HPTAS: An Alignment-Free Haplotype Phasing Algorithm Focused on Allele-Specific Studies Using Transcriptome Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluating the Performance of HPTAS
2.2. Advantages of Using RNA-Seq for Haplotype Phasing of Exonic SNPs
2.3. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
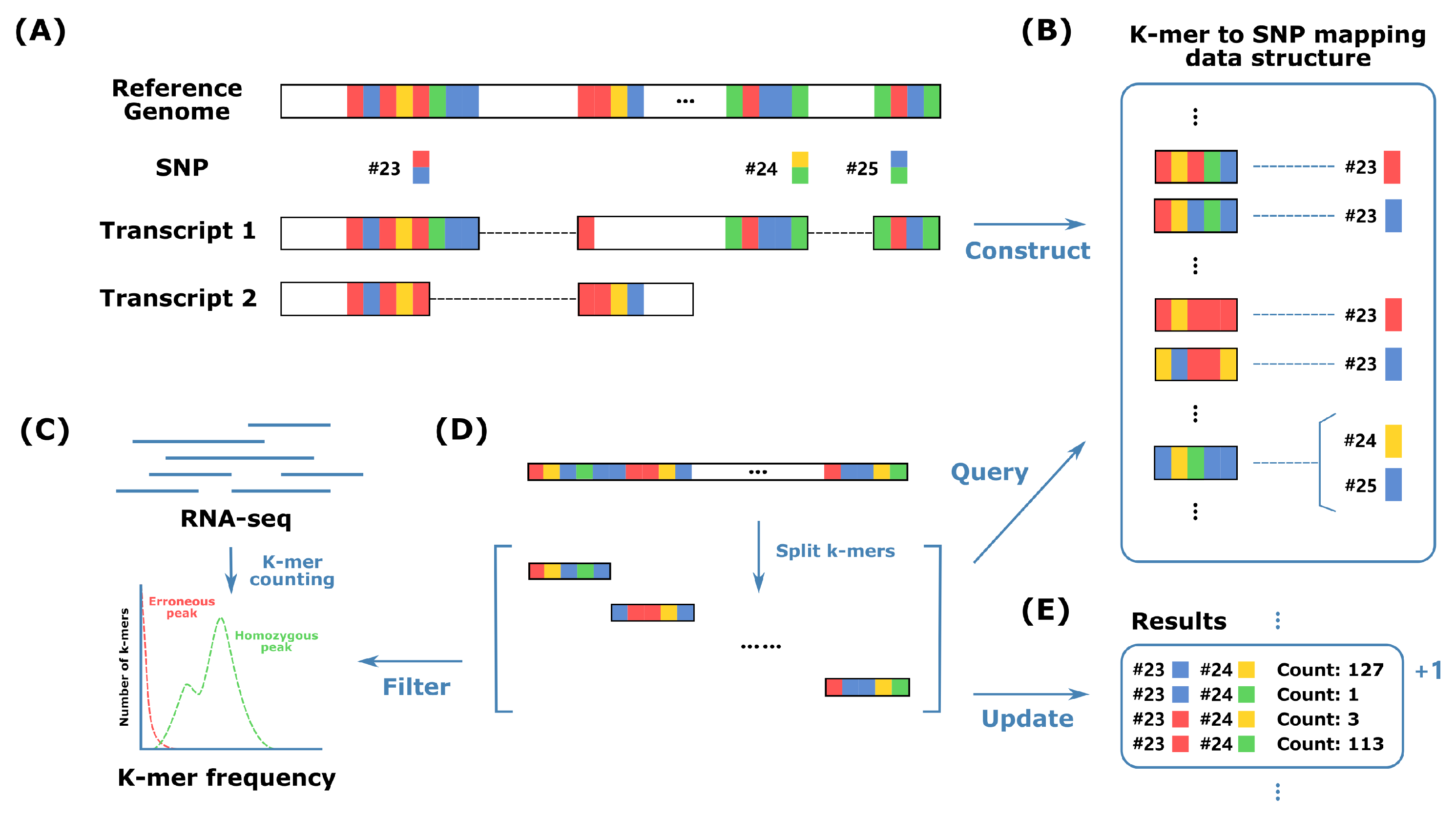
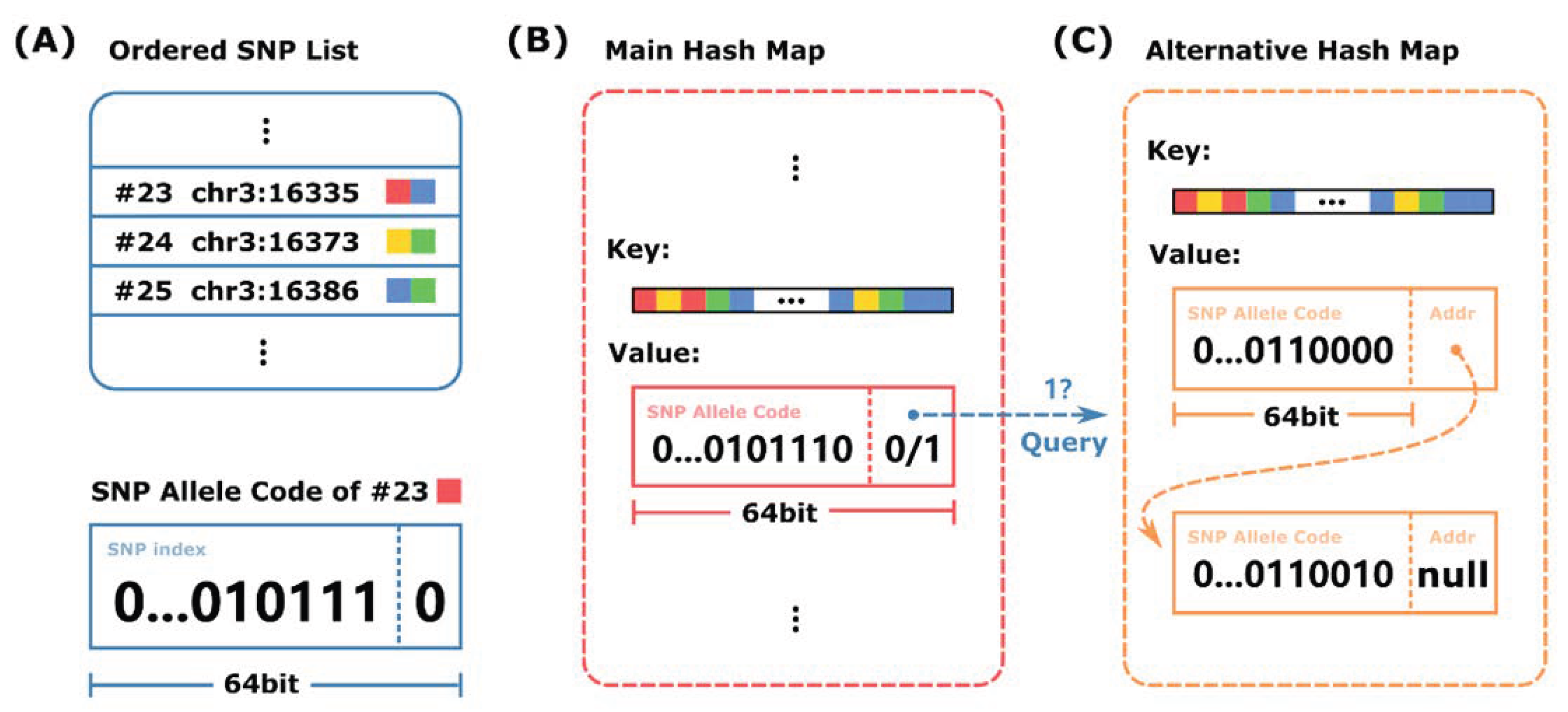
3.1. K-Mer-Based Alignment-Free Algorithm for Haplotype Phasing
| Algorithm 1 Query the codes of SNP alleles covered by a specific sequencing read. |
|
Input: sequencing read R of length L, main hash map H and alternative hash map , and pre-defined k-mer length k Output: set of SNP allele codes S
|
3.2. Internal Structure of HPTAS
3.3. Statistical Analysis
3.4. Datasets for Testing Haplotype Phasing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lancia, G.; Bafna, V.; Istrail, S.; Lippert, R.; Schwartz, R. SNPs Problems, Complexity, and Algorithms. In Algorithms—ESA 2001; auf der Heide, F.M., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 182–193. [Google Scholar]
- Howie, B.; Fuchsberger, C.; Stephens, M.; Marchini, J.; Abecasis, G.R. Fast and accurate genotype imputation in genome-wide association studies through pre-phasing. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Abecasis, G.R.; Browning, B.L. Genotype imputation from large reference panels. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2018, 19, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, B.L.; Zhou, Y.; Browning, S.R. A one-penny imputed genome from next-generation reference panels. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabeti, P.C.; Reich, D.E.; Higgins, J.M.; Levine, H.Z.P.; Richter, D.J.; Schaffner, S.F.; Gabriel, S.B.; Platko, J.V.; Patterson, N.J.; McDonald, G.J.; et al. Detecting recent positive selection in the human genome from haplotype structure. Nature 2002, 419, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanchard, N.A.; Rockett, K.A.; Spencer, C.; Coop, G.; Pinder, M.; Jallow, M.; Kimber, M.; McVean, G.; Mott, R.; Kwiatkowski, D.P. Screening for recently selected alleles by analysis of human haplotype similarity. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bailey, D.K.; Awad, T.; Liu, G.; Xing, G.; Cao, M.; Valmeekam, V.; Retief, J.; Matsuzaki, H.; Taub, M.; et al. A whole genome long-range haplotype (WGLRH) test for detecting imprints of positive selection in human populations. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2122–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastinen, T. Genome-wide allele-specific analysis: Insights into regulatory variation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrel, L.; Willard, H.F. X-inactivation profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression in females. Nature 2005, 434, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoukakis, N.; Deal, C.; Paquette, J.; Goodyer, C.G.; Polychronakos, C. Parental genomic imprinting of the human IGF2 gene. Nat. Genet. 