Polygonum multiflorum Inhibits Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis in PM2.5-Induced Dysfunction Through the Regulation of the TLR4/TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bioactive Constituents of EPM
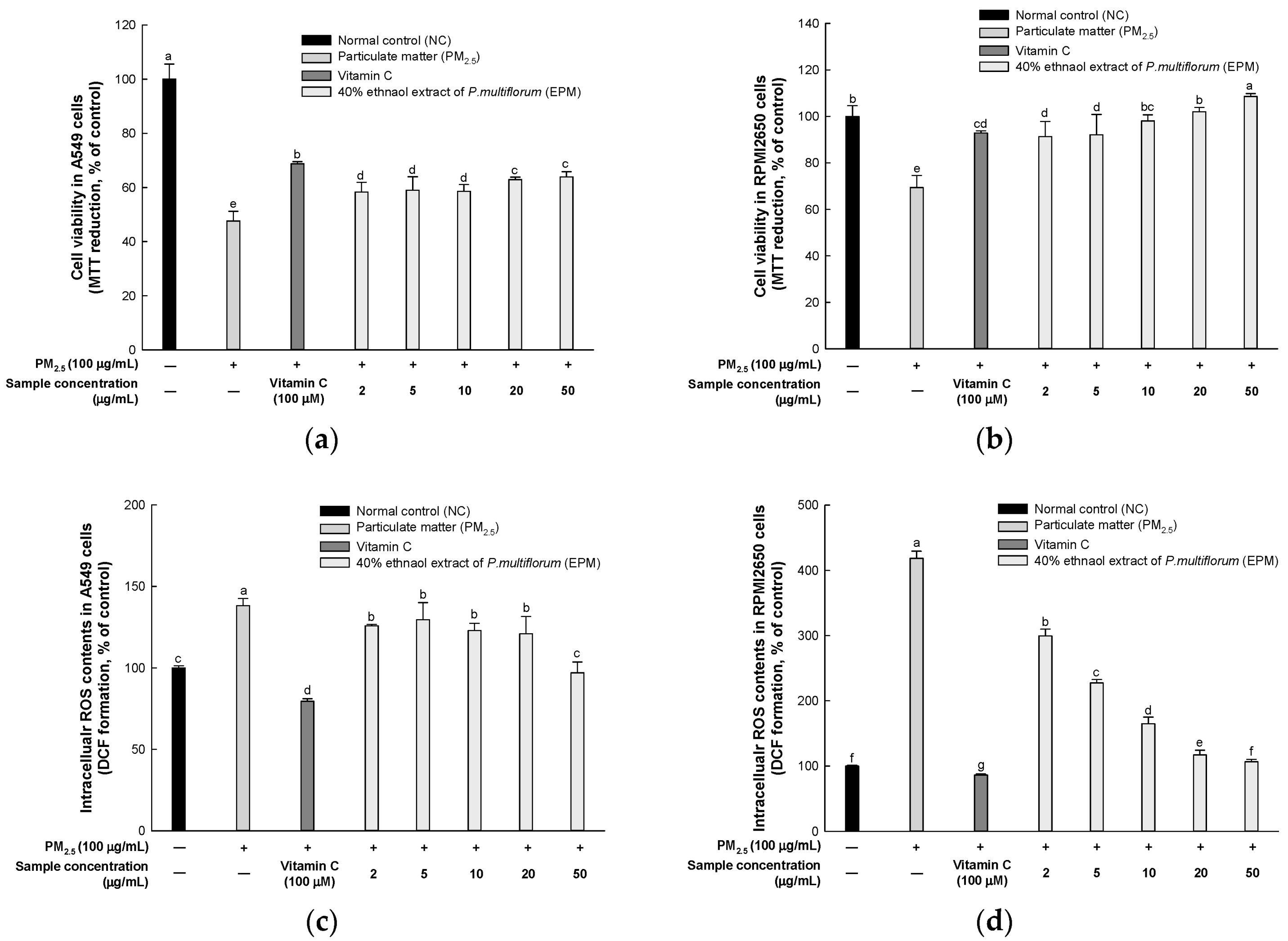
2.2. EPM Improved PM2.5-Induced Cytotoxicity in A549 and RPMI2650 Cells
2.3. EPM Alleviated the Antioxidant System in PM2.5-Induced Pulmonary Dysfunction
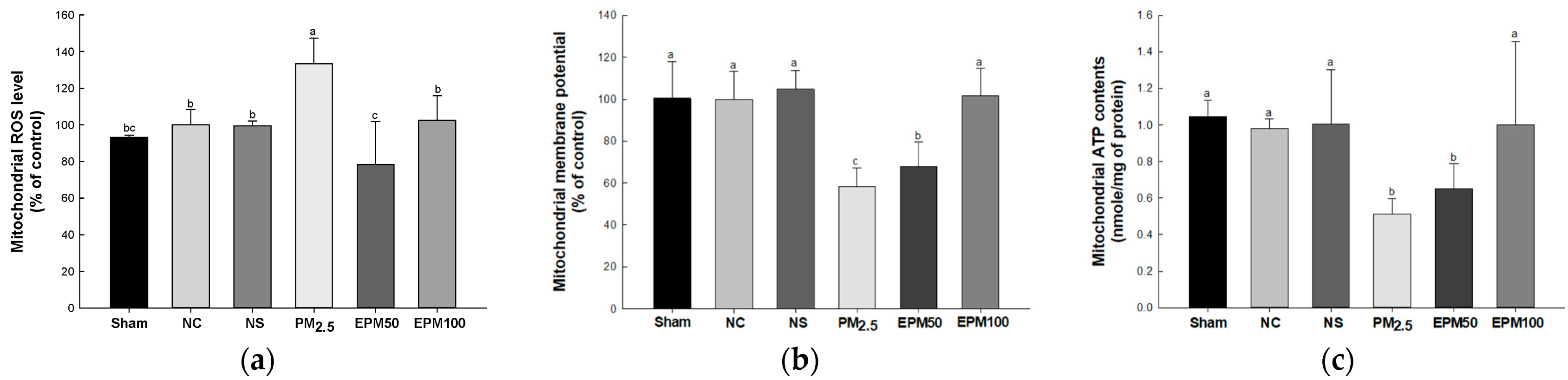
2.4. EPM Improved Mitochondrial Function in PM2.5-Induced Pulmonary Dysfunction
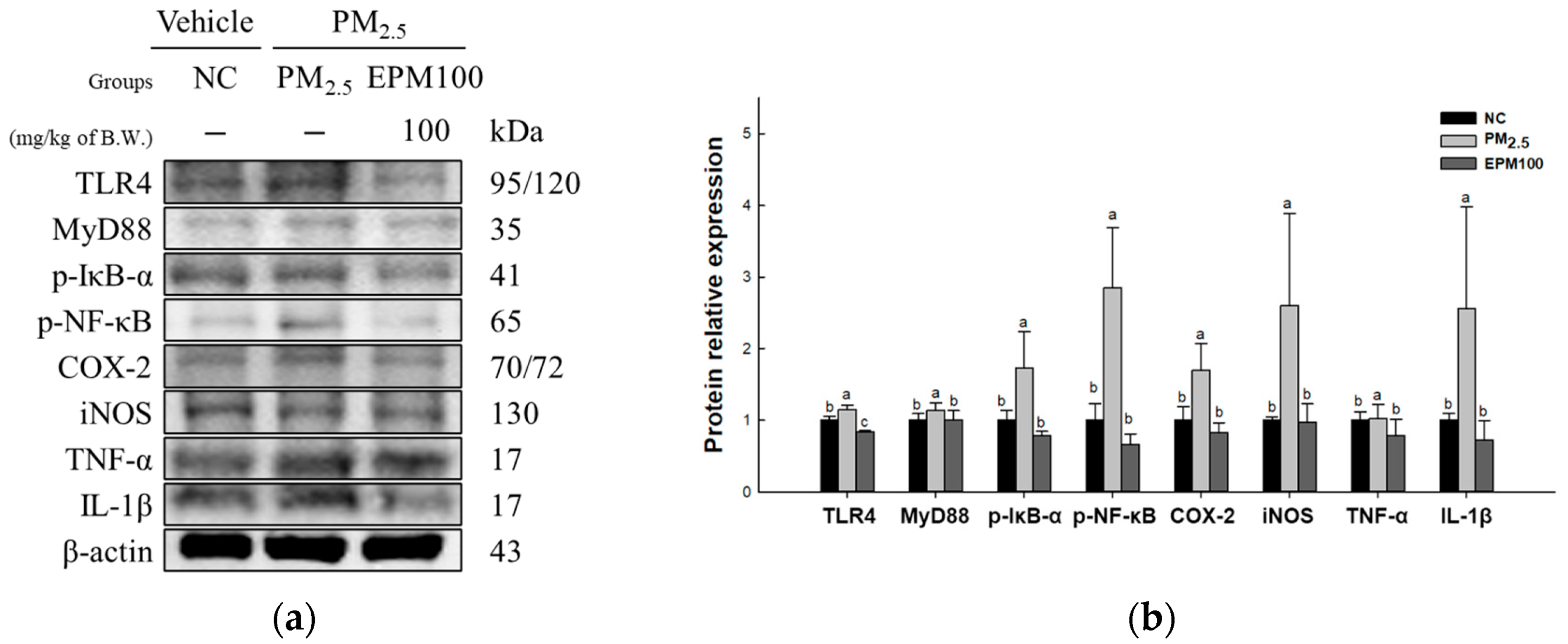
2.5. EPM Inhibited Inflammation in PM2.5-Induced Pulmonary Dysfunction
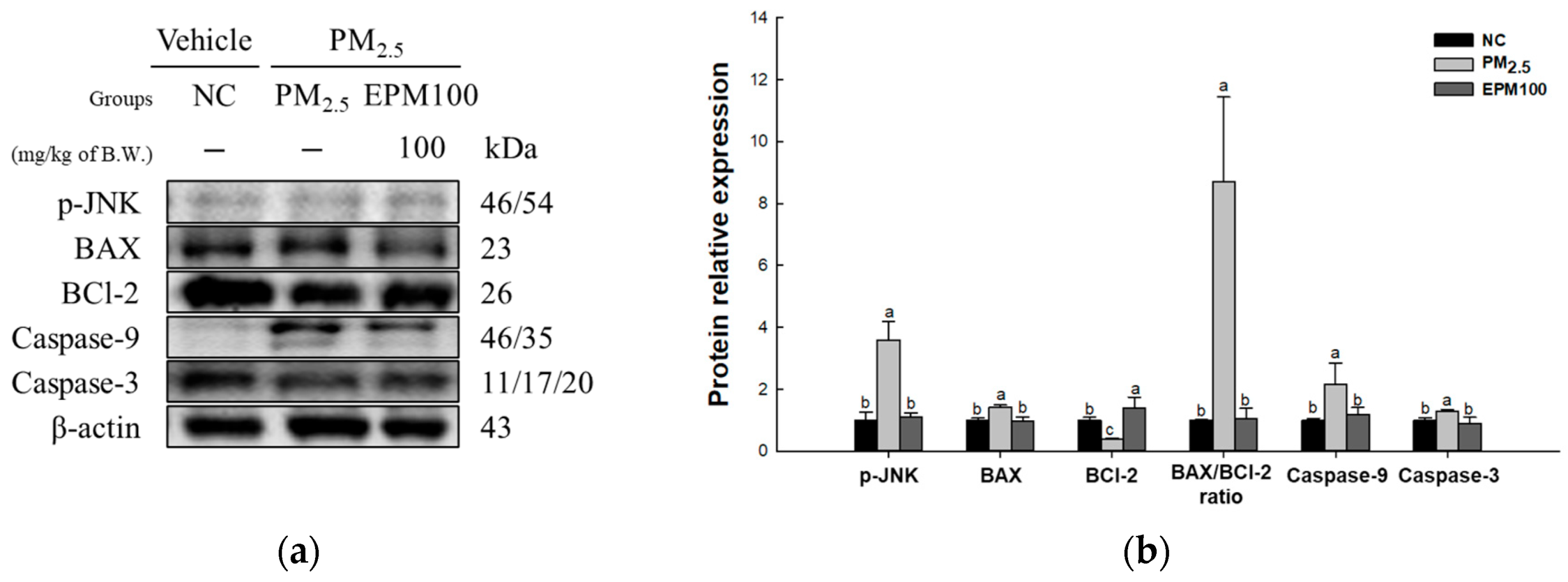
2.6. EPM Regulates Apoptosis in PM2.5-Induced Pulmonary Dysfunction
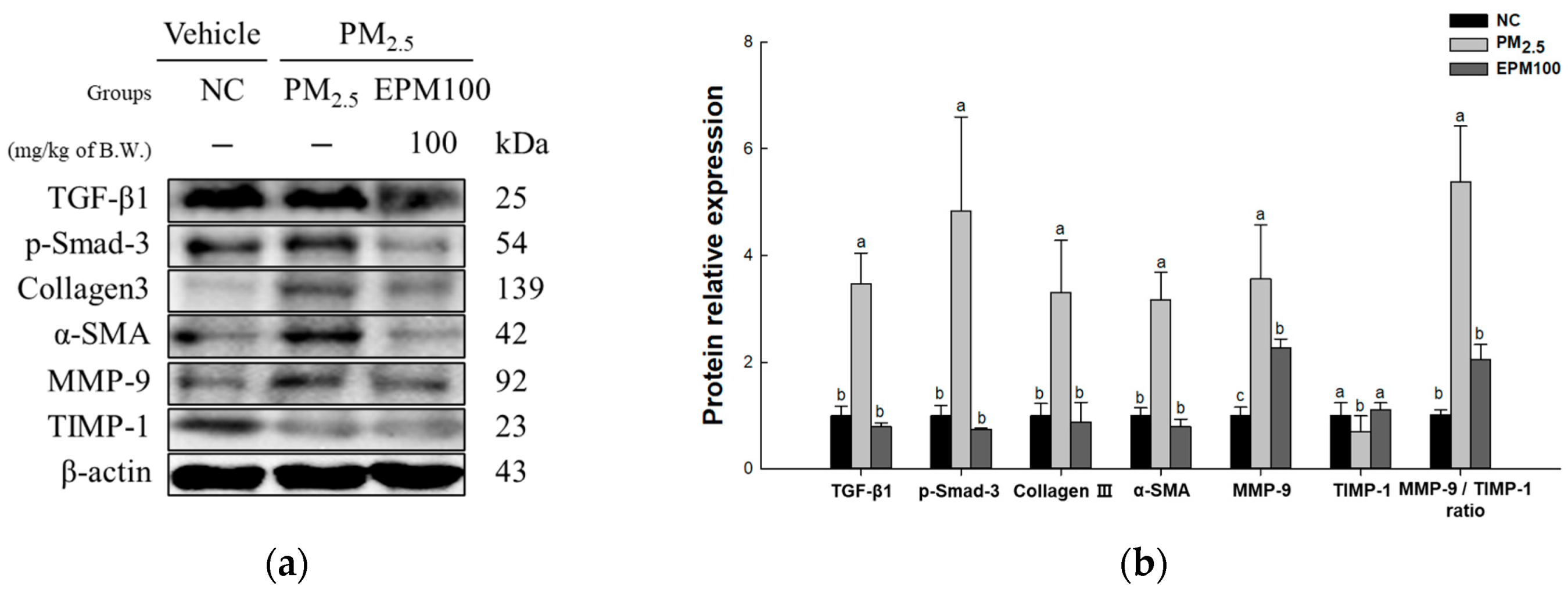
2.7. EPM Decreased Fibrosis in PM2.5-Induced Pulmonary Dysfunction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. Physiological Compound Analysis
4.3. Cytoprotective Effect of A549 and RPMI2650 Cells
4.4. Animals and Treatment
4.5. Pulmonary Antioxidant System
4.6. Pulmonary Mitochondrial Function
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| p-IκB-α | Phospho-nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor-alpha |
| p-NF-κB | Phospho-nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| p-JNK | Phospho-c-Jun N-terminal kinases |
| BCl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BAX | Bcl 2-associated X |
| p-Smad-3 | Phospho-suppressor of mothers against decapentaplegic-3 |
| MMP-9 | Metalloproteinase-9 |
| TIMP-1 | Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein1 |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| α-SMA | Alpha-smooth muscle actin |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2 |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
References
- Wang, Q.; Liu, S. The effects and pathogenesis of PM2.5 and its components on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2023, 18, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangavel, P.