Benchmarking Nanopore Sequencing for CLN2 (TPP1) Mutation Detection: Integrating Rapid Genomics and Orthogonal Validation for Precision Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
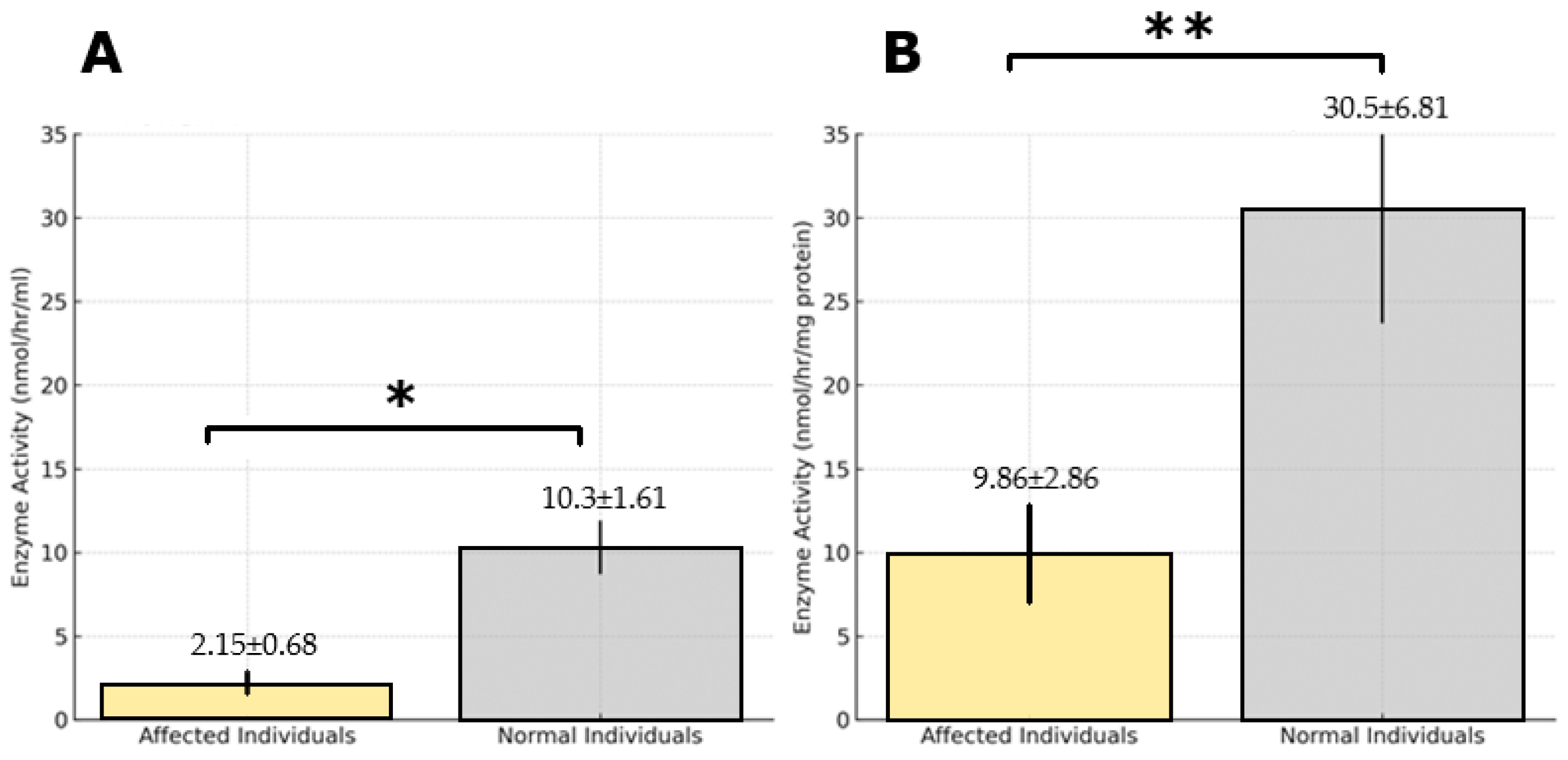
2.1. Study Population and TPP1 Enzyme Activity
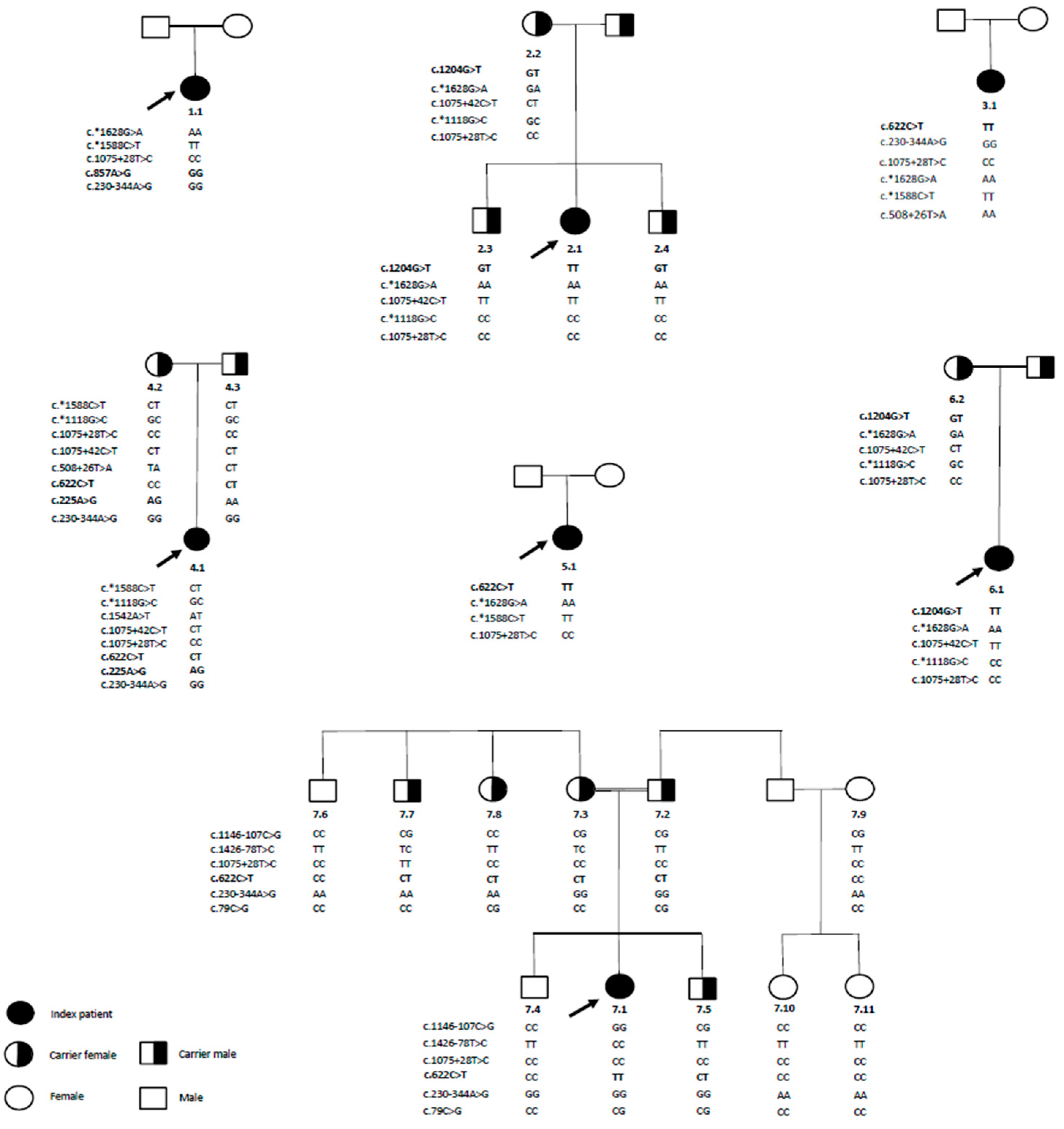
2.2. Mutations in the TPP1 Gene Identified via ONT-LR Sequencing and Sanger Sequencing Validation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Sample Collection
4.1.1. Sample Collection
4.1.2. DBS Sample Preparation
4.1.3. Ethical Compliance and Data Collection
4.2. Biochemical Measurements
Protocols for Precision and Linearity Determination
4.3. Genomic Analysis
4.3.1. DNA Extraction
4.3.2. Primer Design and Target Amplification
4.3.3. Library Construction and Sequencing
4.3.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAF-AMC | Ala-Ala-Phe-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin |
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics |
| CLN2 | Ceroid Lipofuscinosis, Neuronal 2 |
| DBS | Dried Blood Spot |
| LP | Likely Pathogenic |
| NCL | Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis |
| ONT-LRS | Oxford Nanopore Technologies Long-Read Sequencing |
| TPP1 | Tripeptidyl Peptidase 1 |
| UCL | University College London |
| VUS | Variant of Unknown Significance |
References
- Mole, S.E.; Cotman, S.L. Genetics of the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (Batten disease). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 2237–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollmann, K.; Uusi-Rauva, K.; Scifo, E.; Tyynelä, J.; Jalanko, A.; Braulke, T. Cell biology and function of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis-related proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 1866–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mole, S.E.; Williams, R.E.; Goebel, H.H. Correlations between genotype, ultrastructural morphology and clinical phenotype in the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. Neurogenetics 2005, 6, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Kraetzner, R.; Gruene, T.; Grapp, M.; Schreiber, K.; Grønborg, M.; Urlaub, H.; Becker, S.; Asif, A.R.; Gärtner, J.; et al. Structure of tripeptidyl-peptidase I provides insight into the molecular basis of late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3976–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guhaniyogi, J.; Sohar, I.; Das, K.; Stock, A.M.; Lobel, P. Cristal structure and autoactivation pathway of the precursor form of human tripeptidyl-peptidase 1, the enzyme deficient in late infantile ceroid lipofuscinosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3985–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Sohar, I.; Lackland, H.; Lobel, P. The human CLN2 protein/tripeptidyl-peptidase I is a serine protease that autoactivates at acidic pH. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabek, A.A.; Wujek, P.; Walus, M.; Bieler, S.; Soto, C.; Wisniewski, K.E.; Kida, E. Maturation of human tripeptidyl-peptidase I in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31058–31067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golabek, A.A.; Kida, E.; Walus, M.; Wujek, P.; Mehta, P.; Wisniewski, K.E. Biosynthesis, glycosylation, and enzymatic processing in vivo of human tripeptidyl-peptidase I. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 7135–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beersel, G.; Tihon, E.; Demine, S.; Hamer, I.; Jadot, M.; Arnould, T. Different molecular mechanisms involved in spontaneous and oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial fragmentation in tripeptidyl peptidase-1 (TPP-1)-deficient fibroblasts. Biosci. Rep. 2013, 33, e00023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, E.; Bailey, M.; Schulz, A.; Aristorena, M.; Miller, N.; Mole, S.E. Mutation update: Review of TPP1 gene variants associated with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis CLN2 disease. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, E.; Mole, S.E. The Genetic Basis of Phenotypic Heterogeneity in the Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinoses. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 754045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estublier, B.; Cano, A.; Hoebeke, C.; Pichard, S.; Scavarda, D.; Desguerre, I.; Auvin, S.; Chabrol, B. Cerliponase alfa changes the natural history of children with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2: The first French cohort. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2021, 30, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, M.; Simonati, A.; Jacoby, D.; Lezius, S.; Kilian, D.; Van de Graaf, B.; Pagovich, O.E.; Kosofsky, B.; Yohay, K.; Downs, M.; et al. Disease characteristics and progression in patients with late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2 (CLN2) disease: An observational cohort study. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staropoli, J.F.; Karaa, A.; Lim, E.T.; Kirby, A.; Elbalalesy, N.; Romansky, S.G.; Leydiker, K.B.; Coppel, S.H.; Barone, R.; Xin, W.; et al. A homozygous mutation in KCTD7 links neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis to the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.; Guimarães, A.; Bessa, C.; Ferreira, M.J.; Lopes, L.; Pinto, E.; Pinto, R.; Boustany, R.M.; Sá Miranda, M.C.; Ribeiro, M.G. Clinicopathological and molecular characterization of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis in the Portuguese population. J. Neurol. 