Luteolin Potentially Alleviates Methamphetamine Withdrawal-Induced Negative Emotions and Cognitive Deficits Through the AKT/FOXO1/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in the Prefrontal Cortex and Caudate Putamen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
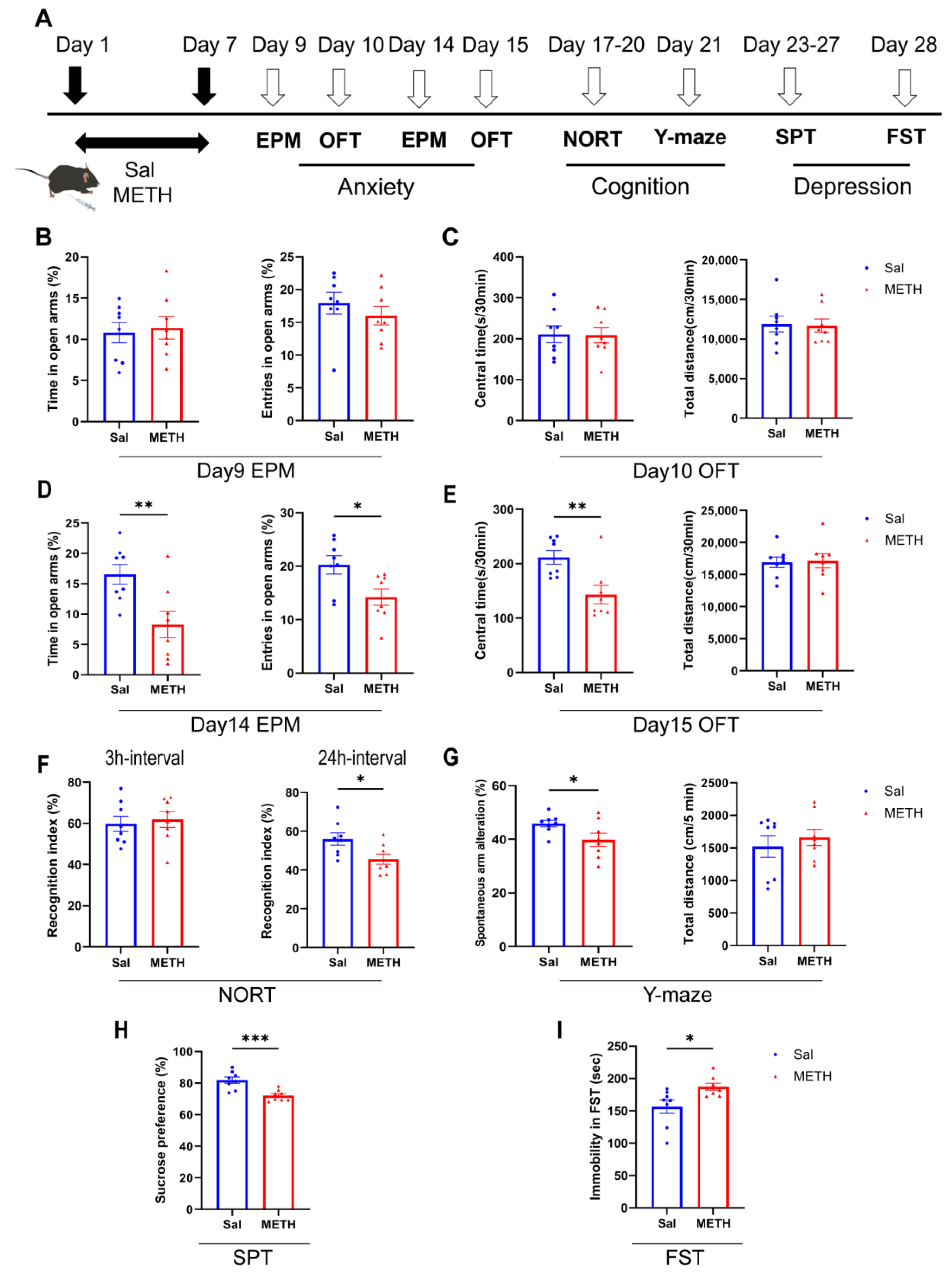
2.1. METH Withdrawal Induces Anxiety and Depressive-like Behaviors, as Well as Cognitive Deficits
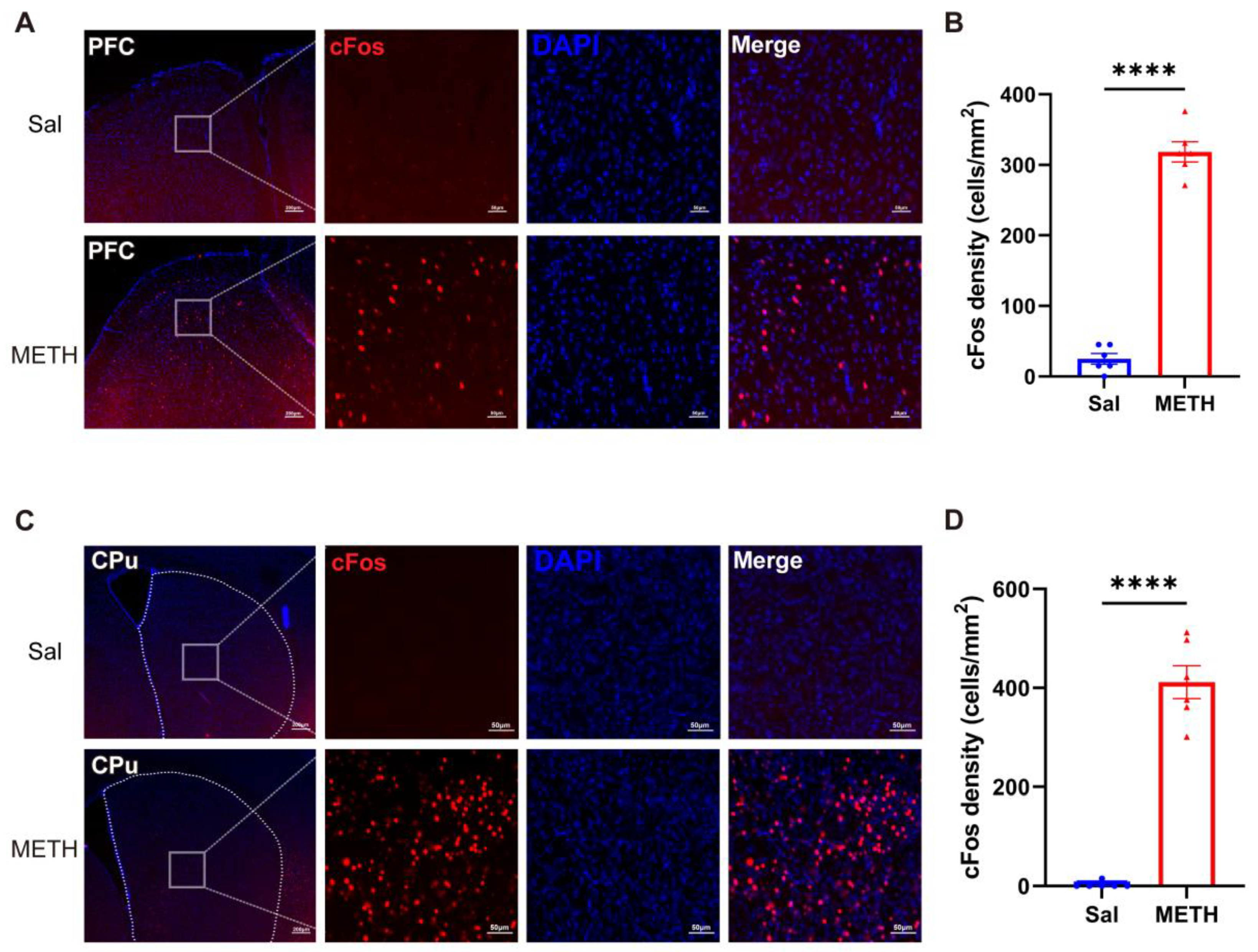
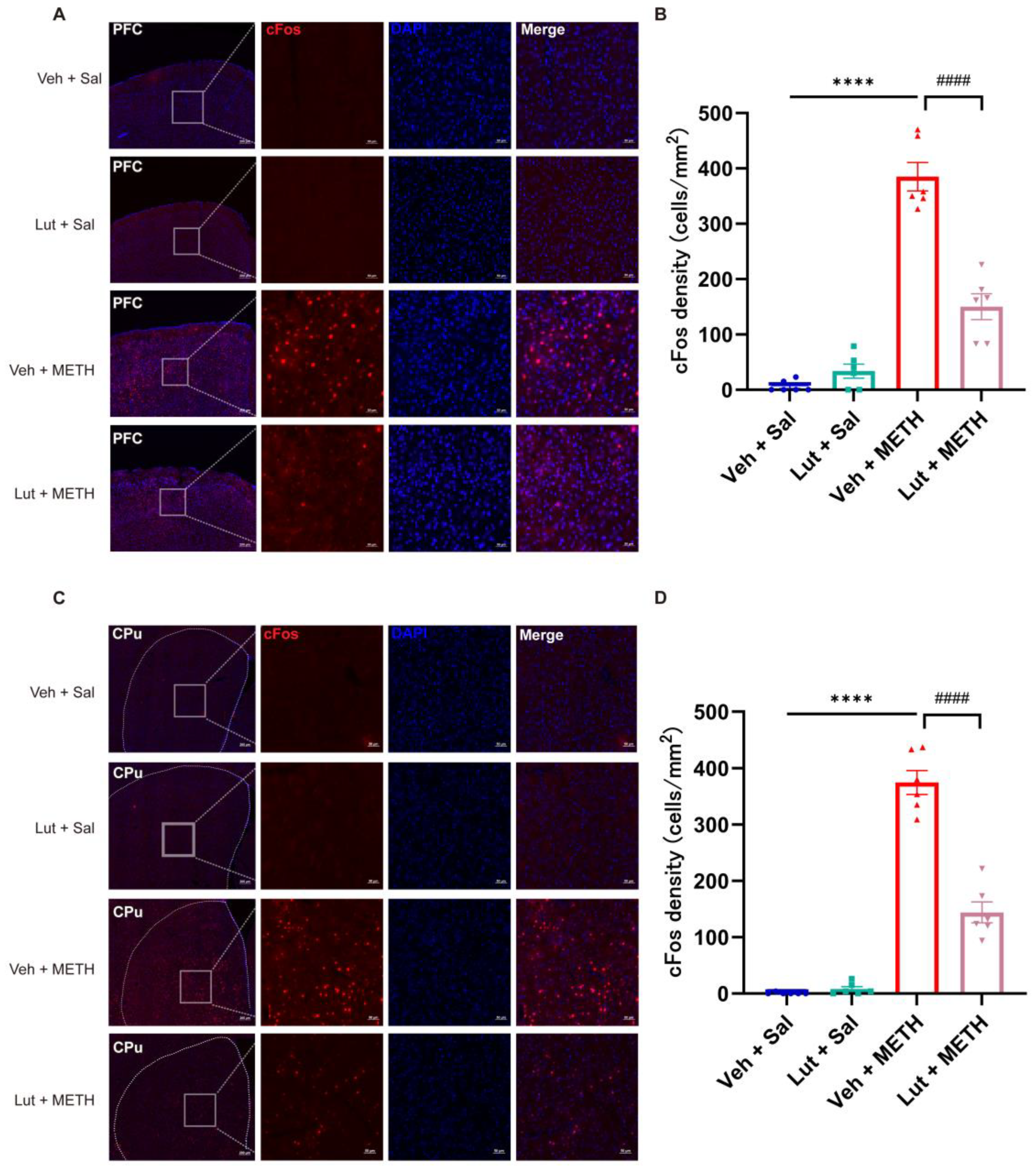
2.2. METH Withdrawal Increases the Neuronal Activity in the PFC and CPu
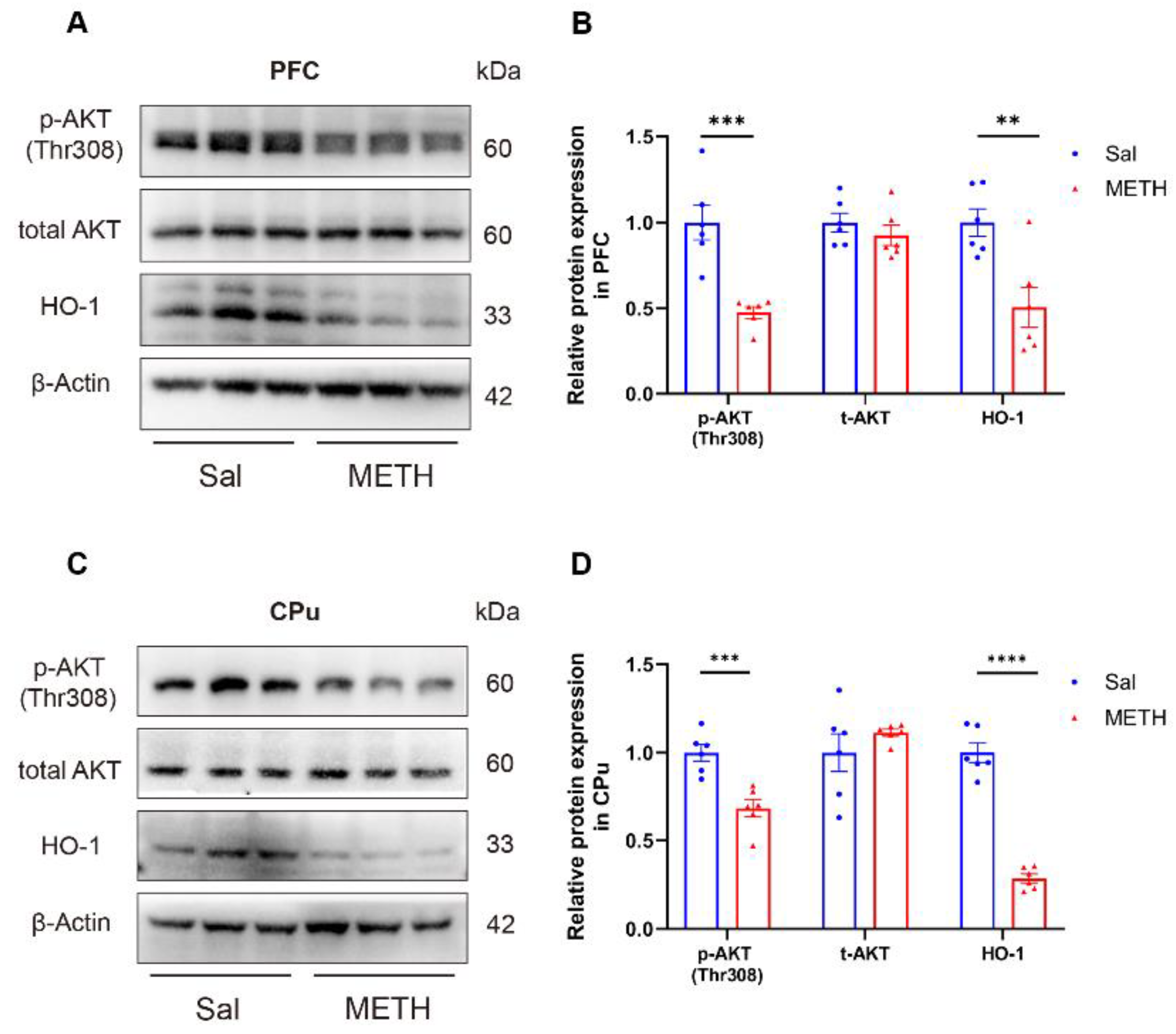
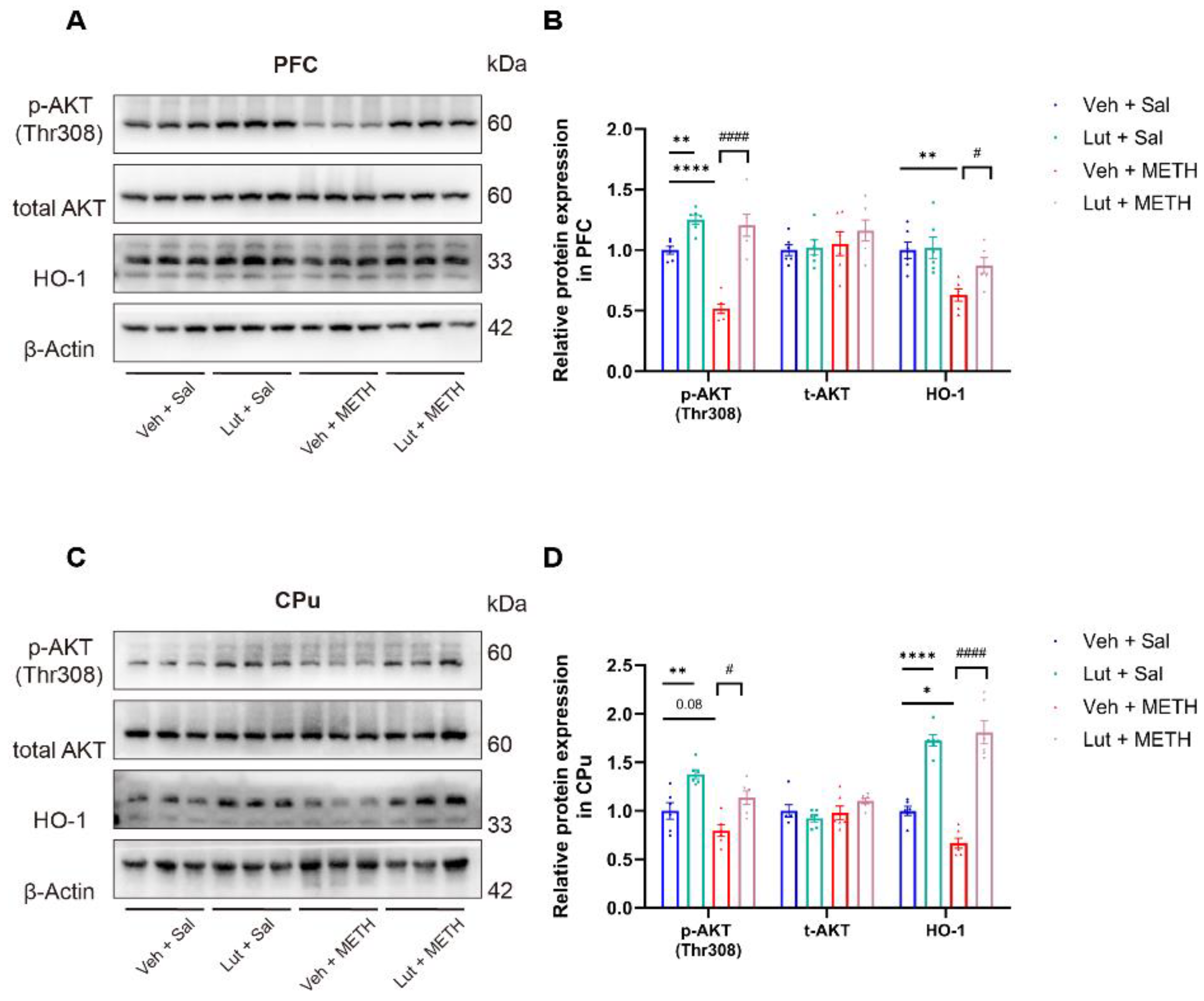
2.3. METH Withdrawal Downregulates p-AKT and HO-1 Expression in the PFC and CPu
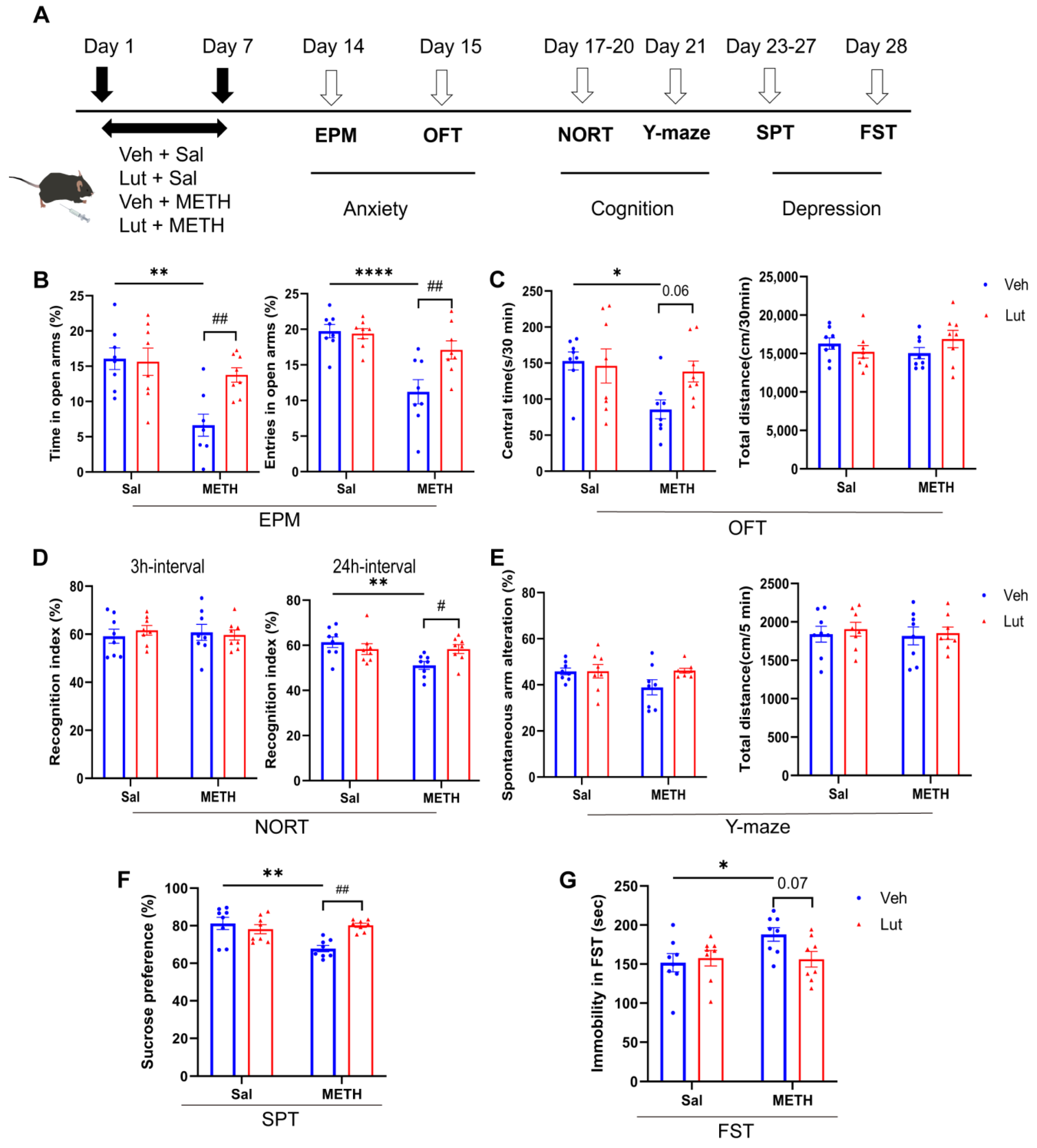
2.4. The Luteolin Pretreatment Potentially Alleviates METH Withdrawal-Induced Anxiety and Depressive-like Behaviors, as Well as Cognitive Deficits
2.5. Luteolin Attenuates the METH Withdrawal-Induced Abnormal Activation of Neurons in the PFC and CPu
2.6. Luteolin Prevents the METH Withdrawal-Induced Downregulation of p-AKT and HO-1 Expression in the PFC and CPu
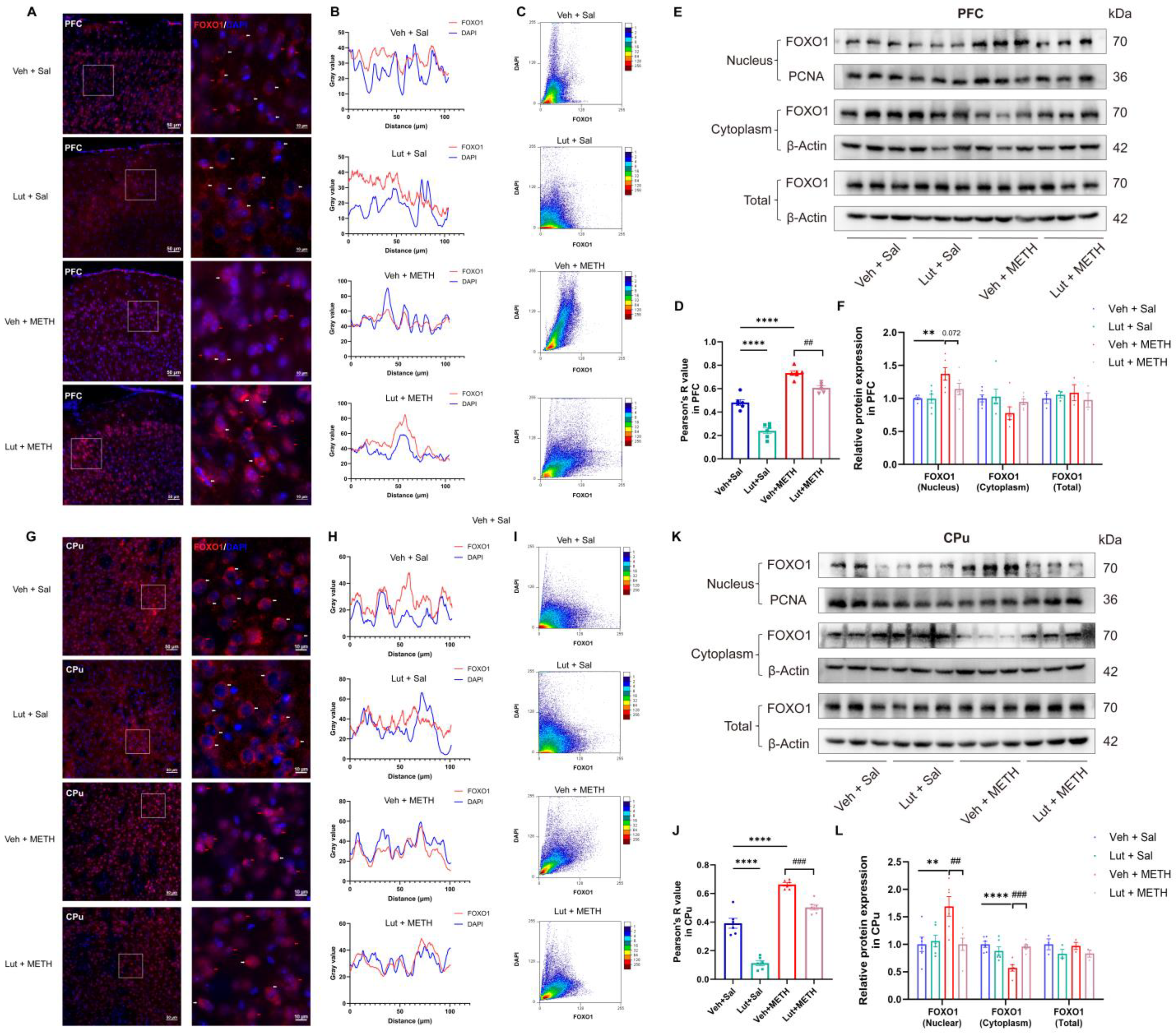
2.7. Luteolin Inhibits METH Withdrawal-Induced Nuclear Translocation of FOXO1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Reagents and Drug Administration Procedure
4.3. Behavioral Tests
4.3.1. Anxiety-like Behaviors
- (1)
- Open field test (OFT)
- (2)
- Elevated plus maze (EPM) test
4.3.2. Cognitive Function Detection
- (1)
- Novel object recognition task (NORT)
- (2)
- Y-maze test
4.3.3. Depressive-like Behaviors
- (1)
- Sucrose preference test (SPT)
- (2)
- Forced swim test (FST)
4.4. Sample Preparation and Western Blotting
4.5. Sample Preparation and Immunofluorescence
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| PFC | prefrontal cortex |
| CPu | caudate putamen |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| FOXO1 | forkhead box protein 1 |
| HO-1 | heme-oxygenase-1 |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| EPM | elevated plus maze |
| OFT | open field test |
| NORT | novel object recognition task |
| SPT | sucrose preference test |
| FST | forced swim test |
References
- Zhang, B.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Lu, Z.; Jia, Z. Trends in Methamphetamine Use in the Mainland of China, 2006–2015. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 852837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Wang, Y. Overview of blood-brain barrier dysfunction in methamphetamine abuse. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C.; Qiao, D.; Wang, H. Methamphetamine exposure induces neuronal programmed necrosis by activating the receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 -related signalling pathway. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2021, 35, e21561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellot, M.; Soria, F.; López-Arnau, R.; Gómez-Canela, C.; Barata, C. Daphnia magna an emerging environmental model of neuro and cardiotoxicity of illicit drugs. Environ. Pollut. (Barking Essex 1987) 2024, 344, 123355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hui, R.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wang, M.; Shi, Y.; Xie, B.; Cong, B.; Ma, C.; Wen, D. Gut microbiota-derived trimethylamine N-oxide involved in methamphetamine-induced depression-like behaviors of male mice. Neuropharmacology 2025, 268, 110339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, R.; Xu, J.; Zhou, M.; Xie, B.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, L.; Cong, B.; Ma, C.; Wen, D. Betaine improves METH-induced depressive-like behavior and cognitive impairment by alleviating neuroinflammation via NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 135, 111093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, M.; Chen, J.; Lou, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Cheng, J.; Ma, T.; Xiong, J.; Gao, R.; et al. Key roles of autophagosome/endosome maturation mediated by Syntaxin17 in methamphetamine-induced neuronal damage in mice. Mol. Med. (Camb. Mass.) 2024, 30, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, M.; Wu, W.; Lou, X.; Gao, R.; Ma, T.; Dheen, S.T.; Cheng, J.; Xiong, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Indole derivatives ameliorated the methamphetamine-induced depression and anxiety via aryl hydrocarbon receptor along “microbiota-brain” axis. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2470386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Hsu, C.; Zeng, J.; et al. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids ameliorate methamphetamine-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in a Sigmar-1 receptor-dependent manner. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 4801–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, X.J.; Wang, R.J.; Wang, T.Y.; Su, M.F.; Liu, M.X.; Li, S.X.; Han, Y.; Meng, S.Q.; Wu, P.; et al. Profile of psychiatric symptoms in methamphetamine users in China: Greater risk of psychiatric symptoms with a longer duration of use. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 262, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Su, H.; Tao, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Liang, H.; He, R.; Han, B.; Lu, Y.; et al. Prevalence and correlates of depressive symptoms during early methamphetamine withdrawal in Han Chinese population. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 142, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratelli, M.; Hakimi, A.M.; Thaker, A.; Jang, H.; Li, H.Q.; Godavarthi, S.K.; Lim, B.K.; Spitzer, N.C. Drug-induced change in transmitter identity is a shared mechanism generating cognitive deficits. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilling, P.D.; Kuczenski, R.; Segal, D.S.; Barrett, T.B.; Kelsoe, J.R. Differential regulation of immediate-early gene expression in the prefrontal cortex of rats with a high vs low behavioral response to methamphetamine. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006, 31, 2359–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Su, H.; Liu, D.; Yan, Z.; Ni, T.; Wei, H.; Goh, E.L.K.; Chen, T. Regulation of miR-128 in the nucleus accumbens affects methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization by modulating proteins involved in neuroplasticity. Addict. Biol. 2021, 26, e12881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilca, S.J.; Margetts, A.V.; Höglund, L.; Fleites, I.; Bystrom, L.L.; Pollock, T.A.; Bourgain-Guglielmetti, F.; Wahlestedt, C.; Tuesta, L.M. Microglia contribute to methamphetamine reinforcement and reflect persistent transcriptional and morphological adaptations to the drug. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 120, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yue, S.; Chen, L.; Singh, A.; Yu, T.; Calipari, E.S.; Wang, Z.J. Prefrontal cortex excitatory neurons show distinct response to heroin-associated cue and social stimulus after prolonged heroin abstinence in mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Huang, J.; Tang, X.; Shen, L.; Hu, S.; He, J.; Liu, T.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Low and high dose methamphetamine differentially regulate synaptic structural plasticity in cortex and hippocampus. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1003617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.B.; Deng, X.; Liu, L.; Cao, C.C.; Su, Y.W.; Gao, Z.J.; Cheng, X.; Kong, D.; Li, Q.; Shi, Y.W.; et al. Distinct roles of excitatory and inhibitory neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex in the expression and reconsolidation of methamphetamine-associated memory in male mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024, 49, 1827–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Mu, S.; Han, W.; Tan, X.; Liu, E.; Hang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Yue, Q.; Sun, J. Dopamine D1 receptor in orbitofrontal cortex to dorsal striatum pathway modulates methamphetamine addiction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 671, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbano, M.F.; Qi, J.; Chen, E.; Mohammad, U.; Espinoza, O.; Candido, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Hahn, S.; Vautier, F.; et al. VTA glutamatergic projections to the nucleus accumbens suppress psychostimulant-seeking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024, 49, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, L.; Zhao, D.; Wang, W.; Xu, L.; Cao, Y.; Meng, F.