Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quality of Resequencing Data and Alignment with Reference Genome
2.2. Detection and Statistical Analysis of SNP Variants
2.3. Population Genetic Diversity
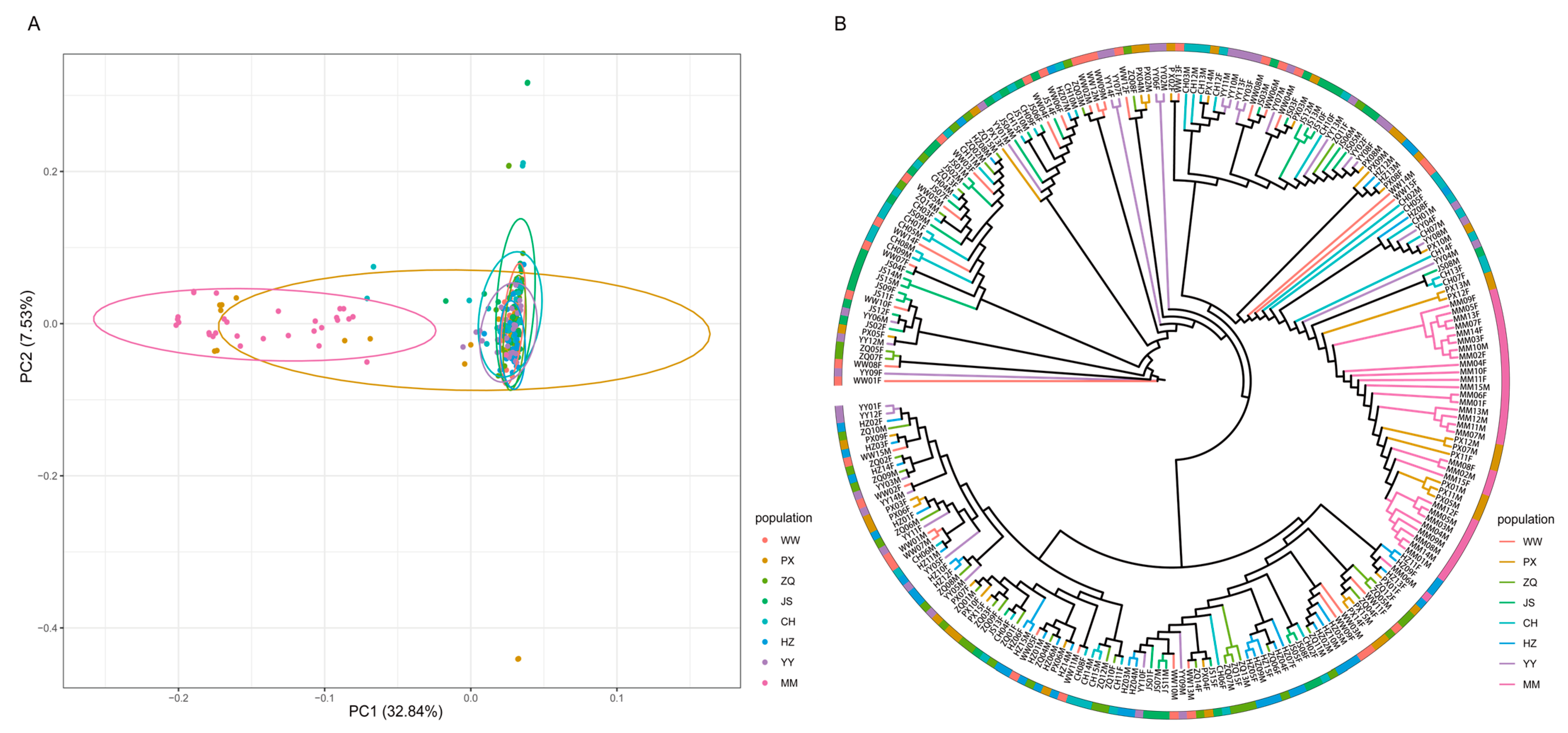
2.4. Phylogenetic Relationship Analysis
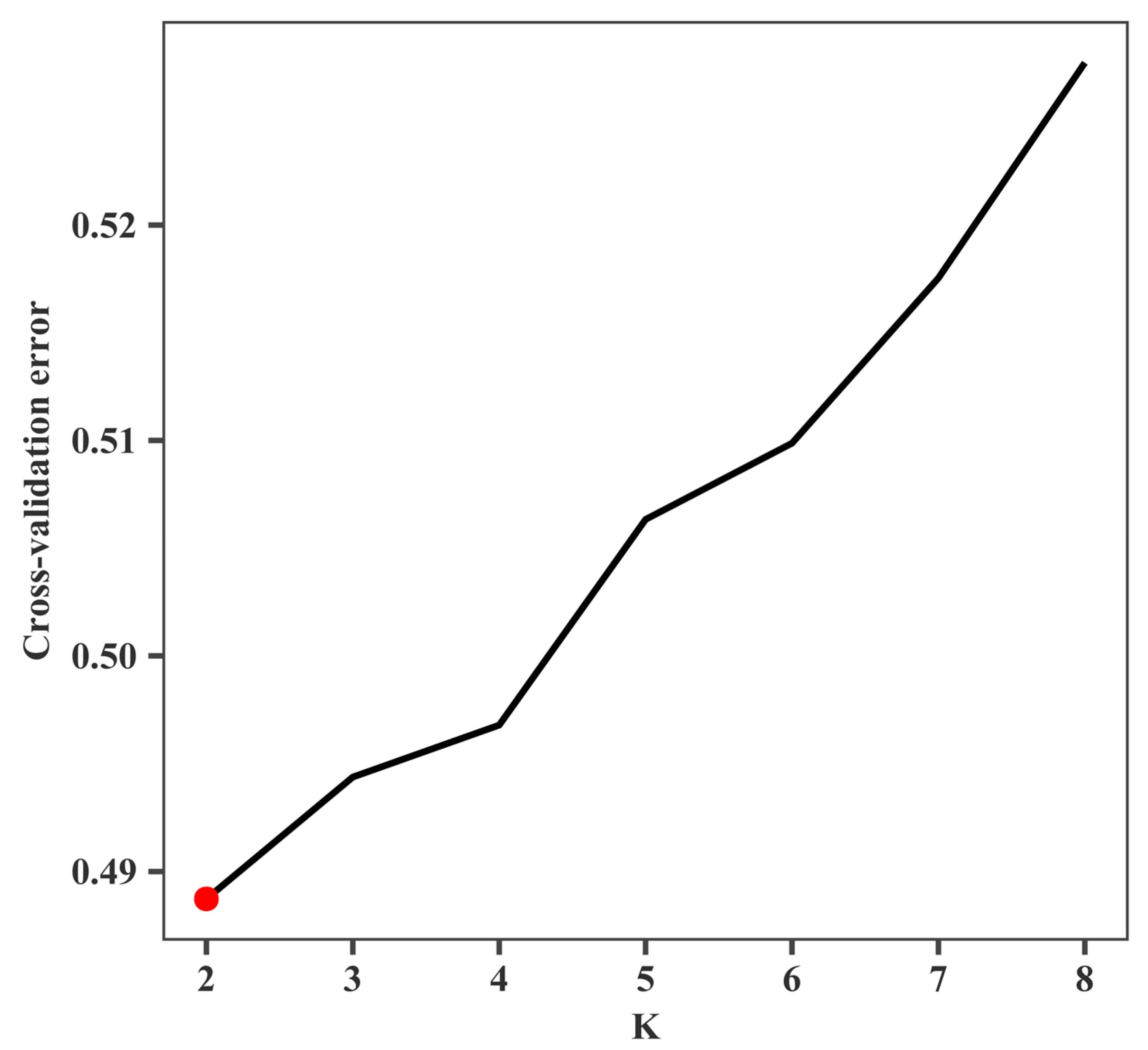
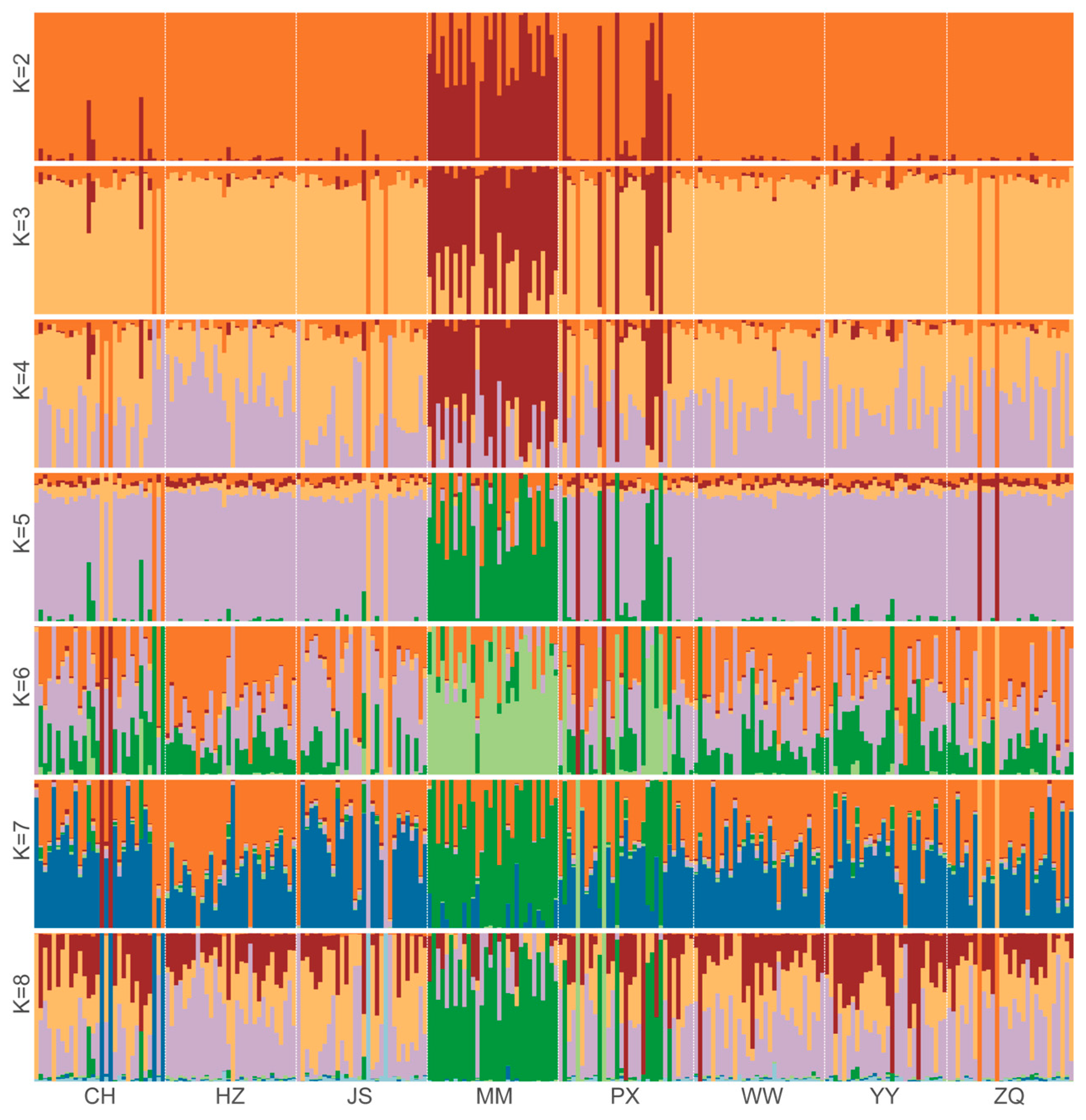
2.5. Genetic Structure Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection
4.2. Morphological Measurement
4.3. DNA Extraction and DNA Library Construction
4.4. Whole-Genome Resequencing and Reference Genome Comparison
4.5. SNP Locus Analysis
4.6. Genetic Diversity Analysis
4.7. Population Genetic Structure Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, H.Z.; Nie, L.W.; Zhao, F.F.; Zhou, H.X.; Li, H.F.; Dong, X.M.; Zhang, H.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Shi, Q.; Li, J. De Novo Assembly and Characterization of the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii) Transcriptome: Presence of Longevity-Related Genes. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.G.; Hu, L.J.; Lu, J.L.; Zhu, L.J. Effects of Incubation Temperature on Embryonic Development Rate, Sex Ratio and Post-Hatching Growth in the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle, Chinemys reevesii. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancient Chinese Turtles: Creatures Symbolizing Longevity and Wisdom. Available online: https://www.qinian.net/c/zhong-guo-gu-dai-wu-gui-xiang-zheng-chang-sho.html (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Xu, Y.Y.; Lai, N.Y.; Shi, Y.; Lin, L.; Jiang, S.T.; Lu, J.F. Nutritional Components Analysis and Quality Evaluation of Chinemys reevesii Tortoise Meat. Meat Ind. 2017, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Yu, Z.Y.; Jiang, S.T.; Lu, J.F.; Lin, L. Comparison of the Physical and Chemical Properties of Collagens Extracted from Tortoise Shell Using Three Methods. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 40, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, H.G. Combined Use and Processing Methods of Tortoise Shell and Tortoise Board. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 1983, 8, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.Y. Discussion on the Medicinal Effects of Tortoise Shell. Chin. J. Hosp. Pharm. 1989, 10, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; He, Q.H.; Tang, Y.; Li, L.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, T. Research Progress on Modern Studies of Tortoise Shell. Hunan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 36, 181–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.G. The Rise and Development of Ornamental Turtle Industry in China. China Fish. 2025, 1, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, M.W. Research into Industrialized Aquaculture Technology and the Reproduction All-Female Hatchlings of Mauremys reevesii. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodin, A.G.J.; Iverson, J.B.; Bour, R.; Fritz, U.; Dijk, P.P.V. Turtles of the World: Annotated Checklist and Atlas of Taxonomy, Synonymy, Distribution, and Conservation Status, 8th ed.; Chelonian Research Foundation: Lunenburg, MA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-5323-5026-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, J.Z.; Li, S.H.; Guo, G. Reflections and Suggestions on Turtle Farming. Fish. Guide Be Rich 2012, 9, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.L.; Yang, Y.K.; Li, T.; Yu, W.; Huang, Z.; Lin, H.Z.; Shu, H. Gonadal Development of First Sexual Maturation of Siganus oramin Cultured in Pond. South China Fish. Sci. 2020, 16, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Gan, X.; He, D.J.; Cheng, R.; Li, G.L.; Bi, J.Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Z.M. Study on Artificial Propagation and Embryonic Development Regularity of Discogobio multilineatus. South China Fish. Sci. 2025, 21, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; He, L.; Cheng, B.J.; Fang, C.L.; Yang, X.H.; Yu, Y.L.; Li, C.G. Research Progress on the Genetic Diversity of the Turtle in China. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2012, 51, 3937–3940. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.P.; Du, H.J.; Zhou, L.; Li, M.Y.; Gui, J.F. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Chinemys reevesii) by RAPD. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2005, 29, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.F. Analysis of Genetic Diversity Amongst Chinemys reevesii in Guangxi Using RAPD Markers. J. South. Agric. 2011, 42, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.N.; Du, W.G.; Zheng, R.Q.; Yang, G. Microsatellite DNA Analysis of Genetic Diversity Among Captive Breeding Stocks of Chinese Pond Turtle (Chinemys reevesii). J. Fish. China 2010, 34, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Cai, W.; Xia, X.; Nie, L. Genetic Diversity of the Captive Chinese Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii) Populations in China Assessed by Microsatellite Markers. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2019, 29, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, H.S.; Park, S.M.; Han, S.H. Mitochondrial Haplotype Distribution and Phylogenetic Relationship of an Endangered Species Reeve’s Turtle (Mauremys reevesii) in East Asia. J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2017, 10, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.D.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, X.H.; Hou, D.M.; Huang, H.W.; Li, C.H.; Rao, D.Q.; Li, Y.X. Genomic Insights into the Evolution of the Critically Endangered Soft-Shelled Turtle Rafetus swinhoei. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2022, 22, 1972–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Wang, Y.K.; Yuan, J.; Liu, F.; Hong, X.Y.; Yu, L.Y.; Chen, C.; Li, W.; Ni, W.; Liu, H.Y.; et al. Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of Asian Yellow Pond Turtle (Mauremys mutica) with Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination System. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7905–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Chen, M.Y.; Zeng, J.W.; Tu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.C.; Tan, M.L.; Wang, X.Q. Whole-Genome Resequencing Reveals Novel Sex-Related Markers and Candidate Gene in the Chinese Soft-Shelled Turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2024, 55, e13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannucci, A.; Benazzo, A.; Natali, C.; Arida, E.A.; Zein, M.S.A.; Jessop, T.S.; Bertorelle, G.; Ciofi, C. Population Structure, Genomic Diversity and Demographic History of Komodo Dragons Inferred from Whole-Genome Sequencing. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 6309–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, K.; Shirasawa, K. Fine-Scale Genetic Structure of the Rice Landrace Population in Japan. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2022, 297, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holsinger, K.E.; Weir, B.S. Genetics in Geographically Structured Populations: Defining, Estimating and Interpreting FST. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. Polymorphic Microsatellite Loci in Two Freshwater Turtles and Genetic Diversity Among Captive Breeding Stocks of Chinese Pond Turtle (Chinemys reevesii). Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Frankham, R. Stress and Adaptation in Conservation Genetics. J. Evol. Biol. 2005, 18, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, A.; Petrovic, S.; Harrisson, K.A.; Cartwright, K.; Dobson, E.; Hurley, L.L.; Lane, M.; Magrath, M.J.L.; Miller, K.A.; Quin, B.; et al. Benefits of Genetic Rescue of a Critically Endangered Subspecies from Another Subspecies Outweigh Risks: Results of Captive Breeding Trials. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 284, 110203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q. Selection Evaluation and Genetic Analysis for the Inner Shell Color and Growth Traits of the Purple Hyriopsis cumingii. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zanella, R.; Peixoto, J.O.; Cardoso, F.F.; Cardoso, L.L.; Biegelmeyer, P.; Cantão, M.E.; Otaviano, A.; Freitas, M.S.; Caetano, A.R.; Ledur, M.C. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Two Commercial Breeds of Pigs Using Genomic and Pedigree Data. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2016, 48, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.P.; Li, W.; Zhao, J.; Hong, X.Y. Method for Extracting DNA from Toenails to Amplify Full-Length Mitochondrial DNA of Cuora trifasciata. Chinese Patent CN103865921B, 20 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.X.; Chen, Y.S.; Shi, C.M.; Huang, Z.B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.K.