Inhibition of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Prevents Docetaxel-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
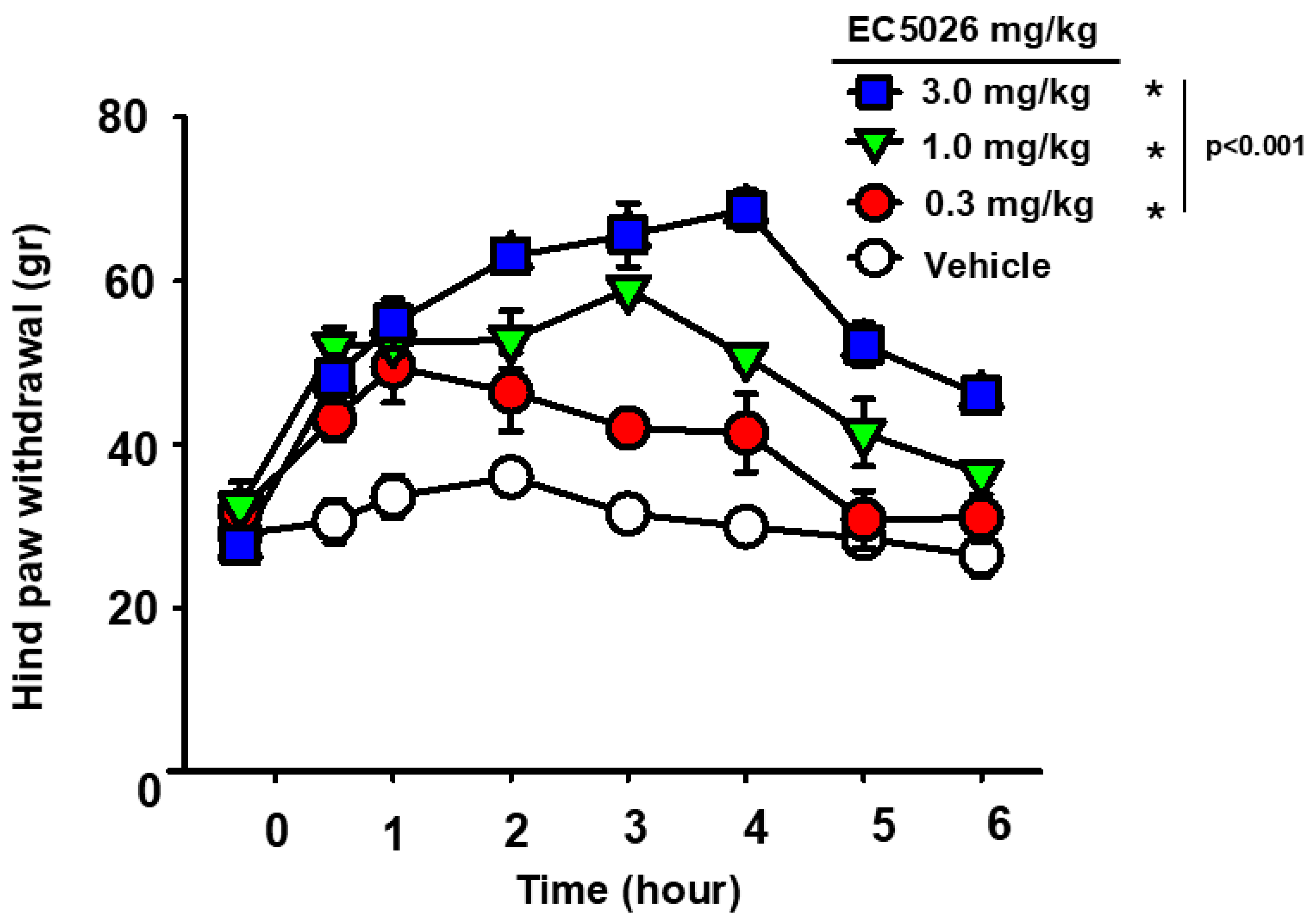
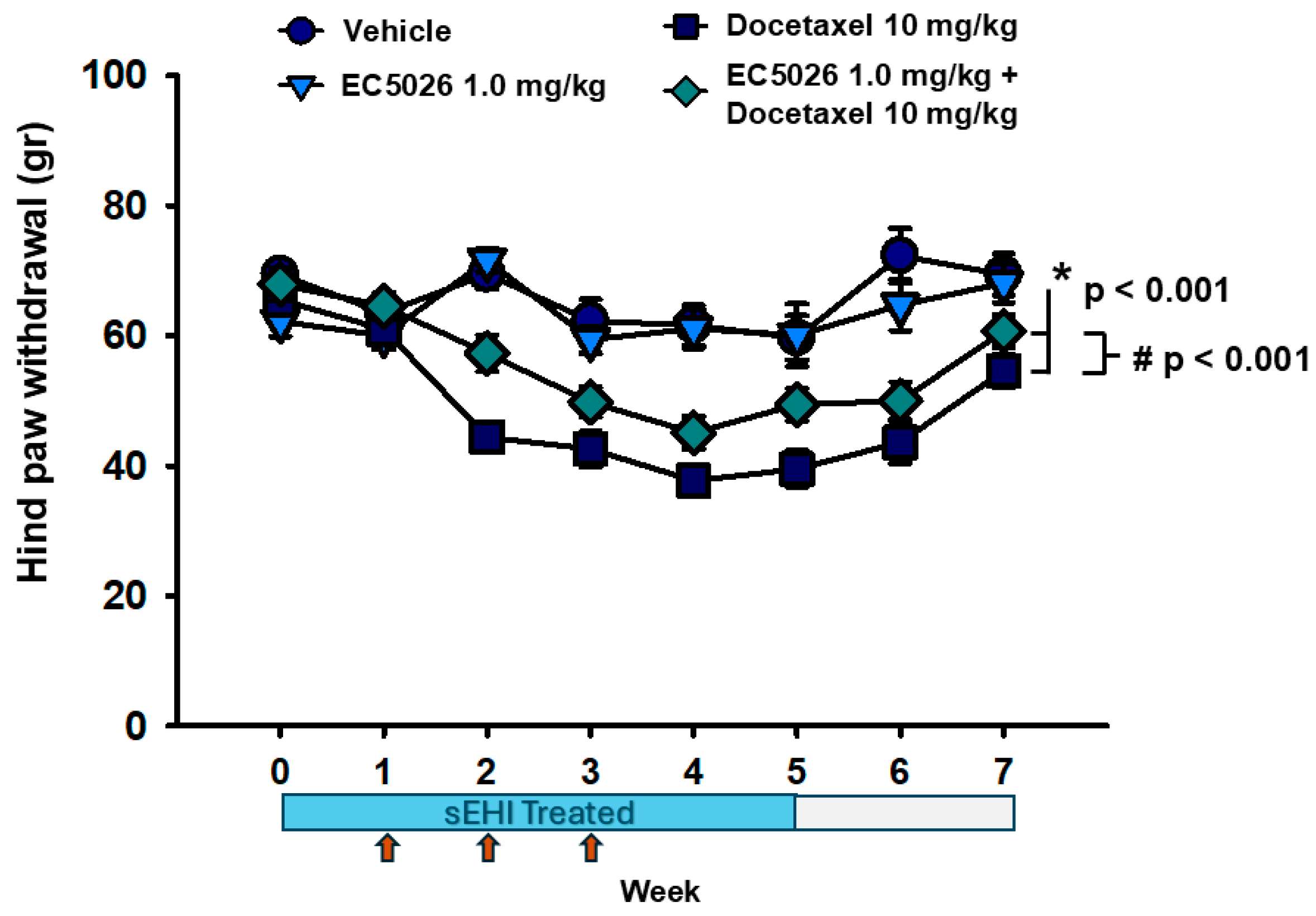
2.1. EC5026 Effects on Mechanical Allodynia
2.2. Cold Pain Response and Blood Concentrations of Ec5026
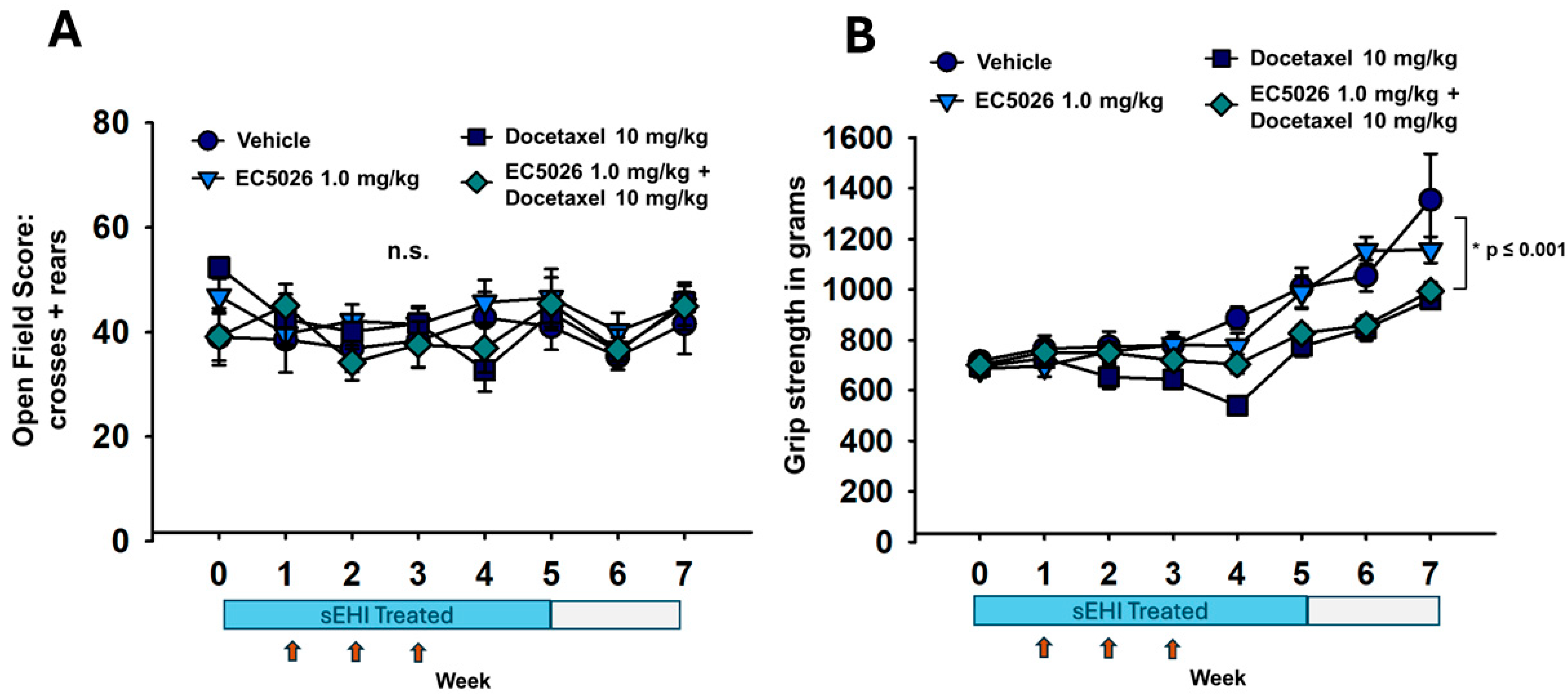
2.3. Open-Field and Grip Strength Functional Assays
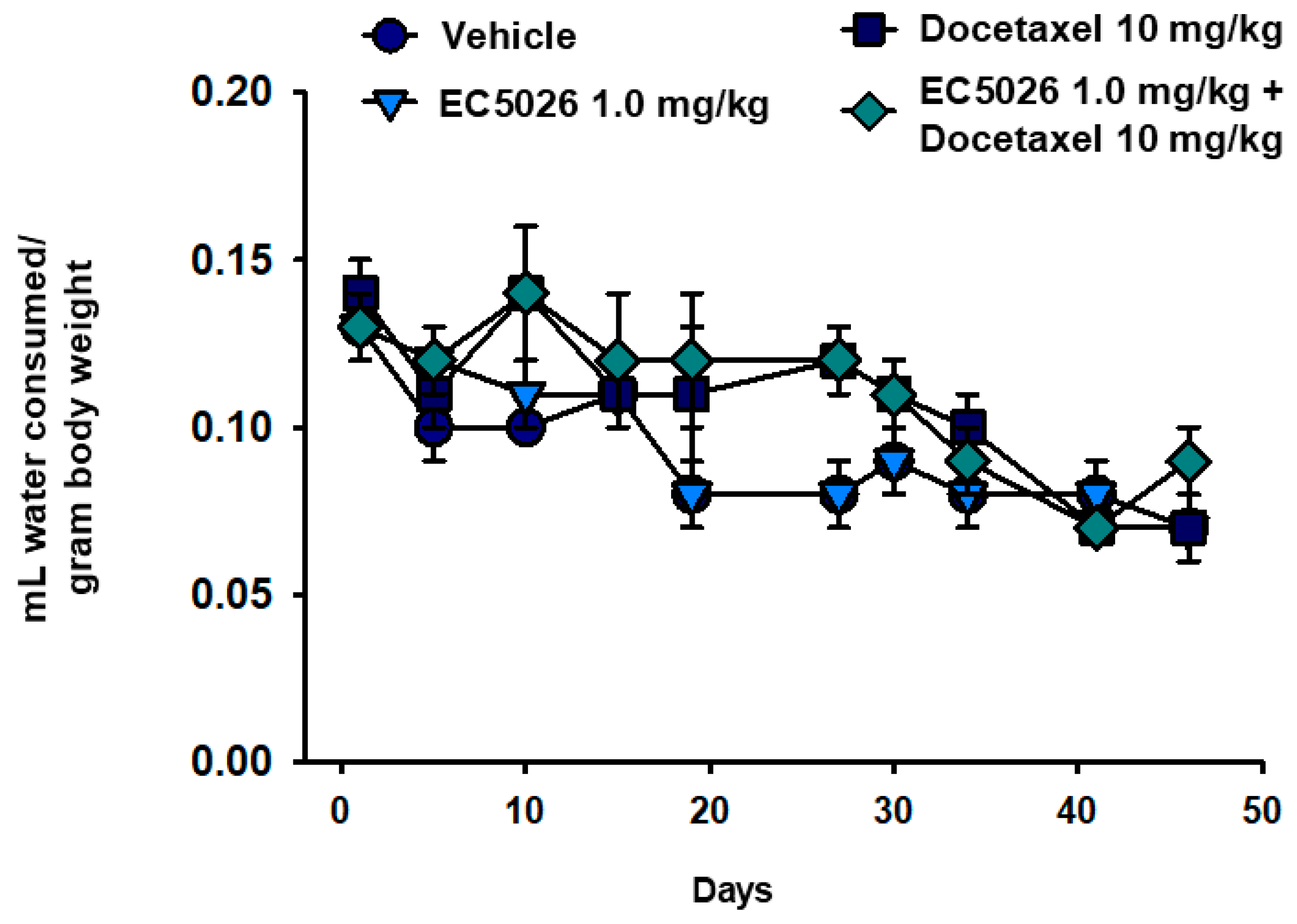
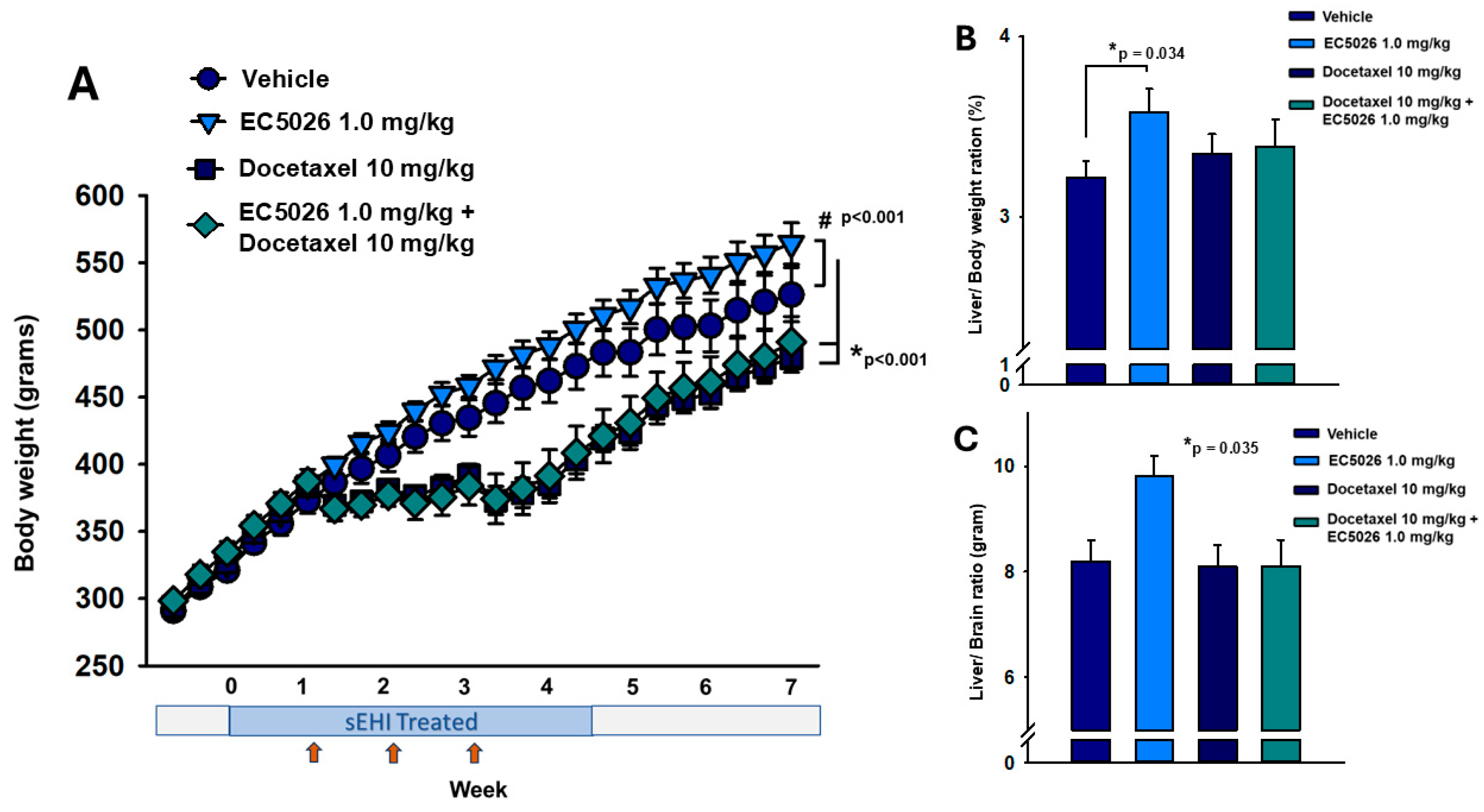
2.4. Body Weight Comparisons
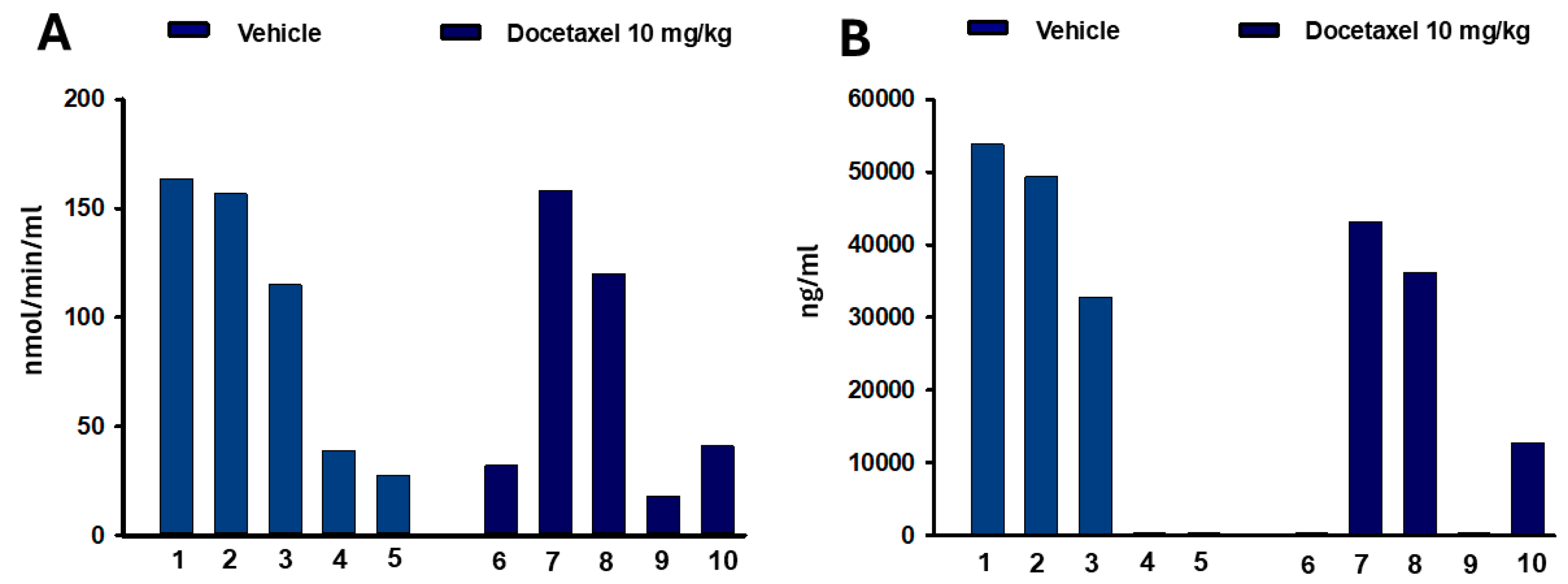
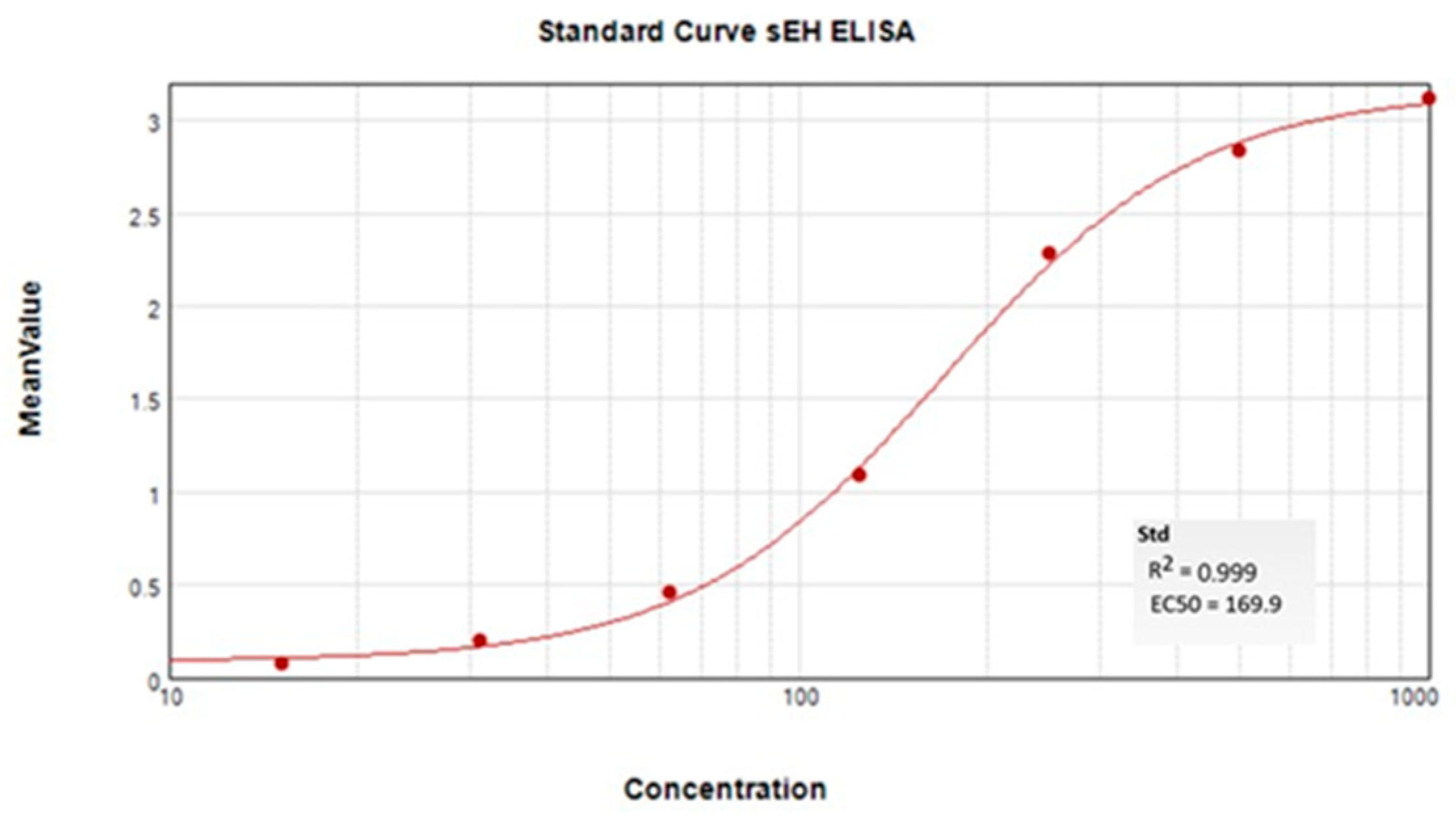
2.5. ELISA Quantification of sEH Protein in Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Blood Concentration Determination
4.4. Behavioral Assessment and Husbandry
4.5. Experimental Design
4.6. Nociceptive and Functional Assays
4.7. sEH ELISA Protein Quantification
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CIPN | Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| sEH | Soluble epoxide hydrolase |
| sEHI | Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor |
Appendix A
| IC50 (nM) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Rat sEH | Mouse sEH | |
| TPPU | 7.6 | 5.0 |
| EC5026 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
Measurement of Inhibitor Potencies on Rat and Mouse sEH
References
- Rahman, N.; Sukumar, J.; Lustberg, M.B. Chronic chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Living with neuropathy during and after cancer treatments. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2025, 14, 196–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and rehabilitation: A review. Semin. Oncol. 2021, 48, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altshuler, R.D.; Minasian, L.M.; Schweppe, C.A.; Kadan-Lottick, N.S. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy research: A National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant portfolio analysis (2014–2023). JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2025, 9, pkaf039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Timmins, H.C.; Mahfouz, F.M.; Trinh, T.; Mizrahi, D.; Horvath, L.G.; Harrison, M.; Grimison, P.; Friedlander, M.; Marx, G.; et al. Validity of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures in Evaluating Nerve Damage Following Chemotherapy. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2424139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withrow, D.; Pilleron, S.; Nikita, N.; Ferlay, J.; Sharma, S.; Nicholson, B.; Rebbeck, T.R.; Lu-Yao, G. Current and projected number of years of life lost due to prostate cancer: A global study. Prostate 2022, 82, 1088–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, E.M.; Srinivas, S.; Adra, N.; An, Y.; Barocas, D.; Bitting, R.; Bryce, A.; Chapin, B.; Cheng, H.H.; D’Amico, A.V.