Dihydroquercetin and Related Flavonoids in Antioxidant Formulations with α-Tocopherol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
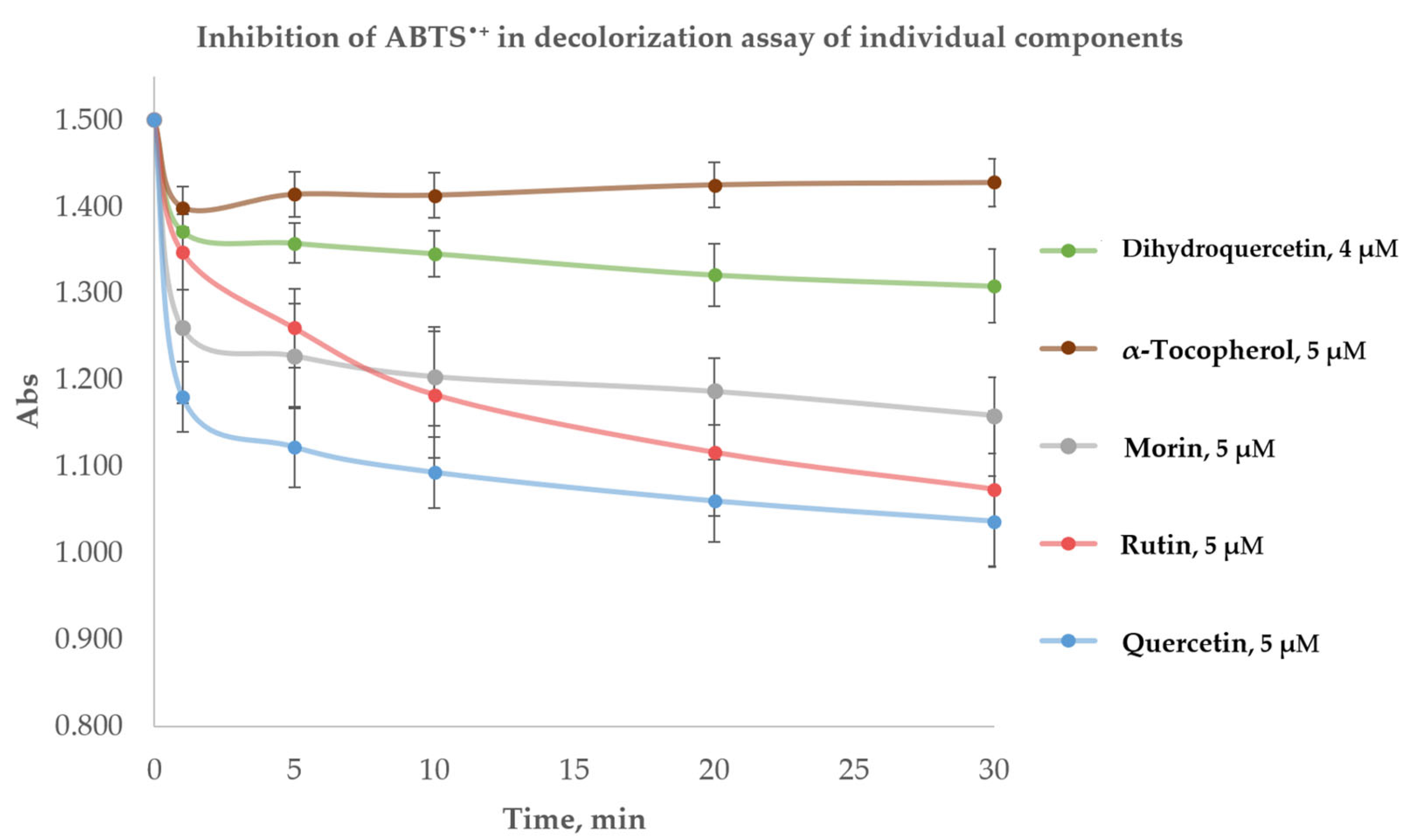
2.1. Antioxidant Capacity in the Decolorization Assay
2.1.1. The ABTS•+ Radical-Cations Self-Bleaching
2.1.2. Individual Compounds in the Decolorization Assay
2.1.3. Flavonoid–α-Tocopherol Formulation at Different Molar Ratios
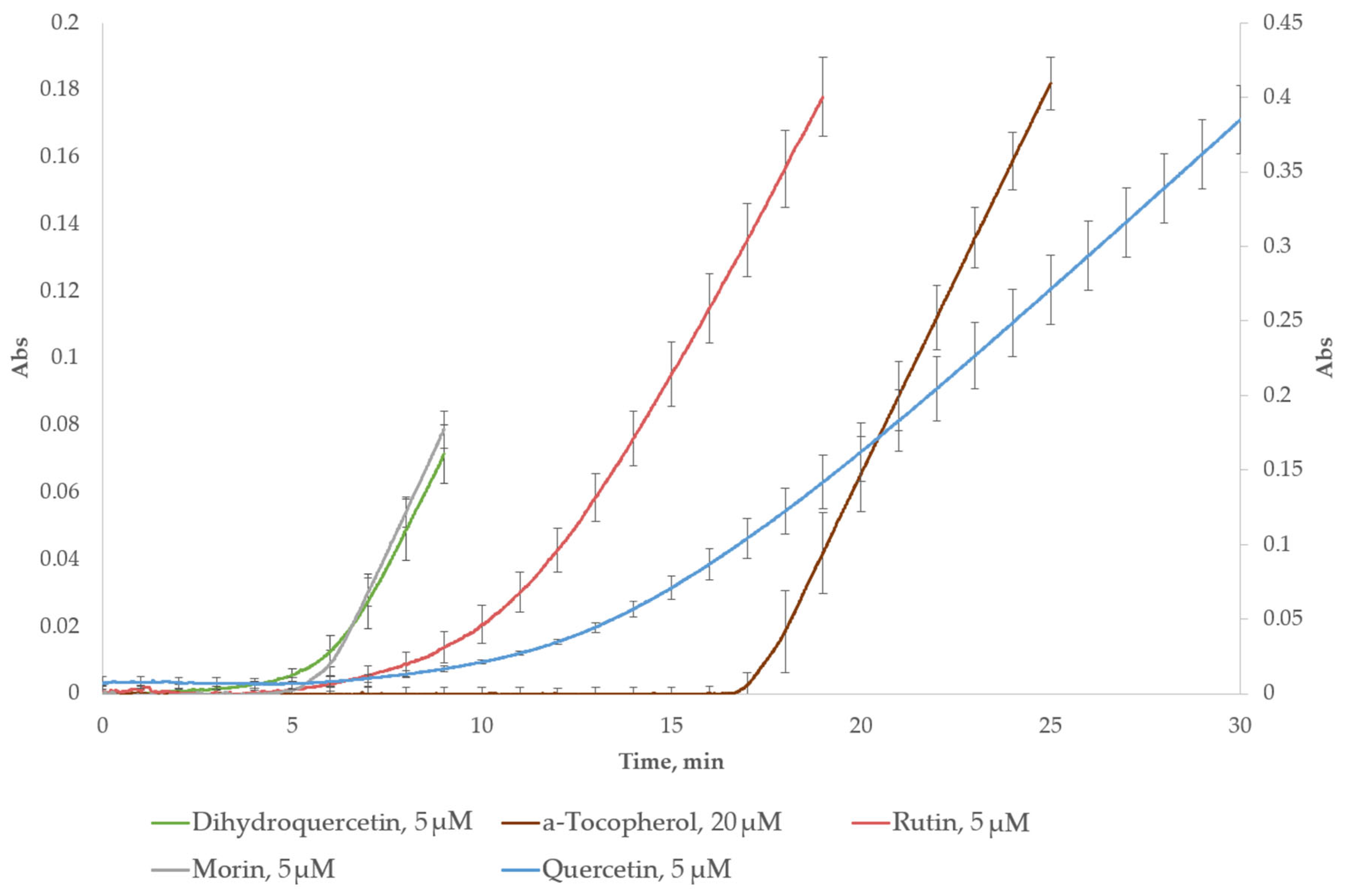
2.2. Antioxidant Capacity in the Lag-Time Assay
2.2.1. ABTS•+ Accumulation Without Antioxidants
2.2.2. Individual Compounds in the Lag-Time Assay
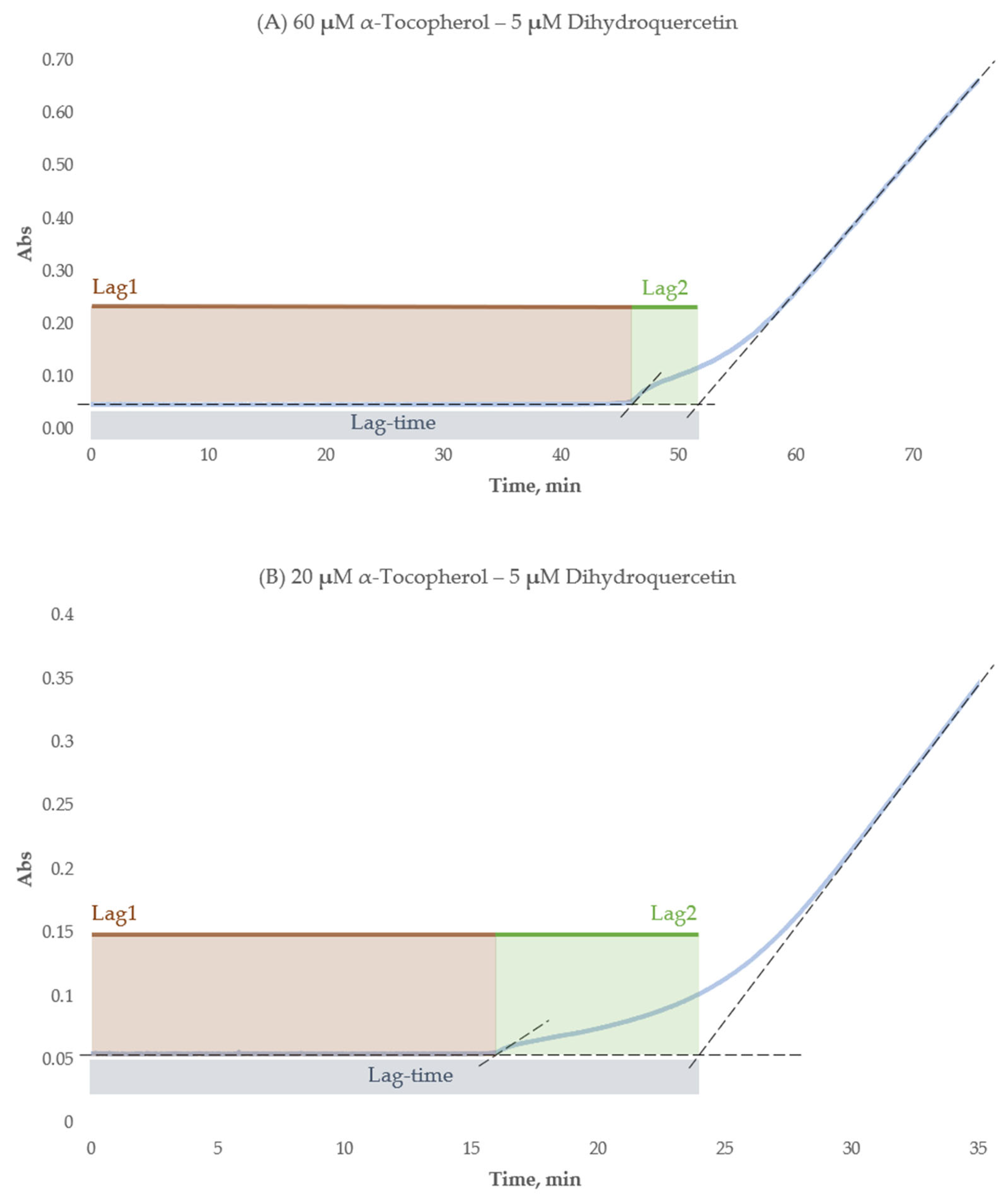
2.2.3. Flavonoid–α-Tocopherol Formulations at Different Molar Ratios
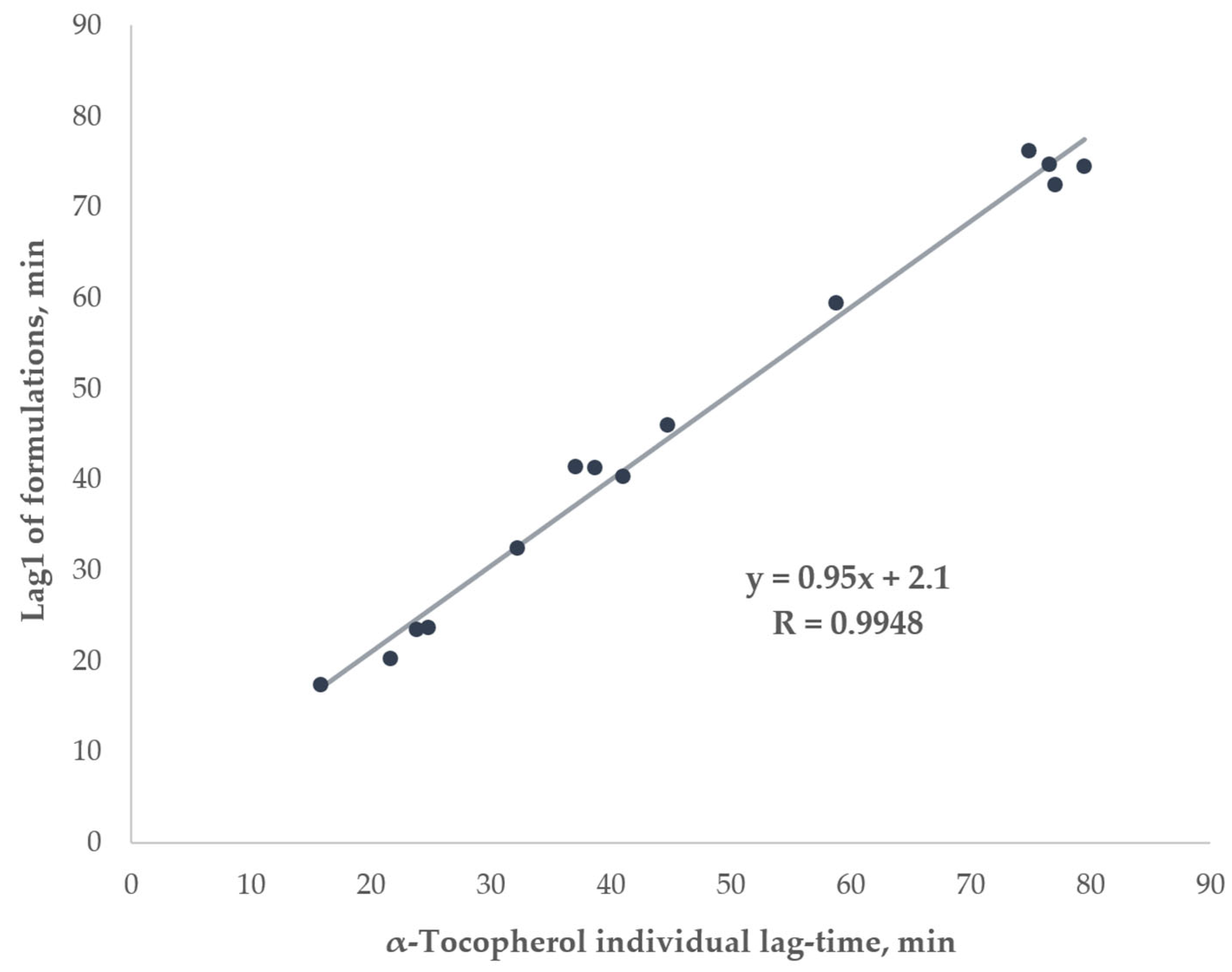
2.2.4. Lag-Time Complexity in Flavonoid–α-Tocopherol Formulations
3. Discussion
3.1. Assessment of the Antioxidant Properties of Dihydroquercetin and Related Flavonoids with α-Tocopherol in Formulations
3.2. Methodological Considerations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Components of Flavonoid–α-Tocopherol Formulations
4.1.2. Components of ABTS/PP Oxidizing System
4.2. Preparation of Solutions
4.3. Methods
4.3.1. Decolorization Assay
4.3.2. Lag-Time Assay
4.4. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, V.; Thakur, S.; Patil, A.; Shukla, A. Quality by Design (QbD) Approaches in Current Pharmaceutical Set-Up. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 737–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrič, A.; Hodnik, Ž.; Pajk, S. Oxidation of Drugs during Drug Product Development: Problems and Solutions. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasraian, K.; Kuzniar, A.A.; Wilson, G.G.; Wood, J.A. Developing an Injectable Formula Containing an Oxygen-Sensitive Drug: A Case Study of Danofloxacin Injectable. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 1999, 4, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsonx, D.M.; Taylor, W.F. Degradation of Fenprostalene in Polyethylene Glycol 400 Solution. J. Pharm. Sci. 1984, 73, 1414–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, T.; He, G.-X.; Samuels, G. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on the Viscosity of a Hydroxyethylcellulose-Based Gel. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calligaris, S.; Manzocco, L.; Anese, M.; Nicoli, M.C. Shelf-Life Assessment of Food Undergoing Oxidation-A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Jamilah, B.; Abbas, K.A.; Rahman, R.A. A Review on Lipid Oxidation of Meat in Active and Modified Atmosphere Packaging and Usage of Some Stabilizers. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2008, 6, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Tallon, M.A.; Malawer, E.G.; Machnicki, N.I.; Brush, P.J.; Wu, C.S.; Cullen, J.P. The Effect of Crosslinker Structure upon the Rate of Hydroperoxide Formation in Dried, Crosslinked Poly(Vinylpyrrolidone). