Alpha-Mangostin: A Review of Current Research on Its Potential as a Novel Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Agent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Antibacterial Applications of -Mangostin
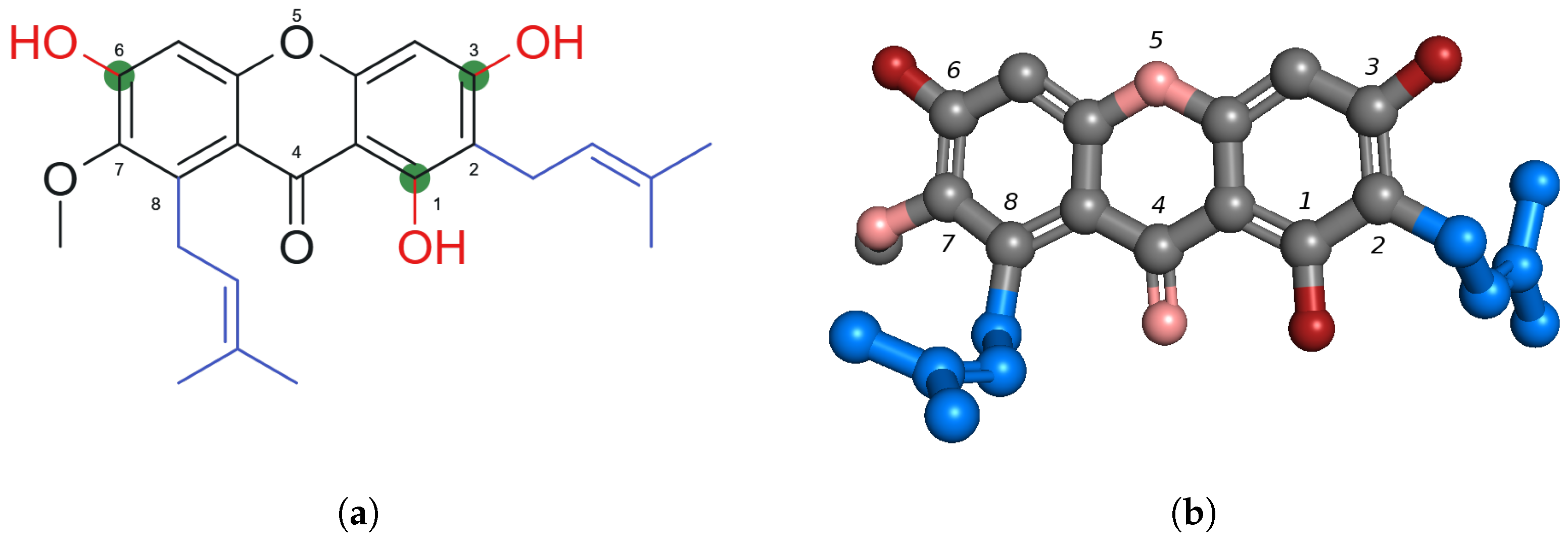
2.1. Chemical Structure of -Mangostin
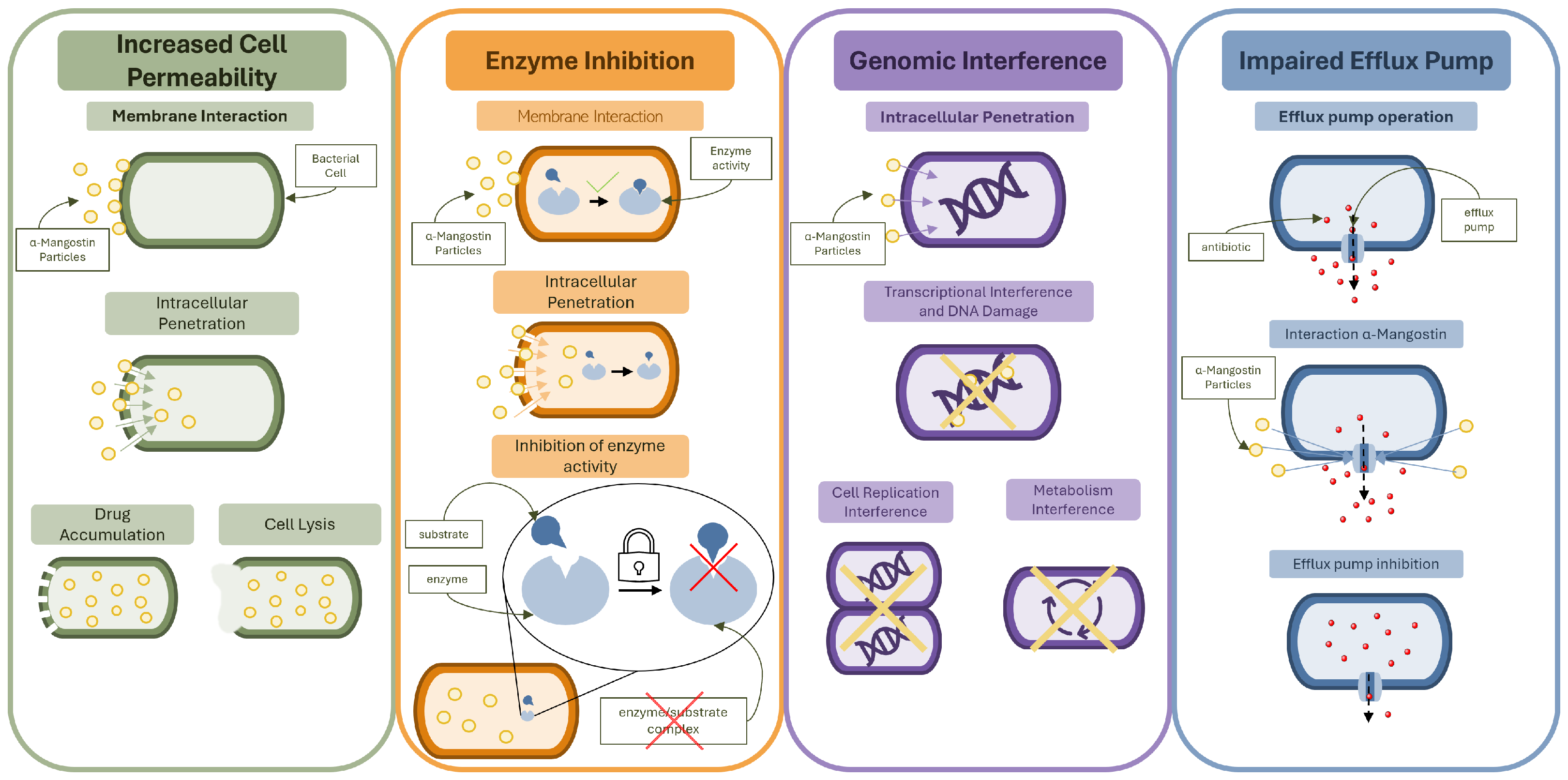
2.2. Mechanisms of Antibacterial Action
2.2.1. Membrane Disruption and Cell Wall Permeability
2.2.2. Inhibition of Bacterial Enzymes and Metabolic Pathways
2.2.3. Activity Against Gram-Negative Bacteria
2.2.4. MIC Comparison
| Study | Bacterial Species and Strains | MIC (g/mL) | Method | Solvent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phitaktim et al. (2016) [14] | S. aureus ATCC 29213(+) | 4 | Broth microdilution | DMSO 2 |
| ORSS strains 1(+) | 8 | |||
| Koh et al. (2013) [15] | S. aureus DM 21455(+) | 1.56 | Broth microdilution | DMF 3 |
| S. aureus DM 09808R(+) | 1.56 | |||
| B. cereus ATCC 11778(+) | 1.56 | |||
| MRSA DB 57964/04(+) | 1.56 | |||
| S. aureus ATCC 29213(+) | 0.78 | |||
| Park et al. (2023) [16] | S. aureus ATCC 29213(+) | 4 | Agar dilution | DMSO 2 |
| 2 | Broth microdilution | |||
| S. carprae KCTC 3583(+) | 2 | Agar/broth microdilution | ||
| S. epidermidis ATCC 12228(+) | 1 | Agar/Broth microdilution | ||
| S. felis ATCC 49168(+) | 2 | Agar dilution | ||
| 1 | Broth microdilution | |||
| S. intermedius KCTC 3344(+) | 2 | Agar dilution | ||
