Pro-Resolving Macrophage-Induced IL-35+ but Not TGF-β1+ Regulatory B Cell Activation Requires the PD-L1/PD-1 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
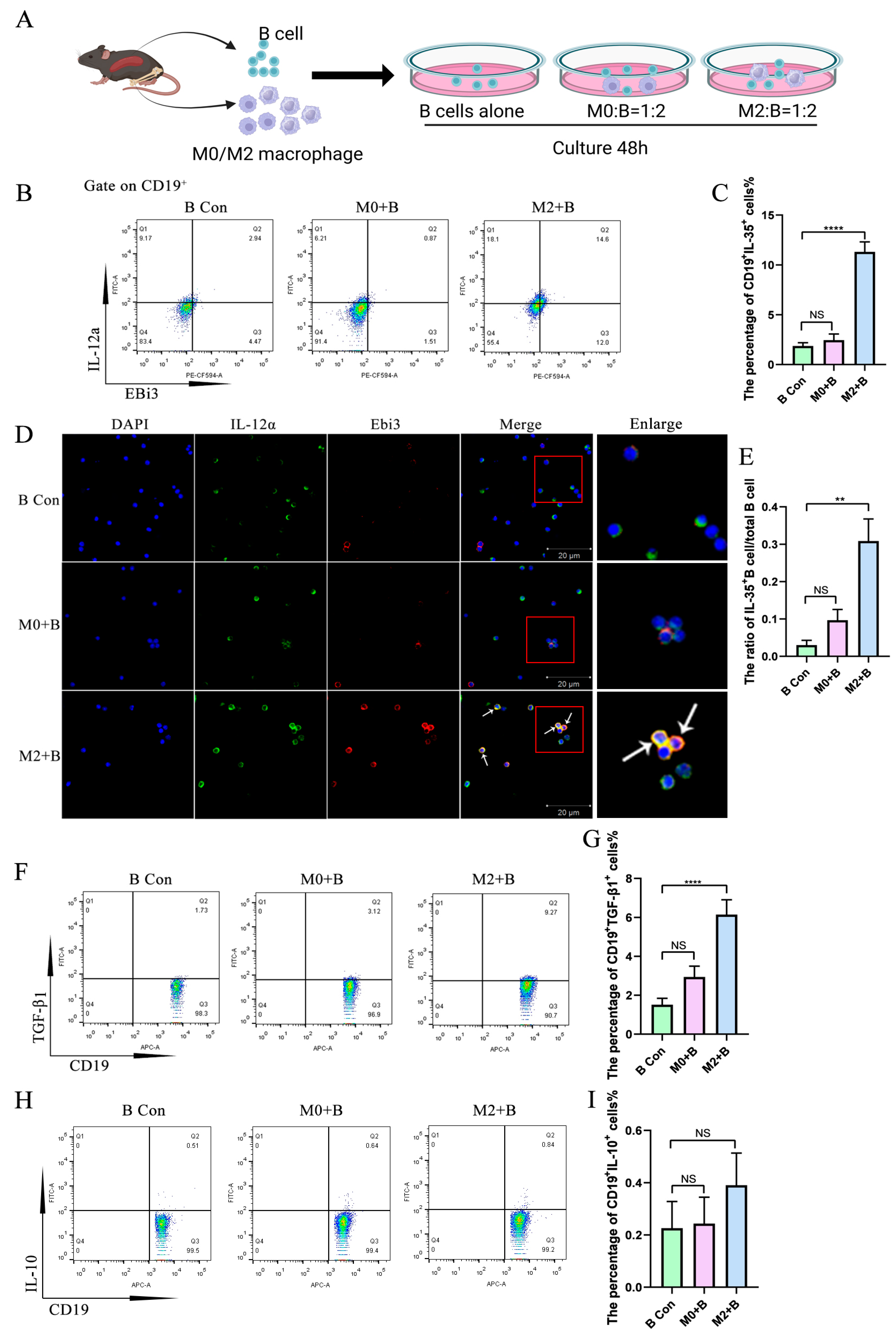
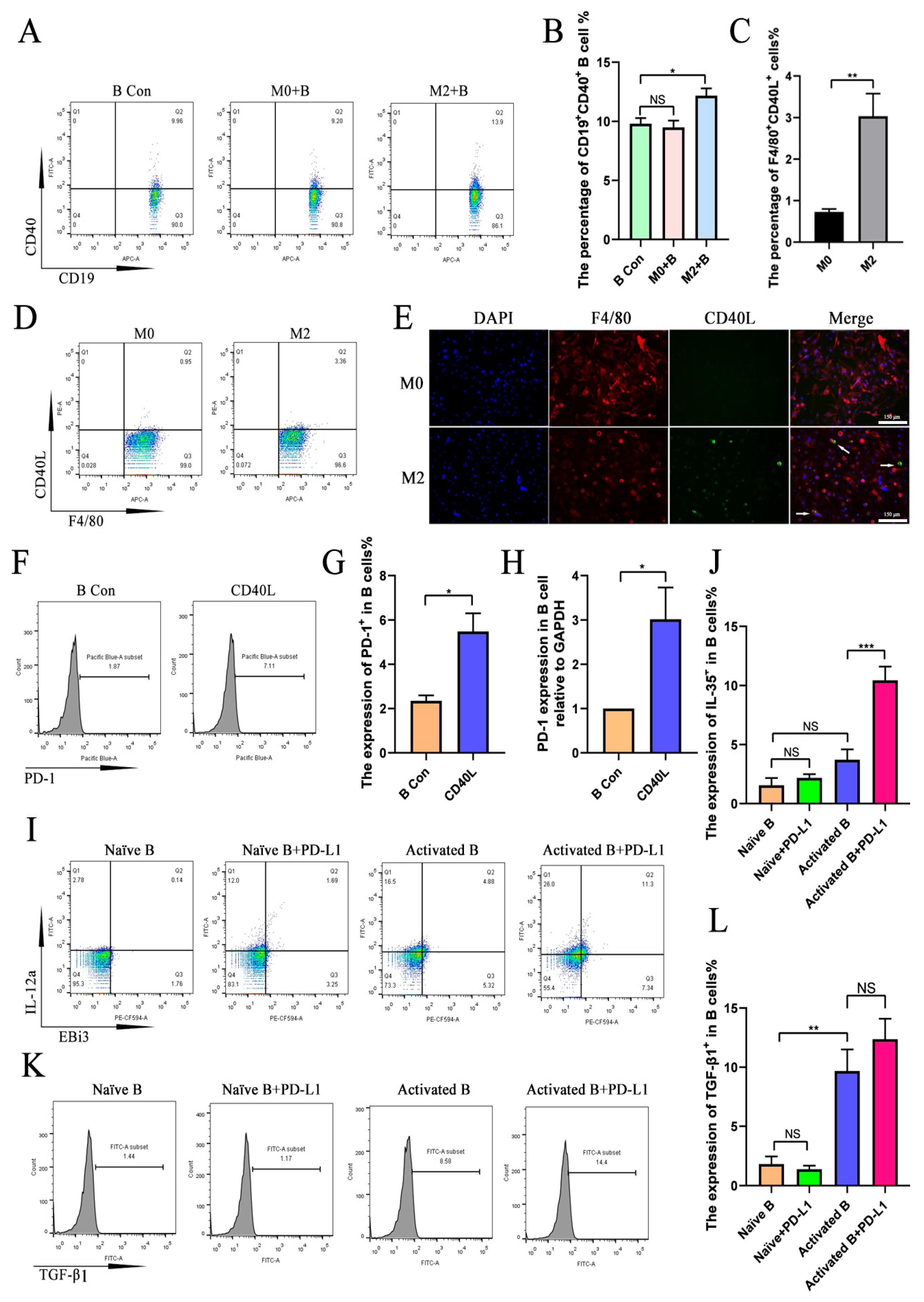
2.1. M2 Macrophages Promoted the Expression of IL-35 and TGF-β1 in B Cells
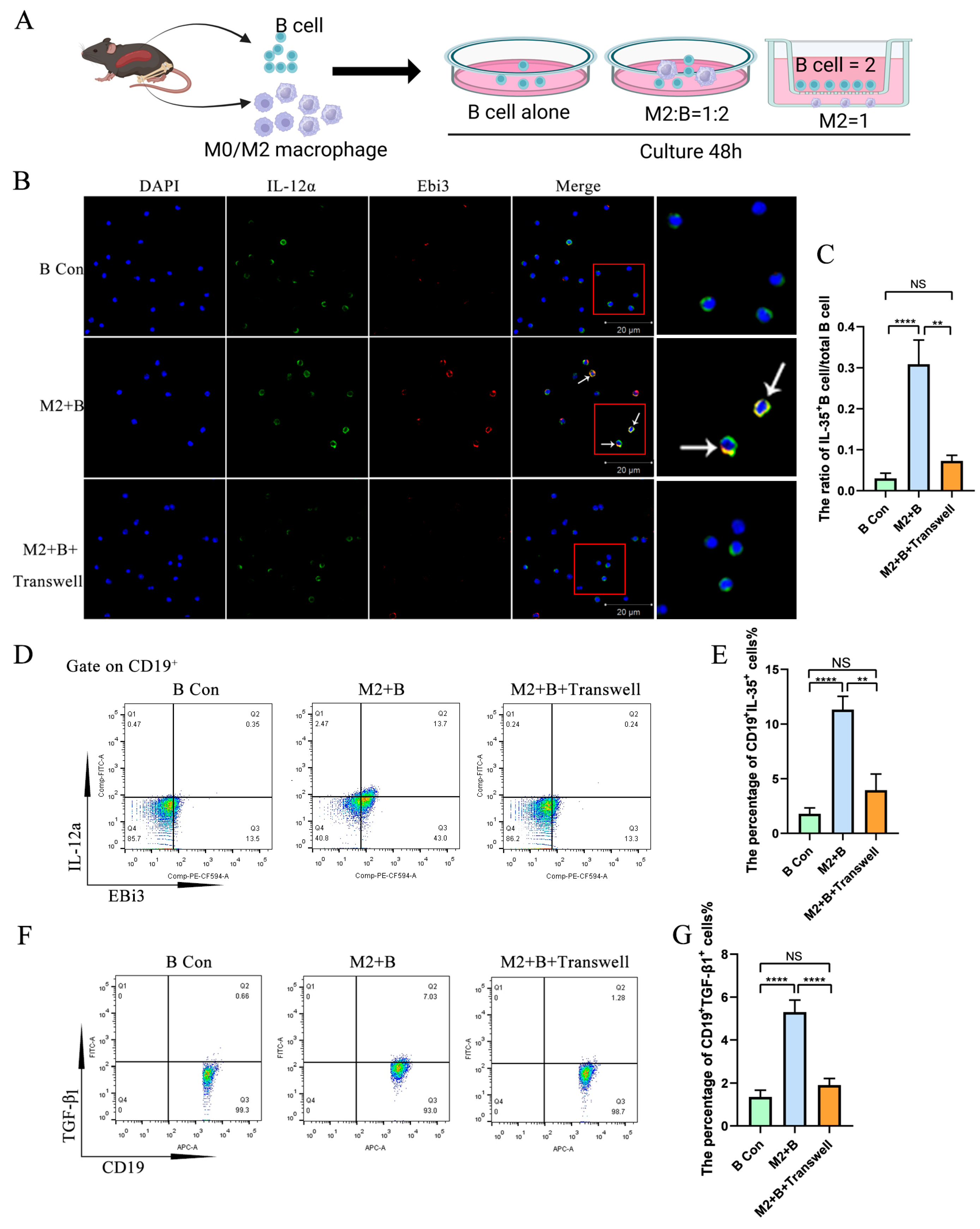
2.2. M2 Macrophages Promoted IL-35 and TGF-β1 Expression in B Cells Through Direct Cell–Cell Contact
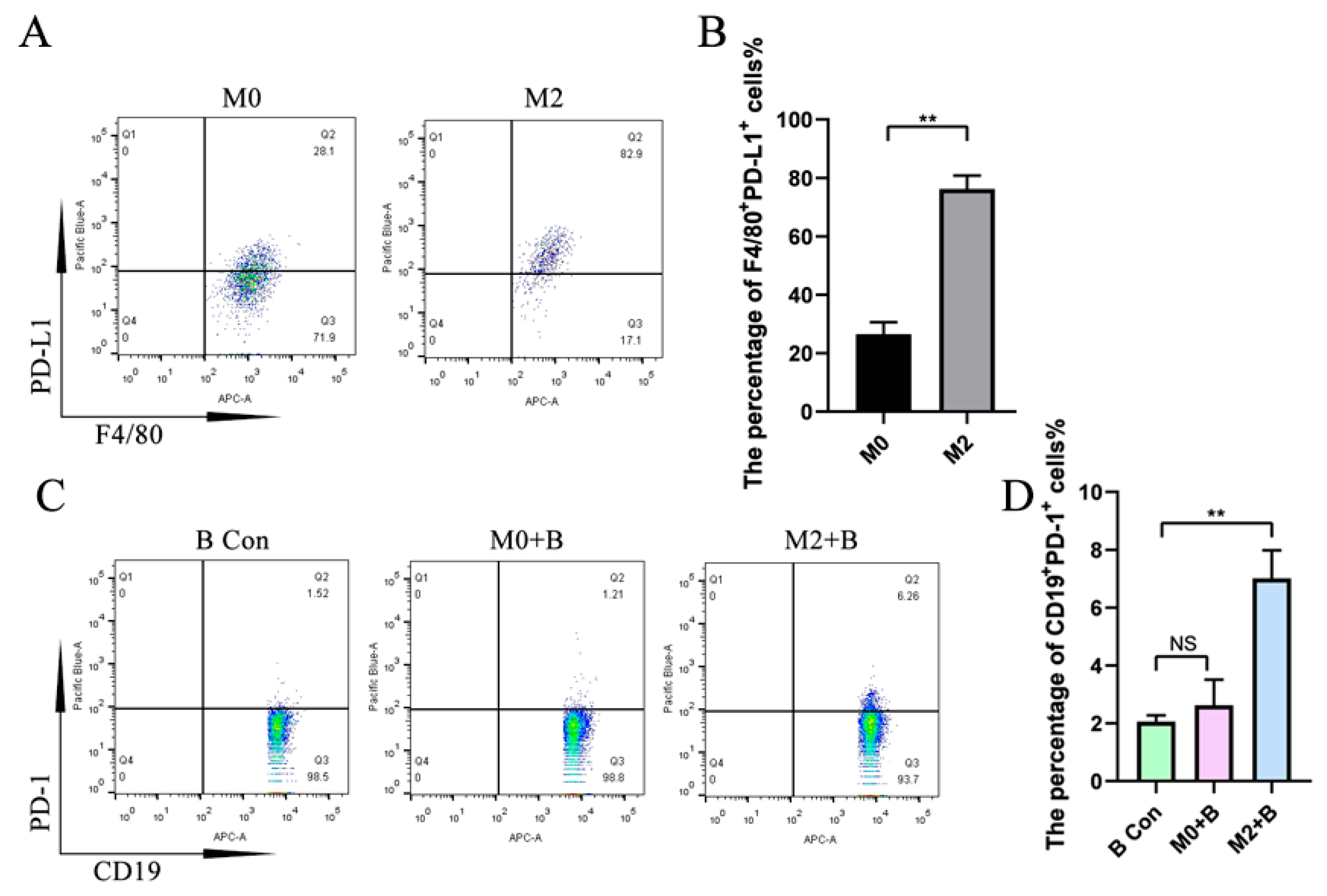
2.3. M2-Induced Upregulation of IL-35 but Not TGF-β1 in B Cells Requires PD-1
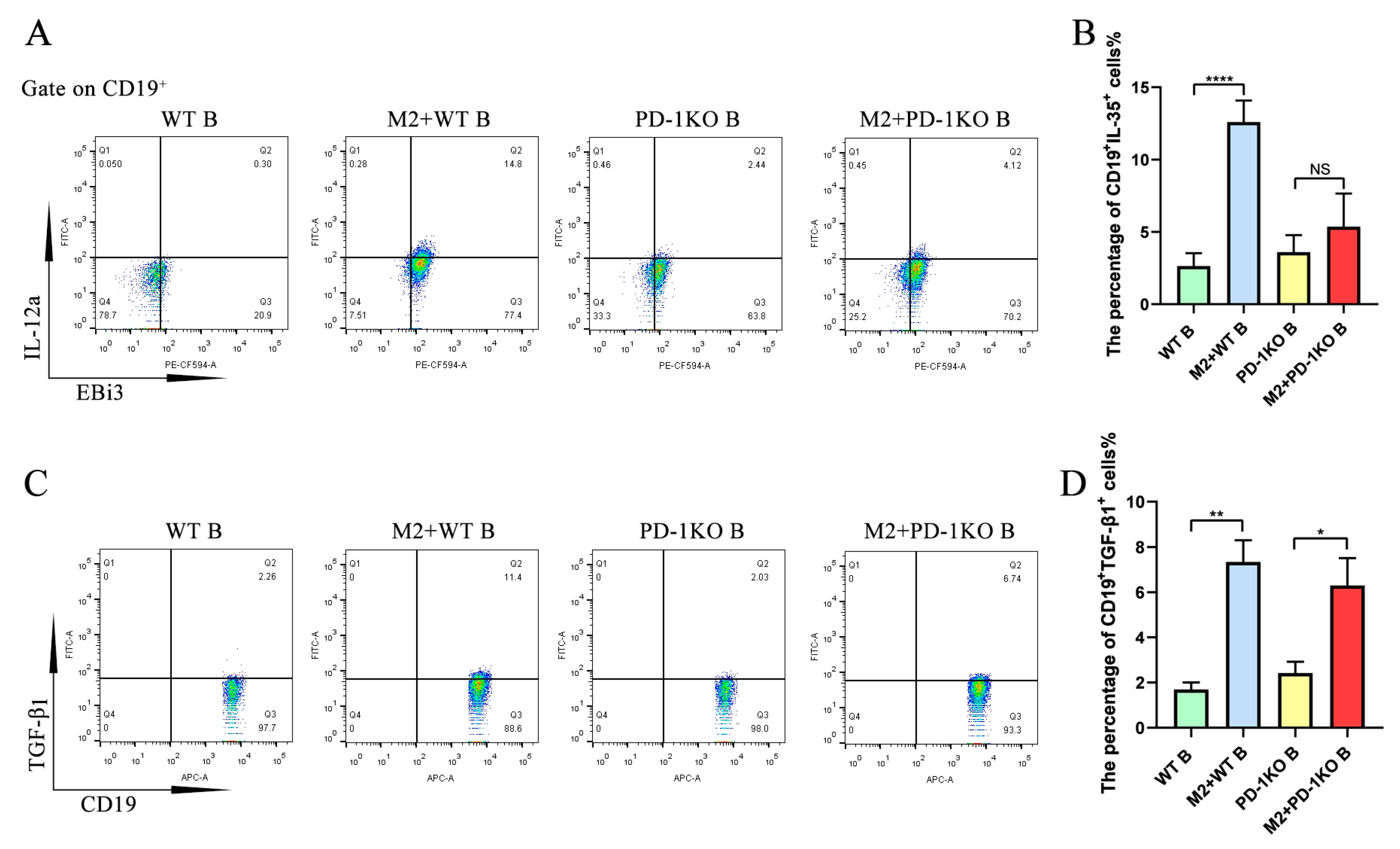
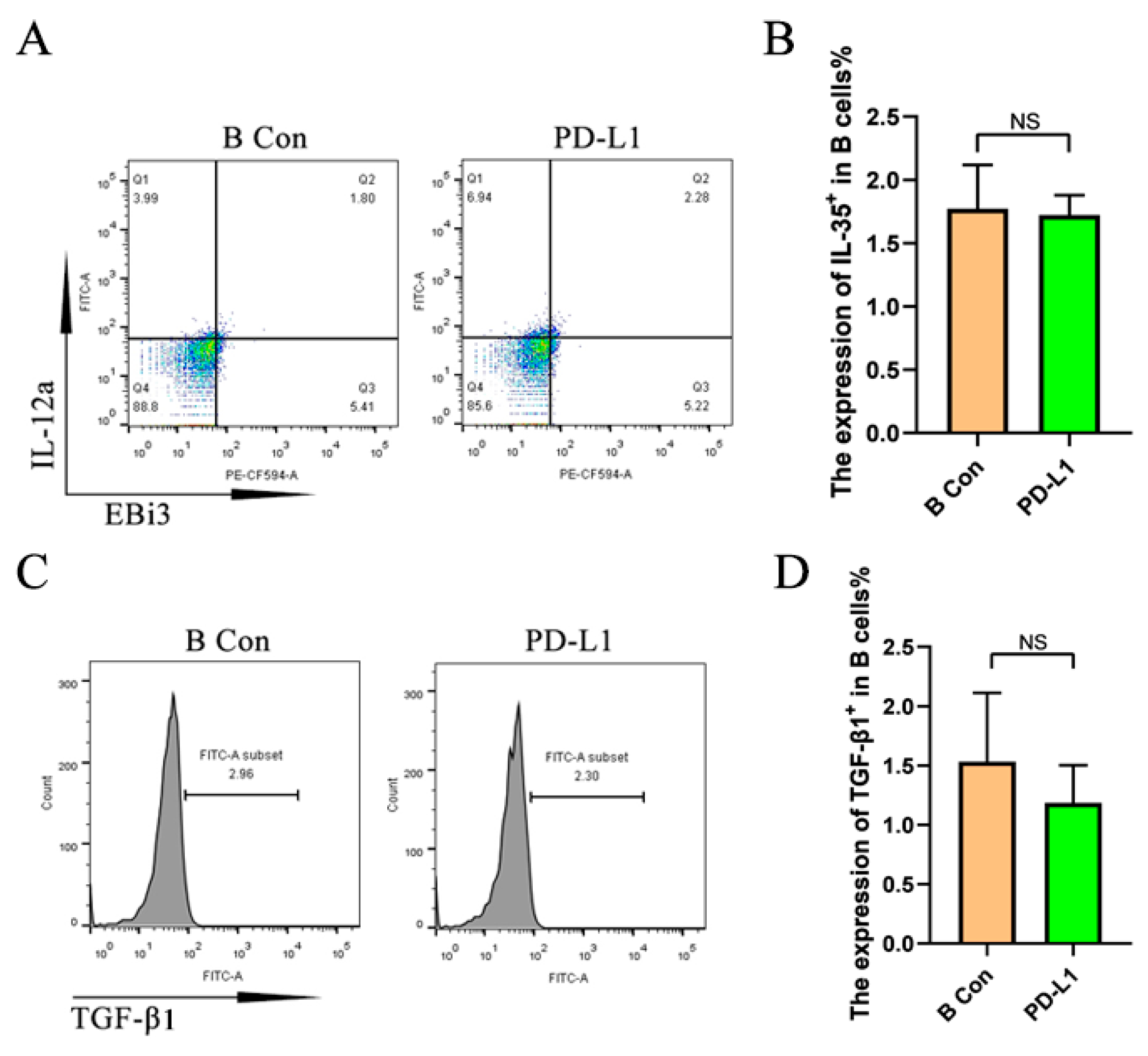
2.4. PD-L1 Promotes the Upregulation of IL-35 but Not TGF-β1 in Activated B Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal
4.2. BMDM Isolation and Culture
4.3. B Cell Isolation
4.4. Co-Culture
4.5. PD-L1 Stimulation
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.8. RT-qPCR
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EAE | Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis |
| IMDM | Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium |
| Breg | Regulatory B Cell |
References
- Rodríguez Murúa, S.; Farez, M.F.; Quintana, F.J. The Immune Response in Multiple Sclerosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022, 17, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parodis, I.; Long, X.; Karlsson, M.C.I.; Huang, X. B Cell Tolerance and Targeted Therapies in SLE. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G. New developments in neutrophil biology and periodontitis. Periodontol 2000 2020, 82, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Jo, M.G.; Min, K.Y.; Choi, M.