Lifetime Variations of Prolactin Receptor Isoforms mRNA in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat—Effects of Aging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
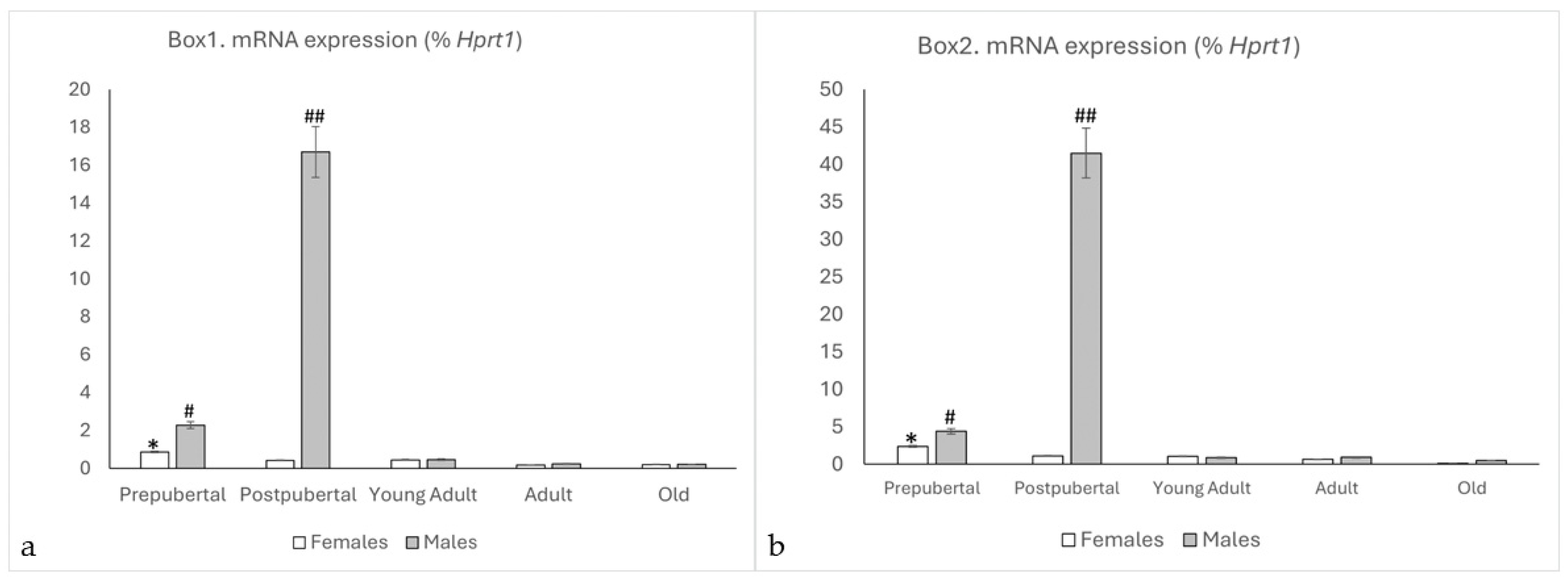
2.1. qPCR Study of Box1 and Box2
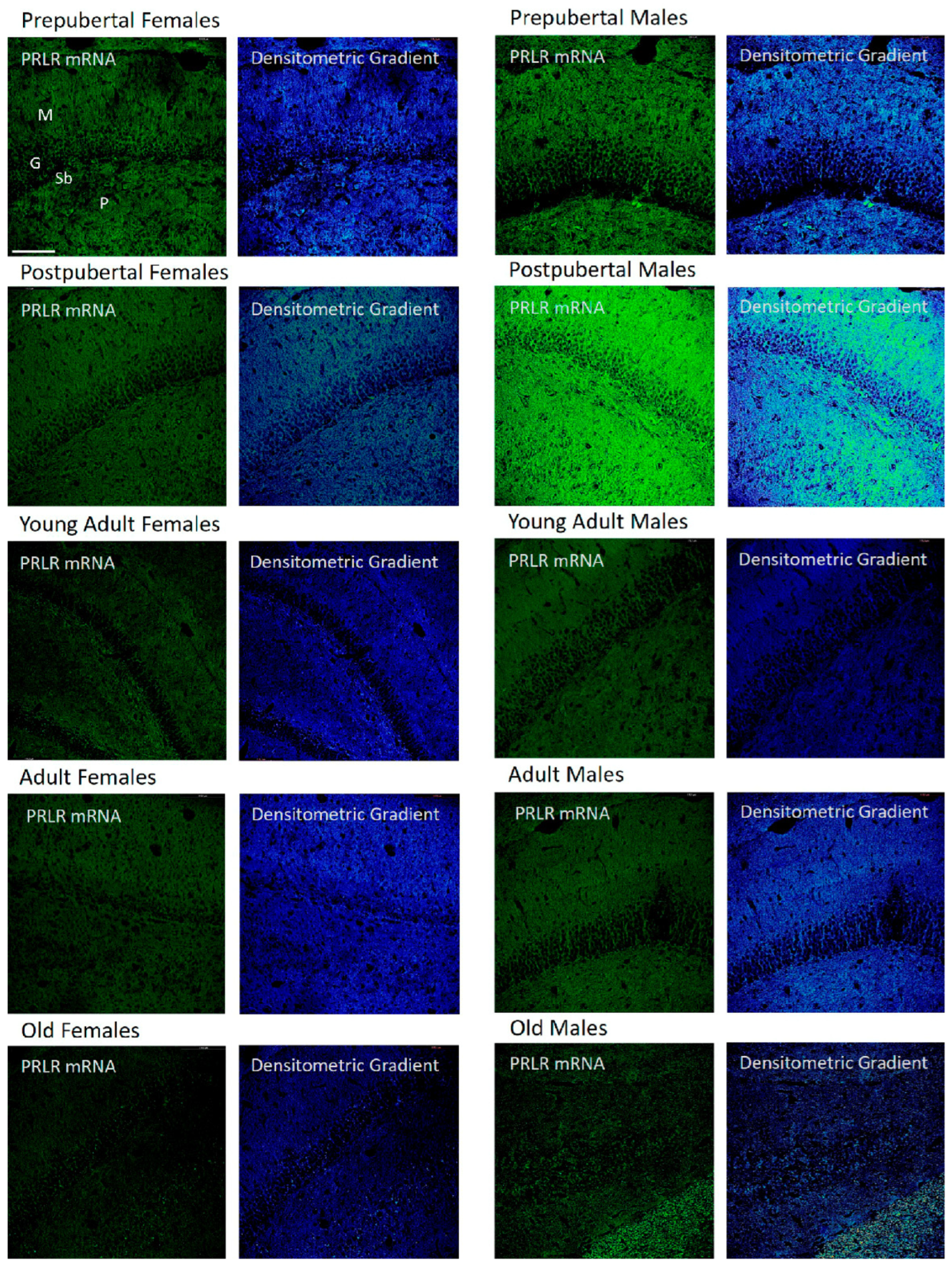
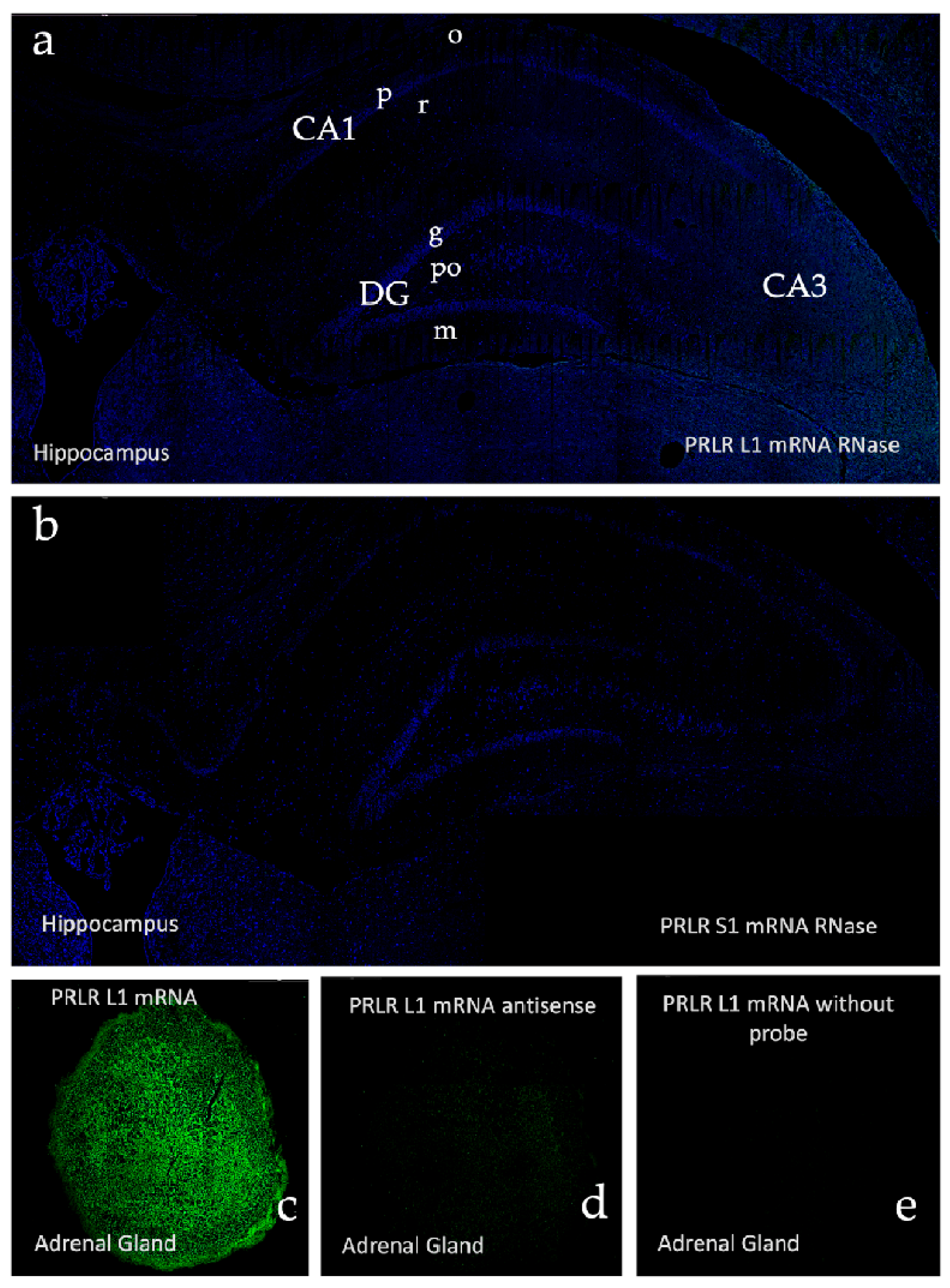
2.2. In Situ Hybridization: Box1 mRNA
