CEST MRI in the Management/Diagnosis of Neuroinfectious Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CNS Infections
3. Imaging of CNS Infections
3.1. CT
3.2. MRI
3.3. Molecular Techniques
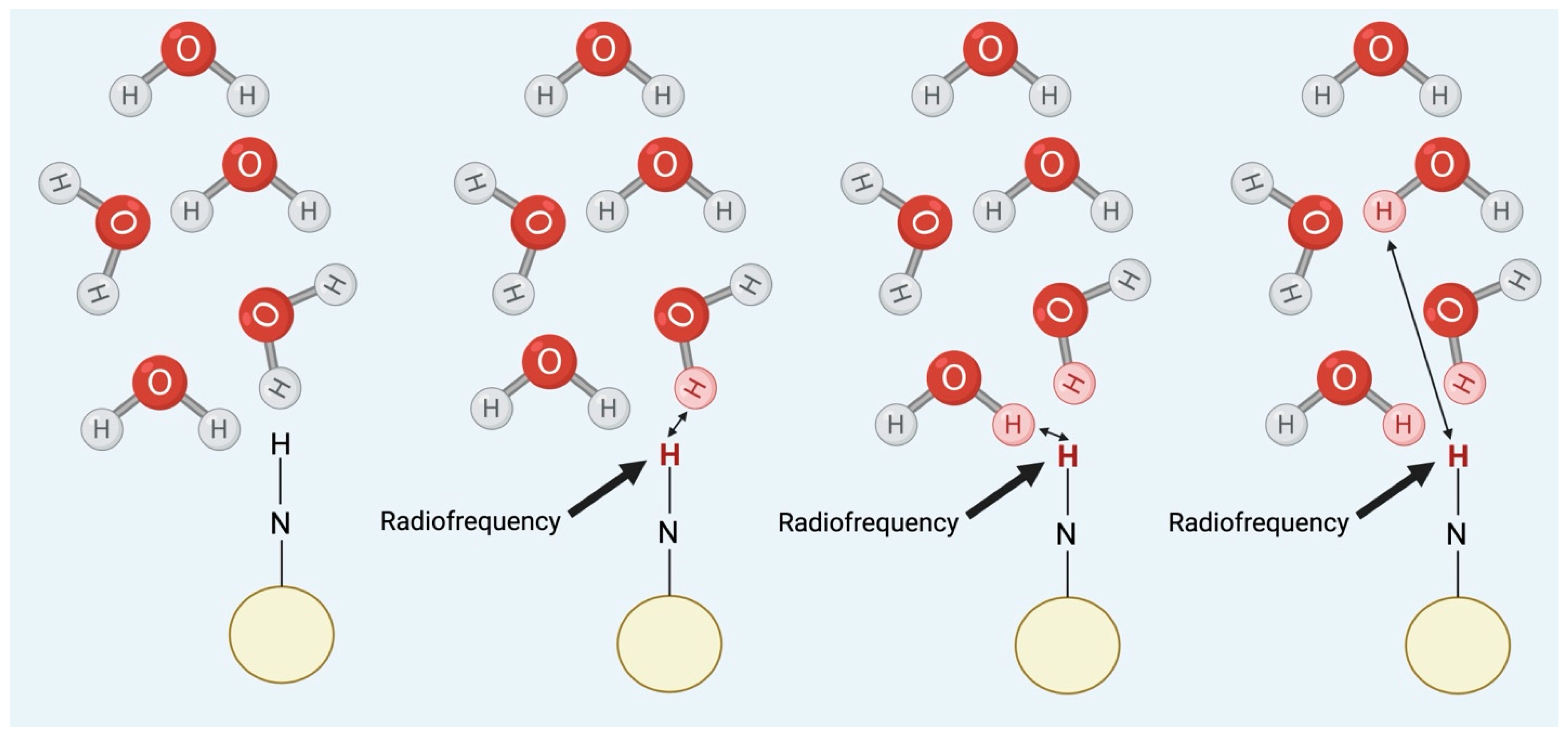
3.4. Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST)
4. Types of CEST
4.1. Paramagnetic Agents
4.2. Diamagnetic Agents
4.3. EndoCEST
4.4. CEST Theranostics
5. Summary
6. Methods
7. Results
7.1. Preclinical Findings
| Strain | Type of Infection | Animal Model | MRI Scanner Used | Type of CEST | Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN | Monitoring treatment with tumor-homing bacteriolytic therapy | F444 Fisher rats (6 weeks old, female) | 11.7 T Bruker Biospec system (Bruker Biosciences, Billerica, MA, USA) | bacCEST |
| [45] |
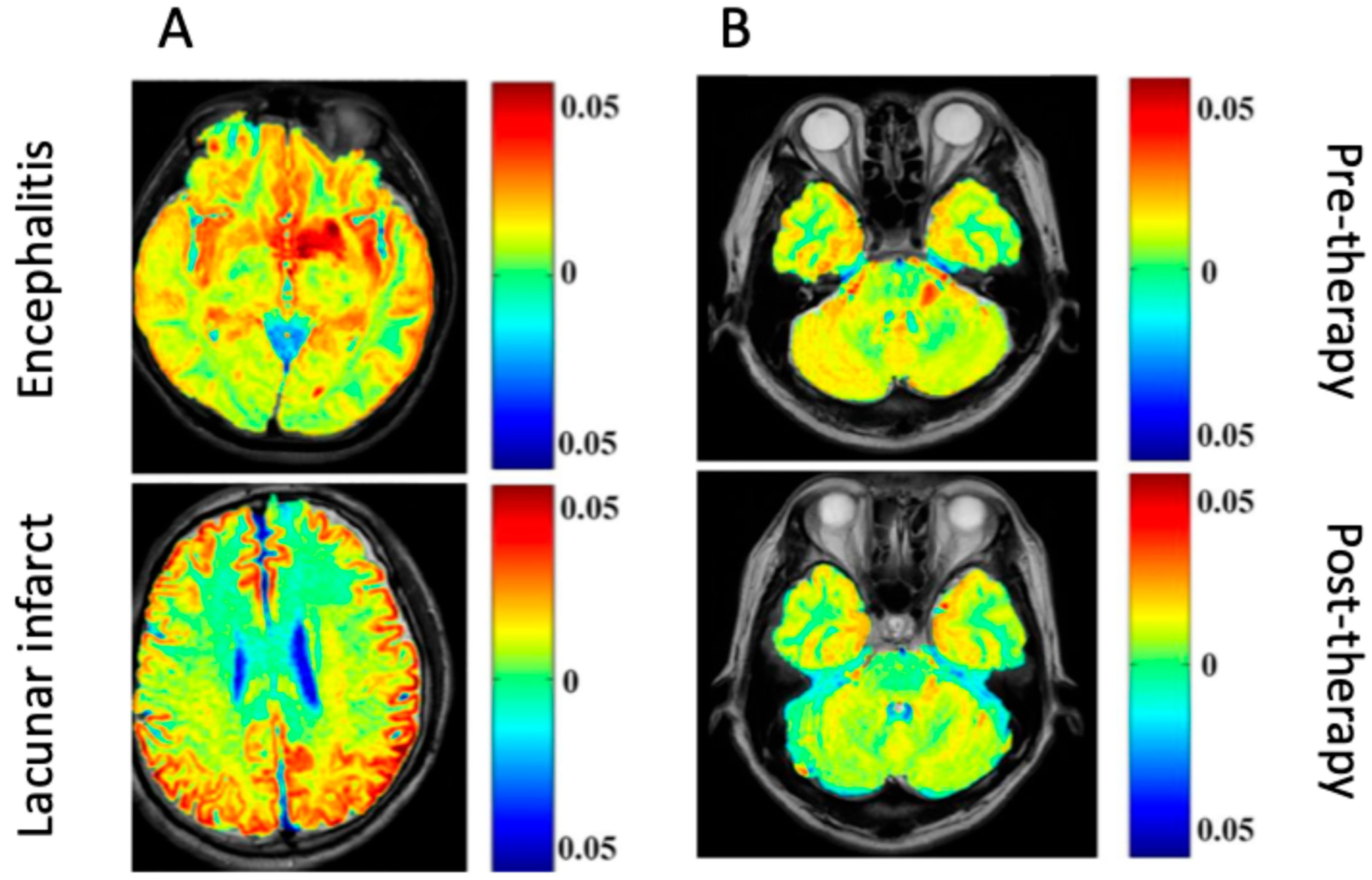
| HIV | Encephalitis—Developed HIV theranostics using CEST contrasts of ARVs—Traced drug biodistribution in brain sub-regions using CEST MRI | Male C57BL/6 mice (14–16 weeks old) | 7.0 T scanner (Bruker PharmaScan 70/16, Billerica, MA, USA) | CEST based on the contrasts of ARV drugs |
| [42] |
| HS | Monitoring of oncolytic herpes simplex virus G47Δ through MR imaging reporter gene known as lysine-rich protein (LRP) | Fisher-344 rats | 9.4 T Bruker BioSpin (Bruker Biosciences, Billerica, MA, USA) | Multiple CEST frequencies (−2100 to +2100 Hz) |
| [49] |
| SA | To differentiate abscesses from brain tumors | Rat–female | 11.7 T Bruker Biospec system (Bruker Biosciences, Billerica, MA, USA) | bacCEST |
| [45] |
| Brain abscess—Changes in glutamate levels in brain abscess | SD rats (female) | Agilent 7 T animal MRI scanner (Agilent Technology, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) | gluCEST |
| [4] | |
| Encephalitis—Differentiation of encephalitis lesions from lacunar infarction | SD rats (adult) | Agilent 7 T MR scanner (Agilent Technology, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) | gluCEST |
| [46] | |
| SAE | Effect of NAC | SD rats | 7.0 T MRI scanner (company not provided) | gluCEST |
| [47] |
| Sepsis-associated encephalopathy evaluating Glu signal changes with H1 MRS vs. gluCEST imaging | 21 SD rats (8 weeks old) | 7 T horizontal-bore PharmaScan 70/16 scanner (Bruker BioSpin GmbH, Ettlingen, Germany) | gluCEST |
| [48] |
7.2. Clinical Findings
| Study | CNS Infection(s) | MRI Scanner Used | Type of CEST | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with encephalitis and LI, and healthy controls Differentiation of encephalitis lesions from lacunar infarction; monitoring of encephalitis response to immunoglobulin treatment | Clinical encephalitis (varied pathology) | Agilent 7 T MR scanner (Agilent Technology, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) | gluCEST |
| [46] |
| Pediatric patients with ICMLs (ages 2 years to 190 months)—Comparison of APTw and Gd-T1w MR findings in various pediatric CNS infections | Abscess, viral encephalitis, meningitis | 3 T MR scanner GE Revolution 256 scanner (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) | APT (amide CEST) |
| [50] |
| Treatment naïve patients Differentiation of infective tuberculosis, tubercular abscess, Aspergillus granuloma) from neoplastic mass lesions (low- and high-grade gliomas) | Infective mass lesions (varied pathologies) | 3T whole body Inginia MRI system (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands) | APT (amide CEST) |
| [51] |
8. Limitations
9. Future Research
