Influence of HLA Class I and II Polymorphisms on COVID-19 Severity in a South Brazilian Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
4.3. HLA Genotyping
4.4. In Silico Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO COVID-19 Dashboard. COVID-19 Cases. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Elrobaa, I.H.; New, K.J. COVID-19: Pulmonary and Extra Pulmonary Manifestations. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 711616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.H.; Tipih, T.; Makoah, N.A.; Vermeulen, J.-G.; Goedhals, D.; Sempa, J.B.; Burt, F.J.; Taylor, A.; Mahalingam, S. Comorbidities in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. mBio 2021, 12, e03647-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smatti, M.K.; Al-Sarraj, Y.A.; Albagha, O.; Yassine, H.M. Host Genetic Variants Potentially Associated With SARS-CoV-2: A Multi-Population Analysis. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 578523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, M.; Shiga, M.A.S.; Silva, P.E.S.; Yamanaka, A.H.U.; Souza, V.H.; Grava, S.; Simão, A.N.C.; Neves, J.S.F.; de Lima Neto, Q.A.; Zacarias, J.M.V.; et al. Association between Polymorphisms in TLR3, TICAM1 and IFNA1 Genes and COVID-19 Severity in Southern Brazil. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2024, 24, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Sato, A. The HLA System. First of Two Parts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. T Cells and MHC Proteins. In Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Augusto, D.G.; Hollenbach, J.A. HLA Variation and Antigen Presentation in COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2022, 76, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhkhari, M.; Caidi, H.; Sadki, K. HLA Alleles Associated with COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity in Different Populations: A Systematic Review. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2023, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, P.; Zannat, K.-E.; Talukder, S.; Bhuiyan, A.H.; Jilani, M.S.A.; Saif-Ur-Rahman, K.M. Association of HLA Gene Polymorphism with Susceptibility, Severity, and Mortality of COVID-19: A Systematic Review. HLA 2022, 99, 281–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrijević, Z.; Gligorijević, N.; Šunderić, M.; Penezić, A.; Miljuš, G.; Tomić, S.; Nedić, O. The Association of Human Leucocyte Antigen (HLA) Alleles with COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2023, 33, e2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitero, A.; Bungau, S.G.; Tit, D.M.; Endres, L.; Khan, S.A.; Bungau, A.F.; Romanul, I.; Vesa, C.M.; Radu, A.