Azvudine Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting the Notch–HEY Signalling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
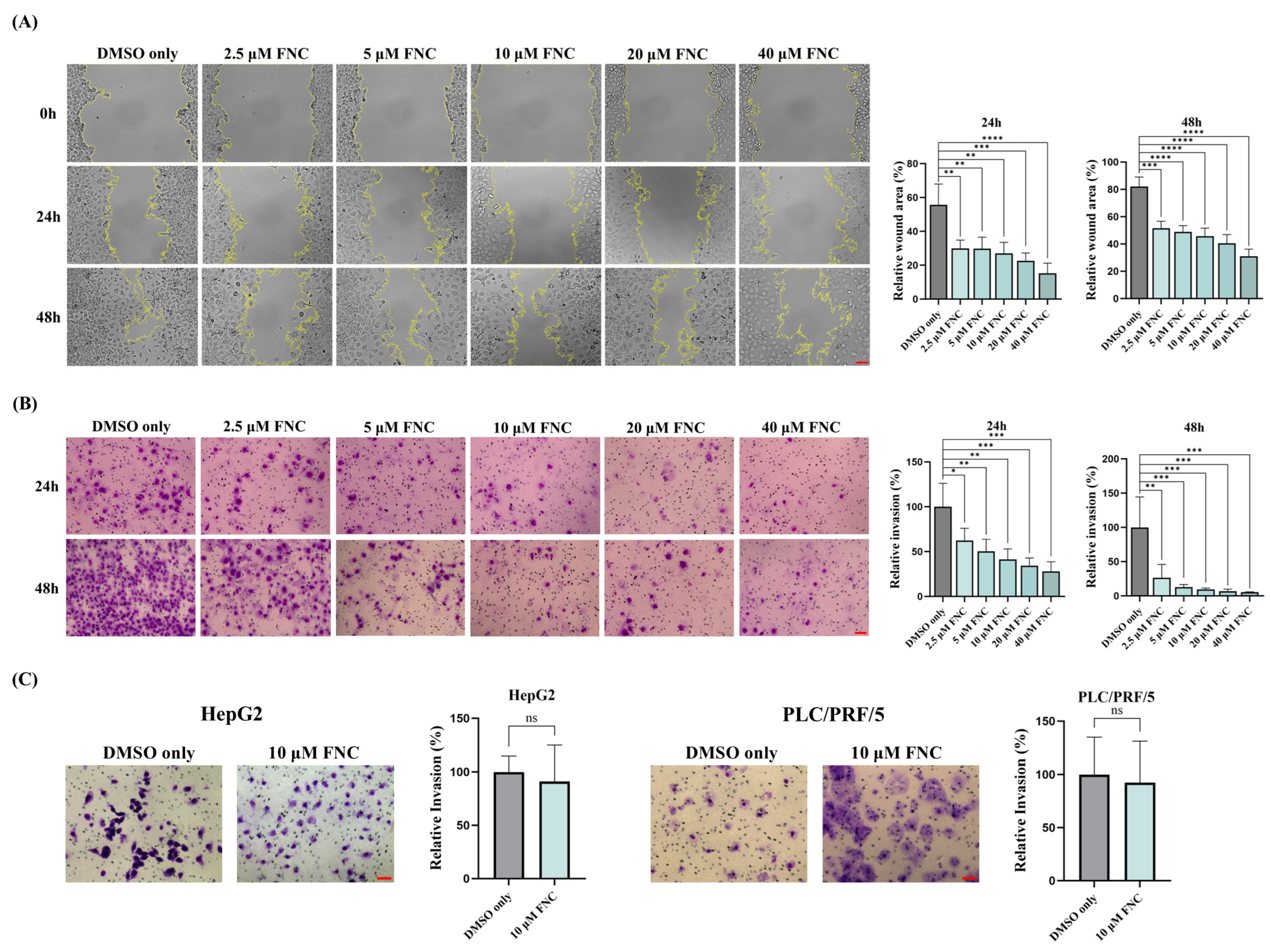
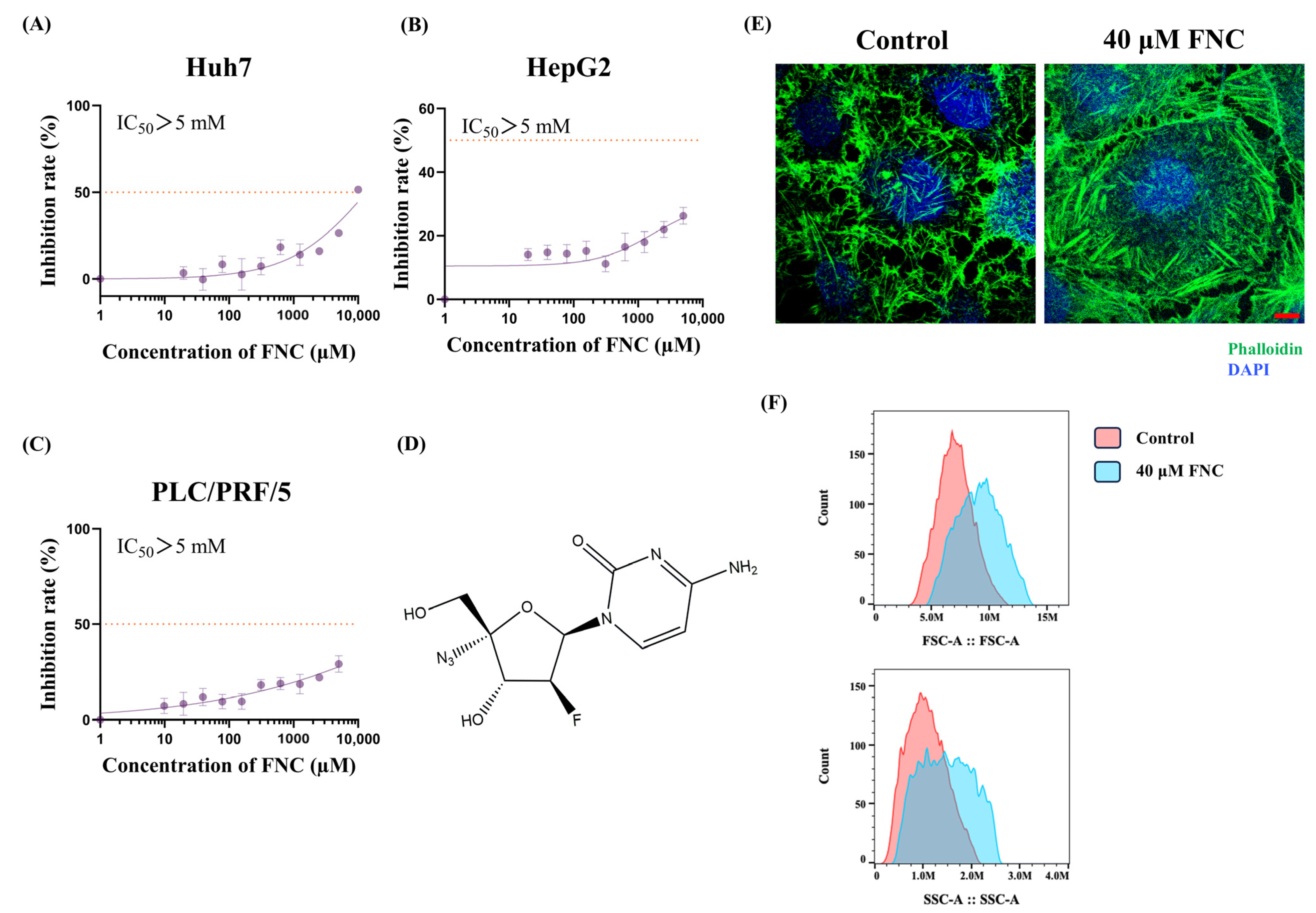
2.1. FNC Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of Huh7 Cells
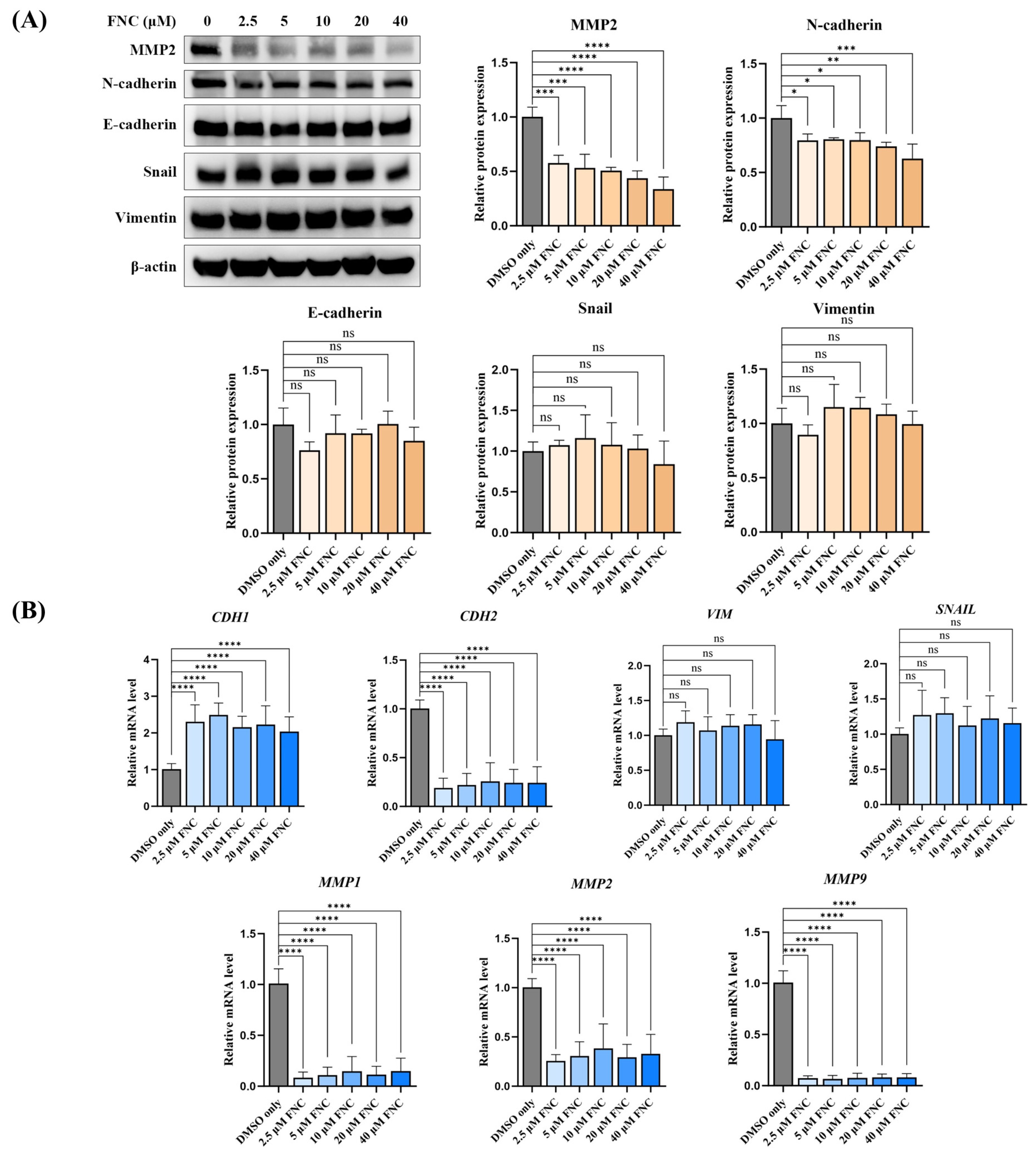
2.2. FNC Modulates a Subset of EMT Markers in Huh7 Cells
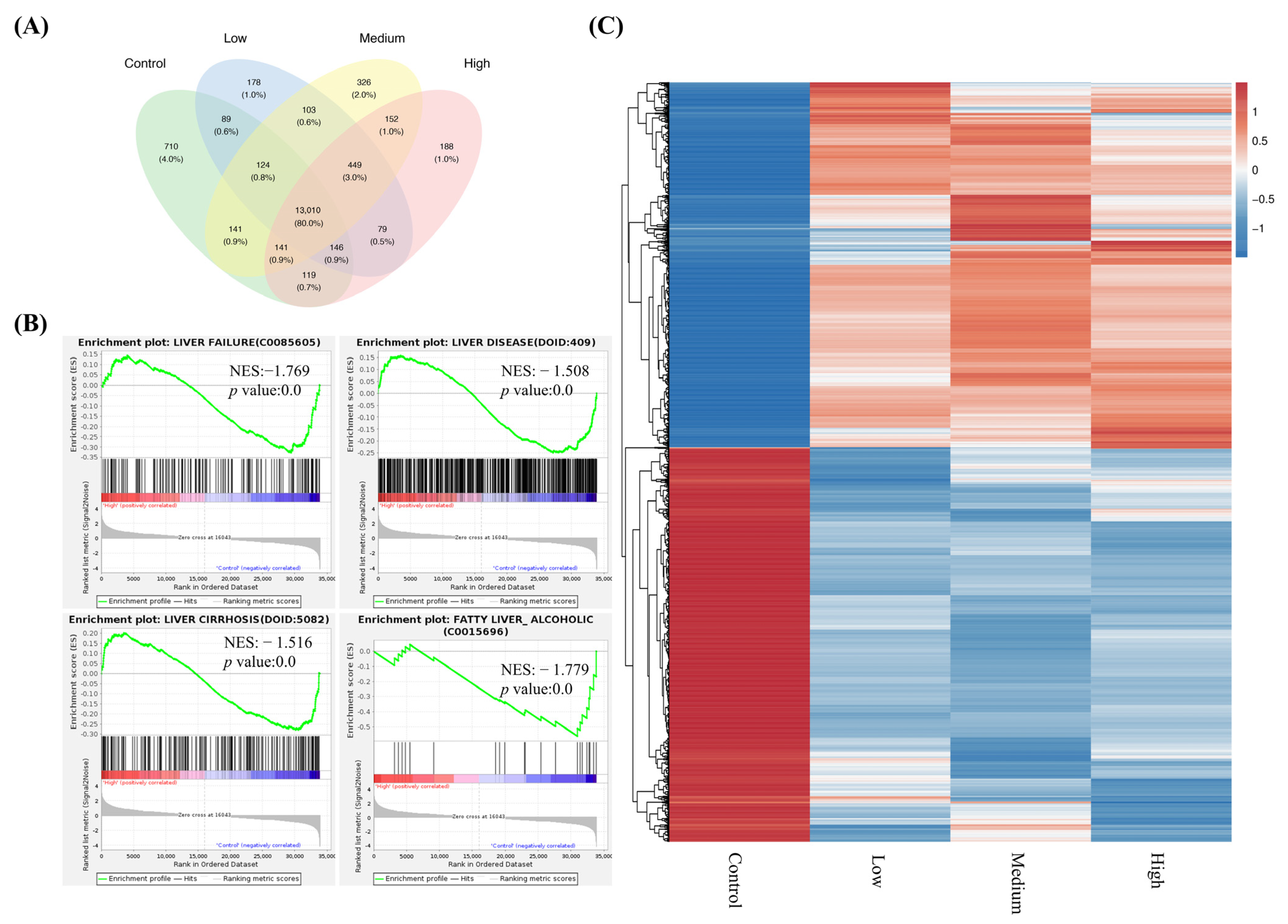
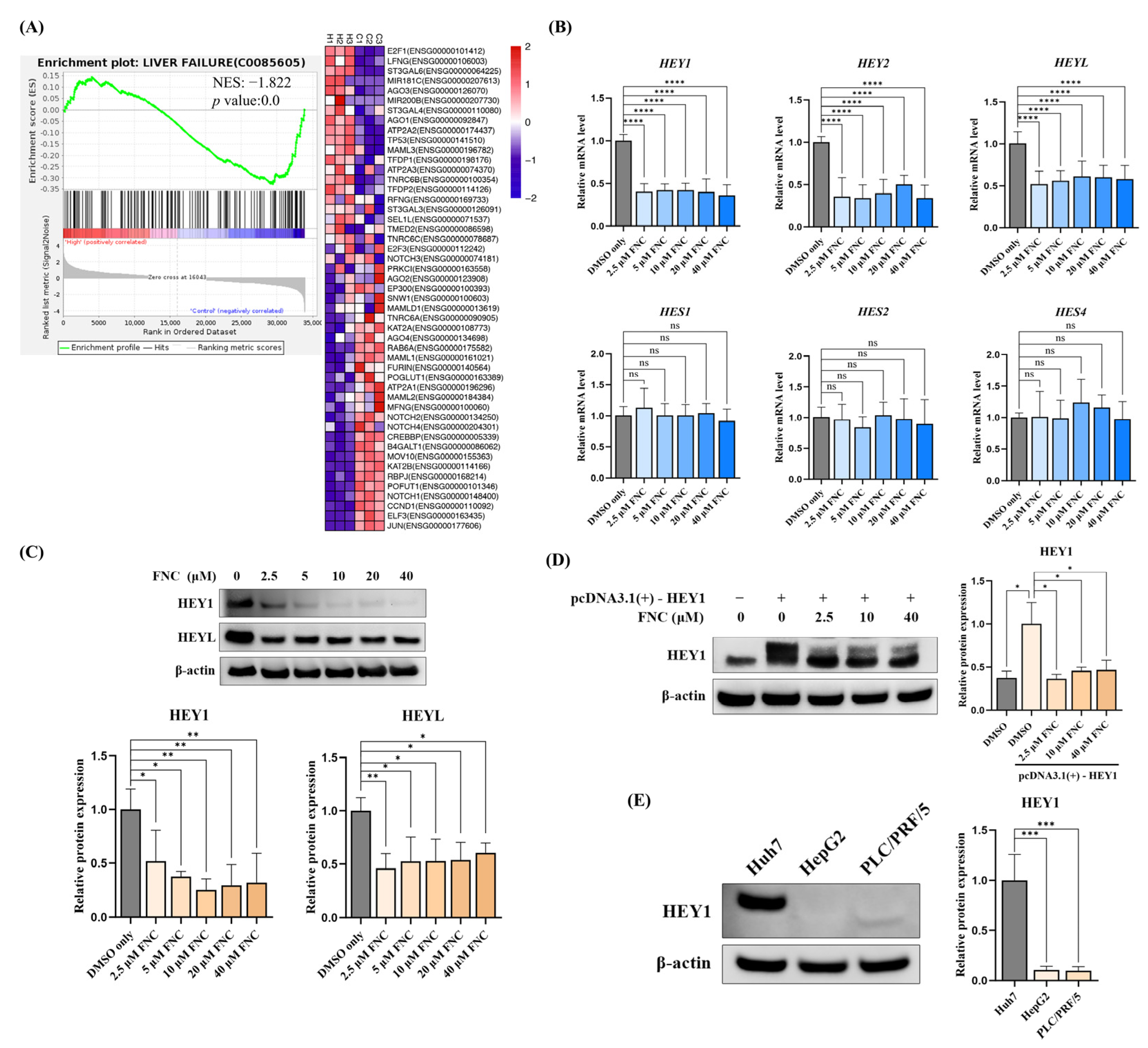
2.3. RNA-Seq Reveals That FNC May Attenuate Liver Diseases and Function
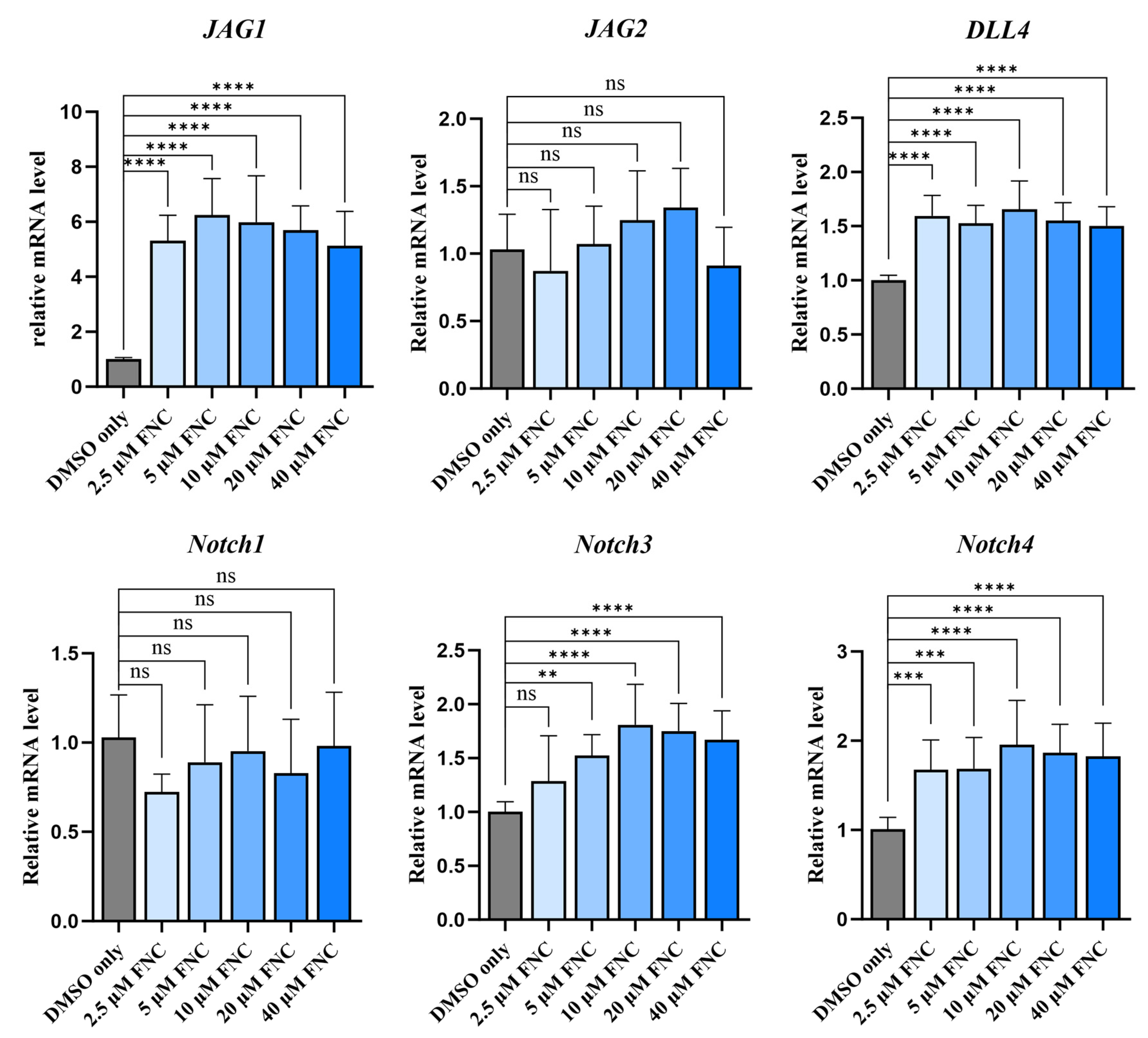
2.4. HEY Family Members Are Downregulated in FNC-Treated HCC Cells
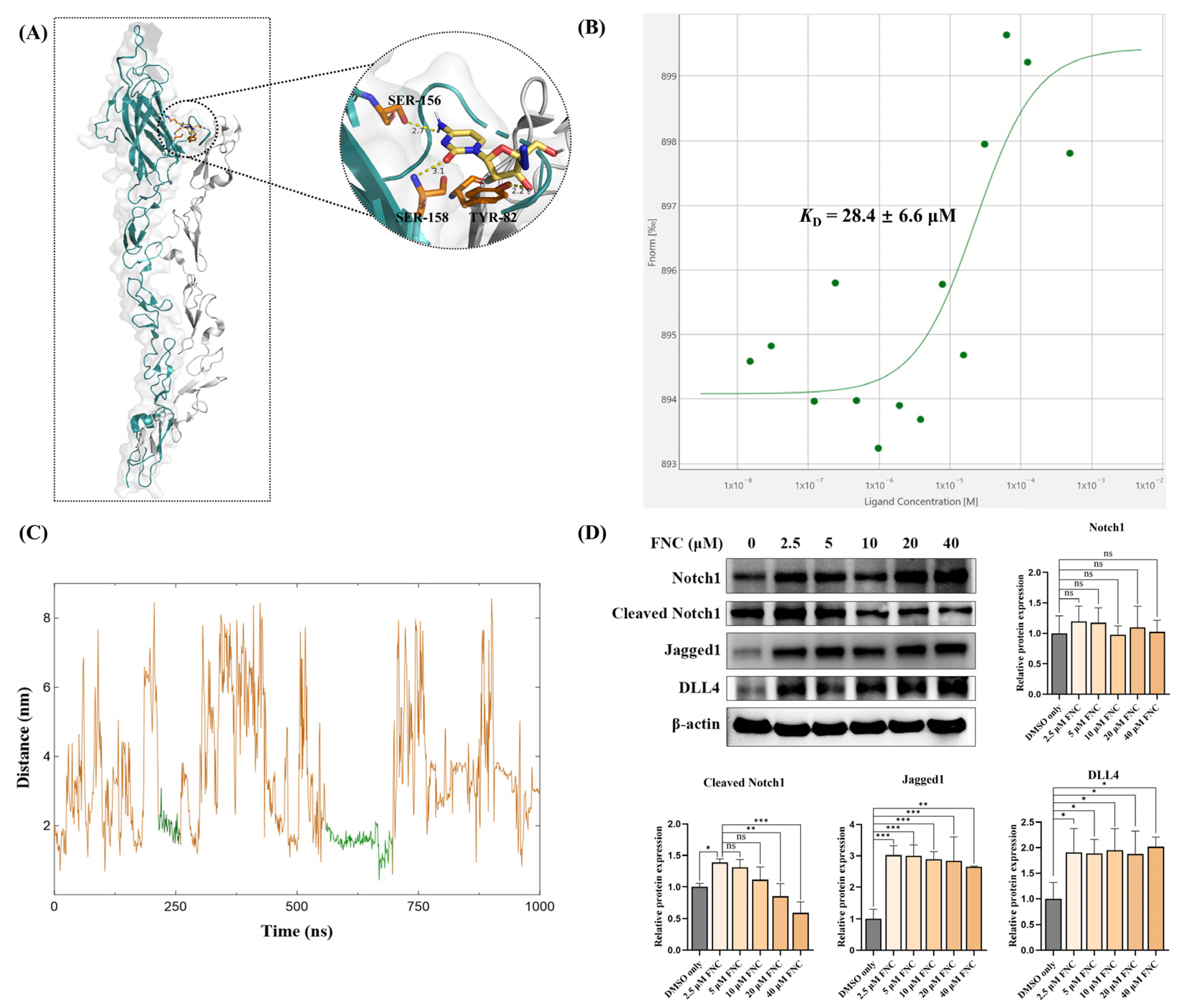
2.5. Molecular Docking, MST and MD Simulations Suggest That Jagged1 Is a Potential Direct Target of FNC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
4.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.3. Wound-Healing Assay
4.4. Invasion Assay
4.5. RNA Sequencing
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Real-Time PCR
4.8. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.9. MST
4.10. Molecular Docking
4.11. MD Simulations
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| H-Bond | Hydrogen Bond |
| Pi-A | Pi-Alkyl |
| Pi-Cat | Pi-Cation |
| Hal | Halogen |
| C-H Bond | Carbon Hydrogen Bond |
| Pi-Pi | Pi-Pi Stacked |
| Pi-S | Pi-Sulphur |
| Attr-Chg | Attractive Charge |
| HIS | Histidine |
| TYR | Tyrosine |
| SER | Serine |
| VAL | Valine |
| ARG | Arginine |
| CYS | Cysteine |
| ASP | Aspartic Acid |
| GLY | Glycine |
| GLN | Glutamine |
| PRO | Proline |
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucman-Rossi, J.; Villanueva, A.; Nault, J.C.; Llovet, J.M. Genetic Landscape and Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1226–1239.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.W.H.; Lo, R.C.L.; Chan, L.K.; Ng, I.O.L. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2016, 5, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Pinyol, R.; Kelley, R.K.; El-Khoueiry, A.; Reeves, H.L.; Wang, X.W.; Gores, G.J.; Villanueva, A. Molecular pathogenesis and systemic therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badwei, N. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Gene Expression: The New Era, Where It goes? iLIVER 2023, 2, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, K.K.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition in tissue repair and degeneration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 720–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.D.; Gao, D.; Redfern, A.; Thompson, E.W. Controversies around epithelial–mesenchymal plasticity in cancer metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, S.; Savagner, P.; Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Mahjoubi, L.; Saintigny, P.; Thiery, J.P.; Chouaib, S. New insights into the role of EMT in tumor immune escape. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 824–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Bo, Z.; Feng, X.; Yang, X.; Handford, P.A. The Notch Signaling Pathway: Mechanistic Insights in Health and Disease. Engineering 2024, 34, 212–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadil, J.; Cermak, L.; Soto-Nieves, N.; Böttinger, E.P. Integration of TGF-β/Smad and Jagged1/Notch signalling in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, D.K.-C.; Tse, A.P.-W.; Law, C.T.; Xu, I.M.-J.; Lee, D.; Chen, M.; Lai, R.K.-H.; Yuen, V.W.-H.; Cheu, J.W.-S.; Ho, D.W.-H.; et al. Hypoxia regulates the mitochondrial activity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through HIF/HEY1/PINK1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuru, A.; Setoguchi, T.; Matsunoshita, Y.; Nagao-Kitamoto, H.; Nagano, S.; Yokouchi, M.; Maeda, S.; Ishidou, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Komiya, S. Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 1 promotes osteosarcoma metastasis via matrix metallopeptidase 9 expression. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Wei, L.; Guo, W.; Zha, R.; Bao, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, C.; Zhao, F.; Chen, T.; et al. Genome-wide copy number analyses identified novel cancer genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Kalayanov, G.; Sund, C.; Winqvist, A.; Pinho, P.; Maltseva, T.; Morisson, V.; Leveque, V.; Rajyaguru, S.; Le Pogam, S.; et al. The design, synthesis, and antiviral activity of 4′-azidocytidine analogues against hepatitis C virus replication: The discovery of 4′-azidoarabinocytidine. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayzullina, D.; Kharwar, R.K.; Acharya, A.; Buzdin, A.; Borisov, N.; Timashev, P.; Ulasov, I.; Kapomba, B. FNC: An Advanced Anticancer Therapeutic or Just an Underdog? Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, H.Q.; Lu, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, B.; Li, S.Y.; Shao, F.M.; et al. Azvudine is a thymus-homing anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug effective in treating COVID-19 patients. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Luo, H.; Yu, Z.; Song, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Cui, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Clinical Trial of Azvudine Tablets in the Treatment of Mild and Common COVID-19, a Pilot Study. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, e2001435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, S.B.; Cabral, P.G.A.; da Silva, R.M.; Arruda, R.F.; Cabral, S.P.d.F.; de Assis, A.L.E.M.; Junior, A.B.V.; Degrave, W.M.S.; Moreira, A.d.S.; Silva, C.G.; et al. Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study: A study on the safety and clinical efficacy of AZVUDINE in moderate COVID-19 patients. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1215916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Song, C.; Hou, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. Mechanistic Insight into Antiretroviral Potency of 2′-Deoxy-2′-β-fluoro-4′-Azidocytidine (FNC) with a Long-Lasting Effect on HIV-1 Prevention. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8554–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Niu, S.; Liang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, N.; Peng, Y.; Ma, F.; Yue, W.; Wang, Q.; Chang, J.; et al. FNC inhibits non-small cell lung cancer by activating the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Genes Genom. 