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Jiang, S. The glutamatergic projections from the PVT to mPFC govern methamphetamine-induced conditional place preference behaviors in mice. J. Affect. Disord. 2025, 371, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Su, H.; Li, R.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Tan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, N.; Du, J.; et al. The exploration of optimized protocol for repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of methamphetamine use disorder: A randomized sham-controlled study. EBioMedicine 2020, 60, 103027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Gonzales, B.J.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Turm, H.; Groysman, M.; Citri, A. Egr2 induction in spiny projection neurons of the ventrolateral striatum contributes to cocaine place preference in mice. eLife 2021, 10, e65228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Li, J.D.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, W.; Duan, F.; Wang, Y.; Xia, L.L.; Jiang, Z.B.; Song, X.; Zhu, Y.Q.; et al. p-Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway Involved in Methamphetamine-induced Executive Dysfunction through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in the Dorsal Striatum. Neurotox. Res. 2023, 41, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Chu, H.; Kong, L.; Ma, H. TBHQ Attenuates Neurotoxicity Induced by Methamphetamine in the VTA through the Nrf2/HO-1 and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8787156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tao, Z.; Yu, M.; Sun, C.; Ye, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuropeptide S promote the recovery of rats with spinal cord injury by activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2025, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Sternberg, P.; Cai, J. Essential roles of the PI3 kinase/Akt pathway in regulating Nrf2-dependent antioxidant functions in the RPE. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Jin, P.; Sherchan, P.; Liu, S.; Cui, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Gong, Y.; Tang, J. Recombinant CCL17-dependent CCR4 activation alleviates neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT/Foxo1 signaling pathway after ICH in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nageswaran, V.; Carreras, A.; Reinshagen, L.; Beck, K.R.; Steinfeldt, J.; Henricsson, M.; Ramezani Rad, P.; Peters, L.; Strässler, E.T.; Lim, J.; et al. Gut Microbial Metabolite Imidazole Propionate Impairs Endothelial Cell Function and Promotes the Development of Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2025, 45, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppula, S.; Wankhede, N.L.; Sammeta, S.S.; Shende, P.V.; Pawar, R.S.; Chimthanawala, N.; Umare, M.D.; Taksande, B.G.; Upaganlawar, A.B.; Umekar, M.J.; et al. Modulation of cholesterol metabolism with Phytoremedies in Alzheimer’s disease: A comprehensive review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 99, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.A.; Katiyar, S.; Song, M. Phytochemicals Targeting BDNF Signaling for Treating Neurological Disorders. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, Z.; Qin, X.Y.; Lan, R.; Hu, Y. Luteolin attenuates cadmium neurotoxicity by suppressing glial inflammation and supporting neuronal survival. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 152, 114406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.X.; Zeng, Y.D.; Zheng, C.X.; Dai, S.S.; Yi, J.; Song, X.D.; Liu, T.; Liu, W.H. Luteolin ameliorates ischemic/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Metab. Brain Dis. 2025, 40, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Li, H.; Mo, Z.; Lei, J.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Y.; Fu, R.; Li, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, K.; et al. Connectivity map identifies luteolin as a treatment option of ischemic stroke by inhibiting MMP9 and activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, M.; Wang, Z.; Qin, F.; Chen, J.; He, Z. Dietary Luteolin: A Narrative Review Focusing on Its Pharmacokinetic Properties and Effects on Glycolipid Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Kempuraj, D.D.; Ahmed, M.E.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Raikwar, S.P.; Zaheer, S.A.; Iyer, S.S.; Govindarajan, R.; Chandrasekaran, P.N.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of flavone luteolin in neuroinflammation and neurotrauma. Biofactors 2021, 47, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Lu, L.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Gong, Q. Dynamics of intrinsic whole-brain functional connectivity in abstinent males with methamphetamine use disorder. Drug Alcohol Depend. Rep. 2022, 3, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulis, L.; Le, S.M.; Hai, V.V.; Huong, D.T.; Minh, K.P.; Oanh, K.T.H.; Rapoud, D.; Quillet, C.; Thi, T.T.N.; Vallo, R.; et al. Gender, homelessness, hospitalization and methamphetamine use fuel depression among people who inject drugs: Implications for innovative prevention and care strategies. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1233844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooijers, J.; Pauwels, L.; Hehl, M.; Seer, C.; Cuypers, K.; Swinnen, S.P. Aging, brain plasticity, and motor learning. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 102, 102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, R.; Chen, B.; Rahman, T.; Cai, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; Tseng, G.C.; Fang, J.; Seney, M.L.; et al. Cocaine-induced neural adaptations in the lateral hypothalamic melanin-concentrating hormone neurons and the role in regulating rapid eye movement sleep after withdrawal. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3152–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Ago, Y.; Umehara, C.; Imoto, E.; Hasebe, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Takuma, K.; Matsuda, T. Role of Prefrontal Serotonergic and Dopaminergic Systems in Encounter-Induced Hyperactivity in Methamphetamine-Sensitized Mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhou, N.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tai, H.; Kim, H.Y.; Fan, Y.; Guan, X. Glutamatergic pathways from medial prefrontal cortex to paraventricular nucleus of thalamus contribute to the methamphetamine-induced conditioned place preference without affecting wakefulness. Theranostics 2025, 15, 1822–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladapo, A.; Deshetty, U.M.; Callen, S.; Buch, S.; Periyasamy, P. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Uncovers Robust Glial Cell Transcriptional Changes in Methamphetamine-Administered Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Mu, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Gong, R.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, L.; Du, Y.; Jin, F.; Wang, J. Wedelolactone activates the PI3K/AKT/NRF2 and SLC7A11/GPX4 signalling pathways to alleviate oxidative stress and ferroptosis and improve sepsis-induced liver injury. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 344, 119557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Zhang, M.; Ma, M.; Rasam, S.; Poulsen, D.; Qu, J. Potential Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Methamphetamine Treatment in Traumatic Brain Injury Defined by Large-Scale IonStar-Based Quantitative Proteomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Peng, Y.; Dong, W.; Shen, B.; Yang, G.; Nie, Q.; Tian, Y.; Qin, L.; Song, C.; Chen, B.; et al. Nrf2 attenuates methamphetamine-induced myocardial injury by regulating oxidative stress and apoptosis in mice. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2023, 42, 9603271231219488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, K.; Yang, L.; Cheng, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; Cao, H.; Zhang, C.; Xing, C.; Hu, G.; et al. Luteolin attenuates LPS-induced damage in IPEC-J2 cells by enhancing mitophagy via AMPK signaling pathway activation. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1552890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.Z.; Bo, Y.W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.D.; Shang, Z.H.; Yu, H.; Chen, X.L.; Kong, X.T.; Zhao, W.Z.; Teimonen, T.; et al. Luteolin inhibits diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cell growth through the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1545779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Duan, H.; Yan, Z.; Xue, C.; Niu, T.