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 2776–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasylaschuk, W.R.; Harmon, P.A.; Wagner, G.; Harman, A.B.; Templeton, A.C.; Xu, H.; Reed, R.A. Evaluation of Hydroperoxides in Common Pharmaceutical Excipients. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Akoh, C.C. Oxidative Stability of Structured Lipid-Based Infant Formula Emulsion: Effect of Antioxidants. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miadonye, A.; Amadu, M.; O’Keefe, T.P. Spectroscopic Determination of the Synergistic Effect of Natural Antioxidants in Bio-Transformer Oils. Results Chem. 2023, 5, 100852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.A.; Grayer, R.J. Anthocyanins and Other Flavonoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.-R.; Kang, G.-H.; Cho, S.-G. Effect of Flavonoids on Human Health: Old Subjects but New Challenges. Recent. Pat. Biotechnol. 2007, 1, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, L.D.S.; Wong, Y.P.; Wu, T.W.; Chan, H.C.; Kwok, T.T.; Fung, K.P. Morin Hydrate: A Potential Antioxidant in Minimizing the Free-Radicals-Mediated Damage to Cardiovascular Cells by Anti-Tumor Drugs. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, J.N.; Mumtaz, S. Prunin: An Emerging Anticancer Flavonoid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, S.V.; Tatarinov, V.V.; Nikitina, E.A.; Sheremeta, A.V.; Ivlev, V.A.; Vasil’ev, V.G.; Paliy, K.V.; Goryainov, S.V. Bioavailability and Safety of Dihydroquercetin (Review). Pharm. Chem. J. 2022, 55, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, C.; Xu, B. An Insight into the Health-Promoting Effects of Taxifolin (Dihydroquercetin). Phytochemistry 2019, 166, 112066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauss, A.G.; Tselyico, S.S.; Kuznetsova, V.A.; Yegorova, I. Toxicological and Genotoxicity Assessment of a Dihydroquercetin-Rich Dahurian Larch Tree (Larix Gmelinii Rupr) Extract (Lavitol). Int. J. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, A.E. Dihydroquercetin: More than Just an Impurity? Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 684, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Saito, S.; Inoue, T.; Satoh-Asahara, N.; Ihara, M. Novel Therapeutic Potentials of Taxifolin for Amyloid-β-Associated Neurodegenerative Diseases and Other Diseases: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Saito, S.; Tanaka, M.; Yamakage, H.; Kusakabe, T.; Shimatsu, A.; Ihara, M.; Satoh-Asahara, N. Pleiotropic Neuroprotective Effects of Taxifolin in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10031–10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taldaev, A.; Savina, A.D.; Olicheva, V.V.; Ivanov, S.V.; Terekhov, R.P.; Ilyasov, I.R.; Zhevlakova, A.K.; Selivanova, I.A. Protective Properties of Spheroidal Taxifolin Form in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terekhov, R.P.; Ilyasov, I.R.; Beloborodov, V.L.; Zhevlakova, A.K.; Pankov, D.I.; Dzuban, A.V.; Bogdanov, A.G.; Davidovich, G.N.; Shilov, G.V.; Utenyshev, A.N.; et al. Solubility Enhancement of Dihydroquercetin via “Green” Phase Modification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turck, D.; Bresson, J.