1993, 4, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozowsky, J.; Abyzov, A.; Wang, J.; Alves, P.; Raha, D.; Harmanci, A.; Leng, J.; Bjornson, R.; Kong, Y.; Kitabayashi, N.; et al. AlleleSeq: Analysis of allele-specific expression and binding in a network framework. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turro, E.; Su, S.; Gonçalves, Â.; Coin, L.J.M.; Richardson, S.; Lewin, A. Haplotype and isoform specific expression estimation using multi-mapping RNA-seq reads. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayba, O.; Gilbert, H.N.; Liu, J.; Haverty, P.M.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Jiang, Z.; Watanabe, C.; Zhang, Z. MBASED: Allele-specific expression detection in cancer tissues and cell lines. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, C.T.; Moyerbrailean, G.A.; Davis, G.O.; Wen, X.; Luca, F.; Pique-Regi, R. QuASAR: Quantitative allele-specific analysis of reads. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deonovic, B.; Wang, Y.; Weirather, J.; Wang, X.; Au, K.F. IDP-ASE: Haplotyping and quantifying allele-specific expression at the gene and gene isoform level by hybrid sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, G. BYASE: A Python library for estimating gene and isoform level allele-specific expression. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4955–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, G. ASAS-EGB: A statistical framework for estimating allele-specific alternative splicing events using transcriptome data. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 160, 106981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, P.; Bafna, V.; Bansal, V. HapCUT2: Robust and accurate haplotype assembly for diverse sequencing technologies. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, L. Progressive approach for SNP calling and haplotype assembly using single molecular sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, S.R.; Browning, B.L. Haplotype phasing: Existing methods and new developments. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bkhetan, Z.; Zobel, J.; Kowalczyk, A.; Verspoor, K.; Goudey, B. Exploring effective approaches for haplotype block phasing. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, M.; Scheet, P. Accounting for decay of linkage disequilibrium in haplotype inference and missing-data imputation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 76, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheet, P.; Stephens, M. A fast and flexible statistical model for large-scale population genotype data: Applications to inferring missing genotypes and haplotypic phase. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Willer, C.J.; Ding, J.; Scheet, P.; Abecasis, G.R. MaCH: Using sequence and genotype data to estimate haplotypes and unobserved genotypes. Genet. Epidemiol. 2010, 34, 816–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howie, B.N.; Donnelly, P.; Marchini, J. A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, S.R.; Browning, B.L. Rapid and accurate haplotype phasing and missing-data inference for whole-genome association studies by use of localized haplotype clustering. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Saha, S.; Finkers, R.; Parida, L. Efficient algorithms for polyploid haplotype phasing. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrinner, S.D.; Mari, R.S.; Ebler, J.; Rautiainen, M.; Seillier, L.; Reimer, J.J.; Usadel, B.; Marschall, T.; Klau, G.W. Haplotype threading: Accurate polyploid phasing from long reads. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Saada, O.; Friedrich, A.; Schacherer, J. Towards accurate, contiguous and complete alignment-based polyploid phasing algorithms. Genomics 2022, 114, 110369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, Z.N.; Rhie, A.; Koren, S.; Concepcion, G.T.; Peluso, P.; Munson, K.M.; Porubsky, D.; Kuhn, K.; Mueller, K.A.; Low, W.Y.; et al. Extended haplotype-phasing of long-read de novo genome assemblies using Hi-C. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Y. DCHap: A divide-and-conquer haplotype phasing algorithm for third-generation sequences. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2020, 19, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.; Yorukoglu, D.; Zhang, L.; Nyquist, S.K.; Shalek, A.K.; Kellis, M.; Numanagić, I.; Berger, B. Improved haplotype inference by exploiting long-range linking and allelic imbalance in RNA-seq datasets. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akogwu, I.; Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Gong, P. A comparative study of k-spectrum-based error correction methods for next-generation sequencing data analysis. Hum. Genom. 2016, 10, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajii, A.; Yorukoglu, D.; William Yu, Y.; Berger, B. Fast genotyping of known SNPs through approximate k-mer matching. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, i538–i544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Patel, H.; Lin, Y. Kmer2SNP: Reference-free Heterozygous SNP Calling Using K-Mer Frequency Distributions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2493, 257–265. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, B.; Gelman, A.; Hoffman, M.D.; Lee, D.; Goodrich, B.; Betancourt, M.; Brubaker, M.A.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Riddell, A. Stan: A probabilistic programming language. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 76, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Ferreira, A.; Johnson, R.; Jungreis, I.; Loveland, J.; Mudge, J.M.; Sisu, C.; Wright, J.; Armstrong, J.; et al. GENCODE reference annotation for the human and mouse genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D766–D773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelly, D.A.; Johansson, M.; Madeoy, J.; Wakefield, J.; Akey, J.M. A powerful and flexible statistical framework for testing hypotheses of allele-specific gene expression from RNA-seq data. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
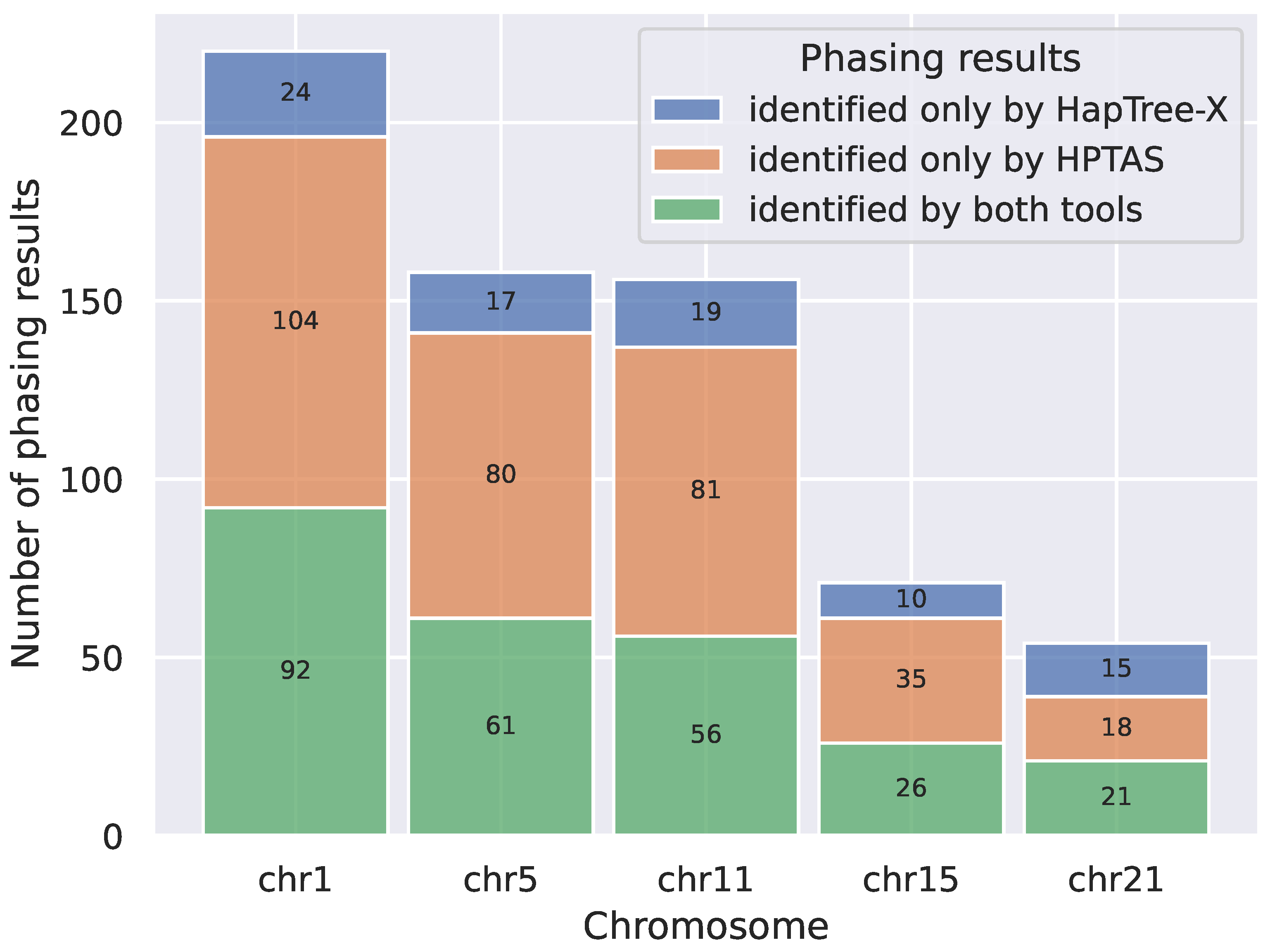
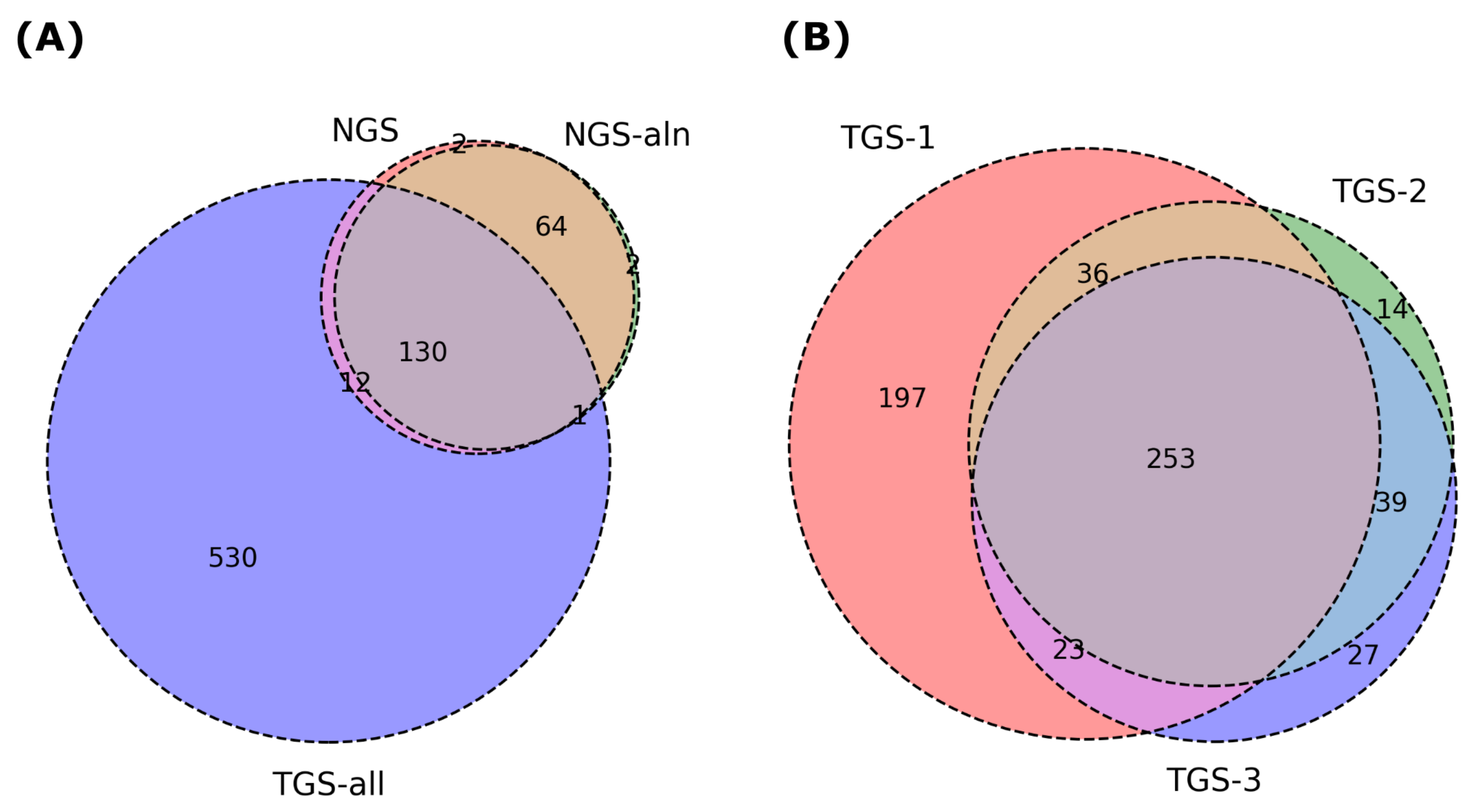
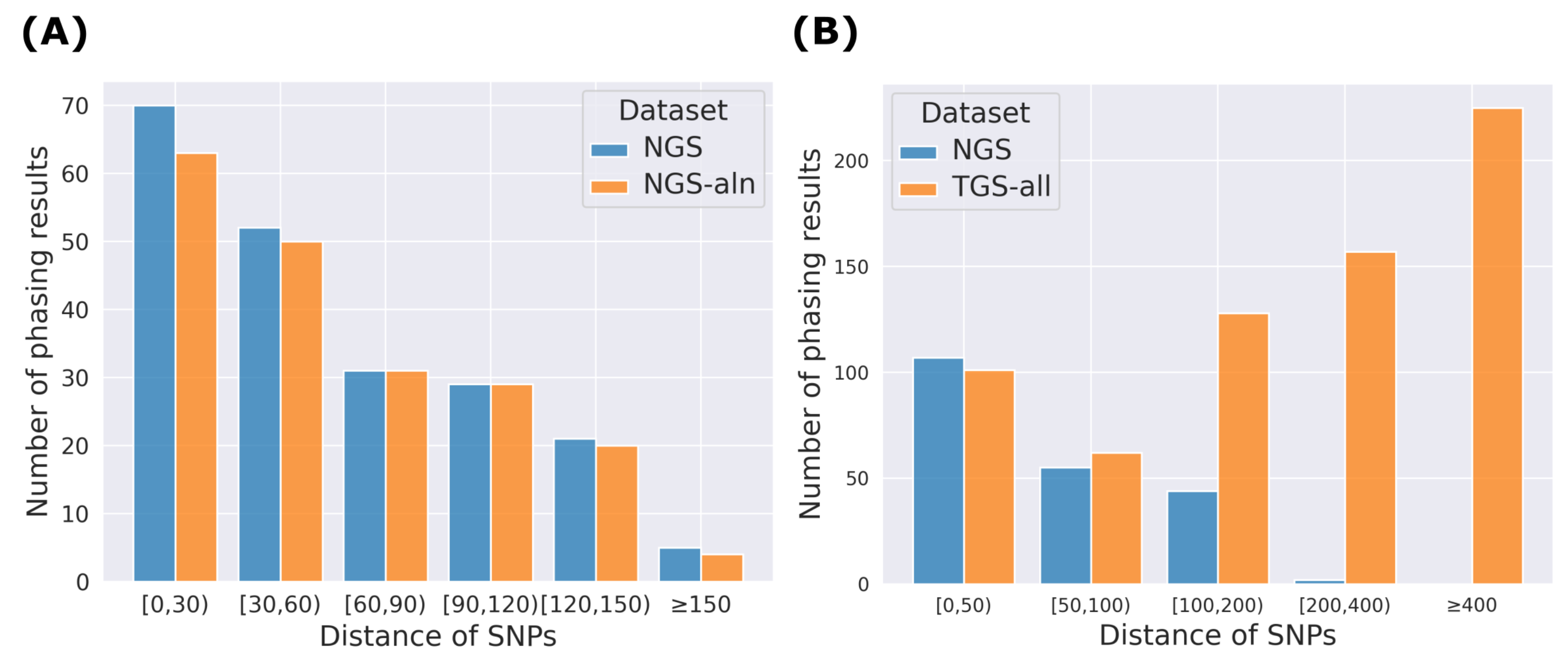
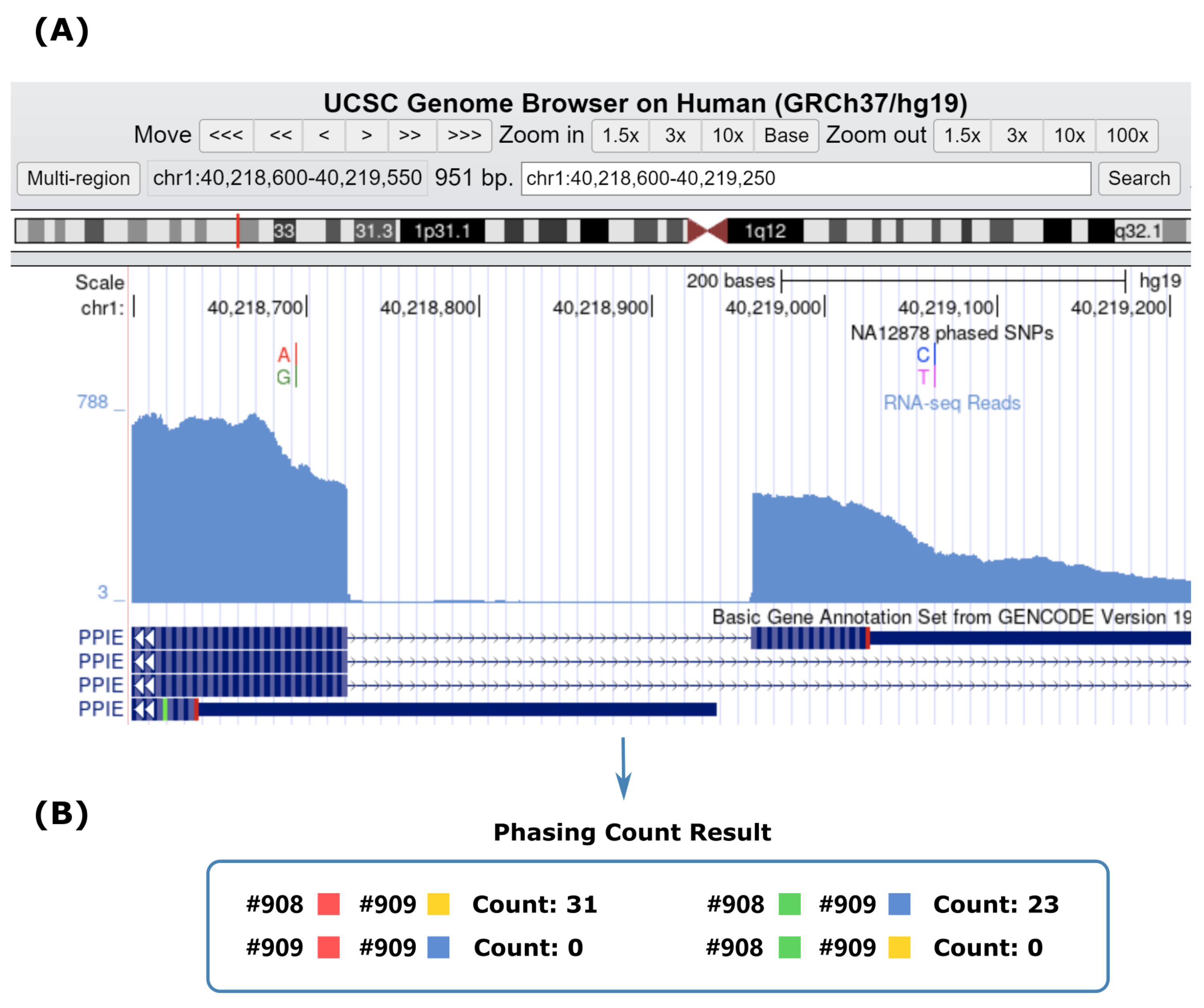
| Chr 1 | Chr 5 | Chr 11 | Chr 15 | Chr 21 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exonic SNPs on the chromosome | 4682 | 2828 | 3226 | 1720 | 822 |
| Valid phasing results for HapTree-X | 230 | 165 | 169 | 76 | 51 |
| Type 1 phasing results for HapTree-X | 116 (50.4%) | 78 (47.3%) | 75 (44.4%) | 36 (47.4%) | 36 (70.6%) |
| Valid phasing results for HPTAS | 208 | 148 | 140 | 62 | 43 |
| Type 1 phasing results for HPTAS | 196 (94.2%) | 141 (95.3%) | 137 (97.9%) | 61 (98.4%) | 39 (90.7%) |
| NGS | NGS-Aln | TGS1 | TGS2 | TGS-3 | TGS-All | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phasing counts valid for inference | 245 | 225 | 630 | 429 | 435 | 804 |
| Valid phasing results | 208 | 197 | 509 | 342 | 342 | 673 |
| Type 1 phasing results | 196 | 194 | 493 | 329 | 329 | 657 |
| Type 2 phasing results | 12 | 3 | 16 | 13 | 13 | 16 |
| Minimum | Maximum | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of SNPs located on gene | 2 | 37 | 4.41 |
| SNP distance on genome | 1 | 1,434,890 | 7613.01 |
| SNP distance on transcriptome | 1 | 32,415 | 546.13 |
