Dual Mechanisms of the Diazepine-Benzimidazole Derivative, DAB-19, in Modulating Glutamatergic Neurotransmission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
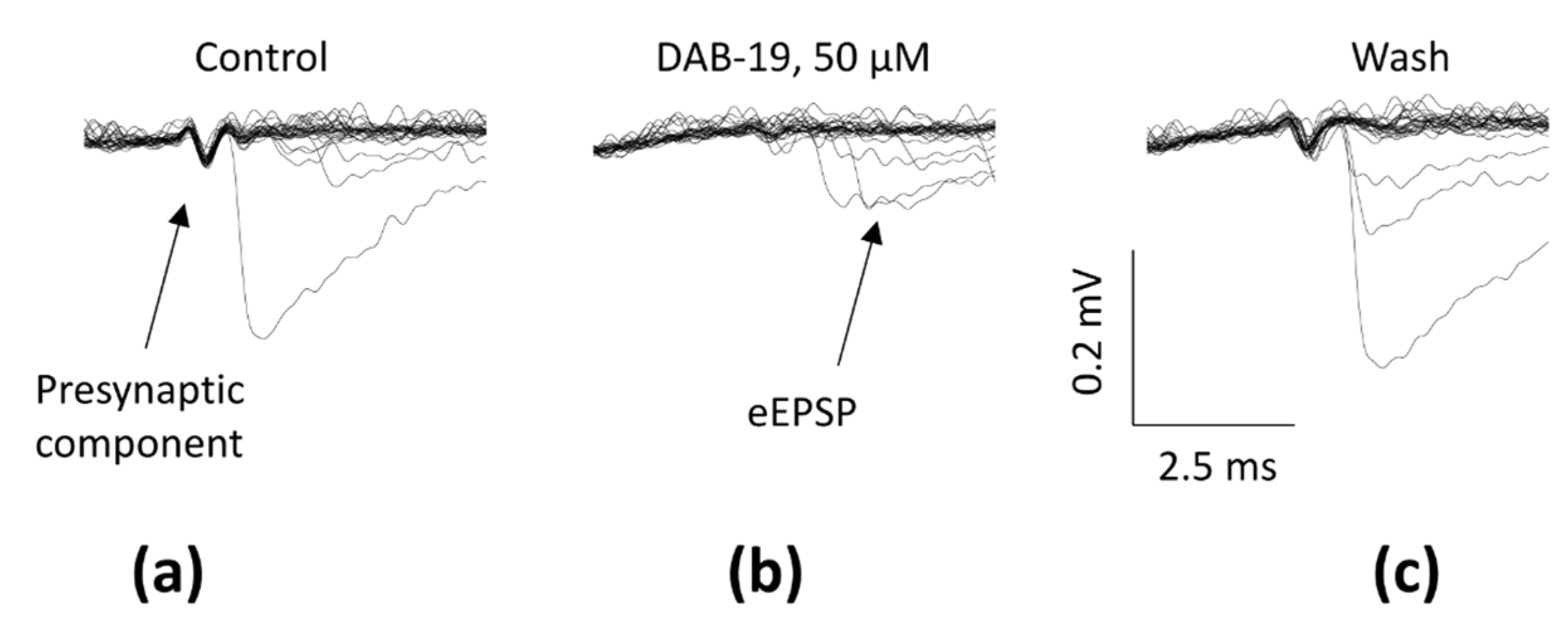
2.1. DAB-19 Inhibits Field Responses in the Rat Hippocampus
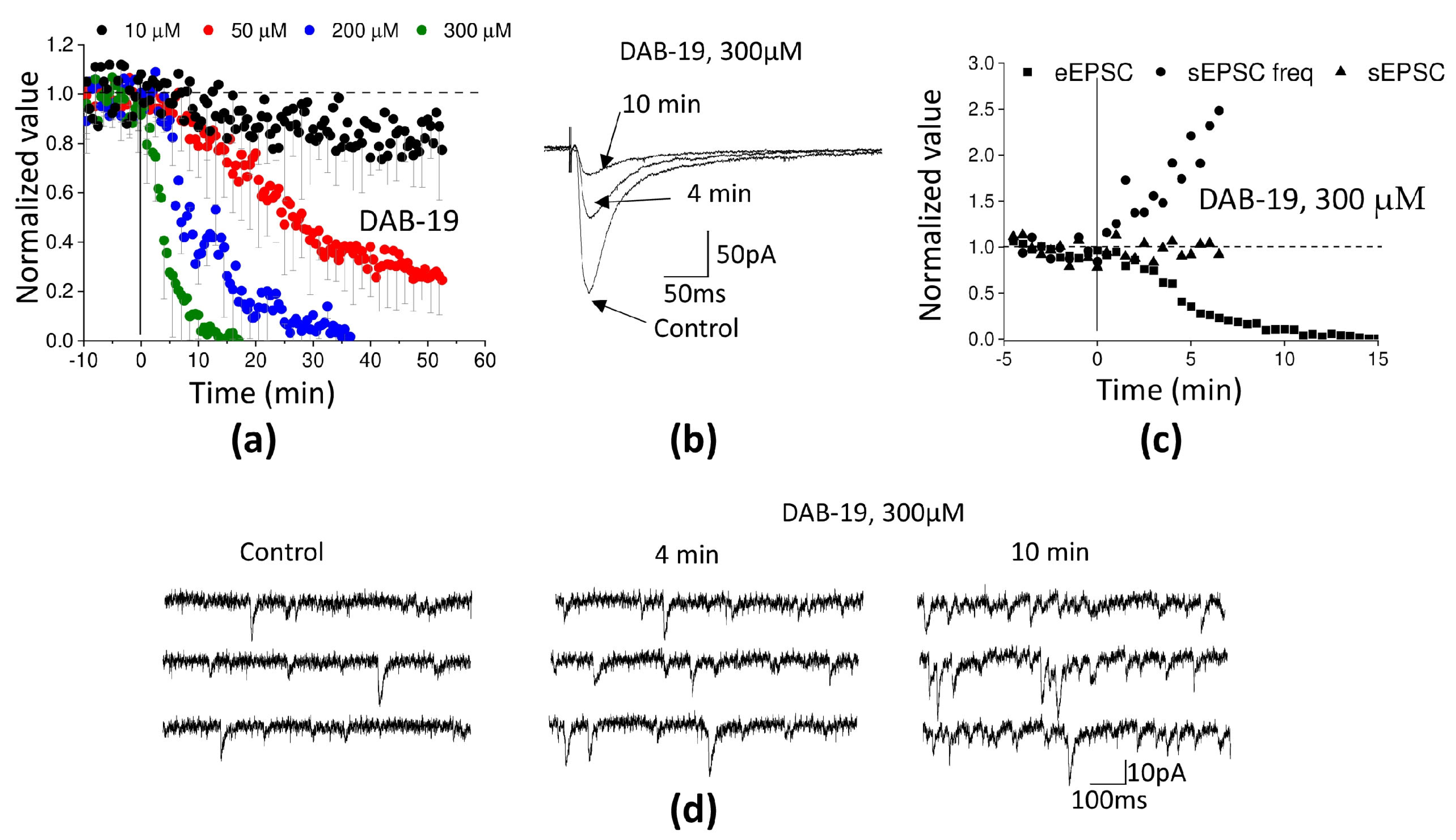
2.2. Opposite Effects of DAB-19 on Evoked and Spontaneous Transmission in Rat Cortex
2.3. Effects of DAB-19 on Neuromuscular Glutamatergic Transmission in Fly Larvae
2.4. Inhibition of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels in Rat Brain Neurons
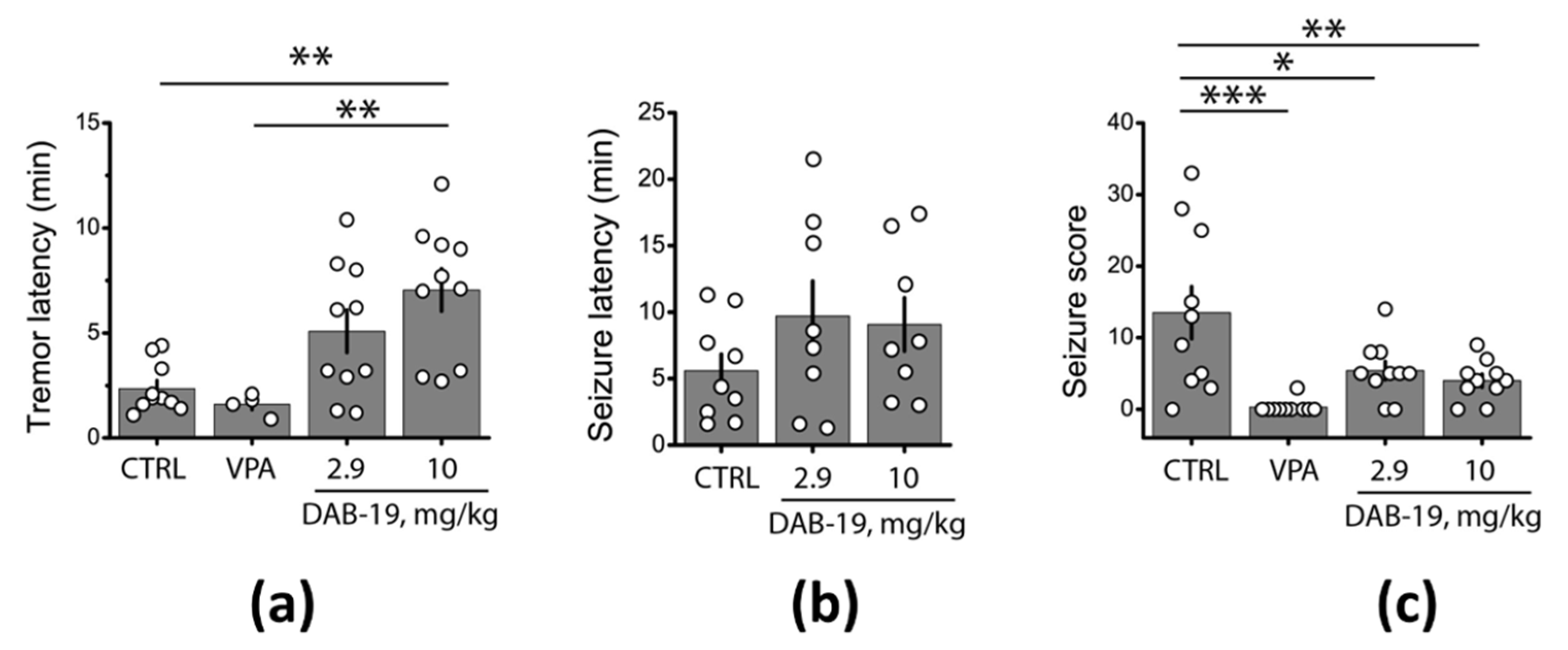
2.5. Suppression of Seizure Activity in Rats by DAB-19 in the Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) Test
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Slice Preparation and Electrophysiological Recordings
4.3. Pentylenetetrazole Test
4.4. Fly Larvae Neuromuscular Preparation
4.5. Data Analysis and Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandelow, B. Current and Novel Psychopharmacological Drugs for Anxiety Disorders. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1191, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechita, D.; Nechita, F.; Motorga, R. A review of the influence the anxiety exerts on human life. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yekkirala, A.S.; Roberson, D.P.; Bean, B.P.; Woolf, C.J. Breaking barriers to novel analgesic drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.D.; Gomez-Carpintero, J.; Gonzalez, J.F.; Menendez, J.C. Twenty-first century antiepileptic drugs. An overview of their targets and synthetic approaches. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 272, 116476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belete, T.M. Recent Progress in the Development of New Antiepileptic Drugs with Novel Targets. Ann. Neurosci. 2023, 30, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Dey, A.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V.; Swati, K.; Ojha, S.; Prakash, A.; Kumar, D.; Ambasta, R.K.; Jha, N.K.; Jha, S.K.; et al. Glutamatergic neurotransmission: A potential pharmacotherapeutic target for the treatment of cognitive disorders. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 85, 101838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, Y.T. Postsynaptic signaling at glutamatergic synapses as therapeutic targets. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2022, 75, 102585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnecka, K.; Chuchmacz, J.; Wojtowicz, P.; Szymanski, P. Memantine in neurological disorders—Schizophrenia and depression. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.L.; Simmonds, M.A. Quantitative studies on some antagonists of N-methyl D-aspartate in slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1985, 84, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, B.; Sachdeva, P.; Ghosh, S.; Ahmad, F.; Sinha, J.K. Ketamine as a therapeutic agent in major depressive disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder: Potential medicinal and deleterious effects. Ibrain 2023, 9, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanacora, G.; Frye, M.A.; McDonald, W.; Mathew, S.J.; Turner, M.S.; Schatzberg, A.F.; Summergrad, P.; Nemeroff, C.B.; for the American Psychiatric Association (APA) Council of Research Task Force on Novel Biomarkers and Treatments. A Consensus Statement on the Use of Ketamine in the Treatment of Mood Disorders. JAMA Psychiatry 2017, 74, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, J.E. Perampanel: A Review in Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. Drugs 2015, 75, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Matt, L.; Hell, J.W.; Rogawski, M.A. Perampanel inhibition of AMPA receptor currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teriakidis, A.; Brown, J.T.; Randall, A. Frequency-dependent inhibition of antidromic hippocampal compound action potentials by anti-convulsants. Pharmacol. Rep. PR 2006, 58, 859–869. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.P.; Tsai, J.J.; Gean, P.W. Frequency-dependent inhibition of neuronal activity by topiramate in rat hippocampal slices. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 125, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragsdale, D.S.; Scheuer, T.; Catterall, W.A. Frequency and voltage-dependent inhibition of type IIA Na+ channels, expressed in a mammalian cell line, by local anesthetic, antiarrhythmic, and anticonvulsant drugs. Mol. Pharmacol. 1991, 40, 756–765. [Google Scholar]
- Barygin, O.I.; Nagaeva, E.I.; Tikhonov, D.B.; Belinskaya, D.A.; Vanchakova, N.P.; Shestakova, N.N. Inhibition of the NMDA and AMPA receptor channels by antidepressants and antipsychotics. Brain Res. 2017, 1660, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boikov, S.I.; Sibarov, D.A.; Stepanenko, Y.D.; Karelina, T.V.; Antonov, S.M. Calcium-Dependent Interplay of Lithium and Tricyclic Antidepressants, Amitriptyline and Desipramine, on N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barygin, O.I.; Komarova, M.S.; Tikhonova, T.B.; Tikhonov, D.B. Non-classical mechanism of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor channel block by fluoxetine. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 41, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dron, M.Y.; Zhigulin, A.S.; Tikhonov, D.B.; Barygin, O.I. Screening for Activity Against AMPA Receptors Among Anticonvulsants-Focus on Phenytoin. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 775040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, D.V.; Spasov, A.A.; Vassiliev, P.M.; Skripka, M.O.; Miroshnikov, M.V.; Kochetkov, A.N.; Eliseeva, N.V.; Lifanova, Y.V.; Kuzmenko, T.A.; Divaeva, L.N.; et al. Synthesis and Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel 2,3,4,5-tetrahydro [1,3]diazepino[1,2-a]benzimidazole Derivatives as Promising Anxiolytic and Analgesic Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltsev, D.V.; Spasov, A.A.; Yakovlev, D.S.; Vassiliev, P.M.; Skripka, M.O.; Miroshnikov, M.V.; Sultanova, K.T.; Kochetkov, A.N.; Divaeva, L.N.; Kuzmenko, T.A.; et al. Searching for new anxiolytic agents among derivatives of 11-dialkylaminoethyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrodiazepino[1,2-a]benzimidazole. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 161, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltsev, D.V.; Spasov, A.A.; Miroshnikov, M.V.; Skripka, M.O.; Divaeva, L.N. Influence of Diazepino[1,2-a]benzimidazole derivative (DAB-19) on behavioral aspects of animals. Res. Results Pharmacol. 2020, 6, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, R.S.; Regehr, W.G. Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2002, 64, 355–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorio, A.; Rubin, L.L.; Mauro, A. Double mode of action of black widow spider venom on frog neuromuscular junction. J. Neurocytol. 1978, 7, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, M.C.; Cohen, R.S.; Siekevitz, P. Release of neurotransmitters and depletion of synaptic vesicles in cerebral cortex slices by alpha-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 4016–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capogna, M.; Gahwiler, B.H.; Thompson, S.M. Calcium-independent actions of alpha-latrotoxin on spontaneous and evoked synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 1996, 76, 3149–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.; Baraibar, A.M.; Albinana, E.; Velasco, P.; Solis, J.M.; Hernandez-Guijo, J.M. Methylmercury reduces synaptic transmission and neuronal excitability in rat hippocampal slices. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2018, 470, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, R.P.; Zahniser, N.R.; Dunwiddie, T.V. Electrophysiological effects of cocaine in the rat hippocampus in vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 1984, 45, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Tsai, J.J.; Huang, C.C. Effects of lamotrigine on field potentials, propagation, and long-term potentiation in rat prefrontal cortex in multi-electrode recording. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 83, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, I.M.; Tikhonov, D.B. Lidocaine and carbamazepine inhibit while phenytoin and lamotrigine paradoxically enhance the insect neuromuscular transmission. Invert. Neurosci. 2019, 19, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuwa, M.; Kageyama, M.; Ohashi, K.; Sasaoka, M.; Sato, R.; Tanaka, M.; Tashiro, K. Nafamostat and sepimostat identified as novel neuroprotective agents via NR2B N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonism using a rat retinal excitotoxicity model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhigulin, A.S.; Barygin, O.I. Mechanisms of NMDA Receptor Inhibition by Sepimostat-Comparison with Nafamostat and Diarylamidine Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhigulin, A.S.; Tikhonov, D.B.; Barygin, O.I. Mechanisms of acid-sensing ion channels inhibition by nafamostat, sepimostat and diminazene. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 938, 175394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.A.; Wheatley, P.; Sawyer, D.A.; Baxter, M.G.; Roth, B. Pharmacological studies on lamotrigine, a novel potential antiepileptic drug: I. Anticonvulsant profile in mice and rats. Epilepsia 1986, 27, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, D.; Katyal, J.; Arava, S.; Gupta, Y.K. Effects of enalapril and losartan alone and in combination with sodium valproate on seizures, memory, and cardiac changes in rats. Epilepsy Behav. EB 2019, 92, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.W.; Wang, W.P.; Dong, R.F.; Tian, S.; Zhang, C. Effect of lamotrigine on epilepsy-induced cognitive impairment and hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in pentylenetetrazole-kindled animal model. Synapse 2017, 71, e21945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; He, M.; Wu, B.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. SAD-B modulates epileptic seizure by regulating AMPA receptors in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and in the PTZ-induced epileptic model. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. = Rev. Bras. De Pesqui. Medicas E Biol. 2020, 53, e9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, L.C.; Burrone, J. The role of spontaneous neurotransmission in synapse and circuit development. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.M.; Kavalali, E.T. Differential regulation of spontaneous and evoked neurotransmitter release at central synapses. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobjev, V.S. Vibrodissociation of sliced mammalian nervous tissue. J. Neurosci. Methods 1991, 38, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnusov, A.N.; Vasilyev, D.S.; Nalivaeva, N.N. Molecular Mechanisms of Valproic Acid Action on Signalling Systems and Brain Functions. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 59, 1740–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaitsev, A.V.; Kim, K.; Vasilev, D.S.; Lukomskaya, N.Y.; Lavrentyeva, V.V.; Tumanova, N.L.; Zhuravin, I.A.; Magazanik, L.G. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel blockers prevent pentylenetetrazole-induced convulsions and morphological changes in rat brain neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 93, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolaev, M.V.; Fedorova, I.M.; Chistyakova, O.V.; Postnikova, T.Y.; Kim, K.K.; Dron, M.Y.; Zaitsev, A.V.; Tikhonov, D.B. Dual Mechanisms of the Diazepine-Benzimidazole Derivative, DAB-19, in Modulating Glutamatergic Neurotransmission. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115299
Nikolaev MV, Fedorova IM, Chistyakova OV, Postnikova TY, Kim KK, Dron MY, Zaitsev AV, Tikhonov DB. Dual Mechanisms of the Diazepine-Benzimidazole Derivative, DAB-19, in Modulating Glutamatergic Neurotransmission. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115299
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolaev, Maxim V., Irina M. Fedorova, Oxana V. Chistyakova, Tatiana Yu. Postnikova, Kira Kh. Kim, Mikhail Yu. Dron, Aleksey V. Zaitsev, and Denis B. Tikhonov. 2025. "Dual Mechanisms of the Diazepine-Benzimidazole Derivative, DAB-19, in Modulating Glutamatergic Neurotransmission" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115299
APA StyleNikolaev, M. V., Fedorova, I. M., Chistyakova, O. V., Postnikova, T. Y., Kim, K. K., Dron, M. Y., Zaitsev, A. V., & Tikhonov, D. B. (2025). Dual Mechanisms of the Diazepine-Benzimidazole Derivative, DAB-19, in Modulating Glutamatergic Neurotransmission. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115299





