iNOS Mediates High-Fat Diet-Associated Aggravation of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced Inflammatory Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
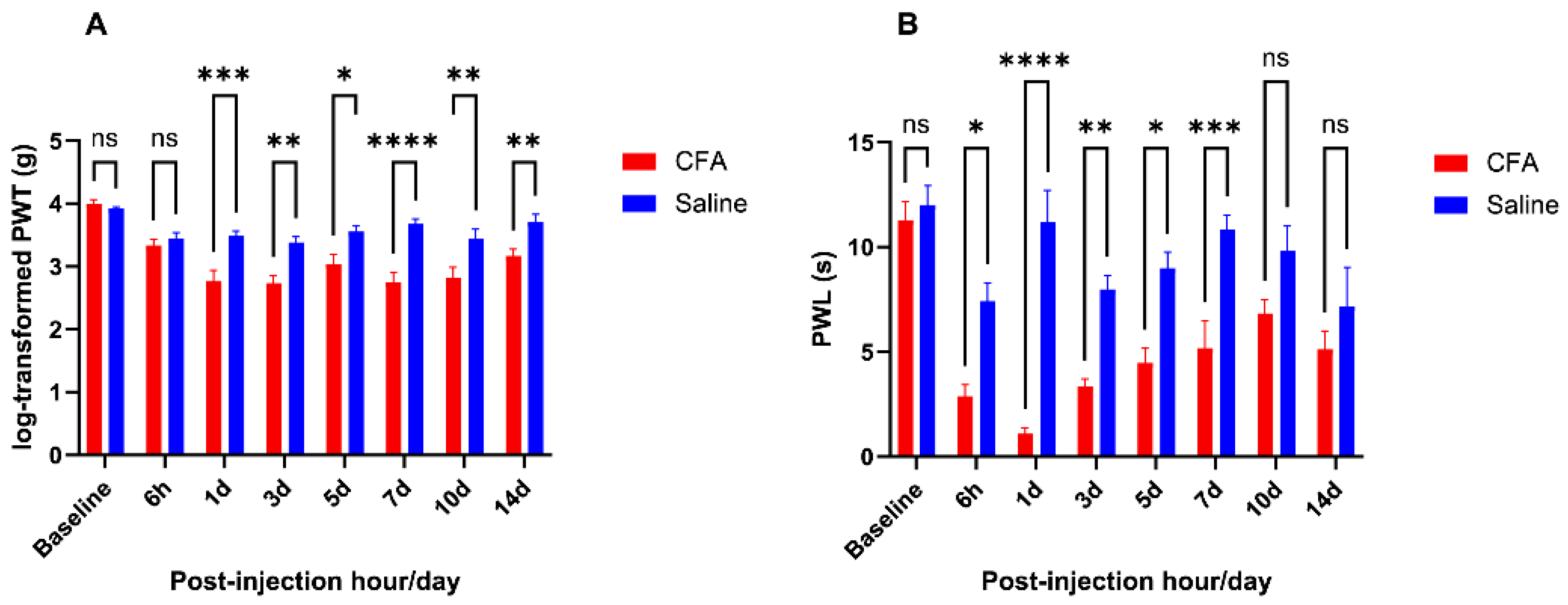
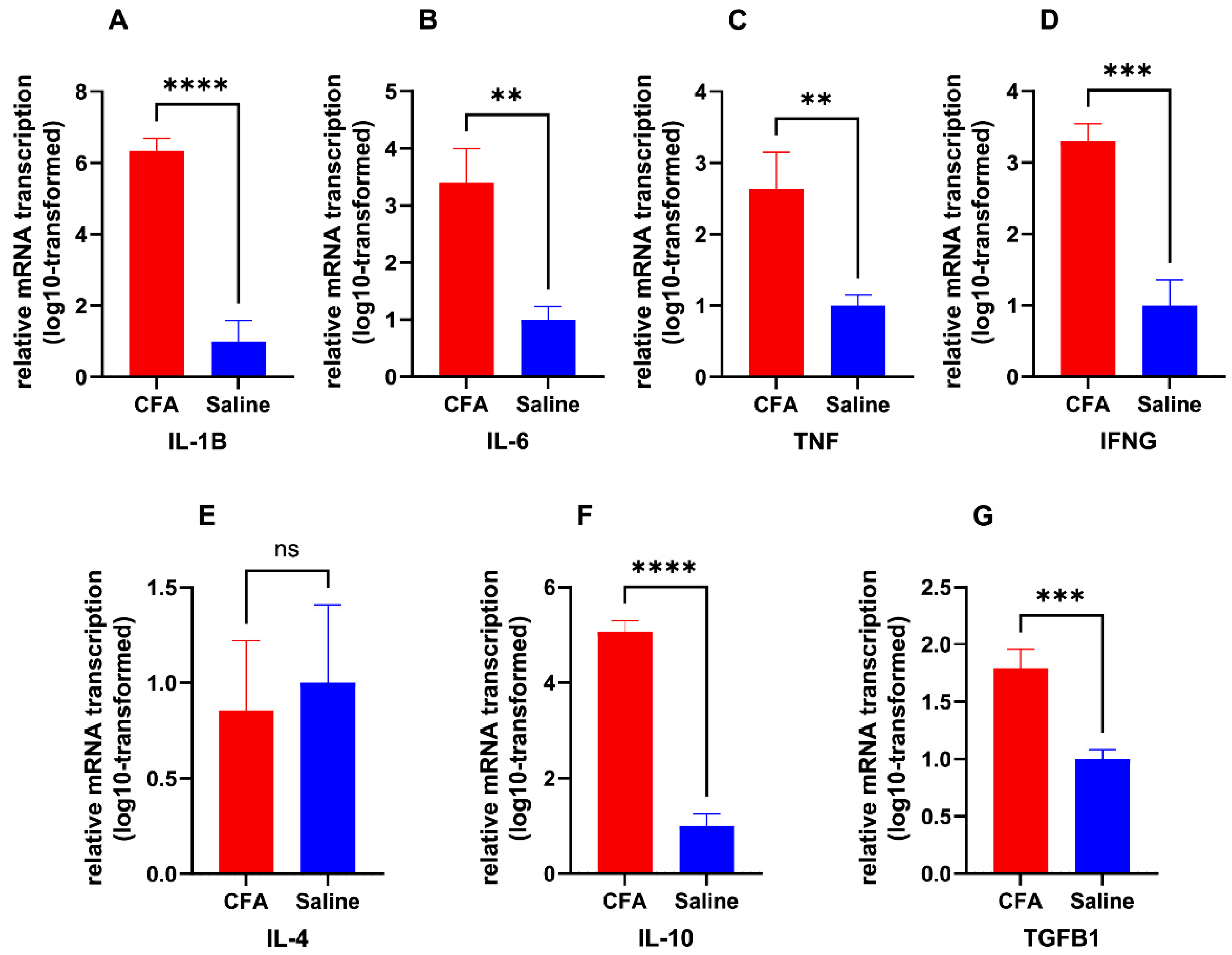
2.1. CFA Injection Induced Inflammatory Pain Persisting for Days
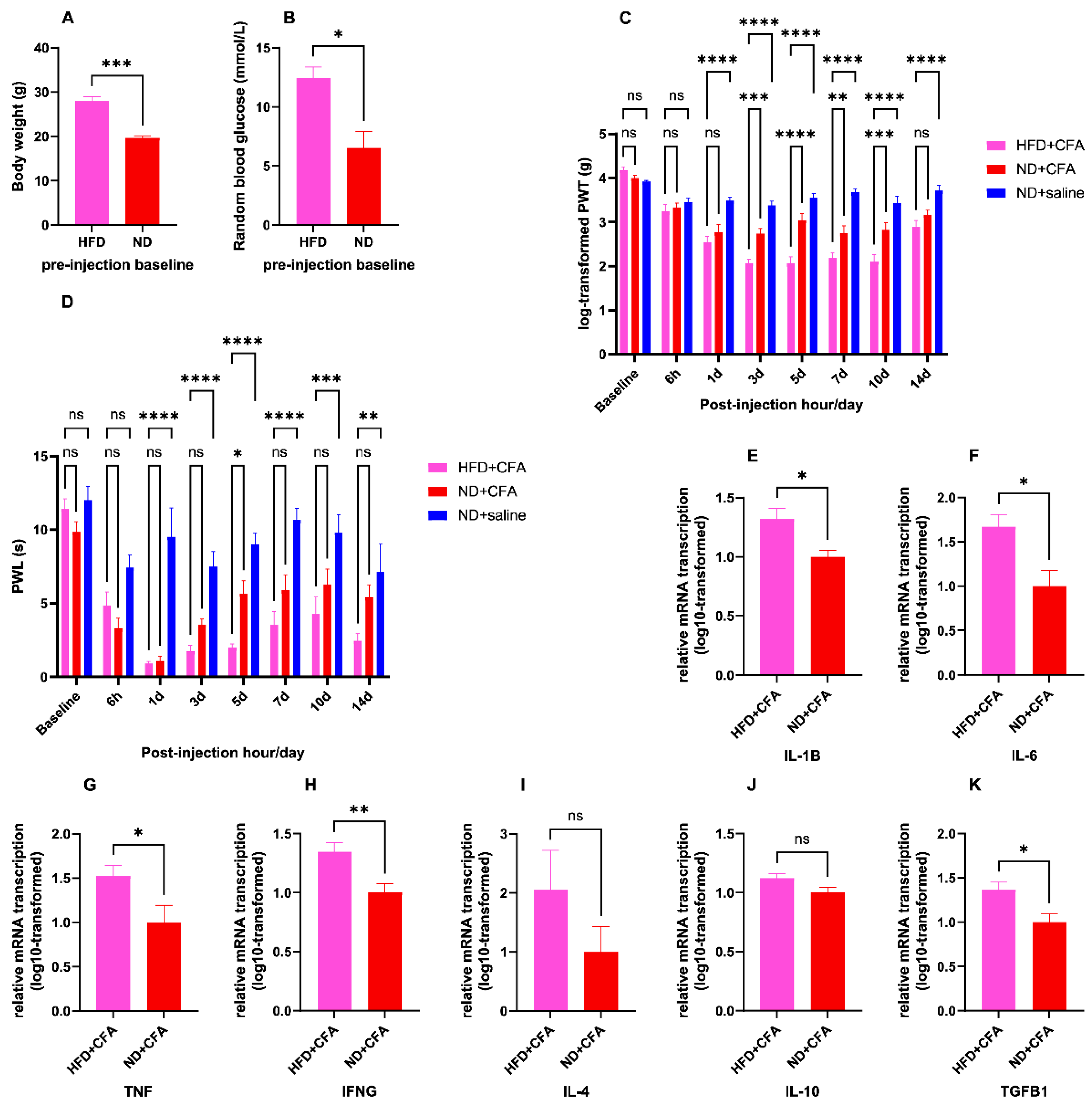
2.2. Short-Term HFD Induced Obesity and Aggravated CFA-Induced IP
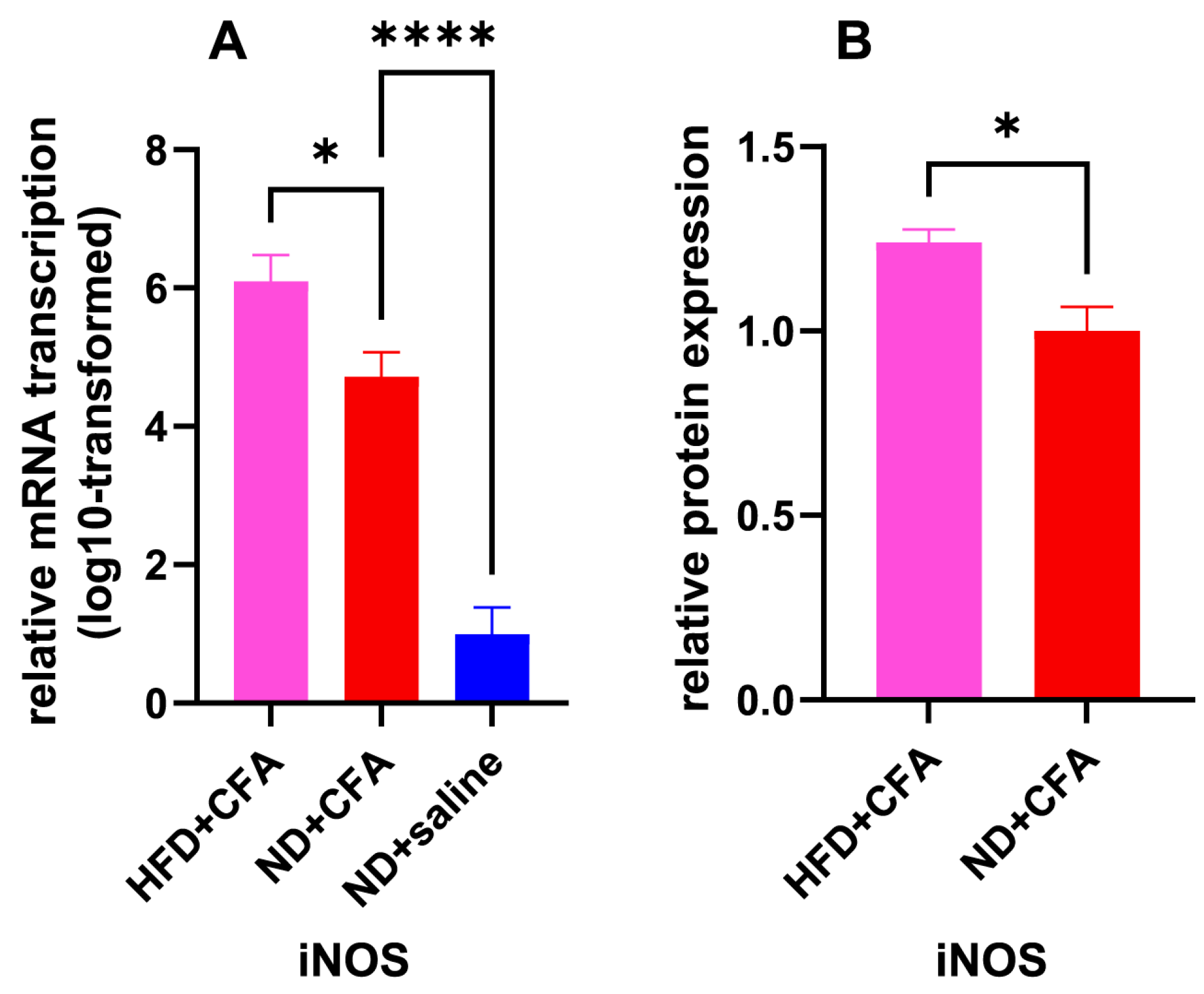
2.3. iNOS as an Upregulated IP Mediator Under HFD Influence
2.4. Analgesic but Pro-Inflammatory Effects of 1400 W
3. Discussion
3.1. Short-Term HFD and IP
3.2. iNOS as the Mediator of HFD-Induced Aggravation of IP
3.3. Clinical Implications of iNOS-Associated Findings
3.4. Limitations
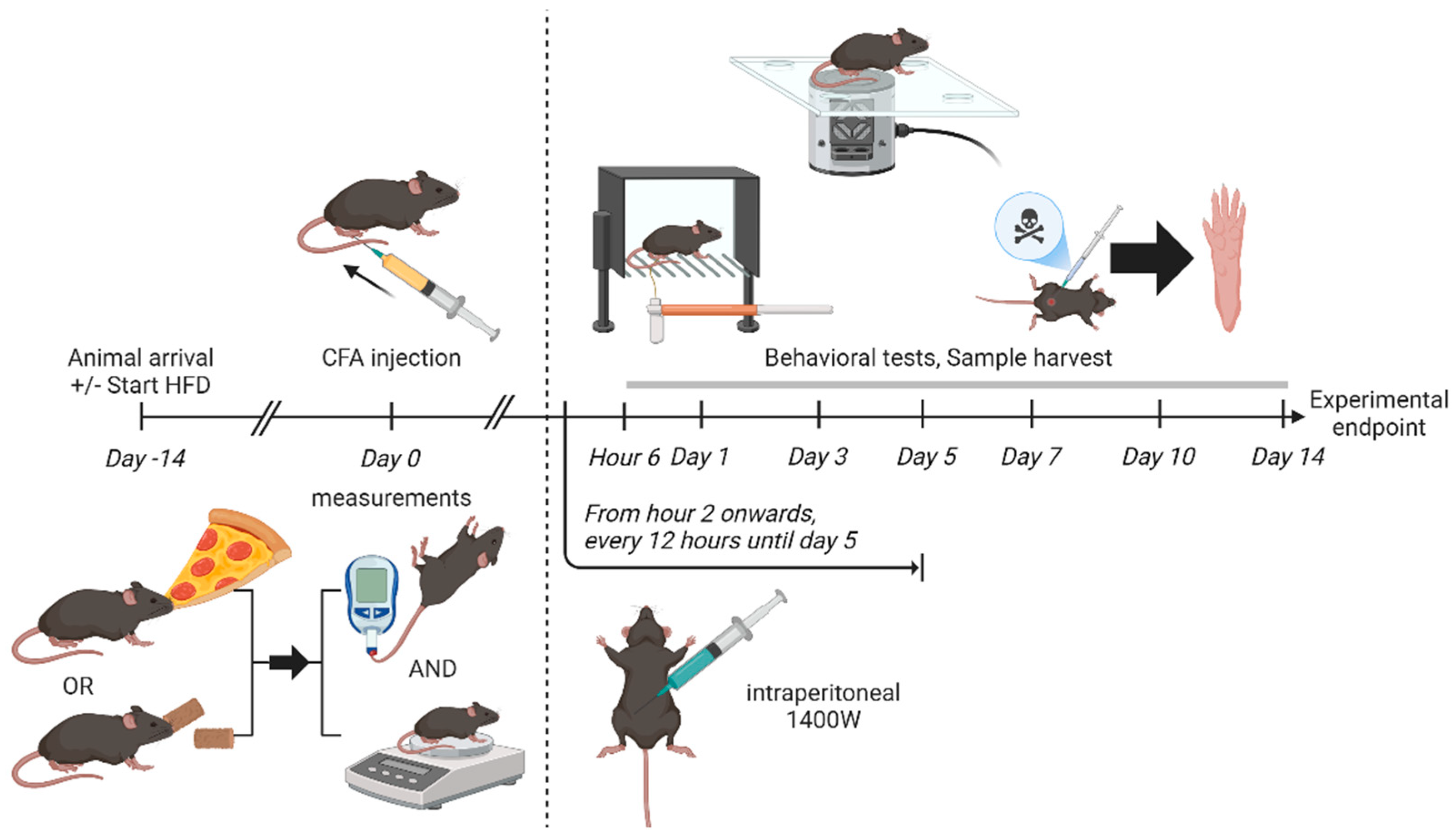
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Husbandry and Feeding
4.2. Random Blood Glucose Testing
4.3. Euthanization and Tissue Isolation
4.4. CFA Injection Model of IP
4.5. Drug Administration
4.6. Behavioral Tests
4.6.1. Manual Von Frey Test
4.6.2. Hargreaves’ Test
4.7. Molecular Assays
4.7.1. RT-qPCR Assay
4.7.2. ELISA
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFA | Complete Freund’s adjuvant |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| iNOS | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
References
- Prescott, S.A.; Ratté, S. Chapter 23—Somatosensation and Pain. In Conn’s Translational Neuroscience; Conn, P.M., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 517–539. [Google Scholar]
- DeMarco, G.J.; Pascoe, P.J. Chapter 1—Anatomy, Physiology, and Effects of Pain. In Anesthesia and Analgesia in Laboratory Animals, 2nd ed.; Fish, R.E., Brown, M.J., Danneman, P.J., Karas, A.Z., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, D.A.; McWilliams, D.F. Pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2012, 16, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Lee, Y.C. Mechanisms for Joint Pain in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): From Cytokines to Central Sensitization. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2018, 16, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernanz, A.; De Miguel, E.; Romera, N.; Perez-Ayala, C.; Gijon, J.; Arnalich, F. Calcitonin gene-related peptide II, substance P and vasoactive intestinal peptide in plasma and synovial fluid from patients with inflammatory joint disease. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1993, 32, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilardi, J.R.; Freeman, K.T.; Jimenez-Andrade, J.M.; Coughlin, K.A.; Kaczmarska, M.J.; Castaneda-Corral, G.; Bloom, A.P.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Mantyh, P.W. Neuroplasticity of sensory and sympathetic nerve fibers in a mouse model of a painful arthritic joint. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V. Chapter One—An Introduction to Pain Pathways and Pain “Targets”. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Price, T.J., Dussor, G., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 131, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Baerwald, C.; Stemmler, E.; Gnuchtel, S.; Jeromin, K.; Fritz, B.; Bernateck, M.; Adolf, D.; Taylor, P.C.; Baron, R. Predictors for severe persisting pain in rheumatoid arthritis are associated with pain origin and appraisal of pain. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohayon, M.M.; Schatzberg, A.F. Using chronic pain to predict depressive morbidity in the general population. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2003, 60, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, L.; McDonald, S.; Correia, H.; Raue, P.J.; Meade, T.; Nicholas, M.; Arean, P. Pain severity predicts depressive symptoms over and above individual illnesses and multimorbidity in older adults. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moieni, M.; Eisenberger, N.I. Effects of inflammation on social processes and implications for health. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1428, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Shaheed, C.; Ferreira, G.E.; Dmitritchenko, A.; McLachlan, A.J.; Day, R.O.; Saragiotto, B.; Lin, C.; Langendyk, V.; Stanaway, F.; Latimer, J.; et al. The efficacy and safety of paracetamol for pain relief: An overview of systematic reviews. Med. J. Aust. 2021, 214, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorczyk-Injeyan, J.A.; Triano, J.J.; Injeyan, H.S. Nonspecific Low Back Pain: Inflammatory Profiles of Patients With Acute and Chronic Pain. Clin. J. Pain 2019, 35, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, B.R.; Pereira, T.V.; Saadat, P.; Rudnicki, M.; Iskander, S.M.; Bodmer, N.S.; Bobos, P.; Gao, L.; Kiyomoto, H.D.; Montezuma, T.