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Recent insights into particulate matter (PM2.5)-mediated toxicity in humans: An overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelieveld, S.; Wilson, J.; Dovrou, E.; Mishra, A.; Lakey, P.S.; Shiraiwa, M.; Poschl, U.; Berkemeier, T. Hydroxyl radical production by air pollutants in epithelial lining fluid governed by interconversion and scavenging of reactive oxygen species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14069–14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, F.; Rui, W.; Long, F.; Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Chen, D.; Ding, W. PM2.5-induced oxidative stress triggers autophagy in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 1762–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Pu, W.; Wazir, J.; Jin, X.; Wei, L.; Song, S.; Su, Z.; Li, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H. Long-term exposure to PM2.5 aggravates pulmonary fibrosis and acute lung injury by disrupting Nrf2-mediated antioxidant function. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Gao, M.; Shi, X.; Yin, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, R.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Xu, S. Quercetin attenuates SiO2-induced ZBP-1-mediated PANoptosis in mouse neuronal cells via the ROS/TLR4/NF-κB pathway. J. Environ. Manage. 2024, 370, 122948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-M.; Pravia, K.G. Oxidative stress and glutathione in TGF-β-mediated fibrogenesis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Askari, A.; Shoorei, H.; Seify, M.; Koohestanidehaghi, Y.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Samsami, M. Antioxidant therapy against TGF-β/SMAD pathway involved in organ fibrosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.L.; Kim, J.M.; Go, M.J.; Kim, T.Y.; Joo, S.G.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Heo, H.J. Protective effect of Lonicera japonica on PM2.5-induced pulmonary damage in BALB/c mice via the TGF-β and NF-κB pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Teng, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L. Association between dietary antioxidant intakes and chronic respiratory diseases in adults. World Allergy Organ. J. 2024, 17, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teka, T.; Wang, L.; Gao, J.; Mou, J.; Pan, G.; Yu, H.; Gao, X.; Han, L. Polygonum multiflorum: Recent updates on newly isolated compounds, potential hepatotoxic compounds and their mechanisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 271, 113864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Praveen, N.; Kim, E.