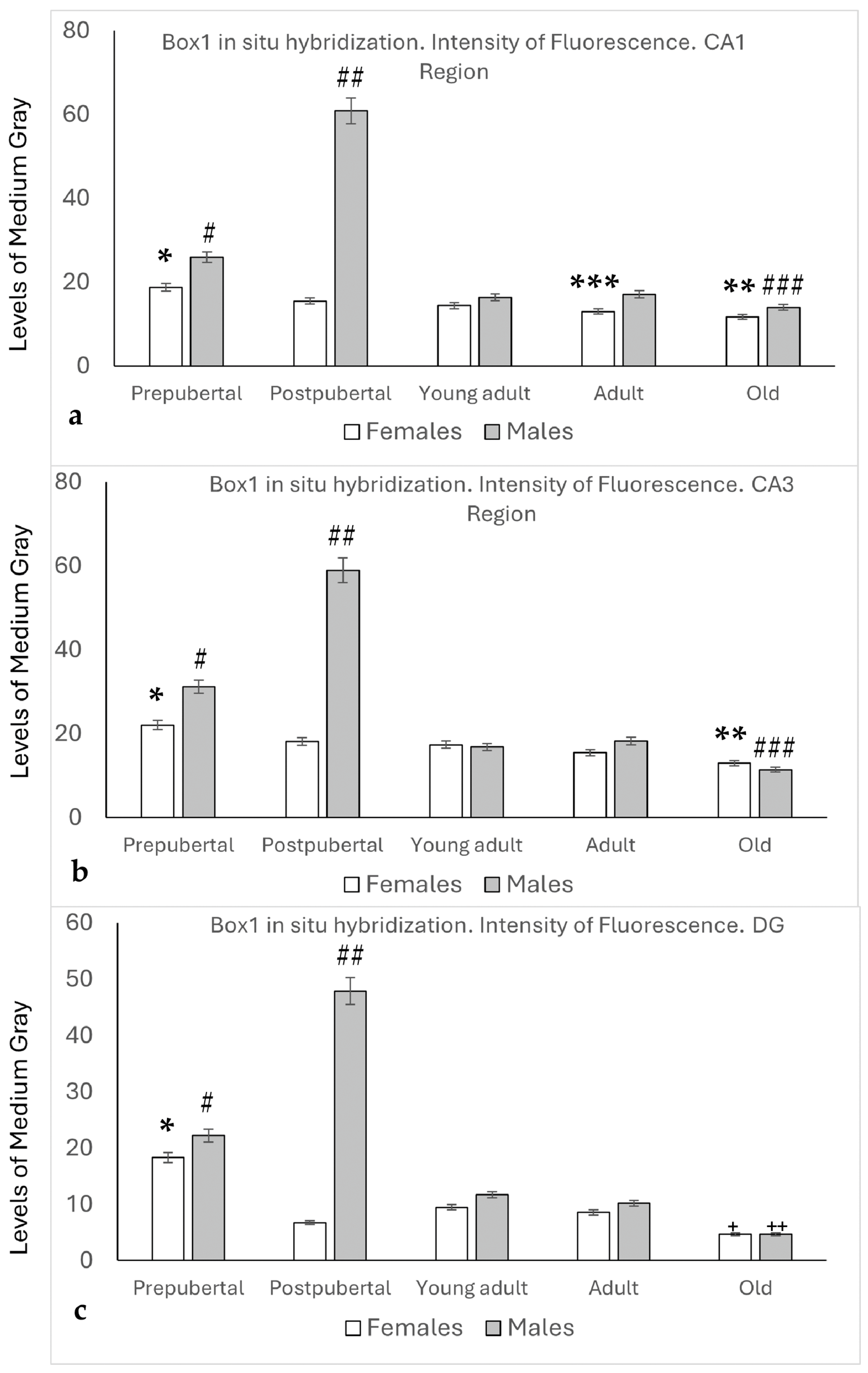
2.3. Distribution of Box1 mRNA in the CA1 Region by In Situ Hybridization (Figure 3)

2.4. Distribution of Box1 mRNA in the CA3 Region by In Situ Hybridization (Figure 4)
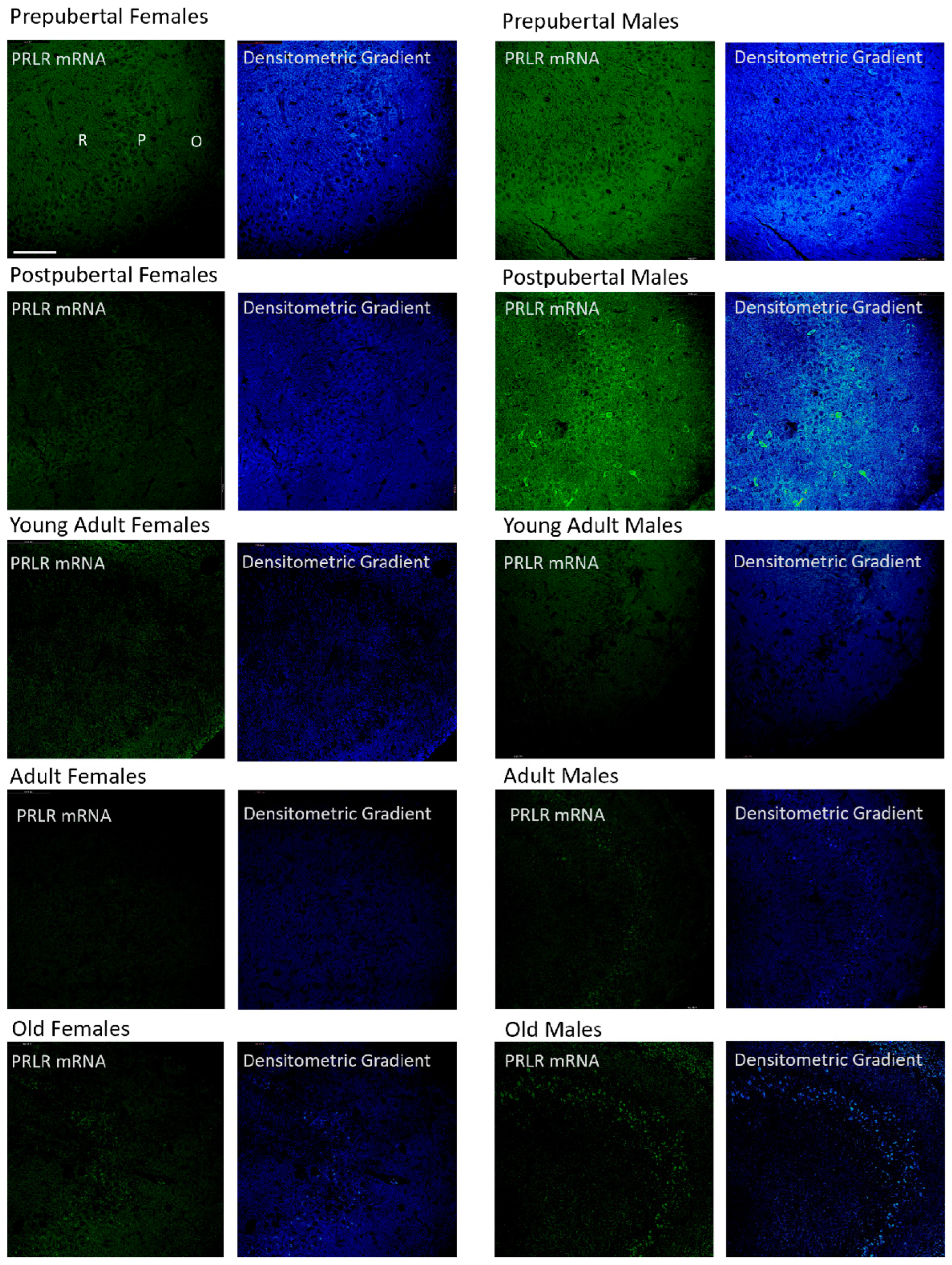
2.5. Distribution of Box1 mRNA in the Dentate as Determined by In Situ Hybridization (Figure 5)