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; et al. SOAPnuke: A MapReduce Acceleration-Supported Software for Integrated Quality Control and Preprocessing of High-Throughput Sequencing Data. GigaScience 2018, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoulatou, E.; Park, S.H.; Humphreys, D.T.; Ho, J.W. Verification and Validation of Bioinformatics Software Without a Gold Standard: A Case Study of BWA and Bowtie. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Dong, S.; Lv, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Meng, Z. ReSeq Tools: An Integrated Toolkit for Large-Scale Next-Generation Sequencing Based Resequencing Analysis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 6275–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Chang, P.C.; Hsu, C.; Hung, M.Z.; Chien, Y.H.; Hwu, W.L.; Lai, F.P.; Lee, N.C. Comparison of GATK and DeepVariant by Trio Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Cai, X.R.; Shang, J.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, J.X. SimHOEPI: A Resampling Simulator for Generating Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Data with a High-Order Epistasis Model. Quant. Biol. 2024, 12, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; Bakker, P.I.W.D.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, A.C.; Banks, E.; DePristo, A.M.; Handsaker, E.R.; Lunter, G.; Marth, T.G.; Sherry, T.S.; et al. The Variant Call Format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.H.; Lange, K. Enhancements to the ADMIXTURE Algorithm for Individual Ancestry Estimation. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, R.M. Pophelper: An R Package and Web App to Analyse and Visualize Population Structure. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retief, J.D. Phylogenetic Analysis Using PHYLIP. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 243–258. [Google Scholar]
| Group | Average Sequencing Number | Average Coverage (%) | Average Sequencing Depth (X) | Average Genome Mapping Rate (%) | GC Content (%) | Q30 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JS | 224,348,094 | 92.51 | 12.83 | 99.87 | 44.25 | 92.16 |