| Dataset Name | Accession Number | Number of Bases | Number of Reads/Pairs | Sequencing Type | Read Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | |||||
| NGS | ENCSR000COQ | 17,917,200,640 | 117,876,320 | paired-end | 76 | 76 |
| TGS-1 | ENCSR962BVU | 2,687,061,689 | 1,673,768 | single-end | 50 | 10,743 |
| TGS-2 | ENCSR838WFC | 3,432,469,562 | 2,137,168 | single-end, replicate 1 | 50 | 12,755 |
| TGS-3 | ENCSR838WFC | 3,840,259,898 | 2,538,701 | single-end, replicate 2 | 50 | 6456 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, G.; Miao, Y. HPTAS: An Alignment-Free Haplotype Phasing Algorithm Focused on Allele-Specific Studies Using Transcriptome Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125700
Wang J, Sun Z, Wang G, Miao Y. HPTAS: An Alignment-Free Haplotype Phasing Algorithm Focused on Allele-Specific Studies Using Transcriptome Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125700
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianan, Zhenyuan Sun, Guohua Wang, and Yan Miao. 2025. "HPTAS: An Alignment-Free Haplotype Phasing Algorithm Focused on Allele-Specific Studies Using Transcriptome Data" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125700
APA StyleWang, J., Sun, Z., Wang, G., & Miao, Y. (2025). HPTAS: An Alignment-Free Haplotype Phasing Algorithm Focused on Allele-Specific Studies Using Transcriptome Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5700. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125700