2003, 250, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claussen, M.; Heim, P.; Knispel, J.; Goebel, H.H.; Kohlschütter, A. Incidence of neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses in West Germany: Variation of a method for studying autosomal recessive disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1992, 42, 536–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvebrant, P.; Hagberg, B. Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses in Scandinavia: Epidemiology and clinical pictures. Neuropediatrics 1997, 28, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fietz, M.; AlSayed, M.; Burke, D.; Cohen-Pfeffer, J.; Cooper, J.D.; Dvořáková, L.; Giugliani, R.; Izzo, E.; Jahnová, H.; Lukacs, Z.; et al. Diagnosis of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2 (CLN2 disease): Expert recommendations for early detection and laboratory diagnosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016, 119, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, S.E.; Schulz, A.; Badoe, E.; Berkovic, S.F.; de Los Reyes, E.C.; Dulz, S.; Gissen, P.; Guelbert, N.; Lourenco, C.M.; Mason, H.L.; et al. Guidelines on the diagnosis, clinical assessments, treatment and management for CLN2 disease patients. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, M.; Khatoon, S.; Marchi, E.J.; Mevs, C.A.; Bolton, D.C.; Velinov, M.T.; Junaid, M.A. Diagnosis of late-infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis using dried blood spot-based assay for TPPI enzyme activity: TPPI diagnostic assay from DBS. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 507, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Cerliponase Alfa: First Global Approval. Drugs. 2017, 77, 1247–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, J.B.; Chen, A.; Kaminsky, S.M.; Crystal, R.G.; Sondhi, D. Advances in the Treatment of Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis. Expert. Opin. Orphan Drugs 2019, 7, 473–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Riley, G.R.; Jang, W.; Rubinstein, W.S.; Church, D.M.; Maglott, D.R. ClinVar: Public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D980–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Albarca Aguilera, M.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The human genomic variant search engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Genome Aggregation Database. Available online: https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org/ (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine. Available online: https://topmed.nhlbi.nih.gov/ (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Steinfeld, G.; Taylor, L.E.; Walkiewicz, M.; Le Moing, M.; Eggers, S.; Yaplito-Lee, J.; Fuller, M.; Dabscheck, G.; Rodriguez-Casero, V.; White, S.M.; et al. Aberrant splicing and transcriptional activity of TPP1 result in CLN2-like disorder. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 64, 104259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.N.; Chan, C.H.; Pearce, D.A. The role of nonsense-mediated decay in neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 2723–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, J.; Mistri, M.; Bhavsar, R.; Pancholi, D.; Kamate, M.; Gupta, N.; Kabra, M.; Mehta, S.; Nampoothiri, S.; Thakker, A.; et al. Batten disease: Biochemical and molecular characterization revealing novel PPT1 and TPP1 gene mutations in Indian patients. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbig, K.L.; Farwell Hagman, K.D.; Shinde, D.N.; Mroske, C.; Powis, Z.; Li, S.; Tang, S.; Helbig, I. Diagnostic exome sequencing provides a molecular diagnosis for a significant proportion of patients with epilepsy. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinfeld, R.; Heim, P.; von Gregory, H.; Meyer, K.; Ullrich, K.; Goebel, H.H.; Kohlschütter, A. Late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis: Quantitative description of the clinical course in patients with CLN2 mutations. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 112, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiakas, K.; Steinfeld, R.; Storch, S.; Ezaki, J.; Lukacs, Z.; Kominami, E.; Kohlschütter, A.; Ullrich, K.; Braulke, T. Mutation of the glycosylated asparagine residue 286 in human CLN2 protein results in loss of enzymatic activity. Glycobiology 2004, 14, 1C–5C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCL Mutation and Patient Database. Available online: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/ncl-disease/mutation-and-patient-database (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- The SpliceAI. Available online: https://spliceailookup.broadinstitute.org/ (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Kousi, M.; Lehesjoki, A.E.; Mole, S.E. Update of the mutation spectrum and clinical correlations of over 360 mutations in eight genes that underlie the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardicli, D.; Haliloglu, G.; Gocmen, R.; Gunbey, C.; Topcu, M. Unraveling neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2 (CLN2) disease: A tertiary center experience for determinants of diagnostic delay. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2021, 33, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, M.; Kose, E.; Ünalp, A.; Yılmaz, Ü.; Edizer, S.; Tekin, H.G.; Karaoğlu, P.; Özdemir, T.R.; Er, E.; Onay, H.; et al. Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis: Genetic and phenotypic spectrum of 14 patients from Turkey. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panjeshahi, S.; Karimzadeh, P.; Movafagh, A.; Ahmadabadi, F.; Rahimian, E.; Alijanpour, S.; Miryounesi, M. Clinical and genetic characterization of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCLs) in 29 Iranian patients: Identification of 11 novel mutations. Hum. Genet. 