Simple Sequence Repeat-Based Genetic Diversity Analysis of Alfalfa Varieties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. SSR Primer Screening
2.2. Genetic Diversity Analysis
2.3. Genetic Diversities of the Population
2.4. Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA)
2.5. Analysis of Genetic Distance and Genetic Identity
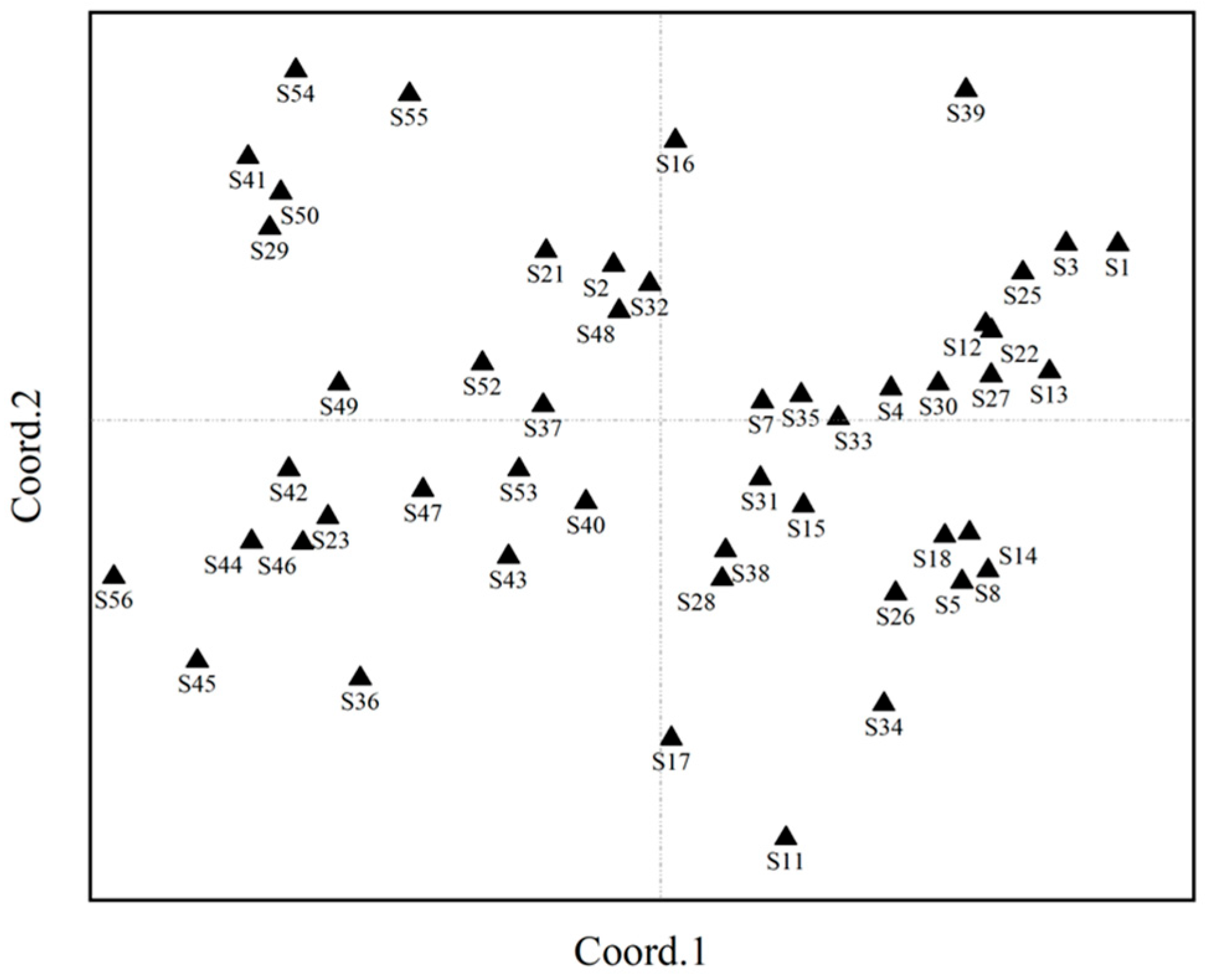
2.6. Principal Coordinate Analysis
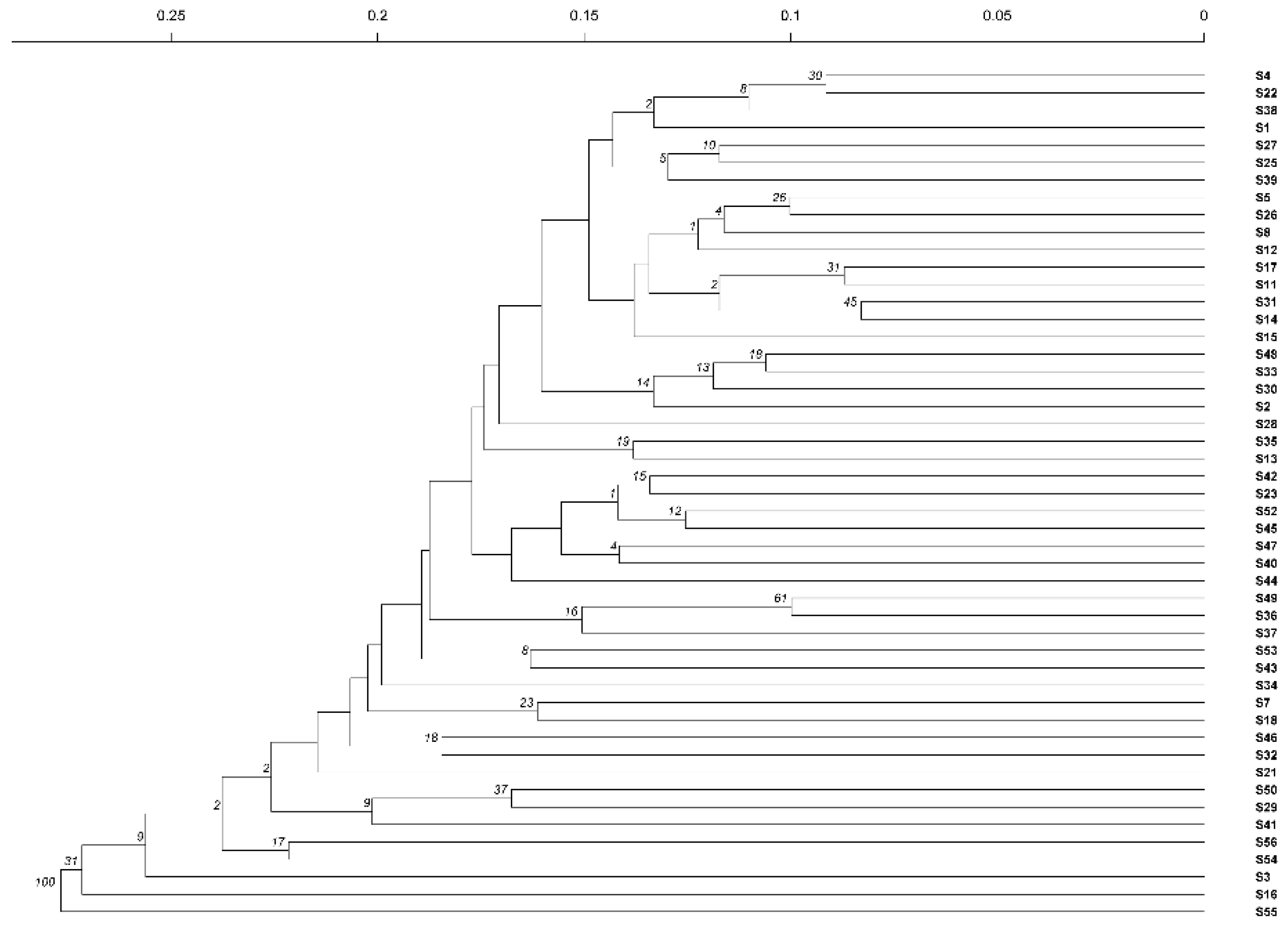
2.7. Cluster Analysis
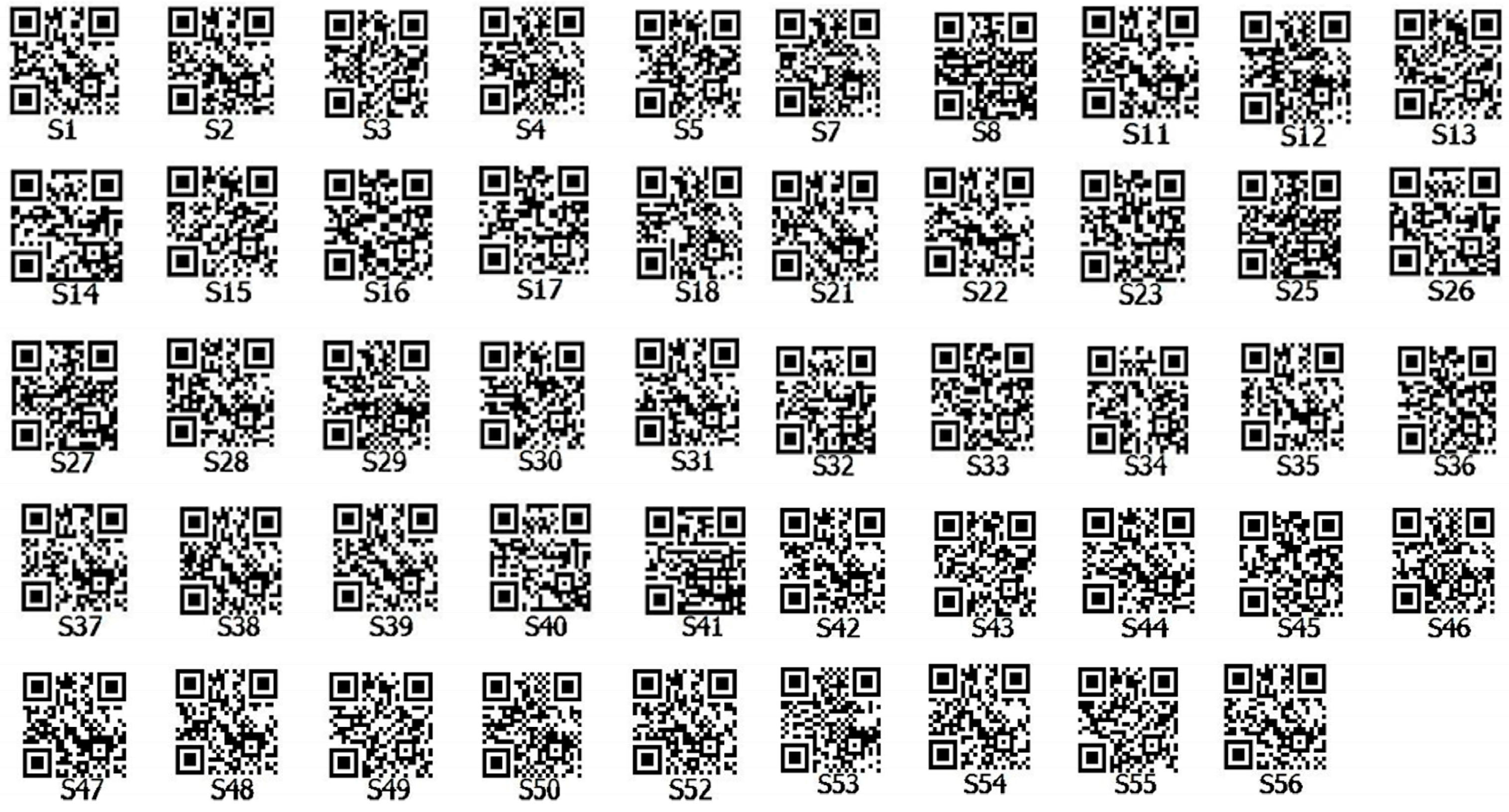
2.8. Construction of DNA Fingerprint Map
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
4.2. Genomic DNA Extraction
4.3. Source and Synthesis of Primers
4.4. The PCR Reaction Procedure and System
4.5. Primer Screening
4.6. Fluorescence Capillary Electrophoresis Detection
4.7. Construction of DNA Fingerprinting
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, J.; Huangfu, W.; Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y.; Cui, Y. “King of the forage”—Alfalfa supplementation improves growth, reproductive performance, health condition and meat quality of pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1025942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, M.; Shen, H.; Xu, L.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xing, A.; Kang, J.; Jing, H.; et al. Yield and quality properties of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and their influencing factors in China. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 141, 126637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.S.; Wang, Y.P.; Yang, F.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Screening a Lactobacillus plantarum strain for good adaption in alfalfa ensiling and demonstrating its improvement of alfalfa silage quality. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Temple, S.; Dixon, R.A. Development and commercialization of reduced lignin alfalfa. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 56, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwignyo, B.; Aristia Rini, E.; Helmiyati, S. The profile of tropical alfalfa in Indonesia: A review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 30, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumacher-Strabel, M.; Stochmal, A.; Cieslak, A.; Kozłowska, M.; Kuznicki, D.; Kowalczyk, M.; Oleszek, W. Structural and quantitative changes of saponins in fresh alfalfa compared to alfalfa silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 99, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, B.; Cao, X.; Wu, J.; Yan, H.; Tian, D. Optimization of Subsurface Drip Irrigation Schedule of Alfalfa in Northwest China. Water 2023, 15, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asseng, S.; Hsiao, T.C. Canopy CO2 assimilation, energy balance, and water use efficiency of an alfalfa crop before and after cutting. Field Crops Res. 2000, 67, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tang, L.; Cui, Y.; Yang, D.; Gao, H.