TGF-β Induced by Allergic Lung Inflammation Enhances Os-Teosarcoma Lung Metastasis in a Mouse Comorbidity Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
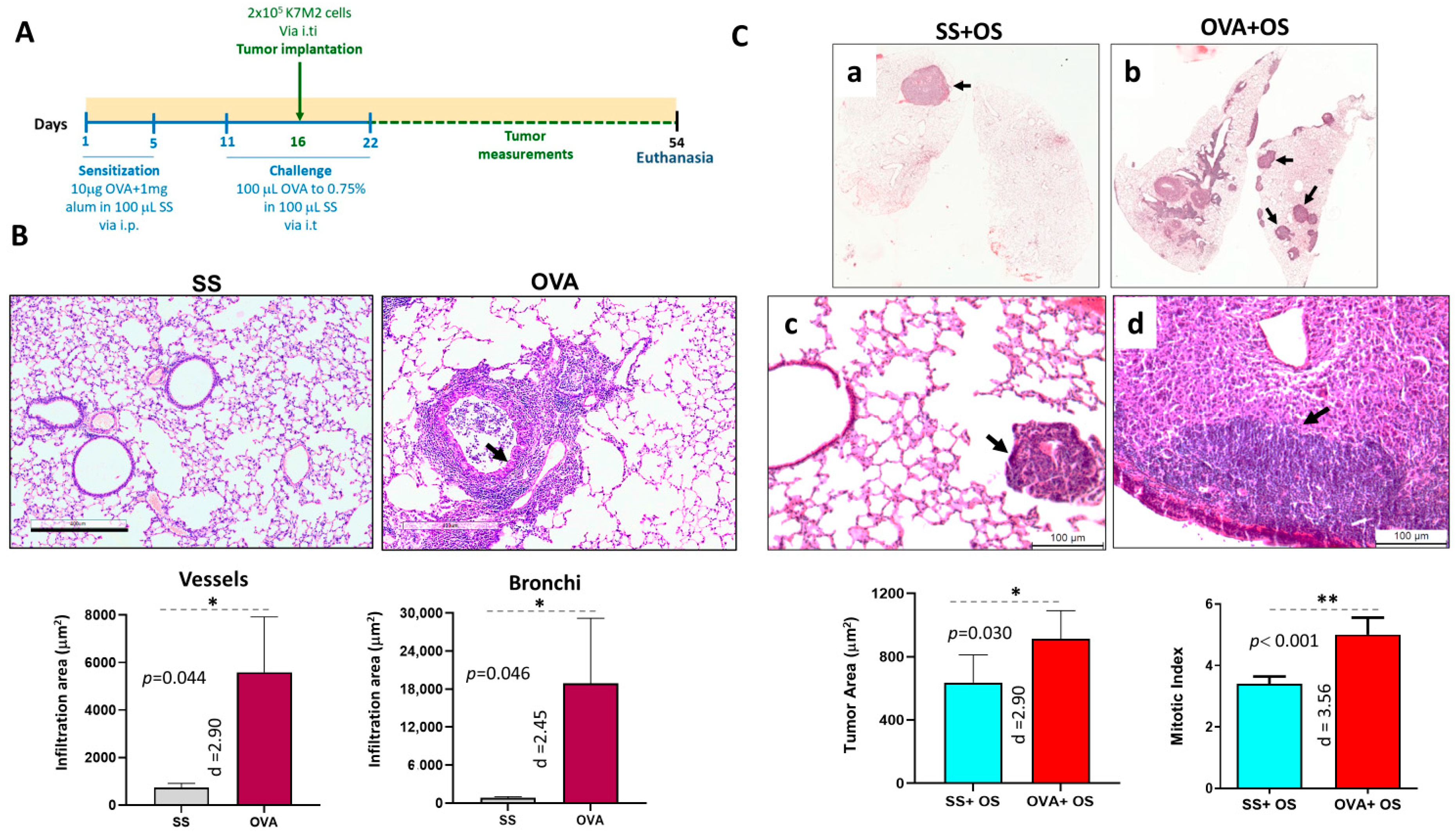
2.1. Allergic Airway Inflammation Promotes Lung Metastasis in Mice
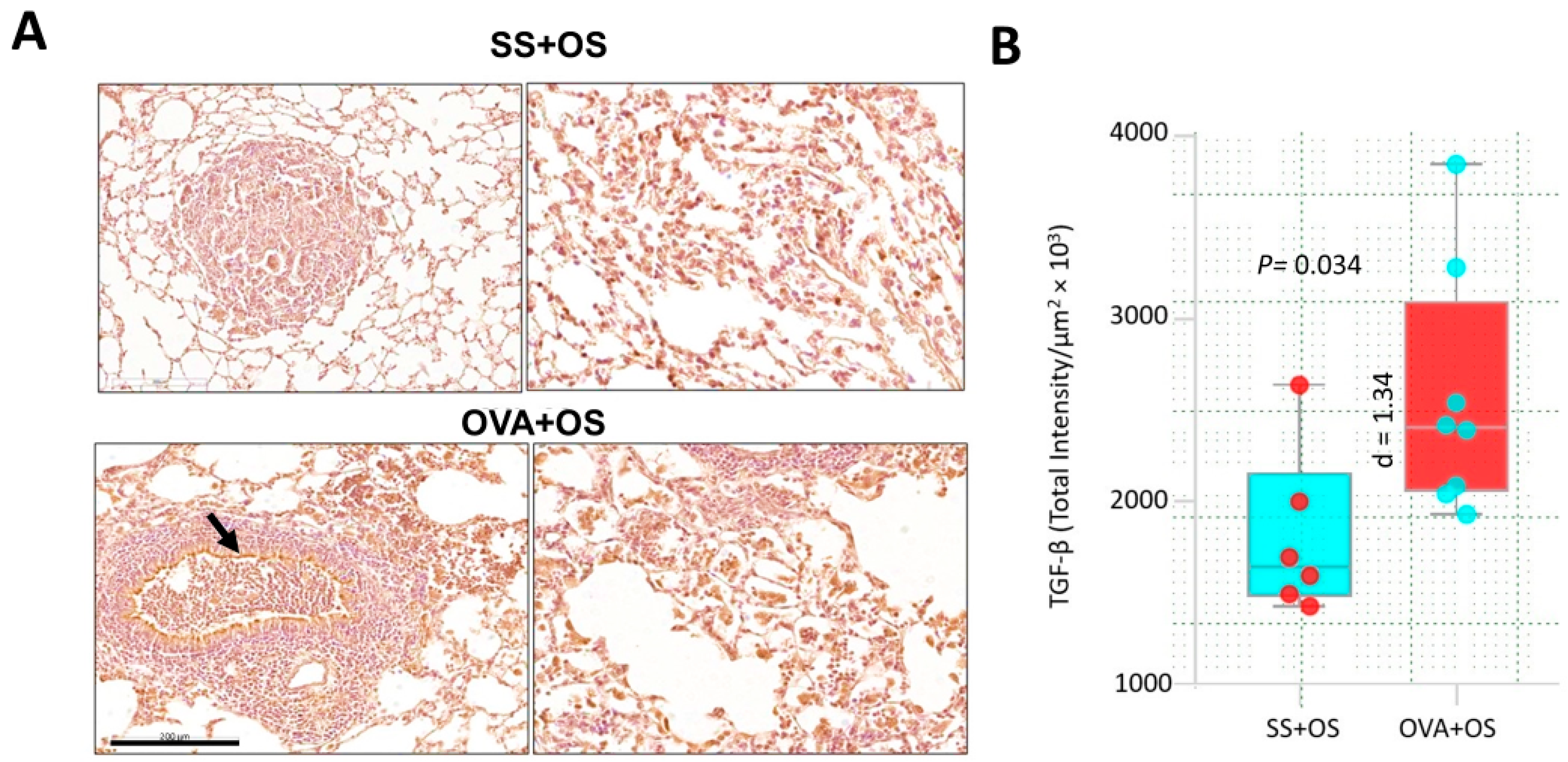
2.2. Pulmonary Allergic Inflammation Upregulates TGF-β Expression and Lung Metastasis of Osteosarcoma
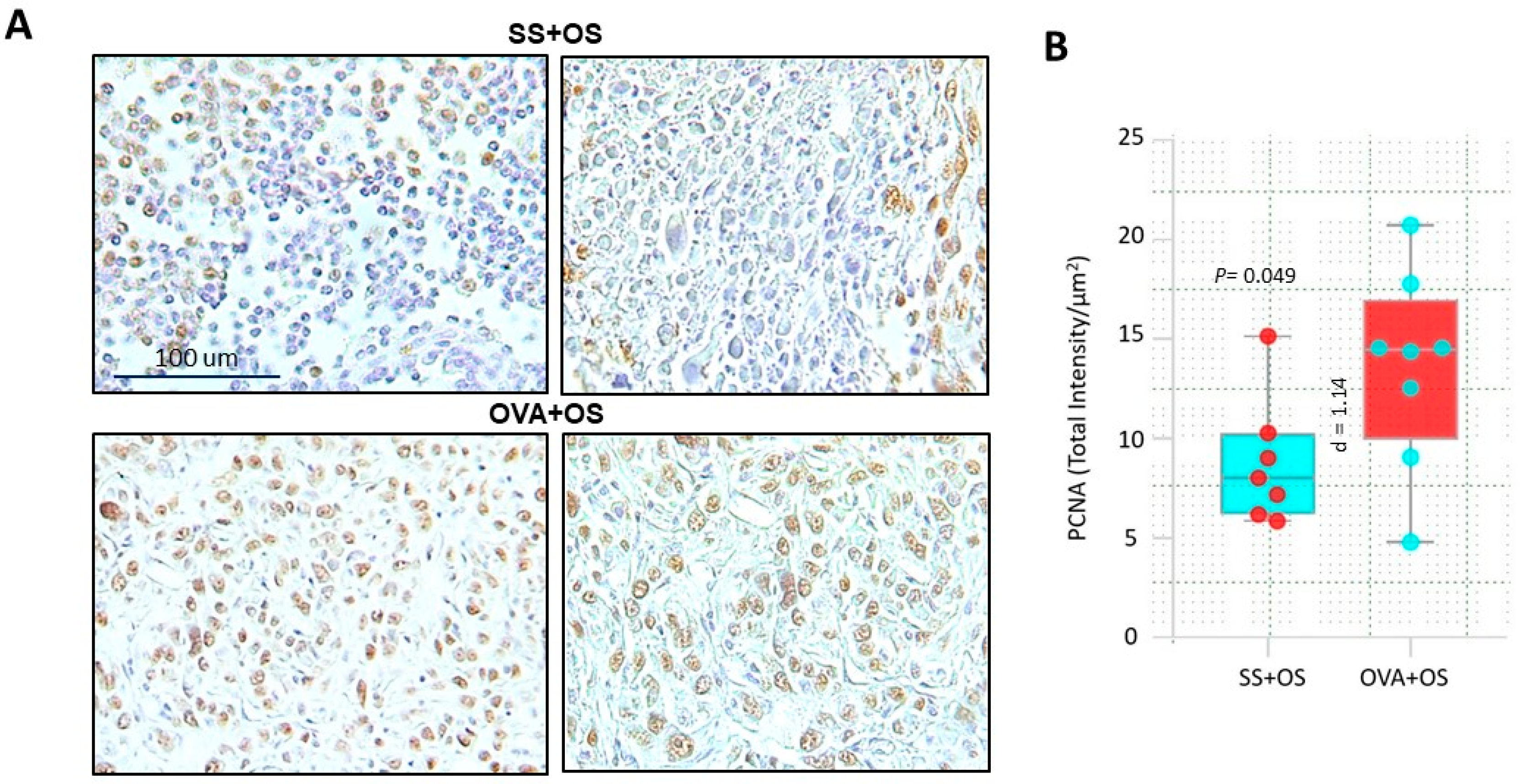
2.3. Pulmonary Allergic Inflammation Increases Neoplastic Cell Proliferation in Lung Metastasis of Osteosarcoma
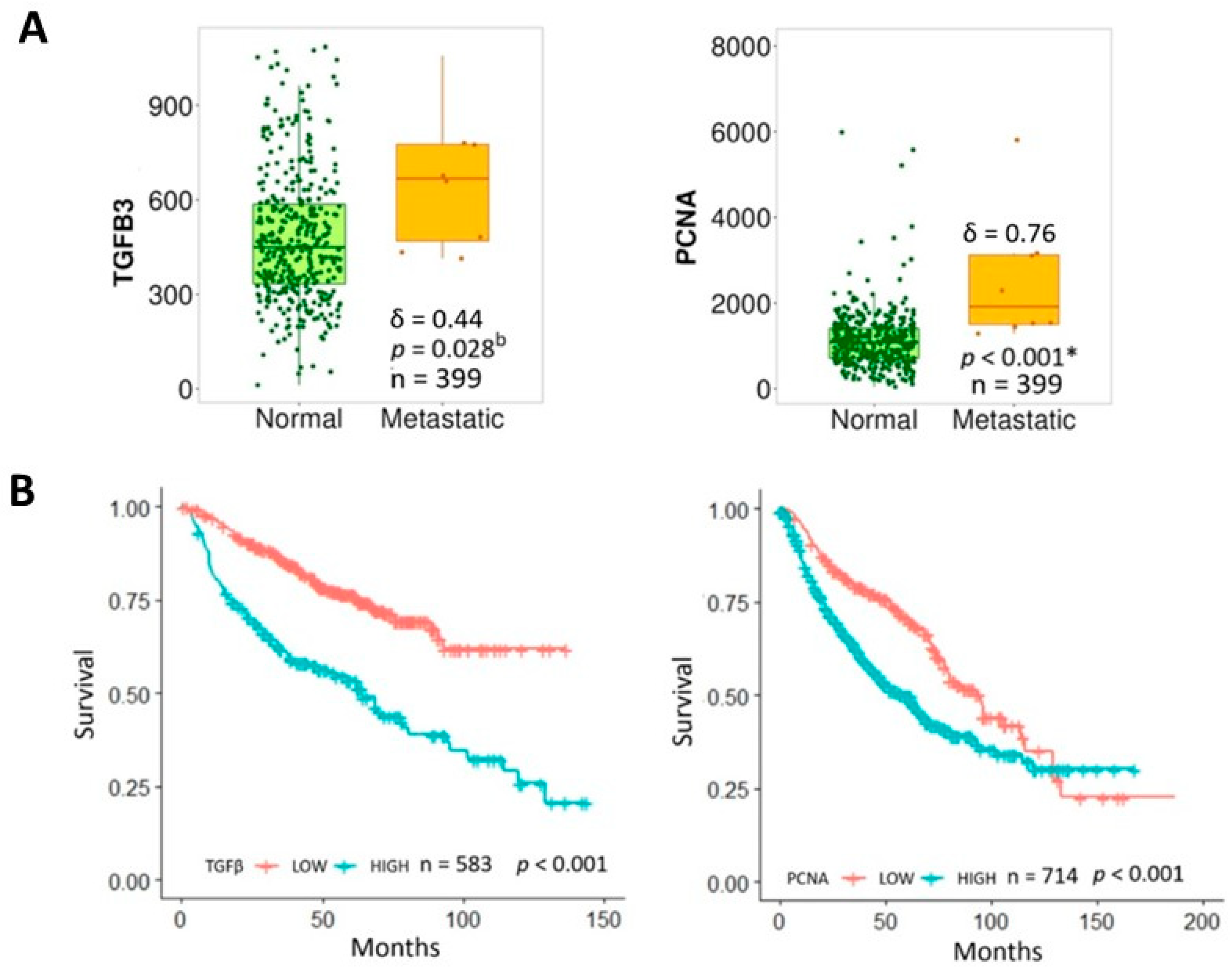
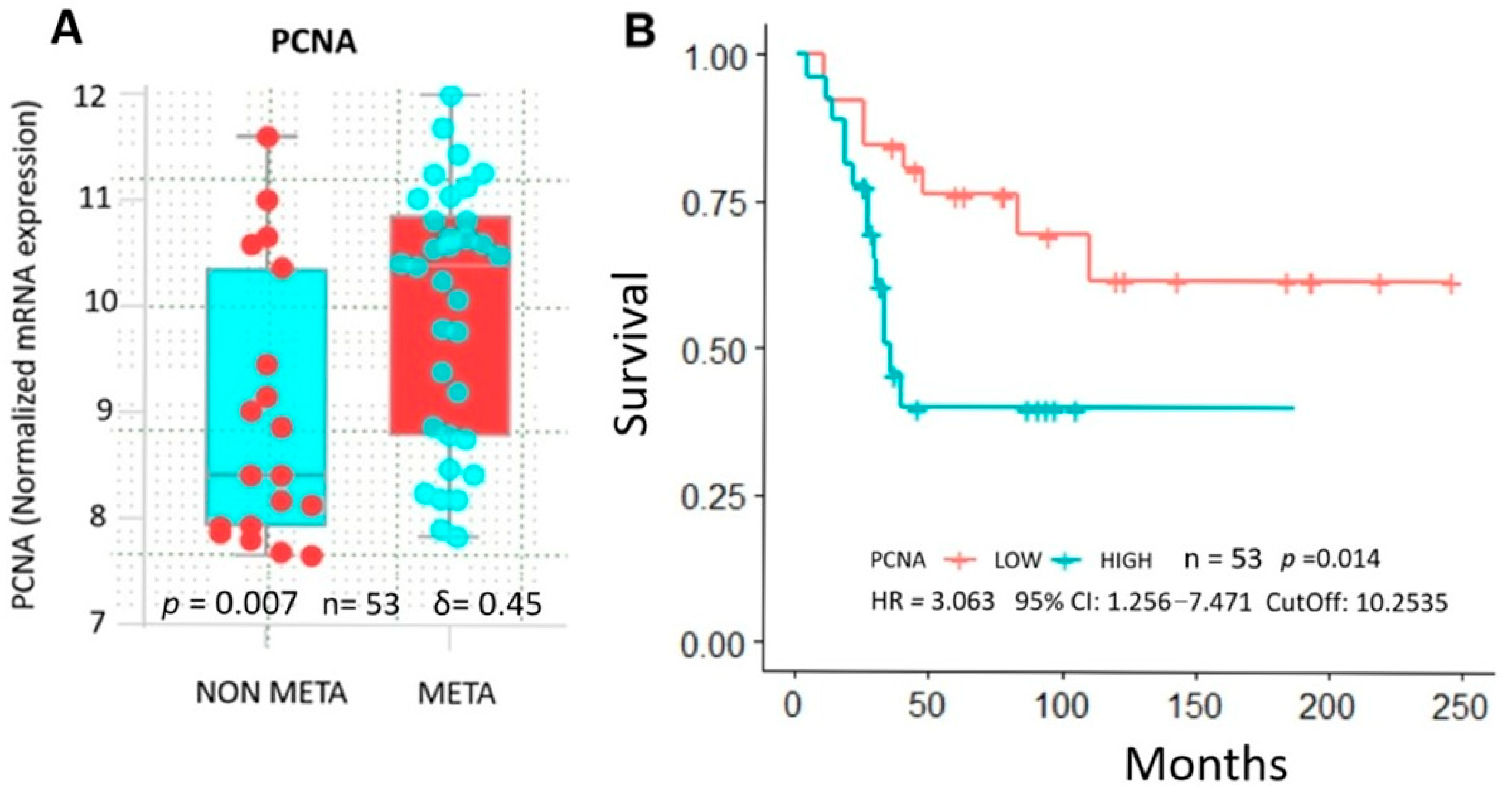
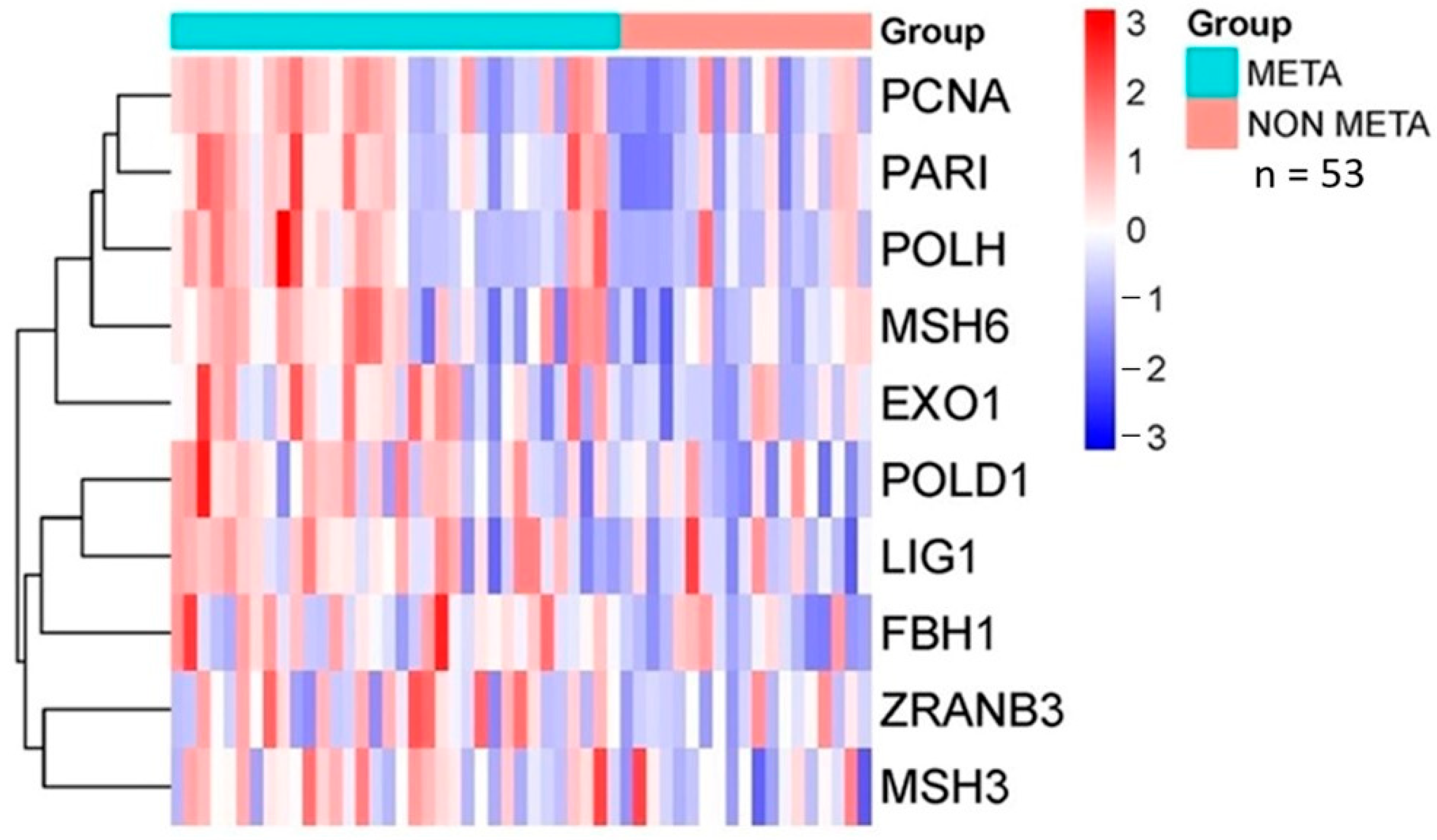
2.4. Database Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents, Antibodies, and Cell Line
4.2. Animals and Ethical Statements
4.3. Allergic Airway Inflammation Model
4.4. Experimental Design for the Osteosarcoma Model (K7M2 Cells)
4.5. Metastasis Evaluation
4.6. Periodic Acid–Schiff (PAS) Staining
4.7. Immunohistochemistry
4.8. Digital Pathology Analysis and Automated Image Quantification
4.9. Database Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, A.; Yang, Z.; Kong, P.; Yu, P.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Bian, S.; Teng, J. Exploring osteosarcoma based on the tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spreafico, M.; Ieva, F.; Fiocco, M. Causal effect of chemotherapy received dose intensity on survival outcome: A retrospective study in osteosarcoma. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2024, 24, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, T.; Zhang, X.; Kang, X. The role of lncRNA and miRNA on the effects of occurrence and development of osteosarcoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 144, 113726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, H.; Zeng, H.; Wang, P. Incidence trends, overall survival, and metastasis prediction using multiple machine learning and deep learning techniques in pediatric and adolescent population with osteosarcoma and Ewing’s sarcoma: Nomogram and webpage. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 27, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ren, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, L. TGFβ family signaling in human stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Cell Regen. 2024, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, P.; Pareek, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Horne, D.; Salgia, R.; Singhal, S.S. Exploring the potential of TGFβ as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target against cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2025, 231, 116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.; Thakur, N. Epigenetic regulation of TGF-β and vice versa in cancers—A review on recent developments. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, G.; Bhat, A.A.; Smriti; Singla, M.; Ali, H.; Singh, S.K.; Dua, K.; Kashyap, M.K. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition to mitigate age-related progression in lung cancer. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 102, 102576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biray Avci, C.; Goker Bagca, B.; Nikanfar, M.; Takanlou, L.S.; Takanlou, M.S.; Nourazarian, A. Tumor microenvironment and cancer metastasis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1442888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, G.; Prakash, S.; Jaiswal, V.; Singh, A.K. Chronic Inflammation and Cancer: Key Pathways and Targeted Therapies. Cancer Investig. 2025, 43, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado-Rodríguez, B.; Huerta-Yépez, S. Allergies: Diseases closely related to cancer. Bol. Med. Hosp. Infant. Mex. 2016, 73, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.F.; Westenberg, L.E.H.; Eurelings, L.E.M.; Otten, R.; Gerth van Wijk, R. The association between allergic diseases and cancer: A systematic review of the literature. Neth. J. Med. 2019, 77, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woo, A.; Lee, S.W.; Koh, H.Y.; Kim, M.A.; Han, M.Y.; Yon, D.K. Incidence of cancer after asthma development: 2 independent population-based cohort studies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fereidouni, M.; Ferns, G.A.; Bahrami, A. Current status and perspectives regarding the association between allergic disorders and cancer. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 1322–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z. Association of asthma and lung cancer risk: A pool of cohort studies and Mendelian randomization analysis. Medicine 2024, 103, e35060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirado-Rodriguez, B.; Baay-Guzman, G.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Antonio-Andres, G.; Vega, M.I.; Rocha-Zavaleta, L.; Bonifaz, L.C.; Huerta-Yepez, S. Inhibition of tumor progression during allergic airway inflammation in a murine model: Significant role of TGF-β. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, K.; Harris, R.; Lowe, G.; Rumley, A.; Yarnell, J.; Gallacher, J.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Ebrahim, S.; Lawlor, D.A. Associations of circulating C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 with cancer risk: Findings from two prospective cohorts and a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 2009, 20, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemes, C.; Visser, L.E.; Coebergh, J.-W.W.; Splinter, T.A.W.; Witteman, J.C.M.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Hofman, A.; Pols, H.A.P.; Stricker, B.H.C. C-Reactive Protein Levels, Variation in the C-Reactive Protein Gene, and Cancer Risk: The Rotterdam Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5216–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Achatz, G.; Turner, M.C.; Karagiannis, S.; Legrand, F.; Capron, M.; Penichet, M.L.