2022, 44, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Fan, Q.; Zheng, L.; Yu, X.; Wang, N.; et al. FNC, a novel nucleoside analogue inhibits cell proliferation and tumor growth in a variety of human cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.P.; Ding, X.X.; Wang, N.; Ma, F.; Jiang, J.H.; Wang, Q.D.; Chang, J.B. FNC, a novel nucleoside analogue, blocks invasion of aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma cell lines via inhibition of the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 6829–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ding, X.; Peng, B.; Wang, N.; Ma, F.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chang, J. FNC efficiently inhibits mantle cell lymphoma growth. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Delu, V.; Ulasov, I.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Shukla, A.; Patel, A.K.; Yadav, L.; Tiwari, R.; et al. Pharmacological Insights: Mitochondrial ROS Generation by FNC (Azvudine) in Dalton’s Lymphoma Cells Revealed by Super Resolution Imaging. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Shukla, A.; Kumar, S.; Ulasov, I.; Singh, R.K.; Kumar, S.; Patel, A.; Yadav, L.; Tiwari, R.; Paswan, R.; et al. FNC (4′-azido-2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro(arbino)cytidine) as an Effective Therapeutic Agent for NHL: ROS Generation, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Mitochondrial-Mediated Apoptosis. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmarini, C.M.; Mackey, J.R.; Dumontet, C. Nucleoside Analogues and Nucleobases in Cancer Treatment. 2002. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(02)00788-X (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Jordheim, L.P.; Durantel, D.; Zoulim, F.; Dumontet, C. Advances in the development of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues for cancer and viral diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.H.; Abdelmalek, M.; Khan, S.; Moylan, C.A.; Rodriquez, L.; Villanueva, A.; Yang, J.D. Current and emerging strategies for the prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Lin, J.T.; Ho, H.J.; Su, C.W.; Lee, T.