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Z.; Guo, C. Inoculation of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and rhizobia changes the protist community of alfalfa rhizosphere soil under saline-alkali environment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 206, 105775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xie, J.; Luo, Z.; Niu, Y.; Coulter, J.A.; Zhang, R.; Lingling, L. Forage yield, water use efficiency, and soil fertility response to alfalfa growing age in the semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Jin, N.; Chu, H.; Jing, L. Deep soil water deficit and recovery in alfalfa fields of the Loess Plateau of China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 260, 107990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhong, J. Creating modern technological system for grass product processing to guarantee macroscopic food security. Curr. Situat. Prospect. Forage Breed. China 2021, 36, 675–684. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Wang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jing, H.; Chong, K. Current situation and prospect of forage breeding in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 660–665. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; An, F.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z. The impact of irrigation on yield of alfalfa and soil chemical properties of saline-sodic soils. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, T.; Bao, A.-K.; Bao, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, L.; Wang, S.-M. The progress of genetic improvement in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2018, 54, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-B.; Xie, Y.-H.; Sun, X.-M. Development and Characterization of Polymorphic Genic-SSR Markers in Larix kaempferi. Molecules 2015, 20, 6060–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaszmann, J.C.; Kilian, B.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Varshney, R.K. Accessing genetic diversity for crop improvement. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said Halima, M.; Krishnamani, K.; Omar Shaheed, V.; Dreyer Andries, W.; Sansom, B.; Fallows, D.; Ismail Nazir, A. Evaluation of Semiautomated IS6110-Based Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Typing for Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a High-Burden Setting. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2547–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.G.K.; Kubelik, A.R.; Livak, K.J.; Rafalski, J.A.; Tingey, S.V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6531–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietkiewicz, E.; Rafalski, A.; Labuda, D. Genome Fingerprinting by Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR)-Anchored Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification. Genomics 1994, 20, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachidanandam, R.; Weissman, D.; Schmidt, S.C.; Kakol, J.M.; Stein, L.D.; Marth, G.; Sherry, S.; Mullikin, J.C.; Mortimore, B.J.; Willey, D.L.; et al. A map of human genome sequence variation containing 1.42 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nature 2001, 409, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vos, P.; Hogers, R.; Bleeker, M.; Reijans, M.; Lee, T.v.d.; Hornes, M.; Friters, A.; Pot, J.; Paleman, J.; Kuiper, M.; et al. AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 4407–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tautz, D.; Renz, M. Simple sequences are ubiquitous repetitive components of eukaryotic genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 4127–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.I.; Martins, A.M.; Gouvea, E.G.; Pessoa-Filho, M.; Ferreira, M.E. Development and validation of microsatellite markers for Brachiaria ruziziensis obtained by partial genome assembly of Illumina single-end reads. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Korol, A.B.; Fahima, T.; Beiles, A.; Nevo, E. Microsatellites: Genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: A review. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2453–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şakiroğlu, M.; Doyle, J.J.; Charles Brummer, E. Inferring population structure and genetic diversity of broad range of wild diploid alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) accessions using SSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 121, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, C.R.; Abd El-Naby, Z.M.; Abd El-Rahman, S.S.; Omar, S.A.; Ali, E.F.; Majrashi, A.; Rady, M.M. Association of saponin concentration, molecular markers, and biochemical factors with enhancing resistance to alfalfa seedling damping-off. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 2148–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W. Genome-Wide Development of MicroRNA-Based SSR Markers in Medicago truncatula with Their Transferability Analysis and Utilization in Related Legume Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, S.; Kunihisa, M.; Taniguchi, F.; Kajiya-Kanegae, H.; Moriya, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Sawamura, Y. Development of SSR Databases Available for Both NGS and Capillary Electrophoresis in Apple, Pear and Tea. Plants 2021, 10, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Kang, M.