Precision Oncology Framework Using Circulating Tumor Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
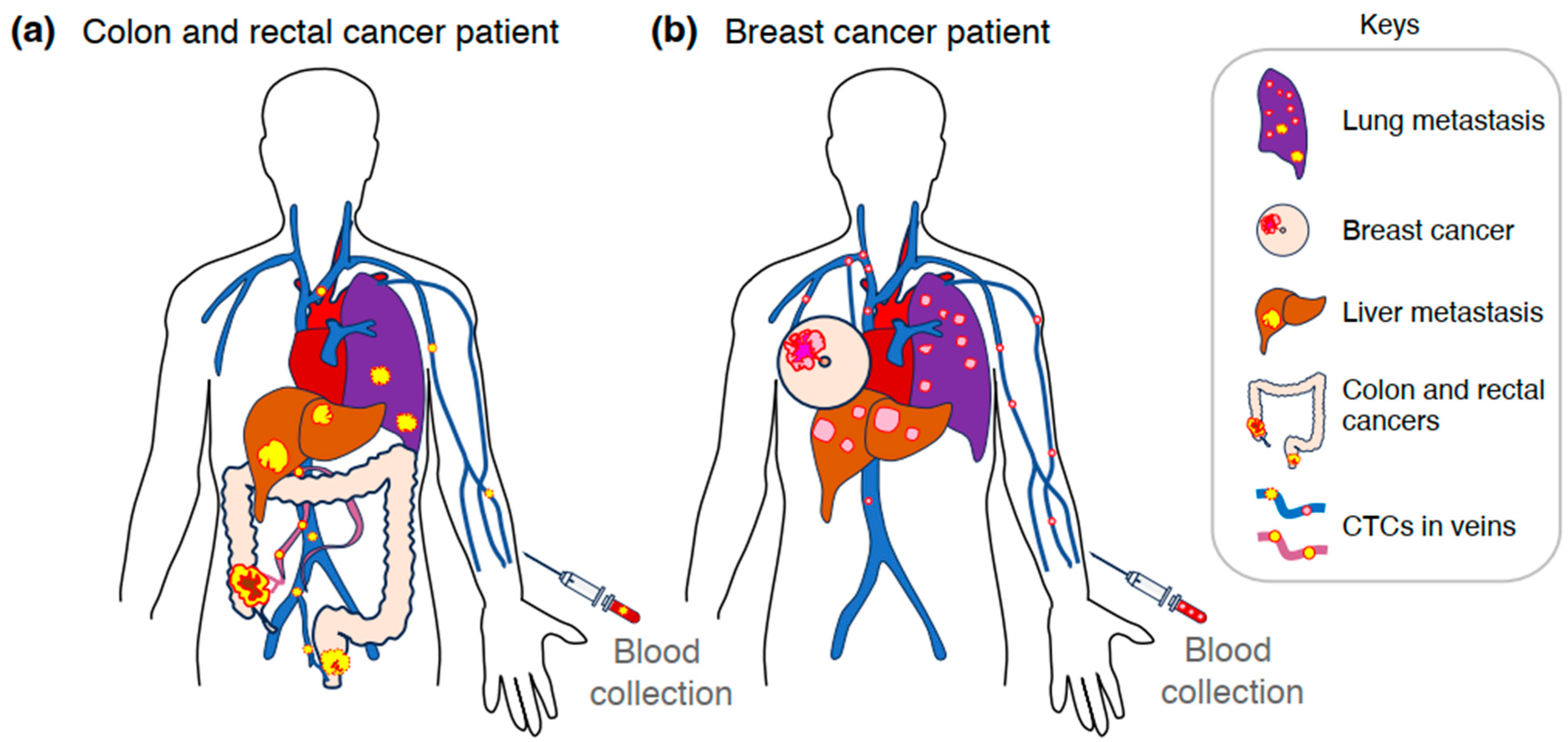
2. CTCs in the Metastatic Process
3. Heterogeneity and Molecular Pathology of CTCs
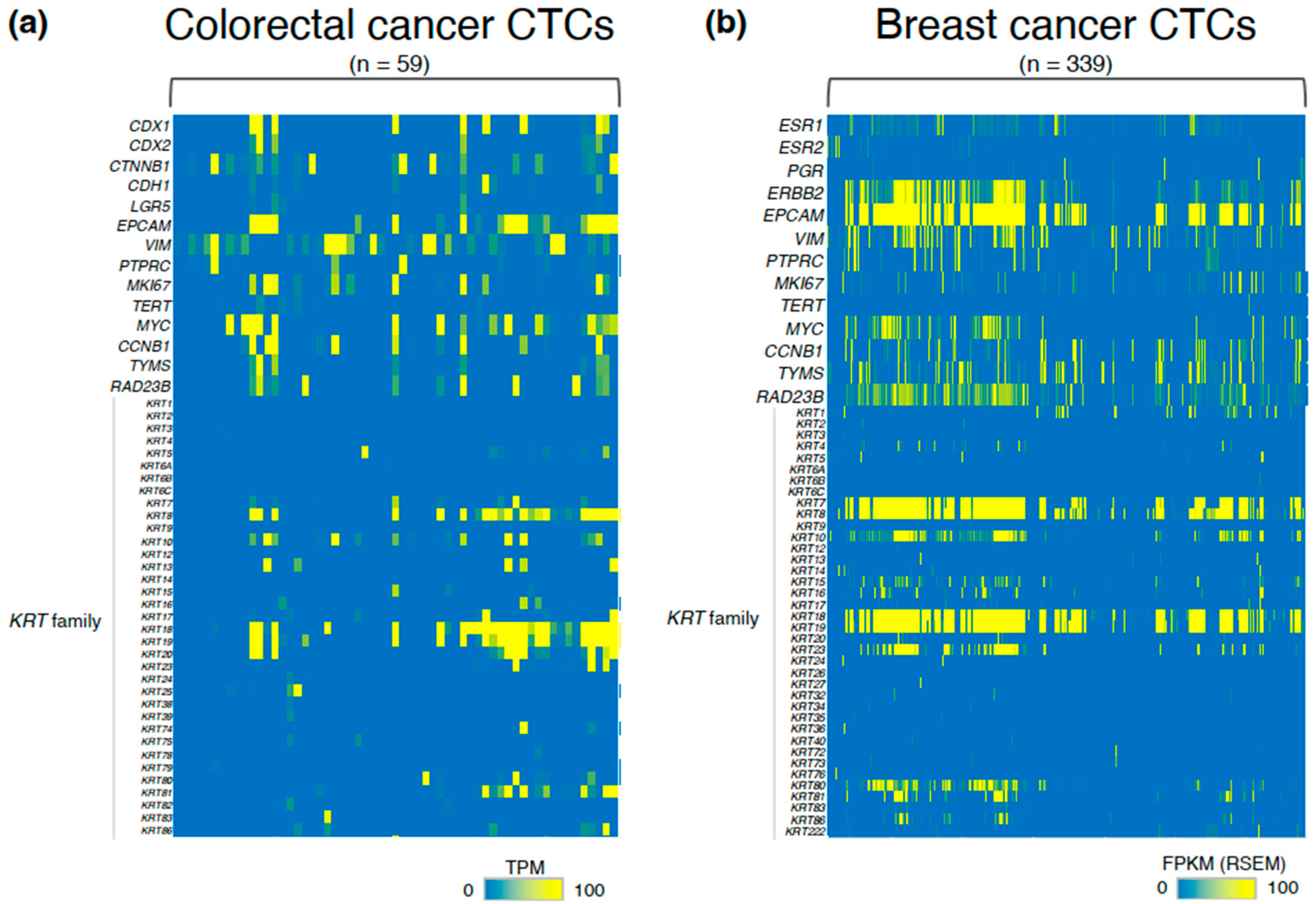
4. CTCs as Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers in Cancer Therapy
5. Feasibility of the CTC Test: A Comparison with the ctDNA Test
6. CTC Separation Techniques
6.1. Size-Based Separation, Including Hydrodynamic Methods
6.2. Density-Based Separation
6.3. Immunoseparation
6.4. Acoustic Separation
6.5. Dielectrophoresis (DEP)
| Separation Technique | Separation Principle | Advantages | Representative Systems | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size-based (including hydrodynamic) | Filtration, microchannel constrictions, inertial microfluidics | Simple, high-throughput, label-free | ClearCell FX1, CROSSORTER, CTC-iChip 1, ISET, Parsortix, VTX-1 | [98,99,100, 106,107,109, 117,118] |
| Density-based | Centrifugation, gradient | Simple, scalable | Ficoll, OncoQuick, RosetteSep | [110,111,119] |
| Immunoseparation | Positive/negative selection | High selectivity, specificity | AdnaTest 2, CellSearch 2, CTC-iChip, GEDI Chip, HB-chip, MagSweeper 2 | [62,106,107, 113,120,121,122] |
| Acoustic-based | Ultrasonic field | Non-invasive, label-free | AcouTrap 3 | [114] |
| DEP-based | Dielectrophoresis | Label-free, precise control | Apostream, CROSSORTER 4, DEPArray, 3DEP | [99,115,116, 122] |
7. Low-Damage CTC Isolation Systems
8. Current Challenges
- (1)
- Definition of CTCs using both gene expression and mutation profiles.
- (2)
- Standardization of CTC isolation devices and protocols.
- (3)
- Formulation of guidelines by an international consortium.