-F.; Tarce, A.G.; et al. Comorbidities, Associated Diseases, and Risk Assessment in COVID-19-A Systematic Review. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 2022, 1571826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littera, R.; Campagna, M.; Deidda, S.; Angioni, G.; Cipri, S.; Melis, M.; Firinu, D.; Santus, S.; Lai, A.; Porcella, R.; et al. Human Leukocyte Antigen Complex and Other Immunogenetic and Clinical Factors Influence Susceptibility or Protection to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Severity of the Disease Course. The Sardinian Experience. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 605688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Bautista, J.F.; Rodriguez-Nicolas, A.; Rosales-Castillo, A.; López-Ruz, M.Á.; Martín-Casares, A.M.; Fernández-Rubiales, A.; Anderson, P.; Garrido, F.; Ruiz-Cabello, F.; López-Nevot, M.Á. Study of HLA-A, -B, -C, -DRB1 and -DQB1 Polymorphisms in COVID-19 Patients. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2022, 55, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouedraogo, A.R.; Traoré, L.; Ouattara, A.K.; Ouedraogo, A.R.; Zongo, S.V.; Savadogo, M.; Lallogo, T.D.; Sombie, H.K.; Sorgho, P.A.; Ouedraogo, T.-W.C.; et al. Association of HLA-DRB1*11 and HLA-DRB1*12 Gene Polymorphism with COVID-19 in Burkina Faso. BMC Med. Genom. 2023, 16, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajebi, R.; Ajam, A.; Saleh, S.K.; Ashraf, H.; Dehaghi, M.O.; Tabriz, H.M.; Pazoki, M.; Khalili, F. Association Between Human Leukocyte Antigen and COVID-19 Severity. Acta Medica Iran. 2021, 59, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolnezhadian, F.; Iranparast, S.; Shohan, M.; Shokati Eshkiki, Z.; Hamed, M.; Seyedtabib, M.; Nashibi, R.; Assarehzadegan, M.-A.; Mard, S.A.; Shayesteh, A.A.; et al. Evaluation the Frequencies of HLA Alleles in Moderate and Severe COVID-19 Patients in Iran: A Molecular HLA Typing Study. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymoniuk, B.; Borowiec, M.; Makowska, J.; Holwek, E.; Sarnik, J.; Styrzyński, F.; Dróżdż, I.; Lewiński, A.; Stasiak, M. Associations Between Clinical Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and HLA Alleles in a Caucasian Population: A Molecular HLA Typing Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, A.; Andreani, M.; Biancolella, M.; Liberatoscioli, L.; Passarelli, C.; Colona, V.L.; Rogliani, P.; Leonardis, F.; Campana, A.; Carsetti, R.; et