-J. Application of Capillary Electrophoresis with Laser-Induced Fluorescence to Immunoassays and Enzyme Assays. Molecules 2019, 24, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Ma, L.; Qin, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, G.; Fu, H. Phylogenetic relationships among five species of Armeniaca Scop. (Rosaceae) using microsatellites (SSRs) and capillary electrophoresis. J. For. Res. 2016, 27, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D. Molecular identification of mung bean accessions (Vigna radiata L.) from Northeast China using capillary electrophoresis with fluorescence-labeled SSR markers. Food Energy Secur. 2019, 9, e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Zheng, R.; Qiu, L.; Zhou, S.; Chao, H.; Li, Y.; Rui, W.; Cui, P.; Ni, X.; Tan, S.; et al. Fluorescence coupled capillary electrophoresis as a strategy for tetrahedron DNA analysis. Talanta 2021, 228, 122225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Xia, Z.L.; Campbell, T.A.; Bauchan, G.R. Development and Characterization of SSR Markers and Their Use to Assess Genetic Relationships among Alfalfa Germplasms. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 2176–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touil, L.; Guesmi, F.; Fares, K.; Zagrouba, C.; Ferchichi, A. Genetic Diversity of Some Mediterranean Populations of the Cultivated Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Using SSR Markers. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 1923–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, S.; Raina, S.N.; Bhat, V.; Aggarwal, R.K.; Goel, S. Development of a set of genomic microsatellite markers in tea (Camellia L.) (Camelliaceae). Mol. Breed. 2013, 32, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, S.S.; Pradhan, K.; Shukla, R.P.; Saraswat, R.; Srivastava, A.; Jena, S.N.; Das, A.B. In silico mining of EST-SSRs in Arachis hypogaea L. and their utilization for genetic structure and diversity analysis in cultivars/breeding lines in Odisha, India. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Q.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis in a large collection of Vicia amoena in China with newly developed SSR markers. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelj, D.; Jakše, J.; Javornik, B. Assessment of genetic variability of olive varieties by microsatellite and AFLP markers. Euphytica 2004, 136, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Xu, H.; Sun, L.; Lu, C.; Wu, R. Genetic diversity analysis of volunteer wheat based on SSR markers. J. Genet. 2023, 102, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thovhogi, F.; Gwata, E.T.; McHau, G.R.A.; Safodien, S.S.; Koopman, T. Molecular Characterization of Spider Plant (Cleome gynandra) Accessions Using SSR Markers. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Fu, J.; Xie, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. SSR markers development and their application in genetic diversity of burdock (Arctium lappa L.) germplasm. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, H.; Fu, X.; Li, X.; Gao, H. Development of simple sequence repeat markers and diversity analysis in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 40, 3291–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z. The development of 204 novel EST-SSRs and their use for genetic diversity analyses in cultivated alfalfa. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 57, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Du, H.; Chen, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhu, F.; Chen, H.; Meng, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, P.; Zheng, L.; et al. The Chromosome-Level Genome Sequence of the Autotetraploid Alfalfa and Resequencing of Core Germplasms Provide Genomic Resources for Alfalfa Research. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; He, F.; Long, R.; Zhang, F.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Kang, J.; Yang, Q. A global alfalfa diversity panel reveals genomic selection signatures in Chinese varieties and genomic associations with root development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1937–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Primer Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| aw01 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTACCTGTTCTAAGGGAGATTTCG | CAGGGGAAGCATACAAAACC |
| AW11 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTATTCGCAGTGAGCTGATCCT | GACATTTGCAGACCACCATT |
| AW166 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTAACGTAACGACAGCAACATCA | CAGATTGCATTTTGGGTTCC |
| aw690665 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTGGTTTTGGAGACATGACGGT | GTGAAGACTTTGCGGTGGAT |
| B14B03 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTGCTTGTTCTTCTTCAAGCTCAC | ACCTGACTTGTGTTTTATGC |
| BI10 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTAAAACGGTACCCGTATCAACA | TCTGGAAGATGAGACCGTGA |
| MTB60 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTAAGAATGACGAAGAGGCGAA | TCAGAAATTCCCTCCCATTG |
| MTIC432 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTTGGAATTTGGGATATAGGAAG | GCCATAAGAACTTCCACTT |
| Act012 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTGTTTGTGCAGCCCTTTGATT | ATGCAAACCAAGATTAAGGC |
| AL73 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTGAATAATGCTGGTGGAAGCAA | GTTGAGTTACCCCACATGACAA |
| AW123 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTAGTCCCTGCAAAATCCCTTC | CATGTTTCCGGTTCTGGTTT |
| AW282 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTCGACCAAATCACTCTTCTTCAA | AATCCAAGACCATTCACCTGAG |
| AW300 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTCCACGTTGTGTCATTGTCTACTC | GTCGAAGAAAGAGGTGGTTGTT |