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opioid treatment for knee and hip osteoarthritis: Network meta-analysis. BMJ 2021, 375, n2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, B.R.; Streicher, J.M.; Majumdar, S. Strategies towards safer opioid analgesics-A review of old and upcoming targets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 180, 975–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miclescu, A.; Gordh, T. Nitric oxide and pain: ‘Something old, something new’. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2009, 53, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.M.; Ashton, D.S.; Moncada, S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature 1988, 333, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, A.; Koesling, D. Regulation of nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhr, F.; Lowry, J.; Zhang, Y.; Brovkovych, V.; Skidgel, R.A. Differential regulation of inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthase by kinin B1 and B2 receptors. Neuropeptides 2010, 44, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meller, S.T.; Gebhart, G.F. Nitric oxide (NO) and nociceptive processing in the spinal cord. Pain 1993, 52, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guhring, H.; Tegeder, I.; Lotsch, J.; Pahl, A.; Werner, U.; Reeh, P.W.; Rehse, K.; Brune, K.; Geisslinger, G. Role of nitric oxide in zymosan induced paw inflammation and thermal hyperalgesia. Inflamm. Res. 2001, 50, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, J.; Stern, E.R.; Pisani, T.M. Isoallergic encephalomyelitis and radiculitis in guinea pigs after one injection of brain and Mycobacteria in water-in-oil emulsion. J. Immunol. 1947, 57, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alba, J.; Clayton, N.M.; Collins, S.D.; Colthup, P.; Chessell, I.; Knowles, R.G. GW274150, a novel and highly selective inhibitor of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), shows analgesic effects in rat models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Pain 2006, 120, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul-Clark, M.J.; Gilroy, D.W.; Willis, D.; Willoughby, D.A.; Tomlinson, A. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors have opposite effects on acute inflammation depending on their route of administration. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cury, Y.; Picolo, G.; Gutierrez, V.P.; Ferreira, S.H. Pain and analgesia: The dual effect of nitric oxide in the nociceptive system. Nitric Oxide 2011, 25, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivancos, G.G.; Parada, C.A.; Ferreira, S.H. Opposite nociceptive effects of the arginine/NO/cGMP pathway stimulation in dermal and subcutaneous tissues. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvemini, D.; Misko, T.P.; Masferrer, J.L.; Seibert, K.; Currie, M.G.; Needleman, P. Nitric oxide activates cyclooxygenase enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7240–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollace, V.; Muscoli, C.; Masini, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Salvemini, D. Modulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis by nitric oxide and nitric oxide donors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 217–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.I.F.; Cunha, F.Q.; Cunha, T.M. Peripheral nitric oxide signaling directly blocks inflammatory pain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 176, 113862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health, U.D.o.; Services, H. 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Krisanits, B.; Randise, J.F.; Burton, C.E.; Findlay, V.J.; Turner, D.P. Chapter Three—Pubertal mammary development as a “susceptibility window” for breast cancer disparity. In Advances in Cancer Research; Ford, M.E., Esnaola, N.F., Salley, J.D., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 146, pp. 57–82. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Z.; Rehm, C.D.; Rogers, G.; Ruan, M.; Wang, D.D.; Hu, F.B.; Mozaffarian, D.; Zhang, F.F.; Bhupathiraju, S.N. Trends in Dietary Carbohydrate, Protein, and Fat Intake and Diet Quality Among US Adults, 1999–2016. JAMA 2019, 322, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micha, R.; Khatibzadeh, S.; Shi, P.; Fahimi, S.; Lim, S.; Andrews, K.G.; Engell, R.E.; Powles, J.; Ezzati, M.; Mozaffarian, D. Global, regional, and national consumption levels of dietary fats and oils in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis including 266 country-specific nutrition surveys. BMJ 2014, 348, g2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Popkin, B.M.; Du, S. Elevated Fat Intake Increases Body Weight and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity among Chinese Adults: 1991–2015 Trends. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasbalg, T.L.