al. HLA Allele Frequencies and Susceptibility to COVID-19 in a Group of 99 Italian Patients. HLA 2020, 96, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaqbi, H.; Tay, G.K.; Jelinek, H.F.; Francis, A.; Alefishat, E.; El Haj Chehadeh, S.; Tahir Saeed, A.; Hussein, M.; Laila Salameh; Mahboub, B.H.; et al. HLA Repertoire of 115 UAE Nationals Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Hum. Immunol. 2022, 83, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulton, K.; Wright, P.; Hughes, P.; Savic, S.; Welberry Smith, M.; Guiver, M.; Morton, M.; van Dellen, D.; Tholouli, E.; Wynn, R.; et al. A Role for Human Leucocyte Antigens in the Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Observed in Transplant Patients. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2020, 47, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, N.; Yadav, B.; Prakash, S.; Yadav, D.; Singh, A.; Gautam, S.; Bhadauria, D.; Kaul, A.; Patel, M.R.; Behera, M.R.; et al. Association of Human Leucocyte Antigen Polymorphism with Coronavirus Disease 19 in Renal Transplant Recipients. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Ghasemi-Basir, H.R.; Majzoobi, M.M.; Rasouli-Saravani, A.; Hajilooi, M.; Solgi, G. HLA-DRB1*04 May Predict the Severity of Disease in a Group of Iranian COVID-19 Patients. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benlyamani, I.; Venet, F.; Coudereau, R.; Gossez, M.; Monneret, G. Monocyte HLA-DR Measurement by Flow Cytometry in COVID-19 Patients: An Interim Review. Cytom. Part A 2020, 97, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grifoni, A.; Sidney, J.; Vita, R.; Peters, B.; Crotty, S.; Weiskopf, D.; Sette, A. SARS-CoV-2 Human T Cell Epitopes: Adaptive Immune Response against COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1076–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcay, O.F.; Yeter, H.H.; Unsal, Y.; Yasar, E.; Gonen, S.; Derici, U. Impact of HLA Polymorphisms on the Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Related Mortality in Patients with Renal Replacement Therapy. Hum. Immunol. 2023, 84, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubnova, L.; Pavlova, I.; Terentieva, M.; Glazanova, T.; Belyaeva, E.; Sidorkevich, S.; Bashketova, N.; Chkhingeria, I.; Kozhemyakina, M.; Azarov, D.; et al. HLA Genotypes in Patients with Infection Caused by Different Strains of SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, P.; Mutti, L.; Pentimalli, F.; Baglio, G.; Saladino, R.E.; Sileri, P.; Giordano, A. HLA-B*44 