Genome-Wide Identification of the PR-1 Gene Family in Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge and Its Expression Analysis Under Fire Blight Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physicochemical Property Analysis of the Pb-PR-1 Gene Family Proteins
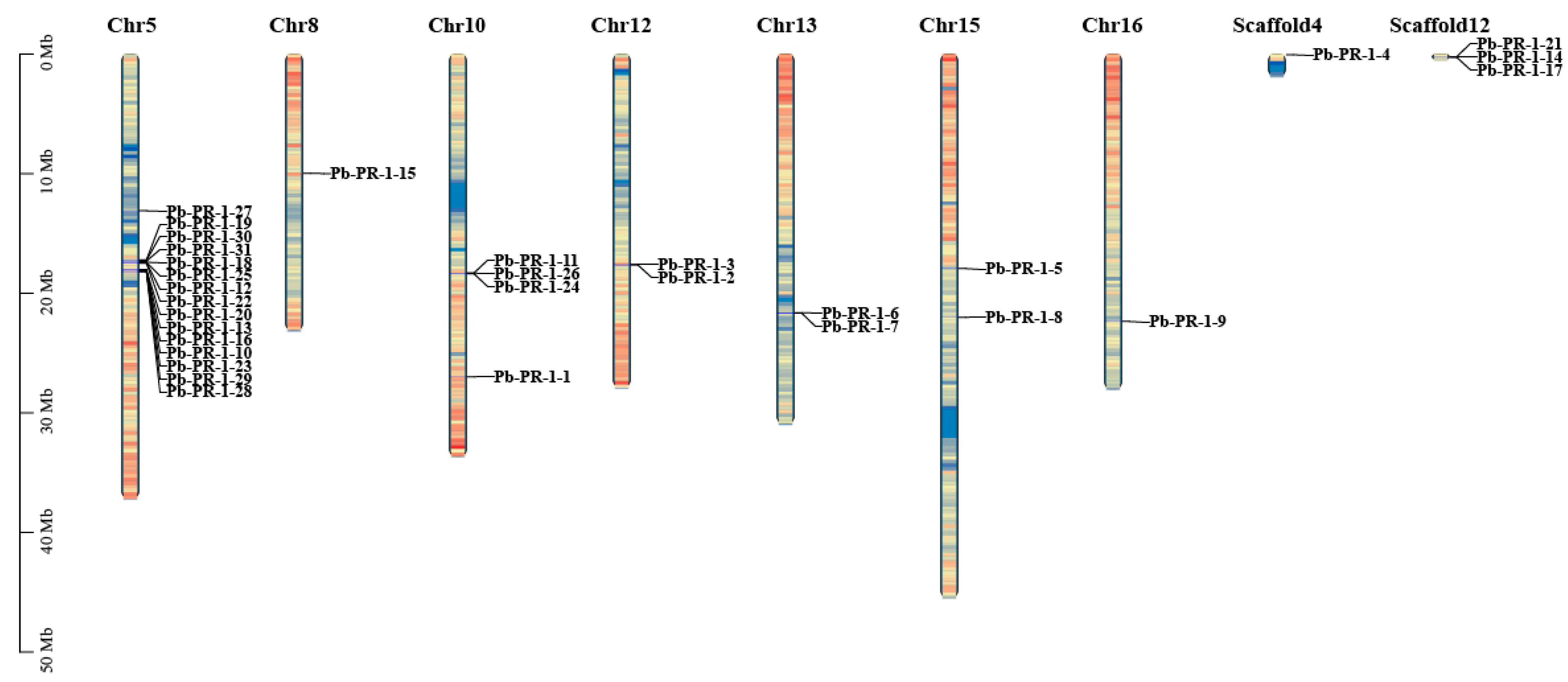
2.2. Chromosomal Localization of Pb-PR-1 Gene Family
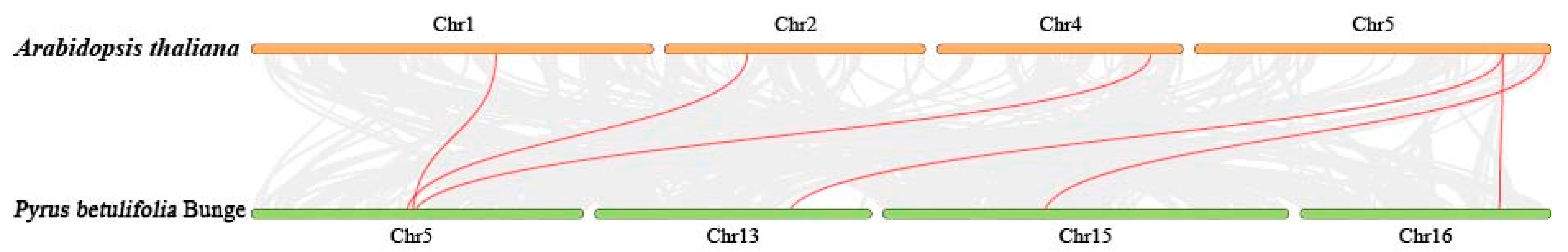
2.3. Gene Duplication and Collinearity Analysis of PbPR-1 Gene Family Members in Duli and Arabidopsis
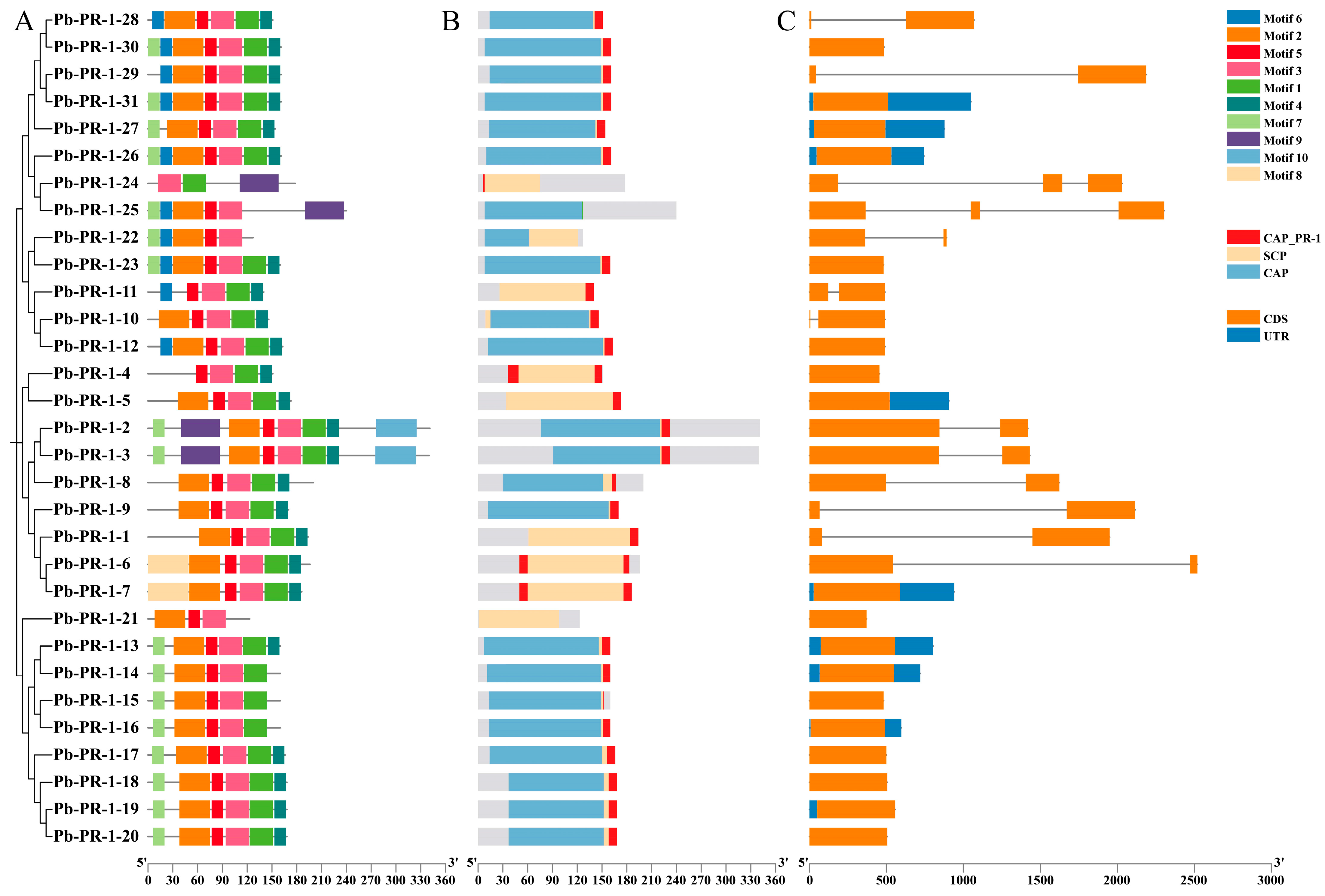
2.4. Phylogenetic Tree Analysis of Pb-PR-1 Gene Family Members
2.5. Analysis of Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs in the Pb-PR-1 Gene Family
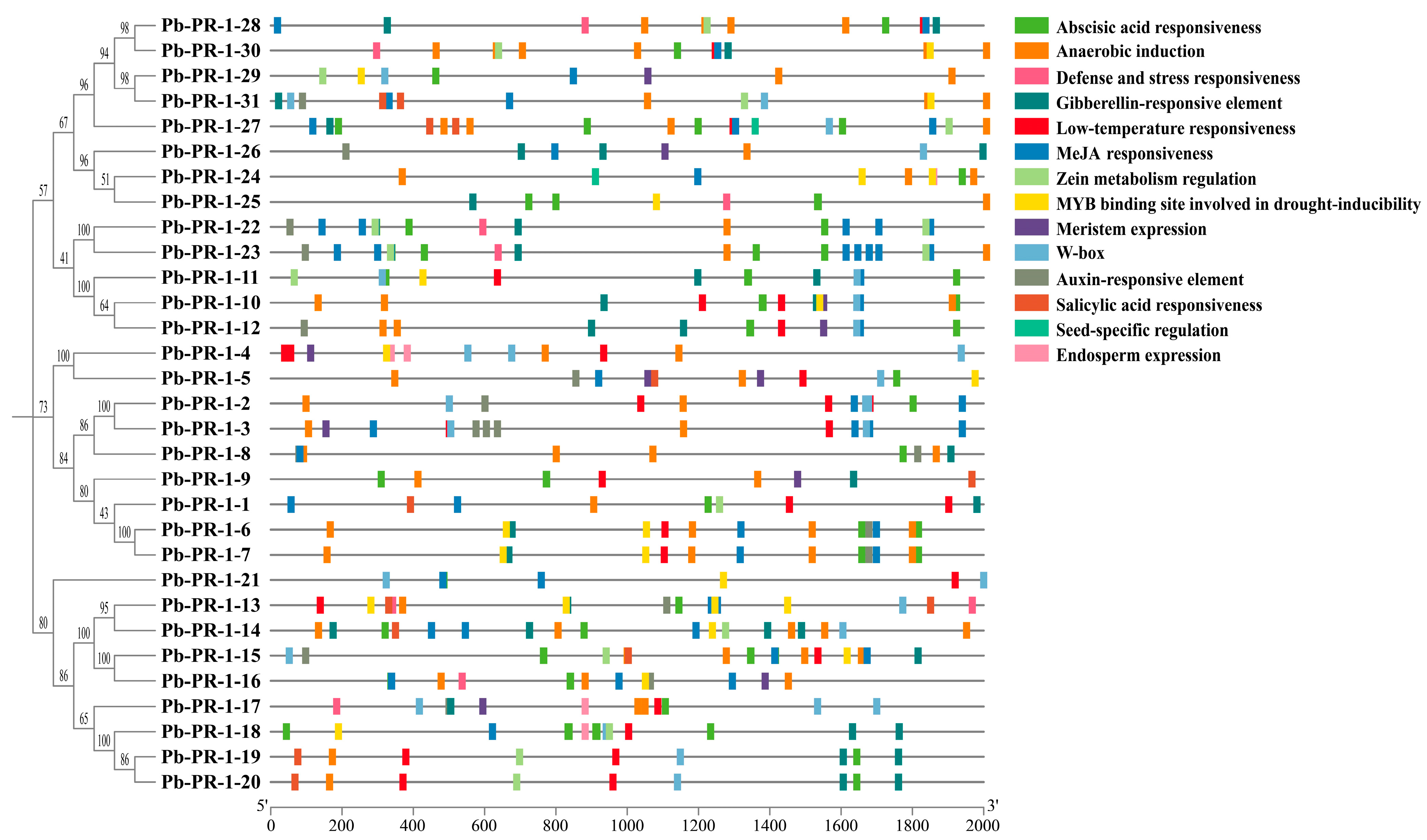
2.6. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter of Pb-PR-1 Gene Family Members
2.7. Secondary Structure Prediction and 3D Modeling of the Pb-PR-1 Gene Family Proteins
2.8. Phenotypic Analysis of Resistant and Susceptible Duli After Inoculation
2.9. Enzymatic Activity and MDA Content Analysis of Resistant and Susceptible Duli After Inoculation
2.10. Differential Expression Analysis of Pb-PR-1 Gene Family in Response to Fire Blight Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Physicochemical Property Analysis of the PR-1 Gene Family
4.2. Chromosomal Localization and Interspecific Collinearity Analysis of the Gene Family
4.3. Constructing a Phylogenetic Tree for the Gene Family
4.4. Conservation of PR-1 Protein Motifs, Gene Structure, and Protein Domain Analysis
4.5. Prediction of Cis-Acting Elements in the Gene Family
4.6. Prediction of Secondary Structure and 3D Modeling of Family Genes
4.7. Pathogen Activation
4.8. In Vitro Leaf Inoculation and Enzyme Activity Assay
4.9. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| POD | Peroxidase dismutase |
| PPO | Polyphenol oxidase |
| CAT | Catalas |
| PAL | Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| DL | Duli |
| RDL | Resistant Duli |
References
- Thomma, B.P.; Nürnberger, T.; Joosten, M.H. Of PAMPs and effectors: The blurred PTI-ETI dichotomy. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Loon, L.; Pierpoin, W.; Boller, T.; Conejero, V. Recommendations for naming plant pathogenesis-related proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1994, 12, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.; Singh, R.; Kushwaha, G.; Iqbal, N.; Singh, A.; Kaushik, S.; Kaur, P.; Sharma, S.; Singh, T.P. Current overview of allergens of plant pathogenesis-related protein families. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 543195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, C.; Franco, O. Pathogenesis-related proteins (PRs) with enzyme activity activating plant defense responses. Plants 2023, 12, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, O.; Shchennikova, A.; Kochieva, E.; Filyushin, M. Pathogenesis-related genes of PR1, PR2, PR4, and PR5 families are involved in the response to Fusarium infection in garlic (Allium sativum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Liu, F.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Kang, B. Zucchini yellow mosaic virus-induced hypersensitive response is associated with pathogenesis-related 1 protein expression and confers resistance in watermelon. Plant Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, L.; Van Kammen, A. Polyacrylamide disc electrophoresis of the soluble leaf proteins from Nicotiana tabacum var. ‘Samsun’ and ‘Samsun NN’: II. Changes in protein constitution after infection with tobacco mosaic virus. Virology 1970, 40, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Lin, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Fang, J.-B.; Sun, Y.; Sun, L.; Qi, X.; et al. Cloning and function analysis of PR-1 gene in Actinidia. J. Fruit Sci. 2024, 41, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarowar, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, E.N.; Kim, K.D.; Hwang, B.K.; Islam, R.; Shin, J.S. Overexpression of a pepper basic pathogenesis-related protein 1 gene in tobacco plants enhances resistance to heavy metal and pathogen stresses. Plant Cell Rep. 2005, 24, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, L.; Van Strien, E. The families of pathogenesis-related proteins, their activities, and comparative analysis of PR-1 type proteins. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1999, 55, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, K.; Pekkari, I.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Domain architecture conservation in orthologs. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Xiong, D.; Schneiter, R.; Tian, C. The function of plant PR1 and other members of the CAP protein superfamily in plant–pathogen interactions. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 24, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouman, W.; Anwar, F.; Gull, T.; Newton, A.; Rosa, E.; Domínguez-Perles, R. Profiling of polyphenolics, nutrients and antioxidant potential of germplasm’s leaves from seven cultivars of Moringa oleifera Lam. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 83, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajah, K.K. ROS Homeostasis in Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Bai, J.; Ahmad, B.; Rahman, M.U.; Chen, Q.; Wen, Z. Detached leaf assay-based screening of anthracnose resistant wild strawberry genotypes. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2024, 49, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Qi, F.; Liang, Y. Fuels for ROS signaling in plant immunity. Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zheng, S.; Jiang, D.; Lu, J.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhuang, C.; Li, J. Initiation and Execution of Programmed Cell Death and Regulation of Reactive Oxygen Species in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Tyagi, A.; Bae, H. ROS interplay between plant growth and stress biology: Challenges and future perspectives. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 203, 108032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dai, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Chen, J.; He, P.; Wang, F.; Ma, Y. The miR7125-MdARF1 module enhances the resistance of apple to Colletotrichum gloeosporioides by promoting lignin synthesis in response to salicylic acid signalling. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 22, 2741–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, N.; Yan, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, Q.S.; Li, X.G.; Chang, Y.H. Evaluation of disease resistance of four early ripe pear varieties to black spot disease and its relationship with antioxidant enzymes. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milčevičová, R.; Gosch, C.; Halbwirth, H.; Stich, K.; Hanke, M.V.; Peil, A.; Flachowsky, H.; Rozhon, W.; Jonak, C.; Oufir, M.; et al. Erwinia amylovora-induced defense mechanisms of two apple species that differ in susceptibility to fire blight. Plant Sci. 2010, 179, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, X.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Changes of Enzyme Activities Related to Resistance of Four Pear Rootstocks to Pear Fire Blight. Mol. Plant Breed. 2024, 1–16. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20220412.1028.010.html (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Shen, M.; Cai, C.; Song, L.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Wei, W.; Zhu, C. Effects of Free-air CO2 Enrichment and Temperature Increase on Related Proteins and Defense Enzymes in Plants Infected with Rice Sheath Blight. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2024, 61, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, L.; Ding, S.; Gao, M.; Yan, Y.; Yu, G.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, W. Plant PR1 rescues condensation of the plastid iron-sulfur protein by a fungal effector. Nat Plants 2024, 10, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Zwet, T.; Keil, H. Fire Blight: A Bacterial Disease of Rosaceous Plants; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1979; p. 510. [Google Scholar]