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Ramsden, C.E.; Majchrzak, S.F.; Rawlings, R.R. Changes in consumption of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the United States during the 20th century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Taylor, D.S.; Yu-Poth, S.; Huth, P.; Moriarty, K.; Fishell, V.; Hargrove, R.L.; Zhao, G.; Etherton, T.D. Polyunsaturated fatty acids in the food chain in the United States. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71 (Suppl. 1), 179S–188S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dam, R.M.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Stampfer, M.J.; Hu, F.B. Dietary patterns and risk for type 2 diabetes mellitus in U.S. men. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Zou, Y.; Gong, J.; Ge, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Zhao, J.; Saw, P.E.; et al. A high-fat diet promotes cancer progression by inducing gut microbiota-mediated leucine production and PMN-MDSC differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2306776121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordeleau, M.; Comin, C.H.; Fernandez de Cossio, L.; Lacabanne, C.; Freitas-Andrade, M.; Gonzalez Ibanez, F.; Raman-Nair, J.; Wakem, M.; Chakravarty, M.; Costa, L.D.F.; et al. Maternal high-fat diet in mice induces cerebrovascular, microglial and long-term behavioural alterations in offspring. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Li, P.; Huh, J.Y.; Hwang, I.J.; Lu, M.; Kim, J.I.; Ham, M.; Talukdar, S.; Chen, A.; Lu, W.J.; et al. Inflammation is necessary for long-term but not short-term high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Olmo, B.M.; Bettes, M.N.; DeMarsh, J.W.; Zhao, F.; Askwith, C.; Barrientos, R.M. Short-term high-fat diet consumption impairs synaptic plasticity in the aged hippocampus via IL-1 signaling. NPJ Sci. Food 2023, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakandakari, S.; Munoz, V.R.; Kuga, G.K.; Gaspar, R.C.; Sant’Ana, M.R.; Pavan, I.C.B.; da Silva, L.G.S.; Morelli, A.P.; Simabuco, F.M.; da Silva, A.S.R.; et al. Short-term high-fat diet modulates several inflammatory, ER stress, and apoptosis markers in the hippocampus of young mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 79, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumer, R.P.; Correa-Velloso, J.C.; Thomas, S.J.; Sandiford, O.A.; Thomas, A.P.; Bartlett, P.J. Short-term high-fat diet feeding of mice suppresses catecholamine-stimulated Ca2+ signalling in hepatocytes and intact liver. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 1383–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabrook, L.T.; Peterson, C.S.; Noble, D.; Sobey, M.; Tayyab, T.; Kenney, T.; Judge, A.K.; Armstrong, M.; Lin, S.; Borgland, S.L. Short- and Long-Term High-Fat Diet Exposure Differentially Alters Phasic and Tonic GABAergic Signaling onto Lateral Orbitofrontal Pyramidal Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 8582–8595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Las Heras, V.; Clooney, A.G.; Ryan, F.J.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Casey, P.G.; Hueston, C.M.; Pinheiro, J.; Rudkin, J.K.; Melgar, S.; Cotter, P.D.; et al. Short-term consumption of a high-fat diet increases host susceptibility to Listeria monocytogenes infection. Microbiome 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majka, Z.; Czamara, K.; Janus, J.; Kepczynski, M.; Kaczor, A. Prominent hypertrophy of perivascular adipocytes due to short-term high fat diet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ato, S.; Mori, T.; Fujita, Y.; Mishima, T.; Ogasawara, R. Short-term high-fat diet induces muscle fiber type-selective anabolic resistance to resistance exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 131, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, S.; Mauro, A.G.; Mezzaroma, E.; Kraskauskas, D.; Marchetti, C.; Buzzetti, R.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Abbate, A.; Toldo, S. A high-sugar and high-fat diet impairs cardiac systolic and diastolic function in mice. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 198, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, S.A.; MacSharry, J.; Casey, P.G.; Kinsella, M.; Murphy, E.F.; Shanahan, F.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Regulation of host weight gain and lipid metabolism by bacterial bile acid modification in the gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7421–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, J.P.; Yi, C.X.; Schur, E.A.; Guyenet, S.J.; Hwang, B.H.; Dietrich, M.O.; Zhao, X.; Sarruf, D.A.; Izgur, V.; Maravilla, K.R.; et al. Obesity is associated with hypothalamic injury in rodents and humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.M.; Murray, A.J.; Holloway, C.J.; Carter, E.E.; Kemp, G.J.; Codreanu, I.; Brooker, H.; Tyler, D.J.; Robbins, P.A.; Clarke, K. Short-term consumption of a high-fat diet impairs whole-body efficiency and cognitive function in sedentary men. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 1088–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrampour, N.; Rasaei, N.; Gholami, F.; Clark, C.C.T. The Association Between Dietary Energy Density and Musculoskeletal Pain in Adult Men and Women. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2022, 11, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijs, J.; D’Hondt, E.; Clarys, P.; Deliens, T.; Polli, A.; Malfliet, A.; Coppieters, I.; Willaert, W.; Tumkaya Yilmaz, S.; Elma, O.; et al. Lifestyle and Chronic Pain across the Lifespan: An Inconvenient Truth? PM&R 2020, 12, 410–419. [Google Scholar]