| WW | 233,554,144 | 92.53 | 13.36 | 99.87 | 44.30 | 93.28 |
| ZQ | 226,259,694 | 92.66 | 12.95 | 99.83 | 44.11 | 91.21 |
| CH | 211,544,440 | 92.30 | 11.83 | 98.54 | 44.08 | 92.20 |
| PX | 234,143,127 | 92.46 | 13.37 | 99.83 | 44.35 | 92.10 |
| YY | 218,711,083 | 92.40 | 12.51 | 99.83 | 44.07 | 92.46 |
| MM | 219,780,573 | 92.35 | 12.43 | 99.75 | 44.06 | 90.86 |
| HZ | 212,729,708 | 92.57 | 12.17 | 99.87 | 44.10 | 91.27 |
| Group | ALL SNP | Ho (Homozygous) | He (Heterozygous) |
|---|---|---|---|
| JS | 14,480,096 | 4,634,133 (32.36%) | 9,845,963 (67.64%) |
| WW | 14,473,593 | 4,593,932 (31.91%) | 9,879,661 (68.09%) |
| ZQ | 14,114,857 | 4,705,758 (33.35%) | 9,409,099 (66.65%) |
| CH | 15,505,440 | 4,705,754 (32.14%) | 10,799,687 (67.86%) |
| PX | 15,451,204 | 4,790,993 (31.45%) | 10,660,212 (68.55%) |
| YY | 14,364,542 | 4,712,537 (32.91%) | 9,652,005 (67.09%) |
| MM | 18,170,044 | 4,854,866 (26.94%) | 13,315,177 (73.06%) |
| HZ | 14,021,985 | 4,725,572 (33.73%) | 9,296,413 (66.27%) |
| Group | Nucleotide Diversity (π) | Inbreeding Coefficient (FHOM) | Polymorphism Information Content (PIC) | Observed Heterozygosity (Ho) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JS | 0.0000373078 | 0.01050 ± 0.10593 | 0.14014 ± 0.01500 | 0.27958 ± 0.02993 |
| WW | 0.000037696 | −0.01454 ± 0.11163 | 0.14379 ± 0.01581 | 0.28666 ± 0.03153 |
| ZQ | 0.000037056 | 0.03127 ± 0.02436 | 0.13721 ± 0.00353 | 0.27370 ± 0.00691 |
| CH | 0.0000369813 | 0.04064 ± 0.05698 | 0.13583 ± 0.00821 | 0.27099 ± 0.01627 |
| PX | 0.0000379257 | 0.00114 ± 0.06090 | 0.14147 ± 0.00849 | 0.28224 ± 0.01724 |
| YY | 0.0000372213 | 0.03081 ± 0.03405 | 0.13725 ± 0.00491 | 0.27382 ± 0.00966 |
| MM | 0.0000358555 | −0.05729 ± 0.08055 | 0.14942 ± 0.01142 | 0.29875 ± 0.02280 |
| HZ | 0.0000369261 | 0.04325 ± 0.03725 | 0.13546 ± 0.00539 | 0.27028 ± 0.01060 |
| WW | PX | ZQ | JS | CH | HZ | YY | MM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WW | — | |||||||
| PX | 0.00692 | — | ||||||
| ZQ | 0.00104 | 0.00726 | — | |||||
| JS | 0.00119 | 0.00807 | 0.00205 | — | ||||