| 1 | Broth microdilution | |||
| S. pseudintermedius ATCC 49051(+) | 2 | Agar dilution | ||
| 1 | Broth microdilution | |||
| S. saprophyticus KCTC 3345(+) | 2 | Agar dilution | ||
| 1 | Broth microdilution | |||
| S. schleiferi ATCC 43808(+) | 1 | Agar/Broth microdilution | ||
| E. coli ATCC 25922(−) | >64 | Agar/Broth microdilution | ||
| P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853(−) | >64 | Agar/Broth microdilution | ||
| Ge et al. (2024) [17] | S. aureus ATCC 29213(+) | 0.5–2 | Broth microdilution | Not specified |
| MRSA2(+) | 0.5–2 | |||
| E. coli ATCC25922(−) | >256 | |||
| E. coli CRE-1(−) | >256 | |||
| Felix et al. (2022) [18] | S. aureus MRSA MW2(+) | 2 | Microdilution | DMSO 2 |
| Meah et al. (2020) [19] | MRSA DMST 20654(+) | 15.6 | Microdilution | DMSO 2 |
| MRSA-142(+) | 31.25 | |||
| MRSA-2468(+) | 31.25 | |||
| MRSA-1096(+) | 7.81 | |||
| Sivaranjani et al. (2017, 2019) [27,44] | S. epidermidis RP62A(+) | 1.25 | Microdilution | Not specified |
| Sakagami et al. (2005) [32] | VRE strains 4(+) | 3.13–6.25 | Agar dilution | DMSO 2 |
| VSE strains 5(+) | 3.13–6.25 | |||
| MRSA strains 6(+) | 6.25–12.5 | |||
| MSSA strains 7(+) | 6.25 | |||
| Tangsuksan et al. (2022) [34] | S. mutans ATCC 25175(+) | 117 | Microdilution | Soluble film |
| P. gingivalis ATCC 33277(−) | 117 |
2.3. Anti-Biofilm Activity
2.3.1. Mechanisms of Anti-Biofilm Action
2.3.2. Multi-Species Biofilms
2.4. Drug Delivery Strategies
2.5. Synergistic Effects
2.5.1. Overview of Synergistic Mechanisms
- Increased membrane permeability: -MG disrupts bacterial membrane integrity, which facilitates the intracellular uptake of co-administered antibiotics. This has been further described above as shown by Koh et al. [15] and other groups. Since antibiotic resistance can be based on bacteria’s limited uptake of a drug, this mechanism can help overcome the boundary and allow for antibiotics’ proper action [75].
- Efflux pump inhibition: Increased multi-drug efflux pump is one of the most common mechanisms of induced bacterial resistance [75,76]. Studies have shown that -MG can downregulate the expression of efflux pump-related genes or interfere with their function, reducing antibiotic clearance from the cell [17].
- Enzyme inhibition: Another mechanism of bacterial antibiotic resistance is ability to destroy the antibiotic molecule. This is the main mechanism for -lactam resistance [76]. In resistant strains, such as MRSA and oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus saprophyticus (ORSS), -MG has been shown to inhibit resistance-related enzymes like -lactamase and PBP2a, restoring the efficacy of -lactam antibiotics [14,17].Together, these mechanisms cam explain the observed synergistic effects of -MG and antibiotics in both planktonic and biofilm-forming bacterial populations.