-L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Scientific Opinion on Taxifolin-rich Extract from Dahurian Larch (Larix Gmelinii). EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Implementing Decision–2017/2079–EN–EUR–Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dec_impl/2017/2079/oj/eng (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Implementing Regulation–2018/461–EN–EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2018/461/oj/eng (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Turck, D.; Bresson, J.-L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Statement on the Safety of Taxifolin-rich Extract from Dahurian Larch (Larix Gmelinii). EFSA J. 2017, 15, e05059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dihydroquercetin Market Size, Share, Trend, Forecast, 2033. Available online: https://www.businessresearchinsights.com/market-reports/dihydroquercetin-market-109137 (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Wang, S.; Zhu, F. Dietary Antioxidant Synergy in Chemical and Biological Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2343–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meckling, K.A.; Marcone, M.F.; Kakuda, Y.; Tsao, R. Synergistic, Additive, and Antagonistic Effects of Food Mixtures on Total Antioxidant Capacities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 960–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyasov, I.; Beloborodov, V.; Antonov, D.; Dubrovskaya, A.; Terekhov, R.; Zhevlakova, A.; Saydasheva, A.; Evteev, V.; Selivanova, I. Flavonoids with Glutathione Antioxidant Synergy: Influence of Free Radicals Inflow. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Chen, W.-F.; Zhou, B. Antioxidant Synergism of Green Tea Polyphenols with α-Tocopherol and l-Ascorbic Acid in SDS Micelles. Biochimie 2008, 90, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, I.; Decker, E.A. Underlying Mechanisms of Synergistic Antioxidant Interactions during Lipid Oxidation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Deng, Z. The Synergistic and Antagonistic Antioxidant Interactions of Dietary Phytochemical Combinations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 5658–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, E.; Zhao, Y.; Coupland, J.N.; Elias, R.J. Assessing Interactions between Lipophilic and Hydrophilic Antioxidants in Food Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10655–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyasov, I.; Beloborodov, V.; Dubrovskaya, A.; Voskoboynikova, I. Flavonoid-Ascorbate Mixtures Ratio—Antioxidant Activity Relationships. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar]
