Blood Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration over Four Decades After Toxic Oil Syndrome: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics
4.2. Study Design and Setting
4.3. Participants
4.4. Biomarker Quantification
- -
- Sample Collection and Handling
- -
- GFAP Quantification (Quanterix SIMOA SR-X)
- -
- pTau217 and NfL Quantification (Fujirebio Lumipulse G600II CLEIA)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tabuenca, M.J. Toxic-allergic syndrome caused by ingestion of rapeseed oil denatured with aniline. Lancet 1981, 2, 567–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilbourne, E.M.; Posada de la Paz, M.; Abaitua Borda, I.; Diez Ruiz-Navarro, M.; Philen, R.M.; Falk, H. Toxic oil syndrome: A current clinical and epidemiologic summary, including comparisons with the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1991, 18, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelpí, E.; de la Paz, M.P.; Terracini, B.; Abaitua, I.; de la Cámara, A.G.; Kilbourne, E.M.; Lahoz, C.; Nemery, B.; Philen, R.M.; Soldevilla, L.; et al. Centro de Investigación para el Síndrome del Aceite Tóxico. The Spanish toxic oil syndrome 20 years after its onset: A multidisciplinary review of scientific knowledge. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yoshida, S.H.; German, J.B.; Fletcher, M.P.; Gershwin, M.E. The toxic oil syndrome: A perspective on immunotoxicological mechanisms. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1994, 19, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Ruiz, A.; Calabozo, M.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Mancebo, L. Toxic oil syndrome: A long-term follow-up of a cohort of 332 patients. Medicine 1993, 72, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Ser Quijano, T.; Esteban García, A.; Martínez Martín, P.; Morales Otal, M.A.; Pondal Sordo, M.; Pérez Vergara, P.; Portera Sánchez, A. Evolución de la afección neuromuscular en el síndrome del aceite tóxico [Course of neuromuscular involvement in the toxic oil syndrome]. Med. Clin. 1986, 87, 231–236. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Castroviejo, I. A multisystemic disease caused by adulterated rapeseed oil. Brain Dev. 1988, 10, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Paz, M.P.; Philen, R.M.; Gerr, F.; Letz, R.; Ferrari Arroyo, M.J.; Vela, L.; Izquierdo, M.; Arribas, C.M.; Borda, I.A.; Ramos, A.; et al. Neurologic outcomes of toxic oil syndrome patients 18 years after the epidemic. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martinez-Tello, F.J.; Tellez, I. Extracardiac vascular and neural lesions in the toxic oil syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1991, 18, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricoy, J.R.; Cabello, A.; Rodríguez, J.; Téllez, I. Neuropathological studies on the toxic syndrome related to adulterated rapeseed oil in Spain. Brain 1983, 106, 817–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Ser, T.; Espasandín, P.; Cabetas, I.; Arredondo, J.M. Trastornos de memoria en el síndrome del aceite tóxico (SAT) [Memory disorders in the toxic oil syndrome (TOS)]. Arch. Neurobiol. 1986, 49, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood–brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fournier, E.; Efthymiou, M.L.; Lecorsier, A. Spanish adulterated oil matter: An important discovery by Spanish toxicologists—The toxicity of anilides of unsaturated fatty acids. Toxicol. Eur. Res. 1982, 4, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Cabot, A.; Morató, A.; Commandeur, J.N.; Vermeulen, N.P.; Messeguer, A. In vitro bioactivation of 3-(N-phenylamino)propane-1,2-diol by human and rat liver microsomes and recombinant P450 enzymes. Implications for toxic oil syndrome. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Ser, T.; Franch, O.; Portera, A.; Muradas, V.; Yebenes, J.G. Neurotransmitter changes in cerebrospinal fluid in the Spanish toxic oil syndrome: Human clinical findings and experimental results in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 1986, 67, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xin, Y.; Meng, S.; He, Z.; Hu, W. Neurofilament light chain protein in neurodegenerative dementia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 102, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhauria, M.; Mondal, R.; Deb, S.; Shome, G.; Chowdhury, D.; Sarkar, S.; Benito-León, J. Blood-Based Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease: Advancing Non-Invasive Diagnostics and Prognostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eratne, D.; Kang, M.J.Y.; Lewis, C.; Dang, C.; Malpas, C.B.; Keem, M.; Grewal, J.; Marinov, V.; Coe, A.; Kaylor-Hughes, C.; et al. Plasma and CSF neurofilament light chain distinguish neurodegenerative from primary psychiatric conditions in a clinical setting. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 7989–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hol, E.M.; Pekny, M. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and the astrocyte intermediate filament system in diseases of the central nervous system. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 32, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhak, A.; Foschi, M.; Abu-Rumeileh, S.; Yue, J.K.; D’Anna, L.; Huss, A.; Oeckl, P.; Ludolph, A.C.; Kuhle, J.; Petzold, A.; et al. Blood GFAP as an emerging biomarker in brain and spinal cord disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.B.; Janelidze, S.; Smith, R.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Teunissen, C.E.; Zetterberg, H.; Stomrud, E.; Ashton, N.J.; Blennow, K.; et al. Plasma GFAP is an early marker of amyloid-β but not tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2021, 144, 3505–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pilotto, A.; Ashton, N.J.; Lupini, A.; Battaglio, B.; Zatti, C.; Trasciatti, C.; Gipponi, S.; Cottini, E.; Grossi, I.; Salvi, A.; et al. Plasma NfL, GFAP, amyloid, and p-tau species as Prognostic biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 7537–7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ammitzbøll, C.; Dyrby, T.B.; Börnsen, L.; Schreiber, K.; Ratzer, R.; Romme Christensen, J.; Iversen, P.; Magyari, M.; Lundell, H.; Jensen, P.E.H.; et al. NfL and GFAP in serum are associated with microstructural brain damage in progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 77, 104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korley, F.K.; Jain, S.; Sun, X.; Puccio, A.M.; Yue, J.K.; Gardner, R.C.; Wang, K.K.W.; Okonkwo, D.O.; Yuh, E.L.; Mukherjee, P.; et al. Prognostic value of day-of-injury plasma GFAP and UCH-L1 concentrations for predicting functional recovery after traumatic brain injury in patients from the US TRACK-TBI cohort: An observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Milà-Alomà, M.; Ashton, N.J.; Shekari, M.; Salvadó, G.; Ortiz-Romero, P.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Vanmechelen, E.; et al. Plasma p-tau231 and p-tau217 as state markers of amyloid-β pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1797–1801, Erratum in Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rossor, A.M.; Kapoor, M.; Wellington, H.; Spaulding, E.; Sleigh, J.N.; Burgess, R.W.; Laura, M.; Zetterberg, H.; Bacha, A.; Wu, X.; et al. A longitudinal and cross-sectional study of plasma neurofilament light chain concentration in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2022, 27, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, N.; Teo, W.P.; Chandra, S.; Chapman, J. Parkinson’s Disease and the Environment. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goldman, S.M. Environmental toxins and Parkinson’s disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 54, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Zafar, M.; Lettenberger, S.E.; Pawlik, M.E.; Kinel, D.; Frissen, M.; Schneider, R.B.; Kieburtz, K.; Tanner, C.M.; De Miranda, B.R.; et al. Trichloroethylene: An Invisible Cause of Parkinson’s Disease? J. Parkinsons Dis. 2023, 13, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abdelhak, A.; Antweiler, K.; Kowarik, M.C.; Senel, M.; Havla, J.; Zettl, U.K.; Kleiter, I.; Skripuletz, T.; Haarmann, A.; Stahmann, A.; et al. Serum glial fibrillary acidic protein and disability progression in progressive multiple sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2024, 11, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Portera, A.; Franch, O.; Del Ser, T. Neuromuscular manifestations of the Toxic Oil Syndrome. In Clinical and Biological Aspects of the Peripheral Nervous Diseases; Battistin, L., Hashim, G., Lajtha, A., Eds.; Alan R. Liss: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ladona, M.G.; Izquierdo-Martinez, M.; Posada de la Paz, M.P.; de la Torre, R.; Ampurdanés, C.; Segura, J.; Sanz, E.J. Pharmacogenetic profile of xenobiotic enzyme metabolism in survivors of the Spanish toxic oil syndrome. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Arranz, J.; Zhu, N.; Rubio-Guerra, S.; Rodríguez-Baz, Í.; Ferrer, R.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Barroeta, I.; Illán-Gala, I.; Santos-Santos, M.; Fortea, J.; et al. Diagnostic performance of plasma pTau217, pTau181, Aβ1-42 and Aβ1-40 in the LUMIPULSE automated platform for the detection of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 139, Erratum in Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rissin, D.M.; Kan, C.W.; Campbell, T.G.; Howes, S.C.; Fournier, D.R.; Song, L.; Piech, T.; Patel, P.P.; Chang, L.; Rivnak, A.J.; et al. Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Quanterix Corporation. SIMOA GFAP Discovery Kit HD-1/HD-X: Data Sheet. Rev03; Quanterix: Billerica, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.quanterix.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Simoa_GFAP_Data_Sheet_HD-1_HD-X_Rev03.pdf (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Arcaro, M.; Fenoglio, C.; Serpente, M.; Arighi, A.; Fumagalli, G.G.; Sacchi, L.; Floro, S.; D’Anca, M.; Sorrentino, F.; Visconte, C.; et al. A Novel Automated Chemiluminescence Method for Detecting Cerebrospinal Fluid Amyloid-Beta 1-42 and 1-40, Total Tau and Phosphorylated-Tau: Implications for Improving Diagnostic Performance in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fujirebio Europe, N.V. LUMIPULSE G600II: High-Throughput Immunoassay Analyzer; Fujirebio: Gent, Belgium, 2025; Available online: https://www.fujirebio.com/en/products-solutions/lumipulse-g600ii (accessed on 3 April 2025).
