SLIT/ROBO Pathway and Prostate Cancer: Gene and Protein Expression and Their Prognostic Values
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
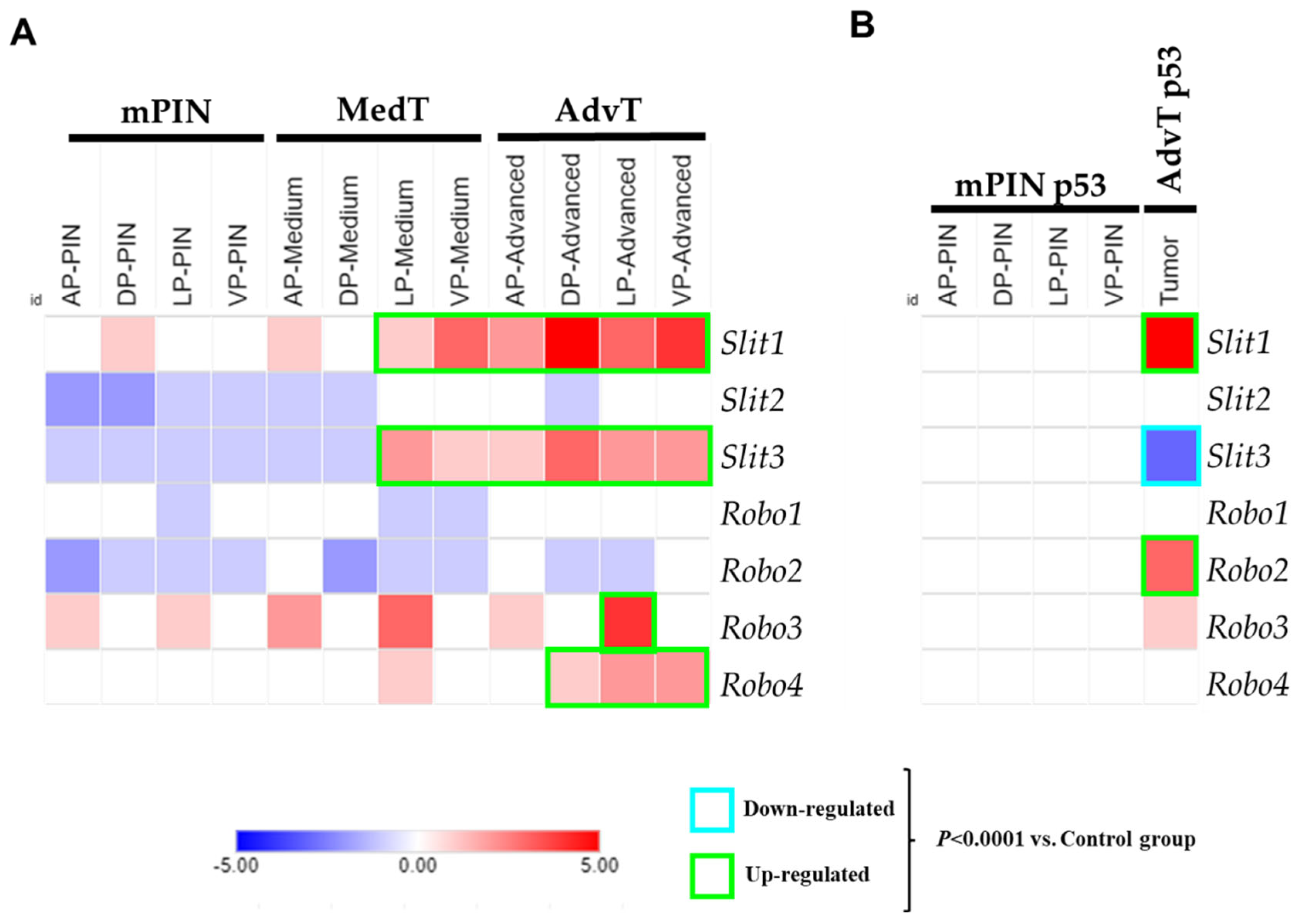
2.1. Analysis of Gene Expression of the SLIT/ROBO Pathway in Prostate Tumors from Knockout Mice
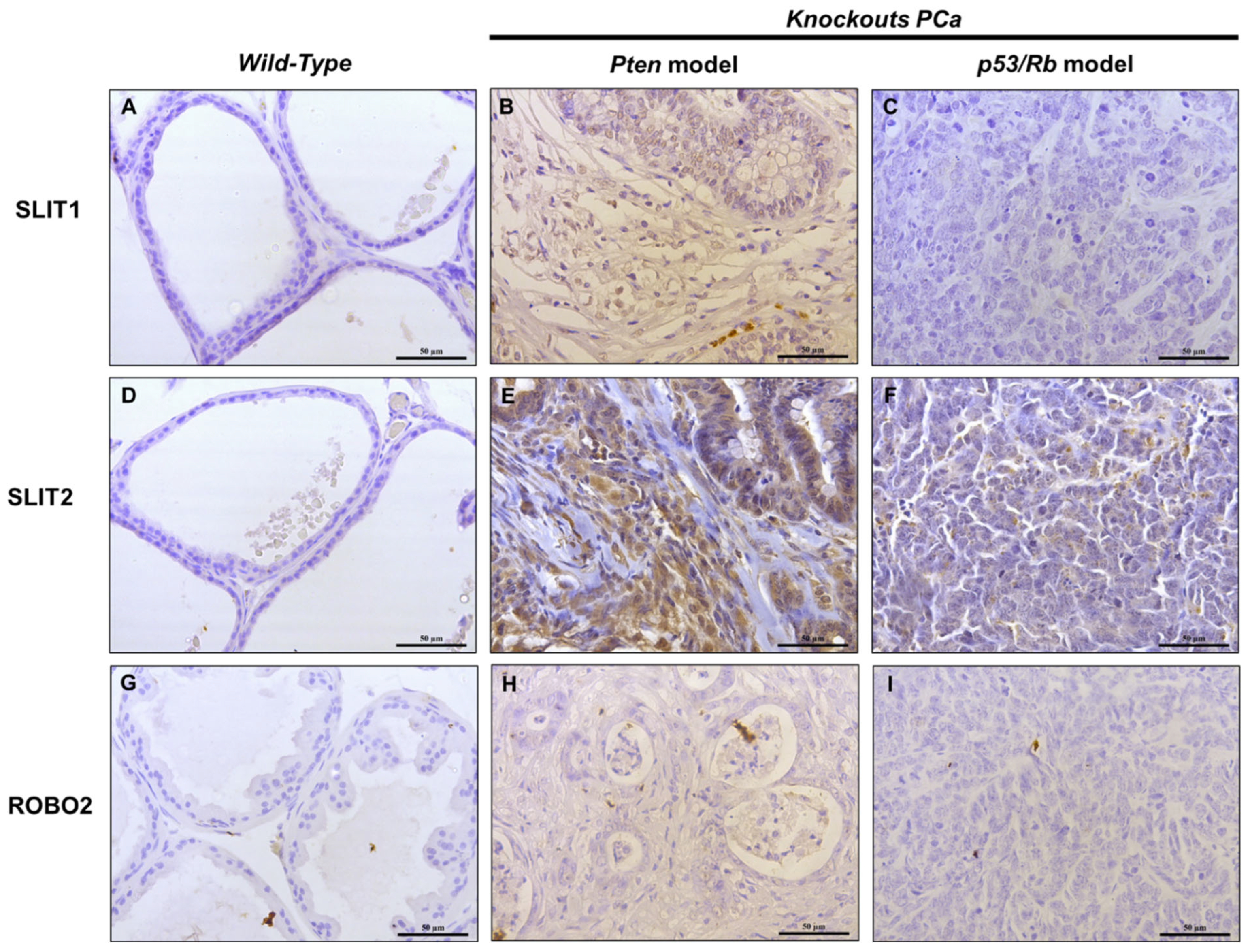
2.2. IHC Analysis of SLIT/ROBO Pathway Proteins in Prostate Tissues from Knockout Mice
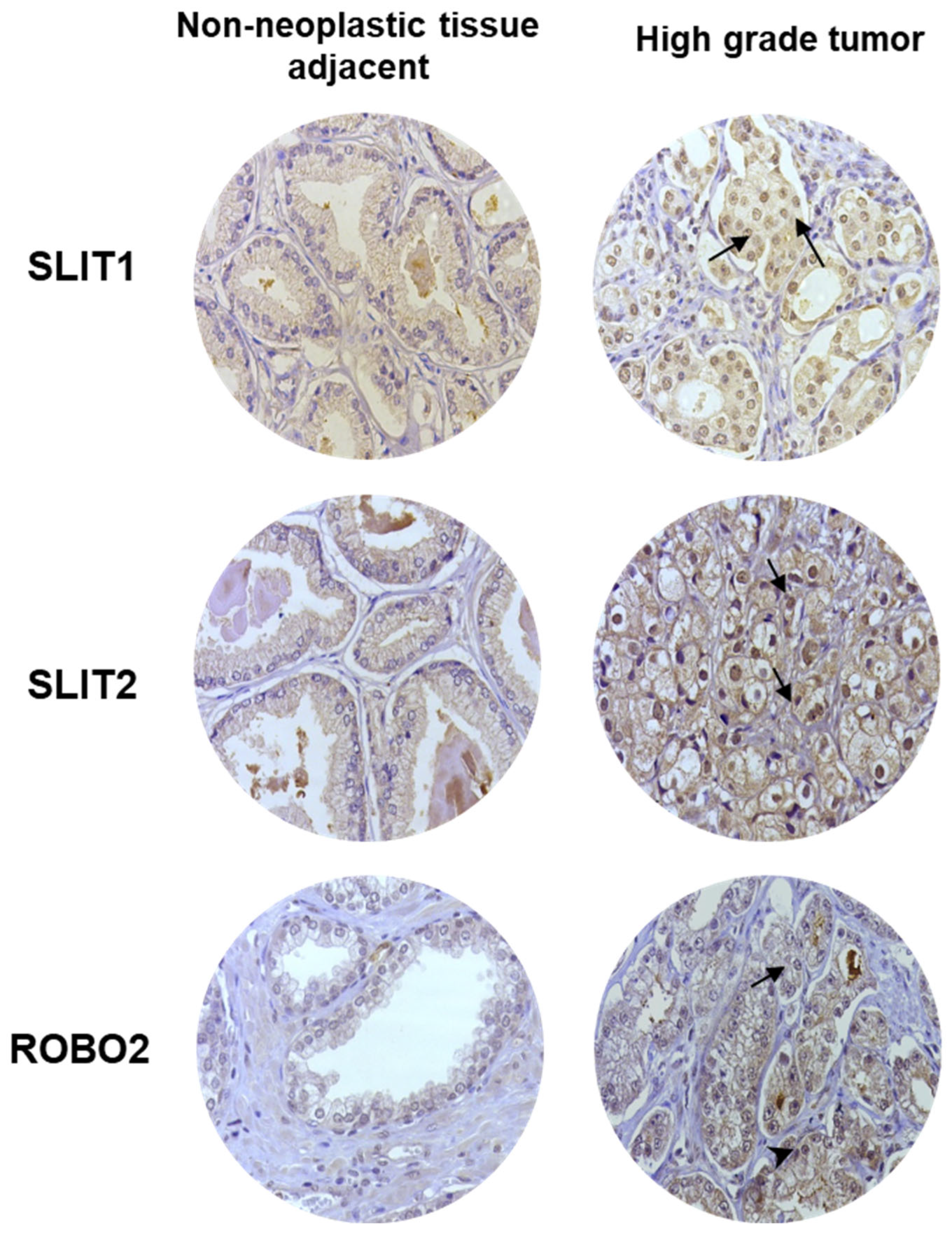
2.3. IHC Analysis of SLIT/ROBO Pathway Proteins in Human Prostate Tissues
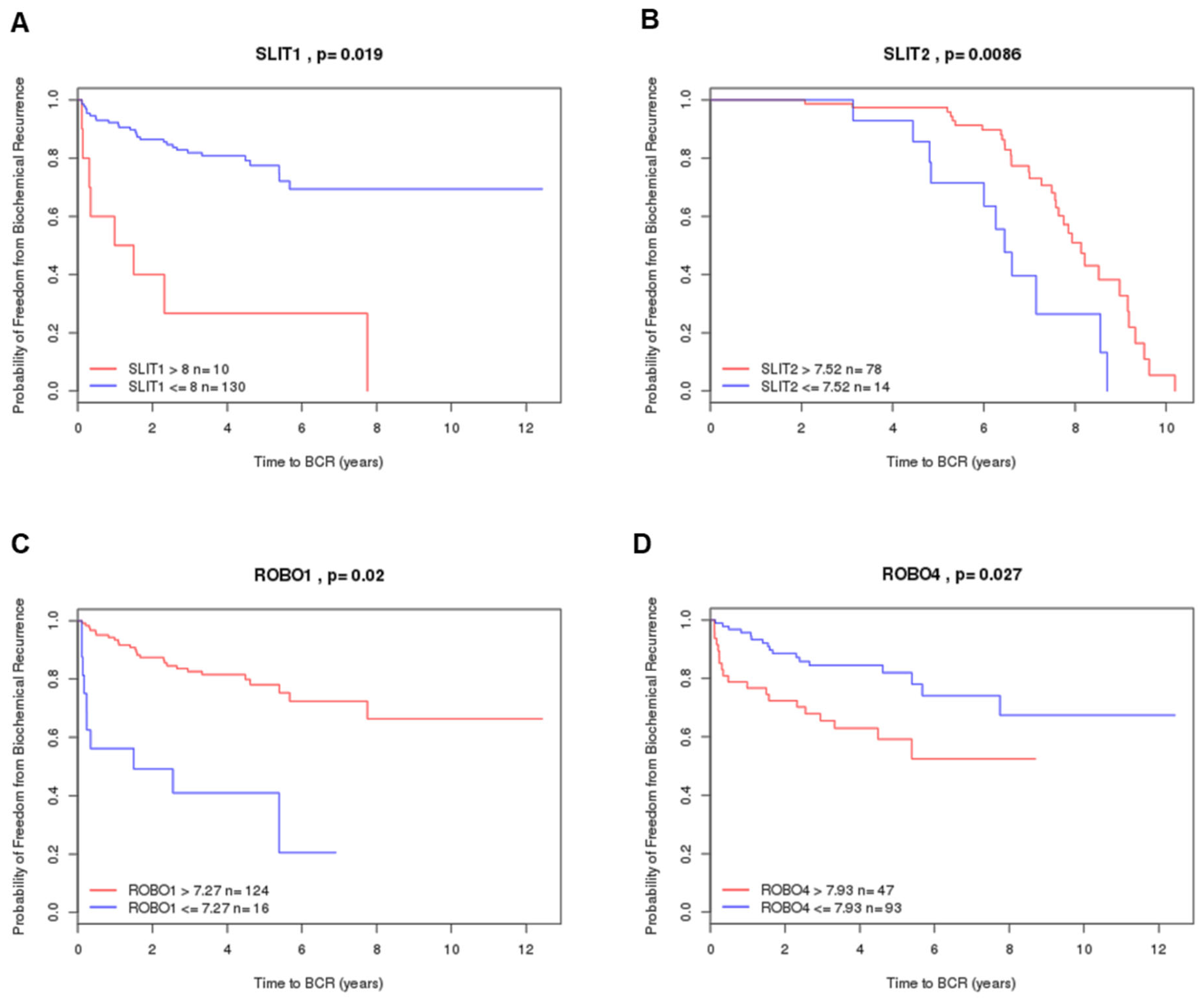
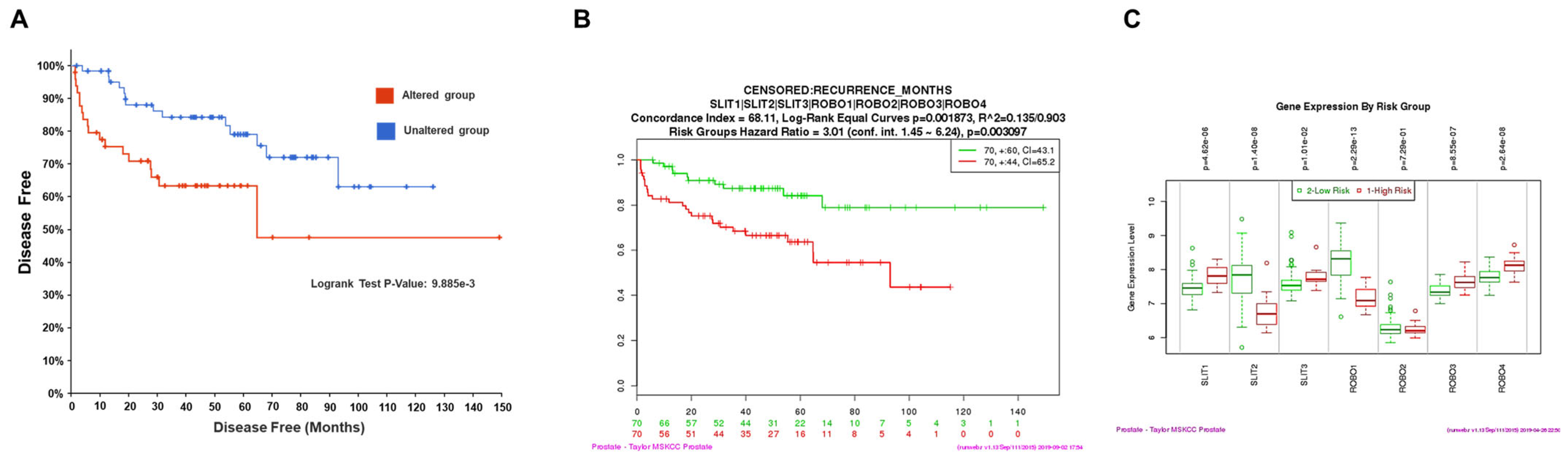
2.4. Prognostic Value by Gene Expression Patterns in Public Datasets
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Analysis of SLIT/ROBO Gene Expression in Two Genetically Modified Mouse Models (GEMM) of PCa: Pb-Cre4/Ptenf/f and Pb-Cre4/Trp53f/f-;Rb1f/f
4.2. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) in Mice Sample Analysis
4.3. Clinical Information of Patients with Prostatic Carcinoma Used for the Construction of Tissue Microarrays (TMAs)
4.4. Prognostic Value Analysis in Public Datasets
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Fernández, E.; Barcelos, L.S.; de Souza, A.G.; Goulart, L.R.; Alonso-Goulart, V. Research landscape of liquid biopsies in prostate cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1309–1328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.T.; Delijani, K.; Mecum, A.; Goldkorn, A. Current status of liquid biopsies for the detection and management of prostate cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 5271–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.D.; Eeles, R.; Freedland, S.J.; Isaacs, W.B.; Pomerantz, M.M.; Schalken, J.A.; Tammela, T.L.; Visakorpi, T. The