9. Precision Oncology Framework Using CTCs
10. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APC | Adenomatous polyposis coli |
| BRAF | V-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B |
| CA15-3 | Carbohydrate antigen 15-3 |
| CA19-9 | Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 |
| CCNB1 | Cyclin B1 |
| CD8 | Cluster of differentiation 8 |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic Antigen |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CR | Complete response |
| CSV | Cell-surface vimentin |
| CTC | Circulating tumor cell |
| CTC-Chip | Circulating tumor cell chip |
| CTC-iChip | Circulating tumor cell inertial chip |
| ctDNA | Circulating tumor DNA |
| DEP | Dielectrophoresis |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| DTC | Disseminated tumor cell |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| EPCAM | Epithelial cell adhesion molecule |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| ESR1 | Estrogen receptor 1 |
| FASL | Fas ligand |
| FDA | The United States Food and Drug Administration |
| FOLFOX | Folinic acid, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin |
| FOLFOXIRI | Folinic acid, fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan |
| HER2 | human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| ISET | Isolation by Size of Epithelial Tumor Cells |
| MKI67 | Marker of proliferation Ki-67 |
| MRD | Minimal/molecular residual disease |
| MYC | Myelocytomatosis oncogene |
| NK | Natural killer |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| KRT | Keratin |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
| PIK3C2G | Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit type 2 gamma |
| PME | Pre-metastatic niche |
| PR | Partial response |
| qPCR | quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RAD23B | RAD23 homolog B |
| SD | Stable disease |
| SMAD4 | SMAD family member 4 |
| TAM | Tumor-associated macrophage |
| TERT | Telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TNM | Tumor, node, and metastasis |
| TP53 | Tumor protein 53 |
| TYMS | Thymidylate synthase |
| VIM | Vimentin |
References
- Le Tourneau, C.; Borcoman, E.; Kamal, M. Molecular profiling in precision medicine oncology. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, L.R.; Seoane, J.; Le Tourneau, C.; Siu, L.L.; Marais, R.; Michiels, S.; Soria, J.C.; Campbell, P.; Normanno, N.; Scarpa, A.; et al. The European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Precision Medicine Glossary. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, J.; Steuten, L.; Aftimos, P.; André, F.; Davies, M.; Garralda, E.; Geissler, J.; Husereau, D.; Martinez-Lopez, I.; Normanno, N.; et al. Delivering precision oncology to patients with cancer. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veyrune, L.; Naumann, D.N.; Christou, N. Circulating Tumour Cells as Prognostic Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Ding, P.; Pei, R.; Wang, Q.; Xing, C. Circulating tumor cells in colorectal cancer in the era of precision medicine. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix-Panabières, C. Clinical Applications of Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA as Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabisiewicz, A.; Szostakowska-Rodzos, M.; Grzybowska, E.A. Improving the Prognostic and Predictive Value of Circulating Tumor Cell Enumeration: Is Longitudinal Monitoring the Answer? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodon, J.; Soria, J.-C.; Berger, R.; Miller, W.H.; Rubin, E.; Kugel, A.; Tsimberidou, A.; Saintigny, P.; Ackerstein, A.; Braña, I.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic profiling expands precision cancer medicine: The WINTHER trial. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.A.; Liu, M.C.; Aleshin, A. Practical recommendations for using ctDNA in clinical decision making. Nature 2023, 619, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, I.J. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: The ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Hu, J.; Yang, D.; Cosgrove, D.P.; Xu, R. Pattern of distant metastases in colorectal cancer: A SEER based study. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38658–38666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riihimäki, M.; Hemminki, A.; Sundquist, J.; Hemminki, K. Patterns of metastasis in colon and rectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Hoffmann, A.D.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Organotropism: New insights into molecular mechanisms of breast cancer metastasis. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Zhang, H.; Matei, I.R.; Costa-Silva, B.; Hoshino, A.; Rodrigues, G.; Psaila, B.; Kaplan, R.N.; Bromberg, J.F.; Kang, Y.; et al. Pre-metastatic niches: Organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Qian, B.-Z.; Pollard, J.W. Immune cell promotion of metastasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patras, L.; Shaashua, L.; Matei, I.; Lyden, D. Immune determinants of the pre-metastatic niche. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 546–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, T. Tumour-associated macrophages as a potential target to improve natural killer cell-based immunotherapies. Essays Biochem. 2023, 67, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Fidler, I.J. Metastasis: Quantitative analysis of distribution and fate of tumor embolilabeled with 125 I-5-iodo-2’-deoxyuridine. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1970, 45, 773–782. [Google Scholar]