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Prostate Cancer, Version 1.2023: Featured Updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Khuri, F.R. Mode of action of docetaxel—A basis for combination with novel anticancer agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2003, 29, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, B.A. How Taxol/paclitaxel kills cancer cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 2677–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, M.; Tavares, I.; Costa-Pereira, J.T. Centralizing the Knowledge and Interpretation of Pain in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Paradigm Shift towards Brain-Centric Approaches. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, N.D.; Tannock, I.; N’ Dow, J.; Feng, F.; Gillessen, S.; Ali, S.A.; Trujillo, B.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Attard, G.; Bray, F.; et al. The Lancet Commission on prostate cancer: Planning for the surge in cases. Lancet 2024, 403, 1683–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, A.A.; Hammock, B.D.; Wagner, K.M. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition alleviates chemotherapy induced neuropathic pain. Front. Pain. Res. 2023, 3, 1100524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, A.A.; Kim, H.-Y. Cytochrome P450 epoxygenase pathway of polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashvili, M.; Tseng, L.F.; Wu, H.E.; Narayanan, J.; Hart, L.M.; Falck, J.R.; Pratt, P.F.; Harder, D.R. Antinociception produced by 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid is mediated by the activation of beta-endorphin and met-enkephalin in the rat ventrolateral periaqueductal gray. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 326, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisseau, C.; Inceoglu, B.; Schmelzer, K.; Tsai, H.J.; Jinks, S.L.; Hegedus, C.M.; Hammock, B.D. Naturally occurring monoepoxides of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid are bioactive antihyperalgesic lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3481–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, Y.; Tong, H.; Chen, L.; Morisseau, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zhuang, J.; Song, C.; Cai, P.; Liu, Z.; et al. Design and Synthesis of sEH/HDAC6 Dual-Targeting Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Pain. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 12887–12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inceoglu, B.; Wagner, K.M.; Yang, J.; Bettaieb, A.; Schebb, N.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Morisseau, C.; Haj, F.G.; Hammock, B.D. Acute augmentation of epoxygenated fatty acid levels rapidly reduces pain-related behavior in a rat model of type I diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11390–11395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.; Gilda, J.; Yang, J.; Wan, D.; Morisseau, C.; Gomes, A.V.