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Luteolin Alleviates Ulcerative Colitis in Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Plasma Metabolism. Nutrients 2025, 17, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahwish; Imran, M.; Naeem, H.; Hussain, M.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Mujtaba, A.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; El-Ghorab, A.H.; et al. Antioxidative and Anticancer Potential of Luteolin: A Comprehensive Approach Against Wide Range of Human Malignancies. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.H.; Zhang, K.K.; Xu, J.T.; Qu, D.; Chen, L.J.; Li, J.H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.J.; Xie, X.L. Luteolin alleviates methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity by suppressing PI3K/Akt pathway-modulated apoptosis and autophagy in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2020, 137, 111179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.K.; Wang, H.; Qu, D.; Chen, L.J.; Wang, L.B.; Li, J.H.; Liu, J.L.; Xu, L.L.; Yoshida, J.S.; Xu, J.T.; et al. Luteolin Alleviates Methamphetamine-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Suppressing the p53 Pathway-Mediated Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Inflammation in Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 641917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Hou, W.C.; Hsiao, B.Y.; Lo, T.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Yang, C.H.; Shih, Y.T.; Liu, J.C. 2-Hydroxyl hispolon reverses high glucose-induced endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction through the PI3K/Akt/eNOS and AMPK/HO-1 pathways. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Fu, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Ma, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, S.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Total flavonoids extracted from the leaves of Murraya paniculata (L.) Jack prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating Keap1/Nrf2 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 344, 119562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Srivastav, S.; Saha, S.; Das, P.K.; Ukil, A. Leishmania donovani inhibits macrophage apoptosis and pro-inflammatory response through AKT-mediated regulation of β-catenin and FOXO-1. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Niu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Herrup, K.; Zhang, Y.W.; Bu, G.; Xu, H.; et al. The roles of Cdk5-mediated subcellular localization of FOXO1 in neuronal death. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 2624–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Tang, L.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J. FoxO1 silencing in Atp7b(-/-) neural stem cells attenuates high copper-induced apoptosis via regulation of autophagy. J. Neurochem. 