, and Dimitrios S. Goumenos. 2025. "Efficacy of Expanded Hemodialysis and Comparison with Standard Hemodialysis and Online Hemodiafiltration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125747
APA StyleBratsiakou, A., Papasotiriou, M., Davoulou, P., Georgopoulou, G. A., Papachristou, E., & Goumenos, D. S. (2025). Efficacy of Expanded Hemodialysis and Comparison with Standard Hemodialysis and Online Hemodiafiltration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125747