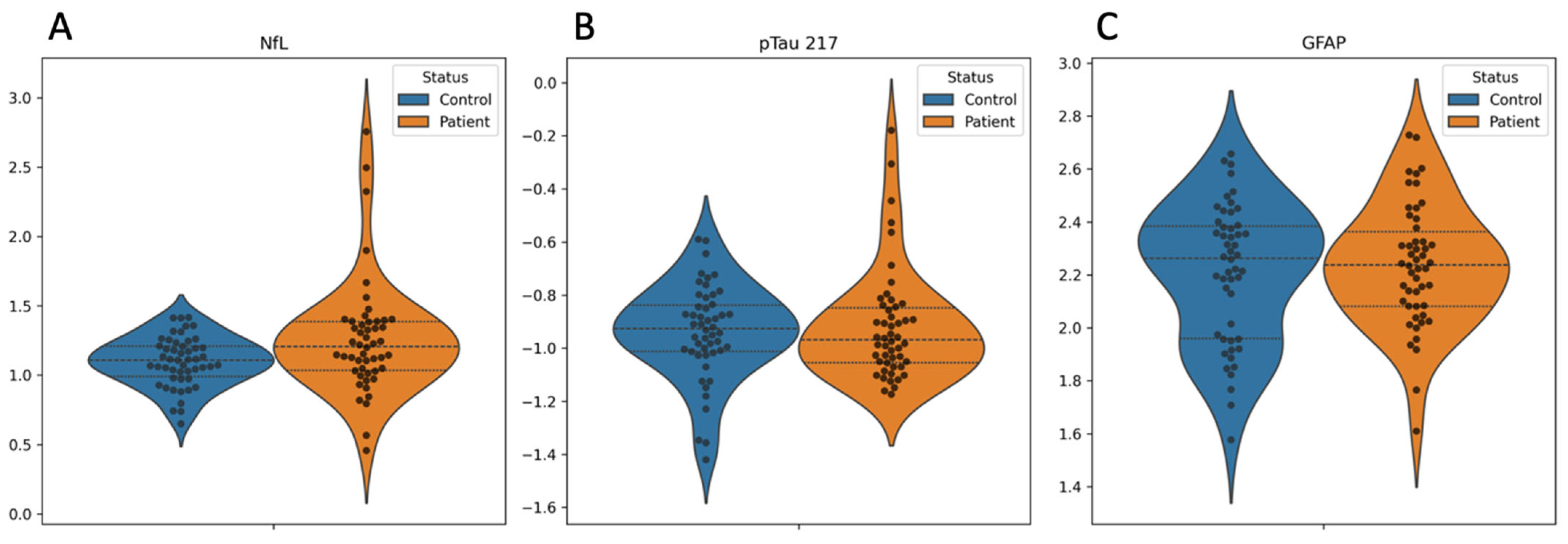

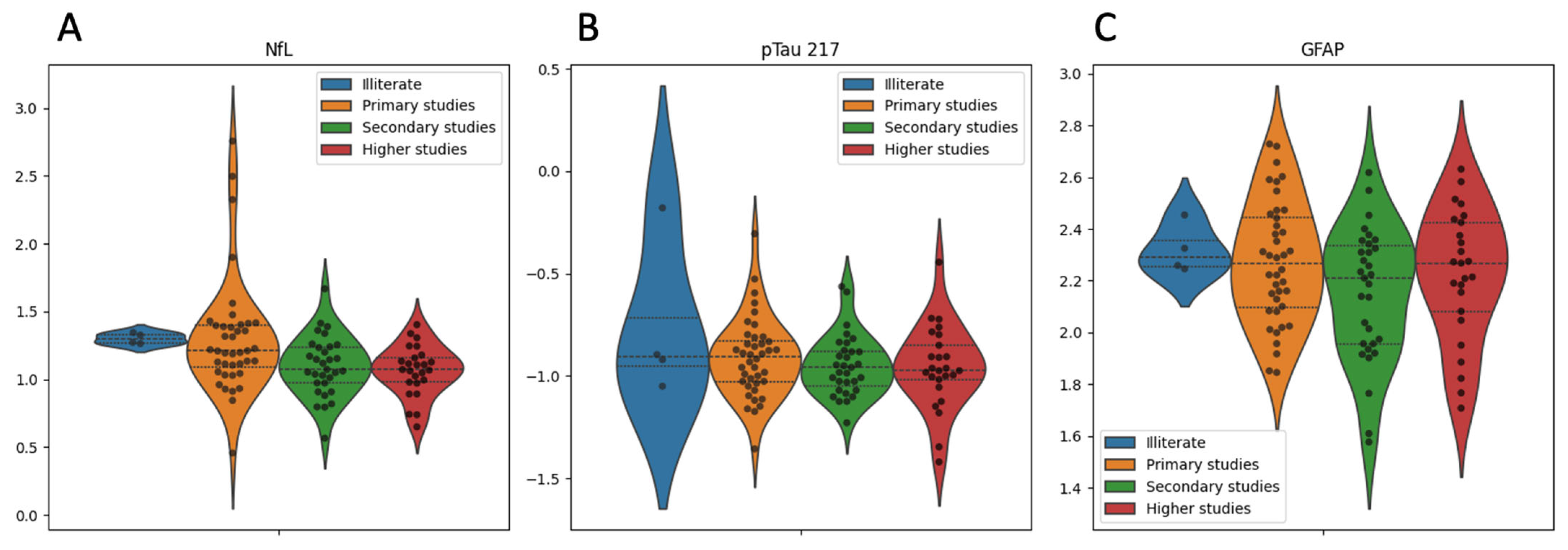
| Variable | Overall | Controls | Patients | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 100 | 50 | 50 | |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.284 a | |||
| Male | 32 (32.0) | 19 (38.0) | 13 (26.0) | |
| Female | 68 (68.0) | 31 (62.0) | 37 (74.0) | |
| Age, mean (SD) | 59.3 (8.0) | 58.7 (8.2) | 59.9 (7.8) | 0.449 b |
| Education, n (%) | 0.161 a | |||
| Illiterate | 4 (4.0) | 1 (2.0) | 3 (6.0) | |
| Primary | 40 (40.0) | 19 (38.0) | 21 (42.0) | |
| Secondary | 31 (31.0) | 13 (26.0) | 18 (36.0) | |
| Higher education | 25 (25.0) | 17 (34.0) | 8 (16.0) | |
| Diabetes mellitus, N (%) | 15 (15.0) | 3 (6.0) | 12 (24.0) | 0.025 a |
| Arterial hypertension, N (%) | 42 (42.0) | 9 (18.0) | 33 (66.0) | <0.001 a |
| Polyneuropathy, N (%) | 35 (35.0) | 0 (0.0) | 35 (70.0) | <0.001 a |
| Cognitive complaints, N (%) | 48 (48.0) | 11 (22.0) | 37 (74.0) | <0.001 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Ortiz, M.; Lapeña-Motilva, J.; Giménez de Bejar, V.; Bartolomé, F.; Alquézar, C.; Martínez-Castillo, M.; Wagner-Reguero, S.; del Ser, T.; Nogales, M.A.; Álvarez-Sesmero, S.; et al. Blood Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration over Four Decades After Toxic Oil Syndrome: A Case-Control Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115122
Ruiz-Ortiz M, Lapeña-Motilva J, Giménez de Bejar V, Bartolomé F, Alquézar C, Martínez-Castillo M, Wagner-Reguero S, del Ser T, Nogales MA, Álvarez-Sesmero S, et al. Blood Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration over Four Decades After Toxic Oil Syndrome: A Case-Control Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115122
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Ortiz, Mariano, José Lapeña-Motilva, Verónica Giménez de Bejar, Fernando Bartolomé, Carolina Alquézar, Minerva Martínez-Castillo, Sonia Wagner-Reguero, Teodoro del Ser, María Antonia Nogales, Sonia Álvarez-Sesmero, and et al. 2025. "Blood Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration over Four Decades After Toxic Oil Syndrome: A Case-Control Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115122
APA StyleRuiz-Ortiz, M., Lapeña-Motilva, J., Giménez de Bejar, V., Bartolomé, F., Alquézar, C., Martínez-Castillo, M., Wagner-Reguero, S., del Ser, T., Nogales, M. A., Álvarez-Sesmero, S., Morales, M., García-Cena, C., & Benito-León, J. (2025). Blood Biomarkers of Neurodegeneration over Four Decades After Toxic Oil Syndrome: A Case-Control Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115122









