Metabolic Imaging of Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate in a Ferret Model of Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
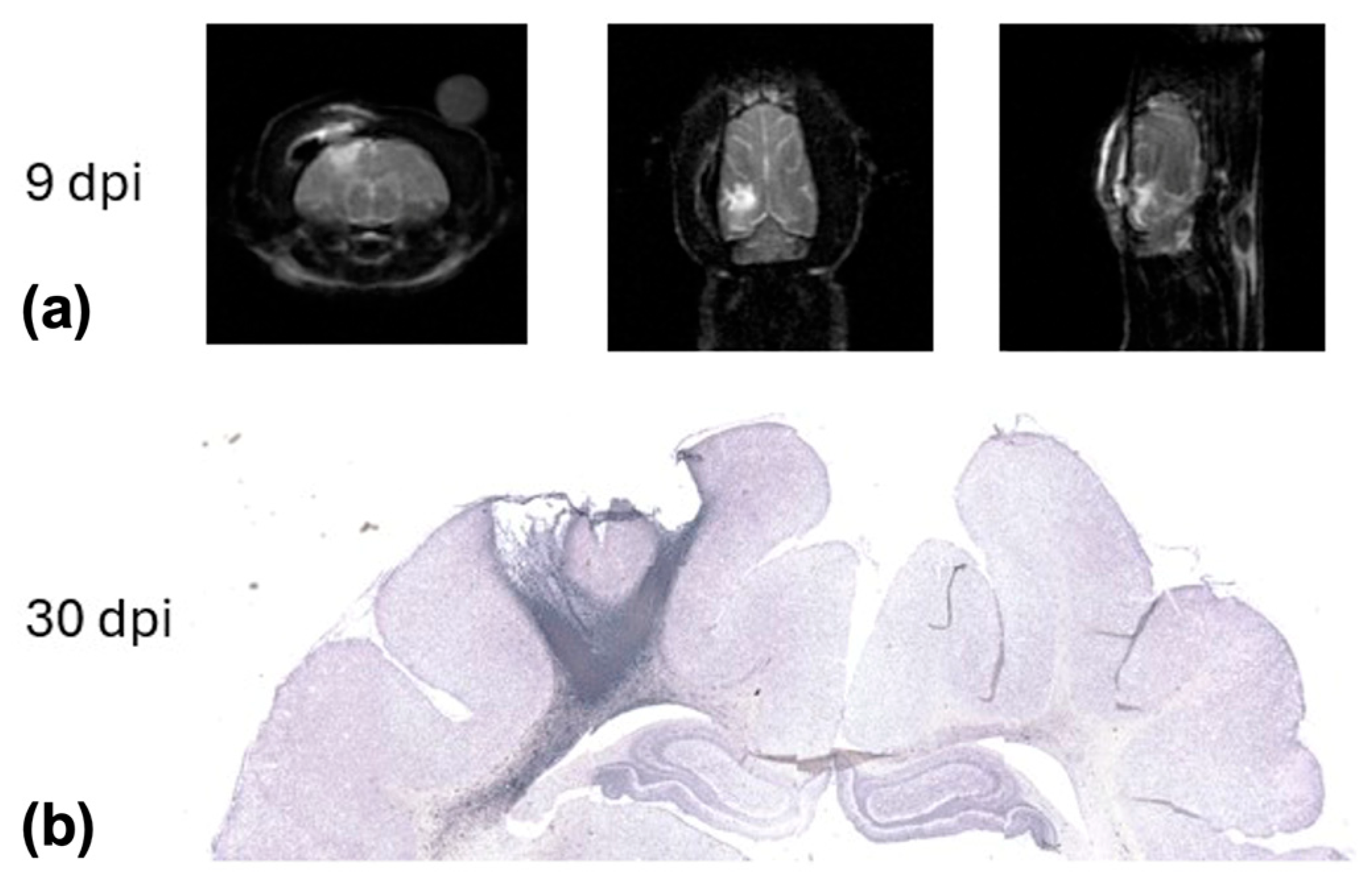
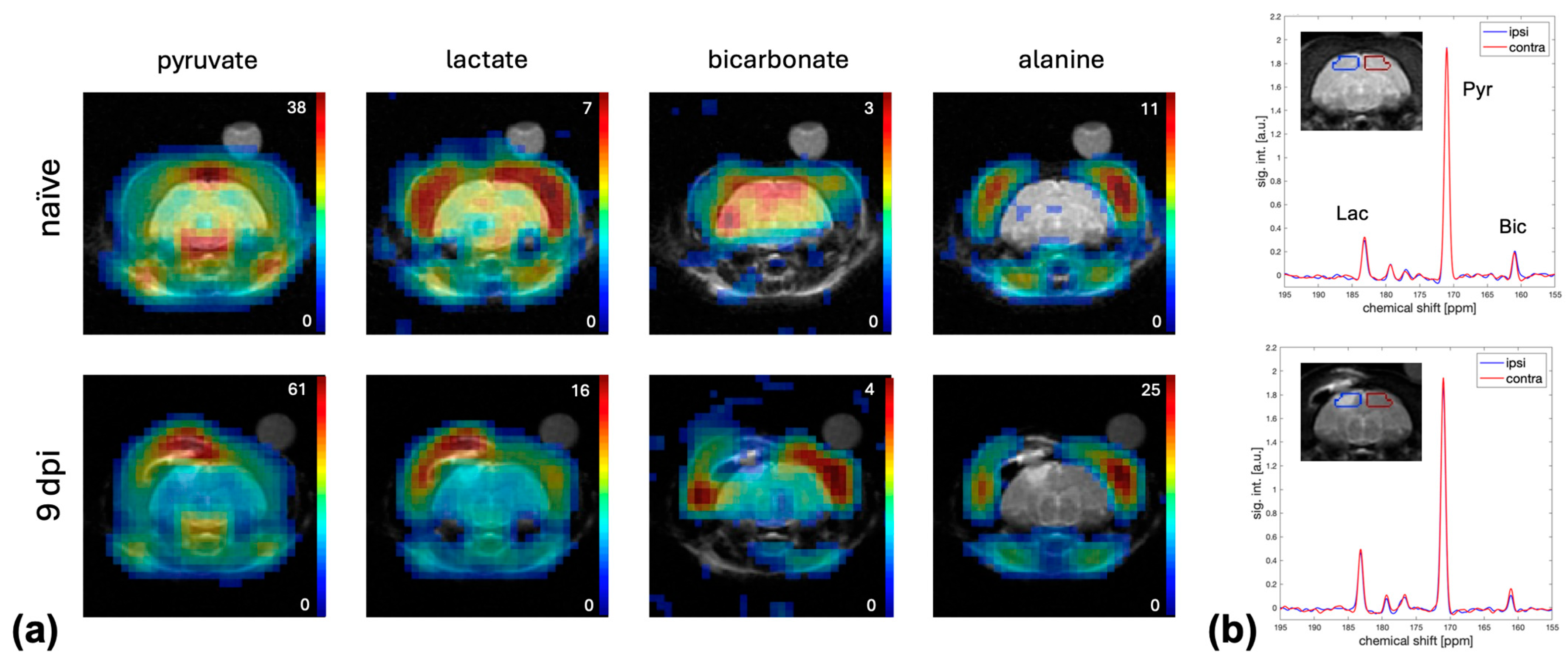
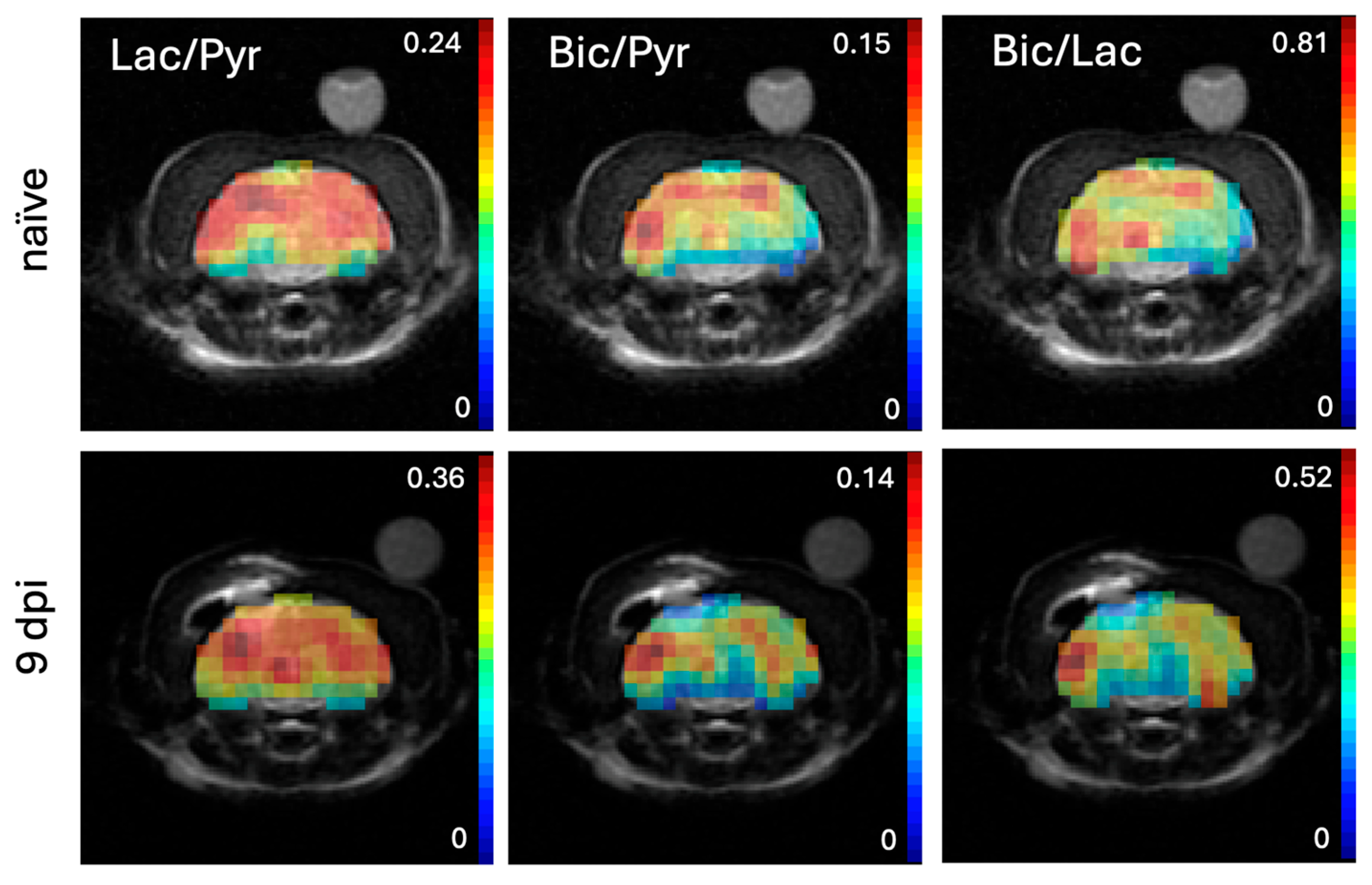
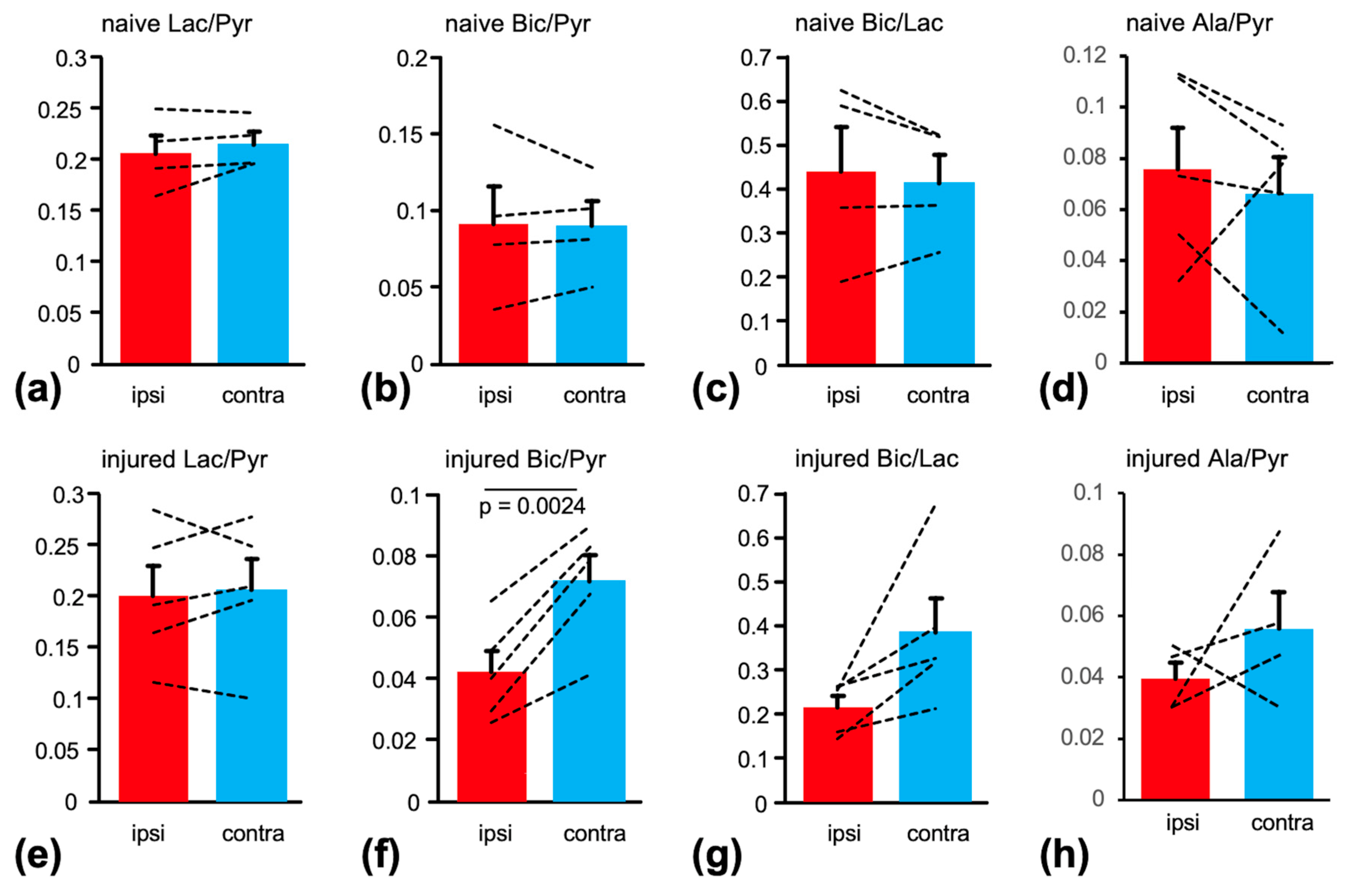
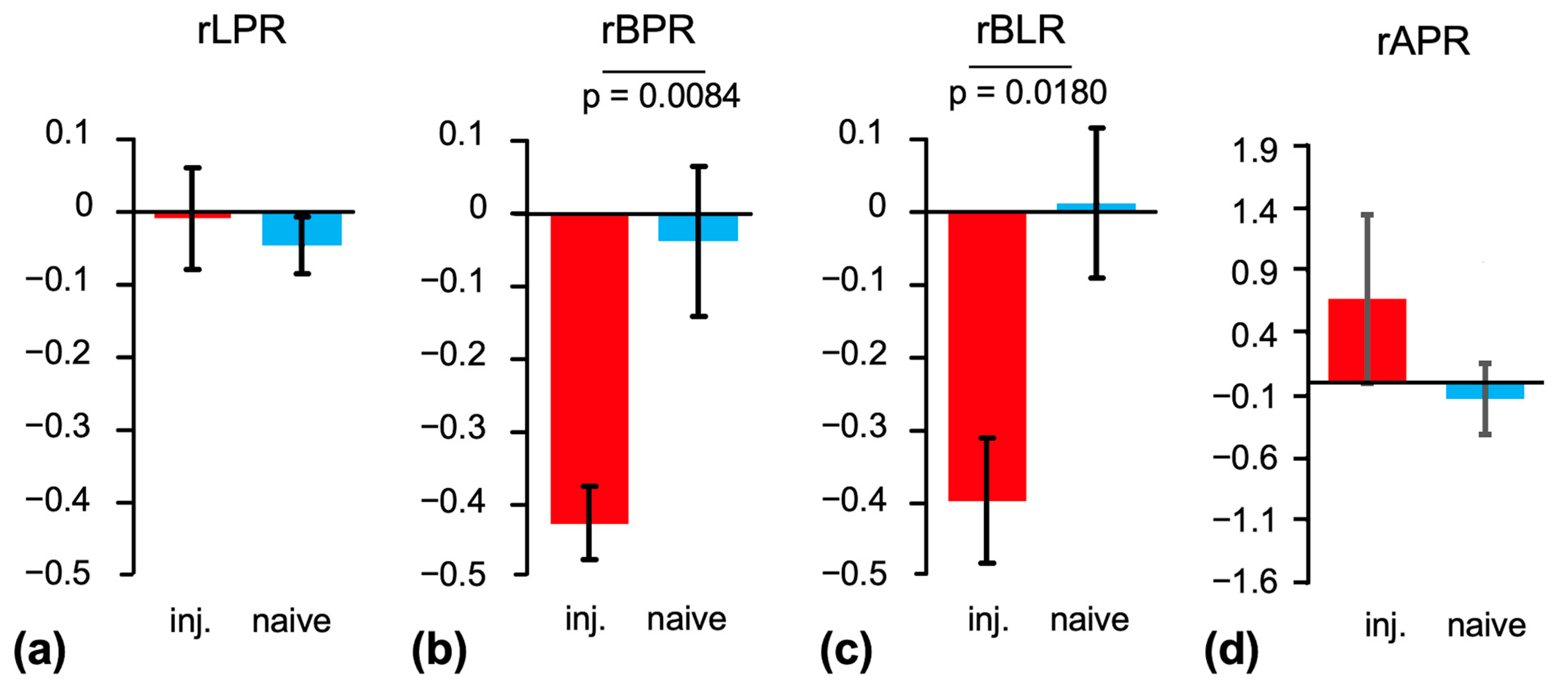
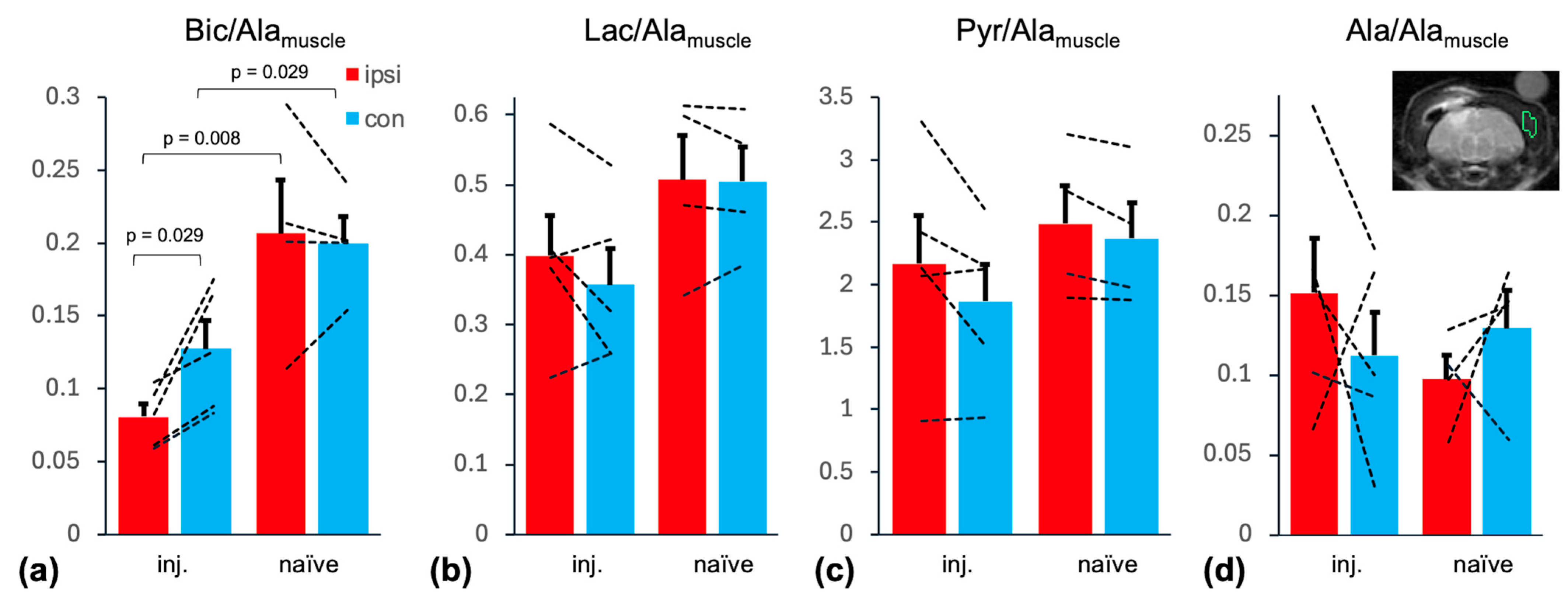
2. Results
3. Discussion
Limitations and Future Studies
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Blast and Controlled Cortical Impact
4.2. Animal Handling for MRI
4.3. Pyruvate Polarization and Injection
4.4. MR Acquisitions
4.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Georges, A.; Das, J.M. Traumatic Brain Injury (Archive). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Palou Martinez, Y.; Arrey Agbor, D.B.; Panday, P.; Ejaz, S.; Gurugubelli, S.; Prathi, S.K.; Nath, T.S. Mood Disorders in the Wake of Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e62524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.C.; Yaffe, K. Epidemiology of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury and Neurodegenerative Disease. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 66, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, D.L.; Mac Donald, C.L.; Shimony, J.S. Current and Future Diagnostic Tools for Traumatic Brain Injury. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 127, pp. 267–275. ISBN 978-0-444-52892-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Benford, B.; Li, Z.Z.; Ling, G.S. Role of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex in Traumatic Brain Injury and Measurement of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Enzyme