| aw695900 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTGCAACCATCTAAACCCAACAA | AGGCTAATCGACGGGAAAAT |
| BE112 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTTTCATTTCATAGTTTTCCATTGC | AGCGAGATAGATTTCACCGAAG |
| BE92 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTAGTTCAAACCCTTACCCTTCA | GATGAGGATGATGATGAATTGG |
| BF123 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTAGAACCTCGTCATCAGGAACAT | GACAGAGACGGAGAAGGAAGAA |
| m206 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTCCCCATTGACGCATTCTTAC | TCCTCAACCAACCACTTCCT |
| m230 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTTTACCATATTAACCCCCGCA | CGCATATCACCTCCCAGAAT |
| Ms-27 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTGTAGTGAAGGACCAAGAAATGA | CAAGAAATTGTAATCTCCATTG |
| Ms-64 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTCGCTTTCGCTGTCGAACT | GGATTCAGCAACCGGAAA |
| MT1E04 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTTCTAGGTATTCGCTGGCGTT | TGTTTCTGATCAGGGCATTG |
| MTIC249 | GAAGGTGACCAAGTTCATGCTTAGGTCATGGCTATTGCTTC | GTGGGTGAGGATGTGTGTAT |
| Name | Number of Alleles | Number of Polymorphic Alleles | Percentage of Polymorphic Loci (%) | Polymorphic Information Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Act012 | 4 | 4 | 100.00 | 0.683 |
| AL73 | 5 | 4 | 80.00 | 0.705 |
| aw01 | 7 | 7 | 100.00 | 0.748 |
| AW11 | 6 | 6 | 100.00 | 0.784 |
| AW123 | 4 | 4 | 100.00 | 0.708 |
| AW166 | 6 | 6 | 100.00 | 0.698 |
| AW282 | 3 | 2 | 66.67 | 0.633 |
| AW300 | 7 | 6 | 85.71 | 0.701 |
| aw690665 | 5 | 4 | 80.00 | 0.751 |
| aw695900 | 5 | 5 | 100.00 | 0.347 |
| B14B03 | 10 | 10 | 100.00 | 0.681 |
| BE112 | 16 | 16 | 100.00 | 0.804 |
| BE92 | 6 | 6 | 100.00 | 0.646 |
| BF123 | 3 | 3 | 100.00 | 0.473 |
| BI10 | 10 | 10 | 100.00 | 0.674 |
| m206 | 6 | 6 | 100.00 | 0.561 |
| m230 | 5 | 5 | 100.00 | 0.694 |
| Ms-27 | 4 | 4 | 100.00 | 0.689 |
| Ms-64 | 4 | 3 | 75.00 | 0.558 |
| MT1E04 | 3 | 3 | 100.00 | 0.649 |
| MTB60 | 7 | 6 | 85.71 | 0.637 |
| MTIC249 | 3 | 2 | 66.67 | 0.648 |
| MTIC432 | 7 | 7 | 100.00 | 0.704 |
| Total | 136 | 129 | 94.85 | 15.174 |
| Average | 5.91 | 5.61 | 0.66 |
| Pop | Na | Ne | I | H | UH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pop1 | 1.191 ± 0.078 | 1.289 ± 0.029 | 0.267 ± 0.023 | 0.176 ± 0.016 | 0.201 ± 0.018 |
| pop2 | 1.581 ± 0.066 | 1.311 ± 0.029 | 0.303 ± 0.021 | 0.192 ± 0.015 | 0.2 ± 0.016 |
| pop3 | 1.265 ± 0.078 | 1.32 ± 0.03 | 0.292 ± 0.024 | 0.192 ± 0.016 | 0.209 ± 0.018 |
| pop4 | 0.941 ± 0.077 | 1.25 ± 0.029 | 0.216 ± 0.025 | 0.147 ± 0.017 | 0.196 ± 0.022 |
| Total | 1.244 ± 0.039 | 1.292 ± 0.015 | 0.27 ± 0.012 | 0.177 ± 0.008 | 0.201 ± 0.009 |
| Average | 1.2445 | 1.2925 | 0.2695 | 0.1768 | 0.202 |
| Source | df | SS | MS | Est. Var. | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among Pops | 3 | 51.340 | 17.113 | 0.320 | 2% |
| Within Pops | 45 | 618.007 | 13.733 | 13.733 | 98% |
