A Comprehensive Review of Radiotherapy-Induced Coronary Artery Disease—Epidemiology, Biological Mechanisms, and Preventive Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Radiotherapy-Induced Coronary Artery Disease: Epidemiology
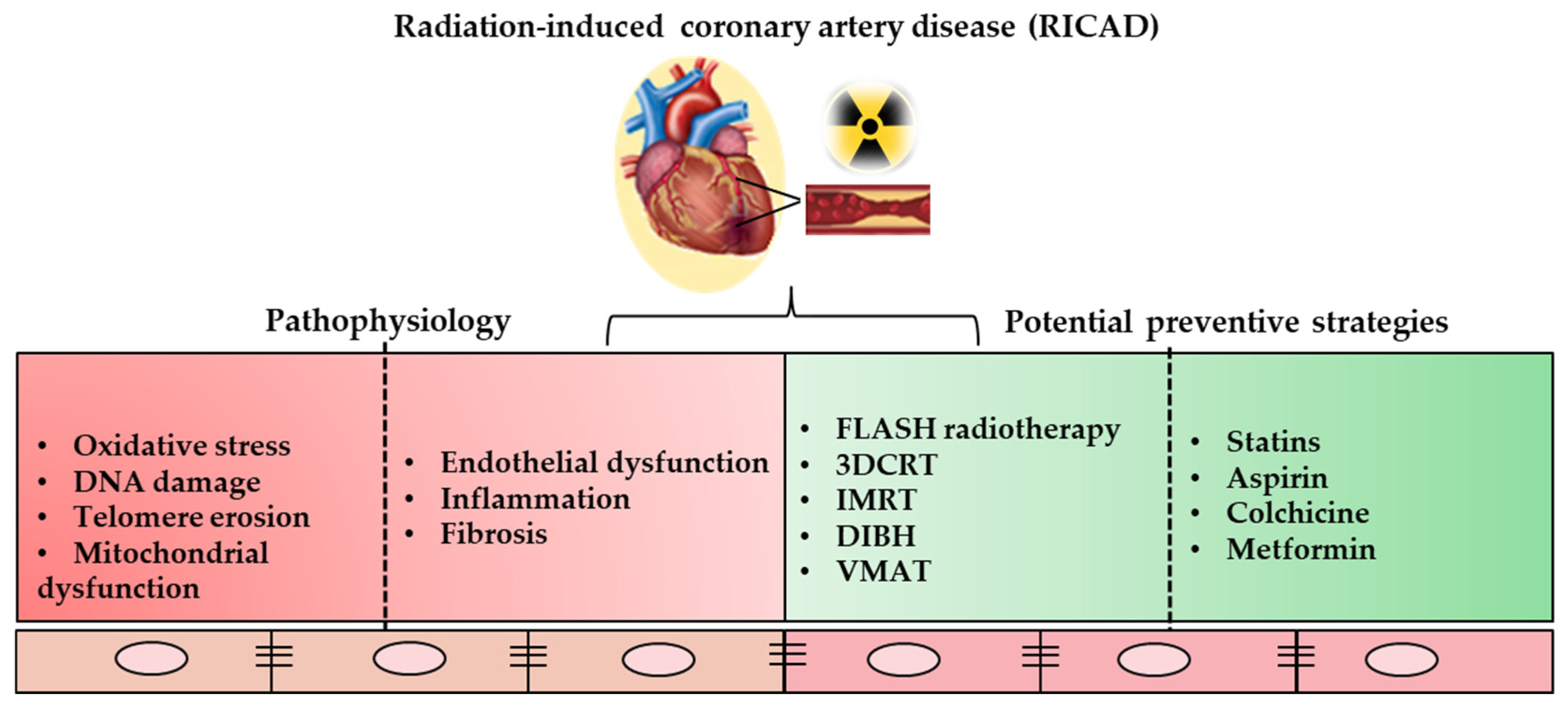
3. Radiotherapy-Induced Coronary Artery Disease: The Underlying Biological Mechanisms
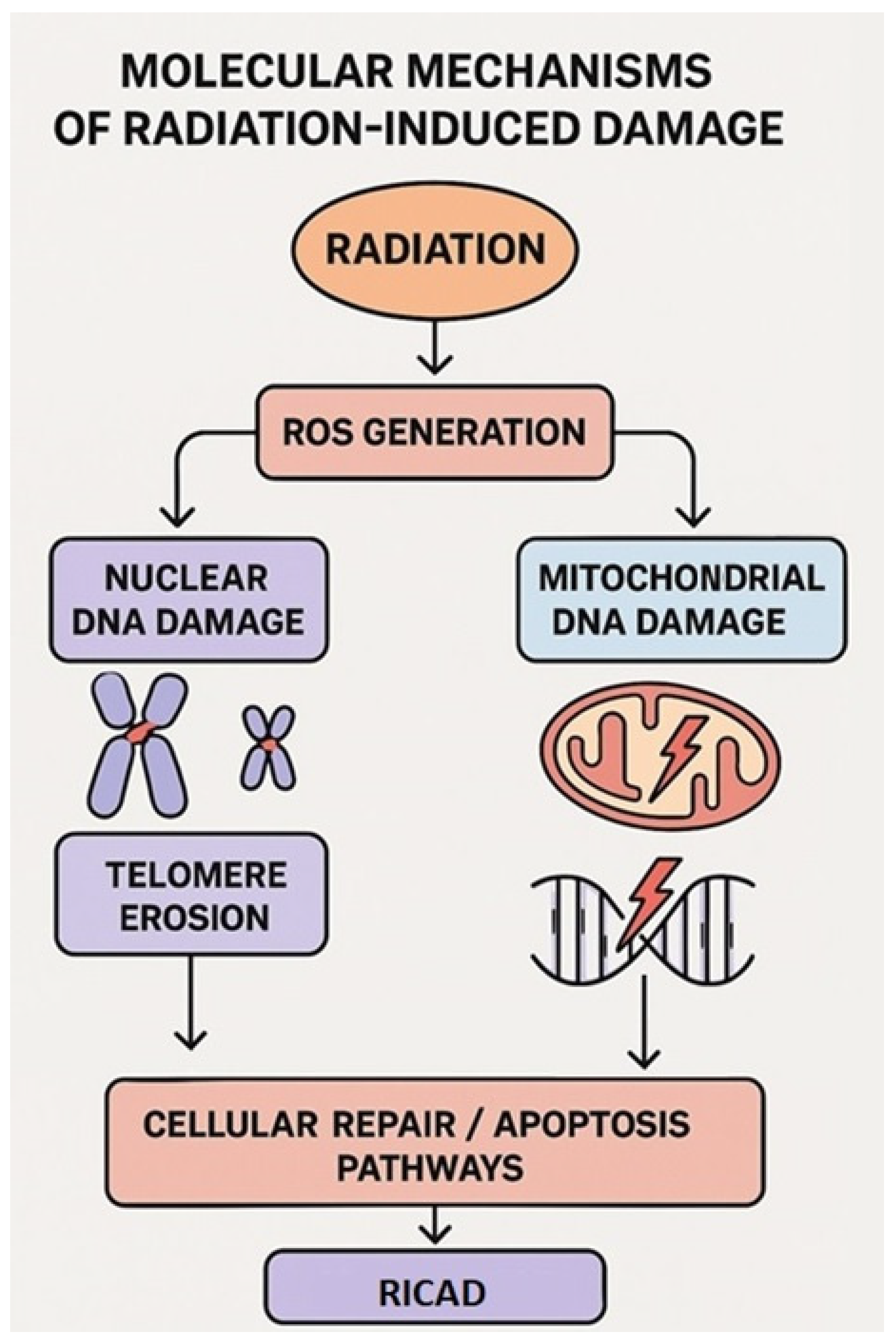
3.1. Focus on Molecular Mechanisms: Nuclear and Mitochondrial Damage
3.2. Focus on Cellular Mechanisms
4. Shielding the Heart: Potential Preventive Strategies in Radiotherapy-Induced Coronary Artery Disease
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3DCRT | Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy |
| CAD | Coronary artery disease |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DAMPs | Danger-associated molecular patterns |
| DIBH | Deep-inspiratory breath hold |
| DSBs | Double-stranded breaks |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cell |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| IMRT | Intensity-modulated radiation therapy |
| LET | Linear energy transfer |
| MACE | Major adverse cardiovascular events |
| mtDNA | Mitochondrial DNA |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa beta |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| RICAD | Radiation-induced coronary artery disease |
| RIHD | Radiation-induced heart disease |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SASP | Senescence-associated secretory phenotype |
| SSBs | Single-stranded breaks |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VHD | Valvular heart disease |
| VMAT | Volumetric modulated arc therapy |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffray, D.A.; Knaul, F.M.; Atun, R.; Adams, C.; Barton, M.B.; Baumann, M.; Lievens, Y.; Lui, T.Y.; Rodin, D.L.; Rosenblatt, E.; et al. Global task force on radiotherapy for cancer control. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1144–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, R.A.; Keane, F.K.; Voncken, F.E.M.; Thomas, C.R., Jr. Contemporary radiotherapy: Present and future. Lancet 2021, 398, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, L.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Dai, R.; Chen, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Song, D.; et al. A retrospective study on the impact of radiotherapy on the survival outcomes of small cell lung cancer patients based on the SEER database. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Gu, P.; Wang, Z. Recent advances progress in radiotherapy for breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery: A review. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1195266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzile-Dugas, E.; Eisenberg, M.J. Radiation-Induced Cardiovascular Disease: Review of an Underrecognized Pathology. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.W.; Venkatesulu, B.P.; Mahadevan, L.S.; Krishnan, S. Radiation-Induced Cardiovascular Disease: A Clinical Perspective. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 4, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, P.; Nkomo, V.T.; Badano, L.P.; Bergler-Klein, J.; Bogaert, J.; Davin, L.; Cosyns, B.; Coucke, P.; Dulgheru, R.; Edvardsen, T.; et al. Expert consensus for multi-modality imaging evaluation of cardiovascular complications of radiotherapy in adults: A report from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging and the American Society of Echocardiography. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Imaging 2013, 14, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnellan, E.; Phelan, D.; McCarthy, C.P.; Collier, P.; Desai, M.; Griffin, B. Radiation-induced heart disease: A practical guide to diagnosis and management. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2016, 83, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.M.; Okwuosa, T.M.; Scarabelli, T.; Moudgil, R.; Yeh, E.T.H. Cardiovascular complications of cancer therapy: Best practices in diagnosis, prevention, and management: Part 2. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2552–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douple, E.B.; Mabuchi, K.; Cullings, H.M.; Preston, D.L.; Kodama, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Fujiwara, S.; Shore, R.E. Long-term radiation-related health effects in a unique human population: Lessons learned from the atomic bomb survivors of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2011, 5, S122–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, V.K.; Maksioutov, M.A.; Chekin, S.Y.; Petrov, A.V.; Biryukov, A.P.; Kruglova, Z.G.; Matyash, V.A.; Tsyb, A.F.; Manton, K.G.; Kravchenko, J.S. The risk of radiation-induced cerebrovascular disease in Chernobyl emergency workers. Health Phys. 2006, 90, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirresh, A.; White, L.; Mitchell, A.; Ahmad, S.; Obika, B.; Davis, S.; Ahmad, M.; Candilio, L. Radiation-induced coronary artery disease: A difficult clinical conundrum. Clin. Med. 2022, 22, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, A.R.; López-Fernández, T.; Couch, L.S.; Asteggiano, R.; Aznar, M.C.; Bergler-Klein, J.; Boriani, G.; Cardinale, D.; Cordoba, R.; Cosyns, B.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4229–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Zheng, Q.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Yin, X.; Jiang, X. Radiation-induced heart disease: A review of classification, mechanism and prevention. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boero, I.J.; Paravati, A.J.; Triplett, D.P.; Hwang, L.; Matsuno, R.K.; Gillespie, E.F.; Yashar, C.M.; Moiseenko, V.; Einck, J.P.; Mell, L.K.; et al. Modern Radiation Therapy and Cardiac Outcomes in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nimwegen, F.A.; Schaapveld, M.; Janus, C.P.; Krol, A.D.; Petersen, E.J.; Raemaekers, J.M.; Kok, W.E.; Aleman, B.M.; van Leeuwen, F.E. Cardiovascular disease after Hodgkin lymphoma treatment: 40-year disease risk. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczwara, B.; Meng, R.; Miller, M.D.; Clark, R.A.; Kaambwa, B.; Marin, T.; Damarell, R.A.; Roder, D.M. Late mortality in people with cancer: A population-based Australian study. Med. J. Aust. 2021, 214, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Qadir, H.; Thavendiranathan, P.; Austin, P.C.; Lee, D.S.; Amir, E.; Tu, J.V.; Fung, K.; Anderson, G.M. The risk of heart failure and other cardio vascular hospitalizations after early stage breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Hancock, S.L.; Vagelos, R.H.; Lee, B.K.; Schnittger, I. Diastolic dysfunction after mediastinal irradiation. Am. Heart J. 2005, 150, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rosendael, A.R.; Daniëls, L.A.; Dimitriu-Leen, A.C.; Smit, J.M.; van Rosendael, P.J.; Schalij, M.J.; Bax, J.J.; Scholte, A.J. Different manifestation of irradiation induced coronary artery disease detected with coronary computed tomography compared with matched non-irradiated controls. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 125, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, D.I.; Wiebe, N.; Cheung, W.Y.; Mackey, J.R.; Pituskin, E.; Reiman, A.; Tonelli, M. Incident cardiovascular disease among adults with cancer. J. CardioOncol. 2022, 4, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velusamy, R.; Nolan, M.; Murphy, A.; Thavendiranathan, P.; Marwick, T.H. Screening for Coronary Artery Disease in Cancer Survivors: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. JACC CardioOncol. 2023, 5, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, G.T.; Chen, Y.; Yasui, Y.; Leisenring, W.; Gibson, T.M.; Mertens, A.C.; Stovall, M.; Oeffinger, K.C.; Bhatia, S.; Krull, K.R.; et al. Reduction in late mortality among 5-year survivors of childhood cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nimwegen, F.A.; Schaapveld, M.; Cutter, D.J.; Janus, C.P.; Krol, A.D.; Hauptmann, M.; Kooijman, K.; Roesink, J.; van der Maazen, R.; Darby, S.C.; et al. Radiation dose-response relationship for risk of coronary heart disease in survivors of Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Nie, X.; Ji, C.; Lin, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Yao, H.; Wu, S. Long-term cardiovascular risk after radiotherapy in women with breast cancer. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornforth, M.N.; Loucas, B.D. A Cytogenetic profile of radiation damage. Radiat. Res. 2019, 191, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, A.; Gianicolo, E.A.L.; Picano, E.; Andreassi, M.G. Ionizing radiation and atherosclerosis: Current knowledge and future challenges. Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Minami, M.; Yoshida, K.; Nagata, M.; Miyata, T.; Yang, T.; Takayama, N.; Suzuki, K.; Okawa, M.; Yamada, K.; et al. Irradiation accelerates plaque formation and cellular senescence in flow-altered carotid arteries of apolipoprotein E knock-out mice. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, K.J.; Bae, S.; Kim, D.H. Characterization of DNA damage-induced cellular senescence by ionizing radiation in endothelial cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2014, 90, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, J.; Le Gleut, R.; von Toerne, C.; Subedi, P.; Azimzadeh, O.; Atkinson, M.J.; Tapio, S. Radiation response of human cardiac endothelial cells reveals a central role of the cGAS-STING pathway in the development of inflammation. Proteomes 2020, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.-X.; Ye, C.; Yang, X.; Ma, P.; Yan, C.; Luo, L. New Insights into the Understanding of Mechanisms of Radiation-Induced Heart Disease. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, L.; Picano, E.; Andreassi, M.G. Telomere shortening and ionizing radiation: A possible role in vascular dysfunction? Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2012, 88, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lange, T. Shelterin: The protein complex that shapes and safeguards human telomeres. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2100–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.J.; Cech, T.R. Shaping human telomeres: From shelterin and CST complexes to telomeric chromatin organization. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Richardson, G.; Haendeler, J.; Altschmied, J.; Andrés, V.; Spyridopoulos, I. Telomerase as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hou, M.; Lou, F.; Björkholm, M.; Xu, D. Telomere dysfunction induced by chemotherapeutic agents and radiation in normal human cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardinelli, F.; Antoccia, A.; Buonsante, R.; Gerardi, S.; Cherubini, R.; De Nadal, V.; Tanzarella, C.; Sgura, A. The role of telomere length modulation in delayed chromosome instability induced by ionizing radiation in human primary fibroblasts. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2013, 54, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuta, O.; Rothkamm, K.; Darroudi, F. The role of telomerase in radiation-induced genomic instability. Radiat. Res. 2020, 193, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Nakamura, K.; Atsumi, K.; Hirakawa, M.; Ueda, Y.; Makino, N. Radiation-associated changes in the length of telomeres in peripheral leukocytes from inpatients with cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2013, 89, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M’Kacher, R.; Girinsky, T.; Colicchio, B.; Ricoul, M.; Dieterlen, A.; Jeandidier, E.; Heidingsfelder, L.; Cuceu, C.; Shim, G.; Frenzel, M.; et al. Telomere shortening: A new prognostic factor for cardiovascular disease post-radiation exposure. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2015, 164, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Guo, Q.; Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Diseases: Potential Targets for Treatment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 841523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Pachouri, U.C.; Khaidem, D.C.; Kundu, A.; Chopra, C.; Singh, P. Mitochondrial DNA Damage and Diseases. F1000Res 2015, 4, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMauro, S.; Schon, E.A. Mitochondrial DNA mutations in human disease. Am. J. Med Genet. 2001, 106, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingston, K.; Schlaak, R.A.; Puckett, L.L.; Bergom, C. The Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Radiation-Induced Heart Disease: From Bench to Bedside. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, G.E.; Sohal, R.S.; Sun, S.C.; Miller, G.C.; Colcolough, H.L. Effects of radiation on the human heart. An electron microscopic study. Arch. Intern. Med. 1968, 121, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjaktarovic, Z.; Schmaltz, D.; Shyla, A.; Azimzadeh, O.; Schulz, S.; Haagen, J.; Dörr, W.; Sarioglu, H.; Schäfer, A.; Atkinson, M.J.; et al. Radiation–Induced signaling results in mitochondrial impairment in mouse heart at 4 weeks after exposure to X-rays. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjaktarovic, Z.; Shyla, A.; Azimzadeh, O.; Schulz, S.; Haagen, J.; Dörr, W.; Sarioglu, H.; Atkinson, M.J.; Zischka, H.; Tapio, S. Ionising radiation induces persistent alterations in the cardiac mitochondrial function of C57BL/6 mice 40 weeks after local heart exposure. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 106, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimzadeh, O.; Scherthan, H.; Sarioglu, H.; Barjaktarovic, Z.; Conrad, M.; Vogt, A.; Calzada-Wack, J.; Neff, F.; Aubele, M.; Buske, C.; et al. Rapid proteomic remodeling of cardiac tissue caused by total body ionizing radiation. Proteomics 2011, 11, 3299–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselet, B.; Sonveaux, P.; Baatout, S.; Aerts, A. Pathological effects of ionizing radiation: Endothelial activation and dysfunction. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 699–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbeck, D.; Rodriguez-Lafrasse, C. Role of mitochondria in radiation responses: Epigenetic, metabolic, and signaling impacts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Shi, Y.; Lees-Miller, S.P.; Tainer, J.A. Function and Molecular Mechanism of the DNA Damage Response in Immunity and Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 797880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, R.M.F.L. Effects of Radiotherapy in Coronary Artery Disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2019, 21, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesulu, B.P.; Mahadevan, L.S.; Aliru, M.L.; Yang, X.; Bodd, M.H.; Singh, P.K.; Yusuf, S.W.; Abe, J.I.; Krishnan, S. Radiation-Induced Endothelial Vascular Injury: A Review of Possible Mechanisms. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2018, 3, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, B.; Metharom, P.; Caplice, N.M. Endothelial progenitor cells. Endothelium 2006, 13, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonca, M.S.; Chin-Sinex, H.; Dhaemers, R.; Mead, L.E.; Yoder, M.C.; Ingram, D.A. Differential mechanisms of x-ray-induced cell death in human endothelial progenitor cells isolated from cord blood and adults. Radiat. Res. 2011, 176, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.; Horvath, S.; Raj, K. Epigenetic clock analyses of cellular senescence and ageing. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8524–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppé, J.-P.; Desprez, P.-Y.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: The dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2010, 5, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Tong, F.; Qian, C.; Zhang, R.; Dong, J.; Wu, G.; Hu, Y. NEMO modulates radiation-induced endothelial senescence of human umbilical veins through NF-κB signal pathway. Radiat. Res. 2015, 183, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turer, A.T.; Hill, J.A. Pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 106, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangie, C.; Daher, J. Role of myeloperoxidase in inflammation and atherosclerosis (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2022, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krigsfeld, G.S.; Kennedy, A.R. Is disseminated intravascular coagulation the major cause of mortality from radiation at relatively low whole body doses? Radiat. Res. 2013, 180, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abderrahmani, R.; François, A.; Buard, V.; Tarlet, G.; Blirando, K.; Hneino, M.; Vaurijoux, A.; Benderitter, M.; Sabourin, J.C.; Milliat, F. PAI-1-dependent endothelial cell death determines severity of radiation-induced intestinal injury. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wei, J.; Meng, L.; Wang, H.; Qu, C.; Chen, X.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. Advances in pathogenic mechanisms and management of radiation-induced fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnold, J.; Brotons, M.-C.V. Pathogenetic mechanisms in radiation fibrosis. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 97, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhey, L.J. Comparison of three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy and intensity-modulated radiation therapy systems. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 1999, 9, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagar, T.M.; Kaidar-Person, O.; Tang, X.; Jones, E.E.; Matney, J.; Das, S.K.; Green, R.L.; Sheikh, A.; Khandani, A.H.; McCartney, W.H.; et al. Utility of deep inspiration breath hold for left-sided breast radiation therapy in preventing early cardiac perfusion defects: A prospective study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, R.; Lee, K.A.; Yeo, R.; Yeoh, K.-W. Cancer and radiation therapy: Current advances and future directions. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhis, J.; Sozzi, W.J.; Jorge, P.G.; Gaide, O.; Bailat, C.; Duclos, F.; Patin, D.; Ozsahin, M.; Bochud, F.; Germond, J.-F.; et al. Treatment of a first patient with FLASH-radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, A.; Labate, L.; Piccinini, S.; Panaino, C.M.V.; Andreassi, M.G.; Gizzi, L.A. FLASH Radiotherapy: Expectations, Challenges, and Current Knowledge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Kim, M.M.; Skoufos, G.; Diffenderfer, E.S.; Motlagh, S.A.O.; Kokkorakis, M.; Koliaki, I.; Morcos, G.; Shoniyozov, K.; Griffin, J.; et al. FLASH Proton Radiation Therapy Mitigates Inflammatory and Fibrotic Pathways and Preserves Cardiac Function in a Preclinical Mouse Model of Radiation-Induced Heart Disease. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 119, 1234–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchio, P.; Guerra-Ojeda, S.; Vila, J.M.; Aldasoro, M.; Victor, V.M.; Mauricio, M.D. Targeting early atherosclerosis: A focus on oxidative stress and inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 8563845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camara Planek, M.I.; Silver, A.J.; Volgman, A.S.; Okwuosa, T.M. Exploratory Review of the Role of Statins, Colchicine, and Aspirin for the Prevention of Radiation-Associated Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulet, J.; Peña, J.; Hulten, E.A.; Neilan, T.G.; Dragomir, A.; Freeman, C.; Lambert, C.; Hijal, T.; Nadeau, L.; Brophy, J.M.; et al. Statin Use and Risk of Vascular Events Among Cancer Patients After Radiotherapy to the Thorax, Head, and Neck. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e005996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, W.; Shia, B.; Wu, S. Statin Therapy Reduces Radiation-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Patients With Breast Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Radiotherapy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e036411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, C.; Kilciksiz, S.C.; Gurgul, S.; Erdal, N.; Yigit, S.; Tamer, L.; Ayaz, L. Inhibition of radiation-induced oxidative damage in the lung tissue: May acetylsalicylic acid have a positive role? Inflammation 2016, 39, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoving, S.; Heeneman, S.; Gijbels, M.J.; Te Poele, J.A.; Bolla, M.; Pol, J.F.; Simons, M.Y.; Russell, N.S.; Daemen, M.J.; Stewart, F.A. NO-donating aspirin and aspirin partially inhibit age-related atherosclerosis but not radiation-induced atherosclerosis in ApoE null mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Herron, T.; Lafferty, J. Prophylactic use of colchicine in preventing radiation induced coronary artery disease. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 111, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-M.; Hsieh, M.-C.; Qin, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.-Y. Metformin reduces radiation-induced cardiac toxicity risk in patients having breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Glanzmann, C.; Kaufmann, P.; Jenni, R.; Hess, O.M.; Huguenin, P. Cardiac risk after mediastinal irradiation for Hodgkin’s disease. Radiother. Oncol. 