by Dipstick Test. J. Emerg. Trauma Shock 2009, 2, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Barry, E.S.; Benford, B.; Grunberg, N.E.; Li, H.; Watson, W.D.; Sharma, P. Impact of Repeated Stress on Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain Expression and Behavioral Responses in Rats. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xing, G.; Ren, M.; O’Neill, J.T.; Verma, A.; Watson, W.D. Controlled Cortical Impact Injury and Craniotomy Result in Divergent Alterations of Pyruvate Metabolizing Enzymes in Rat Brain. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 234, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, G.; Ren, M.; Watson, W.A.; O’Neil, J.T.; Verma, A. Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Expression and Phosphorylation of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase: A Mechanism of Dysregulated Glucose Metabolism. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 454, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, C.L.; Saraswati, M.; Scafidi, S.; Fiskum, G.; Casey, P.; McKenna, M.C. Cerebral Glucose Metabolism in an Immature Rat Model of Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 2066–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golman, K.; Petersson, J.S. Metabolic Imaging and Other Applications of Hyperpolarized 13C1. Acad. Radiol. 2006, 13, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVience, S.J.; Lu, X.; Proctor, J.; Rangghran, P.; Melhem, E.R.; Gullapalli, R.; Fiskum, G.M.; Mayer, D. Metabolic Imaging of Energy Metabolism in Traumatic Brain Injury Using Hyperpolarized [1-(13)C]Pyruvate. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti, C.; Chou, A.; Krukowski, K.; Najac, C.; Feng, X.; Riparip, L.