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, B.; Warnock, G.; Zaiss, M.; Lin, C.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Z.; Mu, L.; Nanz, D.; Tuura, R.; Delso, G. An overview of CEST MRI for non-MR physicists. EJNMMI Phys. 2016, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, H.; Inan, A.; Guven, E.; Hargreaves, S.; Larsen, L.; Shehata, G.; Pernicova, E.; Khan, E.; Bastakova, L.; Namani, S.; et al. The burden and epidemiology of community-acquired central nervous system infections: A multinational study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 36, 1595–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Turner, M.L.; Chen, X.; Ances, B.M.; Hammoud, D.A.; Tucker, E.W. The promise of molecular imaging: Focus on central nervous system infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 228, S311–S321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, Z.; Shen, Z.; Guan, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Mao, Y.; Mao, R. Imaging of glutamate in brain abscess using GLUCEST at 7T. Radiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, M.P.; Varghese, G. Infections of the Nervous System. Mount Sinai Expert Guides; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 259–270. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781118621042.ch24 (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Ziai, W.C.; Lewin, J.J. Update in the diagnosis and management of central nervous system infections. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 427–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govic, Y.L.; Demey, B.; Cassereau, J.; Bahn, Y.-S.; Papon, N. Pathogens infecting the central nervous system. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddell, J.; Shuman, E.K. Epidemiology of central nervous system infection. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2012, 22, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigbigel, N.H. Computed tomography of the head before a lumbar puncture in suspected meningitis—Is it helpful? N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1768–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, G.; Barza, M. Acute bacterial meningitis in children and adults. A perspective. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1985, 69, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Kastrup, O.; Wanke, I.; Maschke, M. Neuroimaging of infections. NeuroTherapeutics 2005, 2, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.V.; Morriss, M.C. Neuroimaging of central nervous system infections. Semin. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2003, 14, 140–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharath Kumar, G.G.; Adiga, C.P.; Iyer, P.P.; Goolahally, L.N. Role of imaging in CNS infections. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2022, 65, S153. [Google Scholar]
- Rangarajan, K.; Das, C.J.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, A.K. MRI in central nervous system infections: A simplified patterned approach. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparetto, E.L.; Cabral, R.F.; da Cruz, L.C.H.; Domingues, R.C. Diffusion imaging in brain infections. Neuroimaging Clin. 2011, 21, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmetti, C.; Veraart, J.; Roelant, E.; Mai, Z.; Daans, J.; Van Audekerke, J.; Naeyaert, M.; Vanhoutte, G.; Delgado y Palacios, R.; Praet, J.; et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaging probes cortical alterations and white matter pathology following cuprizone induced demyelination and spontaneous remyelination. NeuroImage 2016, 125, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, A. MR Spectroscopy|Radiology Reference Article|Radiopaedia.org. Radiopaedia. 