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, W.S. IL-10+ regulatory B cells mitigate atopic dermatitis by suppressing eosinophil activation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Roch, T.; Lampropoulou, V.; O’Connor, R.A.; Stervbo, U.; Hilgenberg, E.; Ries, S.; Dang, V.D.; Jaimes, Y.; Daridon, C.; et al. IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature 2014, 507, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltrecht, N.; Hardtke-Wolenski, M.; Iordanidis, K.; Jonigk, D.; Galla, M.; Schambach, A.; Buitrago-Molina, L.E.; Wedemeyer, H.; Noyan, F.; Jaeckel, E. Graft-Specific Regulatory T Cells for Long-Lasting, Local Tolerance Induction. Cells 2024, 13, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locati, M.; Curtale, G.; Mantovani, A. Diversity, Mechanisms, and Significance of Macrophage Plasticity. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivimaki, K.; Leppanen, T.; Hamalainen, M.; Vuolteenaho, K.; Moilanen, E. Pinosylvin Shifts Macrophage Polarization to Support Resolution of Inflammation. Molecules 2021, 26, 2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnadottir, K.; Benkhoucha, M.; Merkler, D.; Weber, M.S.; Payne, N.L.; Bernard, C.C.A.; Molnarfi, N.; Lalive, P.H. B cell-derived transforming growth factor-beta1 expression limits the induction phase of autoimmune neuroinflammation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipińska-Opałka, A.; Leszczyńska-Pilich, M.; Będzichowska, A.; Tomaszewska, A.; Rustecka, A.; Kalicki, B. The Role of Regulatory B Lymphocytes in Allergic Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, H. The Protective Effect of Esculentoside A on MPL/lpr Mice by Upregulating the Expression of CD19+IL-35+Breg Cells and Interleukin-35. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2025, 186, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dambuza, I.M.; He, C.; Choi, J.K.; Yu, C.R.; Wang, R.; Mattapallil, M.J.; Wingfield, P.T.; Caspi, R.R.; Egwuagu, C.E. IL-12p35 induces expansion of IL-10 and IL-35-expressing regulatory B cells and ameliorates autoimmune disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Saaoud, F.; Drummer, C.T.; Sun, Y.; Xu, K.; Lu, Y.; Shan, H.; Shevach, E.M.; Jiang, X.; et al. IL-35 promotes CD4+Foxp3+ Tregs and inhibits atherosclerosis via maintaining CCR5-amplified Treg-suppressive mechanisms. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e152511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafferata, E.A.; Terraza-Aguirre, C.; Barrera, R.; Faundez, N.; Gonzalez, N.; Rojas, C.; Melgar-Rodriguez, S.; Hernandez, M.; Carvajal, P.; Cortez, C.; et al. Interleukin-35 inhibits alveolar bone resorption by modulating the Th17/Treg imbalance during periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yago, T.; Nanke, Y.; Kawamoto, M.; Kobashigawa, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Kotake, S. IL-35 inhibits human osteoclastogenesis from monocytes induced by receptor-activator of NF-kappaB ligand. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 43, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mirlekar, B.; Johnson, B.M.; Brickey, W.J.; Wrobel, J.A.; Yang, N.; Song, D.; Entwistle, S.; Tan, X.; Deng, M.; et al. STING-induced regulatory B cells compromise NK function in cancer immunity. Nature 2022, 610, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.M.; Stott, R.T.; Zhao, G.; SooHoo, J.; Xiong, W.; Lian, M.M.; Fitzgerald, L.; Shi, S.; Akrawi, E.; Lei, J.; et al. TGF-beta-producing regulatory B cells induce regulatory T cells and promote transplantation tolerance. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, W.; Gu, M.; Qian, C.; Deng, A. Lower Plasma Levels of IL-35 in Patients with Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2018, 244, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamoushi, T.; Ahmadi, M.; Ali-Hassanzadeh, M.; Zare, M.; Hesampour, F.; Gharesi-Fard, B.; Amooee, S. Evaluation of Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 and Interleukin-35 Serum Levels in Patients with Placenta Accreta. Lab. Med. 2021, 52, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Xu, Q.; Huang, S.; Dai, D.