-K.; Rosi, S.; Chaumeil, M.M. In Vivo Metabolic Imaging of Traumatic Brain Injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVience, S.J.; Lu, X.; Proctor, J.L.; Rangghran, P.; Medina, J.A.; Melhem, E.R.; Gullapalli, R.P.; Fiskum, G.; Mayer, D. Enhancing Metabolic Imaging of Energy Metabolism in Traumatic Brain Injury Using Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate and Dichloroacetate. Metabolites 2021, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackett, E.P.; Chen, J.; Ingle, L.; Al Nemri, S.; Barshikar, S.; Da Cunha Pinho, M.; Plautz, E.J.; Bartnik-Olson, B.L.; Park, J.M. Longitudinal Assessment of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Acute Traumatic Brain Injury Using Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 90, 2432–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloots, R.J.H.; Gervaise, H.M.T.; van Dommelen, J.a.W.; Geers, M.G.D. Biomechanics of Traumatic Brain Injury: Influences of the Morphologic Heterogeneities of the Cerebral Cortex. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 36, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grist, J.T.; McLean, M.A.; Riemer, F.; Schulte, R.F.; Deen, S.S.; Zaccagna, F.; Woitek, R.; Daniels, C.J.; Kaggie, J.D.; Matys, T.; et al. Quantifying Normal Human Brain Metabolism Using Hyperpolarized [1–13C]Pyruvate and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. NeuroImage 2019, 189, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, R. Large Animal Models of Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, E.B.; Schwerin, S.C.; Radomski, K.L.; Irfanoglu, M.O.; Juliano, S.L.; Pierpaoli, C.M. Quantitative