Changes in the Protein Profile of Saliva from People with Obesity Treated with Bariatric Surgery and Physical Exercise
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anthropometric Parameters
2.2. Differences in Salivary Proteome Between Individuals with Obesity vs. Individuals with Normal Weight
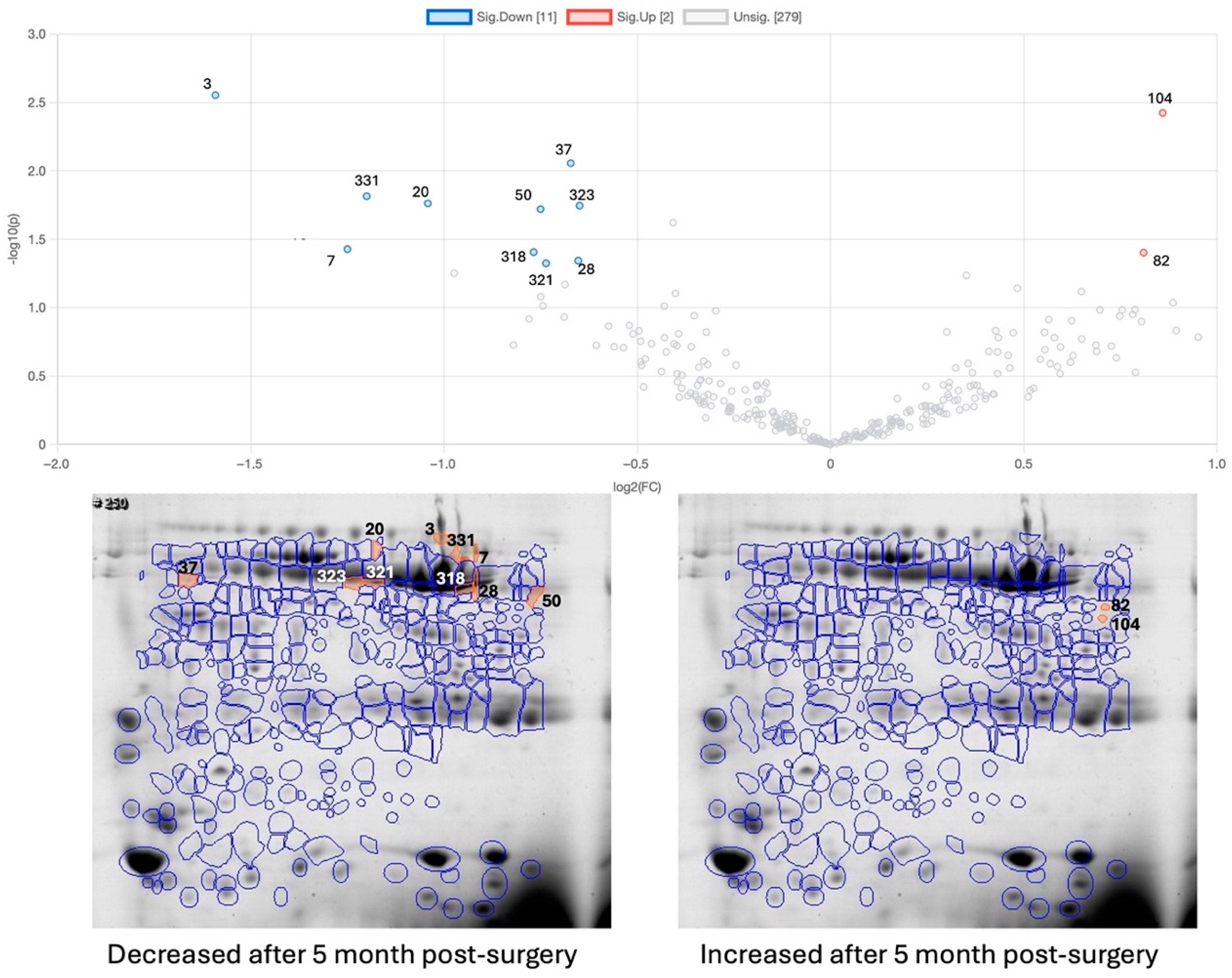
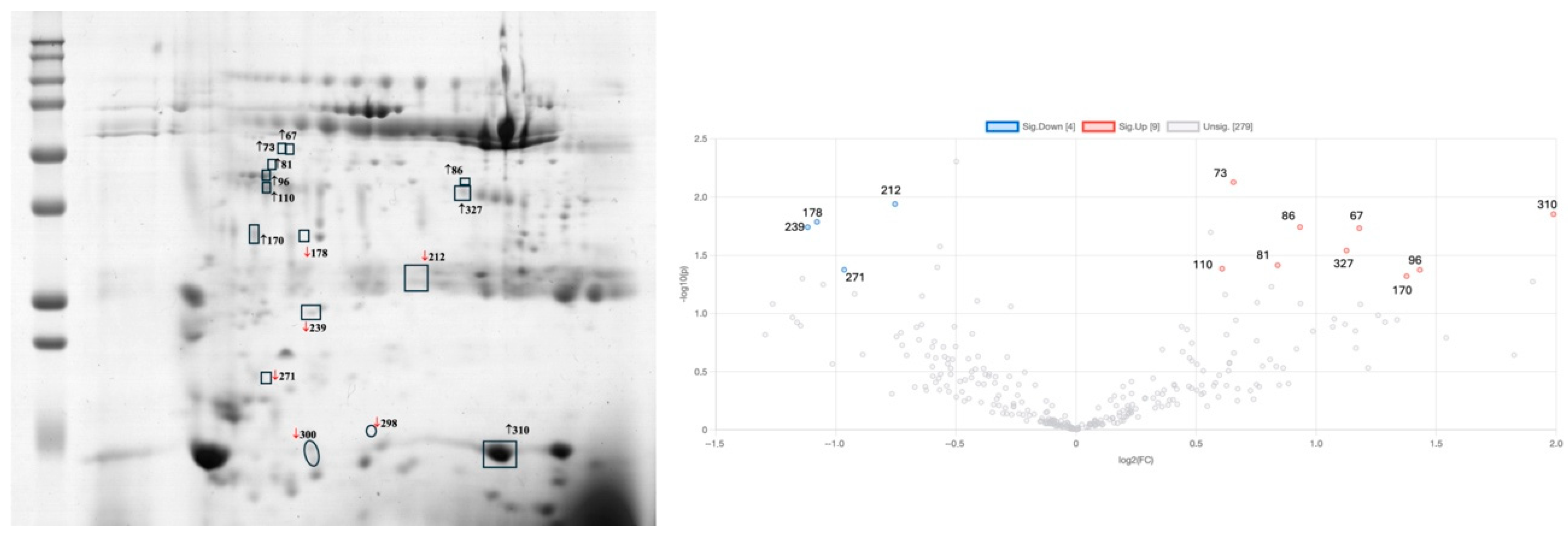
| Spots | OB-BS vs. NW | OB-1M-BS | OB-5M-BS-Control | OB-5M-BS-Exercise | Protein ID | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 | ↓ | Amylase | [18] | |||
| 37 | ↓ | Alpha-1 anti-trypsin | [18] | |||
| 83 | ↑ | ↓ | Actin-related protein 3 | [19] | ||
| 86 | ↑ | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta | [18] | |||
| 96 | ↑ | Actin cytoplasmic 1 | [18,20] | |||
| 110 | ↑ | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | [18,20] | |||
| 123 | ↓ | ↓ | Carbonic-anhydrase VI | [18,20] | ||
| 128 | ↓ | Carbonic-anhydrase VI | [18,20] | |||
| 134 | ↓ | Carbonic anhydrase VI | [18] | |||
| 135 | ↑ | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | [17] | |||
| 139 | ↑ | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | [19] | |||
| 159 | ↑ | Zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein | [17] | |||
| 170 | ↓ | ↑ | SPLUNC | [18] | ||
| 177 | ↑ | SPLUNC | [18] | |||
| 212 | ↑ | ↓ | Ig kappa chain C region | [18] | ||
| 225 | ↑ | Ig kappa chain C region | [18] | |||
| 239 | ↓ | Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta | [18] | |||
| 259 | ↓ | Haptoglobin | [18] | |||
| 260 | ↓ | ↑ | Haptoglobin | [18] | ||
| 290 | ↓ | PIP | [18] | |||
| 310 | ↑ | Cystatin SA | [21] | |||
| 318 | ↓ | Amylase (native) | [18,20] | |||
| 321 | ↓ | Amylase (native) | [18] | |||
| 323 | ↓ | Amylase (native) | [18] | |||
| 327 | ↓ | ↑ | Carbonic anhydrase VI | [18,20] | ||
| 326 | ↓ | Immunoglobulin J chain | [19] | |||
| 333 | ↓ | Zinc-alpha 2 glycoprotein | [17] |
2.3. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Saliva Proteome
2.4. Effect of Exercise Intervention on the Saliva Proteome of Bariatric-Surgery-Submitted Participants
3. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
4. Material and Method
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Anthropometric Parameters
4.3. Whole-Saliva Collection
4.4. Protein Total Determination
4.5. Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis
4.6. Exercise Programme
4.7. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Engin, A. The Definition and Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenackers, N.; Van Der Schueren, B.; Mertens, A.; Lannoo, M.; Grauwet, T.; Augustijns, P.; Matthys, C. Iron Deficiency after Bariatric Surgery: What Is the Real Problem? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, D.A.; Patti, M.E. Glucose Metabolism after Bariatric Surgery: Implications for T2DM Remission and Hypoglycaemia. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, E.; Simões, C.; Rodrigues, L.; Costa, A.R.; Vitorino, R.; Amado, F.; Antunes, C.; do Carmo, I. Changes in the Salivary Protein Profile of Morbidly Obese Women Either Previously Subjected to Bariatric Surgery or Not. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vors, C.; Drai, J.; Gabert, L.; Pineau, G.; Laville, M.; Vidal, H.; Guichard, E.; Michalski, M.C.; Feron, G. Salivary Composition in Obese vs Normal-Weight Subjects: Towards a Role in Postprandial Lipid Metabolism? Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogawa, E.M.; Melo, F.F.; Pires, R.G.; Caetano, P.C.C.; de Lima Rodrigues, J.; Benito, L.A.O.; da Silva, I.C.R.; de Castro Cantuária, A.P.; de Carvalho Sales-Peres, S.H. The Changes on Salivary Flow Rates, Buffering Capacity and Chromogranin A Levels in Adults after Bariatric Surgery. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pîrsean, C.; Neguț, C.; Stefan-van Staden, R.I.; Dinu-Pirvu, C.E.; Armean, P.; Udeanu, D.I. The salivary levels of leptin and interleukin-6 as potential inflammatory markers in children obesity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandò, C.; Abati, S.; Anelli, G.M.; Favero, C.; Serati, A.; Dioni, L.; Zambon, M.; Albetti, B.; Bollati, V.; Cetin, I. Epigenetic Profiling in the Saliva of Obese Pregnant Women. Nutrients. 2022, 14, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foratori-Junior, G.A.; Ventura, T.M.O.; Grizzo, L.T.; Jesuino, B.G.; Castilho, A.V.S.S.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Sales-Peres, S.H.C. Is There a Difference in the Proteomic Profile of Stimulated and Unstimulated Saliva Samples from Pregnant Women with/without Obesity and Periodontitis? Cells 2023, 12, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niebla-Cárdenas, A.; Bueno-Hernández, N.; Hernández, A.P.; Fuentes, M.; Méndez-Sánchez, R.; Arroyo-Anlló, E.M.; Orera, I.; Lattanzio, G.; Juanes-Velasco, P.; Arias-Hidalgo, C.; et al. Potential protein biomarkers in saliva for detection of frailty syndrome by targeted proteomics. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 221, 111974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Silverio, R.; Costa, A.R.; Antunes, C.; Pomar, C.; Infante, P.; Conceição, C.; Amado, F.; Lamy, E. Taste Sensitivity and Lifestyle Are Associated with Food Preferences and BMI in Children. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Dávalos, P.C.; Requena, T.; Pozo-Bayón, M.Á.; Muñoz-González, C. Decreased Retronasal Olfaction and Taste Perception in Obesity Are Related to Saliva Biochemical and Microbiota Composition. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.; Penney, N.; Darzi, A.; Purkayastha, S. Taste Changes after Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppre, G.; Diniz-Sousa, F.; Veras, L.; Oliveira, J.; Fonseca, H. Can Exercise Promote Additional Benefits on Body Composition in Patients with Obesity after Bariatric Surgery? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Obes. Sci. Pr. 2022, 8, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellicha, A.; van Baak, M.A.; Battista, F.; Beaulieu, K.; Blundell, J.E.; Busetto, L.; Carraça, E.V.; Dicker, D.; Encantado, J.; Ermolao, A.; et al. Effect of Exercise Training before and after Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro Santos, C.; Cinza, A.M.; Laranjeira, Â.; Amaro, M.; Carvalho, M.; Martins, S.; Bravo, J.; Raimundo, A. The Impact of Exercise on Prevention of Sarcopenia after Bariatric Surgery: The Study Protocol of the EXPOBAR Randomized Controlled Trial. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2023, 31, 101048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessie, K.; Pang, W.W.; Rahim, Z.H.A.; Hashim, O.H. Proteomic Analysis of Whole Human Saliva Detects Enhanced Expression of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist, Thioredoxin and Lipocalin-1 in Cigarette Smokers Compared to Non-Smokers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4488–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.H.; Rahim, Z.H.A.; Jessie, K.; Hashim, O.H.; Taiyeb-Ali, T.B. Salivary Proteins Associated with Periodontitis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4642–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Espanca, R.; Costa, A.R.; Antunes, C.M.; Pomar, C.; Capela-Silva, F.; Pinheiro, C.C.; Domingues, P.; Amado, F.; Lamy, E. Comparison of Salivary Proteome of Children with Different Sensitivities for Bitter and Sweet Tastes: Association with Body Mass Index. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirtz, C.; Chevalier, F.; Sommerer, N.; Raingeard, I.; Bringer, J.; Rossignol, M.; Deville De Périère, D. Salivary Protein Profiling in Type 1 Diabetes Using Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis and Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Proteom. 2006, 2, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.E.; Hindle, A.; Brennan, L.; Skinner, S.; Burton, P.; Smith, A.; Crosthwaite, G.; Brown, W. Long-Term Outcomes After Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Weight Loss at 10 or More Years for All Bariatric Procedures and a Single-Centre Review of 20-Year Outcomes After Adjustable Gastric Banding. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, S.S.; Lee, P.C.; Lim, C.H.; Wong, A.S.Y.; Ng, A.Y.L.; Lin, J.; Lee, J. Study on Weight Loss Outcomes after Bariatric Surgery to Determine a Metric Least Influenced by Preoperative BMI. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rådholm, K.; Chalmers, J.; Ohkuma, T.; Peters, S.; Poulter, N.; Hamet, P.; Harrap, S.; Woodward, M. Use of the Waist-to-Height Ratio to Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Diabetes: Results from the ADVANCE-ON Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkkila, S.; Kaunisto, K.; Rajaniemi, L.; Kumpulainen, T.; Jokinen, K.; Rajaniemi, H. Immunohistochemical Localization of Carbonic Anhydrase Isoenzymes VI, II, and I in Human Parotid and Submandibular Glands. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1990, 38, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yrjänäinen, A.; Patrikainen, M.S.; Azizi, L.; Tolvanen, M.E.E.; Laitaoja, M.; Jänis, J.; Hytönen, V.P.; Nocentini, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Parkkila, S. Biochemical and Biophysical Characterization of Carbonic Anhydrase VI from Human Milk and Saliva. Protein J. 2022, 41, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.; Costa, G.; Cordeiro, C.; Pinheiro, C.; Amado, F.; Lamy, E. Salivary Proteome and Glucose Levels Are Related with Sweet Taste Sensitivity in Young Adults. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1389208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleissig, Y.; Reichenberg, E.; Redlich, M.; Zaks, B.; Deutsch, O.; Aframian, D.J.; Palmon, A. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Human Oral Fluids According to Gender and Age. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, A.; Jablonska, K.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Ugorski, M.; Dziegiel, P. Prolactin-Induced Protein (PIP)-Characterization and Role in Breast Cancer Progression. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 18, 2150–2164. [Google Scholar]
- Gorr, S.U.; Abdolhosseini, M.; Shelar, A.; Sotsky, J. Dual Host-Defence Functions of SPLUNC2/PSP and Synthetic Peptides Derived from the Protein. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pergola, G.; Di Roma, P.; Paoli, G.; Guida, P.; Pannacciulli, N.; Giorgino, R. Haptoglobin Serum Levels Are Independently Associated with Insulinemia in Overweight and Obese Women. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2007, 30, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, S.; Gamucci, O.; Vottari, T.; Scabia, G.; Funicello, M.; Marchi, M.; Galli, G.; Arisi, I.; Brandi, R.; D’Onofrio, M.; et al. Obesity-Associated Hepatosteatosis and Impairment of Glucose Homeostasis Are Attenuated by Haptoglobin Deficiency. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, D.C.Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Wang, Y.; Tso, A.W.K.; Xu, A. Serum Zinc-Alpha2-Glycoprotein Correlates with Adiposity, Triglycerides, and the Key Components of the Metabolic Syndrome in Chinese Subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2531–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenad, A.M.; Alkaltham, L.F.; Sabico, S.; Khattak, M.N.K.; Wani, K.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Alokail, M.S. Associations of Zinc-α-2-Glycoprotein with Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components among Adult Arabs. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Sánchez, L.; García-Fuentes, E.; Fernández-García, D.; Escoté, X.; Alcaide, J.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Vendrell, J.; Tinahones, F.J. Zinc-Alpha 2-Glycoprotein Gene Expression in Adipose Tissue Is Related with Insulin Resistance and Lipolytic Genes in Morbidly Obese Patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, M.M.; Pessoa, J.S.; Ciamponi, A.L.; Diniz, M.B.; Santos, M.T.B.R.; Alves, H.H.D.O.; Gorjão, R.; Guaré, R.O. Correlation of Salivary Immunoglobulin A with Body Mass Index and Fat Percentage in Overweight/Obese Children. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2018, 27, e20180088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fábián, T.K.; Hermann, P.; Beck, A.; Fejérdy, P.; Fábián, G. Salivary defense proteins: Their network and role in innate and acquired oral immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4295–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, E.; Neves, S.; Ferreira, J.; Rodrigues, L.; da Costa, G.; Cordeiro, C.; Fialho, L.; Lima, M.; Costa, A.R.; Antunes, C.M.; et al. Effects of Hyperleptinemia in Rat Saliva Composition, Histology and Ultrastructure of the Major Salivary Glands. Arch. Oral Biol. 2018, 96, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari, Y.; Park, C.; Brietzke, E.; Iacobucci, M.; Gill, H.; McIntyre, R. Correlation between Improved Leptin Signaling and Cognitive Function Post Bariatric Surgery. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 326, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louro, T.; Simões, C.; Lima, W.; Carreira, L.; Castelo, P.M.; Luis, H.; Moreira, P.; Lamy, E. Salivary Protein Profile and Food Intake: A Dietary Pattern Analysis. J. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 2021, 6629951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| NW (n = 10) | OB (n = 10) (Before BS) | OB-1M-BS (n = 10) | OB-5M-BS-Control (n = 5) | OB-5M-BS Exercise (n = 5) | ANOVA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p-Value | |
| Age (years) | 34.3 ± 9.6 | 49.1 ± 11.1 a | 49.1 ± 11.1 a | 54.0 ± 10.7 a | 44.2 ± 10.1 | 0.007 |
| Height (cm) | 164.6 ± 6.1 | 158.9 ± 8.5 | 158.9 ± 8.5 | 151.8 ± 5.7 a | 166.0 ± 1.6 d | 0.013 |
| Weight (cm) | 62.6 ± 9.9 | 102.7 ± 15.1 a | 90.9 ± 13.5 a | 66.2 ± 8.2 b,c | 79.0 ± 9.6 b | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.2 ± 3.9 | 40.5 ± 3.4 a | 35.9 ± 3.8 a | 28.7 ± 2.6 b,c | 28.7 ± 3.5 b,c | <0.001 |
| Waist (cm) | 77.6 ± 6.8 | 120.9 ± 11.6 a | 109.2 ± 11.8 a | 91.2 ± 13.6 b | 93.2 ± 11.4 b | <0.001 |
| WHtR | 0.471 ± 0.044 | 0.764 ± 0.103 a | 0.690 ± 0.094 a | 0.602 ± 0.095 b | 0.562 ± 0.071 b | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Perez-Jimenez, M.; Bouzas, C.; García, S.; Mendes, C.; Carvalho, M.; Bravo, J.; Martins, S.; Raimundo, A.; Tur, J.A.; et al. Changes in the Protein Profile of Saliva from People with Obesity Treated with Bariatric Surgery and Physical Exercise. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125622
Monserrat-Mesquida M, Perez-Jimenez M, Bouzas C, García S, Mendes C, Carvalho M, Bravo J, Martins S, Raimundo A, Tur JA, et al. Changes in the Protein Profile of Saliva from People with Obesity Treated with Bariatric Surgery and Physical Exercise. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125622
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonserrat-Mesquida, Margalida, Maria Perez-Jimenez, Cristina Bouzas, Silvia García, Cláudia Mendes, Manuel Carvalho, Jorge Bravo, Sandra Martins, Armando Raimundo, Josep A. Tur, and et al. 2025. "Changes in the Protein Profile of Saliva from People with Obesity Treated with Bariatric Surgery and Physical Exercise" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125622
APA StyleMonserrat-Mesquida, M., Perez-Jimenez, M., Bouzas, C., García, S., Mendes, C., Carvalho, M., Bravo, J., Martins, S., Raimundo, A., Tur, J. A., & Lamy, E. (2025). Changes in the Protein Profile of Saliva from People with Obesity Treated with Bariatric Surgery and Physical Exercise. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125622









