Identification of Plasma Growth Factors and Cytokines as Diagnostic Biomarkers for the Lafora Form of Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of CXCL10, S100B, and CCL20 Protein Levels
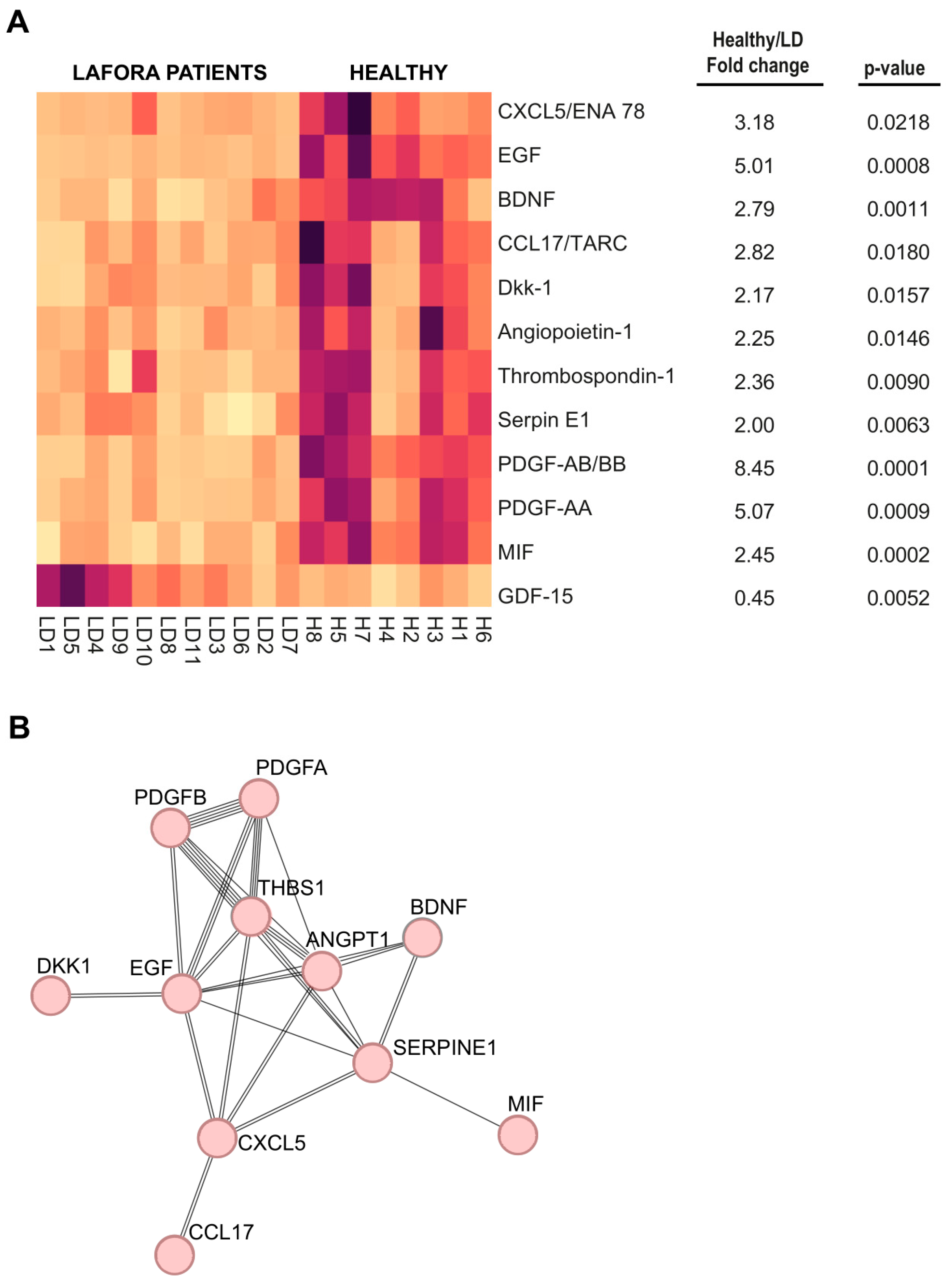
2.2. Analysis of Human Plasma Samples Using High-Throughput Arrays
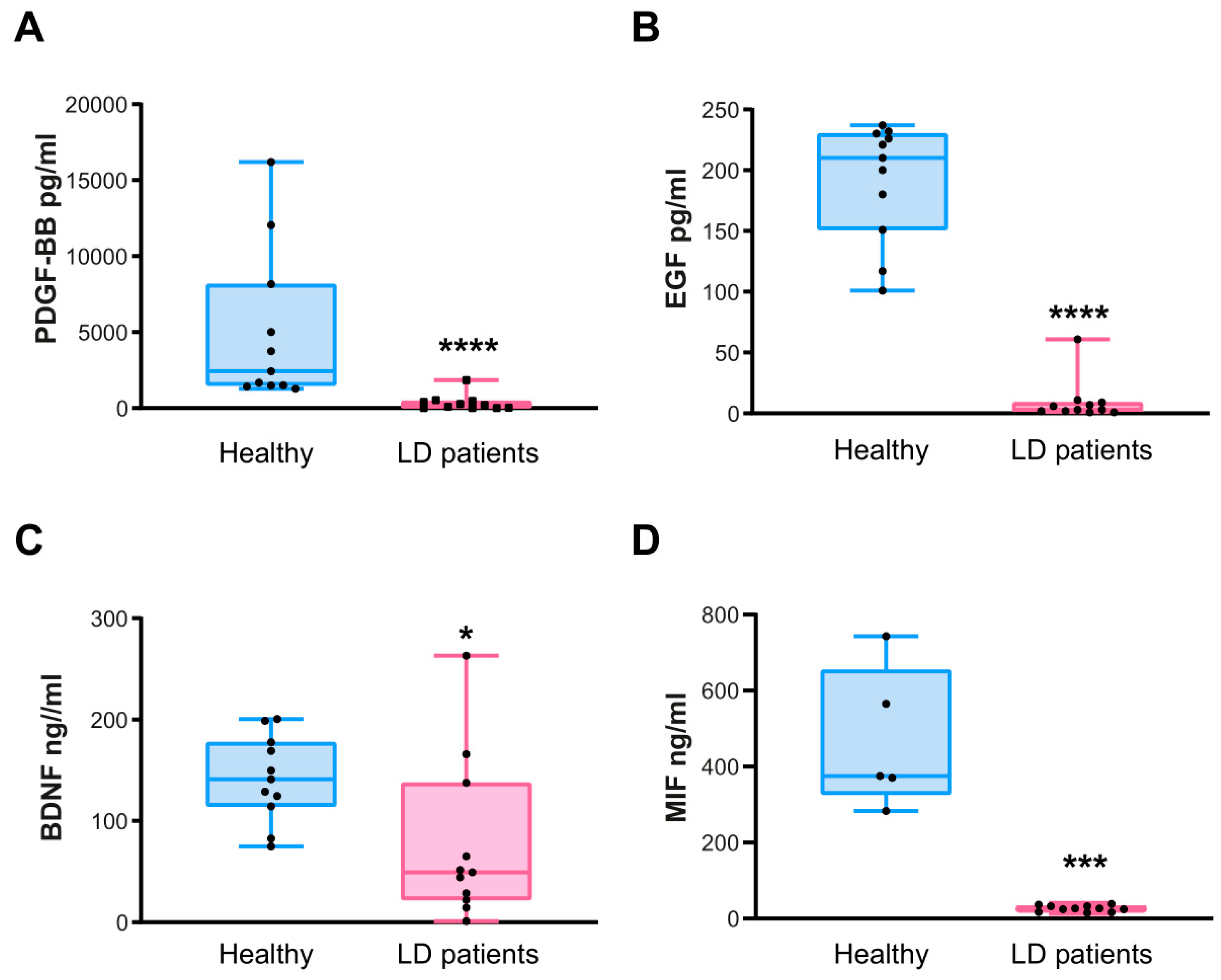
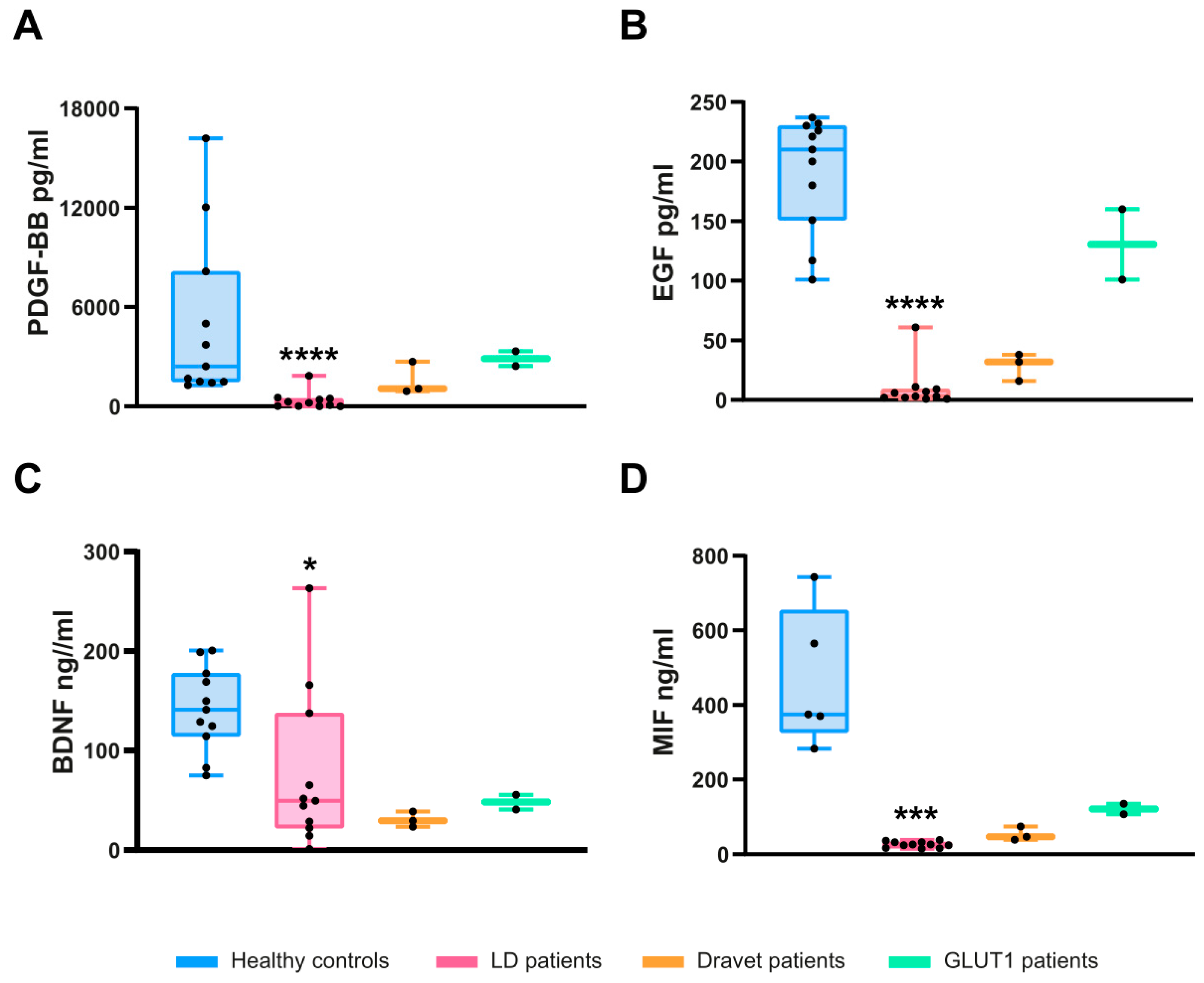
2.3. Confirmation of the Levels of PDGF-AB/BB, EGF, BDNF, and MIF by ELISA Assays
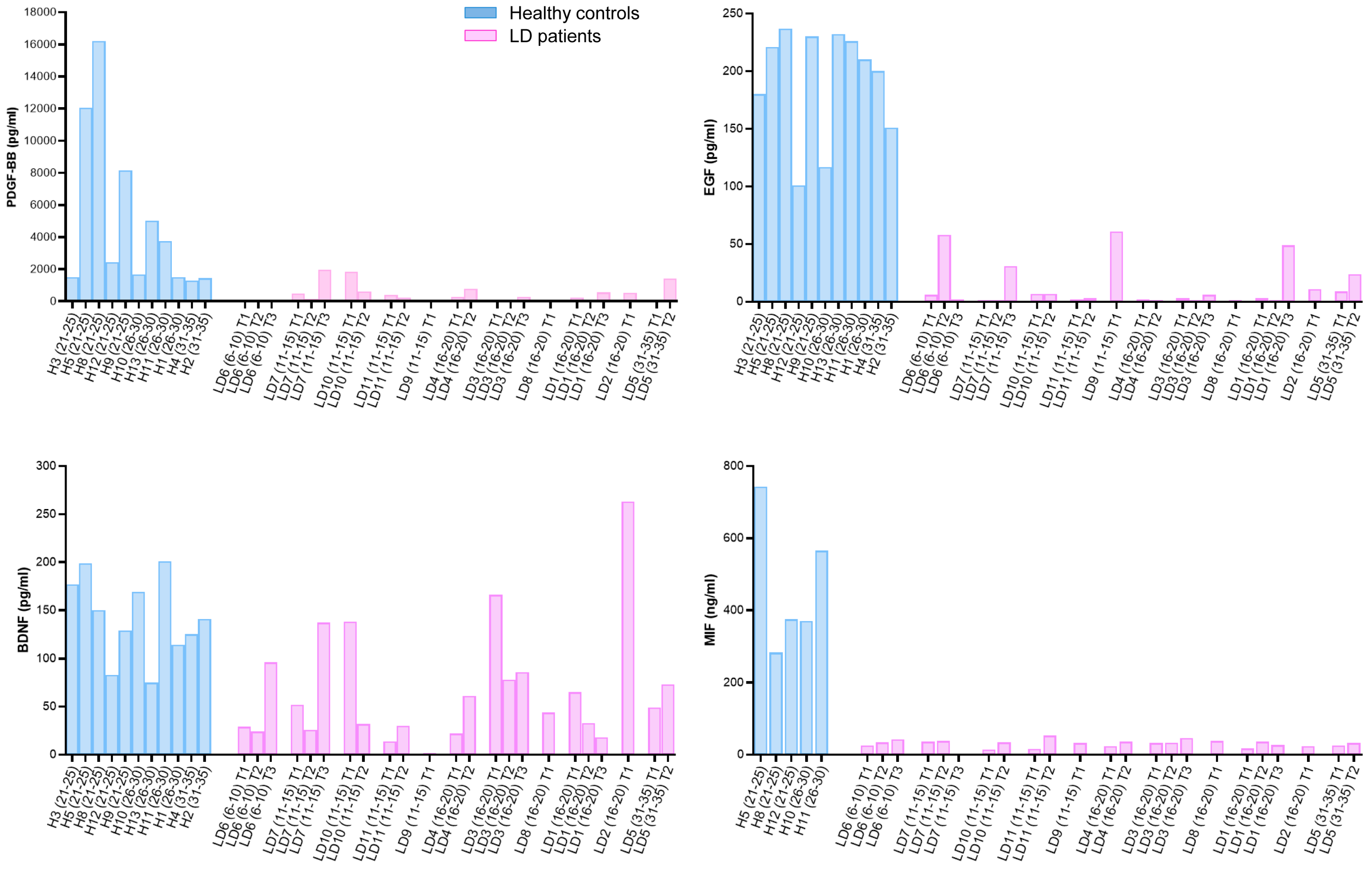
2.4. Correlation of PDGF-BB, EGF, BDNF, and MIF Levels with the Clinical Presentation of LD Patients
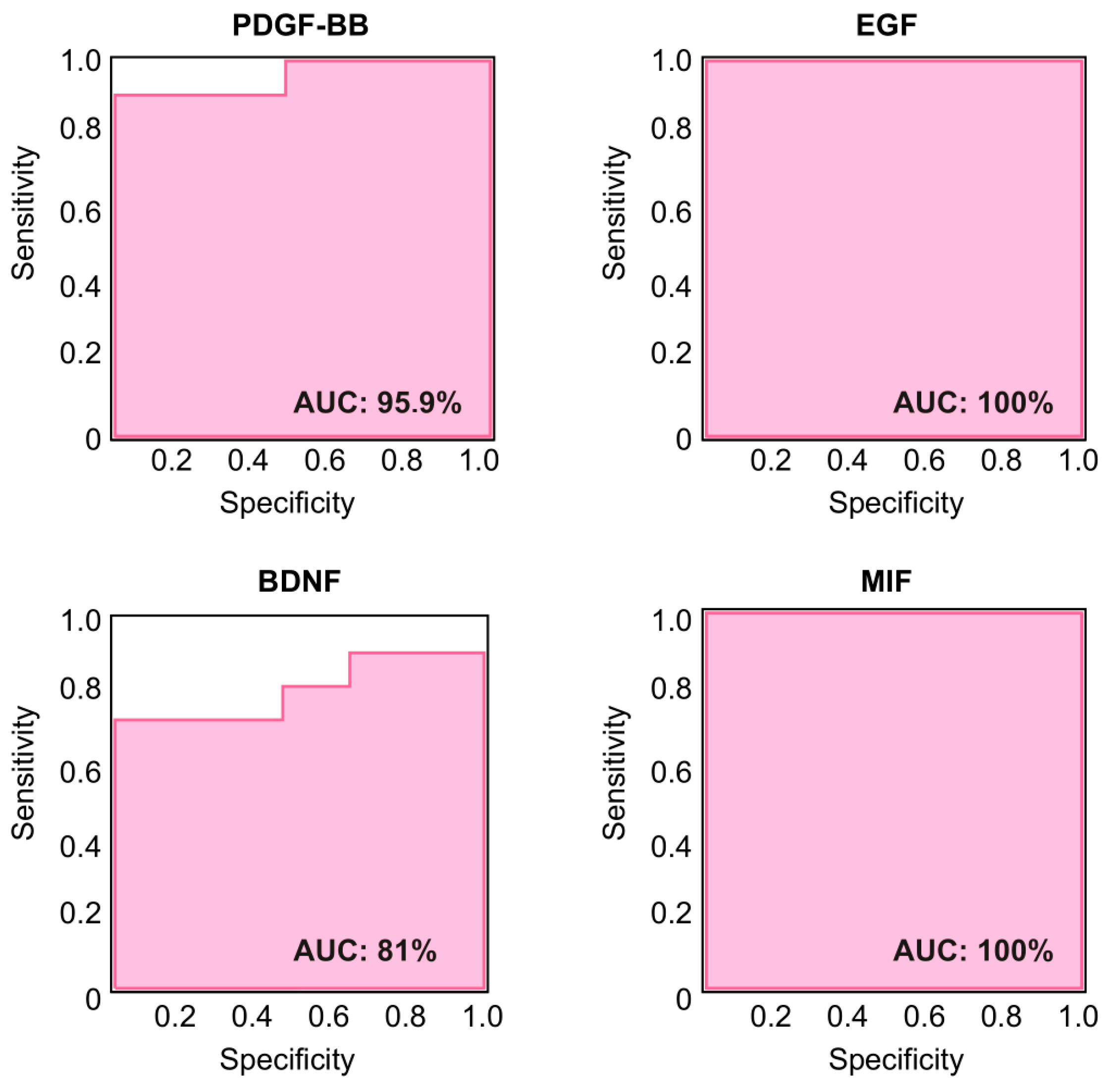
2.5. Specificity of PDGF-BB, EGF, BDNF, and MIF as Biomarkers for LD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Biomarker Validation
4.3. High-Throughput Screening of Inflammatory Mediators
4.4. Protein Interactions
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lafora, G.R.; Glueck, B. Beitrag zur histogpathologie der myoklonischen epilepsie. Gesamte Neurol. Psychiatr. 1911, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahuerta, M.; Gonzalez, D.; Aguado, C.; Fathinajafabadi, A.; Garcia-Gimenez, J.L.; Moreno-Estelles, M.; Roma-Mateo, C.; Knecht, E.; Pallardo, F.V.; Sanz, P. Reactive glia-derived neuroinflammation: A novel hallmark in lafora progressive myoclonus epilepsy that progresses with age. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1607–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, T.; Viana, R.; Moreno-Estelles, M.; Campos-Rodriguez, A.; Sanz, P. Tnf and il6/jak2 signaling pathways are the main contributors of the glia-derived neuroinflammation present in lafora disease, a fatal form of progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 176, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaz-Fuster, M.C.; Gimeno-Alcaniz, J.V.; Ros, S.; Fernandez-Sanchez, M.E.; Garcia-Fojeda, B.; Criado Garcia, O.; Vilchez, D.; Dominguez, J.; Garcia-Rocha, M.; Sanchez-Piris, M.; et al. Regulation of glycogen synthesis by the laforin-malin complex is modulated by the amp-activated protein kinase pathway. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchez, D.; Ros, S.; Cifuentes, D.; Pujadas, L.; Valles, J.; Garcia-Fojeda, B.; Criado-Garcia, O.; Fernandez-Sanchez, E.; Medrano-Fernandez, I.; Dominguez, J.; et al. Mechanism suppressing glycogen synthesis in neurons and its demise in progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccioli, L.; Vignatelli, L.; Tappate, M.; Mazzone, S.; Zenesini, C.; Armstrong, D.; Michelucci, R.; Bisulli, F. VAL-1221 for the treatment of patients with Lafora disease: Study protocol for a single-arm, open-label clinical trial. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e085062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pondrelli, F.; Muccioli, L.; Licchetta, L.; Mostacci, B.; Zenesini, C.; Tinuper, P.; Vignatelli, L.; Bisulli, F. Natural history of lafora disease: A prognostic systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Nguyen, V.H.; Arabi, M.R.; McNamara, N.; Holder, D.; Partikian, A.; Henry, J.; Tantsis, E.; Somoza, R.S.; Garrido, C.; et al. Five stages of lafora disease epilepsy: Early biomarkers are occipital seizures and suppression of eeg polyspike waves and rem during sleep. Abstr. Am. Epilepsy Soc. Meet. 2021, 3348. [Google Scholar]