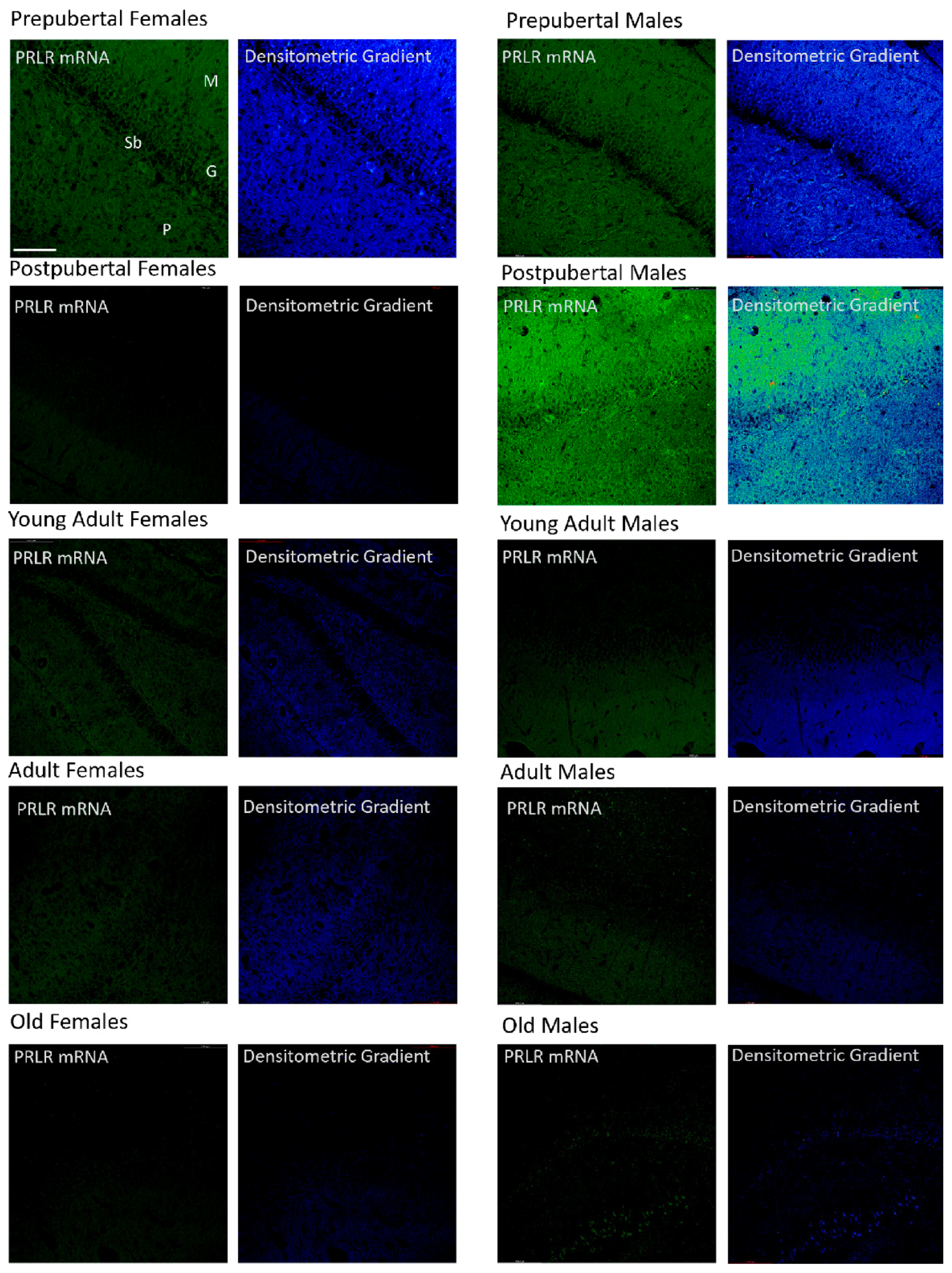
2.6. In Situ Hybridization Study: Box2 mRNA
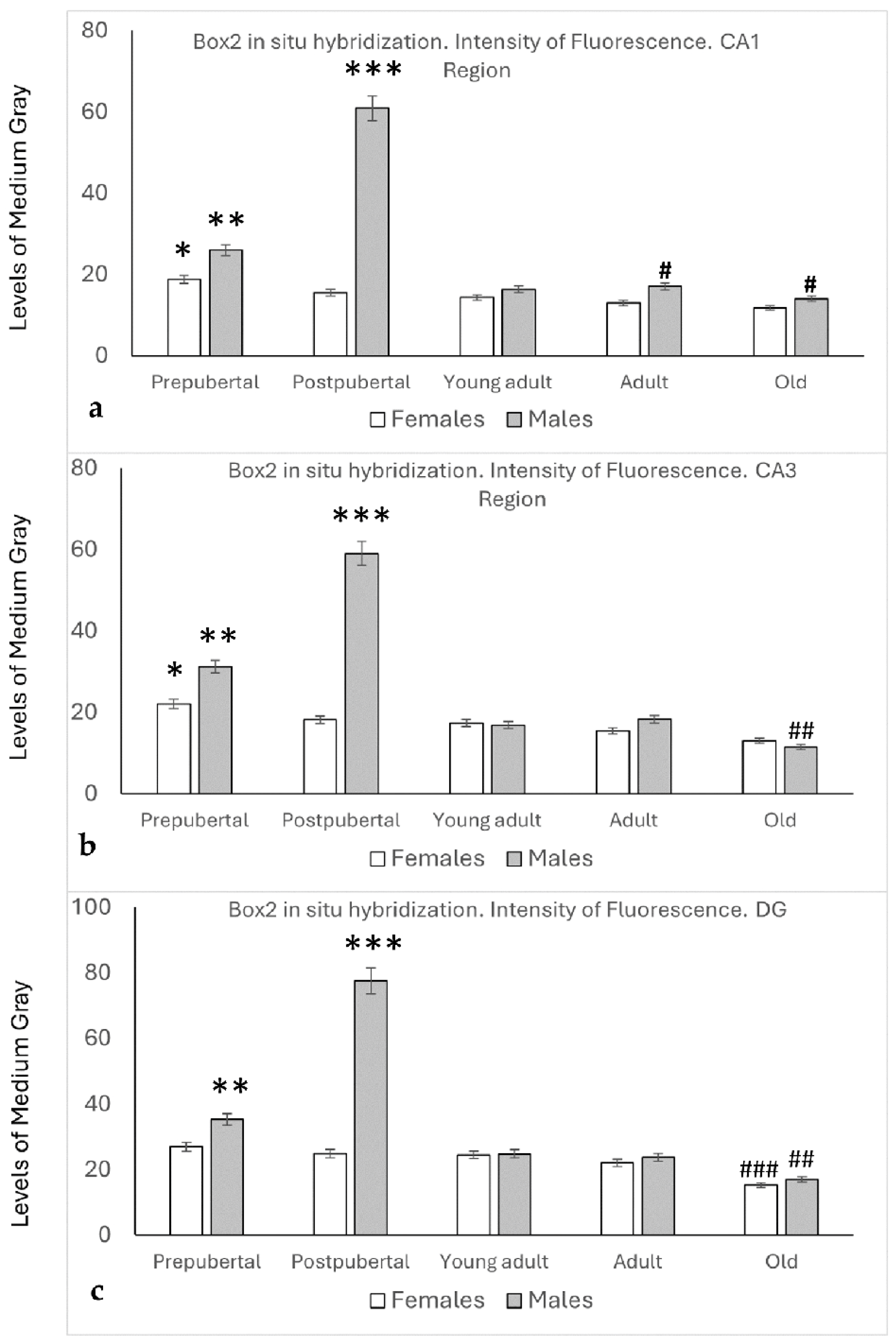
2.7. Distribution of Box2 mRNA in the CA1 Region by In Situ Hybridization (Figure 7)
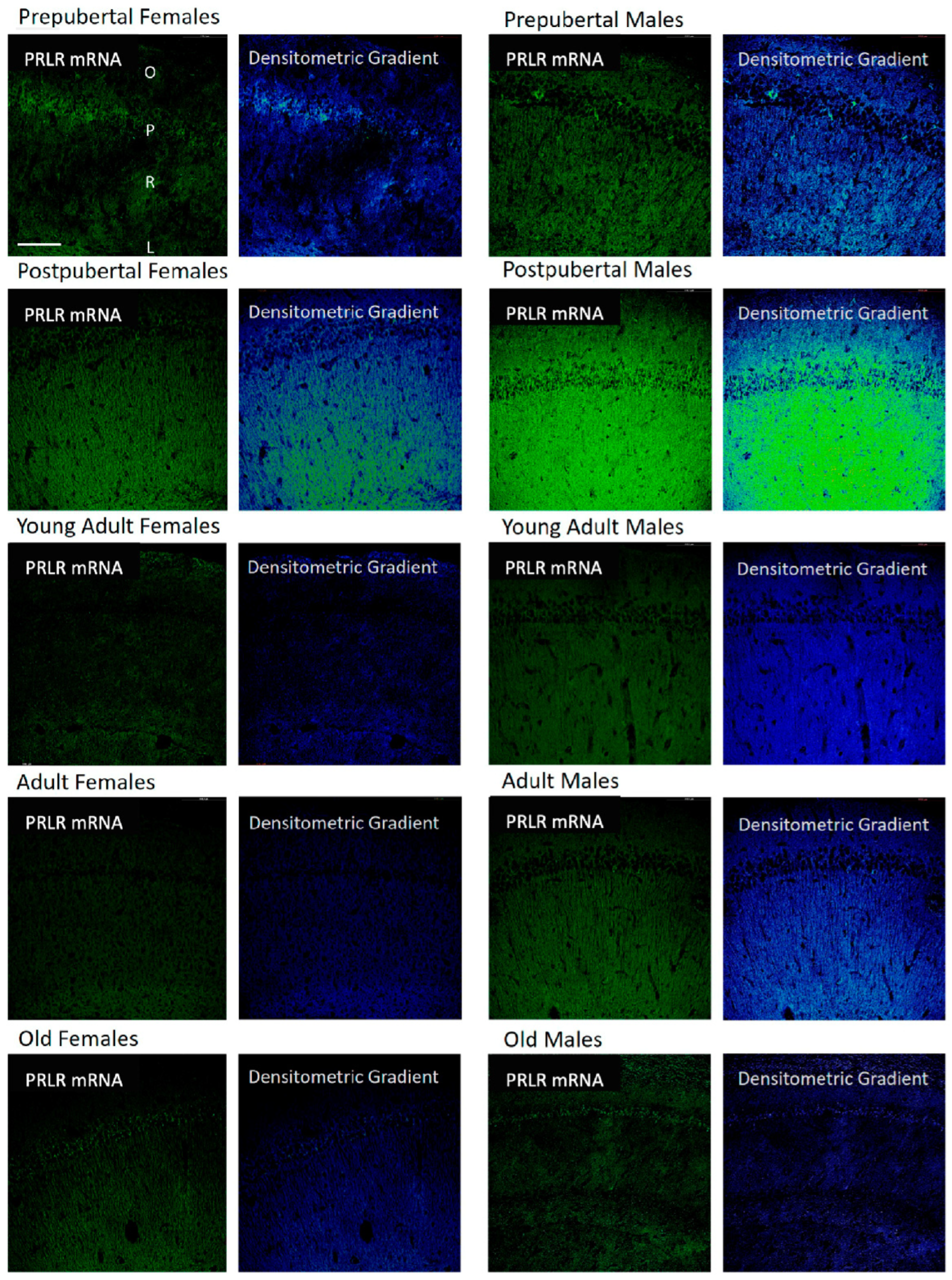
2.8. Distribution of Box2 mRNA in the CA3 Region by In Situ Hybridization (Figure 8)
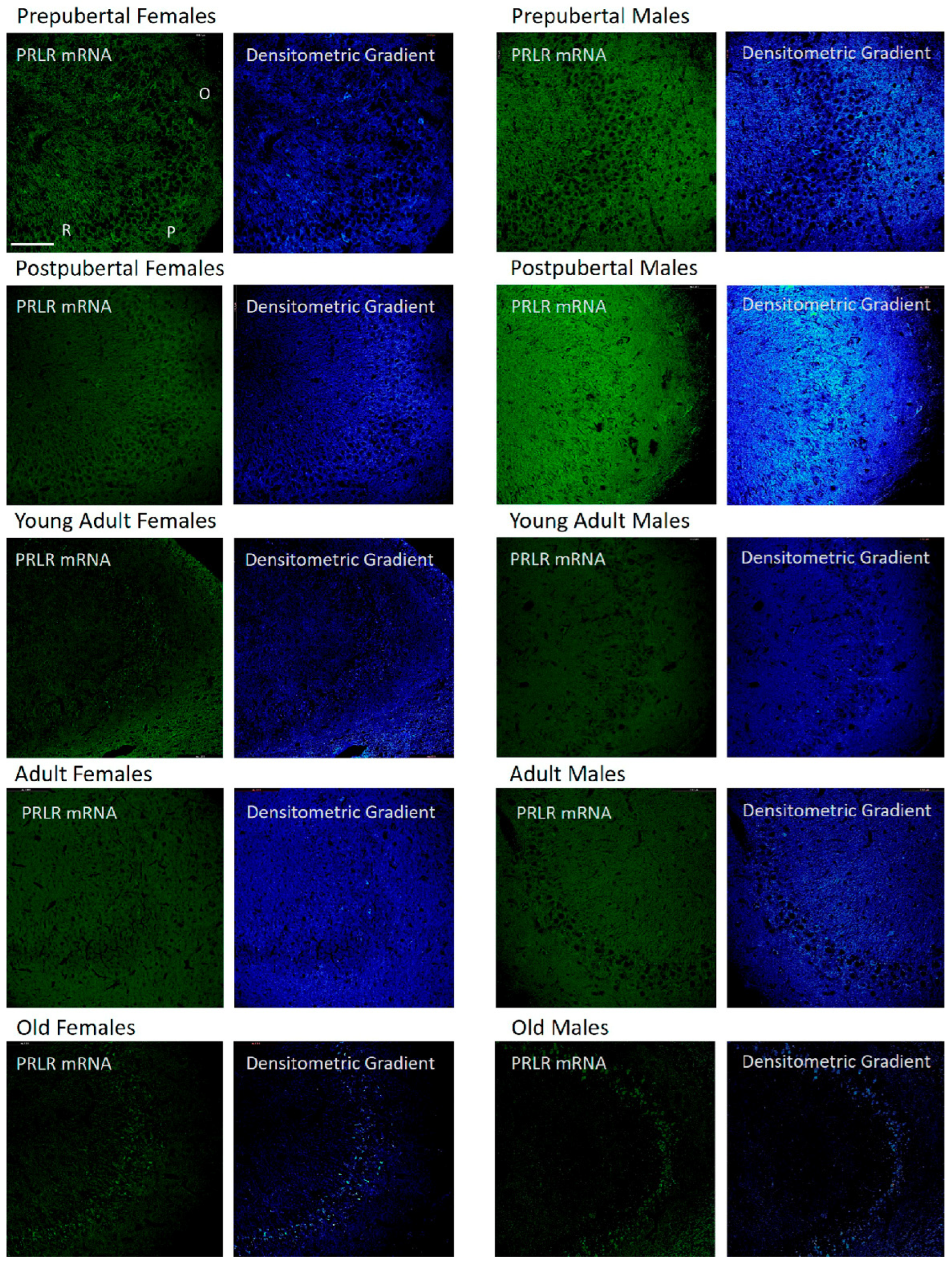