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Wu, C.; Wu, J.C. Association of nucleos(T)ide analogue therapy with reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B—A nationwide cohort study. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 143–151.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosaka, T.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Seko, Y.; Kawamura, Y.; Sezaki, H.; Akuta, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Arase, Y.; et al. Long-term entecavir treatment reduces hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in patients with hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2013, 58, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcellin, P.; Gane, E.; Buti, M.; Afdhal, N.; Sievert, W.; Jacobson, I.M.; Washington, M.K.; Germanidis, G.; Flaherty, J.F.; Schall, R.A.; et al. Regression of cirrhosis during treatment with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for chronic hepatitis B: A 5-year open-label follow-up study. Lancet 2013, 381, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Gao, Y. Clinical outcomes of cessation of nucleoside/nucleotide analogues in Chinese patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. iLIVER 2024, 3, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, M.; Koinuma, D.; Miyazono, K.; Heldin, C.-H. Genome-wide mechanisms of Smad binding. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muguruma, Y.; Yahata, T.; Warita, T.; Hozumi, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Ito, M.; Ando, K. Jagged1-induced Notch activation contributes to the acquisition of bortezomib resistance in myeloma cells. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sanders, A.J.; Liang, G.; Song, E.; Jiang, W.G.; Gong, C. Hey factors at the crossroad of tumorigenesis and clinical therapeutic modulation of hey for anticancer treatment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabletz, T.; Kalluri, R.; Nieto, M.A.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xie, J.; Zou, X.; Pan, T.; Yu, Q.