- Follain, G.; Herrmann, D.; Harlepp, S.; Hyenne, V.; Osmani, N.; Warren, S.C.; Timpson, P.; Goetz, J.G. Fluids and their mechanics in tumour transit: Shaping metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.A.; Miller, J.S. Exploring the NK cell platform for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridlender, Z.G.; Sun, J.; Kim, S.; Kapoor, V.; Cheng, G.; Ling, L.; Worthen, G.S.; Albelda, S.M. Polarization of Tumor-Associated Neutrophil Phenotype by TGF-β: “N1” versus “N2” TAN. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczerba, B.M.; Castro-Giner, F.; Vetter, M.; Krol, I.; Gkountela, S.; Landin, J.; Scheidmann, M.C.; Donato, C.; Scherrer, R.; Singer, J.; et al. Neutrophils escort circulating tumour cells to enable cell cycle progression. Nature 2019, 566, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.M.; Lynch, C.C. How circulating tumor cluster biology contributes to the metastatic cascade: From invasion to dissemination and dormancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023, 42, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, N.; Bardia, A.; Miyamoto, T.D.; Donaldson, C.M.; Wittner, S.B.; Spencer, A.J.; Yu, M.; Pely, A.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters Are Oligoclonal Precursors of Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cell 2014, 158, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, A.-M.; Jansson, S.; Bendahl, P.-O.; Levin Tykjaer Jörgensen, C.; Loman, N.; Graffman, C.; Lundgren, L.; Aaltonen, K.; Rydén, L. Longitudinal enumeration and cluster evaluation of circulating tumor cells improve prognostication for patients with newly diagnosed metastatic breast cancer in a prospective observational trial. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, S.Y.; Nakayama, M.; Morita, A.; Oshima, H.; Oshima, M. Genetic and nongenetic mechanisms for colorectal cancer evolution. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 3478–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, K.; Alix-panabières, C.; Riethdorf, S. Cancer micrometastases. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wu, H. The significant prognostic value of circulating tumor cells in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2018, 42, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, J.G.; Baretti, M.; Gerold, J.M.; Makohon-Moore, A.P.; Daud, A.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Azad, N.S.; Kinzler, K.W.; Nowak, M.A.; Vogelstein, B. An analysis of genetic heterogeneity in untreated cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menyailo, M.E.; Tretyakova, M.S.; Denisov, E.V. Heterogeneity of Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer: Identifying Metastatic Seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crucitta, S.; Crucitta, S.; Cucchiara, F.; Mathijssen, R.; Mateo, J.; Jager, A.; Joosse, A.; Passaro, A.; Attili, I.; Petrini, I.; et al. Treatment-driven tumour heterogeneity and drug resistance: Lessons from solid tumours. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 104, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asleh, K.; Riaz, N.; Nielsen, T.O. Heterogeneity of triple negative breast cancer: Current advances in subtyping and treatment implications. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoudi González, N.; Salvà, F.; Ros, J.; Baraibar, I.; Rodríguez-Castells, M.; García, A.; Alcaráz, A.; Vega, S.; Bueno, S.; Tabernero, J.; et al. Unravelling the Complexity of Colorectal Cancer: Heterogeneity, Clonal Evolution, and Clinical Implications. Cancers 2023, 15, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, E.R.; Bert, V. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 1991, 61, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, T.; Kometani, K.; Hashida, H.; Matsunaga, A.; Miyoshi, H.; Hosogi, H.; Aoki, M.; Oshima, M.; Hattori, M.; Takabayashi, A.; et al. SMAD4-deficient intestinal tumors recruit CCR1+ myeloid cells that promote invasion. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, B.; Siena, S. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopalan, H.; Bardelli, A.; Lengauer, C.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Velculescu, V.E. RAF/RAS oncogenes and mismatch-repair status. Nature 2002, 418, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillet, F.; Bayet, E.; Villeronce, O.; Zappia, L.; Lagerqvist, E.L.; Lunke, S.; Charafe-Jauffret, E.; Pham, K.; Molck, C.; Rolland, N.; et al. Circulating tumour cells from patients with colorectal cancer have cancer stem cell hallmarks in ex vivo culture. Gut 2017, 66, 1802–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, M.; Miyake, Y.; Inoue, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Noda, N.; Kouda, S.; Hata, T.; Ogino, T.; Miyoshi, N.; Takahashi, H.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells from Patients with Colorectal Cancer Captured with a Dielectrophoresis-Based Micropore System. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misale, S.; Yaeger, R.; Hobor, S.; Scala, E.; Janakiraman, M.; Liska, D.; Valtorta, E.; Schiavo, R.; Buscarino, M.; Siravegna, G.; et al. Emergence of KRAS mutations and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Nature 2012, 486, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Jr, L.A.; Williams, R.T.; Wu, J.; Kinde, I.; Hecht, J.R.; Berlin, J.; Allen, B.; Bozic, I.; Reiter, J.G.; Nowak, M.A.; et al. The molecular evolution of acquired resistance to targeted EGFR blockade in colorectal cancers. Nature 2012, 486, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeselsohn, R.; Buchwalter, G.; De Angelis, C.; Brown, M.; Schiff, R. ESR1 mutations--a mechanism for acquired endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Weigelt, B.; Cortes, J.; Won, H.H.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Nuciforo, P.; Bidard, F.-C.; Aura, C.; Saura, C.; Peg, V.; et al. Capturing intra-tumor genetic heterogeneity by de novo mutation profiling of circulating cell-free tumor DNA: A proof-of-principle. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Ciruelos, E.; Rubovszky, G.; Campone, M.; Loibl, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Iwata, H.; Conte, P.; Mayer, I.A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-Mutated, Hormone Receptor–Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.R.; Wu, Y.-M.; Vats, P.; Su, F.; Lonigro, R.J.; Cao, X.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Wang, R.; Ning, Y.; Hodges, L.; et al. Activating ESR1 mutations in hormone-resistant metastatic breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Chen, W.-D.; Parmigiani, G.; Diehl, F.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Antal, T.; Traulsen, A.; Nowak, M.A.; Siegel, C.; Velculescu, V.E.; et al. Comparative lesion sequencing provides insights into tumor evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4283–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuka, M.; Battaglin, F.; Jayachandran, P.; Wang, J.; Arai, H.; Soni, S.; Zhang, W.; Hirai, M.; Matsusaka, S.; Lenz, H.-J. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cell Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer by Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing. Cancers 2021, 13, 4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkountela, S.; Castro-Giner, F.; Szczerba, B.M.; Vetter, M.; Landin, J.; Scherrer, R.; Krol, I.; Scheidmann, M.C.; Beisel, C.; Stirnimann, C.U.