- González, E.A.; Nazareno, M.A. Antiradical Action of Flavonoid–Ascorbate Mixtures. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, E.N.; Huang, S.-W.; Kanner, J.; German, J.B. Interfacial Phenomena in the Evaluation of Antioxidants: Bulk Oils vs Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton-Carabin, C.; Villeneuve, P. Targeting Interfacial Location of Phenolic Antioxidants in Emulsions: Strategies and Benefits. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 14, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernáez, Á.; Jaramillo, S.; García-Borrego, A.; Espejo-Calvo, J.A.; Covas, M.-I.; Blanchart, G.; de la Torre, R.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Mesa, M.D.; Fernández-Prior, M.Á.; et al. From Green Technology to Functional Olive Oils: Assessing the Best Combination of Olive Tree-Related Extracts with Complementary Bioactivities. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gong, M.; Liu, R.; Chang, M.; Wang, X. Interactions between Liposoluble Antioxidants: A Critical Review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal-Eldin, A.; Appelqvist, L.A. The Chemistry and Antioxidant Properties of Tocopherols and Tocotrienols. Lipids 1996, 31, 671–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiume, M.M.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; James, G.; Marks, J.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; et al. Safety Assessment of Tocopherols and Tocotrienols as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 61S–94S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-Antioxidant Activity Relationships of Flavonoids and Phenolic Acids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyasov, I.R.; Beloborodov, V.L.; Selivanova, I.A. Three ABTS•+ Radical Cation-Based Approaches for the Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity: Fast- and Slow-Reacting Antioxidant Behavior. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, L.; Silva, M.; Rocha, R.; Manso, C.F. Measurement of Relative Antioxidant Activityof Compounds: A Methodological Note. Redox Rep. 1999, 4, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, E.; Saito, T.; Kawakami, A.; Kamiya, Y. Inhibition of Oxidation of Methyl Linoleate in Solution by Vitamin E and Vitamin C. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 4177–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, C.-Y.; Takahama, U.; Kimura, M. Inhibition of Photooxidation of α-Tocopherol by Quercetin in Human Blood Cell Membranes in the Presence of Hematoporphyrin as a Photosensitizer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Lipids Lipid Metab. 1991, 1086, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, L.V.; Madsen, H.L.; Thomsen, M.K.; Dragsted, L.O.; Skibsted, L.H. Regeneration of Phenolic Antioxidants from Phenoxyl Radicals: An ESR and Electrochemical Study of Antioxidant Hierarchy. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 30, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, Ł.; Bartosz, G. Subadditive Interactions between Antioxidants in the Protection against Lipid Peroxidation. Z. Für Naturforschung C 2009, 64, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wu, L.-M.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.