2024. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/mr-spectroscopy-1 (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- Wunder, A.; Klohs, J.; Dirnagl, U. Non-invasive visualization of CNS inflammation with nuclear and optical imaging. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell-Saward, H.; Ward, T.H. Bioluminescence imaging to detect late-stage infection of African trypanosomiasis. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 111, e54032. [Google Scholar]
- van Zijl, P.C.M.; Yadav, N.N. Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST): What is in a name and what isn’t? Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 65, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.M.; Aletras, A.H.; Balaban, R.S. A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST). J. Magn. Reson. 2000, 143, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soesbe, T.C.; Wu, Y.; Sherry, A.D. Advantages of paramagnetic CEST complexes having slow-to-intermediate water exchange properties as responsive MRI agents. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; van Zijl, P.C.M. Chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging and spectroscopy. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2006, 48, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terreno, E.; Castelli, D.D.; Viale, A.; Aime, S. Challenges for molecular magnetic resonance imaging. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3019–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, Z.; Tircsó, G.; Rösch, F. The use of the macrocyclic chelator DOTA in radiochemical separations. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 2020, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.; Calabi, L.; Biondi, L.; De Miranda, M.; Ghelli, S.; Paleari, L.; Rebaudengo, C.; Terreno, E. Iopamidol: Exploring the potential use of a well-established x-ray contrast agent for MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffeney, N.; Bulte, J.W.M.; Duyn, J.; Bryant, L.H.; van Zijl, P.C.M. Sensitive NMR detection of cationic-polymer-based gene delivery systems using saturation transfer via proton exchange. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8628–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagher, A.P.; Aletras, A.; Choyke, P.; Balaban, R.S. Imaging of urea using chemical exchange-dependent saturation transfer at 1.5T. J. Magn. Reson. Imag. 2000, 12, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, F.; Hariharan, H.; Reddy, R. Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging: Description of technique and potential clinical applications. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2013, 1, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancu, I.; Dixon, W.T.; Woods, M.; Vinogradov, E.; Sherry, A.D.; Lenkinski, R.E. CEST and PARACEST MR contrast agents. Acta Radiol. 2010, 51, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherry, A.D.; Woods, M. Chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 10, 391–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.K.; Schlosser, M.J.