- Burgos, D.F.; Cusso, L.; Sanchez-Elexpuru, G.; Calle, D.; Perpinya, M.B.; Desco, M.; Serratosa, J.M.; Sanchez, M.P. Structural and functional brain abnormalities in mouse models of lafora disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Panatpur, A.; Messahel, S.; Dahshi, H.; Johnson, T.; Henning, A.; Ren, J.; Minassian, B.A. (1)h and (31)p magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals potential pathogenic and biomarker metabolite alterations in lafora disease. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Orsi, G.; Farolfi, A.; Muccioli, L.; Palumbo, O.; Palumbo, P.; Modoni, S.; Allegri, V.; Garibotto, V.; Di Claudio, M.T.; Di Muro, E.; et al. Association of csf and pet markers of neurodegeneration with electroclinical progression in lafora disease. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1202971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muccioli, L.; Farolfi, A.; Pondrelli, F.; d’Orsi, G.; Michelucci, R.; Freri, E.; Canafoglia, L.; Licchetta, L.; Toni, F.; Bonfiglioli, R.; et al. Fdg-pet assessment and metabolic patterns in lafora disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, M.K.; Uittenbogaard, A.; Austin, G.L.; Segvich, D.M.; DePaoli-Roach, A.; Roach, P.J.; McCarthy, J.J.; Simmons, Z.R.; Brandon, J.A.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Targeting pathogenic lafora bodies in lafora disease using an antibody-enzyme fusion. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 689–705.e686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markussen, K.H.; Corti, M.; Byrne, B.J.; Vander Kooi, C.W.; Sun, R.C.; Gentry, M.S. The multifaceted roles of the brain glycogen. J. Neurochem. 2024, 168, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmers, T.A.; Jin, X.; Hsiao, E.C.; McGrath, S.A.; Esquela, A.F.; Koniaris, L.G. Growth differentiation factor-15/macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 induction after kidney and lung injury. Shock 2005, 23, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wollert, K.C.; Kempf, T.; Lagerqvist, B.; Lindahl, B.; Olofsson, S.; Allhoff, T.; Peter, T.; Siegbahn, A.; Venge, P.; Drexler, H.; et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 for risk stratification and selection of an invasive treatment strategy in non st-elevation acute coronary syndrome. Circulation 2007, 116, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Meloux, A.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Functional roles of gdf15 in modulating microenvironment to promote carcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, A.P.; Chen, M.; Taskar, P.; Rimmington, D.; Patel, S.; Tadross, J.A.; Cimino, I.; Yang, M.; Welsh, P.; Virtue, S.; et al. Gdf15 mediates the effects of metformin on body weight and energy balance. Nature 2020, 578, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, R.; Baez-Jurado, E.; Hidalgo-Lanussa, O.; Echeverria, V.; Ashrad, G.M.; Sahebkar, A.; Barreto, G.E. Growth factors and neuroglobin in astrocyte protection against neurodegeneration and oxidative stress. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 2339–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sil, S.; Periyasamy, P.; Thangaraj, A.; Chivero, E.T.; Buch, S. Pdgf/pdgfr axis in the neural systems. Mol. Aspects Med. 2018, 62, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, W.; Blaquiere, M.; Zub, E.; deBock, F.; Boux, F.; Barbier, E.; Audinat, E.; Lerner-Natoli, M.; Marchi, N. A pericyte-glia scarring develops at the leaky capillaries in the hippocampus during seizure activity. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, O.; Saarma, M. Neurotrophic factors in parkinson’s disease: Clinical trials, open challenges and nanoparticle-mediated delivery to the brain. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 682597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.K.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, R.; He, J.G.; Wang, F.; Chen, J.G. Pdgf-bb-dependent neurogenesis buffers depressive-like behaviors by inhibition of gabaergic projection from medial septum to dentate gyrus. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2301110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerschmidt, T.G.; Encarnacao, M.; Lamberty Faverzani, J.; de Fatima Lopes, F.; Poswar de Oliveira, F.; Fischinger Moura de Sousa, C.; Ribeiro, I.; Alves, S.; Giugliani, R.; Regla Vargas, C. Molecular profile and peripheral markers of neurodegeneration in patients with niemann-pick type c: Decrease in plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 and platelet-derived growth factor type aa. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 735, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutanu, A.; Iancu, M.; Maier, S.; Balasa, R.; Dobreanu, M. Plasma biomarkers as potential predictors of functional dependence in daily life activities after ischemic stroke: A single center study. Ann. Indian. Acad. Neurol. 2020, 23, 496–503. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Simon, E.; Carrasco-Rozas, A.; Gallardo, E.; Figueroa-Bonaparte, S.; Belmonte, I.; Pedrosa, I.; Montiel, E.; Suarez-Calvet, X.; Alonso-Perez, J.; Segovia, S.; et al. Pdgf-bb serum levels are decreased in adult onset pompe patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Lievano, M.; Boussadia, B.; De Terdonck, L.D.T.; Gault, C.; Fontanaud, P.; Lafont, C.; Mollard, P.; Marchi, N.; Jeanneteau, F. Topographic reorganization of cerebrovascular mural cells under seizure conditions. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalabrino, G. New epidermal-growth-factor-related insights into the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis: Is it also epistemology? Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 754270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalabrino, G. Epidermal growth factor in the cns: A beguiling journey from integrated cell biology to multiple sclerosis. An extensive translational overview. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 891–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.D.; Azim, K.; Macchi, V.; Porzionato, A.; Butt, A.M.; De Caro, R. Epidermal growth factor pathway in the age-related decline of oligodendrocyte regeneration. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 838007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Jemii, N.; Tounsi-Kettiti, H.; Yaiche, H.; Mezghanni, N.; Jaballah Gabteni, A.; Fehri, E.; Ben Fayala, C.; Abdelhak, S.; Boubaker, S. Dysregulated pdgfr alpha expression and novel somatic mutations in colorectal cancer: Association to ras wild type status and tumor size. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roma-Mateo, C.; Aguado, C.; Garcia-Gimenez, J.L.; Ibanez-Cabellos, J.S.; Seco-Cervera, M.; Pallardo, F.V.; Knecht, E.; Sanz, P. Increased oxidative stress and impaired antioxidant response in lafora disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 932–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Hu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, A. Macrophage migration inhibitor factor (mif): Potential role in cognitive impairment disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2024, 77, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, W.; Xie, W.; Li, F.; Huang, D.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Lu, B.