2023, 142, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, R.; Pesaola, F.; Guelbert, N.; Pons, P.; Oller-Ramírez, A.M.; Rautenberg, G.; Becerra, A.; Sims, K.; Xin, W.; Cismondi, I.A.; et al. The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses program: A translational research experience in Argentina. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852 Pt B, 2301–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan, R.; Carabelos, M.N.; Xin, W.; Sims, K.; Guelbert, N.; Cismondi, I.A.; Pons, P.; Alonso, G.I.; Troncoso, M.; Witting, S.; et al. Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type CLN2: A new rationale for the construction of phenotypic subgroups based on a survey of 25 cases in South America. Gene 2013, 516, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.J.; Buckley, D.J.; MacMillan, A.; Marshall, H.D.; Steele, L.; Ray, P.N.; Nawaz, Z.; Baskin, B.; Frecker, M.; Carr, S.M.; et al. The clinical and genetic epidemiology of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis in Newfoundland. Clin. Genet. 2008, 74, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.; Zhong, R.; Moore, S.; Moroziewicz, D.; Currie, J.R.; Parfrey, P.; Brown, W.T.; Zhong, N. Identification of novel CLN2 mutations shows Canadian specific NCL2 alleles. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 39, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestak, A.G.; Bukaeva, A.A.; Saber, S.; Zaklyazminskaya, E.V. Allelic Dropout Is a Common Phenomenon That Reduces the Diagnostic Yield of PCR-Based Sequencing of Targeted Gene Panels. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 620337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; de Castro, M.J.; Crujeiras, P.; Duat-Rodriguez, A.; Marco, A.V.; Del Toro, M.; Couce, M.L.; Colón, C. The LINCE Project: A Pathway for Diagnosing NCL2 Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 876688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civallero, G.; Michelin, K.; de Mari, J.; Viapiana, M.; Burin, M.; Coelho, J.C.; Giugliani, R. Twelve different enzyme assays on dried-blood filter paper samples for detection of patients with selected inherited lysosomal storage diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 372, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strovel, E.T.; Cusmano-Ozog, K.; Wood, T.; Yu, C.; ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. Electronic address: Documents@acmg.net. Measurement of lysosomal enzyme activities: A technical standard of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet. Med. 2022, 24, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, L. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primer BLAST. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 4 May 2023).