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Pomper, M.G.; Golay, X.; Zhou, J. Amide proton transfer imaging of human brain tumors at 3T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 56, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.; Regatte, R.R.; Navon, G.; Jerschow, A. Assessment of glycosaminoglycan concentration in vivo by chemical exchange-dependent saturation transfer (gagCEST). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2266–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, N.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Dai, B.; Shen, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, X.; Fu, F.; Li, Z.; et al. Glucose chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI for predicting the histological grade of rectal cancer: A comparative study with amide proton transfer-weighted and diffusion-weighted imaging. Insights Imaging 2024, 15, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.W.Y.; McMahon, M.T.; Kato, Y.; Liu, G.; Bulte, J.W.M.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Artemov, D.; van Zijl, P.C.M. Natural D-glucose as a biodegradable MRI contrast agent for detecting cancer. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 68, 1764–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrallah, F.A.; Pagès, G.; Kuchel, P.W.; Golay, X.; Chuang, K.-H. Imaging brain deoxyglucose uptake and metabolism by glucocest MRI. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, T.; Frydman, L.; Le Bihan, D.; Ciobanu, L. Brain sugar consumption during neuronal activation detected by CEST functional MRI at ultra-high magnetic fields. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Haris, M.; Singh, A.; Kogan, F.; Greenberg, J.H.; Hariharan, H.; Deter, J.A.; Reddy, R. Magnetic resonance imaging of glutamate. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Lin, G.; Wu, R. Imaging of glutamate in acute traumatic brain injury using chemical exchange saturation transfer. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Bettegowda, C.; Qiao, Y.; Staedtke, V.; Chan, K.W.Y.; Bai, R.; Li, Y.; Riggins, G.J.; Kinzler, K.W.; Bulte, J.W.; et al. Noninvasive imaging of infection after treatment with tumor-homing bacteria using Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST) MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanherp, L.; Poelmans, J.; Weerasekera, A.; Hillen, A.; Croitor-Sava, A.R.; Sorrell, T.C.; Lagrou, K. Trehalose as quantitative biomarker for in vivo diagnosis and treatment follow-up in cryptococcomas. Transl. Res. 2021, 230, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, A.N.; Gendelman, H.E.; McMillan, J.; Liu, Y. Chemical exchange saturation transfer for detection of antiretroviral drugs in brain tissue. AIDS 2021, 35, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Islam, R.; Akash, S.; Harun-Or-Rashid, M.; Ray, T.K.; Rahaman, S.; Islam, M.; Anika, F.; Hosain, M.K.; Aovi, F.I.; et al. Recent advancements of nanoparticles application in cancer and neurodegenerative disorders: At a glance. Biomed. Pharmacoth. 2022, 153, 113305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreifuss, T.; Betzer, O.; Shilo, M.; Popovtzer, A.; Motiei, M.; Popovtzer, R. A challenge for theranostics: Is the optimal particle for therapy also optimal for diagnostics? Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15175–15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bai, R.; Li, Y.; Staedtke, V.; Zhang, S.; van Zijl, P.C.M.; Liu, G. MRI detection of bacterial brain abscesses and monitoring of antibiotic treatment using bacCEST. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Chen, Y.; Geng, K.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiu, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, R. Glutamate chemical exchange saturation transfer (GluCEST) magnetic resonance imaging in pre-clinical and clinical applications for encephalitis. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Guan, J.; Ma, Y.; Xu, M.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R. Role of imaging modalities and N-acetylcysteine treatment in sepsis-associated encephalopathy. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-W.; Kwon, J.-I.; Heo, H.; Woo, C.-W.; Yu, N.H.; Kim, K.W.; Woo, D.C. Cerebral glutamate alterations using chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis. Metabolites 2023, 13, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.T.; Buhrman, J.S.; Liu, G.; Kleijn, A.; Lamfers, M.L.M.; McMahon, M.T.; Gilad, A.A.; Fulci, G. Establishing the lysine-rich protein CEST reporter gene as a CEST MR imaging detector for oncolytic virotherapy. Radiology 2015, 275, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Y. Amide proton transfer–weighted MR imaging of pediatric central nervous system diseases. Magn. Reson. Imag. Clin. 2021, 29, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Singh, A. Evaluating the role of amide proton transfer (APT)–weighted contrast, optimized for normalization and region of interest selection, in differentiation of neoplastic and infective mass lesions on 3T MRI. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020, 22, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, E.; Sherry, A.D.; Lenkinski, R.E. CEST: From basic principles to applications, challenges and opportunities. J. Magn. Reson. 2013, 229, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Akasaka, T.; Thuy, D.H.; Isa, T. Safety for human MR scanners at 7T. Magn. Res. Med. Sci. 2022, 21, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Features | Mechanism | Subtypes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paramagnetic | Typically exogenous. Contain metallic ions. More significant frequency shift than their diamagnetic counterparts (faster proton exchange) | Exchange drive by large chemical shift induced by a paramagnetic metal ion (typically lanthanide) in the contrast agent. | ParaCEST SupraCEST |
| Diamagnetic | Do not contain metallic ions. Can be endogenous, closer chemical shift to water (typically 0–7 ppm) | Exchange driven by the chemical shift of exchangeable protons on the contrast agent (either exogenous or endogenous) | LMW diaCEST-NH4Cl Macromolecular diaCEST–Poly-lysine, G-5 PAMAM dendrimer EndoCEST–Amide protons (APT), OH protons, amine protons, BacCEST, CryptoCEST |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kortje, Z.A.; Bach, H. CEST MRI in the Management/Diagnosis of Neuroinfectious Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125650
Kortje ZA, Bach H. CEST MRI in the Management/Diagnosis of Neuroinfectious Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125650
Chicago/Turabian StyleKortje, Zoe A., and Horacio Bach. 2025. "CEST MRI in the Management/Diagnosis of Neuroinfectious Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125650
APA StyleKortje, Z. A., & Bach, H. (2025). CEST MRI in the Management/Diagnosis of Neuroinfectious Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125650