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Chung, I.-M. Production of anthraquinones, phenolic compounds and biological activities from hairy root cultures of Polygonum multiflorum thunb. Protoplasma 2014, 251, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-L.; Wang, C.-N.; Tsai, H.-C.; Chiu, C.-L.; Liu, L.F.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wu, R. Polygonum multiflorum decreases airway allergic symptoms in a murine model of asthma. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Son, H.; Hwang, C.E.; Cho, K.M.; Park, S.W.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.J. The Root of Polygonum multiflorum Thunb. alleviates non-alcoholic steatosis and insulin resistance in high fat diet-fed mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-P.; Li, Y.-J.; Wang, T.; Tao, Y.-X.; Zhang, M.; Gu, W.; Yu, J.; Yang, X.-X. In vivo recognition of bioactive substances of Polygonum multiflorum for protecting mitochondria against metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L. Oxidative stress is the pivot for PM2.5-induced lung injury. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 184, 114362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Ni, B.; Lin, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Yin, X.; Qu, C.; Ni, J. Traditional usages, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Polygonum multiflorum thunb.: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 159, 158–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Gu, X.; Tang, J.; Ho, C.-T. Antioxidant activity of stilbene glycoside from Polygonum multiflorum thunb in vivo. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1678–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, H.; Yee, S.-T. The protective effects of 2, 3, 5, 4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d-glucoside in the OVA-induced asthma mice model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, X.; Gui, J.; Wan, Y.; Chen, J.; Tan, T.; Liu, F.; Guo, L. Ultrasonic solvent extraction followed by dispersive solid phase extraction (d-SPE) cleanup for the simultaneous determination of five anthraquinones in Polygonum multiflorum by UHPLC-PDA. Foods 2022, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Quan, Y.; Gong, L.; Gong, X.; Li, Y. A review of the