- Guillemot-Legris, O.; Buisseret, B.; Mutemberezi, V.; Hermans, E.; Deumens, R.; Alhouayek, M.; Muccioli, G.G. Post-operative pain in mice is prolonged by diet-induced obesity and rescued by dietary intervention. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 74, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.E.; Ma, Z.; Gu, X. Antinociceptive effects of caloric restriction on post-incisional pain in nonobese rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xie, W.; Chen, S.; Strong, J.A.; Print, M.S.; Wang, J.I.; Shareef, A.F.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Zhang, J.-M. High-fat diet increases pain behaviors in rats with or without obesity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Xie, W.; Strong, J.A.; Berta, T.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.M. High-fat diet exacerbates postoperative pain and inflammation in a sex-dependent manner. Pain 2018, 159, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, J.A.; Uong, C.D.; Lenert, M.E.; Williams, M.; Burton, M.D. High-fat diet causes mechanical allodynia in the absence of injury or diabetic pathology. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, K.; Vieira, M.; Younas, H.; Shin, M.K.; Bevans-Fonti, S.; Berger, S.; Lee, R.; D’Alessio, F.R.; Zhong, Q.; Nelson, A.; et al. High fat diet induces airway hyperresponsiveness in mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moura, E.D.M.; Dos Reis, S.A.; da Conceicao, L.L.; Sediyama, C.; Pereira, S.S.; de Oliveira, L.L.; Gouveia Peluzio, M.D.C.; Martinez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I. Diet-induced obesity in animal models: Points to consider and influence on metabolic markers. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdousi, M.I.; Calcagno, P.; Sanchez, C.; Smith, K.L.; Kelly, J.P.; Roche, M.; Finn, D.P. Characterization of pain-, anxiety-, and cognition-related behaviors in the complete Freund’s adjuvant model of chronic inflammatory pain in Wistar-Kyoto rats. Front. Pain Res. 2023, 4, 1131069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Qin, Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, L.F.; Ma, X.; Wu, Y.M.; Liu, S.B.; et al. Sophoridine alleviates hyperalgesia and anxiety-like behavior in an inflammatory pain mouse model induced by complete freund’s adjuvant. Mol. Pain 2023, 19, 17448069231177634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyachkova, U.; Vigovskiy, M.; Basalova, N.; Efimenko, A.; Grigorieva, O. M2-Macrophage-Induced Chronic Inflammation Promotes Reversible Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Senescence and Reduces Their Anti-Fibrotic Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, G.J.; To, B.; White, I.; Millecamps, M.; Beier, F.; Grol, M.W.; Stone, L.S.; Seguin, C.A. Diet-induced obesity leads to behavioral indicators of pain preceding structural joint damage in wild-type mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.M.; Matsumura, S.; Katano, T.; Funatsu, N.; Ito, S. Diabetic neuropathy research: From mouse models to targets for treatment. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1870–1879. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burek, D.J.; Massaly, N.; Doering, M.; Zec, A.; Gaelen, J.; Moron, J.A. Long-term inflammatory pain does not impact exploratory behavior and stress coping strategies in mice. Pain 2021, 162, 1705–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi, H. Bonferroni and Šidák corrections for multiple comparisons. Encycl. Meas. Stat. 2007, 3, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, C.; Leblond, D.; Joshi, S.; Zhu, C.; Hsieh, G.; Jacobson, P.; Meyer, M.; Decker, M. Estimating efficacy and drug ED50′s using von Frey thresholds: Impact of weber’s law and log transformation. J. Pain 2012, 13, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamashita, S.; Hattori, K.; Matsuda, N.; Hattori, Y. Impact of a long-term high-glucose environment on pro-inflammatory responses in macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Wei, Q.; Yang, J.; Hu, C.; Sun, X.; Cao, P. Soufeng sanjie formula alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization and modulating intestinal metabolites. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 339, 119147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Kou, X.; Yang, R.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Luo, Q.; Song, Y.; Liu, F.; Yan, Y.; Gan, Y.; et al. M1-like Macrophage Polarization Promotes Orthodontic Tooth Movement. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Kou, X.; Luo, Q.; Yang, R.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Cao, H.; Zeng, M.; Gan, Y.; et al. Enhanced M1/M2 macrophage ratio promotes orthodontic root resorption. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yang, H.; Qu, R.; Qiu, Y.; Hao, J.; Bi, H.; Guo, D. Regulatory Mechanism of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in the Development of Autoimmune Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 8821610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Ma, Y.; Luo, Q.; Song, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Jia, D.; Li, S.; Liu, X. Therapeutic potential of melatonin in the intervertebral disc degeneration through inhibiting the ferroptosis of nucleus pulpous cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 2340–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-kappaB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Kim, B.J.; Lim, E.J.; Back, S.K.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, S.W.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, W.W.; et al. Complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced intervertebral discitis as an animal model for discogenic low back pain. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 109, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki, S.; Chang, K.; Sakai, M.; Shimizu, N.; Yamada, M.; Tanaka, T.; Nakazawa, H.; Ichinose, F.; Yamada, Y.; Ishigami, A.; et al. Inflammatory stimuli induce inhibitory S-nitrosylation of the deacetylase SIRT1 to increase acetylation and activation of p53 and p65. Sci. Signal 2014, 7, ra106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, Y.T.; Chae, S.W. Tendinosis-like histologic and molecular changes of the Achilles tendon to repetitive stress: A pilot study in rats. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 3172–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisugi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Kawakami, T.; Kirita, T. Mechanical stretch enhances NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression and poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis in synovial cells. J. Biochem. 2010, 147, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Wang, Q.; Shapiro, R.A.; Billiar, T.R.; Geller, D.A. Nitric oxide down-regulates hepatocyte-inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression. Arch. Surg. 1997, 132, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnefous, C.; Payne, J.E.; Roppe, J.; Zhuang, H.; Chen, X.; Symons, K.T.; Nguyen, P.M.; Sablad, M.; Rozenkrants, N.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Discovery of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) inhibitor development candidate KD7332, part 1: Identification of a novel, potent, and selective series of quinolinone iNOS dimerization inhibitors that are orally active in rodent pain models. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3047–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.F.; Zheng, X.Q.; Lin, J.L.; Zhang, K.; Tian, H.J.; Zhou, W.X.; Wang, H.; Gao, Z.; Jin, H.M.; Wu, A.M. Sinapic Acid Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Apoptosis and Catabolism in Nucleus Pulposus Cells and Ameliorates Intervertebral Disk Degeneration. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 13, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Kang, L.; Tu, J.; Zhao, K.; Li, S.; Wang, K.; Song, Y.; Luo, R.; et al. Icariin Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Inflammatory Response in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 6071–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobai, I.A. Cardiomyocyte reprogramming in animal models of septic shock. Shock 2023, 59, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Lan, Y.; Hu, L.; Qin, R.; Li, H.; Weng, T.; Zou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Ge, W.; et al. AMPK activation mitigates inflammatory pain by modulating STAT3 phosphorylation in inflamed tissue macrophages of adult male mice. Mol. Pain 2025, 21, 17448069251321339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucattelli, M.; Lunghi, B.; Fineschi, S.; Mirone, V.; d’Emmanuele di Villa Bianca, R.; Longo, N.; Imbimbo, C.; De Palma, R.; Sorrentino, R.; Lungarella, G.; et al. A new mouse model of Peyronie’s disease: An increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 target genes during the development of penile changes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 2638–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marfella, R.; Esposito, K.; Nappo, F.; Siniscalchi, M.; Sasso, F.C.; Portoghese, M.; Di Marino, M.P.; Baldi, A.