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, J.; Han, X. B10 cells regulate macrophage polarization to alleviate inflammation and bone loss in periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2025, 96, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memida, T.; Abdolahinia, E.D.; Cao, G.; Ruiz, S.; Huang, S.; Shindo, S.; Nakamura, S.; Lin, J.; Kawai, T.; Han, X. B10 Cells Promote Pro-Resolving Macrophage Function Through Direct Cell-Cell Contact and IL-10 Secretion in Raw 264.7 Cells. Int. Immunol. 2025; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Du, H.; Zhan, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Lan, J.; PuYang, L.; Wan, Y.; Qu, Q.; Wang, S.; et al. The interaction between the soluble programmed death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) and PD-1+ regulator B cells mediates immunosuppression in triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 830606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, L.; Kachler, K.; Siegmund, R.; Trufa, D.I.; Mittler, S.; Geppert, C.I.; Friedrich, J.; Rieker, R.J.; Sirbu, H.; Finotto, S. Increased expression of the immunosuppressive interleukin-35 in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tang, C.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Rao, J.; Chen, S.; Qu, W.; Wu, D.; Lei, L.; Chen, L. PD-1/PD-L1 regulates Treg differentiation in pregnancy-induced hypertension. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celada, L.J.; Kropski, J.A.; Herazo-Maya, J.D.; Luo, W.; Creecy, A.; Abad, A.T.; Chioma, O.S.; Lee, G.; Hassell, N.E.; Shaginurova, G.I.; et al. PD-1 up-regulation on CD4(+) T cells promotes pulmonary fibrosis through STAT3-mediated IL-17A and TGF-beta1 production. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibult, M.L.; Mamessier, E.; Gertner-Dardenne, J.; Pastor, S.; Just-Landi, S.; Xerri, L.; Chetaille, B.; Olive, D. PD-1 is a novel regulator of human B-cell activation. Int. Immunol. 