processed Polygonum multiflorum (thunb.) for hepatoprotection: Clinical use, pharmacology and toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 261, 113121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Han, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, J. Protective effects of 2, 3, 5, 4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-beta-d-glucoside, an active component of Polygonum multiflorum thunb, on experimental colitis in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 578, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Gao, X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Song, W.; Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Kou, X. Biochanin A alleviates oxidative damage caused by the urban particulate matter. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, L.; Su, B.; Tian, D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, S. Overexpression of HO-1 assisted PM2.5-induced apoptosis failure and autophagy-related cell necrosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.; Tan, J.; Zhong, S.; Lai, L.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J.; Yi, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Tang, T. Nrf2 mitigates prolonged PM2.5 exposure-triggered liver inflammation by positively regulating SIKE activity: Protection by juglanin. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ju, Y.; Yan, Z.; Ji, M.; Yang, M.; Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Sun, G. Protective role of wogonin following traumatic brain injury by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis via the PI3K/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Sui, J.; Fan, R.; Qu, W.; Dong, X.; Sun, D. Emodin protects against acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury by inhibiting NLPR3 inflammasome activation via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 1971–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.B. Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Lv, S.; Ma, R.; Qi, Y.; Abulikemu, A.; Duan, H.; Guo, C.; Li, Y. PM2.5 triggered apoptosis in lung epithelial cells through the mitochondrial apoptotic way mediated by a ROS-DRP1-mitochondrial fission axis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.; Xu, F.; Shemesh, M.; Qiu, X.; Barak, Y.; Zhu, T.; Rudich, Y. Nrf2 protects against diverse PM2.5 components-induced mitochondrial oxidative damage in lung cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Song, J.; Hu, P.; Zhu, Y. Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside (TSG) restores the effect of transient hypoxia on reperfusion injury in senescent H9c2 cells by regulating mitochondrial energy metabolism. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 2545024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.-y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sun, X.-J.; Li, L. Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside protects against sodium azide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in human neuroblastoma cells. Chin. Herb. Med. 2021, 13, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Xin, L. PM2.5 induces inflammatory responses via oxidative stress-mediated mitophagy in human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Res. 2022, 11, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Yu, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Kou, X. Amelioration of PM2.5-induced lung toxicity in rats by nutritional supplementation with biochanin A. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 202, 110878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Pei, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z. Astragaloside IV alleviates PM2.5-induced lung injury in rats by modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 91, 107290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; You, S.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Yin, J.; Shi, Y.; Qi, L.; Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, S. Effect of TLR4/MyD88/NF-kB axis in paraventricular nucleus on ventricular arrhythmias induced by sympathetic hyperexcitation in post-myocardial infarction rats. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 2959–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, M.J. Nano-gold displayed anti-inflammatory property via NF-kB pathways by suppressing COX-2 activity. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.-F.; Guan, S.-Y.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.-J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, X.-X.; Guo, G.-D.; Zhao, M.-G.; Yang, Q.; Liu, G. Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside relieves the chronic inflammatory pain by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis, microglia activation, and GluN2B overexpression in anterior cingulate cortex. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918814367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, B.; Sun, T.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, B.; Li, C.; Wan, H.; Ding, Z. Investigation on the mechanism of 2, 3, 4′, 5-tetrahydroxystilbene 2-o-D-glucoside in the treatment of inflammation based on network pharmacology. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 145, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morioka, S.; Broglie, P.; Omori, E.; Ikeda, Y.; Takaesu, G.; Matsumoto, K.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J. TAK1 kinase switches cell fate from apoptosis to necrosis following TNF stimulation. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 204, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yin, X.; Huang, X.; Guo, Q.; Ma, M.; Guo, L. Astragaloside IV ameliorates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction by regulating NOX4/JNK/BAX pathway. Life Sci. 2022, 310, 121123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-L.; Hu, R.-C.; Dai, A.-G.; Tan, S.-X.; Xu, M.; Kong, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-R.; Fu, D.-Y. CHOP overexpression sensitizes human non-small cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin treatment by Bcl-2/JNK pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 6279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nazeri, M.; Mirzaie-Asl, A.; Saidijam, M.; Moradi, M. Methanolic extract of Artemisia absinthium prompts apoptosis, enhancing expression of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, cell cycle arrest, caspase-3 activation and mitochondrial membrane potential destruction in human colorectal cancer HCT-116 cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 8831–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gu, J.; Wu, P.-F.; Wang, F.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, Y.-J.; Wu, W.-N.; Dong, L.-D.; Chen, J.