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Di Filippo, C.; et al. Expression of angiogenic factors during acute coronary syndromes in human type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2383–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, L.W.; Wang, J.; Chang, P.L.; Hsieh, Y.L. Hyaluronan modulates accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and matrix metalloproteinase-3 in the synovium of rat adjuvant-induced arthritis model. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navone, S.E.; Peroglio, M.; Guarnaccia, L.; Beretta, M.; Grad, S.; Paroni, M.; Cordiglieri, C.; Locatelli, M.; Pluderi, M.; Rampini, P.; et al. Mechanical loading of intervertebral disc modulates microglia proliferation, activation, and chemotaxis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.S.; Jang, H.J.; Oh, M.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Eom, D.W.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, S.N.; Kwan, H.C.; Ham, J.Y.; et al. 5,7-dihydroxy-3,4,6-trimethoxyflavone attenuates ischemic damage and apoptosis in mouse islets. Transpl. Proc. 2015, 47, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.S.; Eun, J.S.; Jeon, H. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive properties of the leaves of Eriobotrya japonica. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Huang, Y.; Pang, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Wang, D.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, X. Leptin Enhances M1 Macrophage Polarization and Impairs Tendon-Bone Healing in Rotator Cuff Repair: A Rat Model. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2025, 483, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthys, K.E.; Bult, H. Nitric oxide function in atherosclerosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 1997, 6, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, V.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Ramirez, B.; Ortega, V.A.; Hernandez-Lizoain, J.L.; Baixauli, J.; Becerril, S.; Rotellar, F.; Valenti, V.; et al. IL-32alpha-induced inflammation constitutes a link between obesity and colon cancer. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1328338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Gong, R.; Liu, L.; Feng, Y.; Hu, P.; Sun, W.; Hao, Q.; Kang, L.; et al. Negative feedback regulation of IL-32 production by iNOS activation in response to dsRNA or influenza virus infection. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starka, L.; Hill, M.; Pospisilova, H.; Duskova, M. Estradiol, obesity and hypogonadism. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69 (Suppl. 2), S273–S278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, X.X.; Wang, X.D.; Li, C.S.; Bi, R.Y.; Meng, Z.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.H.; Gan, Y.H. Estradiol-potentiated cadherin-11 in synovial membrane involves in temporomandibular joint inflammation in rats. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 143, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da S Rocha, J.C.; Peixoto, M.E.; Jancar, S.; de Q Cunha, F.; de A Ribeiro, R.; da Rocha, F.A. Dual effect of nitric oxide in articular inflammatory pain in zymosan-induced arthritis in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossato, M.F.; Hoffmeister, C.; Trevisan, G.; Bezerra, F.; Cunha, T.M.; Ferreira, J.; Silva, C.R. Monosodium urate crystal interleukin-1β release is dependent on Toll-like receptor 4 and transient receptor potential V1 activation. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciociola, F.; Colpi, G.M. Peyronie’s disease: A “triple oxygenant therapy”. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2013, 85, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Wang, X.Q. cGMP-mediated negative-feedback regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression by nitric oxide. Hypertension 1999, 34, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, A.; Bronte, V.; Visintin, A.; Spitzer, J.H.; Apolloni, E.; Serafini, P.; Zanovello, P.; Segal, D.M. Myeloid suppressor lines inhibit T cell responses by an NO-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, P.; Tomiuk, S.; Kammler, A.; Fandrich, F.; Schlitt, H.J.; Geissler, E.K.; Hutchinson, J.A. IFN-gamma-induced iNOS expression in mouse regulatory macrophages prolongs allograft survival in fully immunocompetent recipients. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.; Zacharowski, K.; Boehm, O.; Stevens, M.; Lipfert, P.; von Giesen, H.J.; Wolf, A.; Freynhagen, R. Nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory cytokines correlate with pain intensity in chronic pain patients. Inflamm. Res. 2007, 56, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagny, S.; Bouaouiche, S.; Lucchi, G.; Ducoroy, P.; Bertoldo, J.B.; Terenzi, H.; Bettaieb, A.; Plenchette, S. S-Nitrosylation of cIAP1 Switches Cancer Cell Fate from TNFalpha/TNFR1-Mediated Cell Survival to Cell Death. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, F.F.; Dumlao, J.M.; Lee, A.H.; Choy, J.C. Endogenous production of nitric oxide by iNOS in human cells restricts inflammatory activation and cholesterol/fatty acid biosynthesis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 231, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, E.M.; Gonzalez-Cotto, M.; Baseler, W.A.; Davies, L.C.; Ghesquiere, B.; Maio, N.; Rice, C.M.; Rouault, T.A.; Cassel, T.; Higashi, R.M.; et al. Nitric oxide orchestrates metabolic rewiring in M1 macrophages by targeting aconitase 2 and pyruvate dehydrogenase. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.F.; Yang, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Wu, B.C.; Huang, S.C.; Liu, C.M.; Chen, S.L.; Pan, Y.F.; Chou, S.S.; Chou, M.Y.; et al. Aspirin-induced inhibition of adipogenesis was p53-dependent and associated with inactivation of pentose phosphate pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Moreno, M.; Hermida-Gómez, T.; Larkins, N.; Reynolds, A.; Blanco, F.J. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of APPA (Apocynin and Paeonol) in Human Articular Chondrocytes. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, V.; Toti, A.; Lucarini, E.; Parisio, C.; Micheli, L.; Ciampi, C.; Margiotta, F.; Crocetti, L.; Vergelli, C.; Giovannoni, M.P.; et al. Protective and Pain-Killer Effects of AMC3, a Novel N-Formyl Peptide Receptors (FPRs) Modulator, in Experimental Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Y.; Huo, L.; Liu, M. Pulsed Red Photobiomodulation Boosts the Inhibition of Oxytocin-Induced Primary Dysmenorrhea in Mice by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. J. Biophotonics 2025, 18, e202400398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, T.Y.; Huang, S.K.; Lee, C.J.; Tsai, P.W.; Wang, C.C. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Afify, A.S.A.; El-Akabawy, G.; El-Sherif, N.M.; El-Safty, F.E.A.; El-Habiby, M.M. Avocado soybean unsaponifiables ameliorates cartilage and subchondral bone degeneration in mono-iodoacetate-induced knee osteoarthritis in rats. Tissue Cell 2018, 52, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, T.Y.; Jin, B.R.; Hong, C.H.; Park, J.H.; An, H.J. Astilbe Chinensis ethanol extract suppresses inflammation in macrophages via NF-κB pathway. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, T.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Caudullo, S.; Raffone, E.; Macrí, F.; Interdonato, L.; Gugliandolo, E.; Interlandi, C.; et al. Molecular and Biochemical Mechanism of Cannabidiol in the Management of the Inflammatory and Oxidative Processes Associated with Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippis, D.; D’Amico, A.; Cinelli, M.P.; Esposito, G.; Di Marzo, V.; Iuvone, T. Adelmidrol, a palmitoylethanolamide analogue, reduces chronic inflammation in a carrageenin-granuloma model in rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, H.S.; Kang, O.H.; Choi, J.G.; Oh, Y.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.; Jung, K.Y.; Sohn, D.H.; et al. 5-hydroxytryptophan acts on the mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular-signal regulated protein kinase pathway to modulate cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in RAW 264.7 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.H.; Wu, Z.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Chou, T.L.; Cheng, H.J.; Lo, Y.H.; Jean, Y.H.; Sung, C.S. Local Magnesium Sulfate Administration Ameliorates Nociception, Peripheral Inflammation, and Spinal Sensitization in a Rat Model of Incisional Pain. Neuroscience 2024, 547, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolahi, M.; Jafarieh, A.; Sarraf, P.; Sedighiyan, M.; Yousefi, A.; Tafakhori, A.; Abdollahi, H.; Salehinia, F.; Djalali, M. The Neuromodulatory Effects of ω-3 Fatty Acids and Nano-Curcumin on the COX-2/iNOS Network in Migraines: A Clinical Trial Study from Gene Expression to Clinical Symptoms. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 19, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King-Himmelreich, T.S.; Möser, C.V.; Wolters, M.C.; Olbrich, K.; Geisslinger, G.; Niederberger, E. Age-Dependent Changes in the Inflammatory Nociceptive Behavior of Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27508–27519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, C.A.; Rovira, J.; Colandré, M.E.; Cussó, R.; Cadefau, J.A. Effects of dietary cis and trans unsaturated and saturated fatty acids on the glucose metabolites and enzymes of rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 95, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prego-Dominguez, J.; Hadrya, F.; Takkouche, B. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pain Physician 2016, 19, 521–535. [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin, D.N.; Suter, T.A.; Ross, J.L.; Masino, S.A. Ketogenic diets and thermal pain: Dissociation of hypoalgesia, elevated ketones, and lowered glucose in rats. J. Pain 2013, 14, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdrighi, N.; Blom, A.B.; Vago, J.P.; van Beuningen, H.M.; Vitters, E.L.; Helsen, M.M.; Walgreen, B.; Arntz, O.J.; Koenders, M.I.; van der Kraan, P.M.; et al. Innate Immunity and Sex: Distinct Inflammatory Profiles Associated with Murine Pain in Acute Synovitis. Cells 2023, 12, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gühring, H.; Görig, M.; Ates, M.; Coste, O.; Zeilhofer, H.U.; Pahl, A.; Rehse, K.; Brune, K. Suppressed injury-induced rise in spinal prostaglandin E2 production and reduced early thermal hyperalgesia in iNOS-deficient mice. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 6714–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersoz, N.; Guven, A.; Cayci, T.; Uysal, B.; Turk, E.; Oztas, E.; Akgul, E.O.; Korkmaz, A.; Cetiner, S. Comparison of the efficacy of melatonin and 1400W on renal ischemia/reperfusion injury: A role for inhibiting iNOS. Ren. Fail. 2009, 31, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inada, T.; Hamano, N.; Yamada, M.; Shirane, A.; Shingu, K. Inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in delayed gastric emptying and gastrointestinal transit induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2006, 39, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplan, S.R.; Bach, F.W.; Pogrel, J.W.; Chung, J.M.; Yaksh, T.L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, K.; Dubner, R.; Brown, F.; Flores, C.; Joris, J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 1988, 32, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaniuk-Drapala, A.; Kosicka-Noworzyn, K.; Sheng, Y.H.; Yohn, C.; Brunetti, L.; Kagan, L. Evaluation of reference genes for qPCR in human liver and kidney tissue from individuals with obesity. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gomez, J.M.; Porcel-Pastrana, F.; De La Luz-Borrero, M.; Montero-Hidalgo, A.J.; Gomez-Gomez, E.; Herrera-Martinez, A.D.; Guzman-Ruiz, R.; Malagon, M.M.; Gahete, M.D.; Luque, R.M. LRP10, PGK1 and RPLP0: Best Reference Genes in Periprostatic Adipose Tissue under Obesity and Prostate Cancer Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragni, E.; Piccolo, S.; Taiana, M.; Visconte, C.; Grieco, G.; de Girolamo, L. Inflammation and Starvation Affect Housekeeping Gene Stability in Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzystek-Korpacka, M.; Diakowska, D.; Bania, J.; Gamian, A. Expression stability of common housekeeping genes is differently affected by bowel inflammation and cancer: Implications for finding suitable normalizers for inflammatory bowel disease studies. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward | Reverse | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence | Ln | Tm (°C) | Sequence | Ln | Tm (°C) | |
| IFN-γ | AAATCCTGCAGAGCCAGATTAT | 22 | 54.1 | GCTGTTGCTGAAGAAGGTAGTA | 22 | 54.5 |
| IL-10 | GAGGCGCTGTCATCGATTT | 19 | 55.5 | CACCTTGGTCTTGGAGCTTATT | 22 | 54.9 |
| IL-1β | CCACCTCAATGGACAGAATATCA | 23 | 54.4 | CCCAAGGCCACAGGTATTT | 19 | 55.1 |
| IL-4 | TTGAGAGAGATCATCGGCATTT | 22 | 54.0 | CTCACTCTCTGTGGTGTTCTTC | 22 | 54.9 |
| IL-6 | AAGACAAAGCCAGAGTCCTTC | 21 | 54.7 | CCTTCTGTGACTCCAGCTTATC | 22 | 54.8 |
| iNOS | GTCTGCATGGACCAGTATAAGG | 22 | 54.9 | TTCTTCAGAGTCTGCCCATTG | 21 | 54.8 |
| RPLP0 | AGAAACTGCTGCCTCACATC | 20 | 55.2 | CAGCAGCTGGCACCTTATT | 19 | 55.6 |
| TGF-β1 | GCAACAATTCCTGGCGTTAC | 20 | 54.7 | GTATTCCGTCTCCTTGGTTCAG | 22 | 55.0 |
| TNF | CCTCTTCTCATTCCTGCTTGT | 21 | 54.5 | TGGGAACTTCTCATCCCTTTG | 21 | 54.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, E.W.-Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.A.-J.; Cheung, C.-W. iNOS Mediates High-Fat Diet-Associated Aggravation of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced Inflammatory Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115422
Lee EW-Y, Wang L, Liu JA-J, Cheung C-W. iNOS Mediates High-Fat Diet-Associated Aggravation of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced Inflammatory Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115422
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Elmo Wing-Yiu, Lin Wang, Jessica Ai-Jia Liu, and Chi-Wai Cheung. 2025. "iNOS Mediates High-Fat Diet-Associated Aggravation of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced Inflammatory Pain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115422
APA StyleLee, E. W.-Y., Wang, L., Liu, J. A.-J., & Cheung, C.-W. (2025). iNOS Mediates High-Fat Diet-Associated Aggravation of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant-Induced Inflammatory Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115422