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, R.; et al. Single-cell multiomics reveals heterogeneous cell states linked to metastatic potential in liver cancer cell lines. iScience 2022, 25, 103857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Chen, M.J.M.; Luo, Y.; Ju, Z.; Nesser, N.K.; Johnson-Camacho, K.; Boniface, C.T.; Lawrence, Y.; Pande, N.T.; et al. Large-Scale Characterization of Drug Responses of Clinically Relevant Proteins in Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 829–843.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, H.; Taketa, K.; Miyano, K.; Yamane, T.; Sato, J. Growth of Human Hepatoma Cell Lines with Differentiated Functions in Chemically Defined Medium, n.d. Available online: http://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article-pdf/42/9/3858/2414447/cr0420093858.pdf (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Aden, D.P.; Fogel, A.; Plotkin, S.; Damjanov, I.; Knowles, B.B. Controlled synthesis of HBsAg in a differentiated human liver carcinoma-derived cell line. Nature 1979, 282, 615–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuyama, K.; Asagiri, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Tsushima, H.; Seo, S.; Taura, K.; Uemoto, S.; Iwaisako, K. Gene expression profiles of liver cancer cell lines reveal two hepatocyte-like and fibroblast-like clusters. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Weng, S.; Li, C.; Jiang, Y.; Qian, X.; Xu, P.; Ying, W. Proteomic overview of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines and generation of the spectral library. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Björling, E.; Agaton, C.; Szigyarto, C.A.K.; Amini, B.; Andersen, E.; Andersson, A.C.; Angelidou, P.; Asplund, A.; Asplund, C.; et al. A human protein atlas for normal and cancer tissues based on antibody proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 1920–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontén, F.; Jirström, K.; Uhlen, M. The Human Protein Atlas—A tool for pathology. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Sanlidag, S.; Jensen, S.A.; Burnap, S.A.; Struwe, W.B.; Larsen, A.H.; Feng, X.; Mittal, S.; Sansom, M.S.P.; Sahlgren, C.; et al. An N-glycan on the C2 domain of JAGGED1 is important for Notch activation. Sci. Signal 2022, 15, eabo3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeronian, M.R.; Klykov, O.; de Montserrat, J.P.I.; Konijnenberg, M.J.; Gaur, A.; Scheltema, R.A.; Janssen, B.J.C. Notch-Jagged signaling complex defined by an interaction mosaic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102502118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Takeuchi, H.; Sheppard, D.; Chillakuri, C.; Lea, S.M.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Handford, P.A. Fringe-mediated extension of O-linked fucose in the ligand-binding region of Notch1 increases binding to mammalian Notch ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7290–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, V.C.; Jude, K.M.; Pierce, N.W.; Nachury, M.V.; Fischer, S.; Garcia, K.C. Structural basis for Notch1 engagement of Delta-like 4. Science 2015, 347, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, V.C.; Kim, B.C.; Ge, C.; Kakuda, S.; Wu, D.; Roein-Peikar, M.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Zhu, C.; Ha, T.; Garcia, K.C. Notch-Jagged complex structure implicates a catch bond in tuning ligand sensitivity. Science 2017, 355, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chillakuri, C.R.; Sheppard, D.; Xenia, M.; Ilagan, G.; Holt, L.R.; Abbott, F.; Liang, S.; Kopan, R.; Handford, P.A.; Lea, S.M. Structural Analysis Uncovers Lipid-Binding Properties of Notch Ligands. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suckling, R.J.; Korona, B.; Whiteman, P.; Chillakuri, C.; Holt, L.; Handford, P.A.; Lea, S.M. Structural and functional dissection of the interplay between lipid and Notch binding by human Notch ligands. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienken, C.J.; Baaske, P.; Rothbauer, U.; Braun, D.; Duhr, S. Protein-binding assays in biological liquids using microscale thermophoresis. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; van der Spoel, D.; van Drunen, R. GROMACS: A message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 91, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindah, E. Gromacs: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Piana, S.; Palmo, K.; Maragakis, P.; Klepeis, J.L.