- Gusberti, M.; Klemm, U.; Meier, M.; Maurhofer, M.; Hunger-Glaser, I. Fire blight control: The struggle goes on. A comparison of different fire blight control methods in Switzerland with respect to biosafety, efficacy and durability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 11422–11447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sheng, Q.; Luo, M.; Ma, D.; Zhang, C. Occurrence characteristics and Control suggestions of fire blight on Korla Xiangli in Xinjiang. Plant Prot. 2022, 48, 207–213+231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ming, L.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, W. Progress in the occurrence and control of pear fire blight in China. Deciduous Fruits 2023, 55, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; He, Q.; Zhang, W. Efficacy of Different Control Measures against Pear Fire Blight in Orchards. Xinjiang Farm Res. Sci. Technol. 2023, 46, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhai, R.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, F.; Xu, L. Efficient Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation using cotyledons, hypocotyls and roots of ‘Duli’ (Pyrus betulifolia Bunge). Sci. Hortic. 2022, 296, 110906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, Q.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Luo, M. Resistance evaluation of 20 pear varieties (germplasms) in China to foreign strains of Erwinia amylovora. J. Fruit Sci. 2019, 36, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.B. Leaf Structure, Enzyme Activity and Transcriptome Analysis of Duli Pear (Pyrus Betulifolia Bunge) in Response to Erwinia Amylovora Infection. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Xinjiang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Pandey, S.; Pati, P.K. Interaction between pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins and phytohormone signaling pathways in conferring disease tolerance in plants. Physiol. Plant. 2025, 177, e70174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, S.; Williams, S.J.; Outram, M.; Kobe, B.; Solomon, P.S. Emerging in-sights into the functions of pathogenesis-related protein 1. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wei, B.; Li, C. Expression Patterns of Rice PR1 Family Genes in Response to Biotic Stresses. Mol. Plant Breed. 2024, 1–24. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.s.20230619.1458.002.html (accessed on 20 September 2024).