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Siccardi, A.G.; Vangelista, L.; et al. AllergoOncology: The role of IgE-mediated allergy in cancer. Allergy 2008, 63, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrilli, A.S.; de Camargo, B.; Filho, V.O.; Bruniera, P.; Brunetto, A.L.; Jesus-Garcia, R.; Camargo, O.P.; Pena, W.; Péricles, P.; Davi, A.; et al. Results of the Brazilian Osteosarcoma Treatment Group Studies III and IV: Prognostic Factors and Impact on Survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yang, S.; Sun, G.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Polymorphisms and Serum Level in the Development of Osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Ding, Q.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Mao, K.; Sun, B.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zang, Y.Q.; Chen, Y. In Vivo Disruption of TGF-β Signaling by Smad7 in Airway Epithelium Alleviates Allergic Asthma but Aggravates Lung Carcinogenesis in Mouse. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baay-Guzman, G.J.; Bebenek, I.G.; Zeidler, M.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Vega, M.I.; Garcia-Zepeda, E.A.; Antonio-Andres, G.; Bonavida, B.; Riedl, M.; Kleerup, E.; et al. HIF-1 expression is associated with CCL2 chemokine expression in airway inflammatory cells: Implications in allergic airway inflammation. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.D.; Baxter, K.M.; Stephenson, S.T.; Esper, A.M.; Brown, L.A.S.; Fitzpatrick, A.M. Airway TGF-β1 and oxidant stress in children with severe asthma: Association with airflow limitation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 388–396.E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, N.J. TGF-β1 causes airway fibrosis and increased collagen I and III mRNA in mice. Thorax 2003, 58, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blobe, G.C.; Schiemann, W.P.; Lodish, H.F. Role of Transforming Growth Factor β in Human Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.B.; Wakefield, L.M. The two faces of transforming growth factor β in carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 