| CH | 0.00191 | 0.00608 | 0.00242 | 0.00193 | — | |||
| HZ | 0.00093 | 0.00684 | 0.00043 | 0.00242 | 0.00266 | — | ||
| YY | 0.00063 | 0.00545 | 0.00103 | 0.00181 | 0.00139 | 0.00081 | — | |
| MM | 0.04681 | 0.02500 | 0.04684 | 0.04758 | 0.04329 | 0.04608 | 0.04405 | — |
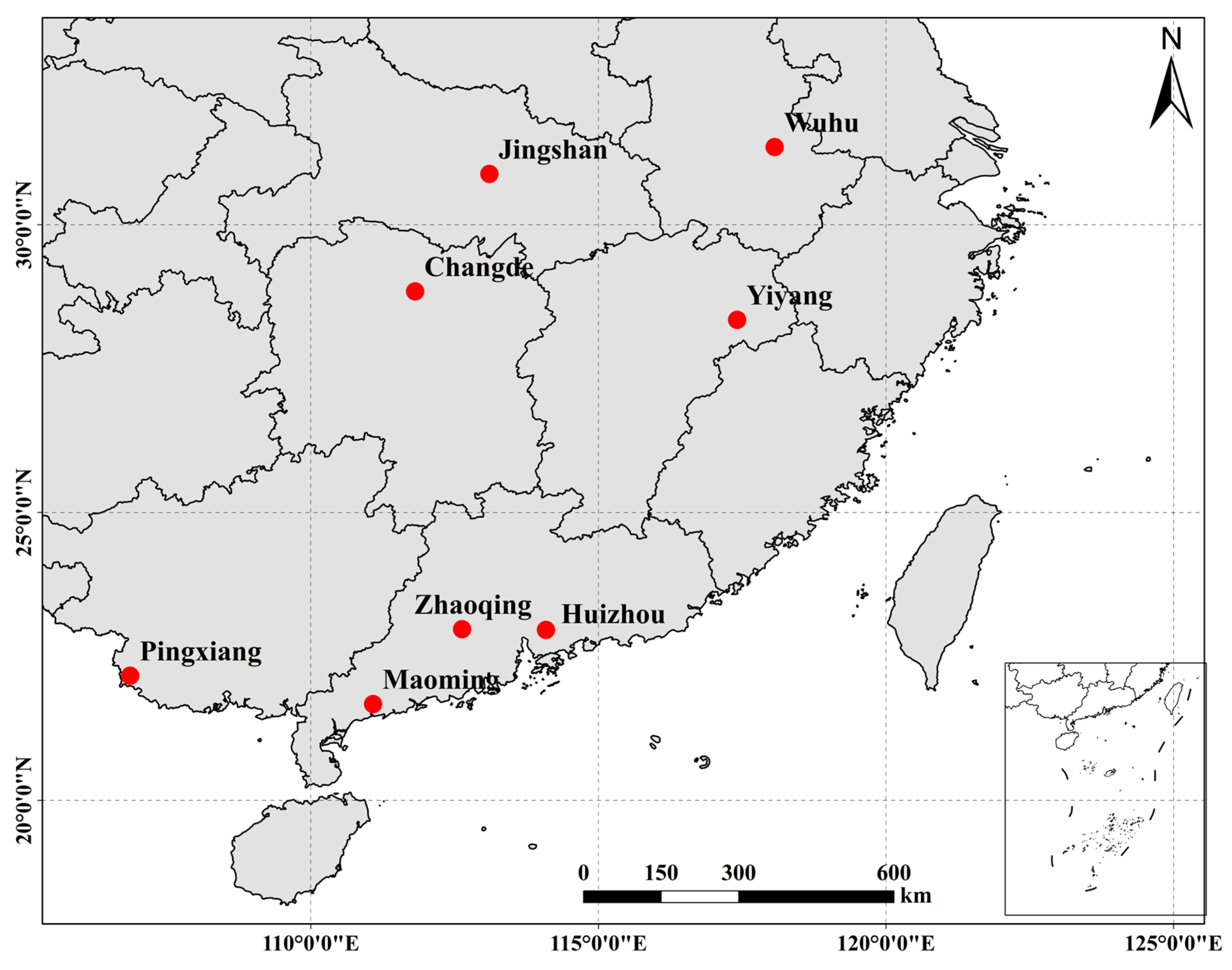
| Sampling Sites (Abbreviation Used) | Day/Month/Year | Sample Locality | GPS Coordinates | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuwei (WW) | 2 July 2021 | Wuhu city, Anhui province | 31°35′ N, 118°06′ E | 30 |
| Jingshan (JS) | 5 November 2021 | Jingshan City, Hubei Province | 30°88′ N, 113°11′ E | 30 |
| Yiyang (YY) | 1 November 2021 | Yiyang County, Jiangxi Province | 28°35′ N, 117°41′ E | 28 |
| Zhaoqing (ZQ) | 29 October 2021 | Zhaoqing City, Guangdong Province | 22°97′ N, 112°63′ E | 30 |
| Huizhou (HZ) | 28 October 2021 | Huizhou City, Guangdong Province | 22°86′ N, 113°68′ E | 30 |
| Maoming (MM) | 25 October 2021 | Maoming City, Guangdong Province | 21°67′ N, 111°09′ E | 30 |
| Changhan (CH) | 2 November 2021 | Changde City, Hunan Province | 28°84′ N, 111°82′ E | 30 |
| Pingxiang (PX) | 9 November 2021 | Pingxiang City, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous region | 22°16′ N, 106°86′ E | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Hong, X.; Chen, C.; Ji, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, B.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125614
Zhou C, Xu H, Liu H, Li J, Li W, Hong X, Chen C, Ji L, Zhu X, Zhao B, et al. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125614
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Chenyao, Haoyang Xu, Haiyang Liu, Jipeng Li, Wei Li, Xiaoyou Hong, Chen Chen, Liqin Ji, Xinping Zhu, Bo Zhao, and et al. 2025. "Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125614
APA StyleZhou, C., Xu, H., Liu, H., Li, J., Li, W., Hong, X., Chen, C., Ji, L., Zhu, X., Zhao, B., & Liu, X. (2025). Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of the Chinese Three-Keeled Pond Turtle (Mauremys reevesii). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5614. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125614