- Chen, N.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Shao, Q. Cloning Expression and Function Analysis Under Ralstonia solanacearum Stress of Pathogenesis-related Protein SlPR1b Gene in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 31, 2477–2489. [Google Scholar]
- Akbudak, M.; Yildiz, S.; Filiz, E. Pathogenesis related protein-1 (PR-1) genes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.): Bioinformatics analyses and expression profiles in response to drought stress. Genomics 2020, 112, 4089–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, F.; Venancio, T. Pathogenesis-related protein 1 (PR-1) genes in soybean: Genome-wide identification, structural analysis and expression profiling under multiple biotic and abiotic stresses. Gene 2022, 809, 146013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, C.; Yang, X.; Peng, L.; Lu, T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, F.; et al. Genome-wide identification of the mango pathogenesis-related 1 (PR1) gene family and functional analysis of MiPR1A genes in transgenic Arabidopsis. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 321, 112254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Bai, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, K.; Liang, J.; Shang, Q.; Sa, W.; Wang, L. Genome-wide analysis of pathogenesis-related protein-1 (PR-1) genes from Qingke (Hordeum vulgare L. var. nudum) reveals their roles in stress responses. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Friesen, T.L.; Faris, J.D. Molecular characterization and genomic mapping of the pathogenesis-related protein 1 (PR-1) gene family in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2011, 285, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuradha, C.; Chandrasekar, A.; Backiyarani, S.; Thangavelu, R.; Giribabu, P.; Uma, S. Genome-wide analysis of pathogenesis-related protein 1 (PR-1) gene family from Musa spp. and its role in defense response during stresses. Gene 2022, 821, 146334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; El-Sappah, A.; Ali, H.; Zandi, P.; Huang, Q.; Soaud, S.A.; Alazizi, E.M.Y.; Wafa, H.A.; Hossain, M.D.A.; Liang, Y. Pathogenesis-related proteins (PRs) countering environmental stress in plants: A review. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 160, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzosa, E.; Xia, Y. Independent effects of protein core size and expression on residue-level structure-evolution relationships. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pečenková, T.; Pleskot, R.; Žárský, V. Subcellular localization of Arabidopsis pathogenesis-related 1 (PR1) protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Meng, W.; Chen, G.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, A.; Xu, M.; Hu, G.; Tan, M.; Xiang, Z. The Regulation Mechanism of MYC on MeJA-Induced Flavonoids Synthesis in Dendrobium officinale. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 44, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.M.; Bordin, N.; Kandathil, S.M.; Sillitoe, I.; Waman, V.P.; Wells, J.; Orengo, C.A.; Jones, D.T. Exploring structural diversity across the protein universe with The Encyclopedia of Domains. Science 2024, 386, eadq4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, G.; Meng, W.; Lin, C.; Bao, H. Research progress on the underlying mechanisms of plant defense enzymes in response to pest stress. Yingyong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2018, 29, 4248–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Ma, R.; Wang, D.; Zhang, P. Evaluation of resistance of Xinjiang wild walnuts to walnut canker. J. Fruit Sci. 2022, 39, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jia, T. Association analysis of leaf structure and defense enzyme activity with fire blight resistance in different pear germplasms. China Fruits 2024, 10, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, S. Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Analysis of Pathogenesis-Related 1 (PR-1) Gene Family in Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) in Response to Blister-Blight Disease Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Mir, Z.A.; Tyagi, A.; Bhat, J.A.; Chandrashekar, N.; Papolu, P.K.; Rawat, S.; Grover, A. Identification and comparative analysis of Brassica juncea pathogenesis-related genes in response to hormonal, biotic and abiotic stresses. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.; Song, L.; Wu, W.; Chen, Y. Arabidopsis Di19 functions as a transcription factor and modulates PR1, PR2, and PR5 expression in response to drought stress. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1487–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Human Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

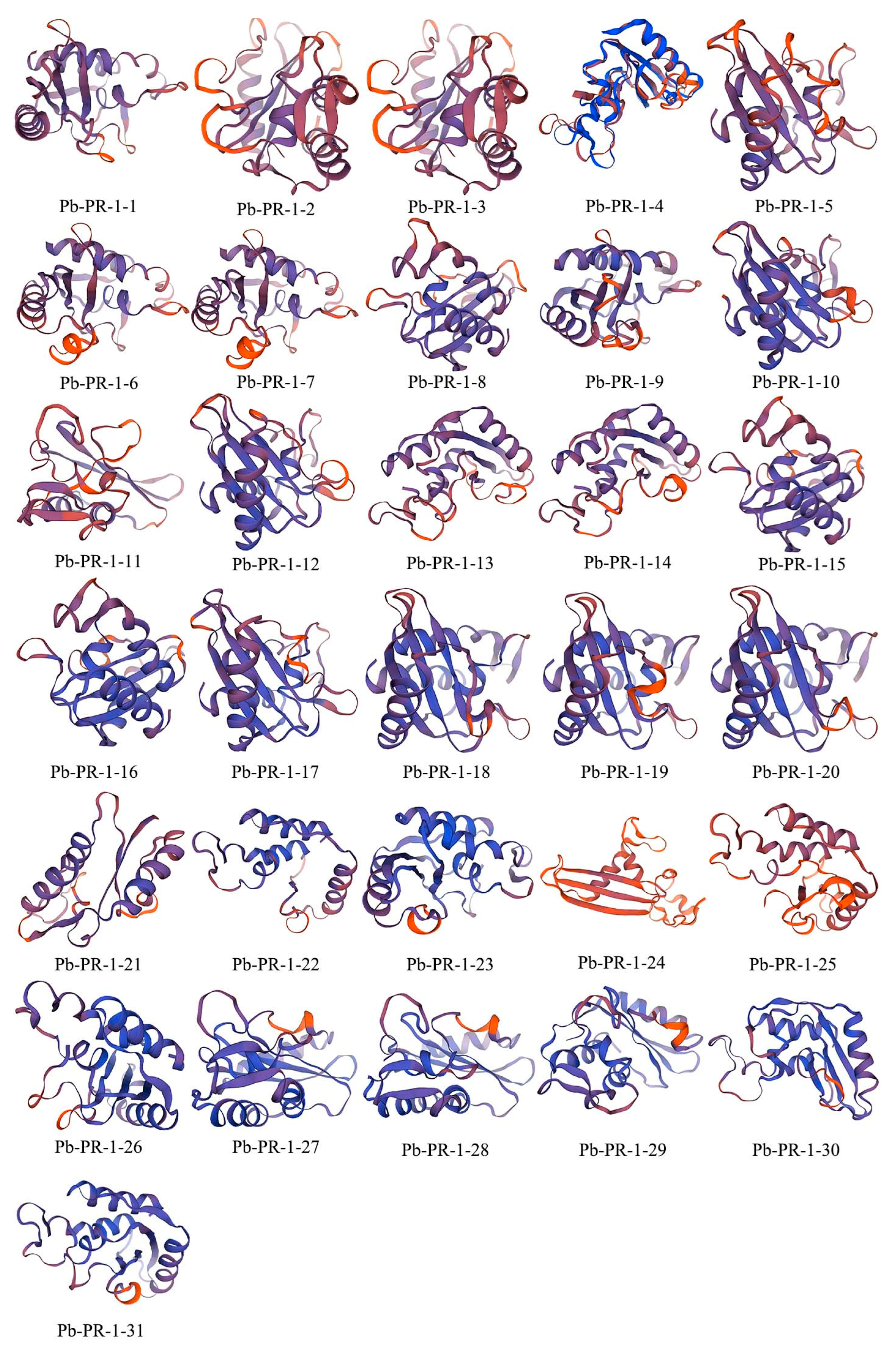
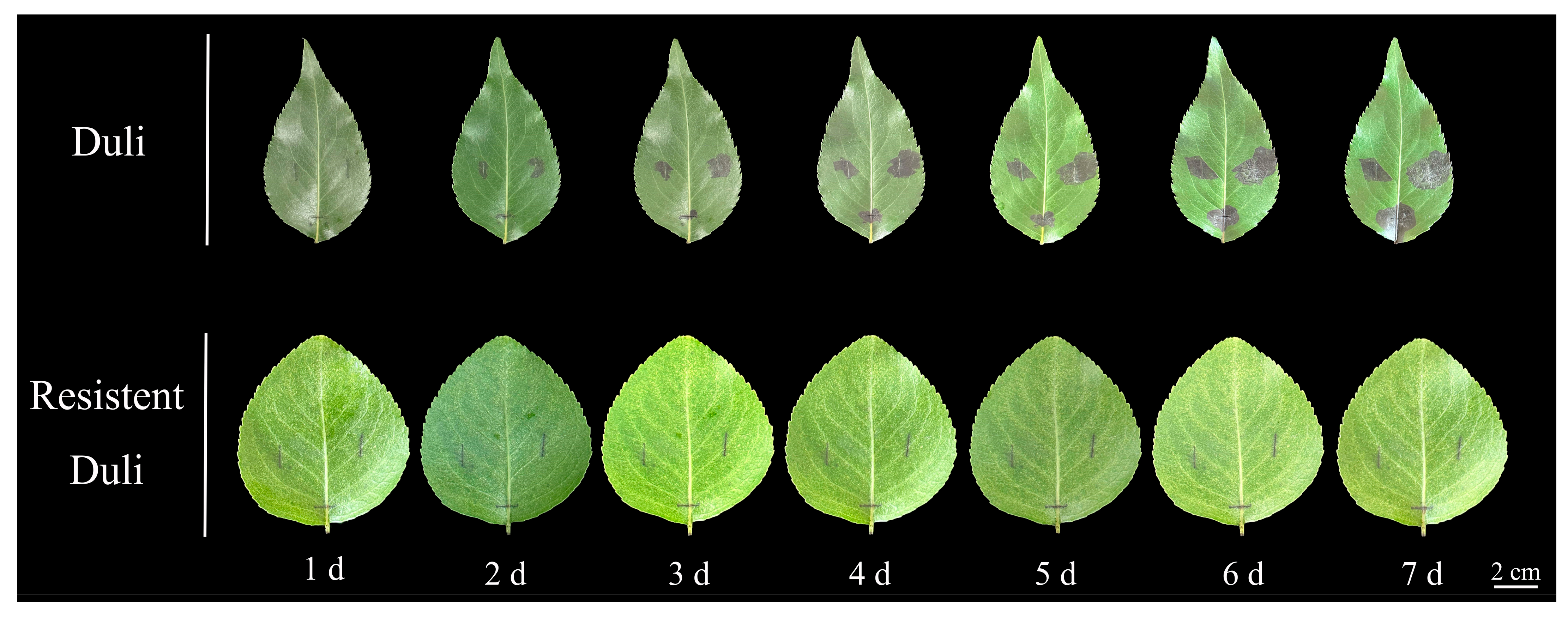
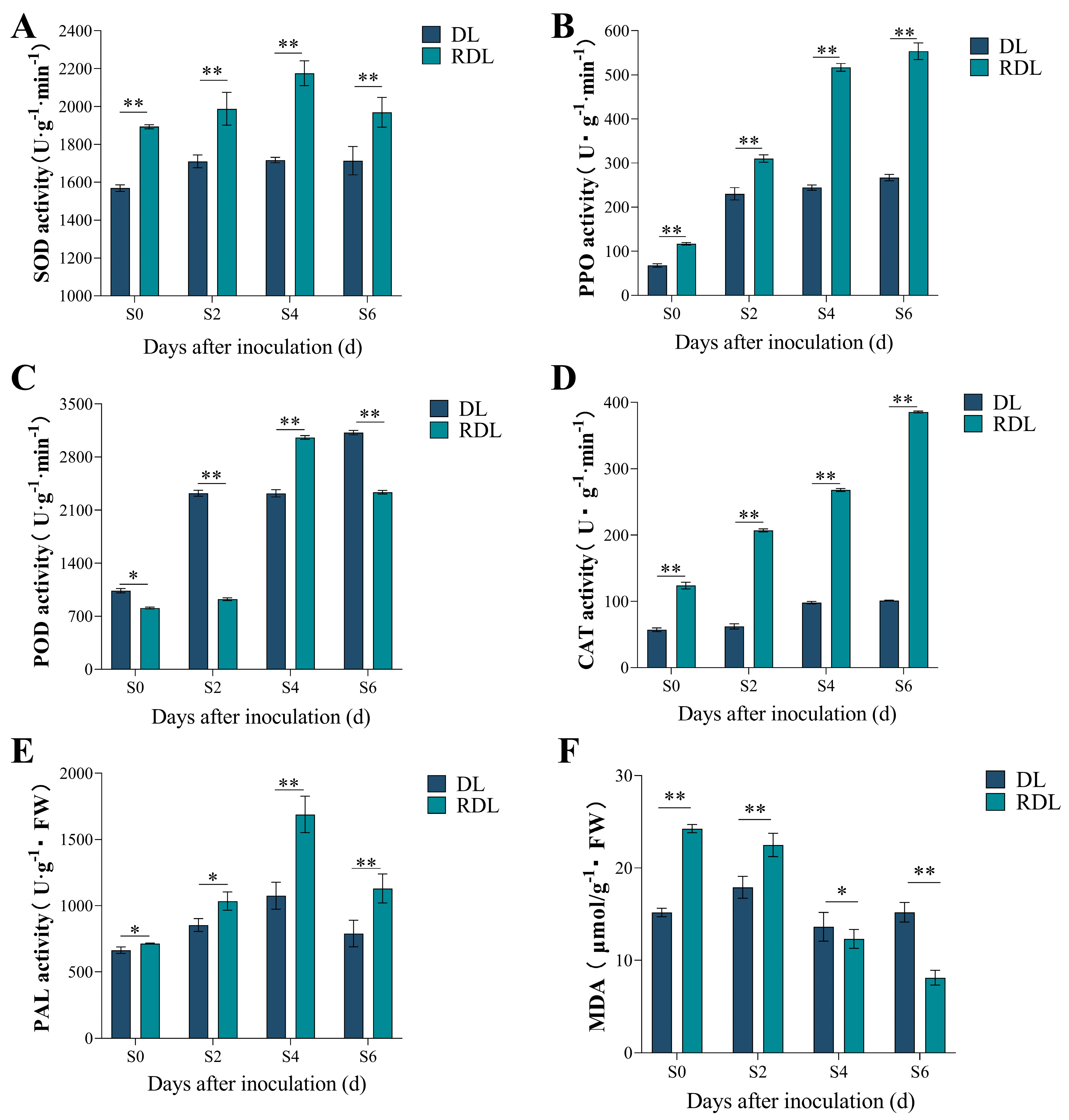

