Prolonged Intestinal Ethanol Absorption and Oxidative Stress: Revisiting the Gut–Liver Axis in Alcohol-Associated Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ethanol Metabolism and Redox Imbalance
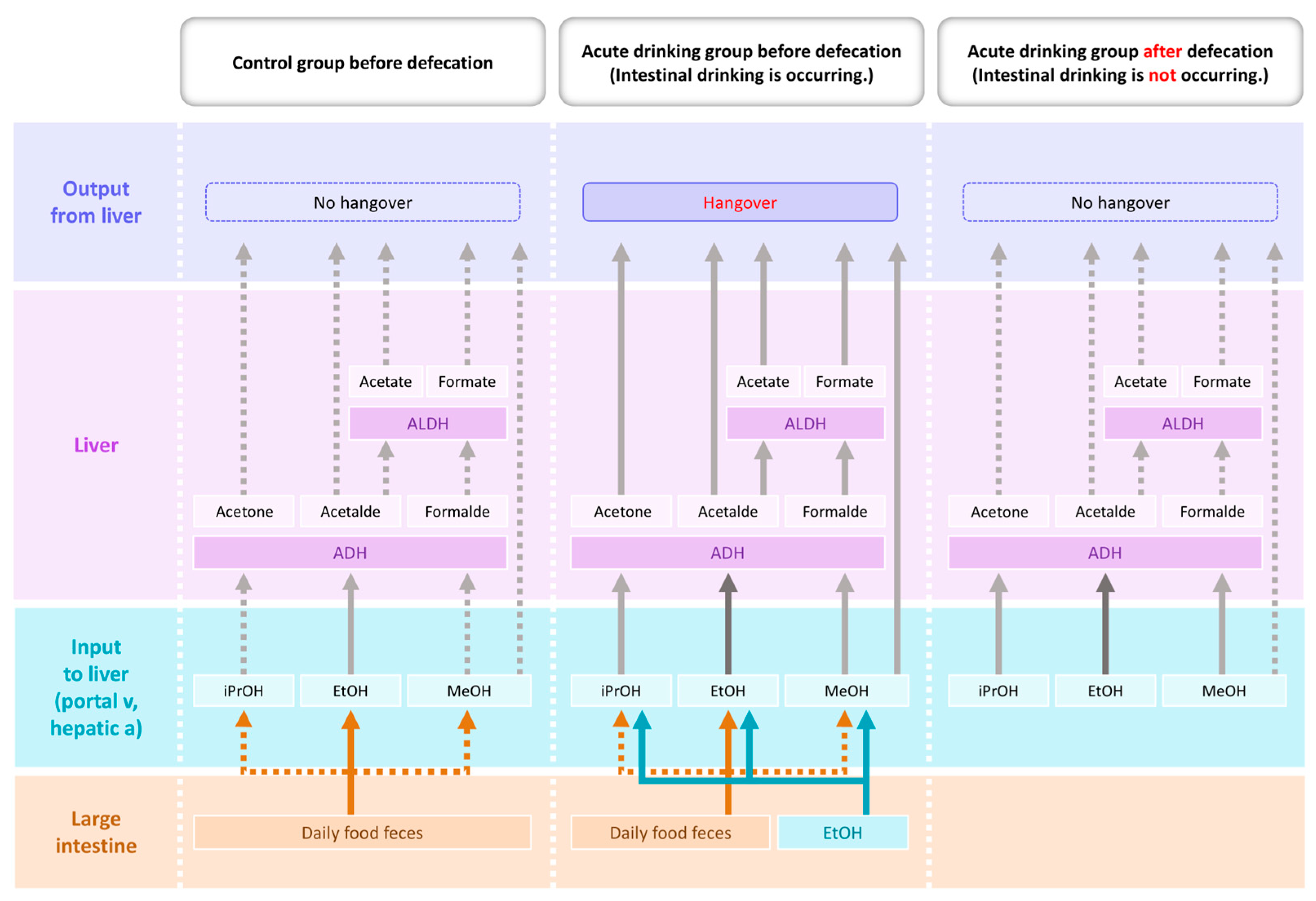
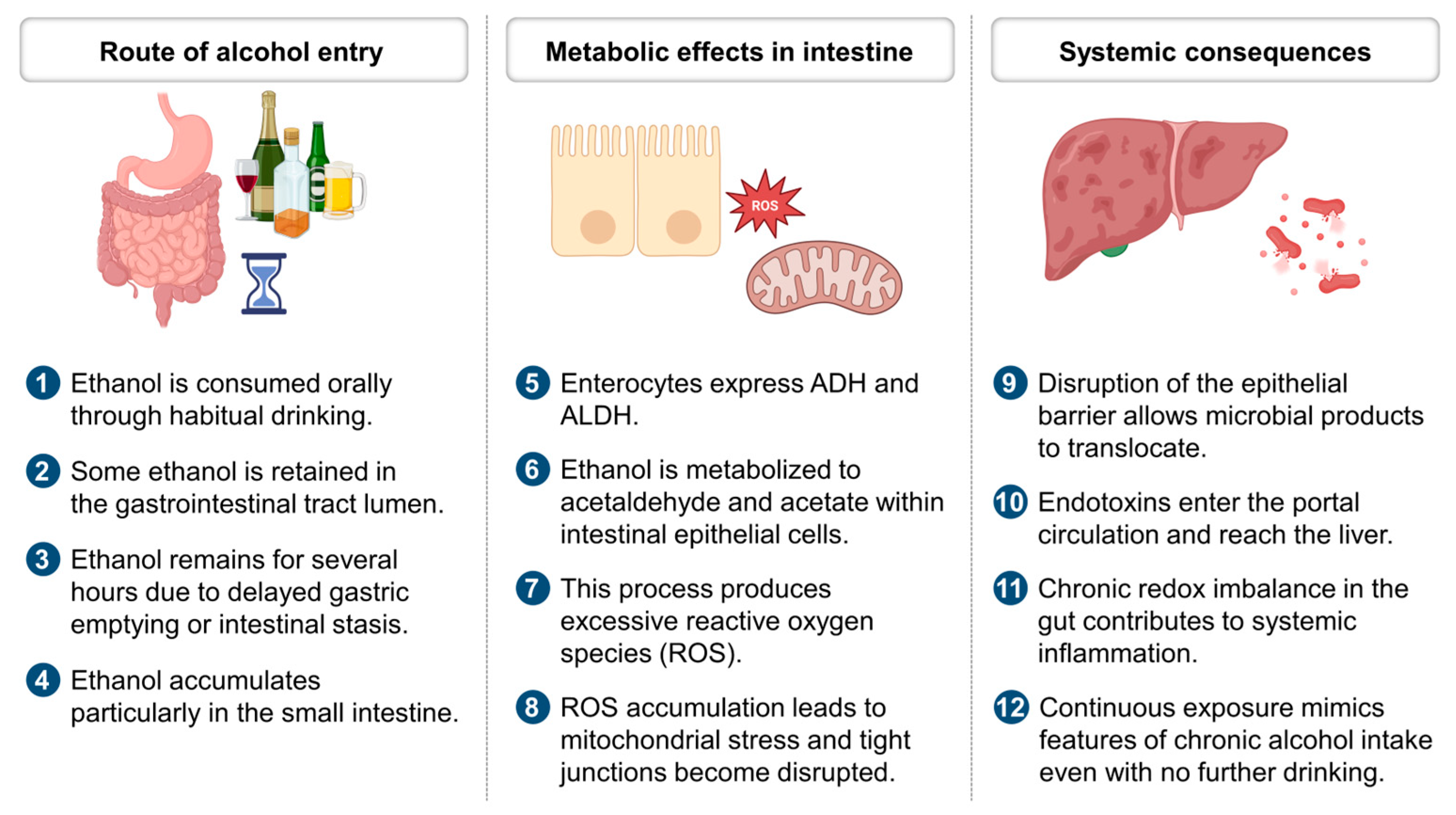
3. Prolonged Intestinal Ethanol Absorption and Redox Imbalance
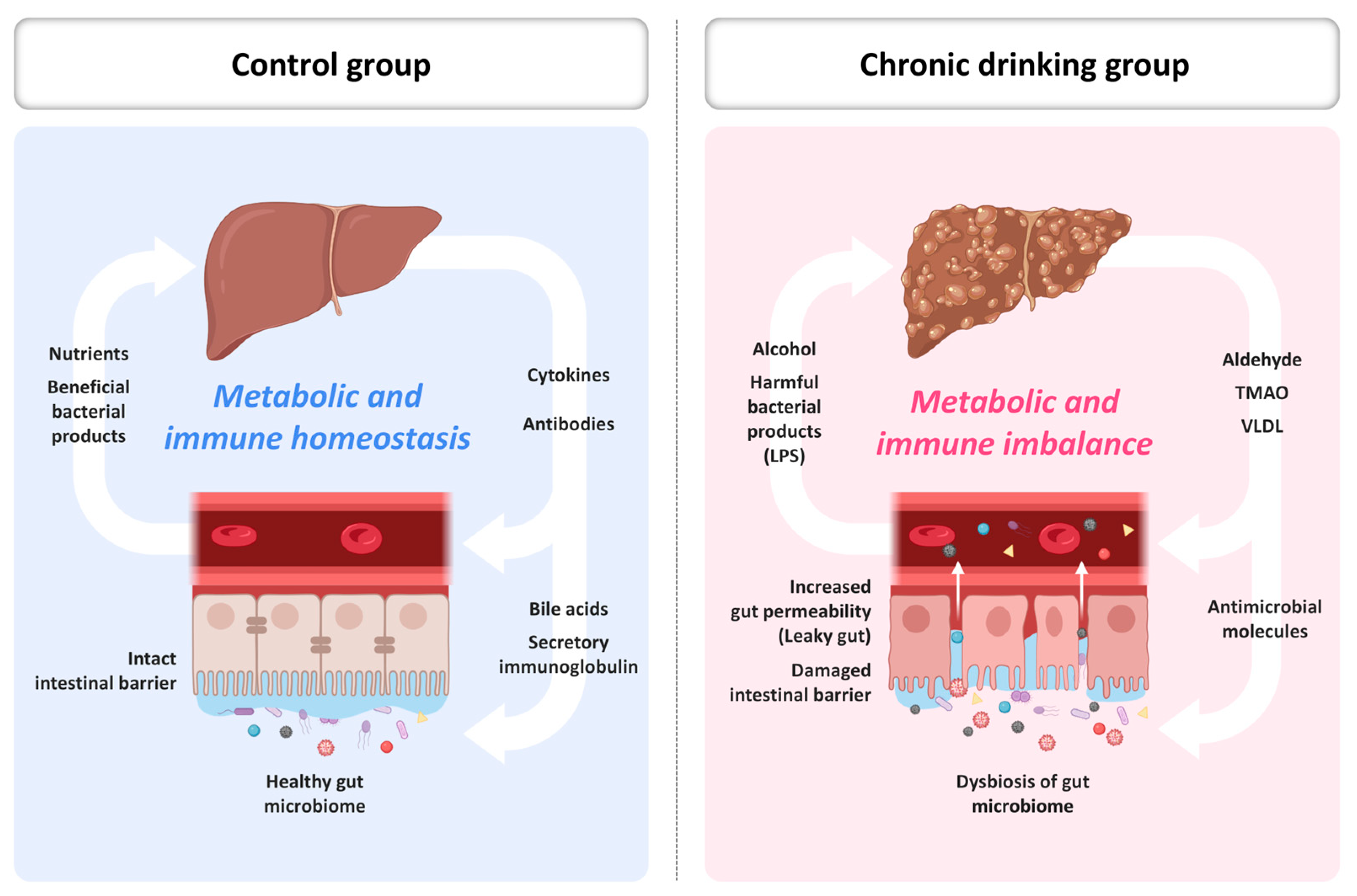
4. Gut–Liver Axis and Redox Amplification
5. Possible Therapeutic Strategies Targeting the Gut–Liver Redox Axis
6. Microbiome–Mitochondria Crosstalk and Translational Interventions
7. Strategic Implications and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADH | Alcohol Dehydrogenase |
| ALD | Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease |
| ALDH | Aldehyde Dehydrogenase |
| AP-1 | Activator Protein 1 |
| BAC | Blood Alcohol Concentration |
| CYP2E1 | Cytochrome P450 2E1 |
| FXR | Farnesoid X Receptor |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| IgA | Immunoglobulin A |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin 10 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MEOS | Microsomal Ethanol Oxidizing System |
| NAD+/NADH | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (oxidized/reduced) |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| NMN | Nicotinamide Mononucleotide |
| NR | Nicotinamide Riboside |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2 |
| PGC-1α | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Coactivator 1-Alpha |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SCFA | Short-Chain Fatty Acid |
| SIRT | Sirtuin |
| TGR5 | Takeda G-Protein Receptor 5 |
| TLR4 | Toll-Like Receptor 4 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| ZO-1 | Zonula Occludens 1 |
References
- Lu, Y.; Cederbaum, A.I. CYP2E1 and oxidative liver injury by alcohol. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamin, E.E.; Masclee, A.A.; Dekker, J.; Jonkers, D.M. Ethanol metabolism and its effects on the intestinal epithelial barrier. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oneta, C.M.; Simanowski, U.A.; Martinez, M.; Allali-Hassani, A.; Pares, X.; Homann, N.; Seitz, H.K. First pass metabolism of ethanol is strikingly influenced by the speed of gastric emptying. Gut 1998, 43, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, T.; Yang, K.; Chung, B.S. Defecation alleviates hangover by terminating intestinal drinking. Arch. Med. Sci. 2023, 19, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Ryu, T.; Chung, B.S. Psyllium fiber improves hangovers and inflammatory liver injury by inhibiting intestinal drinking. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1378653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Yao, Y.; Tao, L.S.; Wang, S.X.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.Y.; Xu, T. The role of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. Cell. Signal. 