and C*01 Prevalence Correlates with Covid19 Spreading across Italy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vică, M.L.; Dobreanu, M.; Curocichin, G.; Matei, H.V.; Bâlici, Ș.; Vușcan, M.E.; Chiorean, A.D.; Nicula, G.Z.; Pavel Mironescu, D.C.; Leucuța, D.C.; et al. The Influence of HLA Polymorphisms on the Severity of COVID-19 in the Romanian Population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajeer, A.; Jawdat, D.; Massadeh, S.; Aljawini, N.; Abedalthagafi, M.S.; Arabi, Y.M.; Alaamery, M. Association between Human Leukocyte Antigen Alleles and COVID-19 Disease Severity. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 102498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuraba, A.; Haider, H.; Sato, T. Population Difference in Allele Frequency of HLA-C*05 and Its Correlation with COVID-19 Mortality. Viruses 2020, 12, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M. de M.; Gonzalez-Galarza, F.F.; Silva, B.C.C. da; Middleton, D.; Santos, E.J.M. dos Predictive Immunogenetic Markers in COVID-19. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkurnikov, M.; Nersisyan, S.; Jankevic, T.; Galatenko, A.; Gordeev, I.; Vechorko, V.; Tonevitsky, A. Association of HLA Class I Genotypes With Severity of Coronavirus Disease-19. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 641900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basir, H.R.G.; Majzoobi, M.M.; Ebrahimi, S.; Noroozbeygi, M.; Hashemi, S.H.; Keramat, F.; Mamani, M.; Eini, P.; Alizadeh, S.; Solgi, G.; et al. Susceptibility and Severity of COVID-19 Are Both Associated With Lower Overall Viral–Peptide Binding Repertoire of HLA Class I Molecules, Especially in Younger People. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 891816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naemi, F.M.A.; Al-Adwani, S.; Al-Khatabi, H.; Al-Nazawi, A. Frequency of HLA Alleles among COVID-19 Infected Patients: Preliminary Data from Saudi Arabia. Virology 2021, 560, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanti, S.; Deelen, J.; Gallina, A.M.; Caputo, M.; Citro, M.; Abate, M.; Sacchi, N.; Vecchione, C.; Martinelli, R. Correlation of the Two Most Frequent HLA Haplotypes in the Italian Population to the Differential Regional Incidence of COVID-19. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, E.C.; Cortez-Escalante, J.; Cavalcante, F.V.; Barreto, I.C.; de, H.C.; Sanchez, M.N.; Santos, L.M.P. COVID-19: Temporal Evolution and Immunization in the Three Epidemiological Waves, Brazil, 2020–2022. Rev. Saude Publica 2022, 56, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustani-Buss, E.; Buss, C.E.; de Biagi, C.A.O.; de Oliveira, I.M.; Peronni, K.C.; Vitiello, G.A.F.; Fermino, B.L.; Ivanski, F.; Chao, B.M.P.; Tuon, F.F.B.; et al. Unveiling the Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Gamma and Delta Waves in Paraná, Brazil-Delta Displacing a Persistent Gamma Through Alternative Routes of Dispersal. J. Med. Virol. 2025, 97, e70318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Hunt, B.J.; Stegemann, M.; Rochwerg, B.; Lamontagne, F.; Siemieniuk, R.A.; Agoritsas, T.; Askie, L.; Lytvyn, L.; Leo, Y.-S.; et al. A Living WHO Guideline on Drugs for COVID-19. BMJ 2020, 370, m3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.G.; Ambrosio-Albuquerque, E.P.; Fabreti-Oliveira, R.A.; Moliterno, R.A.; de Souza, V.H.; Sell, A.M.; Visentainer, J.E.L. HLA-A, -B, -DRB1, -DQA1, and -DQB1 Profile in a Population from Southern Brazil. HLA 2018, 92, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurtz, V.; Paul, S.; Andreatta, M.; Marcatili, P.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M. NetMHCpan 4.0: Improved Peptide-MHC Class I Interaction Predictions Integrating Eluted Ligand and Peptide Binding Affinity Data. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3360–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin Suite Ver 3.5: A New Series of Programs to Perform Population Genetics Analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauderman, W.J. Sample Size Requirements for Matched Case-Control Studies of Gene-Environment Interaction. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Migdal, M.; Ruan, D.F.; Forrest, W.F.; Horowitz, A.; Hammer, C. MiDAS-Meaningful Immunogenetic Data at Scale. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, D.J.; Marin, W.; Hollenbach, J.A.; Mack, S.J. Bridging ImmunoGenomic Data Analysis Workflow Gaps (BIGDAWG): An Integrated Case-Control Analysis Pipeline. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
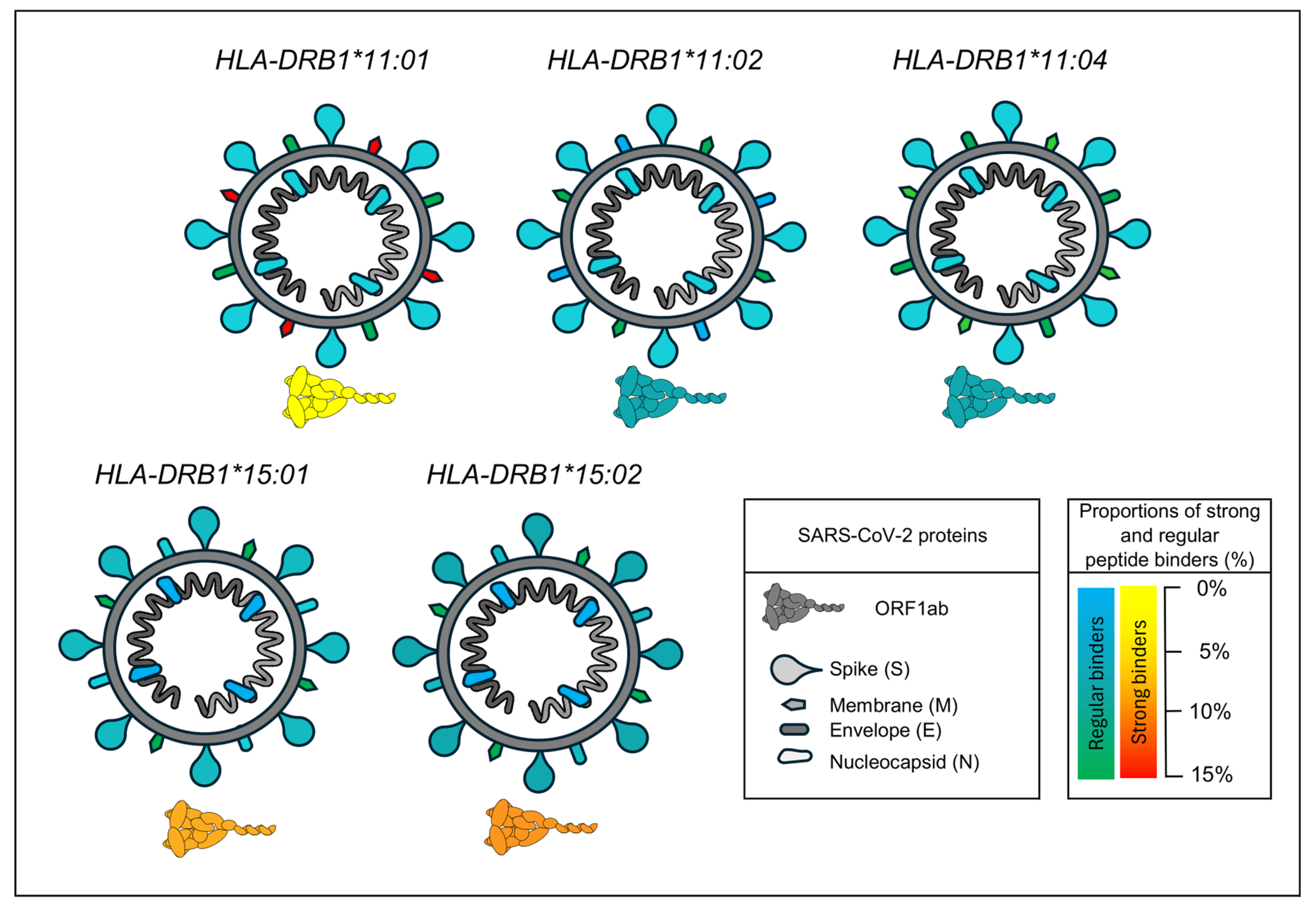
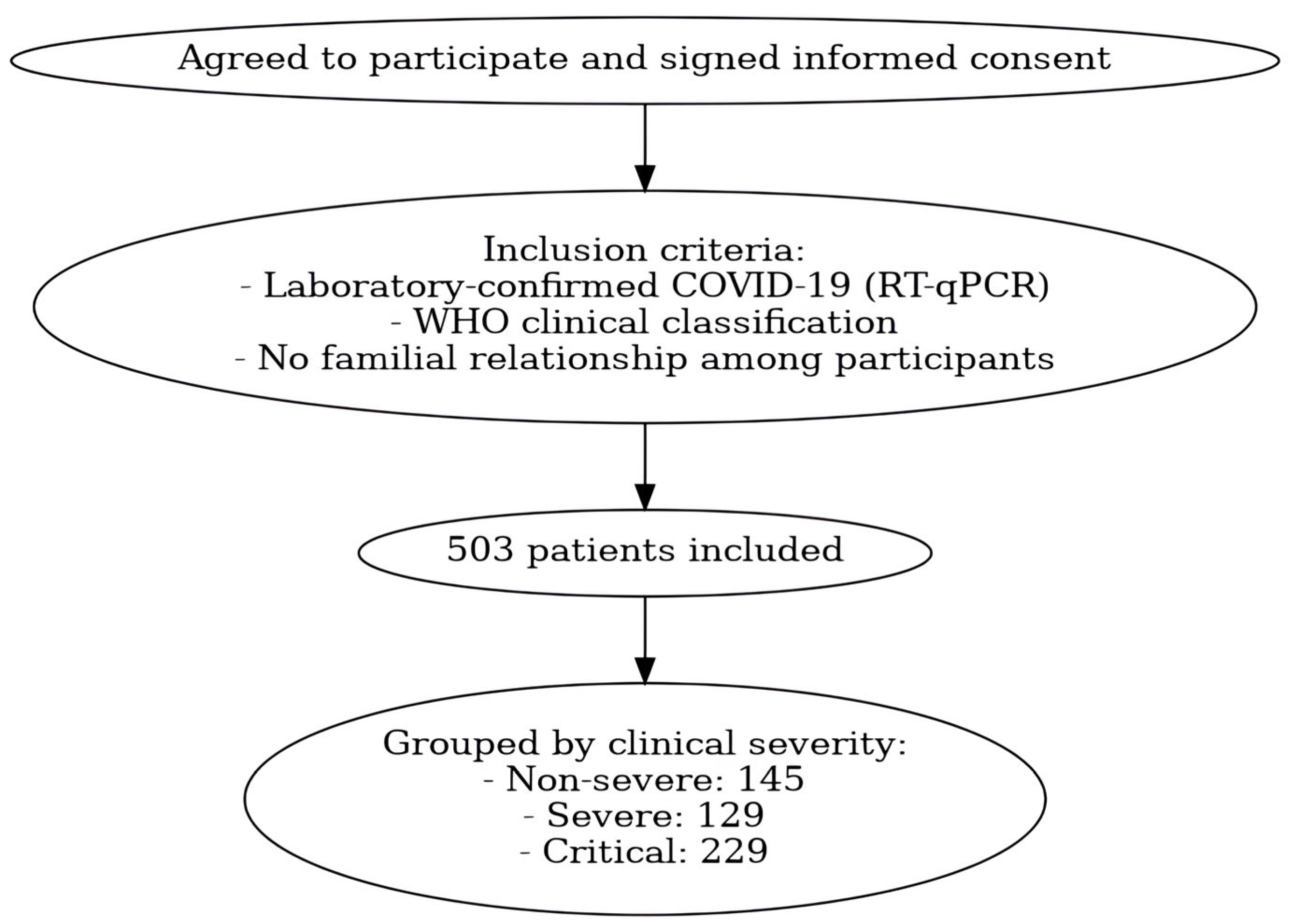
| Characteristics | Non-Severe N: 145 | Severe N: 129 | Critical N: 229 | p-Value a | p-Value b | p-Value c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 46.74 ± 14.41 | 60.58 ± 16.20 | 65.02±16.60 | <0.01 d | <0.01 d | 0.01 d |
| ≤50 | 79 (54%) | 40 (31%) | 44 (24%) | <0.01 e | <0.01 e | 0.01 e |
| >50 | 66 (46%) | 89 (69%) | 185 (76%) | |||
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | 90 (62%) | 62 (48%) | 81 (35%) | 0.02 e | <0.01 e | 0.02 e |