role of genetic markers in the management of prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brose, K.; Bland, K.S.; Wang, K.H.; Arnott, D.; Henzel, W.; Goodman, C.S.; Tessier-Lavigne, M.; Kidd, T. Slit proteins bind Robo receptors and have an evolutionarily conserved role in repulsive axon guidance. Cell 1999, 96, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, T.; Bland, K.S.; Goodman, C.S. Slit is the midline repellent for the robo receptor in Drosophila. Cell 1999, 96, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, J.Y.; Rao, Y.; Ornitz, D.M. The mouse SLIT family: Secreted ligands for ROBO expressed in patterns that suggest a role in morphogenesis and axon guidance. Dev. Biol. 1999, 212, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blockus, H.; Chédotal, A. Slit-Robo signaling. Development 2016, 143, 3037–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimi, T. Roles of Slit Ligands and Their Roundabout (Robo) Family of Receptors in Bone Remodeling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 21, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigemann, P.; Molitor, A.; Fellert, S.; Jäckle, H.; Vorbrüggen, G. Heparan sulfate proteoglycan syndecan promotes axonal and myotube guidance by slit/robo signaling. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Li, Y.; Xing, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Dai, M. Research Progress on Slit/Robo Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer: Emerging and Promising. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 2845906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, N.J.; Barquilha, C.N.; Barbosa, I.C.; Macedo, R.T.; Lima, F.O.; Justulin, L.A.; Barbosa, G.O.; Carvalho, H.F.; Felisbino, S.L. Syndecan Family Gene and Protein Expression and Their Prognostic Values for Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escot, S.; Willnow, D.; Naumann, H.; Di Francescantonio, S.; Spagnoli, F.M. Robo signalling controls pancreatic progenitor identity by regulating Tead transcription factors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pircher, A.; Schäfer, G.; Eigentler, A.; Pichler, R.; Puhr, M.; Steiner, E.; Horninger, W.; Gunsilius, E.; Klocker, H.; Heidegger, I. Robo 4—The double-edged sword in prostate cancer: Impact on cancer cell aggressiveness and tumor vasculature. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurmeister, S.; Ramos-Montoya, A.; Sandi, C.; Pertega-Gomes, N.; Wadhwa, K.; Lamb, A.D.; Dunning, M.J.; Attig, J.; Carroll, J.S.; Fryer, L.G.; et al. Identification of potential therapeutic targets in prostate cancer through a cross-species approach. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaspishvili, T.; Berman, D.M.; Ross, A.E.; Scher, H.I.; De Marzo, A.M.; Squire, J.A.; Lotan, T.L. Clinical implications of PTEN loss in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, R.U.; Haverkamp, J.M.; Thedens, D.R.; Cohen, M.B.; Ratliff, T.L.; Henry, M.D. Slow disease progression in a C57BL/6 pten-deficient mouse model of prostate cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.S.; Schultz, N.; Hieronymus, H.; Gopalan, A.; Xiao, Y.; Carver, B.S.; Arora, V.K.; Kaushik, P.; Cerami, E.; Reva, B.; et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, K.; Czerwińska, P.; Wiznerowicz, M. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 19, A68–A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, M.J.; Vowler, S.L.; Lalonde, E.; Ross-Adams, H.; Boutros, P.; Mills, I.G.; Lynch, A.G.; Lamb, A.D. Mining Human Prostate Cancer Datasets: The “camcAPP” Shiny App. eBioMedicine 2017, 17, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross-Adams, H.; Lamb, A.D.; Dunning, M.J.; Halim, S.; Lindberg, J.; Massie, C.M.; Egevad, L.A.; Russell, R.; Ramos-Montoya, A.; Vowler, S.L.; et al. Integration of copy number and transcriptomics provides risk stratification in prostate cancer: A discovery and validation cohort study. eBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre-Gamboa, R.; Gomez-Rueda, H.; Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Martinez-Torteya, A.; Chacolla-Huaringa, R.; Rodriguez-Barrientos, A.; Tamez-Pena, J.G.; Trevino, V. SurvExpress: An online biomarker validation tool and database for cancer gene expression data using survival analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barquilha, C.N.; Santos, N.J.; Monção, C.C.D.; Barbosa, I.C.; Lima, F.O.; Justulin, L.A.; Pértega-Gomes, N.; Felisbino, S.L. Sulfiredoxin as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Advanced and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2148562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.F.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, P.S.; Patankar, M.S.; Zheng, J. Expression and roles of Slit/Robo in human ovarian cancer. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 135, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qin, F.; Fu, L. Function of Slit/Robo signaling in breast cancer. Front. Med. 2015, 9, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozhan, A.; Tombaz, M.; Konu, O. Discovery of Cancer-Specific and Independent Prognostic Gene Subsets of the Slit-Robo Family Using TCGA-PANCAN Datasets. OMICS 2021, 25, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latil, A.; Chêne, L.; Cochant-Priollet, B.; Mangin, P.; Fournier, G.; Berthon, P.; Cussenot, O. Quantification of expression of netrins, slits and their receptors in human prostate tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 103, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacar, S.; Bektur Aykanat, N.E.; Sahinturk, V. Silymarin inhibited DU145 cells by activating SLIT2 protein and suppressing expression of CXCR4. Med. Oncol. 2020, 37, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Qin, T.; Chen, X.; Wu, E.; Ma, Q.; Wang, Z. Targeting the SLIT/ROBO pathway in tumor progression: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919855238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, P.; Real, F.X. Mouse Models Shed Light on the SLIT/ROBO Pathway in Pancreatic Development and Cancer. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, A.V.; Van Bulck, M.; Chantrill, L.; Arshi, M.; Sklyarova, T.; Herrmann, D.; Vennin, C.; Gallego-Ortega, D.; Mawson, A.; Giry-Laterriere, M.; et al. ROBO2 is a stroma suppressor gene in the pancreas and acts via TGF-β signalling. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.H.; Hwang-Verslues, W.