MRI and DTI Abnormalities During the Acute Period Following CCI in the Ferret. Shock 2016, 46, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwerin, S.C.; Hutchinson, E.B.; Radomski, K.L.; Ngalula, K.P.; Pierpaoli, C.M.; Juliano, S.L. Establishing the Ferret as a Gyrencephalic Animal Model of Traumatic Brain Injury: Optimization of Controlled Cortical Impact Procedures. J. Neurosci. Methods 2017, 285, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinn, D.A.; McIntyre, R.W.; Reves, J.G. Isoflurane-Induced Vasodilation: Role of the Alpha-Adrenergic Nervous System. Anesth. Analg. 1990, 71, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josan, S.; Hurd, R.; Billingsley, K.; Senadheera, L.; Park, J.M.; Yen, Y.-F.; Pfefferbaum, A.; Spielman, D.; Mayer, D. Effects of Isoflurane Anesthesia on Hyperpolarized 13C Metabolic Measurements in Rat Brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Jhajharia, A.; Josan, S.; Park, J.M.; Yen, Y.; Pfefferbaum, A.; Hurd, R.E.; Spielman, D.M.; Mayer, D. Investigating the Origin of the 13C Lactate Signal in the Anesthetized Healthy Rat Brain in Vivo after Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate Injection. NMR Biomed. 2023, 37, e5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, E.P.; Pinho, M.C.; Harrison, C.E.; Reed, G.D.; Liticker, J.; Raza, J.; Hall, R.G.; Malloy, C.R.; Barshikar, S.; Madden, C.J.; et al. Imaging Acute Metabolic Changes in Patients with Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Using Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate. iScience 2020, 23, 101885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.S.; Karlsson, M.; Mazandi, V.M.; Ranganathan, A.; Hallowell, T.; Delso, N.; Kilbaugh, T.J. Axonal Transport Dysfunction of Mitochondria in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Novel Therapeutic Target. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 329, 113311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, K.; Khan, H.; Singh, T.G.; Kaur, A. Traumatic Brain Injury: Mechanistic Insight on Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutic Targets. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 1725–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiebert, J.B.; Shen, Q.; Thimmesch, A.R.; Pierce, J.D. Traumatic Brain Injury and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 350, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.L.; Singh, I.N.; Wang, J.A.; Hall, E.D. Time Courses of Post-Injury Mitochondrial Oxidative Damage and Respiratory Dysfunction and Neuronal Cytoskeletal Degradation in a Rat Model of Focal Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 111, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, J.D.; Leung, L.Y.; Hwang, H.M.; Yang, X.; Deng-Bryant, Y.; Shear, D.A. Time-Course Evaluation of Brain Regional Mitochondrial Bioenergetics in a Pre-Clinical Model of Severe Penetrating Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 2323–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzel, R.M.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Khan, N.; Doran, S.J.; Faden, A.I.; Wu, J. Sustained Neuronal and Microglial Alterations Are Associated with Diverse Neurobehavioral Dysfunction Long after Experimental Brain Injury. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 136, 104713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, M.J.; Medina, J.A.; Proctor, J.L.; Xu, S.; Gullapalli, R.P.; Rangghran, P.; Miller, C.; Vesselinov, A.; Fiskum, G. Combined Traumatic Brain Injury and Hemorrhagic Shock in Ferrets Leads to Structural, Neurochemical, and Functional Impairments. J. Neurotrauma 2022, 39, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyppönen, V.; Stenroos, P.; Nivajärvi, R.; Ardenkjær-Larsen, J.H.; Gröhn, O.; Paasonen, J.; Kettunen, M.I. Metabolism of Hyperpolarised [1–13C]Pyruvate in Awake and Anaesthetised Rat Brains. NMR Biomed. 2021, 35, e4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjańska, M.; Shestov, A.A.; Deelchand, D.K.; Kittelson, E.; Henry, P.-G. Brain Metabolism under Different Anesthetic Conditions Using Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate and [2-13C]Pyruvate. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31, e4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healicon, R.; Rooney, C.H.E.; Ball, V.; Shinozaki, A.; Miller, J.J.; Smart, S.; Radford-Smith, D.; Anthony, D.; Tyler, D.J.; Grist, J.T. Assessing the Effect of Anesthetic Gas Mixtures on Hyperpolarized 13C Pyruvate Metabolism in the Rat Brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2022, 88, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erakovic, V.; Zupan, G.; Varljen, J.; Laginja, J.; Simonic, A. Altered Activities of Rat Brain Metabolic Enzymes in Electroconvulsive Shock-Induced Seizures. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.S.; Vo, A.H.; Neal, C.J.; Tigno, J.; Roberts, R.; Mossop, C.; Dunne, J.R.; Armonda, R.A. Military Traumatic Brain and Spinal Column Injury: A 5-Year Study of the Impact Blast and Other Military Grade Weaponry on the Central Nervous System. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2009, 66, S104–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, C.J.; McLean, M.A.; Schulte, R.F.; Robb, F.J.; Gill, A.B.; McGlashan, N.; Graves, M.J.; Schwaiger, M.; Lomas, D.J.; Brindle, K.M.; et al. A Comparison of Quantitative Methods for Clinical Imaging with Hyperpolarized (13)C-Pyruvate. NMR Biomed. 2016, 29, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, P.E.Z.; Chen, H.-Y.; Gordon, J.W.; Korn, N.; Maidens, J.; Arcak, M.; Tang, S.; Criekinge, M.; Carvajal, L.; Mammoli, D.; et al. Investigation of Analysis Methods for Hyperpolarized 13C-Pyruvate Metabolic MRI in Prostate Cancer Patients: Hyperpolarized Pyruvate Prostate Cancer Analysis Methods. NMR Biomed. 2018, 31, e3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, J.L.; Leonard, A.V.; Tuner, R.J.; Corrigan, F. Characterization of Traumatic Brain Injury in a Gyrencephalic Ferret Model Using the Novel Closed Head Injury Model of Engineered Rotational Acceleration (CHIMERA). Neurotrauma Rep. 2023, 4, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, J.L.; Fourney, W.L.; Leiste, U.H.; Fiskum, G. Rat Model of Brain Injury Caused by Under-Vehicle Blast-Induced Hyperacceleration. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2014, 77, S83–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Xu, S.; Fourney, W.L.; Leiste, U.H.; Proctor, J.L.; Fiskum, G.; Gullapalli, R.P. Central Nervous System Changes Induced by Underbody Blast-Induced Hyperacceleration: An in Vivo Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 1972–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, S.J.; Yen, Y.; Wolber, J.; Chen, A.P.; Albers, M.J.; Bok, R.; Zhang, V.; Tropp, J.; Nelson, S.; Vigneron, D.B.; et