-L. Evidence for α-Tocopherol Regeneration Reaction of Green Tea Polyphenols in SDS Micelles. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, Y.; Xie, P.; Zhang, C.; Huang, L. A New Insight into Synergistic Effects between Endogenous Phenolic Compounds Additive and α-Tocopherol for the Stability of Olive Oil. Food Chem. 2023, 427, 136667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyasov, I.R.; Beloborodov, V.L.; Selivanova, I.A.; Terekhov, R.P. ABTS/PP Decolorization Assay of Antioxidant Capacity Reaction Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaich, K.M.; Tian, X.; Xie, J. Hurdles and Pitfalls in Measuring Antioxidant Efficacy: A Critical Evaluation of ABTS, DPPH, and ORAC Assays. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apak, R.; Gorinstein, S.; Böhm, V.; Schaich, K.M.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K. Methods of Measurement and Evaluation of Natural Antioxidant Capacity/Activity (IUPAC Technical Report)*. Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 957–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Bartosz, G. Evaluation of The Antioxidant Capacity of Food Products: Methods, Applications and Limitations. Processes 2022, 10, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi Sadeer, N.; Montesano, D.; Albrizio, S.; Zengin, G.; Mahomoodally, M.F. The Versatility of Antioxidant Assays in Food Science and Safety—Chemistry, Applications, Strengths, and Limitations. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotha, R.R.; Tareq, F.S.; Yildiz, E.; Luthria, D.L. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants—A Critical Review on In Vitro Antioxidant Assays. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical Methods Used in Determining Antioxidant Activity: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, M.J.T.J.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Voss, H.-P.; Bast, A. Antioxidant Capacity of Reaction Products Limits the Applicability of the Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity (TEAC) Assay. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, M.J.T.J.; Sebastiaan Dallinga, J.; Voss, H.-P.; Haenen, G.R.M.M.; Bast, A. A New Approach to Assess the Total Antioxidant Capacity Using the TEAC Assay. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, C.; Aliaga, C.; Lissi, E. Kinetics Profiles in the Reaction of Abts Derived Radicals with Simple Phenols and Polyphenols. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2004, 49, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, O.I.; Kulikova, N.A.; Filimonov, I.S.; Koroleva, O.V.; Konstantinov, A.I. Long-Term Kinetics Study and Quantitative Characterization of the Antioxidant Capacities of Humic and Humic-like Substances. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kut, K.; Cieniek, B.; Stefaniuk, I.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. A Modification of the ABTS• Decolorization Method and an Insight into Its Mechanism. Processes 2022, 10, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, L.M.; Segundo, M.A.; Reis, S.; Lima, J.L.F.C. Methodological Aspects about in Vitro Evaluation of Antioxidant Properties. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 613, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Saura-Calixto, F. Anti-Oxidant Capacity of Dietary Polyphenols Determined by ABTS Assay: A Kinetic Expression of the Results. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebayashi, J.; Tai, A.; Yamamoto, I. pH-Dependent Long-Term Radical Scavenging Activity of AA-2G and 6-Octa-AA-2G against 2,2′-Azinobis(3-Ethylbenzothiazoline-6-Sulfonic Acid) Radical Cation. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1368–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tian, X.; Schaich, K.M. Effects of Molecular Structure on Kinetics and Dynamics of the Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity Assay with ABTS+•. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5511–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.B.; Everette, J.D. Comparative Reaction Rates of Various Antioxidants with ABTS Radical Cation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, M.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, Q.; Su, G. Practical Problems When Using ABTS Assay to Assess the Radical-Scavenging Activity of Peptides: Importance of Controlling Reaction pH and Time. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrat-Maillard, M.N.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic Compounds in 2,2′-Azobis (2-Amidinopropane) Dihydrochloride (AAPH)-Induced Oxidation: Synergistic and Antagonistic Effects. J. Amer. Oil Chem. Soc. 2003, 80, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, M.B.; Cano, A.; Hernández-Ruiz, J.; García-Cánovas, F.; Acosta, M. Inhibition by L-Ascorbic Acid and Other Antioxidants of the 2.2’-Azino-Bis(3-Ethylbenzthiazoline-6-Sulfonic Acid) Oxidation Catalyzed by Peroxidase: A New Approach for Determining Total Antioxidant Status of Foods. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 236, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.W.; Ong, C.N. Lag-Time Measurement of Antioxidant Capacity Using Myoglobin and 2, 2’-Azino-Bis(3-Ethylbenzthiazoline-6-Sulfonic Acid): Rationale, Application, and Limitation. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 275, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambayashi, Y.; Binh, N.T.; Asakura, H.W.; Hibino, Y.; Hitomi, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Ogino, K. Efficient Assay for Total Antioxidant Capacity in Human Plasma Using a 96-Well Microplate. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 44, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, F.R.; Hernández-Ruiz, J.; Arnao, M.B. A Colorimetric Method for the Determination of Different Functional Flavonoids Using 2,2’-Azino-Bis-(3-Ethylbenzthiazoline-6-Sulphonic Acid) (ABTS) and Peroxidase. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.W.; Doba, T.; Gabe, E.; Hughes, L.; Lee, F.L.; Prasad, L.; Ingold, K.U. Autoxidation of Biological Molecules. 