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clustering Shapes DNA Methylation to Enable Metastasis Seeding. Cell 2019, 176, 98–112.e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Madden, M.W.; Donaldson, M.C.; Desai, R.; Zhu, H.; Comaills, V.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Ex vivo culture of circulating breast tumor cells for individualized testing of drug susceptibility. Science 2014, 345, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarioglu, A.F.; Aceto, N.; Kojic, N.; Donaldson, M.C.; Zeinali, M.; Hamza, B.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Miyamoto, D.T.; et al. A microfluidic device for label-free, physical capture of circulating tumor cell clusters. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, N.V.; Bardia, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Benes, C.; Ligorio, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, M.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Licausi, J.A.; Desai, R.; et al. HER2 expression identifies dynamic functional states within circulating breast cancer cells. Nature 2016, 537, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, N.; Bardia, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Donaldson, M.C.; O’Keefe, R.; Engstrom, A.; Bersani, F.; Zheng, Y.; Comaills, V.; Niederhoffer, K.; et al. AR Expression in Breast Cancer CTCs Associates with Bone Metastases. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satelli, A.; Mitra, A.; Cutrera, J.J.; Devarie, M.; Xia, X.; Ingram, D.R.; Dibra, D.; Somaiah, N.; Torres, K.E.; Ravi, V.; et al. Universal Marker and Detection Tool for Human Sarcoma Circulating Tumor Cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satelli, A.; Mitra, A.; Brownlee, Z.; Xia, X.; Bellister, S.; Overman, M.J.; Kopetz, S.; Ellis, L.M.; Meng, Q.H.; Li, S. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transitioned Circulating Tumor Cells Capture for Detecting Tumor Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satelli, A.; Batth, I.S.; Brownlee, Z.; Rojas, C.; Meng, Q.H.; Kopetz, S.; Li, S. Potential role of nuclear PD-L1 expression in cell-surface vimentin positive circulating tumor cells as a prognostic marker in cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Yang, M.; Peng, T.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y. Evaluation of cell surface vimentin positive circulating tumor cells as a prognostic biomarker for stage III/IV colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, V.; Stahmann, N.; Riethdorf, S.; Rau, T.; Zabel, T.; Goetz, A.; Jänicke, F.; Pantel, K. Circulating tumor cells in breast cancer: Correlation to bone marrow micrometastases, heterogeneous response to systemic therapy and low proliferative activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3678–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliotaki, M.; Mavroudis, D.; Kapranou, K.; Markomanolaki, H.; Kallergi, G.; Koinis, F.; Kalbakis, K.; Georgoulias, V.; Agelaki, S. Evaluation of proliferation and apoptosis markers in circulating tumor cells of women with early breast cancer who are candidates for tumor dormancy. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, A.A.; Talasaz, A.H.; Zhang, H.; Coram, M.A.; Reddy, A.; Deng, G.; Telli, M.L.; Advani, R.H.; Carlson, R.W.; Mollick, J.A.; et al. Single Cell Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells: Transcriptional Heterogeneity and Diversity from Breast Cancer Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Toom, E.E.; Verdone, J.E.; Gorin, M.A.; Pienta, K.J. Technical challenges in the isolation and analysis of circulating tumor cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62754–62766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Li, T.; Luo, J.; Dong, D. ctcRbase: The gene expression database of circulating tumor cells and microemboli. Database 2020, 2020, baaa020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Hu, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, B.; Yuan, H. Circulating tumor cells as an independent prognostic factor in advanced colorectal cancer: A retrospective study in 121 patients. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2019, 34, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Kiavue, N.; Ychou, M.; Cabel, L.; Stern, M.-H.; Madic, J.; Saliou, A.; Rampanou, A.; Decraene, C.; Bouché, O.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells and Circulating Tumor DNA Detection in Potentially Resectable Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Prospective Ancillary Study to the Unicancer Prodige-14 Trial. Cells 2019, 8, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Kou, T.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z. Prognostic models based on postoperative circulating tumor cells can predict poor tumor recurrence-free survival in patients with stage II-III colorectal cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4552–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Lai, W.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, H.; Lan, Q.; Chu, Z.; Chu, Z. Mesenchymal and Phosphatase of Regenerating Liver-3 Status in Circulating Tumor Cells May Serve as a Crucial Prognostic Marker for Assessing Relapse or Metastasis in Postoperative Patients With Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsusaka, S.; Suenaga, M.; Mishima, Y.; Kuniyoshi, R.; Takagi, K.; Terui, Y.; Mizunuma, N.; Hatake, K. Circulating tumor cells as a surrogate marker for determining response to chemotherapy in Japanese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.; Meropol, N.J.; Punt, C.J.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.A.; Mitchell, E.; et al. Relationship among circulating tumor cells, CEA and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, J.; Vidaurreta, M.; Gómez, A.; Rivera, F.; Massutí, B.; López, M.R.; Abad, A.; Gallen, M.; Benavides, M.; Aranda, E.; et al. Prognostic Value of the Combination of Circulating Tumor Cells Plus KRAS in Patients With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated With Chemotherapy Plus Bevacizumab. Clin. Color. Cancer 2013, 12, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, E.; Viéitez, J.M.; Gómez-España, A.; Gil Calle, S.; Salud-Salvia, A.; Graña, B.; Garcia-Alfonso, P.; Rivera, F.; Quintero-Aldana, G.A.; Reina-Zoilo, J.J.; et al. FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab versus FOLFOX plus bevacizumab for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer and ≥3 circulating tumour cells: The randomised phase III VISNÚ-1 trial. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.G.; Renehan, A.G.; Backen, A.; Gollins, S.; Chau, I.; Hasan, J.; Valle, J.W.; Morris, K.; Beech, J.; Ashcroft, L.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Enumeration in a Phase II Trial of a Four-Drug Regimen in Advanced Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Color. Cancer 2015, 14, 115–122.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Ureña, M.; Ortega, F.G.; De Miguel-Pérez, D.; Rodriguez-Martínez, A.; García-Puche, J.L.; Ilyine, H.; Lorente, J.A.; Exposito-Hernandez, J.; Garrido-Navas, M.C.; Delgado-Ramirez, M.; et al. Circulating tumor cells criteria (CyCAR) versus standard RECIST criteria for treatment response assessment in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncarelli Flores, B.C.; Souza E Silva, V.; Ali Abdallah, E.; Mello, C.A.L.; Gobo Silva, M.L.; Gomes Mendes, G.; Camila Braun, A.; Aguiar Junior, S.; Thomé Domingos Chinen, L. Molecular and Kinetic Analyses of Circulating Tumor Cells as Predictive Markers of Treatment Response in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Patients. Cells 2019, 8, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mego, M.; Karaba, M.; Minarik, G.; Benca, J.; Silvia, J.; Sedlackova, T.; Manasova, D.; Kalavska, K.; Pindak, D.; Cristofanilli, M.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells With Epithelial–to–mesenchymal Transition Phenotypes Associated with Inferior Outcomes in Primary Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magbanua, M.J.M.; Yau, C.; Wolf, D.M.; Lee, J.S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Scott, J.H.; Bowlby-Yoder, E.; Hwang, E.S.; Alvarado, M.; Ewing, C.A.; et al. Synchronous Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Blood and Disseminated Tumor Cells in Bone Marrow Predicts Adverse Outcome in Early Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5388–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini Silveira, A.; Bidard, F.-C.; Tanguy, M.-L.; Girard, E.; Trédan, O.; Dubot, C.; Jacot, W.; Goncalves, A.; Debled, M.; Levy, C.; et al. Multimodal liquid biopsy for early monitoring and outcome prediction of chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magbanua, M.J.M.; Hendrix, L.H.; Hyslop, T.; Barry, W.T.; Winer, E.P.; Hudis, C.; Toppmeyer, D.; Carey, L.A.; Partridge, A.H.; Pierga, J.-Y.; et al. Serial Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells in Metastatic Breast Cancer Receiving First-Line Chemotherapy. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Michiels, S.; Riethdorf, S.; Mueller, V.; Esserman, L.J.; Lucci, A.; Naume, B.; Horiguchi, J.; Gisbert-Criado, R.; Sleijfer, S.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells in Breast Cancer Patients Treated by Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, C.; Miao, J.; Dolce, E.M.; Darga, E.P.; Repollet, M.I.; Doyle, G.V.; Gralow, J.R.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Smerage, J.B.; Barlow, W.E.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Clusters in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A SWOG S0500 Translational Medicine Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6089–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magbanua, M.J.M.; Savenkov, O.; Asmus, E.J.; Ballman, K.V.; Scott, J.H.; Park, J.W.; Dickler, M.; Partridge, A.; Carey, L.A.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Clinical Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells in Hormone Receptor-positive Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients who Received Letrozole with or Without Bevacizumab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4911–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shliakhtunou, Y.A. CTCs-oriented adjuvant personalized cytostatic therapy non-metastatic breast cancer patients: Continuous non-randomized prospective study and prospective randomized controlled study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 186, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Mu, Z.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Abu-Khalaf, M.M.; Silver, D.P.; Palazzo, J.P.; Jagannathan, G.; Fellin, F.M.; Bhattacharya, S.; et al. Prognostic value of HER2 status on circulating tumor cells in advanced-stage breast cancer patients with HER2-negative tumors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 181, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Peeters, D.J.; Fehm, T.; Nolé, F.; Gisbert-Criado, R.; Mavroudis, D.; Grisanti, S.; Generali, D.; Garcia-Saenz, J.A.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Clinical validity of circulating tumour cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer: A pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smerage, J.B.; Barlow, W.E.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Winer, E.P.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Srkalovic, G.; Tejwani, S.; Schott, A.F.; O’Rourke, M.A.; Lew, D.L.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells and Response to Chemotherapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer: SWOG S0500. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiopoulou, D.; Markou, A.; Strati, A.; Zavridou, M.; Tzanikou, E.; Mastoraki, S.; Kallergi, G.; Georgoulias, V.; Lianidou, E. Comprehensive liquid biopsy analysis as a tool for the early detection of minimal residual disease in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radovich, M.; Jiang, G.; Hancock, B.A.; Chitambar, C.; Nanda, R.; Falkson, C.; Lynce, F.C.; Gallagher, C.; Isaacs, C.; Blaya, M.; et al. Association of Circulating Tumor DNA and Circulating Tumor Cells After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy With Disease Recurrence in Patients With Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerratana, L.; Davis, A.A.; Polano, M.; Zhang, Q.; Shah, A.N.; Lin, C.; Basile, D.; Toffoli, G.; Wehbe, F.; Puglisi, F.; et al. Understanding the organ tropism of metastatic breast cancer through the combination of liquid biopsy tools. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 143, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patelli, G.; Vaghi, C.; Tosi, F.; Mauri, G.; Amatu, A.; Massihnia, D.; Ghezzi, S.; Bonazzina, E.; Bencardino, K.; Cerea, G.; et al. Liquid Biopsy for Prognosis and Treatment in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Circulating Tumor Cells vs Circulating Tumor DNA. Target. Oncol. 2021, 16, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanikou, E.; Markou, A.; Politaki, E.; Koutsopoulos, A.; Psyrri, A.; Mavroudis, D.; Georgoulias, V.; Lianidou, E. PIK3CA hotspot mutations in circulating tumor cells and paired circulating tumor DNA in breast cancer: A direct comparison study. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 2515–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Oki, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Yuda, J.; Shibuki, T.; Bando, H.; Yoshino, T. Bridging horizons beyond CIRCULATE-Japan: A new paradigm in molecular residual disease detection via whole genome sequencing-based circulating tumor DNA assay. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 29, 495–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, J.R.M.; Bartha, G.; Abbott, C.W.; Boyle, S.M.; Karasaki, T.; Li, B.; Chen, R.; Harris, J.; Veeriah, S.; Colopi, M.; et al. Ultrasensitive ctDNA detection for preoperative disease stratification in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese Promotion Council for Laboratory Testing. Perspectives on Quality Assurance of ctDNA Testing. 2022. Available online: https://www.jpclt.org/message/#ctDNA (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Riethdorf, S. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in Peripheral Blood of Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Validation Study of the CellSearch System. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.X.; Sun, Y.F.; Jin, W.X.; Cheng, J.W.; Peng, H.X.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, K.Q.; Chen, L.M.; Huang, K.; Wu, S.Y.; et al. Circulating tumor cell detection and single-cell analysis using an integrated workflow based on ChimeraX®-i120 Platform: A prospective study. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 2345–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Tumor Cells Circulate in the Peripheral Blood of All Major Carcinomas but not in Healthy Subjects or Patients With Nonmalignant Diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccioli, M.; Kim, K.; Khazan, N.; Khoury, J.D.; Cooke, M.J.; Miller, M.C.; O’Shannessy, D.J.; Pailhes-Jimenez, A.-S.; Moore, R.G. Identification of circulating tumor cells captured by the FDA-cleared Parsortix® PC1 system from the peripheral blood of metastatic breast cancer patients using immunofluorescence and cytopathological evaluations. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, K.; Wakizaka, Y.; Takano, M.; Itoi, T.; Ohge, H.; Koba, K.; Yarimizu, K.; Fujiyoshi, S.; Maruyama, F. Fabrication of a new all-in-one microfluidic dielectrophoresis integrated chip and living cell separation. iScience 2022, 25, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Wu, L.; Tay, A.K.P.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Ultra-fast, label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood using spiral microfluidics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zou, K.; Zheng, L.; Xiong, B. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of circulating tumor cells detected by RT-PCR in non-metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, T.R. A case of cancer in which cells similar to those in the tumours were seen in the blood after death. Aust. Med. J. 1869, 14, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Leon, S.A.; Shapiro, B.; Sklaroff, D.M.; Yaros, M.J. Free DNA in the serum of cancer patients and the effect of therapy. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 646–650. [Google Scholar]
- Descamps, L.; Le Roy, D.; Deman, A.-L. Microfluidic-Based Technologies for CTC Isolation: A Review of 10 Years of Intense Efforts towards Liquid Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterlini-Brechot, P.; Linda Benali, N. Circulating tumor cells (CTC) detection: Clinical impact and future directions. Cancer Lett. 2007, 253, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelievre, L.; Paterlini-Brechot, P.; Camatte, S.; Tartour, E.; Aggerbeck, M.; Vilde, F.; Lecuru, F. Effect of laparoscopy versus laparotomy on circulating tumor cells using isolation by size of epithelial tumor cells. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2004, 14, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkumur, E.; Shah, A.M.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Emmink, B.L.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Brachtel, E.; Yu, M.; Chen, P.-I.; Morgan, B.; Trautwein, J.; et al. Inertial Focusing for Tumor Antigen–Dependent and –Independent Sorting of Rare Circulating Tumor Cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 179ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Guan, G.; Luan, K.B.; Lee, W.C.; Bhagat, A.A.S.; Kant Chaudhuri, P.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lim, W.T.; Lee, S.C.; Chen, P.C.Y.; et al. Slanted spiral microfluidics for the ultra-fast, label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.R.; Cox, E.C.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Continuous Particle Separation Through Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Science 2004, 304, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolovic, D.; Galindo, L.; Carstens, A.; Rahbari, N.; Büchler, M.W.; Weitz, J.; Koch, M. Heterogeneous detection of circulating tumor cells in patients with colorectal cancer by immunomagnetic enrichment using different EpCAM-specific antibodies. BMC Biotechnol. 2010, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balic, M.; Dandachi, N.; Hofmann, G.; Samonigg, H.; Loibner, H.; Obwaller, A.; Van Der Kooi, A.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; et al. Comparison of two methods for enumerating circulating tumor cells in carcinoma patients. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2005, 68B, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.X.; Perebikovsky, A.; Moebius, J.; Kulinsky, L.; Madou, M. Lab-on-a-CD: A Fully Integrated Molecular Diagnostic System. SLAS Technol. 