al. In Vivo 13carbon Metabolic Imaging at 3T with Hyperpolarized 13C-1-Pyruvate. Magn. Reson. Med. 2007, 58, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althouse, A.D. Adjust for Multiple Comparisons? It’s Not That Simple. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 101, 1644–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayer, D.; Eldirdiri, A.; Hrdlick, A.L.; Piskoun, B.; Rogers, J.C.; Jhajharia, A.; Zhu, M.; Proctor, J.L.; Leiste, U.H.; Fourney, W.L.; et al. Metabolic Imaging of Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate in a Ferret Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115327
Mayer D, Eldirdiri A, Hrdlick AL, Piskoun B, Rogers JC, Jhajharia A, Zhu M, Proctor JL, Leiste UH, Fourney WL, et al. Metabolic Imaging of Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate in a Ferret Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115327
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayer, Dirk, Abubakr Eldirdiri, Amanda L. Hrdlick, Boris Piskoun, Joshua C. Rogers, Aditya Jhajharia, Minjie Zhu, Julie L. Proctor, Ulrich H. Leiste, William L. Fourney, and et al. 2025. "Metabolic Imaging of Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate in a Ferret Model of Traumatic Brain Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115327
APA StyleMayer, D., Eldirdiri, A., Hrdlick, A. L., Piskoun, B., Rogers, J. C., Jhajharia, A., Zhu, M., Proctor, J. L., Leiste, U. H., Fourney, W. L., Cantu, J. C., Fiskum, G., & Goodfellow, M. J. (2025). Metabolic Imaging of Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate in a Ferret Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115327