4. Maximizing the Antioxidant Activity of Phenols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 7053–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.W.; Ingold, K.U. Autoxidation of Biological Molecules. 1. Antioxidant Activity of Vitamin E and Related Chain-Breaking Phenolic Antioxidants in Vitro. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorati, R.; Baschieri, A.; Cowden, A.; Valgimigli, L. The Antioxidant Activity of Quercetin in Water Solution. Biomimetics 2017, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwinienko, G.; Ingold, K.U. Solvent Effects on the Rates and Mechanisms of Reaction of Phenols with Free Radicals. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, C.; Aliaga, C.; Lissi, E. Formation and Decay of the ABTS Derived Radical Cation: A Comparison of Different Preparation Procedures. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2002, 34, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redemann, C.E. Peroxides in Isopropanol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1942, 64, 3049–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.E. Peroxides and Peroxide-Forming Compounds. Chem. Health Saf. 2001, 8, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Time Interval, min | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–5 | 5–10 | 10–20 | 20–30 | |
| Decrease rate, µM × min−1 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| Absolute absorbance loss, a.u. × min−1 | 0.015 ± 0.002 | 0.008 ± 0.001 | 0.008 ± 0.002 | 0.008 ± 0.002 |
| Component | n-Value SD (% of the Total n-Value *) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 min | 5 min | 10 min | 20 min | 30 min | |
| Dihydroquercetin | 2.14 ± 0.20 (76 ± 7) | 2.25 ± 0.19 (80 ± 7) | 2.40 ± 0.22 (85 ± 8) | 2.67 ± 0.31 (95 ± 11) | 2.82 ± 0.41 |
| Quercetin | 4.21 ± 0.44 (66 ± 3) | 5.10 ± 0.20 (81 ± 3) | 5.78 ± 0.32 (91 ± 8) | 6.48 ± 0.68 (102 ± 6) | 6.34 ± 0.46 |
| Rutin | 2.09 ± 0.39 (47 ± 12) | 2.99 ± 1.02 (64 ± 7) | 3.73 ± 1.44 (78 ± 7) | 4.37 ± 1.70 (91 ± 7) | 4.73 ± 1.60 |
| Morin | 3.78 ± 0.91 (74 ± 11) | 4.16 ± 0.71 (82 ± 5) | 4.56 ± 0.74 (89 ± 5) | 4.73 ± 0.64 (93 ± 2) | 5.08 ± 0.60 |
| α-Tocopherol | 1.52 ± 0.17 (110 ± 23) | 1.44 ± 0.25 (102 ± 14) | 1.43 ± 0.22 (102 ± 16) | 1.36 ± 0.27 (96 ± 11) | 1.45 ± 0.45 |
| Formulation | Ratio | Concentrations, μM–μM | Decolorization Mixture Effect, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dihydroquercetin–α-Tocopherol | 1:1 | 12–12 | −13.0 ± 2.9 b |
| 1:5 | 4–20 | −11.1 ± 2.7 b | |
| 1:10 | 4–40 | −9.1 ± 3.2 b | |
| Quercetin–α-Tocopherol | 1:1 | 5–5 | −8.9 ± 5.0 a |
| 1:5 | 2.5–12.5 | −7.1 ± 3.6 a | |
| 1:10 | 2.5–25 | −8.0 ± 1.5 b | |
| Rutin–α-Tocopherol | 1:1 | 5–5 | −10.3 ± 3.1 b |
| 1:5 | 2.5–12.5 | −4.4 ± 1.4 b | |
| 1:10 | 2.5–25 | −3.2 ± 3.3 a | |
| Morin–α-Tocopherol | 1:1 | 7.5–7.5 | −9.4 ± 3.7 b |
| 1:5 | 5–25 | −9.5 ± 5.8 a | |
| 1:10 | 2.5–25 | −12.5 ± 1.4 b |
| Formulation | Ratio | Concentration, µM–μM | Lag-Time Mixture Effect, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dihydroquercetin–α-Tocopherol | 1:4 | 5–20 | 1.2 ± 3.8 a |