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, P. Dualistic roles and mechanistic insights of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in brain injury and neurodegenerative diseases. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2023, 43, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Nie, K.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, M.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor mediates neuroprotective effects by regulating inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy in parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2019, 416, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaiya, K.; Langford, D.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Shanmughapriya, S. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (mif): A multifaceted cytokine regulated by genetic and physiological strategies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 233, 108024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matejuk, A.; Benedek, G.; Bucala, R.; Matejuk, S.; Offner, H.; Vandenbark, A.A. Mif contribution to progressive brain diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Healthy Subjects | Age Range (Years)/ Gender | Patient (Gene Mutated) | Age Range (Years) at the Beginning of the Study (T1)/Gender | Samples Obtained During the Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 $ | 26–30/F | LD1 (EPM2A) | 16–20/F | T1, T2, T3 |
| H2 $ | 31–35/M | LD2 (EPM2A) | 16–20/M | T1 |
| H3 $ | 21–25/F | LD3 (EPM2B) | 16–20/F | T1, T2, T3 |
| H4 $ | 31–35/M | LD4 (EPM2A) | 16–20/M | T1, T2 |
| H5 $ | 21–25/F | LD5 (EPM2A) | 31–35/M | T1, T2 |
| H6 $ | 26–30/M | LD6 (EPM2A) | 6–10/F | T1, T2, T3 |
| H7 $ | 21–25/F | LD7 (EPM2A) | 11–15/M | T1, T2, T3 |