8621–8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Cerrato, V.; Viñals, F.; Lambert, J.R.; Pérez-Tomás, R. The anticancer agent prodigiosin induces p21WAF1/CIP1 expression via transforming growth factor-beta receptor pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, N.R.; Xiang, X.; Mishra, L. TGF-β Signaling in Liver, Pancreas, and Gastrointestinal Diseases and Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 434–452.E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Rédini, F. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Plays a Pivotal Role in the Interplay Between Osteosarcoma Cells and Their Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Fan, T.; Xiao, C.; Tian, H.; Zheng, Y.; Li, C.; He, J. TGF-β signaling in health, disease and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.E. Non-Smad Signaling Pathways of the TGF-β Family. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a022129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgis, P. TGF β Signaling in Tumor Initiation, Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition, and Metastasis. J. Oncol. 2015, 2015, 587193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-H.; Chen, Z.-G.; Xu, R.-L.; Lv, C.-Q.; Liu, J.; Du, B. TGF-β1 signaling pathway serves a role in HepG2 cell regulation by affecting the protein expression of PCNA, gankyrin, p115, XIAP and survivin. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3239–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barcellos-Hoff, M.H.; Gulley, J.L. Molecular Pathways and Mechanisms of TGFβ in Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 2025–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamora, A.; Talbot, J.; Bougras, G.; Amiaud, J.; Leduc, M.; Chesneau, J.; Taurelle, J.; Stresing, V.; Le Deley, M.C.; Heymann, M.F.; et al. Overexpression of Smad7 Blocks Primary Tumor Growth and Lung Metastasis Development in Osteosarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5097–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Liu, G.; Peng, H.; Chen, A.; Zha, L.; Wang, Z. SOX4 contributes to TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition and stem cell characteristics of gastric cancer cells. Genes Dis. 2018, 5, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, A.J.; Deitz, S.L.; Palam, L.R.; Craven, K.E.; Korc, M. Pancreatic cancer–associated retinoblastoma 1 dysfunction enables TGF-β to promote proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Halder, S.K.; Zhang, S.; Datta, P.K. Targeting transforming growth factor-β signaling in liver metastasis of colon cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009, 277, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Massagué, J. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling in Immunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Aluja, A.S. Animales de laboratorio y la Norma Oficial Mexicana (NOM-062-ZOO-1999). Gac. Medica Mex. 2002, 138, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wan Mohammad, W.M.Z. Sample Size Calculation in Animal Studies Using Resource Equation Approach. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 24, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaro, M.; Souza, V.R.; Oliveira, F.A.; Ferreira, C.M. OVA-Induced Allergic Airway Inflammation Mouse Model. In Pre-Clinical Models; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska, M.M. Mouse Models of Asthma. In Lung Innate Immunity and Inflammation; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.A.; Hodgkins, S.R.; Dixon, A.E.; Poynter, M.E. Aligning mouse models of asthma to human endotypes of disease. Respirology 2014, 19, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.P.; Merkel, A.R.; Masood-Campbell, S.K.; Elefteriou, F.; Sterling, J.A. Models of Bone Metastasis. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 67, e4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MaruYama, T.; Chen, W.; Shibata, H. TGF-β and Cancer Immunotherapy. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, N.; Naik, A.; Moryani, K.; Soni, M.; Shah, J.; Dave, H. TGF-β at the crossroads of multiple prognosis in breast cancer, and beyond. Life Sci. 2022, 310, 121011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ten Dijke, P.; Miyazono, K.; Heldin, C.-H.; Moustakas, A. Special issue: TGF-β and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2024, 102–103, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaner, V.D.; Chick, J.F.; Donninger, H.; Linniola, I.; Mendoza, A.; Khanna, C.; Birrer, M.J. Inhibition of AP-1 Transcriptional Activity Blocks the Migration, Invasion, and Experimental Metastasis of Murine Osteosarcoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrique, C.; Morardet, L.; Linares, L.K.; Cissé, M.Y.; Merle, C.; Chibon, F.; Provot, S.; Haÿ, E.; Ea, H.-K.; Cohen-Solal, M.; et al. Calpain-6 controls the fate of sarcoma stem cells by promoting autophagy and preventing senescence. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e121225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montecillo-Aguado, M.; Tirado-Rodriguez, B.; Antonio-Andres, G.; Morales-Martinez, M.; Tong, Z.; Yang, J.; Hammock, B.D.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; Huerta-Yepez, S. Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Enhance Tumor Aggressiveness in Experimental Lung Cancer Model: Important Role of Oxylipins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartha, Á.; Győrffy, B. TNMplot.com: A Web Tool for the Comparison of Gene Expression in Normal, Tumor and Metastatic Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lánczky, A.; Győrffy, B. Web-Based Survival Analysis Tool Tailored for Medical Research (KMplot): Development and Implementation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e27633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using Effect Size—Or Why the P Value Is Not Enough. J. Grad. Med. Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, N.L.; Selles, R.W.; ter Stege, M.H.P.; Arends, G.R.D.; Hoogendam, L.; van Kooij, Y.E.; Veltkamp, J.; Wouters, R.M. Using Outcome Information During Consultation Yields Better Shared Decision Making, Better Patient Experiences, and More Positive Expectations: A Comparative Effectiveness Study. Value Health 2025, 28, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez-Rojas, M.J.; Tirado-Rodriguez, B.; Antonio-Andres, G.; Soca-Chafre, G.; Hernandez-Cueto, D.D.; Martinez-Calderon, C.O.; Montecillo-Aguado, M.; Hernandez-Guerrero, J.C.; Duran-Padilla, M.A.; Hernandez-Pando, R.; et al. TGF-β Induced by Allergic Lung Inflammation Enhances Os-Teosarcoma Lung Metastasis in a Mouse Comorbidity Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115073
Sanchez-Rojas MJ, Tirado-Rodriguez B, Antonio-Andres G, Soca-Chafre G, Hernandez-Cueto DD, Martinez-Calderon CO, Montecillo-Aguado M, Hernandez-Guerrero JC, Duran-Padilla MA, Hernandez-Pando R, et al. TGF-β Induced by Allergic Lung Inflammation Enhances Os-Teosarcoma Lung Metastasis in a Mouse Comorbidity Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115073
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez-Rojas, Marco J., Belen Tirado-Rodriguez, Gabriela Antonio-Andres, Giovanny Soca-Chafre, Daniel D. Hernandez-Cueto, Cesar O. Martinez-Calderon, Mayra Montecillo-Aguado, Juan C. Hernandez-Guerrero, Marco A. Duran-Padilla, Rogelio Hernandez-Pando, and et al. 2025. "TGF-β Induced by Allergic Lung Inflammation Enhances Os-Teosarcoma Lung Metastasis in a Mouse Comorbidity Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115073
APA StyleSanchez-Rojas, M. J., Tirado-Rodriguez, B., Antonio-Andres, G., Soca-Chafre, G., Hernandez-Cueto, D. D., Martinez-Calderon, C. O., Montecillo-Aguado, M., Hernandez-Guerrero, J. C., Duran-Padilla, M. A., Hernandez-Pando, R., & Huerta-Yepez, S. (2025). TGF-β Induced by Allergic Lung Inflammation Enhances Os-Teosarcoma Lung Metastasis in a Mouse Comorbidity Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115073