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Improved side-chain torsion potentials for the Amber ff99SB protein force field, Proteins: Structure. Funct. Bioinform. 2010, 78, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T. Sobtop, Version [1.0(dev5)]. Available online: http://sobereva.com/soft/Sobtop (accessed on 2 December 2024).

| Protein * | Residue | Binding Mode | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jagged1 | TYR 82 | H-Bond | −6.592 |
| SER 156 | H-Bond | ||
| SER 158 | H-Bond | ||
| VAL 86 | Pi-A | ||
| Jagged2 | SER 204 | SER 204 | −6.506 |
| ARG 114 | ARG 114 | ||
| CYS 198 | CYS 198 | ||
| ASP 176 | ASP 176 | ||
| TYR 203 | TYR 203 | ||
| DLL1 | HIS 182 | H-Bond | −5.707 |
| ASP 180 | H-Bond | ||
| TYR 183 | H-Bond | ||
| GLY 185 | H-Bond | ||
| CYS 179 | Hal/Pi-S | ||
| DLL4 | GLN 153 | H-Bond | −6.058 |
| CYS 175 | H-Bond | ||
| GLY 181 | H-Bond | ||
| ASP 182 | H-Bond/Attr-Chg | ||
| PRO 202 | C-H Bond |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Y.; Sun, P.; Ren, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Xu, C.; Dong, L.; Li, H.; Zheng, Z.; You, X.; et al. Azvudine Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting the Notch–HEY Signalling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115127
Meng Y, Sun P, Ren Y, Li G, Liu X, Xu C, Dong L, Li H, Zheng Z, You X, et al. Azvudine Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting the Notch–HEY Signalling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115127
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Yao, Peiyi Sun, Yixin Ren, Guoqing Li, Xiujun Liu, Chunjie Xu, Luyao Dong, Hanhan Li, Zhonghui Zheng, Xuefu You, and et al. 2025. "Azvudine Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting the Notch–HEY Signalling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115127
APA StyleMeng, Y., Sun, P., Ren, Y., Li, G., Liu, X., Xu, C., Dong, L., Li, H., Zheng, Z., You, X., & Yang, X. (2025). Azvudine Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting the Notch–HEY Signalling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115127