| Total | 48 | 669.347 | 14.054 | 100% |
| ID | pop1 | pop2 | pop3 | pop4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pop1 | 0.978 | 0.956 | 0.952 | |
| pop2 | 0.023 | 0.980 | 0.960 | |
| pop3 | 0.045 | 0.020 | 0.949 | |
| pop4 | 0.049 | 0.041 | 0.052 |
| Sample | Variety | Origin | Hibernation Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | WL354HQ | America | 4 |
| S2 | Hetian | China | 4 |
| S3 | Qianjing | America | - |
| S4 | Jinneng5020 | Canada | 5 |
| S5 | Yongshi | America | - |
| S7 | Longmu803 | China | 1 |
| S8 | Zhongmu No1 | China | 2 |
| S11 | MF4020 | Canada | 4 |
| S12 | Qiji | America | 3 |
| S13 | Jiguang | Australia | 3 |
| S14 | Weisheng | America | 4.6 |
| S15 | Baimu202 | America | 2 |
| S16 | Jianeng | America | 4 |
| S17 | MT4015 | Canada | 4 |
| S18 | Xunlu | Canada | 1 |
| S21 | 701-421476 | - | |
| S22 | 42IQ | America | - |
| S23 | Handi | America | 3 |
| S25 | 310SC | America | - |
| S26 | Qingtianzhu | America | 4 |
| S27 | Qishi No.2 | America | 3.4 |
| S28 | Kangsai | America | 3 |
| S29 | Longmu 801 | China | 1 |
| S30 | Juneng No.2 | America | 3.2 |
| S31 | 4030 | Canada | 4 |
| S32 | Yinhe | America | 4.2 |
| S33 | 6010 | China | 6 |
| S34 | 420YQ | America | - |
| S35 | Panshi | America | - |
| S36 | SF8001 | Canada | - |
| S37 | Daye No.3 | China | - |
| S38 | Kangkuan | - | - |
| S39 | Beijixiong | America | 2 |
| S40 | Baimu201 | America | 2 |
| S41 | Bolatu | Germany | - |
| S42 | Ningxia xibei | China | - |
| S43 | 218TR | America | 2 |
| S44 | Jinhuanghou | America | 2 |
| S45 | Yinsite | America | 4 |
| S46 | Kangsai I | America | 3 |
| S47 | Xubao | Canada | - |
| S48 | Tiaozhanzhe | America | 2.5 |
| S49 | Gongnong No.1 | China | 1 |
| S50 | Baimu 341 | Canada | 3.4 |
| S52 | WL168HQ | America | 2 |
| S53 | Dinamo | - | - |
| S54 | YS401 | - | - |
| S55 | YS40 | - | - |
| S56 | YS402 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Guo, C.; Xu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Pu, X.; Wang, W. Simple Sequence Repeat-Based Genetic Diversity Analysis of Alfalfa Varieties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115246
Wang J, Wei X, Guo C, Xu C, Zhao Y, Pu X, Wang W. Simple Sequence Repeat-Based Genetic Diversity Analysis of Alfalfa Varieties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115246
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jie, Xiaoli Wei, Changying Guo, Chengti Xu, Yuanyuan Zhao, Xiaojian Pu, and Wei Wang. 2025. "Simple Sequence Repeat-Based Genetic Diversity Analysis of Alfalfa Varieties" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115246
APA StyleWang, J., Wei, X., Guo, C., Xu, C., Zhao, Y., Pu, X., & Wang, W. (2025). Simple Sequence Repeat-Based Genetic Diversity Analysis of Alfalfa Varieties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115246