2.5.2. Synergy with Other Bactericidal Drugs
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naeem, A.; Hu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, Q. Natural Products as Anticancer Agents: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Deng, L. Bioactivity and pharmacological properties of α-mangostin from the mangosteen fruit: A review. Expert Opin. Ther. Patents 2018, 28, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Rashid, S.; Fatima, K.; Adnan, M.; Shafie, A.; Akhtar, M.S.; Ganie, A.; Eldin, S.M.; Islam, A.; Khan, I.; et al. Biochemical features and therapeutic potential of α-Mangostin: Mechanism of action, medicinal values, and health benefits. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.Y.; Hashim, N.M.; Mariod, A.A.; Mohan, S.; Abdulla, M.A.; Abdelwahab, S.I.; Arbab, I.A. α-Mangostin from Garcinia mangostana Linn: An updated review of its pharmacological properties. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Fei, X.; Cho, S.C.; Choi, B.Y.; Ahn, H.C.; Lee, K.; Seo, S.Y.; Keum, Y.S. Discovery of α-mangostin as a novel competitive inhibitor against mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase-1. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5625–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meah, M.S.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Sayeed, M.A.; Kim, M.G. Isolation and Pharmacochemistry of α-Mangostin as a Chemotherapeutic Agent. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2025, 21, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumrung, J.; Chanchao, C.; Intasanta, V.; Palaga, T.; Wanichwecharungruang, S. Water-dispersible unadulterated α-mangostin particles for biomedical applications. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzing, A.W. Publish or Perish, Version 8; Software. Harzing.com 2024. Available online: https://harzing.com/resources/publish-or-perish (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Fatima, Z.; Purkait, D.; Rehman, S.; Rai, S.; Hameed, S. Chapter 11—Multidrug resistance: A threat to antibiotic era. In Biological and Environmental Hazards, Risks, and Disasters, 2nd ed.; Sivanpillai, R., Shroder, J.F., Eds.; Hazards and Disasters Series; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.K.; Hussein, S.; Qurbani, K.; Ibrahim, R.H.; Fareeq, A.; Mahmood, K.A.; Mohamed, M.G. Antimicrobial Resistance: Impacts, Challenges, and Future Prospects. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 2024, 2, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, T.; Newton, R.; Kimbell, L.; LaMartina, E.; O’Malley, K.; Thomson, S.; Marshall, C.; McNamara, P. Targeting current and future threats: Recent methodological trends in environmental antimicrobial resistance research and their relationships to risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2022, 8, 1787–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugaiyan, J.; Kumar, P.A.; Rao, G.S.; Iskandar, K.; Hawser, S.; Hays, J.P.; Mohsen, Y.; Adukkadukkam, S.; Awuah, W.A.; Jose, R.A.M.; et al. Progress in Alternative Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: Focus on Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suksamrarn, S.; Suwannapoch, N.; Phakhodee, W.; Thanuhiranlert, J.; Ratananukul, P.; Chimnoi, N.; Suksamrarn, A. Antimycobacterial Activity of Prenylated Xanthones from the Fruits of Garcinia mangostana. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 857–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phitaktim, S.; Chomnawang, M.; Sirichaiwetchakoon, K.; Dunkhunthod, B.; Hobbs, G.; Eumkeb, G. Synergism and the mechanism of action of the combination of α-mangostin isolated from Garcinia mangostana L. and oxacillin against an oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus saprophyticus. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.J.; Qiu, S.; Zou, H.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Tang, C.; Saraswathi, P.; Verma, C.; Tan, D.T.; et al. Rapid bactericidal action of alpha-mangostin against MRSA as an outcome of membrane targeting. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, S.Y.; Kim, N.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.C. Antimicrobial activity of alpha-mangostin against Staphylococcus species from companion animals in vitro and therapeutic potential of alpha-mangostin in skin diseases caused by S. pseudintermedius. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1203663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Q.; Chandarajoti, K.; Bai, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Ye, W.; Han, X.; Wang, C.; et al. A novel α-mangostin derivative synergistic to antibiotics against MRSA with unique mechanisms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e01631-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, L.; Mishra, B.; Khader, R.; Ganesan, N.; Mylonakis, E. In Vitro and In Vivo Bactericidal and Antibiofilm Efficacy of Alpha Mangostin Against Staphylococcus aureus Persister Cells. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 898794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meah, M.S.; Lertcanawanichakul, M.; Pedpradab, P.; Lin, W.; Zhu, K.; Li, G.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Synergistic effect on anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among combinations of α-mangostin-rich extract, lawsone methyl ether and ampicillin. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 71, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairunnisa, V.; Isnaeni, F.Q.; Afiyah, Z.G.; Rizqiawan, A.; Rahman, M.Z. Exploring the antibacterial potency of α-mangostin against Prevotella intermedia through the diffusion method. J. Int. Oral Health 2023, 15, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhou, W.; Li, P.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y. Mode of action of pentocin 31-1: An antilisteria bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus pentosus from Chinese traditional ham. Food Control 2008, 19, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaranjani, M.; Srinivasan, R.; Aravindraja, C.; Pandian, S.K.; Ravi, A.V. Inhibitory effect of α-mangostin on Acinetobacter baumannii biofilms—An in vitro study. Biofouling 2018, 34, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.L.; Chou, C.C.; Hung, D.J.; Lin, S.H.; Pao, I.C.; Lin, J.H.; Huang, F.L.; Dong, R.X.; Lin, J.J. The disruption of bacterial membrane integrity through ROS generation induced by nanohybrids of silver and clay. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5979–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.H.L.; Wang, C.H.; Liao, Y.T.; Chan, F.Y.; Kanaoka, Y.; Uchihashi, T.; Kato, K.; Lai, L.; Chang, Y.W.; Ho, M.C.; et al. Visualizing the membrane disruption action of antimicrobial peptides by cryo-electron tomography. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.T.M.; Marquis, R.E. Antimicrobial actions of α-mangostin against oral streptococci. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühle, T.; Leister, D. Assembly of F1F0-ATP synthases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2015, 1847, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaranjani, M.; Leskinen, K.; Aravindraja, C.; Saavalainen, P.; Pandian, S.K.; Skurnik, M.; Ravi, A.V. Deciphering the Antibacterial Mode of Action of Alpha-Mangostin on Staphylococcus epidermidis RP62A Through an Integrated Transcriptomic and Proteomic Approach. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaidomy, A.H.; Shady, N.H.; Abdeljawad, K.M.; Elzamkan, M.B.; Helmy, H.H.; Tarshan, E.A.; Adly, A.N.; Hussien, Y.H.; Sayed, N.G.; Zayed, A.; et al. Antimicrobial potentials of natural products against multidrug resistance pathogens: A comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 29078–29102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, P.; Jayaprakasha, G.; Jena, B. Antibacterial activity of the extracts from the fruit rinds of Garcinia cowa and Garcinia pedunculata against food borne pathogens and spoilage bacteria. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, P.; Qiao, Y.; Kang, Y.; Guo, S.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, H. Bacteria-activated chlorin e6 ionic liquid based on cation and anion dual-mode antibacterial action for enhanced photodynamic efficacy. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guern, F.; Ouk, T.S.; Grenier, K.; Joly, N.; Lequart, V.; Sol, V. Enhancement of photobactericidal activity of chlorin-e6-cellulose nanocrystals by covalent attachment of polymyxin B. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6953–6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakagami, Y.; Iinuma, M.; Piyasena, K.; Dharmaratne, H. Antibacterial activity of alpha-mangostin against vancomycin resistant Enterococci (VRE) and synergism with antibiotics. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Keach, J.; Behl, T. Synergistic effect of α-mangostin on antibacterial activity of tetracycline, erythromycin, and clindamycin against acne involved bacteria. Chin. Herb. Med. 2019, 11, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangsuksan, P.; Srichana, T.; Kettratad, M.; Nittayananta, W. Antimicrobial and Anti-inflammatory Effects of α-Mangostin Soluble Film. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2022, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunle, O.F.; Egharevba, H.O.; Ahmadu, P.O. Standardization of herbal medicines—A review. Int. J. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 4, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, S.; Chen, Y.; Saravanan, D.; Sundram, K.M.; Yoga Latha, L. Extraction, Isolation and Characterization of Bioactive Compounds from Plants’ Extracts. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohman, A.; Arifah, F.H.; Arifah, I.G.A.; Muchtaridi, M. The application of FTIR spectroscopy and chemometrics for classification of Mangosteen extract and its correlation with alpha-mangostin. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerapattana, J.; Otsuka, K.; Otsuka, M. Application of NIR spectroscopy for the quality control of mangosteen pericarp powder: Quantitative analysis of alpha-mangostin in mangosteen pericarp powder and capsule. J. Nat. Med. 2012, 67, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardhanan, S.; Mahendra, J.; Smiline Girija, A.S.; Mahendra, L.; Priyadharsini, V. Antimicrobial Effects of Garcinia Mangostana on Cariogenic Microorganisms. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, ZC68–ZC71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatiya-aphiradee, N.; Chatuphonprasert, W.; Jarukamjorn, K. In vivo antibacterial activity of Garcinia mangostana pericarp extract against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a mouse superficial skin infection model. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 2606–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, A.; Mazlan, N.; Yusuf, E.; Anua, S.M.; Thung, T.Y.; Baktir, A. Synergistic effect of commercial mangosteen extract (Garcinia mangostana L.) and amoxicillin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Int. Food Res. J. 2023, 30, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsuprom, L.; Rungroj, N.; Lekcharoensuk, C.; Pruksakorn, C.; Kongkiatpaiboon, S.; Chen, C.; Sukatta, U. In vitro antibacterial activity of mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana Linn.) crude extract against Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates from canine pyoderma. Vet. World 2023, 16, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothitirat, W.; Chomnawang, M.T.; Gritsanapan, W. Anti-Acne-Inducing Bacterial Activity of Mangosteen Fruit Rind Extracts. Med. Princ. Pract. 2010, 19, 281–286. Available online: https://karger.com/mpp/article-pdf/19/4/281/3121279/000312714.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2025). [CrossRef]
- Sivaranjani, M.; Prakash, M.; Gowrishankar, S.; Rathna, J.; Pandian, S.K.; Ravi, A.V. In vitro activity of alpha-mangostin in killing and eradicating Staphylococcus epidermidis RP62A biofilms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3349–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, J.Y.; Centeleghe, I. How biofilm changes our understanding of cleaning and disinfection. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2023, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunardi, W.D.; Karuniawati, A.; Umbas, R.; Bardosono, S.; Lydia, A.; Soebandrio, A.; Safari, D. Biofilm-Producing Bacteria and Risk Factors (Gender and Duration of Catheterization) Characterized as Catheter-Associated Biofilm Formation. Int. J. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 8869275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, M.A.; Gupta, K.; Bardhan, P.; Borah, M.; Sarkar, A.; Eldiehy, K.S.H.; Bhuyan, S.; Mandal, M. Microbial biofilm: A matter of grave concern for human health and food industry. J. Basic Microbiol. 2021, 61, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.M.; Falsetta, M.L.; Hwang, G.; Gonzalez-Begne, M.; Koo, H. α-Mangostin Disrupts the Development of Streptococcus mutans Biofilms and Facilitates Its Mechanical Removal. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossard, K.A.; Campagnari, A.A. The Acinetobacter baumannii Biofilm-Associated Protein Plays a Role in Adherence to Human Epithelial Cells. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.T.M.; Quang, N.V.; Mai, T.T.; Anh, N.V.; Kuhakarn, C.; Reutrakul, V.; Bolhuis, A. Antibiofilm activity of α-mangostin extracted from Garcinia mangostana L. against Staphylococcus aureus. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Marquis, R.E.; Abranches, J.; Lapirattanakul, J.; Aduse-Opoku, J.; Bostanci, N.; Grenier, D.; Herzberg, M.C.; Burne, R.A.; Hua, Z.; et al. Anti-biofilm activity of α-mangostin isolated from Garcinia mangostana L. Z. Für Naturforschung C 2015, 70, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leelapornpisid, W. Efficacy of alpha-mangostin for antimicrobial activity against endodontopathogenic microorganisms in a multi-species bacterial-fungal biofilm model. Arch. Oral Biol. 2022, 135, 105304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisha, A.F.; Ismail, Z.; Abu-Salah, K.M.; Majid, A.M.S.A. Solid Dispersions of α-Mangostin Improve Its Aqueous Solubility through Self-Assembly of Nanomicelles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodalee, K.; Sapsuphan, P.; Wongsirikul, R.