Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum
Abstract
1. Introduction
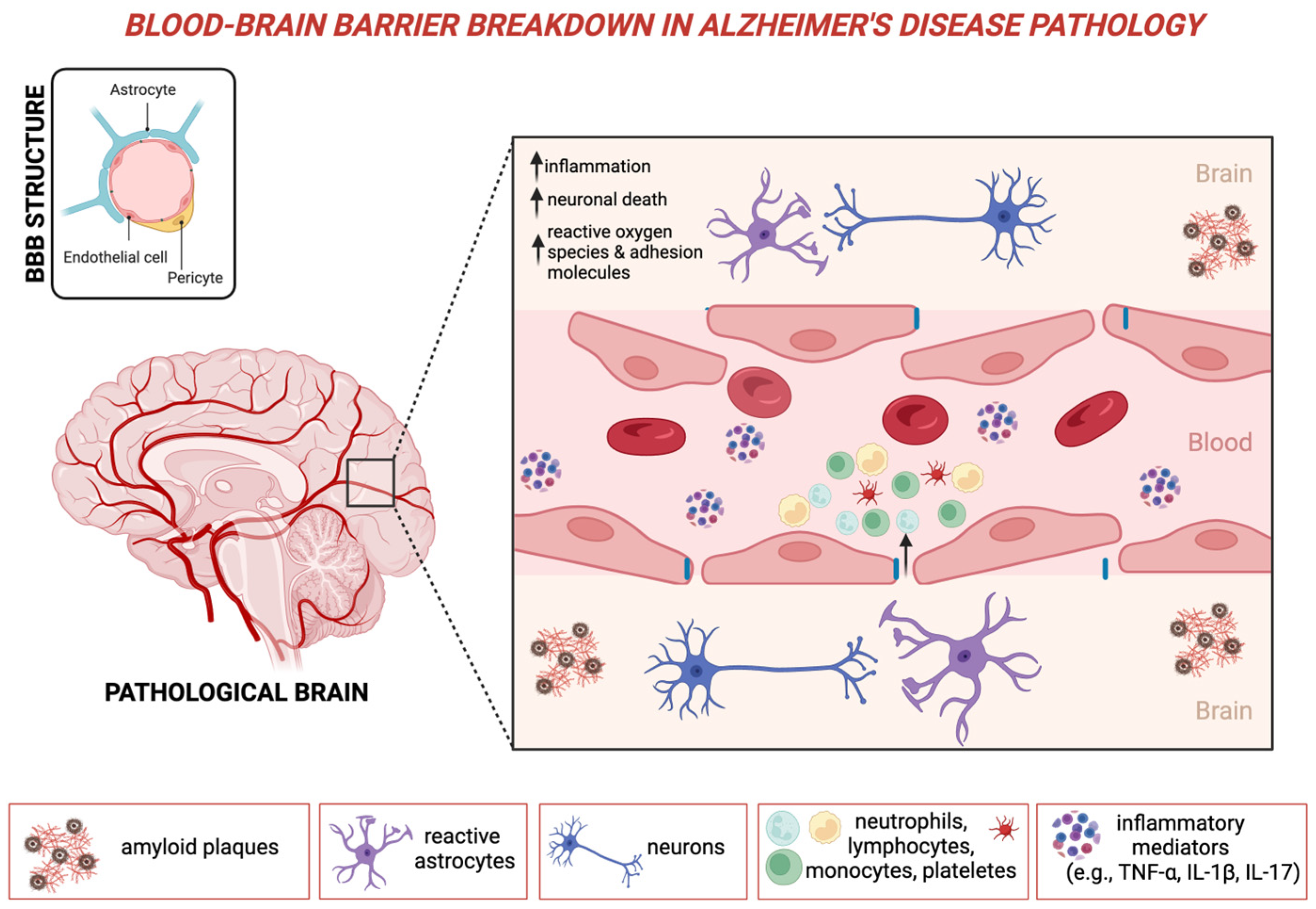
2. Peripheral Inflammation as a Primary Driver in Alzheimer’s Disease
2.1. The Role of Neutrophils in Neuroinflammatory Responses
2.2. The Role of Lymphocytes in Neuroinflammatory Responses
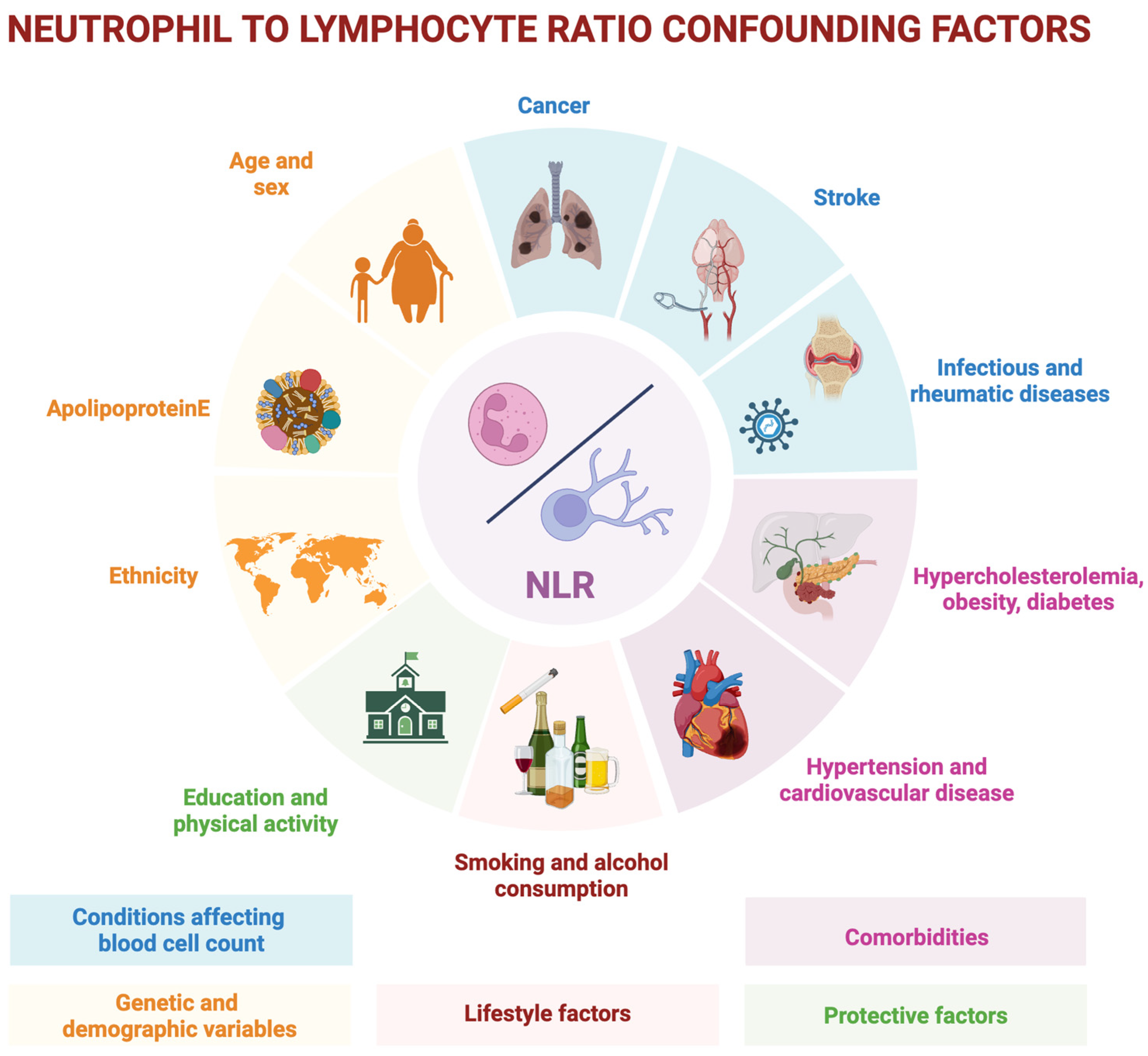
2.3. Peripheral Immune Dysregulation and the NLR
3. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in the Alzheimer’s Disease Spectrum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Dementia Forecasting Collaborators. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Cao, Z.; Nandi, A.; Counts, N.; Jiao, L.; Prettner, K.; Kuhn, M.; Seligman, B.; Tortorice, D.; Vigo, D.; et al. The global macroeconomic burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: Estimates and projections for 152 countries or territories. Lancet Glob. Health 2024, 12, e1534–e1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradfield, N.I. Mild cognitive impairment: Diagnosis and subtypes. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2023, 54, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.Y.Y.; Zhou, Z.; Kan, M.M.P.; Chan, D.H.Y.; Wong, A.C.T.; Mok, K.H.Y.; Lam, F.M.H.; Chan, S.C.C.; Cheung, C.K.C.; Yeung, M.K.C.; et al. Modifiable risk factors for mild cognitive impairment among cognitively normal community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 99, 102350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lee, G.; Zhong, K.; Fonseca, J.; Cheng, F. Alzheimer’s disease drug development pipeline: 2024. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2024, 10, e12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, J.C.; Mitew, S.; Woodhouse, A.; Fernandez-Martos, C.M.; Kirkcaldie, M.T.; Canty, A.J.; McCormack, G.H.; King, A.E. Defining the earliest pathological changes of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostagno, A.A. Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondo, G.; De Marchi, F.; Bonardi, F.; Menegon, F.; Verrini, G.; Aprile, D.; Anselmi, M.; Mazzini, L.; Comi, C. Novel therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer’s disease: Pitfalls and challenges of anti-amyloid therapies and beyond. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comi, C.; Tondo, G. Insights into the protective role of immunity in neurodegenerative disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2017, 12, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, R.; Reddy, P.H. Amyloid-beta and phosphorylated tau accumulations cause abnormalities at synapses of Alzheimer’s disease neurons. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 57, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.E.; Lee, J.S. Mechanisms and Emerging Regulators of Neuroinflammation: Exploring New Therapeutic Strategies for Neurological Disorders. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 47, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taipa, R.; das Neves, S.P.; Sousa, A.L.; Fernandes, J.; Pinto, C.; Correia, A.P.; Santos, E.; Pinto, P.S.; Carneiro, P.; Costa, P.; et al. Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the CSF of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and their correlation with cognitive decline. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 76, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, K.; Nallapu, B.; Lipton, R.; Ezzati, A. CSF levels of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines as predictors of cognitive decline across Alzheimer’s disease spectrum (N4. 004). Neurology 2024, 102, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouilly, D.; Saint-Aubert, L.; Ribeiro, M.J.; Salabert, A.S.; Tauber, C.; Péran, P.; Arlicot, N.; Pariente, J.; Payoux, P. Neuroinflammation PET imaging of the translocator protein (TSPO) in Alzheimer’s disease: An update. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 55, 1322–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossano, S.M.; Johnson, A.S.; Smith, A.; Ziaggi, G.; Roetman, A.; Guzman, D.; Okafor, A.; Klein, J.; Tomljanovic, Z.; Stern, Y.; et al. Microglia measured by TSPO PET are associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology and mediate key steps in a disease progression model. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondo, G.; Boccalini, C.; Caminiti, S.P.; Presotto, L.; Filippi, M.; Magnani, G.; Frisoni, G.B.; Iannaccone, S.; Perani, D. Brain metabolism and microglia activation in mild cognitive impairment: A combined [18F] FDG and [11C]-(R)-PK11195 PET study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2021, 80, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamelin, L.; Lagarde, J.; Dorothée, G.; Leroy, C.; Labit, M.; Comley, R.A.; de Souza, L.C.; Corne, H.; Dauphinot, L.; Bertoux, M.; et al. Early and protective microglial activation in Alzheimer’s disease: A prospective study using 18 F-DPA-714 PET imaging. Brain 2016, 139, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Brooks, D.J.; Okello, A.; Edison, P. An early and late peak in microglial activation in Alzheimer’s disease trajectory. Brain 2017, 140, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Martinez, L.; Maccioni, R.B.; Andrade, V.; Navarrete, L.P.; Pastor, M.G.; Ramos-Escobar, N. Neuroinflammation as a common feature of neurodegenerative disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Jiang, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, S. Microglia in neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanism and potential therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, J.P.; Terry, A.; de Natale, E.R.; Politis, M. Research evidence of the role of the glymphatic system and its potential pharmacological modulation in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio: An emerging marker of the relationships between the immune system and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahorec, R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts--rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2001, 102, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aries, M.L.; Hensley-McBain, T. Neutrophils as a potential therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1123149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.H.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; McIntire, L.B.; Nordvig, A.; Butler, T.; de Leon, M.; Chiang, G.C. Peripheral immune cell imbalance is associated with cortical beta-amyloid deposition and longitudinal cognitive decline. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.W.; Liu, G.Y. Expanding roles of neutrophils in aging hosts. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 29, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigerblad, G.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophil extracellular traps in systemic autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Tatsumi, L.; Tomita, T. Mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 912995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, S.J.; Bachstetter, A.D.; Nelson, P.T.; Schmitt, F.A.; Van Eldik, L.J. Using mice to model Alzheimer’s dementia: An overview of the clinical disease and the preclinical behavioral changes in 10 mouse models. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Hernández, J.C.; Bracko, O.; Kersbergen, C.J.; Muse, V.; Haft-Javaherian, M.; Berg, M.; Park, L.; Vinarcsik, L.K.; Ivasyk, I.; Rivera, D.A.; et al. Neutrophil adhesion in brain capillaries reduces cortical blood flow and impairs memory function in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.H.; Cha, M.Y.; Hyun, Y.M.; Cho, H.; Hamza, B.; Kim, D.K.; Han, S.H.; Choi, H.; Kim, K.H.; Moon, M.; et al. Migration of neutrophils targeting amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Liu, K.; Hua, T.; Zhang, C.; Sun, B.; Guan, Y. PET imaging of neutrophils infiltration in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 523798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, L.C.D.; Murray, H.C.; Hill, M.; van Leeuwen, E.; Highet, B.; Magon, N.J.; Osanlouy, M.; Mathiesen, S.N.; Mockett, B.; Singh-Bains, M.K.; et al. Neutrophil-vascular interactions drive myeloperoxidase accumulation in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkman, R.; Ben-Zur, T.; Kahana, A.; Garty, B.Z.; Offen, D. Myeloperoxidase deficiency inhibits cognitive decline in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Yang, Y.T.; Guo, Q.; ZIB Consortium; Zhao, X. M. Cellular transcriptional alterations of peripheral blood in Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varathan, P.; Gorijala, P.; Jacobson, T.; Chasioti, D.; Nho, K.; Risacher, S.L.; Saykin, A.J.; Yan, J. Integrative analysis of eQTL and GWAS summary statistics reveals transcriptomic alteration in Alzheimer brains. BMC Med. Genom. 