2013, 25, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Lao, X.M.; Chen, M.M.; Liu, R.X.; Wei, Y.; Ouyang, F.Z.; Chen, D.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.F.; et al. PD-1hi Identifies a Novel Regulatory B-cell Population in Human Hepatoma That Promotes Disease Progression. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, B.; Cao, Y.; Yao, S.; Liu, Y.; Jin, G.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cui, K.; Zhou, L.; et al. Colorectal Cancer-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Tumor Immune Evasion by Upregulating PD-L1 Expression in Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2102620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.L.; Chang, Y.W.; Lee, W.; Chiang, C.S.; Liu, S.P.; Lee, H.T.; Jeng, L.B.; Shyu, W.C. Role of STAT3-FOXO3 Signaling in the Modulation of Neuroplasticity by PD-L1-HGF-Decorated Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in a Murine Stroke Model. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2404882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ning, X.; Liu, Y.; Shen, T.; Liu, M.; Yin, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yin, R.; Cai, L.; et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells from tumour-bearing mice induce the population expansion of CD19(hi)FcgammaRIIb(hi) regulatory B cells via PD-L1. Immunology 2024, 172, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaba, K.; Bouaziz, J.D.; Haas, K.M.; Poe, J.C.; Fujimoto, M.; Tedder, T.F. A regulatory B cell subset with a unique CD1dhiCD5+ phenotype controls T cell-dependent inflammatory responses. Immunity 2008, 28, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.G.; Chavez-Rueda, K.A.; Eddaoudi, A.; Meyer-Bahlburg, A.; Rawlings, D.J.; Ehrenstein, M.R.; Mauri, C. Novel suppressive function of transitional 2 B cells in experimental arthritis. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 7868–7878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielle, J.; Audo, R.; Hahne, M.; Macia, L.; Combe, B.; Morel, J.; Daien, C. IL-10 Producing B Cells Ability to Induce Regulatory T Cells Is Maintained in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.H.; Li, K.P.; Chu, K.H.; Chiang, B.L. A B-1a cell subset induces Foxp3(-) T cells with regulatory activity through an IL-10-independent pathway. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, C.; Guo, Y.; He, Y.; Guo, P.; Wei, Z.; Xia, Y.; Dai, Y. Mitochondrial fusion induced by transforming growth factor-β1 serves as a switch that governs the metabolic reprogramming during differentiation of regulatory T cells. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyzik, M.; Piccirillo, C.A. TGF-beta1 modulates Foxp3 expression and regulatory activity in distinct CD4+ T cell subsets. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 82, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestone, J.A.; McKenzie, B.S.; Beilke, J.; Ramsdell, F. Opportunities for Treg cell therapy for the treatment of human disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1166135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, E.C.; Mauri, C. Regulatory B cells: Origin, phenotype, and function. Immunity 2015, 42, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Xu, F.; Ma, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, W.; Chen, X. Electroacupuncture Alleviates CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain via PD-L1/PD-1-SHP-1 Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 2922–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Carper, K.; Malone, F.; Latchman, Y.; Perkins, J.; Fu, Y.; Reyes, J.; Li, W. PD-L1/PD-1 signal deficiency promotes allogeneic immune responses and accelerates heart allograft rejection. Transplantation 2008, 86, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.B.; Bi, E.; Chen, H.; Yu, J.J.; Ye, B.H. IL-21 and CD40L synergistically promote plasma cell differentiation through upregulation of Blimp-1 in human B cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1827–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsman, C.; Verstegen, N.J.; Streutker, M.; Jorritsma, T.; Boon, L.; Brinke, A.T.; van Ham, S.M. Termination of CD40L co-stimulation promotes human B cell differentiation into antibody-secreting cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 1662–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkinen, T.; Karkola, K.; Yla-Herttuala, S. Macrophages, smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and T-cells express CD40 and CD40L in fatty streaks and more advanced human atherosclerotic lesions. Colocalization with epitopes of oxidized low-density lipoprotein, scavenger receptor, and CD16 (Fc gammaRIII). Virchows Arch. 2000, 437, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filion, L.G.; Matusevicius, D.; Graziani-Bowering, G.M.; Kumar, A.; Freedman, M.S. Monocyte-derived IL12, CD86 (B7-2) and CD40L expression in relapsing and progressive multiple sclerosis. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 106, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardell, J.L.; Parker, D.C. CD40L is transferred to antigen-presenting B cells during delivery of T-cell help. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Han, N.; Li, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Q.; et al. PD-1-expressing B cells suppress CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells via PD-1/PD-L1-dependent pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 109, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Xu, J.; Shen, C.; An, X.; Shen, G.; Yang, M.; et al. The Unknown Aspect of BAFF: Inducing IL-35 Production by a CD5(+)CD1d(hi)FcgammaRIIb(hi) Regulatory B-Cell Subset in Lupus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 2532–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, D.; Chen, Q.; Guo, X.; Yang, L.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Yang, Y.; He, J.; et al. BAFF is involved in macrophage-induced bortezomib resistance in myeloma. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, K.; Fujii, W.; Yamagishi, J.; Sanjoba, C.; Goto, Y. Inflammatory CD11b(+) Macrophages Produce BAFF in Spleen of Mice Infected with Leishmania donovani. Pathogens 2024, 13, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, V.V.; Prasad, D.V.; Banerjee, P.P.; Joshi, B.N.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, G.C. B cells activated by lipopolysaccharide, but not by anti-Ig and anti-CD40 antibody, induce anergy in CD8+ T cells: Role of TGF-beta 1. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5897–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, G.; Memida, T.; Huang, S.; Dalir Abdolahinia, E.; Ruiz, S.; Hassantash, S.; Ari, J.; Shindo, S.; Lin, J.; Kawai, T.; et al. Pro-Resolving Macrophage-Induced IL-35+ but Not TGF-β1+ Regulatory B Cell Activation Requires the PD-L1/PD-1 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115332
Cao G, Memida T, Huang S, Dalir Abdolahinia E, Ruiz S, Hassantash S, Ari J, Shindo S, Lin J, Kawai T, et al. Pro-Resolving Macrophage-Induced IL-35+ but Not TGF-β1+ Regulatory B Cell Activation Requires the PD-L1/PD-1 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115332
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Guoqin, Takumi Memida, Shengyuan Huang, Elaheh Dalir Abdolahinia, Sunniva Ruiz, Sahar Hassantash, Jayant Ari, Satoru Shindo, Jiang Lin, Toshihisa Kawai, and et al. 2025. "Pro-Resolving Macrophage-Induced IL-35+ but Not TGF-β1+ Regulatory B Cell Activation Requires the PD-L1/PD-1 Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115332
APA StyleCao, G., Memida, T., Huang, S., Dalir Abdolahinia, E., Ruiz, S., Hassantash, S., Ari, J., Shindo, S., Lin, J., Kawai, T., & Han, X. (2025). Pro-Resolving Macrophage-Induced IL-35+ but Not TGF-β1+ Regulatory B Cell Activation Requires the PD-L1/PD-1 Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115332