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S. Preparation and evaluation of alpha-mangostin solid self-emulsifying drug delivery system. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Asasutjarit, R.; Meesomboon, T.; Adulheem, P.; Kittiwisut, S.; Sookdee, P.; Samosornsuk, W.; Fuongfuchat, A. Physicochemical properties of alpha-mangostin loaded nanomeulsions prepared by ultrasonication technique. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, O.S.; Kantilal, H.K.A.; Phaik, K.S.; Choudhury, H.; Davamani, F. Formulation and Characterization of a Novel Palm-Oil-Based α-Mangostin Nano-Emulsion (PO-AMNE) as an Antimicrobial Endodontic Irrigant: An In Vitro Study. Processes 2023, 11, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.A.; Wahab, R.A.; Rehman, G.U.; Abidin, M.H.Z.; Wong, K.Y. A Novel Water-in-Oil-in-Water Double Nanoemulsion of α-Mangostin and Kojic Acid for Topical Applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 9291–9305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambala, R.; Vemula, S. Formulation and Characterization of Ketoprofen Emulgels. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungpud, C.; Panpipat, W.; Chaijan, M.; Sae Yoon, A. Techno-biofunctionality of mangostin extract-loaded virgin coconut oil nanoemulsion and nanoemulgel. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQahtani, S.A.; Harisa, G.I.; Badran, M.M.; AlGhamdi, K.M.; Kumar, A.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Ahmad, S.F.; Alanazi, F.K. Nano-erythrocyte membrane-chaperoned 5-fluorouracil liposomes as biomimetic delivery platforms to target hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Artif. Cells, Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J. A Review of Liposomes as a Drug Delivery System: Current Status of Approved Products, Regulatory Environments, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang Phan, T.K.; Tran, T.Q.; Nguyen Pham, D.T.; Nguyen, D.T. Characterization, Release Pattern, and Cytotoxicity of Liposomes Loaded With α-Mangostin Isolated From Pericarp of Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana L.). Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20974559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, R.; Kongkaneramit, L.; Sarisuta, N.; Moongkarndi, P.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Cytotoxic effect and mechanism inducing cell death of α-mangostin liposomes in various human carcinoma and normal cells. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2015, 26, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, N.; Oh, H.N.; Yoo, S.Y.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, J.C. Therapeutic Potential of Mangosteen Pericarp Extract-Loaded Liposomes against Superficial Skin Infection Caused by Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in a Murine Model. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meylina, L.; Muchtaridi, M.; Joni, I.M.; Mohammed, A.F.A.; Wathoni, N. Nanoformulations of α-Mangostin for Cancer Drug Delivery System. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhandi, C.; Wilar, G.; Lesmana, R.; Zulhendri, F.; Suharyani, I.; Hasan, N.; Wathoni, N. Propolis-Based Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for α-Mangostin Delivery: Formulation, Characterization, and In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Evaluation. Molecules 2023, 28, 6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatphakdee, G.; Yostawonkul, J.; Oontawee, S.; Rodprasert, W.; Sawangmake, C.; Kornsuthisopon, C.; Yata, T.; Tabtieang, S.P.; Nowwarote, N.; Pirarat, N. Feasibility of Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Loaded with Alpha-Mangostin and Clove Oil for Canine Periodontal Therapy. Animals 2024, 14, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Nguyen, M.T.; Bolhuis, A. Inhibition of biofilm formation by alpha-mangostin loaded nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan-In, P.; Wongsomboon, A.; Kokpol, C.; Chaichanawongsaroj, N.; Wanichwecharungruang, S. Depositing α-mangostin nanoparticles to sebaceous gland area for acne treatment. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 129, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suharyani, I.; Mohammed, A.; Muchtaridi, M.; El-Rayyes, A.; Abdassah, M.; Suhandi, C.; Wathoni, N. Complexation of α-Mangostin with γ-Cyclodextrin and Its Application in Alginate/Chitosan Hydrogel Mucoadhesive Film for Treatment of Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 2185–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitamia, C.; Iftinan, G.N.; Latarissa, I.R.; Wilar, G.; Cahyanto, A.; Mohammed, A.F.A.; El-Rayyes, A.; Wathoni, N. α-Mangostin hydrogel film with chitosan alginate base for recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS) treatment: Study protocol for double-blind randomized controlled trial. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1353503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, S.; Khan, I.U.; Khalid, I. α-Mangostin encapsulated gellan gum membranes for enhanced antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and wound healing activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojnicz, D.; Korzekwa, K.; Guźniczak, M.; Wernecki, M.; Ulatowska-Jarża, A.; Buzalewicz, I.; Tichaczek-Goska, D. Can α-Mangostin and Photodynamic Therapy Support Ciprofloxacin in the Inactivation of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus Strains? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reygaert, W.C. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. In Foodborne Pathogens: Virulence Factors and Host Resistance; Kudva, I.T., Cornick, N.A., Plummer, P.J., Zhang, Q., Nicholson, T.L., Bannantine, J.P., Bellaire, B.H., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samprasilt, W.; Chamsai, B.; Settharaksa, S.; Opanasopit, P. Synergistic antibacterial activity of alpha mangostin and resveratrol loaded polymer-based films against bacteria infected wound. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, R.; Gao, M.; Li, Z.; Feng, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. Improvement of antibacterial activity of polysaccharides via chemical modification: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 132163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Qiao, H.; Ma, P.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, H. Antibacterial activity of xanthan-oligosaccharide against Staphylococcus aureus via targeting biofilm and cell membrane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.N.; Jang, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, S.A.; Choo, G.S.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, S.K.; Jung, J.Y. Antitumor and apoptosis-inducing effects of α-mangostin extracted from the pericarp of the mangosteen fruit (Garcinia mangostana L.) in YD-15 tongue mucoepidermoid carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Gregorio, A.; Aranda-Rivera, A.K.; Aparicio-Trejo, O.E.; Medina-Campos, O.N.; Sciutto, E.; Fragoso, G.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. α-Mangostin induces oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis in a triple-negative breast cancer model. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 3394–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.; Shaaban, M.I.; Ross, S.A. Mangostanaxanthones I and II, new xanthones from the pericarp of Garcinia mangostana. Fitoterapia 2014, 98, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Query | Source | Papers | Citations | Cites per Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| alpha-mangostin [title] antibacterial; bacteria | Google Scholar | 51 | 422 | 84.40 |
| alpha-mangostin [title] antibacterial; biofilm | Google Scholar | 17 | 177 | 35.40 |
| alpha-mangostin; antibacterial | PubMed | 29 | 0 | 0.00 |
| alpha-mangostin [title] antibacterial | PubMed | 11 | 0 | 0.00 |
| alpha-mangostin [title] antibacterial; biofilm | PubMed | 1 | 0 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Górecka, H.; Guźniczak, M.; Buzalewicz, I.; Ulatowska-Jarża, A.; Korzekwa, K.; Kaczorowska, A. Alpha-Mangostin: A Review of Current Research on Its Potential as a Novel Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115281
Górecka H, Guźniczak M, Buzalewicz I, Ulatowska-Jarża A, Korzekwa K, Kaczorowska A. Alpha-Mangostin: A Review of Current Research on Its Potential as a Novel Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Agent. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115281
Chicago/Turabian StyleGórecka, Hanna, Mateusz Guźniczak, Igor Buzalewicz, Agnieszka Ulatowska-Jarża, Kamila Korzekwa, and Aleksandra Kaczorowska. 2025. "Alpha-Mangostin: A Review of Current Research on Its Potential as a Novel Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Agent" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115281
APA StyleGórecka, H., Guźniczak, M., Buzalewicz, I., Ulatowska-Jarża, A., Korzekwa, K., & Kaczorowska, A. (2025). Alpha-Mangostin: A Review of Current Research on Its Potential as a Novel Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Agent. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5281. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115281