2022, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenaro, E.; Pietronigro, E.; Della Bianca, V.; Piacentino, G.; Marongiu, L.; Budui, S.; Turano, E.; Rossi, B.; Angiari, S.; Dusi, S.; et al. Neutrophils promote Alzheimer’s disease–like pathology and cognitive decline via LFA-1 integrin. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, G.L.; Dayon, L.; Kirkland, R.; Wojcik, J.; Peyratout, G.; Severin, I.C.; Henry, H.; Oikonomidi, A.; Migliavacca, E.; Bacher, M.; et al. Blood-brain barrier breakdown, neuroinflammation, and cognitive decline in older adults. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lagarde, J.; Xicota, L.; Corne, H.; Chantran, Y.; Chaigneau, T.; Crestani, B.; Bottlaender, M.; Potier, M.C.; Aucouturier, P.; et al. Neutrophil hyperactivation correlates with Alzheimer’s disease progression. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Mikami, N.; Wing, J.B.; Tanaka, A.; Ichiyama, K.; Ohkura, N. Regulatory T cells and human disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mietelska-Porowska, A.; Wojda, U. T lymphocytes and inflammatory mediators in the interplay between brain and blood in Alzheimer’s disease: Potential pools of new biomarkers. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 4626540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Huang, Y.; Bao, T.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, X. The role of Th17 cells/IL-17A in AD, PD, ALS and the strategic therapy targeting on IL-17A. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Weiner, H.L. Unraveling the dual nature of brain CD8+ T cells in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener 2024, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, G.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chi, H.; Tian, G. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Insights from peripheral immune cells. Immun. Ageing 2024, 21, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ke, K.F.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Y.H.; Peng, Y.P. Th17 cell-mediated neuroinflammation is involved in neurodegeneration of aβ1-42-induced Alzheimer’s disease model rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigas, H.C.; Ribeiro, M.; Coelho, J.E.; Gomes, R.; Gomez-Murcia, V.; Carvalho, K.; Faivre, E.; Costa-Pereira, S.; Darrigues, J.; de Almeida, A.A.; et al. IL-17 triggers the onset of cognitive and synaptic deficits in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, C.; Volpicelli, F.; Lippiello, P.; Buono, B.; Raucci, F.; Piccolo, M.; Iqbal, A.J.; Irace, C.; Miniaci, M.C.; Perrone Capano, C.; et al. Neutralization of IL-17 rescues amyloid-β-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairment. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 3544–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, M.S.; Li, E.; Scharnagl, L.; Poupardin, R.; Altendorfer, B.; Mrowetz, H.; Hutter-Paier, B.; Weiger, T.M.; Heneka, M.T.; Attems, J.; et al. CD8+ T-cells infiltrate Alzheimer’s disease brains and regulate neuronal-and synapse-related gene expression in APP-PS1 transgenic mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansokho, C.; Ait Ahmed, D.; Aid, S.; Toly-Ndour, C.; Chaigneau, T.; Calle, V.; Cagnard, N.; Holzenberger, M.; Piaggio, E.; Aucouturier, P.; et al. Regulatory T cells delay disease progression in Alzheimer-like pathology. Brain 2016, 139, 1237–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberstein, T.J.; Taha, L.; Spitzer, P.; Hellstern, J.; Herrmann, M.; Kornhuber, J.; Maler, J.M. Imbalance of circulating Th17 and regulatory T cells in Alzheimer’s disease: A case control study. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-T.; Zhang, C.-P.; Wang, Y.-B.; Wang, J.-H. Association of peripheral blood cell profile with Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis. Front. Aging. Neurosci. 2022, 14, 888946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, M.S.; Marschallinger, J.; Kaindl, J.; Klein, B.; Johnson, M.; Khundakar, A.A.; Roßner, S.; Heneka, M.T.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Rockenstein, E.; et al. Doublecortin expression in CD8+ T-cells and microglia at sites of amyloid-β plaques: A potential role in shaping plaque pathology? Alzheimer’s Dementia 2018, 14, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldgaard, M.; Benfield, T.; Tingsgård, S. Blood neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with 90-day mortality and 60-day readmission in Gram negative bacteremia: A multi-center cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K.; Nishito, Y.; Fukuda, H.; Sadahiro, R.; Yoshida, Y.; Watanabe, S.I.; Motoi, N.; Sonobe, Y.; Mizuno, H.; Tsunoda, H.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a prognostic factor reflecting immune condition of tumor microenvironment in squamous cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 429. [Google Scholar]
- Cupp, M.A.; Cariolou, M.; Tzoulaki, I.; Aune, D.; Evangelou, E.; Berlanga-Taylor, A.J. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and cancer prognosis: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses of observational studies. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Yang, J.; Fu, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zou, L. Association between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and short-term all-cause mortality in patients with cerebrovascular disease admitted to the intensive care unit-a study based on the MIMIC-IV database. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1457364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Cai, Z.; Yu, T.; Shao, B. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a prognostic marker in acute ischemic stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridlender, Z.G.; Albelda, S.M. Tumor-associated neutrophils: Friend or foe? Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmat-Ghahdarijani, K.; Sarmadi, V.; Heidari, A.; Falahati Marvasti, A.; Neshat, S.; Raeisi, S. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a new prognostic factor in cancers: A narrative review. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1228076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMaio, A.; Mehrotra, S.; Sambamurti, K.; Husain, S. The role of the adaptive immune system and T cell dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Almasi-Dooghaee, M.; Mirmosayyeb, O. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0305322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, P.; Sancesario, G.M.; Bovenzi, R.; Zenuni, H.; Bissacco, J.; Mascioli, D.; Simonetta, C.; Forti, P.; Degoli, G.R.; Pieri, M.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lymphocyte count reflect alterations in central neurodegeneration-associated proteins and clinical severity in Parkinson Disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2023, 112, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Delgado, L.; Macías-García, D.; Jesús, S.; Martín-Rodríguez, J.F.; Labrador-Espinosa, M.Á.; Jiménez-Jaraba, M.V.; Adarmes-Gómez, A.; Carrillo, F.; Mir, P. Peripheral immune profile and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2426–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nona, R.J.; Henderson, R.D.; McCombe, P.A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio at diagnosis as a biomarker for survival of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2024, 25, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotet, C.; Alarcan, H.; Hérault, O.; Corcia, P.; Vourc’h, P.; Andres, C.R.; Blasco, H.; Veyrat-Durebex, C. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassano, M.; Manera, U.; De Marchi, F.; Cugnasco, P.; Matteoni, E.; Daviddi, M.; Solero, L.; Bombaci, A.; Palumbo, F.; Vasta, R.; et al. The role of peripheral immunity in ALS: A population-based study. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2023, 10, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, S.M.; Shin, J.Y.; Suh, Y.J.; Sung, J.J. High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts short survival duration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselbalch, I.C.; Søndergaard, H.B.; Koch-Henriksen, N.; Olsson, A.; Ullum, H.; Sellebjerg, F.; Oturai, A.B. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis J.–Exp. Transl. Clin. 2018, 4, 2055217318813183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyumcu, M.E.; Yesil, Y.; Oztürk, Z.A.; Kizilarslanoğlu, C.; Etgül, S.; Halil, M.; Ulger, Z.; Cankurtaran, M.; Arıoğul, S. The evaluation of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2012, 34, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rembach, A.; Watt, A.D.; Wilson, W.J.; Rainey-Smith, S.; Ellis, K.A.; Rowe, C.C.; Villemagne, V.L.; Macaulay, S.L.; Bush, A.I.; Martins, R.N.; et al. An increased neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio in Alzheimer’s disease is a function of age and is weakly correlated with neocortical amyloid accumulation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 273, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalelioglu, T.; Yuruyen, M.; Gultekin, G.; Yavuzer, H.; Özturk, Y.; Kurt, M.; Topcu, Y.; Doventas, A.; Emul, M. The neutrophil and platelet to lymphocyte ratios in people with subjective, mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. Psychiatry 2017, 41, S655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Nao, J.; Shi, J.; Zheng, D. Predictive value of routine peripheral blood biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evlice, A.; Sanli, Z.S.; Boz, P.B. The importance of Vitamin-D and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio for Alzheimer’s Disease. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algul, F.E.; Kaplan, Y. Increased Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index as a Novel Indicator of Alzheimer’s Disease Severity. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2024, 38, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannelli, R.; Canale, P.; Del Carratore, R.; Falleni, A.; Bernardeschi, M.; Forini, F.; Biagi, E.; Curzio, O.; Bongioanni, P. Ultrastructural and molecular investigation on peripheral leukocytes in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervellati, C.; Pedrini, D.; Pirro, P.; Guindani, P.; Renzini, C.; Brombo, G.; Zuliani, G. Neutrophil–Lymphocytes Ratio as Potential Early Marker for Alzheimer’s Disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2024, 2024, 6640130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, S.; Heck, J.; Groh, A.; Frieling, H.; Bleich, S.; Kahl, K.G.; Bosch, J.J.; Krichevsky, B.; Schulze-Westhoff, M. White blood cell and platelet counts are not suitable as biomarkers in the differential diagnostics of dementia. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, S.P.; Altunan, B.; Unal, A. Investigation of the peripheral inflammation (neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio) in two neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duara, R.; Barker, W. Heterogeneity in Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis and progression rates: Implications for therapeutic trials. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegon, F.; De Marchi, F.; Aprile, D.; Zanelli, I.; Decaroli, G.; Comi, C.; Tondo, G. From mild cognitive impairment to dementia: The impact of comorbid conditions on disease conversion. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Liang, S.K.; Chuang, T.Y.; Chu, C.Y.; Tu, C.H.; Yeh, Y.J.; Wei, Y.F.; Chen, K.Y. The impact of comorbidities, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and drug toxicities on quality of life in lung cancer patients receiving EGFR-TKI therapy. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2024, 123, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.C.; Liu, C.C.; Wu, J.Y.; Ho, C.N.; Lin, M.C.; Hsing, C.H.; Chen, I.W. Association between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1265637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tondo, G.; Aprile, D.; De Marchi, F.; Sarasso, B.; Serra, P.; Borasio, G.; Rojo, E.; Arenillas, J.F.; Comi, C. Investigating the prognostic role of peripheral inflammatory markers in mild cognitive impairment. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, S.F.; Wang, H.F.; Li, Y.Z.; Ou, Y.N.; Huang, S.Y.; Chen, S.D.; Cheng, W.; Feng, J.F.; et al. Peripheral immunity is associated with the risk of incident dementia. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1956–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irwin, K.; Sexton, C.; Daniel, T.; Lawlor, B.; Naci, L. Healthy aging and dementia: Two roads diverging in midlife? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, P.; Zhou, X.; Du, Y.; Zhao, J.; Song, A.; Liu, H.; Ma, F.; Huang, G. Association of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio with mild cognitive impairment in elderly Chinese adults: A case-control study. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Tong, X.W.; Zhang, Y.T.; Gao, X.Y. Association between the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and mild cognitive impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2023, 35, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, O.H.I.; Zhou, J.; Li, L.; Chan, J.S.K.; Satti, D.I.; Chou, V.H.C.; Wong, W.T.; Lee, S.; Cheung, B.M.Y.; Tse, G.; et al. The association between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and variability with new-onset dementia: A population-based cohort study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 94, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Cejudo, J.; Johnson, A.D.; Beiser, A.; Seshadri, S.; Salinas, J.; Berger, J.S.; Fillmore, N.R.; Do, N.; Zheng, C.; Kovbasyuk, Z.; et al. The neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with the risk of subsequent dementia in the framingham heart study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 773984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Willik, K.D.; Fani, L.; Rizopoulos, D.; Licher, S.; Fest, J.; Schagen, S.B.; Ikram, M.K.; Ikram, M.A. Balance between innate versus adaptive immune system and the risk of dementia: A population-based cohort study. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Du, X.; Liu, P.; Yang, F.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y. Associations between neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and risk of cognitive impairment among Chinese older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2025, 25, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.H.; Ou, Y.N.; Xu, W.; Zhang, P.F.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.T.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association of peripheral immunity with cognition, neuroimaging, and Alzheimer’s pathology. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2022, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, B.; Zheng, D.; Cai, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, F.; Wang, X.; Lin, H. Mediation effect of brain volume on the relationship between peripheral inflammation and cognitive decline. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 95, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.R.; Wang, H.F.; Guo, Y.; Shen, X.N.; Li, M.M.; Song, J.H.; Tan, L.; Xie, A.M.; Yu, J.T. Exploring the links among peripheral immunity, biomarkers, cognition, and neuroimaging in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2023, 15, e12517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, T.; Jacobson, S.R.; Fortea, J.; Berger, J.S.; Vedvyas, A.; Marsh, K.; He, T.; Gutierrez-Jimenez, E.; Fillmore, N.R.; Gonzalez, M.; et al. The neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio associates with markers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology in cognitively unimpaired elderly people. Immun. Ageing 2024, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; van der Flier, W.M.; Jessen, F.; Hoozemanns, J.; Thal, D.R.; Boche, D.; Brosseron, F.; Teunissen, C.; Zetterberg, H.; Jacobs, A.H.