| Sequence ID | Number of Amino Acid (aa) | Molecular Weight (Da) | pI | Instability Index | Aliphatic Index | Grand Average of Hydropathicity | Subcellular Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb-PR-1-1 | 194 | 22,221.31 | 9.85 | 34.55 | 57.84 | −0.632 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-2 | 341 | 37,556.87 | 8.81 | 38.33 | 59.59 | −0.870 | Nucleus. |
| Pb-PR-1-3 | 340 | 37,544.85 | 8.94 | 38.97 | 58.91 | −0.882 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-4 | 151 | 16,709.98 | 9.85 | 43.45 | 66.49 | −0.505 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-5 | 173 | 18,781.16 | 8.97 | 36.61 | 75.03 | −0.245 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-6 | 196 | 22,468.42 | 5.80 | 27.56 | 62.76 | −0.382 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-7 | 186 | 21,503.33 | 5.39 | 27.69 | 61.40 | −0.403 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-8 | 200 | 22,804.20 | 9.63 | 42.76 | 68.75 | −0.481 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-9 | 170 | 19,296.70 | 9.25 | 42.81 | 60.35 | −0.455 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-10 | 146 | 15,282.81 | 4.67 | 43.08 | 61.58 | −0.400 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-11 | 140 | 14,606.29 | 4.77 | 38.64 | 76.07 | −0.159 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-12 | 163 | 17,199.18 | 4.86 | 43.50 | 71.90 | −0.266 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-13 | 160 | 17,836.25 | 6.09 | 41.40 | 63.44 | −0.416 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-14 | 160 | 18,203.49 | 4.96 | 38.14 | 69.56 | −0.438 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-15 | 160 | 17,504.76 | 5.51 | 38.31 | 70.19 | −0.142 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-16 | 160 | 17,835.12 | 5.90 | 38.04 | 73.19 | −0.254 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-17 | 166 | 18,534.98 | 6.88 | 32.79 | 67.53 | −0.395 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-18 | 168 | 18,805.92 | 5.67 | 21.85 | 62.74 | −0.426 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-19 | 168 | 18,722.90 | 6.04 | 22.06 | 63.27 | −0.460 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-20 | 168 | 18,706.85 | 6.04 | 21.89 | 60.95 | −0.492 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-21 | 123 | 13,268.70 | 9.69 | 25.16 | 60.24 | −0.518 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-22 | 127 | 13,543.99 | 7.69 | 36.17 | 73.86 | −0.335 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-23 | 160 | 17,200.27 | 8.69 | 37.09 | 73.19 | −0.284 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-24 | 178 | 19,785.51 | 9.35 | 41.97 | 71.80 | −0.354 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-25 | 240 | 26,547.70 | 5.74 | 37.02 | 82.88 | −0.365 | Nucleus. |