1998, 46, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, S.C.; Ewertz, M.; McGale, P.; Bennet, A.M.; Blom-Goldman, U.; Brønnum, D.; Correa, C.; Cutter, D.; Gagliardi, G.; Gigante, B.; et al. Risk of ischemic heart disease in women after radiotherapy for breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.W.; Habel, L.A.; Weltzien, E.; Castillo, A.; Gupta, D.; Kroenke, C.H.; Kwan, M.L.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Scott, J.; Sternfeld, B.; et al. Exercise and risk of cardiovascular events in women with nonmetastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGale, P.; Darby, S.C.; Hall, P.; Adolfsson, J.; Bengtsson, N.-O.; Bennet, A.M.; Fornander, T.; Gigante, B.; Jensen, M.-B.; Peto, R.; et al. Incidence of heart disease in 35,000 women treated with radiotherapy for breast cancer in Denmark and Sweden. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 100, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCORE2 Working Group; ESC Cardiovascular Risk Collaboration. SCORE2 risk prediction algorithms: New models to estimate 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease in Europe. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2439–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Preventive Strategy | Mode of Action |
|---|---|
| Three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3DCRT) | Relies on computed tomography technology for more accurate delivery |
| Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) | Simultaneously delivers multiple radiation beams with variable individual intensities; is very efficient; spares non-target tissues |
| Deep-inspiratory breath hold (DIBH) | Displaces the breast and chest wall away from the heart during radiation therapy; reduces cardiac dose |
| FLASH radiotherapy | Delivers ultra-high doses of radiation in an extremely short span of milliseconds; specifically targets the tumor tissue; protective for neighboring non-tumor tissues |
| Statins | May reduce the effects of radiation-induced cell injuries |
| Aspirin | Can provide radioprotective effects by reducing oxidative damage |
| Metformin | May reduce the risk of radiation-induced cardiac toxicity in patients with breast cancer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daher, J.; Rizza, A.; Tonacci, A.; Borghini, A. A Comprehensive Review of Radiotherapy-Induced Coronary Artery Disease—Epidemiology, Biological Mechanisms, and Preventive Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115401
Daher J, Rizza A, Tonacci A, Borghini A. A Comprehensive Review of Radiotherapy-Induced Coronary Artery Disease—Epidemiology, Biological Mechanisms, and Preventive Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115401
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaher, Jalil, Antonio Rizza, Alessandro Tonacci, and Andrea Borghini. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of Radiotherapy-Induced Coronary Artery Disease—Epidemiology, Biological Mechanisms, and Preventive Strategies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115401
APA StyleDaher, J., Rizza, A., Tonacci, A., & Borghini, A. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of Radiotherapy-Induced Coronary Artery Disease—Epidemiology, Biological Mechanisms, and Preventive Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5401. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115401