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 25, 321–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadry, H.; Noorani, B.; Cucullo, L. A blood–brain barrier overview on structure, function, impairment, and biomarkers of integrity. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, L.; Engelhardt, B. Immune cell trafficking across the blood-brain barrier in the absence and presence of neuroinflammation. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 2, H1–H18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanashiro, A.; Hiroki, C.H.; da Fonseca, D.M.; Birbrair, A.; Ferreira, R.G.; Bassi, G.S.; Fonseca, M.D.; Kusuda, R.; Cebinelli, G.C.M.; da Silva, K.P.; et al. The role of neutrophils in neuro-immune modulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 151, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, U.C.; Bhol, N.K.; Swain, S.K.; Samal, R.R.; Nayak, P.K.; Raina, V.; Panda, S.K.; Kerry, R.G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. Oxidative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of neurological disorders: Mechanisms and implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhi, S.; Di Spirito, A.; Poggi, A.; Mortara, L. Immune Modulation in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Immunotherapy. Cells 2025, 14, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, Y.; Hou, Z.; Gomez-Isaza, L.; Luongo, M.; Troncoso, J.C.; Miller, M.I.; Mori, S.; Oishi, K. Quantification of perforant path fibers for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, e70142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, Y.; Kan, H.; Sakurai, K.; Oishi, K.; Matsukawa, N. Contributions of blood–brain barrier imaging to neurovascular unit pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1111448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, Y.; Kan, H.; Sakurai, K.; Horimoto, Y.; Hayashi, E.; Iida, A.; Okamura, N.; Oishi, K.; Matsukawa, N. APOE ɛ4 dose associates with increased brain iron and β-amyloid via blood–brain barrier dysfunction. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA research framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Andrews, S.J.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised criteria for the diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2121–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, M.V.; Forlenza, O.V.; Diniz, B.S. Plasma biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: A review of available assays, recent developments, and implications for clinical practice. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2023, 7, 355–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosyreva, A.M.; Sentyabreva, A.V.; Tsvetkov, I.S.; Makarova, O.V. Alzheimer’s disease and inflammaging. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbatecola, A.M.; Giuliani, A.; Biscetti, L.; Scisciola, L.; Battista, P.; Barbieri, M.; Sabbatinelli, J.; Olivieri, F. Circulating biomarkers of inflammaging and Alzheimer’s disease to track age-related trajectories of dementia: Can we develop a clinically relevant composite combination? Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 96, 102257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hou, M.; Ding, Z.; Liu, X.; Shao, Y.; Li, X. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 686983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.; Yu, F.; Luo, Y.; Feng, X.; Liao, D.; Wei, M.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictive biomarker for stroke severity and short-term prognosis in acute ischemic stroke with intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 705949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Weng, G.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W.; Deng, B.; Luo, Y.; Tao, X.; Deng, M.; Guo, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio, and neutrophil-to-high-density-lipoprotein ratio are correlated with the severity of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1322228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Lin, H.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, N.C.; Tsai, W.C.; Cheng, B.C.; Tsai, N.W. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio are associated with a 2-year relapse in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 58, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tondo, G.; De Marchi, F. From biomarkers to precision medicine in neurodegenerative diseases: Where are we? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestia, A.; Caroli, A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Van Berckel, B.; Barkhof, F.; Teunissen, C.E.; Wall, A.E.; Carter, S.F.; Schöll, M.; et al. Prediction of dementia in MCI patients based on core diagnostic markers for Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2013, 80, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| First Author, Year (Chronological Order) | Number of Included Participants | Main Results |
|---|---|---|
| Kuyumcu, M.E., 2012 [69] | 241 AD, 175 HC | Higher NLR in AD vs. HC |
| Rembach, A., 2014 [70] | 130 MCI, 205 AD, 759 HC | Higher NLR in AD vs. HC (if not corrected for age, sex, and APOEε4); NLR stable over disease course |
| Kalelioglu, T., 2017 [71] | 31 AD, 30 MCI, 31 SCD, 31 HC | Higher NLR in AD and MCI vs. SCD and HC |
| Dong, X., 2019 [72] | 56 AD, 57 MCI, 59 HC | Higher NLR in AD vs. HC; no differences between AD and MCI |
| An, P., 2019 [86] | 186 MCI, 153 HC | Higher NLR in MCI vs. HC |
| Ramos-Cejudo, J., 2021 [89] | 1684, of whom 51 had dementia (41 AD) | Individuals with higher NLR were at a greater risk of dementia |
| Kara, S.P., 2022 [78] | 94 AD, 61 HC (and 100 PD) | Higher NLR in PD vs. HC and AD; no difference between AD and HC |
| Zhang, Y., 2022 [84] | 361,653, of whom 4239 had dementia | Increased neutrophils, NLR, and SII were associated with higher dementia risk |
| Schröder, S., 2022 [77] | 77 with dementia (of whom 33 had AD), 20 HC | No difference between different causes of dementia and HC |
| Hou, J., 2022 [92] | 1107 AD | Elevated neutrophils and NLR were associated with lower global cognition, reduced brain metabolism by FDG-PET, and greater ventricular volume |
| Evlice, A., 2023 [73] | 132 AD, 38 HC | Higher NLR in AD vs. HC |
| Li, J.Q., 2023 [94] | 1579, of whom 440 AD | Higher neutrophils, monocytes, NLR, SII, PLR, and LMR were associated with cognitive decline |
| Tondo, G., 2023 [83] | 130 MCI | Higher NLR, PLR, and SII in MCI converters to dementia |
| Yu, Z.W., 2023 [87] | 376 MCI with diabetes, 441 only with diabetes | Elevated NLR is associated with MCI in patients with diabetes |
| Chou O, 2023 [88] | 9760 (of whom 529 developed AD, 56 other dementias) | Higher NLR was associated with risk of development (no other dementia) |
| Zhuo, 2023 [93] | 20,381 participants | SII and NLR were associated with general cognitive function and with the grey matter volume |
| Giannelli, 2023 [75] | 51 MCI, 84 AD, 45 HC | Higher NLR in MCI and AD vs. HC |
| Algul, F., 2024 [74] | 175 AD, 61 HC | Higher NLR and PLR in AD vs. HC |
| Cervellati, C., 2024 [76] | 103 AD, 212 MCI, 34 VAD, 61 HC | NLR was higher in MCI or AD compared to VAD and HC |
| Jacobs, T., 2024 [95] | 201 participants without cognitive impairment (from ADNI and NYU) | Associations between NLR and Aβ42 in the older ADNI cohort, and NLR and t-tau and p-tau in younger NYU cohort |
| Wang, 2025 [91] | 2375 participants without cognitive impairment and 838 with dementia | Elevated NLR is elevated in demented and associated with increased risk of cognitive impairment |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aprile, D.; De Marchi, F.; Menegon, F.; Comi, C.; Tondo, G. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115157
Aprile D, De Marchi F, Menegon F, Comi C, Tondo G. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115157
Chicago/Turabian StyleAprile, Davide, Fabiola De Marchi, Federico Menegon, Cristoforo Comi, and Giacomo Tondo. 2025. "Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115157
APA StyleAprile, D., De Marchi, F., Menegon, F., Comi, C., & Tondo, G. (2025). Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in the Alzheimer’s Disease Continuum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5157. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115157