| Male | 55 (38%) | 67 (52%) | 148 (65%) | |||
| CVD | ||||||
| No | 117 (81%) | 62 (40%) | 95 (41%) | <0.01 e | <0.01 e | 0.27 e |
| Yes | 28 (19%) | 67 (60%) | 134 (59%) | |||
| Diabetes | ||||||
| No | 134 (92%) | 99 (77%) | 146 (64%) | <0.01 e | <0.01 e | 0.01 e |
| Yes | 11 (8%) | 30 (23%) | 83 (36%) | |||
| Tobacco smoking | <0.01 e | <0.01 e | 0.4 e | |||
| No | 140 (97%) | 106 (82%) | 180 (79%) | |||
| Yes | 5 (3%) | 23 (18%) | 49 (21%) |
| Characteristics | Survival—N: 115 | Death—N: 114 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| Mean ± SD | 58.11 ± 15.29 | 72 ± 14.92 | <0.01 a |
| ≤50 | 32 (28%) | 12 (11%) | <0.01 b |
| >50 | 83 (72%) | 102 (89%) | |
| Sex | |||
| Female | 39 (34%) | 42 (37%) | 0.70 b |
| Male | 76 (66%) | 72 (63%) | |
| CVD | |||
| No | 57 (50%) | 38 (33%) | 0.01 b |
| Yes | 58 (50%) | 76 (67%) | |
| Diabetes | |||
| No | 86 (75%) | 60 (53%) | <0.01 b |
| Yes | 29 (25%) | 54 (47%) | |
| Tobacco smoking | |||
| No | 87 (76%) | 93 (82%) | 0.30 |
| Yes | 28 (24%) | 21 (18%) |
| Non-Severe (145) vs. Severe (129) | |||||
| Allele | Non-Severe N (%) | Severe N (%) | OR (CI) | p-value | Bonferroni |
| DRB1*11 | 55 (18.97%) | 27 (10.47%) | 0.37 (0.20–0.68) | <0.01 | 0.03 |
| DRB1*15 | 20 (6.90%) | 38 (14.73%) | 2.80 (1.43–5.59) | <0.01 | 0.04 |
| Non-Severe (145) vs. Critical (229) | |||||
| Allele | Non-Severe N (%) | Critical N (%) | OR (CI) | p-value | Bonferroni |
| B*49 | 4 (1.38%) | 15 (3.28%) | 3.79 (1.13–15.33) | 0.04 | 1.00 |
| DRB1*11 | 55 (18.97%) | 54 (11.79%) | 0.51 (0.29–0.88) | 0.01 | 0.13 |
| Non-Severe (145) vs. Severe + Critical (358) | |||||
| Allele | Non-Severe N (%) | Severe + Critical N (%) | OR (CI) | p-value | Bonferroni |
| B*37 | 5 (1.72%) | 4 (0.56%) | 0.16 (0.03–0.83) | 0.02 | 1.00 |
| DRB1*11 | 55 (18.97%) | 81 (11.31%) | 0.46 (0.28–0.75) | <0.01 | 0.04 |
| DRB1*15 | 20 (6.90%) | 91 (12.71%) | 1.88 (1.05–3.45) | 0.03 | 0.39 |
| Severe (129) vs. Critical (229) | |||||
| Allele | Severe N (%) | Critical N (%) | OR (CI) | p-value | Bonferroni |
| B*08 | 18 (6.98%) | 13 (2.84 %) | 0.40 (0.18–0.87) | 0.02 | 0.31 |
| B*50 | 2 (0.78%) | 17 (3.71 %) | 6.28 (1.67–41.26) | 0.01 | 0.62 |
| Critical-Survival (115) vs. Death (114) | |||||
| Allele | Survival N (%) | Death N (%) | OR (CI) | p-value | Bonferroni |
| A*03 | 28 (12.17%) | 15 (6.58%) | 0.37 (0.17–0.77) | 0.01 | 0.19 |
| Non-Severe (145) vs. Severe (129) | ||||
| Haplotype | Non-Severe N (%) | Severe N (%) | OR (CI) | p-Value |