| 1:8 | 5–40 | 3.6 ± 3.6 a | |
| 1:12 | 5–60 | 2.3 ± 4.4 a | |
| 1:16 | 5–80 | 2.7 ± 5.9 a | |
| 1:20 | 5–100 | 7.2 ± 1.7 b | |
| Quercetin–α-Tocopherol | 1:5 | 5–25 | −1.7 ± 7.5 a |
| 1:10 | 5–50 | −14.4 ± 15.2 a | |
| 1:20 | 5–100 | −12.9 ± 2.0 b | |
| Rutin–α-Tocopherol | 1:5 | 5–25 | −2.3 ± 7.2 a |
| 1:10 | 5–50 | −9.3 ± 2.2 b | |
| 1:20 | 5–100 | −6.1 ± 3.9 a | |
| Morin–α-Tocopherol | 1:5 | 5–25 | 0.6 ± 2.2 a |
| 1:10 | 5–50 | 1.0 ± 13.9 a | |
| 1:20 | 5–100 | 4.6 ± 6.5 a |
| Formulation | Ratio | Concentration, µM | Duration of Lags in Lag-Time of Flavonoid–α-Tocopherol Formulation, min | Individual Lag-Time of Component with Concentration Corresponding to Formulation, min | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lag1 | Lag2 | α-Toc | Flavonoid | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Dihydroquercetin – α-Tocopherol | 1:4 | 5–20 | 15.8 ± 0.2 b | 7.4 ± 0.9 a | 17.2 ± 0.6 | 5.7 ± 0.2 |
| 1:8 | 5–40 | 32.2 ± 0.3 a | 6.8 ± 0.4 b | 32.4 ± 1.3 | ||
| 1:12 | 5–60 | 44.8 ± 3.2 a | 7.3 ± 2.1 a | 46.0 ± 2.8 | ||
| 1:16 | 5–80 | 58.8 ± 3.7 a | 6.6 ± 0.9 a | 59.4 ± 3.9 | ||
| 1:20 | 5–100 | 77.0 ± 1.2 b | 6.2 ± 0.5 a | 72.3 ± 2.1 | ||
| Quercetin – α-Tocopherol | 1:5 | 5–25 | 21.7 ± 1.4 b | 10.6 ± 0.9 b | 20.2 ± 0.7 | 13.3 ± 2.0 |
| 1:10 | 5–50 | 37.2 ± 1.4 a | 9.2 ± 3.7 a | 41.3 ± 1.8 | ||
| 1:20 | 5–100 | 74.9 ± 3.3 a | 8.8 ± 0.3 b | 76.0 ± 0.1 | ||
| Rutin – α-Tocopherol | 1:5 | 5–25 | 24.9 ± 1.2 a | 8.2 ± 1.2 b | 23.6 ± 1.5 | 11.5 ± 0.5 |
| 1:10 | 5–50 | 38.8 ± 2.4 b | 9.1 ± 0.9 b | 41.1 ± 3.1 | ||
| 1:20 | 5–100 | 76.7 ± 2.2 a | 8.6 ± 3.4 b | 74.7 ± 5.5 | ||
| Morin – α-Tocopherol | 1:5 | 5–25 | 23.5 ± 2.3 a | 6.0 ± 0.3 b | 23.4 ± 1.9 | 5.5 ± 0.2 |
| 1:10 | 5–50 | 41.0 ± 4.2 a | 4.8 ± 0.5 b | 40.3 ± 3.6 | ||
| 1:20 | 5–100 | 78.8 ± 4.0 a | 4.8 ± 1.2 a | 74.4 ± 5.9 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olicheva, V.; Beloborodov, V.; Sharifi, S.; Dubrovskaya, A.; Zhevlakova, A.; Selivanova, I.; Ilyasov, I. Dihydroquercetin and Related Flavonoids in Antioxidant Formulations with α-Tocopherol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125659
Olicheva V, Beloborodov V, Sharifi S, Dubrovskaya A, Zhevlakova A, Selivanova I, Ilyasov I. Dihydroquercetin and Related Flavonoids in Antioxidant Formulations with α-Tocopherol. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125659
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlicheva, Vera, Vladimir Beloborodov, Shamimeh Sharifi, Anna Dubrovskaya, Anastasiya Zhevlakova, Irina Selivanova, and Igor Ilyasov. 2025. "Dihydroquercetin and Related Flavonoids in Antioxidant Formulations with α-Tocopherol" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125659
APA StyleOlicheva, V., Beloborodov, V., Sharifi, S., Dubrovskaya, A., Zhevlakova, A., Selivanova, I., & Ilyasov, I. (2025). Dihydroquercetin and Related Flavonoids in Antioxidant Formulations with α-Tocopherol. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125659