| Pb-PR-1-26 | 161 | 17,697.60 | 5.64 | 24.10 | 69.07 | −0.478 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-27 | 154 | 16,491.48 | 6.01 | 27.30 | 79.16 | −0.084 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-28 | 151 | 16,123.67 | 5.34 | 23.89 | 57.48 | −0.444 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-29 | 161 | 17,169.90 | 5.10 | 28.27 | 63.60 | −0.293 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-30 | 161 | 17,079.88 | 5.10 | 31.37 | 69.07 | −0.227 | Vacuole. |
| Pb-PR-1-31 | 161 | 17,089.90 | 5.10 | 29.50 | 71.49 | −0.230 | Vacuole. |
| Reagent | Volume (μL) |
|---|---|
| 5×gDNA Buffer | 2 μL |
| Total RNA | 6 μL |
| RNase-Free ddH2O | 2 μL |
| 5×gDNA Buffer | 2 μL |
| Reagent | Volume (μL) |
|---|---|
| 10×Fast RT Buffer | 2 μL |
| RT Enzyme Mix | 6 μL |
| FQ-RT Primer Mix | 2 μL |
| RNase-Free ddH2O | 2 μL |
| Component | Volume (μL) |
|---|---|
| BlasTaqTM 2×qPCR MM | 10 μL |
| Forward Primer | 0.4 μL |
| Reverse Primer | 0.4 μL |
| Template DNA | 1.5 μL |
| Nuclease-free H2O | 7.7 μL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wufuerjiang, A.; Sai, J.; Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Tian, J. Genome-Wide Identification of the PR-1 Gene Family in Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge and Its Expression Analysis Under Fire Blight Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115074
Wufuerjiang A, Sai J, Wen Y, Wang L, Chen C, Li X, Tian J. Genome-Wide Identification of the PR-1 Gene Family in Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge and Its Expression Analysis Under Fire Blight Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115074
Chicago/Turabian StyleWufuerjiang, Abudusufuer, Jingyi Sai, Yue Wen, Lei Wang, Chen Chen, Xu Li, and Jia Tian. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification of the PR-1 Gene Family in Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge and Its Expression Analysis Under Fire Blight Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115074
APA StyleWufuerjiang, A., Sai, J., Wen, Y., Wang, L., Chen, C., Li, X., & Tian, J. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification of the PR-1 Gene Family in Pyrus betulaefolia Bunge and Its Expression Analysis Under Fire Blight Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115074