| A*02~DRB1*11 | 18 (6.20%) | 2 (0.77%) | 0.12 (0.01–0.50) | <0.01 |
| A*02~DRB1*15 | 2 (0.68%) | 15 (5.81%) | 8.89 (2.03–80.61) | <0.01 |
| Non-Severe (145) vs. Critical (229) | ||||
| Haplotype | Non-Severe N (%) | Critical N (%) | OR (CI) | p-Value |
| A*11~B*35 | 10 (3.44%) | 3 (0.65%) | 0.18 (0.03–0.73) | <0.01 |
| A*24~DRB1*11 | 9 (3.10%) | 2 (0.43%) | 0.14 (0.01–0.67) | <0.01 |
| A*24~DRB1*13 | 8 (2.75%) | 3 (0.65%) | 0.23 (0.04–0.98) | 0.01 |
| A*24~DRB1*14 | 1 (0.34%) | 11 (2.40%) | 7.11 (1.02–306.76) | 0.02 |
| B*18~DRB1*11 | 8 (2.75%) | 3 (0.65%) | 0.23 (0.04–0.98) | 0.01 |
| Non-Severe (145) vs. Severe + Critical (358) | ||||
| Haplotype | Non-Severe N (%) | Severe + Critical N (%) | OR (CI) | p-Value |
| A*11~B*35 | 11 (3.79%) | 9 (1.25%) | 0.32 (0.12–0.87) | <0.01 |
| A*02~DRB1*15 | 3 (1.03%) | 29 (4.05%) | 4.04 (1.24–20.86) | 0.01 |
| Severe (129) vs. Critical (229) | ||||
| Haplotype | Severe N (%) | Critical N (%) | OR (CI) | p-Value |
| A*02~DRB1*11 | 3 (1.16%) | 21 (4.58%) | 4.08 (1.20–21.56) | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grava, S.; Braga, M.; Souza, V.H.d.; Pepineli, A.C.; Yamanaka, A.H.U.; Ayo, C.M.; Zacarias, J.M.V.; Simão, A.N.C.; Pinto, L.D.B.; Neto, Q.A.d.L.; et al. Influence of HLA Class I and II Polymorphisms on COVID-19 Severity in a South Brazilian Population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115341
Grava S, Braga M, Souza VHd, Pepineli AC, Yamanaka AHU, Ayo CM, Zacarias JMV, Simão ANC, Pinto LDB, Neto QAdL, et al. Influence of HLA Class I and II Polymorphisms on COVID-19 Severity in a South Brazilian Population. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115341
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrava, Sergio, Matheus Braga, Victor Hugo de Souza, Afonso Carrasco Pepineli, Aléia Harumi Uchibaba Yamanaka, Christiane Maria Ayo, Joana Maira Valentini Zacarias, Andréa Name Colado Simão, Larissa Danielle Bahls Pinto, Quirino Alves de Lima Neto, and et al. 2025. "Influence of HLA Class I and II Polymorphisms on COVID-19 Severity in a South Brazilian Population" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115341
APA StyleGrava, S., Braga, M., Souza, V. H. d., Pepineli, A. C., Yamanaka, A. H. U., Ayo, C. M., Zacarias, J. M. V., Simão, A. N. C., Pinto, L. D. B., Neto, Q. A. d. L., & Visentainer, J. E. L. (2025). Influence of HLA Class I and II Polymorphisms on COVID-19 Severity in a South Brazilian Population. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5341. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115341