| H8 $ | 21–25/M | LD8 (EPM2B) | 16–20/F | T1 |
| H9 | 21–25/F | LD9 (EPM2A) | 11–15/M | T1 |
| H10 | 26–30/F | LD10 (EPM2B) | 11–15/F | T1, T2 |
| H11 | 26–30/M | LD11 (EPM2B) | 11–15/F | T1, T2 |
| H12 | 21–25/F | |||
| H13 | 26–30/M | |||
| OME01 (SCNA1) | 16–20/M | T1 | ||
| OME02 (SCNA1) | 16–20/M | T1 | ||
| OME03 (SCNA1) | 26–30/M | T1 | ||
| OME04 (SLC2A1) | 26–30/M | T1 | ||
| OME05 (SLC2A1) | 26–30/M | T1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno-Estellés, M.; Machio, M.; González, L.; Albuixech, M.; Abraira, L.; Quintana, M.; Toledo, M.; Sánchez, M.P.; Serratosa, J.M.; Sanz, P. Identification of Plasma Growth Factors and Cytokines as Diagnostic Biomarkers for the Lafora Form of Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115354
Moreno-Estellés M, Machio M, González L, Albuixech M, Abraira L, Quintana M, Toledo M, Sánchez MP, Serratosa JM, Sanz P. Identification of Plasma Growth Factors and Cytokines as Diagnostic Biomarkers for the Lafora Form of Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115354
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno-Estellés, Mireia, María Machio, Laura González, Marta Albuixech, Laura Abraira, Manuel Quintana, Manuel Toledo, Marina P. Sánchez, José M. Serratosa, and Pascual Sanz. 2025. "Identification of Plasma Growth Factors and Cytokines as Diagnostic Biomarkers for the Lafora Form of Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115354
APA StyleMoreno-Estellés, M., Machio, M., González, L., Albuixech, M., Abraira, L., Quintana, M., Toledo, M., Sánchez, M. P., Serratosa, J. M., & Sanz, P. (2025). Identification of Plasma Growth Factors and Cytokines as Diagnostic Biomarkers for the Lafora Form of Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115354






