Integrative Proteome and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal the Metabolic Disturbance of the Articular Cartilage in Kashin–Beck Disease, an Endemic Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
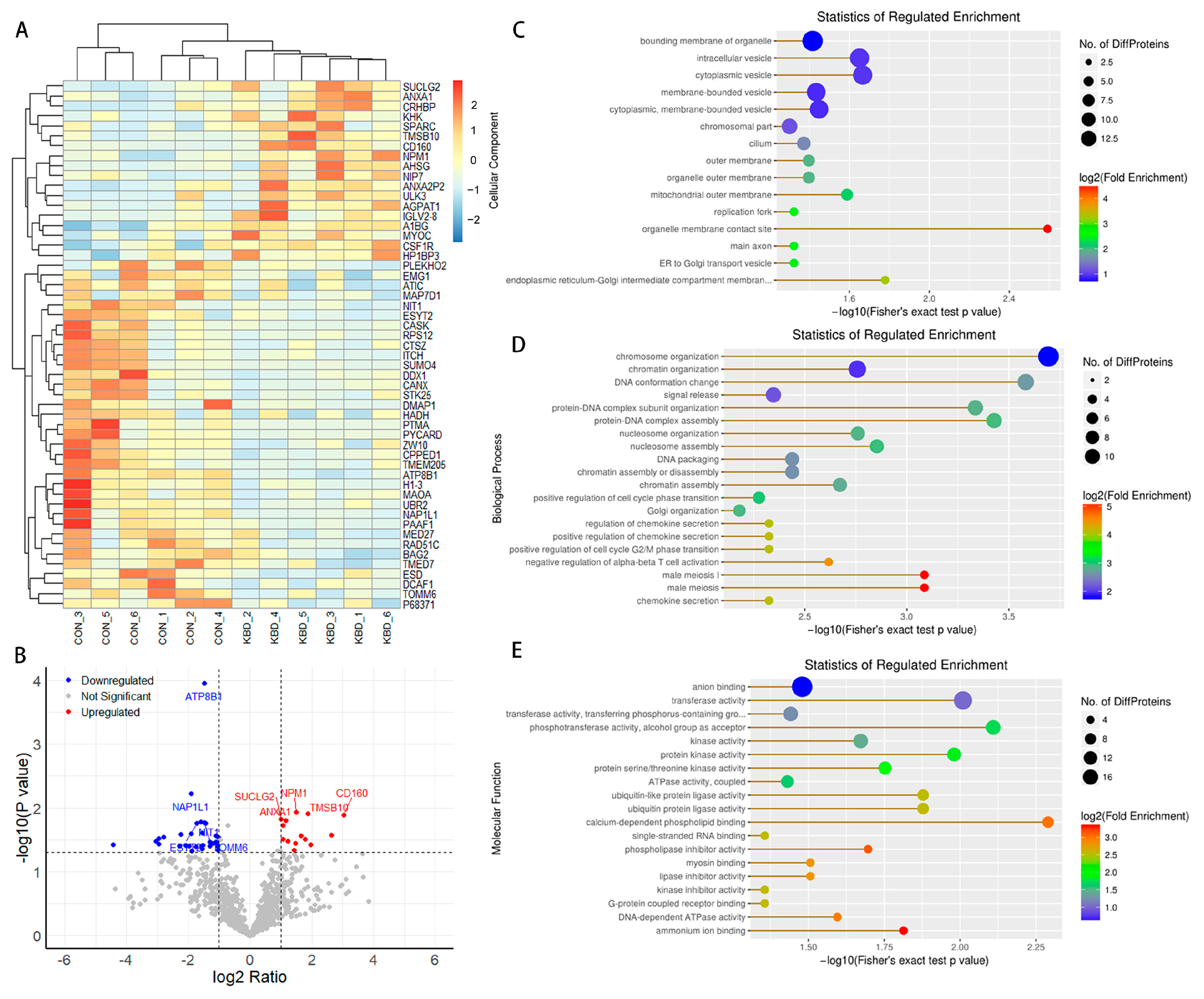
2.1. Proteomic Profiles of Cartilage from Patients with and Without KBD
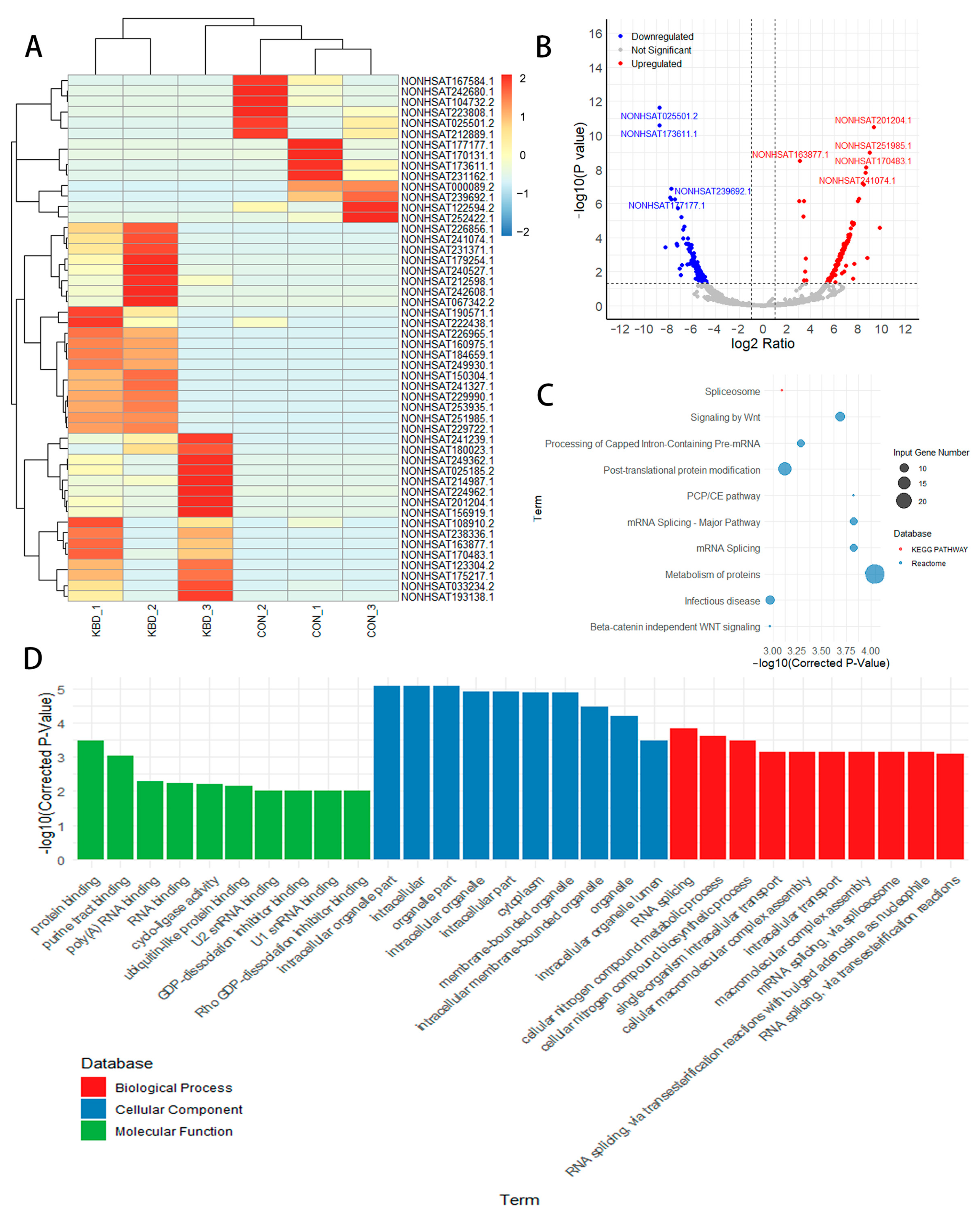
2.2. mRNA Differences in Cartilage from Patients with and Without KBD
2.3. Differential lncRNA Expression and Target Gene Prediction and Functional Analysis
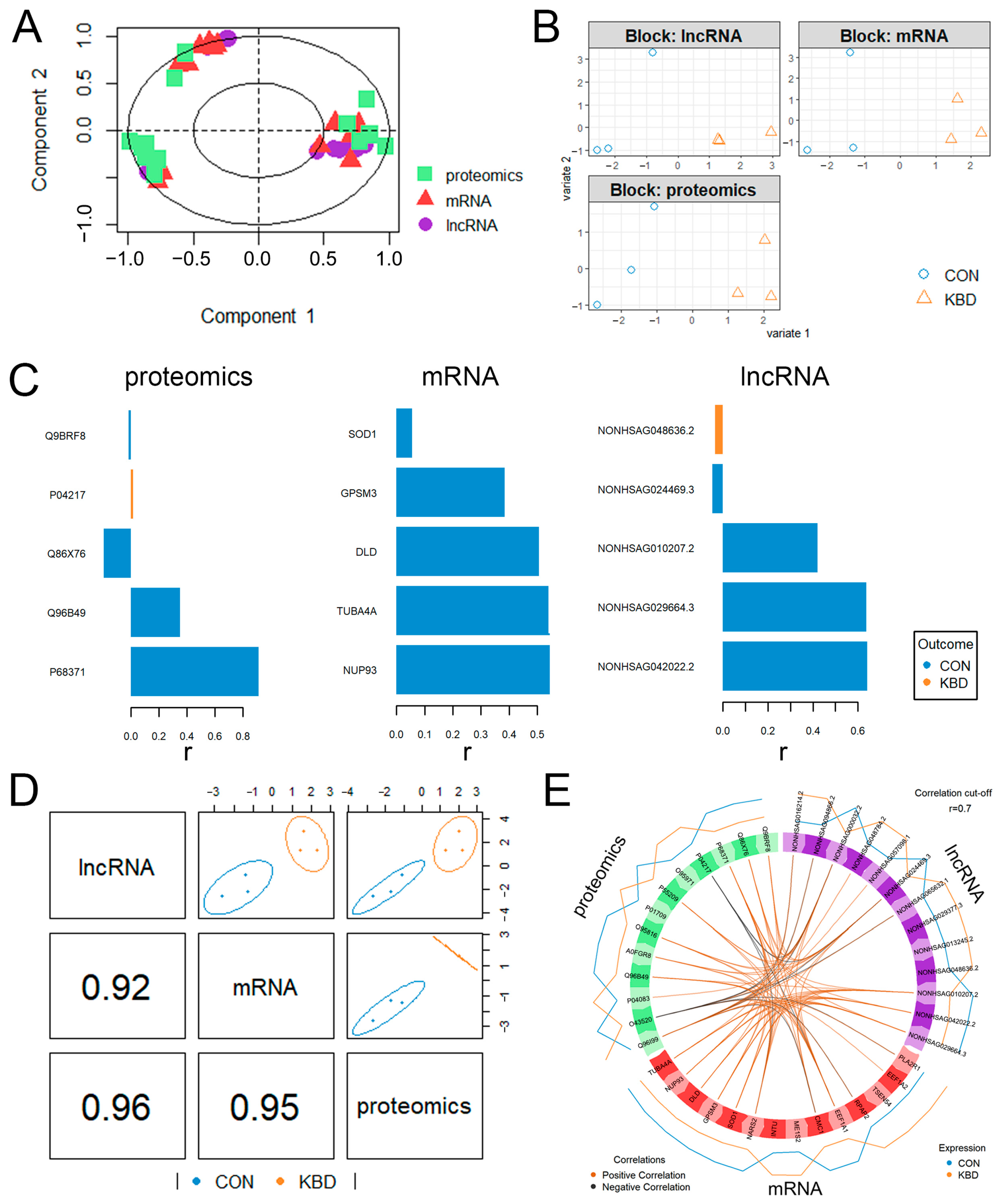
2.4. Functional Enrichment Comparison Among Multi-Omics Data
2.5. Integrative Analysis of Proteome and Transcriptome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Samples
4.3. Proteomic Analysis
4.3.1. Sample Preparation
4.3.2. LC-MS Analysis
4.3.3. DIA Proteomics Analysis
4.3.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.4. Transcriptomic Analysis
4.4.1. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and RNA-Sequencing
4.4.2. LncRNA Identification
4.4.3. Different Expression Analysis of mRNAs and lncRNAs
4.4.4. Target Gene Prediction and Functional Analysis of lncRNAs
4.5. Integration Analysis of Multi-Omics Datasets
4.6. Data and Software Availability
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H. The Prevalence of Kashin-Beck Disease in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 3175–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Liao, Y.; Yue, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Deng, C.; Chen, L. Effects of five types of selenium supplementation for treatment of Kashin-Beck disease in children: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e017883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, G. Diagnostic, clinical and radiological characteristics of Kashin-Beck disease in Shaanxi Province, PR China. Int. Orthop. 2001, 25, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Liang, C.; Yang, X.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Cheng, S.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, M.; Qi, X.; et al. Genetic association scan of 32 osteoarthritis susceptibility genes identified TP63 associated with an endemic osteoarthritis, Kashin-Beck disease. Bone 2021, 150, 115997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Hu, M.; Chen, S.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gong, Y.; Huang, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; et al. Investigation of selenium nutritional status and dietary pattern among children in Kashin-Beck disease endemic areas in Shaanxi Province, China using duplicate portion sampling method. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Duan, C. RNA-seq analysis reveals different gene ontologies and pathways in rheumatoid arthritis and Kashin-Beck disease. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 1686–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; He, A.; Wen, Y.; Xiao, X.; Hao, J.; Zhang, F.; Guo, X. Comparison of microRNA expression profiles of Kashin-Beck disease, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F.; Shao, W.; Yang, L.; Ning, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, G.; Lee, B.J.; Lammi, M. Long noncoding RNA expression profile reveals lncRNAs signature associated with extracellular matrix degradation in kashin-beck disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.D.; Yu, H.J.; Yan, H.; Gao, Y.; Ma, W.J.; Gao, Z.Q.; Xu, P.; Lammi, M. Comparative analysis of gene expression profiles between primary knee osteoarthritis and an osteoarthritis endemic to Northwestern China, Kashin-Beck disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, C.C.; Ramilowski, J.A.; Harshbarger, J.; Bertin, N.; Rackham, O.J.; Gough, J.; Denisenko, E.; Schmeier, S.; Poulsen, T.M.; Severin, J.; et al. An atlas of human long non-coding RNAs with accurate 5′ ends. Nature 2017, 543, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Jian, C.; Wang, X.; Dai, X. Comprehensive expression profiles of mRNAs, lncRNAs and miRNAs in Kashin-Beck disease identified by RNA-sequencing. Mol. Omics 2022, 18, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, D.C.; Swiderek, K.M.; Davis, M.T.; Lee, T.D. Data-controlled automation of liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry analysis of peptide mixtures. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 7, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venable, J.D.; Dong, M.Q.; Wohlschlegel, J.; Dillin, A.; Yates, J.R. Automated approach for quantitative analysis of complex peptide mixtures from tandem mass spectra. Nat. Methods 2004, 1, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Kouvonen, P.; Koh, C.C.; Gillet, L.C.; Wolski, W.E.; Röst, H.L.; Rosenberger, G.; Collins, B.C.; Blum, L.C.; Gillessen, S.; et al. Rapid mass spectrometric conversion of tissue biopsy samples into permanent quantitative digital proteome maps. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundgaard, L.; Åhrman, E.; Malmström, J.; Auf dem Keller, U.; Walters, M.; Jacobsen, S. Effective protein extraction combined with data independent acquisition analysis reveals a comprehensive and quantifiable insight into the proteomes of articular cartilage and subchondral bone. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KA, L.C.; Boitard, S.; Besse, P. Sparse PLS discriminant analysis: Biologically relevant feature selection and graphical displays for multiclass problems. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 253. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.; Lin, X.; Xiang, R.; Bao, M.; Qiao, L.; Liu, H.; He, H.; Wen, X.; Han, J. Low selenium and T-2 toxin may be involved in the pathogenesis of Kashin-Beck disease by affecting AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 pathway mediated autophagy. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 279, 116503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, S.; Wu, H.; Dong, J.; Zeng, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, M.; et al. LncRNA XIST inhibits mitophagy and increases mitochondrial dysfunction by promoting BNIP3 promoter methylation to facilitate the progression of KBD. Mol. Immunol. 2025, 182, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ning, Y.; Li, C.; Gong, Y.; Huang, R.; Hu, M.; Poulet, B.; Xu, K.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, R.; et al. Alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolite profiles of patients with Kashin-Beck disease, an endemic osteoarthritis in China. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckwalter, J.A.; Anderson, D.D.; Brown, T.D.; Tochigi, Y.; Martin, J.A. The Roles of Mechanical Stresses in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis: Implications for Treatment of Joint Injuries. Cartilage 2013, 4, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Pang, Q.; Wu, S.; Wu, C.; Xu, P.; Bai, Y. The role of mitochondria in T-2 toxin-induced human chondrocytes apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Fang, X.; Qin, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhan, X. LncRNA PVT1 regulates biological function of osteoarthritis cells by regulating miR-497/AKT3 axis. Medicine 2022, 101, e31725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, Y.; Hao, J.; Wen, Y.; Han, J.; Hou, W.; Liu, R.; Zhao, B.; He, A.; Li, P.; et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling of articular cartilage reveals significant epigenetic alterations in Kashin-Beck disease and osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, K.; Ebata, T.; Liyile, C.; Nishida, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Tokuhiro, T.; Shiota, J.; Nagano, T.; Takasuka, T.E.; Endo, T.; et al. Chondroprotective functions of neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles by promoting the production of secreted frizzled-related protein 5 in cartilage. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Ren, J.; Ye, H.; Chu, W.; Ding, X.; Ding, L.; Fu, Y. Thymosin beta 10 loaded ZIF-8/sericin hydrogel promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis for bone regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267 Pt 1, 131562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.S.; Rhee, Y.; Lim, S.K. Fibroblast growth factor 2-induced cytoplasmic asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase promotes survival of osteoblasts by regulating anti-apoptotic PI3K/Akt signaling. Bone 2009, 45, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cheng, B.; Wei, W.; Liu, L.; Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Jia, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, F. Whole-Transcriptome Sequencing of Knee Joint Cartilage from Kashin-Beck Disease and Osteoarthritis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binvignat, M.; Emond, P.; Mifsud, F.; Miao, B.; Courties, A.; Lefèvre, A.; Maheu, E.; Crema, M.D.; Klatzmann, D.; Kloppenburg, M.; et al. Serum tryptophan metabolites are associated with erosive hand osteoarthritis and pain: Results from the DIGICOD cohort. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023, 31, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Xie, W. The role of 3D genome organization in development and cell differentiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Ricci, E.P.; Mercier, B.C.; Moore, M.J.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, K.; Fei, L.; Pett, J.P.; Roberts, K.; Blain, R.; Polański, K.; Li, T.; Yayon, N.; He, P.; Xu, C.; et al. A multi-omic atlas of human embryonic skeletal development. Nature 2024, 635, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohart, F.; Gautier, B.; Singh, A.; KA, L.C. mixOmics: An R package for ‘omics feature selection and multiple data integration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Fang, W.; Long, X. Glycyrrhizin regulates antioxidation through Nrf2 signaling pathway in rat temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2024, 51, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Peng, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhou, M.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, C. Sirtuin 2 expression suppresses oxidative stress and senescence of nucleus pulposus cells through inhibition of the p53/p21 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, D.; Nojiri, H.; Saita, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Watanabe, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Koike, M.; Asou, Y.; Takaku, T.; Kaneko, K.; et al. Cytoplasmic reactive oxygen species and SOD1 regulate bone mass during mechanical unloading. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 2368–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahasrabudhe, S.A.; Terluk, M.R.; Kartha, R.V. N-acetylcysteine Pharmacology and Applications in Rare Diseases-Repurposing an Old Antioxidant. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Luo, P.; Wen, P.; Xu, P. Effects of selenium and iodine on Kashin-Beck disease: An updated review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1402559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Bai, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Yuan, Y.; Lv, X.; Wang, H.; Qin, Y.; et al. Exploring the role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of Kashin-Beck Disease: A Focus on selenium deficiency and T-2 toxin exposure. Med. Hypotheses 2025, 197, 111606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WS/T 207-2010; Diagnosis of Kashin-Beck Disease. National Health and Family Planning Commission of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W345–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, H.; Bu, D.; Zhao, G.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.B.; Li, H.Y.; Yu, W.J.; Ying, Y.Z.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, X.K.; Wang, Y.G.; Shi, G.Z.; Huang, H.W. Occurrence and risk factors for post-stroke delirium: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J. Psychiatry 2024, 99, 104132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Shannon, C.P.; Gautier, B.; Rohart, F.; Vacher, M.; Tebbutt, S.J.; KA, L.C. DIABLO: An integrative approach for identifying key molecular drivers from multi-omics assays. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, L.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J.; Cheng, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F. Integrative Proteome and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal the Metabolic Disturbance of the Articular Cartilage in Kashin–Beck Disease, an Endemic Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115146
Han L, Cheng B, Xia J, Cheng S, Yang X, Zhang F. Integrative Proteome and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal the Metabolic Disturbance of the Articular Cartilage in Kashin–Beck Disease, an Endemic Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115146
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Lixin, Bolun Cheng, Jinyu Xia, Shiqiang Cheng, Xuena Yang, and Feng Zhang. 2025. "Integrative Proteome and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal the Metabolic Disturbance of the Articular Cartilage in Kashin–Beck Disease, an Endemic Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115146
APA StyleHan, L., Cheng, B., Xia, J., Cheng, S., Yang, X., & Zhang, F. (2025). Integrative Proteome and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal the Metabolic Disturbance of the Articular Cartilage in Kashin–Beck Disease, an Endemic Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115146