-G. Protection by tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside against cerebral ischemia: Involvement of JNK, SIRT1, and NF-κB pathways and inhibition of intracellular ROS/RNS generation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwanabol, P.A.; Seedial, S.M.; Zhang, F.; Shi, X.; Si, Y.; Liu, B.; Kent, K.C. TGF-β and Smad3 modulate PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H2211–H2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.h.; Liu, L.J.; Lv, B.; Che, C.L.; Fan, D.P.; Wang, L.F.; Zhang, Y.M. Inhibition of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells might be mediated by decreasing MMP9, TIMP-1, INF-γ and TGF-β. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2015, 33, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mack, J.A.; Maytin, E.V. CD44 inhibits α-SMA gene expression via a novel G-actin/MRTF-mediated pathway that intersects with TGFβR/p38MAPK signaling in murine skin fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 12779–12794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.J.; Senior, R.M. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in lung remodeling. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 28, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esa, S.A.; Rawy, A.M.; EL-Behissy, M.M.; Kamel, M.H.; El-Hwaitty, H.M.M.M. Study of the level of sputum matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in COPD patients. Egypt. J. Chest. Dis. Tuberc. 2014, 63, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, C.H.; Li, F.; Zhu, W.Z. 2, 3, 4′, 5-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d-glucoside suppresses matrix metalloproteinase expression and inflammation in atherosclerotic rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2008, 35, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Kang, J.Y.; Park, S.K.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, H.L.; Jeong, H.R.; Kim, J.C.; Heo, H.J. Powdered green tea (matcha) attenuates the cognitive dysfunction via the regulation of systemic inflammation in chronic PM2.5-exposed BALB/c mice. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambient (Outdoor) Air Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health (accessed on 30 March 2025).
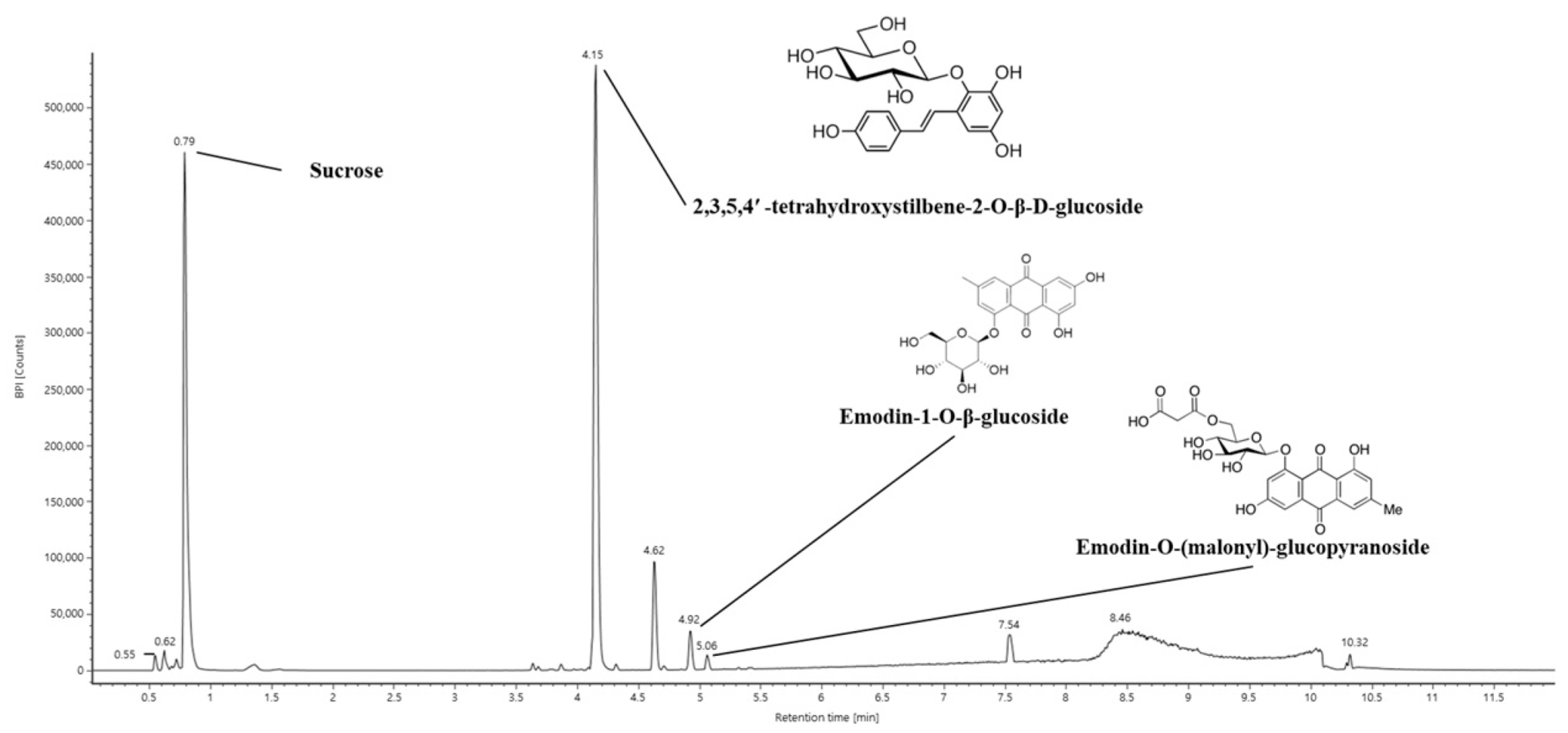

| No. | Retention Time (min) | Parent Ion (m/z) | MSE Fragment (m/z) | Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.79 | 341 | 179, 161, 143, 119 | Sucrose |
| 2 | 4.15 | 405 | 243, 225, 215, 149 | 2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside |
| 3 | 4.62 | 301 | 283, 259, 268, 151 | Unknown |
| 4 | 4.92 | 431 | 269, 240, 225 | Emodin-1-O-β-glucoside |
| 5 | 5.06 | 517 | 473, 269, 225 | Emodin-O-(malonyl)-glucopyranoside |
| Antibody | Catalog NO. | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | sc-69879 | |
| TLR4 | sc-293072 | |
| MyD88 | sc-74532 | |
| p-IκB-α | sc-8404 | |
| p-NF-κB | sc-136548 | |
| TNF-α | sc-33639 | |
| IL-1β | sc-515598 | |
| p-JNK | sc-6254 | |
| BCl-2 | sc-7382 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) |
| BAX | sc-7480 | |
| Caspase-9 | sc-56076 | |
| Caspase-3 | sc-56053 | |
| TGF-β1 | sc-130348 | |
| p-Smad-3 | sc-517575 | |
| MMP-9 | sc-13520 | |
| TIMP-1 | sc-21734 | |
| Keap1 | sc-514914 | |
| HO-1 | sc-136960 | |
| COX-2 | ab15191 | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) |
| Collagen III | ab184993 | |
| α-SMA | ab5694 | |
| Nrf2 | ab62352 | |
| iNOS | 18985-1-AP | Proteintech (Rosemont, IL, USA) |
| Goat-anti-rabbit IgG | #7074 | Cell Signaling Tech (Rosemont, IL, USA) |
| Goat-anti-mouse IgG | #1724044 | Bio-Rad (Richmond, CA, USA) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.J.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, I.Y.; Heo, H.J. Polygonum multiflorum Inhibits Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis in PM2.5-Induced Dysfunction Through the Regulation of the TLR4/TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115080
Choi HJ, Lee HL, Kim IY, Heo HJ. Polygonum multiflorum Inhibits Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis in PM2.5-Induced Dysfunction Through the Regulation of the TLR4/TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115080
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hye Ji, Hyo Lim Lee, In Young Kim, and Ho Jin Heo. 2025. "Polygonum multiflorum Inhibits Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis in PM2.5-Induced Dysfunction Through the Regulation of the TLR4/TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115080
APA StyleChoi, H. J., Lee, H. L., Kim, I. Y., & Heo, H. J. (2025). Polygonum multiflorum Inhibits Pulmonary Inflammation and Fibrosis in PM2.5-Induced Dysfunction Through the Regulation of the TLR4/TGF-β1 Signaling Pathway in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5080. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115080