2024, 168, 2762–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Huang, D.; Ma, N.; Xia, J.; Zhao, X.; Duan, Y.; Li, F.; Lin, S.; Tang, S.; et al. Chidamide triggers pyroptosis in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia via the FOXO1/GSDME axis. Chin. Med. J. 2025, 138, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.T.; Yang, C.C.; Lin, Y.J.; Wu, W.B.; Lin, W.N.; Lee, C.W.; Tseng, H.C.; Tsai, F.J.; Hsiao, L.D.; Yang, C.M. Mevastatin-Induced HO-1 Expression in Cardiac Fibroblasts: A Strategy to Combat Cardiovascular Inflammation and Fibrosis. Environ. Toxicol. 2025, 40, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Ma, M.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.C.; Yao, W.; Hashimoto, K. BDNF-TrkB signaling in the nucleus accumbens shell of mice has key role in methamphetamine withdrawal symptoms. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.J.; Shi, J.Z.; He, Y.Y.; Hao, J.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Luo, D.M.; Song, J.K.; Yan, Y.; Xie, X.M.; Du, G.H.; et al. Luteolin alleviates cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent neuroinflammation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, B.; An, R.; Liang, M.; Wang, X.; Peng, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Luteolin Potentially Alleviates Methamphetamine Withdrawal-Induced Negative Emotions and Cognitive Deficits Through the AKT/FOXO1/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in the Prefrontal Cortex and Caudate Putamen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125739
Gao B, An R, Liang M, Wang X, Peng J, Chen X, Liu Z, Li T, Liu X, Zhang J, et al. Luteolin Potentially Alleviates Methamphetamine Withdrawal-Induced Negative Emotions and Cognitive Deficits Through the AKT/FOXO1/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in the Prefrontal Cortex and Caudate Putamen. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125739
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Baoyao, Ran An, Min Liang, Xinglin Wang, Jianhang Peng, Xingyao Chen, Zijun Liu, Tao Li, Xinshe Liu, Jianbo Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Luteolin Potentially Alleviates Methamphetamine Withdrawal-Induced Negative Emotions and Cognitive Deficits Through the AKT/FOXO1/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in the Prefrontal Cortex and Caudate Putamen" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125739
APA StyleGao, B., An, R., Liang, M., Wang, X., Peng, J., Chen, X., Liu, Z., Li, T., Liu, X., Zhang, J., & Han, W. (2025). Luteolin Potentially Alleviates Methamphetamine Withdrawal-Induced Negative Emotions and Cognitive Deficits Through the AKT/FOXO1/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in the Prefrontal Cortex and Caudate Putamen. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125739