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition alleviates neuropathy in Akita (Ins2 Akita) mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 326, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, J.; Chapman, V. Targeting the soluble epoxide hydrolase pathway as a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of pain. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2024, 78, 102477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inceoglu, B.; Bettaieb, A.; Trindade da Silva, C.A.; Lee, K.S.; Haj, F.G.; Hammock, B.D. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the peripheral nervous system is a significant driver of neuropathic pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9082–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katragadda, D.; Batchu, S.N.; Cho, W.J.; Chaudhary, K.R.; Falck, J.R.; Seubert, J.M. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids limit damage to mitochondrial function following stress in cardiac cells. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2009, 46, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, S.N.; Lee, S.B.; Samokhvalov, V.; Chaudhary, K.R.; El-Sikhry, H.; Weldon, S.M.; Seubert, J.M. Novel soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor protects mitochondrial function following stress. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 90, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, Y.; Fouda, R.; Gupta, K. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Emerging Role of Phytochemicals. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Xiao, W.H.; Bennett, G.J. Functional deficits in peripheral nerve mitochondria in rats with paclitaxel- and oxaliplatin-evoked painful peripheral neuropathy. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 232, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, K.; Doyle, T.; Bryant, L.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Ryerse, J.; Bennett, G.J.; Salvemini, D. Bioenergetic deficits in peripheral nerve sensory axons during chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain resulting from peroxynitrite-mediated post-translational nitration of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase. Pain 2013, 154, 2432–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.M.; Salvemini, D. Mini-Review: Mitochondrial dysfunction and chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 760, 136087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammock, B.D.; McReynolds, C.B.; Wagner, K.; Buckpitt, A.; Cortes-Puch, I.; Croston, G.; Lee, K.S.S.; Yang, J.; Schmidt, W.K.; Hwang, S.H. Movement to the Clinic of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor EC5026 as an Analgesic for Neuropathic Pain and for Use as a Nonaddictive Opioid Alternative. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1856–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.M.; Atone, J.