2016, 21, 323–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagrath, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Maheswaran, S.; Bell, D.W.; Irimia, D.; Ulkus, L.; Smith, M.R.; Kwak, E.L.; Digumarthy, S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 2007, 450, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustsson, P.; Magnusson, C.; Nordin, M.; Lilja, H.; Laurell, T. Microfluidic, Label-Free Enrichment of Prostate Cancer Cells in Blood Based on Acoustophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7954–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, F.; Carloni, S.; Zoli, W.; Ulivi, P.; Gallerani, G.; Fici, P.; Chiadini, E.; Passardi, A.; Frassineti, G.L.; Ragazzini, A.; et al. Detection and recovery of circulating colon cancer cells using a dielectrophoresis-based device: KRAS mutation status in pure CTCs. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahabadi, S.; Labeed, F.H.; Hughes, M.P. Effects of cell detachment methods on the dielectric properties of adherent and suspension cells. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadali, R.; Bayareh, M.; Nadooshan, A.A. Performance optimization of a DLD microfluidic device for separating deformable CTCs. Electrophoresis 2024, 45, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaire, C.A.; Liu, S.Z.; Wilkerson, C.L.; Ramani, V.C.; Barzanian, N.A.; Huang, K.-W.; Che, J.; Chiu, M.W.; Vuppalapaty, M.; Dimmick, A.M.; et al. Fast and Label-Free Isolation of Circulating Tumor Cells from Blood: From a Research Microfluidic Platform to an Automated Fluidic Instrument, VTX-1 Liquid Biopsy System. SLAS Technol. 2018, 23, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Kularatne, S.A.; Kalli, K.R.; Prendergast, F.G.; Amato, R.J.; Klee, G.G.; Hartmann, L.C.; Low, P.S. Quantitation of circulating tumor cells in blood samples from ovarian and prostate cancer patients using tumor-specific fluorescent ligands. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1968–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Foekens, J.A. Circulating tumor cells in blood of primary breast cancer patients assessed by a novel RT-PCR test kit and comparison with status of bone marrow-disseminated tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2009, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Antin, P.; Berx, G.; Blanpain, C.; Brabletz, T.; Bronner, M.; Campbell, K.; Cano, A.; Casanova, J.; Christofori, G.; et al. Guidelines and definitions for research on epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-L.; Tsai, T.-H.; Huang, C.-K.; Yang, C.-Y.; Liao, W.-Y.; Ho, C.-C.; Ruan, S.-Y.; Chen, K.-Y.; Shih, J.-Y.; Yang, P.-C. Monitoring levels of vimentin-positive circulating cancer stem cells and tumor cells in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2021, 156, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-P.; Giret, T.M.; Cote, R.J. Circulating Tumor Cells from Enumeration to Analysis: Current Challenges and Future Opportunities. Cancers 2021, 13, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrial.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Jiang, Z.F.; Cristofanilli, M.; Shao, Z.M.; Tong, Z.S.; Song, E.W.; Wang, X.J.; Liao, N.; Hu, X.C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Circulating tumor cells predict progression-free and overall survival in Chinese patients with metastatic breast cancer, HER2-positive or triple-negative (CBCSG004): A multicenter, double-blind, prospective trial. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2766–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallwiener, M.; Riethdorf, S.; Hartkopf, A.D.; Modugno, C.; Nees, J.; Madhavan, D.; Sprick, M.R.; Schott, S.; Domschke, C.; Baccelli, I.; et al. Serial enumeration of circulating tumor cells predicts treatment response and prognosis in metastatic breast cancer: A prospective study in 393 patients. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza E Silva, V.; Ali Abdallah, E.; Lopes de Mello, C.A.; Tariki, M.S.; Calsavara, V.F.; Chinen, L.T.D. Prospective study with circulating tumor cells as potential prognosis biomarker in metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Bidard, F.-C.; Kiavue, N.; Jacot, W.; Bachelot, T.; Dureau, S.; Bourgeois, H.; Goncalves, A.; Brain, E.; Ladoire, S.; et al. Overall Survival With Circulating Tumor Cell Count–Driven Choice of Therapy in Advanced Breast Cancer: A Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Factor | CTCs | ctDNA |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery year | 1869 1 | 1977 2 |
| Detection target | Viable tumor cells | Cell-free DNA fragments |
| Release mechanism | Intravasation and circulation | Apoptosis or necrosis |
| Sensitivity | Varies by separation technique 3 | Relatively high |
| Amplification in detection | Not required (but available) 4 | Required |
| Monitoring MRD | Yes | Yes |
| Heterogeneity | Intra- and intertumor cells | Intra-/intertumor + mutated benign cells |
| Pathology/cytology | Yes | Not applicable |
| Functional assay | Yes | Not applicable |
| Gene expression | Yes | Not applicable |
| Gene alteration | Yes | Yes |
| Epigenetic changes | Yes | Yes (DNA methylation) |
| Characteristics | Preserved cell morphology and phenotype | DNA sequence and methylation |
| Chemosensitivity test | Yes | No |
| Feasibility in hospital setting | High (routine practice) 5 | Limited (specialized setting) 6 |
| Outsourced service | Available from commercial services | Available from commercial services |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kakizaki, F.; Oshiro, K.; Enoki, Y.; Kawanishi, K.; Masuda, N.; Maekawa, H.; Matsubayashi, J.; Kawashima, M.; Miyoshi, H.; Takemura, Y.; et al. Precision Oncology Framework Using Circulating Tumor Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125539
Kakizaki F, Oshiro K, Enoki Y, Kawanishi K, Masuda N, Maekawa H, Matsubayashi J, Kawashima M, Miyoshi H, Takemura Y, et al. Precision Oncology Framework Using Circulating Tumor Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125539
Chicago/Turabian StyleKakizaki, Fumihiko, Kyoichi Oshiro, Yuya Enoki, Kana Kawanishi, Norikazu Masuda, Hisatsugu Maekawa, Jun Matsubayashi, Masahiro Kawashima, Hiroyuki Miyoshi, Yukitoshi Takemura, and et al. 2025. "Precision Oncology Framework Using Circulating Tumor Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125539
APA StyleKakizaki, F., Oshiro, K., Enoki, Y., Kawanishi, K., Masuda, N., Maekawa, H., Matsubayashi, J., Kawashima, M., Miyoshi, H., Takemura, Y., & Obama, K. (2025). Precision Oncology Framework Using Circulating Tumor Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125539