2023, 102, 110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjumäki, R.; Pridgeon, C.S.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. CYP2E1 in alcoholic and non-alcoholic liver injury. Roles of ROS, reactive intermediates and lipid overload. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S.W. Intragastric ethanol infusion model for cellular and molecular studies of alcoholic liver disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2001, 8, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas-Paz, A.; Hao, F.; Nelson, L.J.; Vázquez, M.T.; Canals, S.; Del Moral, M.G.; Cubero, F.J. Alcoholic liver disease: Utility of animal models. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell Jr, M.C.; Teigen, E.L.; Ramchandani, V.A. Absorption and peak blood alcohol concentration after drinking beer, wine, or spirits. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishii, N.; Oshima, T.; Li, M.; Eda, H.; Nakamura, K.; Tamura, A.; Miwa, H. Lubiprostone induces claudin-1 and protects intestinal barrier function. Pharmacology 2020, 105, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.Y.; Nguyen, D.; Bui, V.; Nguyen, H.; Hoa, N. Ethanol modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 1999, 276, G965–G974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, M.D. Endotoxin and Kupffer cell activation in alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Res. Health 2003, 27, 300. [Google Scholar]
- Bode, C.; Bode, J.C. Alcohol-induced gut dysbiosis. Alcohol Alcohol. 2003, 38, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Philips, C.A.; Schnabl, B.; Bajaj, J.S. Gut microbiome and alcohol-associated liver disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butts, M.; Sundaram, V.L.; Murughiyan, U.; Borthakur, A.; Singh, S. The influence of alcohol consumption on intestinal nutrient absorption: A comprehensive review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.R.; Harris, R.Z. Drug interactions involving ethanol and alcoholic beverages. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2007, 3, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Voigt, R.M.; Shaikh, M.; Tang, Y.; Cederbaum, A.I.; Turek, F.W.; Keshavarzian, A. Role for intestinal CYP2E1 in alcohol-induced circadian gene-mediated intestinal hyperpermeability. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G185–G195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederbaum, A. Nrf2 and antioxidant defense against CYP2E1 toxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 1223–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballway, J.W.; Song, B.J. Translational approaches with antioxidant phytochemicals against alcohol-mediated oxidative stress, gut dysbiosis, intestinal barrier dysfunction, and fatty liver disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzian, A.; Fields, J.Z. Gastrointestinal motility disorders induced by ethanol. In Alcohol and the Gastrointestinal Tract; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 235–253. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Behara, R.; Swanson, G.R.; Forsyth, C.B.; Voigt, R.M.; Keshavarzian, A. Alcohol and the intestine. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 2573–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakhari, S. Overview: How is alcohol metabolized by the body? Alcohol Res. Health 2006, 29, 245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lieber, C.S. Metabolism of alcohol. Clin. Liver Dis. 2005, 9, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, U.S.; O’Connor, S.; Ramchandani, V.A. Modeling alcohol self-administration in the human laboratory. Behav. Neurobiol. Alcohol Addict. 2011, 315, 315–353. [Google Scholar]
- Justice, M.; Ferrugia, A.; Beidler, J.; Penprase, J.C.; Cintora, P.; Erwin, D.; Hong, M.Y. Effects of moderate ethanol consumption on lipid metabolism and inflammation through regulation of gene expression in rats. Alcohol Alcohol. 2019, 54, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.L.; Colgan, S.P. Control and dysregulation of redox signalling in the gastrointestinal tract. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Voigt, R.M.; Keshavarzian, A. Intestinal CYP2E1: A mediator of alcohol-induced gut leakiness. Redox Biol. 2014, 3, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, S.; Jeong, J.H.; Ko, S.; Chun, Y.L.; Yoon, J.H. Targeting of CYP2E1 by miRNAs in alcohol-induced intestine injury. Mol. Cells 2024, 47, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goasduff, T.; Cederbaum, A.I. NADPH-dependent microsomal electron transfer increases degradation of CYP2E1 by the proteasome complex: Role of reactive oxygen species. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 370, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairfield, B.; Schnabl, B. Gut dysbiosis as a driver in alcohol-induced liver injury. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishehsari, F.; Magno, E.; Swanson, G.; Desai, V.; Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Alcohol and gut-derived inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 313, G107–G116. [Google Scholar]
- Tonetti, F.R.; Eguileor, A.; Mrdjen, M.; Pathak, V.; Travers, J.; Nagy, L.E.; Llorente, C. Gut-liver axis: Recent concepts in pathophysiology in alcohol-associated liver disease. Hepatology 2024, 80, 1342–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.D.; Eom, S.Y.; Ogawa, M.; Oyama, T.; Isse, T.; Kang, J.W.; Kim, H. Ethanol-induced oxidative DNA damage and CYP2E1 expression in liver tissue of Aldh2 knockout mice. J. Occup. Health 2007, 49, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmegeed, M.A.; Banerjee, A.; Jang, S.; Yoo, S.H.; Yun, J.W.