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor mediated analgesia lacks tolerance in rat models. Brain Res. 2020, 1728, 146573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.A.; Zidell, R.H.; Perry, R.W. Relationships Between Organ Weight and Body/Brain Weight in the Rat: What Is the Best Analytical Endpoint? Toxicol. Pathol. 2004, 32, 448–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, R.S.; Mortan, D.; Michael, B.; Roome, N.; Johnson, J.K.; Yano, B.L.; Perry, R.; Schafer, K. Society of Toxicologic Pathology Position Paper: Organ Weight Recommendations for Toxicology Studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, M.S.; Maguire, A.D.; Simmen, T.; Kerr, B.J. Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interplay in chronic pain: The calcium connection. Mol. Pain. 2020, 16, 1744806920946889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.; Shen, S. Endoplasmic reticular stress as an emerging therapeutic target for chronic pain: A narrative review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2024, 132, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trecarichi, A.; Flatters, S.J.L. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 145, 83–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molassiotis, A.; Cheng, H.L.; Lopez, V.; Au, J.S.K.; Chan, A.; Bandla, A.; Leung, K.T.; Li, Y.C.; Wong, K.H.; Suen, L.K.P.; et al. Are we mis-estimating chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy? Analysis of assessment methodologies from a prospective, multinational, longitudinal cohort study of patients receiving neurotoxic chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, K.A.; Dorsey, S.G.; Renn, C.L.; Zhu, S.; Johantgen, M.E.; Cornblath, D.R.; Argyriou, A.A.; Cavaletti, G.; Merkies, I.S.; Alberti, P.; et al. Correspondence between neurophysiological and clinical measurements of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Secondary analysis of data from the CI-PeriNomS study. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2014, 19, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolignier, S.; Bonnet, C.; Gaudioso, C.; Noël, J.; Ruel, J.; Amsalem, M.; Ferrier, J.; Rodat-Despoix, L.; Bouvier, V.; Aissouni, Y.; et al. The Nav1.9 Channel Is a Key Determinant of Cold Pain Sensation and Cold Allodynia. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.D.; Wolf, N.M.; Morisseau, C.; Whetstone, P.; Hock, B.; Hammock, B.D. Fluorescent substrates for soluble epoxide hydrolase and application to inhibition studies. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 343, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisseau, C.; Beetham, J.K.; Pinot, F.; Debernard, S.; Newman, J.W.; Hammock, B.D. Cress and potato soluble epoxide hydrolases: Purification, biochemical characterization, and comparison to mammalian enzymes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 378, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.F.; Spencer, W.A. Habituation: A model phenomenon for the study of neuronal substrates of behavior. Psychol. Rev. 1966, 73, 16–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofthagen, C.; McAllister, R.D.; Visovsky, C. Peripheral neuropathy caused by Paclitaxel and docetaxel: An evaluation and comparison of symptoms. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2013, 4, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ventzel, L.; Madsen, C.S.; Karlsson, P.; Tankisi, H.; Isak, B.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; Jensen, A.B.; Jensen, A.R.; Jensen, T.S.; Finnerup, N.B. Chronic Pain and Neuropathy Following Adjuvant Chemotherapy. Pain Med. 2017, 19, 1813–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatem, S.; Attal, N.; Willer, J.C.; Bouhassira, D. Psychophysical study of the effects of topical application of menthol in healthy volunteers. Pain 2006, 122, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Roh, S.H.; Lee, J.Y. Body regional heat pain thresholds using the method of limit and level: A comparative study. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikandar, S.; Patel, R.; Patel, S.; Sikander, S.; Bennett, D.L.H.; Dickenson, A.H. Genes, molecules and patients—Emerging topics to guide clinical pain research. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 716, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolignier, S.; Eijkelkamp, N.; Wood, J.N. Mechanical allodynia. Pflugers Arch. 2015, 467, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inceoglu, B.; Schmelzer, K.R.; Morisseau, C.; Jinks, S.L.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition reveals novel biological functions of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2007, 82, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.; Inceoglu, B.; Dong, H.; Yang, J.; Hwang, S.H.; Jones, P.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Comparative efficacy of 3 soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors in rat neuropathic and inflammatory pain models. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 700, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.T.; Hasegawa, T.; Noma, H.; Sugita, H.; Ota, E. Efficacy and safety of drug therapy for the prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e070645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maihöfner, C.; Diel, I.; Tesch, H.; Quandel, T.; Baron, R. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): Current therapies and topical treatment option with high-concentration capsaicin. Support. Care Cancer 2021, 29, 4223–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.M.; McReynolds, C.B.; Schmidt, W.K.