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, C.C.; Hsiao, M.; Jeng, Y.M.; Chang, K.J.; Lee, E.Y.; Shew, J.Y.; Lee, W.H. Activation of Robo1 signaling of breast cancer cells by Slit2 from stromal fibroblast restrains tumorigenesis via blocking PI3K/Akt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4652–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, R.C.; Lee, S.H.; Hsu, H.S.; Chen, B.H.; Tsai, W.C.; Tzao, C.; Wang, Y.C. SLIT2 attenuation during lung cancer progression deregulates beta-catenin and E-cadherin and associates with poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahirwar, D.K.; Charan, M.; Mishra, S.; Verma, A.K.; Shilo, K.; Ramaswamy, B.; Ganju, R.K. Slit2 Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis by Activating M1-Like Phagocytic and Antifibrotic Macrophages. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5255–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhou, D.L.; Lei, Y.; Zheng, L.; Chen, S.X.; Gou, H.J.; Gu, Q.L.; He, X.D.; Lan, T.; Qi, C.L.; et al. Slit2/Robo1 signaling promotes intestinal tumorigenesis through Src-mediated activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3123–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.H.; Baek, S.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.S. Specific expression and methylation of SLIT1, SLIT2, SLIT3, and miR-218 in gastric cancer subtypes. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, B.B.; Kim, D.; Um, S.W.; Han, J.; Shim, Y.M.; Kim, D.H. Aberrant Methylation of SLIT2 Gene in Plasma Cell-Free DNA of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.J.; Ximenes, P.P.; Constantino, F.B.; Carvalho, H.F.; Felisbino, S.L. Mucinous metaplasia in Pten conditional knockout mice and mucin family genes as prognostic markers for prostate cancer. Life Sci. 2022, 293, 