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Song, B.J. CYP2E1 potentiates binge alcohol-induced gut leakiness, steatohepatitis, and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Seki, E.; Brenner, D.A.; Friedman, S.; Cohen, J.I.; Nagy, L.; Zakhari, S. Innate immunity in alcoholic liver disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G516–G525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I.; Chen, X.; Nagy, L.E. Redox signaling and the innate immune system in alcoholic liver disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Niu, M.; Ni, H.M.; Ding, W.X. Mitochondrial dynamics, quality control, and mtDNA in Alcohol-associated liver disease and liver cancer. Hepatology 2024, 10.1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.M.; Cunningham, C.C. Contribution of mitochondria to oxidative stress associated with alcoholic liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 909–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, N.; Ikejima, K.; Bradford, B.U.; Rivera, C.A.; Kono, H.; Goto, M.; Thurman, R.G. Role of Kupffer cells and gut-derived endotoxins in alcoholic liver injury. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 15, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goverse, G.; Molenaar, R.; Macia, L.; Tan, J.; Erkelens, M.N.; Konijn, T.; Mebius, R.E. Diet-derived short chain fatty acids stimulate intestinal epithelial cells to induce mucosal tolerogenic dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.M.; Pietsch, E.C.; Cunningham, C.C. Ethanol stimulates the production of reactive oxygen species at mitochondrial complexes I and III. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 891–900. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, H.; Adachi, M.; Miura, S.; Gores, G.J.; Ishii, H. The mitochondrial permeability transition contributes to acute ethanol-induced apoptosis in rat hepatocytes. Hepatology 2001, 34, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.C.; Liu, J.; Klaassen, C.D. Role of Nrf2 in preventing ethanol-induced oxidative stress and lipid accumulation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 262, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, L.; Niu, L.; Zhao, Y. Sodium butyrate protects against rotavirus-induced intestinal epithelial barrier damage by activating AMPK-Nrf2 signaling pathway in IPEC-J2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Vella, A. What to do about the leaky gut. Gut 2022, 71, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.D.; Chi, X.J.; Jin, Y.; Li, X.; Ge, M.; Gao, W.L.; Hei, Z.Q. Intestinal injury following liver transplantation was mediated by TLR4/NF-κB activation-induced cell apoptosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, J.E.; Blikslager, A.T. Interactions between lipopolysaccharide and the intestinal epithelium. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkas, A.; Zarkovic, N. 4-Hydroxynonenal in redox homeostasis of gastrointestinal mucosa: Implications for the stomach in health and diseases. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S.; Bindu, S.; De, R.; Debsharma, S.; Pramanik, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Emerging role of mitochondrial DAMPs, aberrant mitochondrial dynamics and anomalous mitophagy in gut mucosal pathogenesis. Life Sci. 2022, 305, 120753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Neve, E.; Matsumoto, H.; Nishitani, Y.; Minowa, Y.; Sun, G.Y. Ethanol and oxidative stress. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 237S–243S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. Endotoxemia and gut barrier dysfunction in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2009, 50, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H. Gut-liver axis in liver cirrhosis: How to manage leaky gut and endotoxemia. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, P.; Chen, W.C.; Schnabl, B. The intestinal microbiome and the leaky gut as therapeutic targets in alcoholic liver disease. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Cheng, C.M. Alcohol addiction, gut microbiota, and alcoholism treatment: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.M.; Shekhar, A.C. Lipopolysaccharide, arbiter of the gut–liver axis, modulates hepatic cell pathophysiology in alcoholism. Anat. Rec. 2025, 308, 975–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Han, M.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Zhen, X.; Schlaak, J.F.; Lu, M. Pattern recognition receptors and liver failure. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 39, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, Y.S.; Seki, E. Toll-like receptors in alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and carcinogenesis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, M.; Zhao, J.; Martin, B.N.; Roychowdhury, S.; McMullen, M.R.; Li, X. IRAKM-Mincle axis links cell death to inflammation: Pathophysiological implications for chronic alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1978–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comporti, M.; Signorini, C.; Leoncini, S.; Gardi, C.; Ciccoli, L.; Giardini, A.; Arezzini, B. Ethanol-induced oxidative stress: Basic knowledge. Genes Nutr. 2010, 5, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xia, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, J.; Tuo, Q.; Lin, L.; Liao, D. Crosstalk between bile acids and intestinal epithelium: Multidimensional roles of farnesoid X receptor and Takeda G protein receptor 5. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, A.A.; Lazaropoulos, M.P.; Elrod, J.W. Myofibroblasts and fibrosis: Mitochondrial and metabolic control of cellular differentiation. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 427–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Min, T.; Bai, Y.; He, J.; Su, Z. Oxidative stress in alcoholic liver disease, focusing on proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, K. Proteome analysis identified proteins associated with mitochondrial function and inflammation activation crucially regulating the pathogenesis of fatty liver disease. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andringa, K.K.; King, A.L.; Eccleston, H.B.; Mantena, S.K.; Landar, A.; Jhala, N.C.; Bailey, S.M. Analysis of the liver mitochondrial proteome in response to ethanol and S-adenosylmethionine treatments: Novel molecular targets of disease and hepatoprotection. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G732–G745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeFort, K.R.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Song, B.J. Contributing roles of mitochondrial dysfunction and hepatocyte apoptosis in liver diseases through oxidative stress, post-translational modifications, inflammation, and intestinal barrier dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, B.G.; Schnabl, B. From intestinal dysbiosis to alcohol-associated liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Cortes, K.; Villageliu, D.N.; Samuelson, D.R. Innate lymphocytes: Role in alcohol-induced immune dysfunction. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 934617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimeyer, H.; Llorente, C.; Schnabl, B. Influence of alcohol on the intestinal immune system. Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2025, 45, 03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamine, T.; Schnabl, B. Immunoglobulin A and liver diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliou, E.; Farias-Pereira, R. Impact of lipid metabolism on macrophage polarization: Implications for inflammation and tumor immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siggins, R.W.; McTernan, P.M.; Simon, L.; Souza-Smith, F.M.; Molina, P.E. Mitochondrial dysfunction: At the nexus between alcohol-associated immunometabolic dysregulation and tissue injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosnowski, K.; Przybyłkowski, A. Ethanol-induced changes to the gut microbiome compromise the intestinal homeostasis: A review. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2393272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Yang, K.; Hou, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, X.; Xie, G. Alleviation of alcoholic liver injury through composite postbiotics regulation of intestinal flora and promotion of bile acid metabolism. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarewicz, M.; Drożdż, I.; Tarko, T.; Duda-Chodak, A. The interactions between polyphenols and microorganisms, especially gut microbiota. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hong, W. The combination of Clostridium butyricum and Akkermansia muciniphila mitigates DSS-induced colitis and attenuates colitis-associated tumorigenesis by modulating gut microbiota and reducing CD8+ T cells in mice. mSystems 2025, 10, e01567-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Teng, X.; Guo, P.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liang, H. Garlic oil alleviates high triglyceride levels in alcohol-exposed rats by inhibiting liver oxidative stress and regulating the intestinal barrier and intestinal flora. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2479–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grander, C.; Adolph, T.E.; Wieser, V.; Lowe, P.; Wrzosek, L.; Gyongyosi, B.; Tilg, H. Recovery of ethanol-induced Akkermansia muciniphila depletion ameliorates alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2018, 67, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, J.Y. Inhibition of alcohol-induced inflammation and oxidative stress by astaxanthin is mediated by its opposite actions in the regulation of sirtuin 1 and histone deacetylase 4 in macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2021, 1866, 158838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shasthry, S.M. Fecal microbiota transplantation in alcohol-related liver diseases. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnadieu-Rigole, H.; Pansu, N.; Mura, T.; Pelletier, S.; Alarcon, R.; Gamon, L.; Dunyach-Remy, C. Beneficial effect of alcohol withdrawal on gut permeability and microbial translocation in patients with alcohol use disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, B.S.; Yang, K.; Park, C.; Ryu, T. Prolonged Intestinal Ethanol Absorption and Oxidative Stress: Revisiting the Gut–Liver Axis in Alcohol-Associated Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125442
Chung BS, Yang K, Park C, Ryu T. Prolonged Intestinal Ethanol Absorption and Oxidative Stress: Revisiting the Gut–Liver Axis in Alcohol-Associated Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125442
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Beom Sun, Keungmo Yang, Chihyun Park, and Tom Ryu. 2025. "Prolonged Intestinal Ethanol Absorption and Oxidative Stress: Revisiting the Gut–Liver Axis in Alcohol-Associated Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125442
APA StyleChung, B. S., Yang, K., Park, C., & Ryu, T. (2025). Prolonged Intestinal Ethanol Absorption and Oxidative Stress: Revisiting the Gut–Liver Axis in Alcohol-Associated Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125442