- Karamitros, T.; Magiorkinis, G. Multiplexed Targeted Sequencing for Oxford Nanopore MinION: A Detailed Library Preparation Procedure. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1712, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Holt, K.E. Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junhao, S.; Zhenxian, Z.; Syed, S.A.; Tak-Wah, L.; Ruibang, L. Clair3-trio: High-performance Nanopore long-read variant calling in family trios with trio-to-trio deep neural networks. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvignes, J.P.; Bartoli, M.; Delague, V.; Krahn, M.; Miltgen, M.; Béroud, C.; Salgado, D. VarAFT: A variant annotation and filtration system for human next generation sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W545–W553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazan, H.H.; Karaca, M.; Akan, G.; Özgen, Ö.; Tuncel, G.; Özketen, A.Ç.; Balcı, M.C.; Körbeyli, H.K.; Atalar, F.; Gökçay, G.F. Oxford nanopore sequencing-based assay for BTD gene screening: Design, clinical validation, and variant frequency assessment in the Turkish population. Gene 2024, 928, 148782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HGVSc | HGVSp | Frequency (gnomAD/TOPMed) | Classification | Type | # Affected Alleles | RS ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.622C>T | p.Arg208Ter | 0.00022/0.00023 | P | Stop codon | 7 | rs119455955 |
| c.1204G>T | p.Glu402Ter | 0.00000 | P | Stop codon | 4 | - |
| c.857A>G | p.Asn286Ser | 0.00000/0.00001 | P | Missense codon | 2 | rs119455958 |
| c.225A>G | p.Gln75 = | 0.0002/0.00006 | LP | Aberrant splicing | 1 | rs368709098 |
| Primer Pair | Sequence | Tm. (°C) | Genomic Location Start-End | Fragment Length (bp) | Exons | Seq. Pools | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TPP1_6089_F | GGCCAGTAAGTTGCAAATGTCGCACC | 67.1 | 11_6617790-6618015 | 1551 | 1-2-3 | A |
| TPP1_7639_R | CCACCCTTGCCTAGCATTTGGGACC | 67.6 | 11_6619516-6619540 | ||||
| 2 | TPP1_4859_F | GTCCAACCACACGGGCTACTGATGC | 67.7 | 11_6616760-6616784 | 1512 | 4-5-6-7 | B |
| TPP1_6370_R | TTCACAGCAGGGGGAGTGTGTGC | 67.2 | 11_6618249-6618271 | ||||
| 3 | TPP1_3391_F | TGGGGGCTAGAGCTCAGGAACTTCG | 67.6 | 11_6615292-6615316 | 1600 | 7-8-9-10-11 | A |
| TPP1_4990_R | ACCCACGATCTCTGCTCTGACTCCC | 67.3 | 11_6616867-6616891 | ||||
| 4 | TPP1_2167_F | GGAGAGGGAGTGGGCAACTATGATGG | 66.2 | 11_6614068-6614093 | 1579 | 10-11-12-13 | B |
| TPP1_3745_R | ACCTGGGCTATACTCACCCCTCCC | 66.8 | 11_6615623-6615646 | ||||
| 5 | TPP1_793_F | GCTGTAGGAGGAGGAGGAGTTTCAGC | 66.1 | 11_6612694-6612719 | 1502 | 13 | A |
| TPP1_2294_R | CTGCAAGGAGACCTCTACTGTCACCG | 66.3 | 11_6614170-6614195 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teker, B.; Akan, G.; Kazan, H.H.; Özgen, Ö.; Tatonyan, S.; Balci, M.C.; Karaca, M.; Kurekci, F.; Yıldız, E.P.; Güngor, O.; et al. Benchmarking Nanopore Sequencing for CLN2 (TPP1) Mutation Detection: Integrating Rapid Genomics and Orthogonal Validation for Precision Diagnostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115037
Teker B, Akan G, Kazan HH, Özgen Ö, Tatonyan S, Balci MC, Karaca M, Kurekci F, Yıldız EP, Güngor O, et al. Benchmarking Nanopore Sequencing for CLN2 (TPP1) Mutation Detection: Integrating Rapid Genomics and Orthogonal Validation for Precision Diagnostics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115037
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeker, Betül, Gökce Akan, Hasan Hüseyin Kazan, Özge Özgen, Suzin Tatonyan, Mehmet Cihan Balci, Meryem Karaca, Fulya Kurekci, Edibe Pembegül Yıldız, Olcay Güngor, and et al. 2025. "Benchmarking Nanopore Sequencing for CLN2 (TPP1) Mutation Detection: Integrating Rapid Genomics and Orthogonal Validation for Precision Diagnostics" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115037
APA StyleTeker, B., Akan, G., Kazan, H. H., Özgen, Ö., Tatonyan, S., Balci, M. C., Karaca, M., Kurekci, F., Yıldız, E. P., Güngor, O., Deniz, A., Gedikbasi, A., Atalar, F., Gokcay, G. F., & Poda, M. (2025). Benchmarking Nanopore Sequencing for CLN2 (TPP1) Mutation Detection: Integrating Rapid Genomics and Orthogonal Validation for Precision Diagnostics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115037