120264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Corney, D.C.; Wang, W.; Goodrich, D.W.; Roy-Burman, P.; Nikitin, A.Y. Synergy of p53 and Rb deficiency in a conditional mouse model for metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7889–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A.; Committee, G. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, N.J.; Mosele, F.C.; Barquilha, C.N.; Barbosa, I.C.; Lima, F.d.O.; Barbosa, G.O.; Carvalho, H.F.; Delella, F.K.; Felisbino, S.L. SLIT/ROBO Pathway and Prostate Cancer: Gene and Protein Expression and Their Prognostic Values. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115265
Santos NJ, Mosele FC, Barquilha CN, Barbosa IC, Lima FdO, Barbosa GO, Carvalho HF, Delella FK, Felisbino SL. SLIT/ROBO Pathway and Prostate Cancer: Gene and Protein Expression and Their Prognostic Values. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115265
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Nilton J., Francielle C. Mosele, Caroline N. Barquilha, Isabela C. Barbosa, Flávio de Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Oliveira Barbosa, Hernandes F. Carvalho, Flávia Karina Delella, and Sérgio Luis Felisbino. 2025. "SLIT/ROBO Pathway and Prostate Cancer: Gene and Protein Expression and Their Prognostic Values" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115265
APA StyleSantos, N. J., Mosele, F. C., Barquilha, C. N., Barbosa, I. C., Lima, F. d. O., Barbosa, G. O., Carvalho, H. F., Delella, F. K., & Felisbino, S. L. (2025). SLIT/ROBO Pathway and Prostate Cancer: Gene and Protein Expression and Their Prognostic Values. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5265. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115265