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble epoxide hydrolase as a therapeutic target for pain, inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 180, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, N.A.; Smith, A.G.; Singleton, J.R.; Beck, S.L.; Stoddard, G.J.; Brown, S.; Mooney, K. The Association of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms and the Risk of Falling. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visovsky, C.; Wodzinski, P.T.; Haladay, D.; Ji, M.; Coury, J. Fall Risk Associated with Taxanes: Focus on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2024, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Walsh, D.; Brito-Dellan, N. Opioid and adjuvant analgesics: Compared and contrasted. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Care 2011, 28, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Canabal, A.; Grim, T.W.; Schmid, C.L.; McFague, N.; Stahl, E.L.; Kennedy, N.M.; Bannister, T.D.; Bohn, L.M. Hyperactivity in Mice Induced by Opioid Agonists with Partial Intrinsic Efficacy and Biased Agonism Administered Alone and in Combination with Morphine. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çağlar Okur, S.; Vural, M.; Pekin Doğan, Y.; Mert, M.; Sayıner Çağlar, N. The effect of pregabalin treatment on balance and gait in patients with chronic low back pain: A retrospective observational study. J. Drug Assess. 2019, 8, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartanian, M.G.; Radulovic, L.L.; Kinsora, J.J.; Serpa, K.A.; Vergnes, M.; Bertram, E.; Taylor, C.P. Activity profile of pregabalin in rodent models of epilepsy and ataxia. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 68, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, B.; Fan, R.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; He, Z. Preparation and evaluation of duloxetine hydrochloride enteric-coated pellets with different enteric polymers. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-H.; Wu, Z.; Dong, J.-H.; Zeng, Y.-N.; Xiong, W.-C.; Liu, C.; Wang, M.-Y.; Zhu, M.-Z.; Chen, W.-J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Liver Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Regulates Behavioral and Cellular Effects of Chronic Stress. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 3223–3234.e3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Ma, M.; Ishima, T.; Morisseau, C.; Yang, J.; Wagner, K.M.; Zhang, J.C.; Yang, C.; Yao, W.; Dong, C.; et al. Gene deficiency and pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase confers resilience to repeated social defeat stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1944–E1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chang, L.; Hammock, B.D.; Hashimoto, K. Increased expression of soluble epoxide hydrolase in the brain and liver from patients with major psychiatric disorders: A role of brain—Liver axis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 270, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Ma, M.; Yang, J.; Nonaka, R.; Yamaguchi, A.; Ishikawa, K.I.; Kobayashi, K.; Murayama, S.; Hwang, S.H.; Saiki, S.; et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase plays a key role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5815–E5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, B.; Huang, Y.; Qiao, D.; Yue, X. Proteomic analysis discovers potential biomarkers of early traumatic axonal injury in the brainstem. Int. J. Legal Med. 2024, 138, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, A.; Hsu, M.-F.; Koike, S.; Chu, B.; Cheng, J.; Yang, J.; Morisseau, C.; Torok, N.J.; Hammock, B.D.; Haj, F.G. Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Hepatic Deficiency Ameliorates Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 11, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Hammock, B.D. Distribution and properties of a mammalian soluble epoxide hydrase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1980, 29, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inceoglu, B.; Zolkowska, D.; Yoo, H.J.; Wagner, K.M.; Yang, J.; Hackett, E.; Hwang, S.H.; Lee, K.S.; Rogawski, M.A.; Morisseau, C.; et al. Epoxy fatty acids and inhibition of the soluble epoxide hydrolase selectively modulate GABA mediated neurotransmission to delay onset of seizures. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, M.; Hassett, C.; Adman, E.T.; Meijer, J.; Omiecinski, C.J. Identification and functional characterization of human soluble epoxide hydrolase genetic polymorphisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28873–28881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornage, M.; Lee, C.R.; Doris, P.A.; Bray, M.S.; Heiss, G.; Zeldin, D.C.; Boerwinkle, E. The soluble epoxide hydrolase gene harbors sequence variation associated with susceptibility to and protection from incident ischemic stroke. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Sharma, V.K.; Kalonia, D.S.; Grant, D.F. Polymorphisms in human soluble epoxide hydrolase: Effects on enzyme activity, enzyme stability, and quaternary structure. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2004, 427, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Mao, Z.; Liu, M.; Fu, B.; Yuan, X.; Wang, L. Association between the sEH rs751141 polymorphism and the risk of ischemic stroke and hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2025, 34, 108176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duflot, T.; Laurent, C.; Soudey, A.; Fonrose, X.; Hamzaoui, M.; Iacob, M.; Bertrand, D.; Favre, J.; Etienne, I.; Roche, C.; et al. Preservation of epoxyeicosatrienoic acid bioavailability prevents renal allograft dysfunction and cardiovascular alterations in kidney transplant recipients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisseau, C.; Wecksler, A.T.; Deng, C.; Dong, H.; Yang, J.; Lee, K.S.; Kodani, S.D.; Hammock, B.D. Effect of soluble epoxide hydrolase polymorphism on substrate and inhibitor selectivity and dimer formation. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, S.; Meijerman, I.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M. The role of nuclear receptors in pharmacokinetic drug–drug interactions in oncology. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, L.; Cliff, J.; Carr, D.F.; Jorgensen, A.; Lord, R.; Pirmohamed, M. CYP3A genetic variation and taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and candidate gene study. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1178421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, M.; Zhang, J.; Gaffney, C.M.; Kalakuntla, N.; Nguyen, N.T.; Trinh, R.T.; Aguilar, C.; Pham, H.V.; Milutinovic, B.; Nichols, J.M.; et al. Sensory neuron dysfunction in orthotopic mouse models of colon cancer. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, P.; Salvalaggio, A.; Argyriou, A.A.; Bruna, J.; Visentin, A.; Cavaletti, G.; Briani, C. Neurological Complications of Conventional and Novel Anticancer Treatments. Cancers 2022, 14, 6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubblefield, M.D.; Burstein, H.J.; Burton, A.W.; Custodio, C.M.; Deng, G.E.; Ho, M.; Junck, L.; Morris, G.S.; Paice, J.A.; Tummala, S.; et al. NCCN task force report: Management of neuropathy in cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2009, 7 (Suppl. S5), S1–S26, quiz S27–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staff, N.P.; Grisold, A.; Grisold, W.; Windebank, A.J. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A current review. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cui, Y.; Morisseau, C.; Wagner, K.M.; Cho, Y.S.; Hammock, B.D. Development of a Highly Sensitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Mouse Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Detection by Combining a Polyclonal Capture Antibody with a Nanobody Tracer. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11654–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagner, K.M.; Yang, J.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Inhibition of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Prevents Docetaxel-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125630
Wagner KM, Yang J, Morisseau C, Hammock BD. Inhibition of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Prevents Docetaxel-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125630
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagner, Karen M., Jun Yang, Christophe Morisseau, and Bruce D. Hammock. 2025. "Inhibition of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Prevents Docetaxel-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125630
APA StyleWagner, K. M., Yang, J., Morisseau, C., & Hammock, B. D. (2025). Inhibition of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Prevents Docetaxel-Induced Painful Peripheral Neuropathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125630