2.9. Distribution of Box2 mRNA in the Dentate Gyrus by In Situ Hybridization (Figure 9)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Groups to Study
4.2. Animal Sacrifice and Sample Collection
4.3. In Situ Hybridization
4.4. Image Analysis
4.5. Immunofluorescence Gradient Python Script
4.6. q-PCR Technique
4.6.1. Messenger RNA Extraction and Complementary DNA Synthesis
4.6.2. Cycling Chain Reaction
4.6.3. Primers and Data Normalization
Prolactin receptor Box1 reverse AGCAGTTCTTCAGACTTGCCCTT,
Prolactin receptor Box2 forward GCAGGTGAATGTTTCCTTGTC,
Prolactin receptor Box2 reverse CTTGCTTTCGTCCTACTTGTTC,
Hprt-1 forward CCCAGCGTCGTGATTAGCGAT,
Hprt-1 reverse CGAGCAAGTCTTTCAGTCCTGTCCATA.
4.7. Statistic Treatment of Data
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Akt | Protein Kinase B, also known as Akt, is the collective name for a set of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases. Oncogene isolated from tumors produced by the murine retrovirus AKT8 |
| Btn | Biotinylated |
| CA1 | Hippocampal Cornus Amonii 1 region |
| CA3 | Hippocampal Cornus Amonii 3 region |
| cDNA | Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DG | Dentate Gyrus |
| Hprt1 | House-keeping genes. It is a gene that provides instructions for producing an enzyme called hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 |
| JAK2 | Janus Kinase 2 |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MEK | Also known as MAPKK, it is a kinase that phosphorylates and activates MAPK (MAPK kinase/ERK kinase) |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| mTor | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| PBS | Phosphate saline buffer |
| PI3K | phosphatidyl-inositol 3-kinase |
| PRLR | Prolactin receptor |
| qPCR | Quantitative polimerase chain reaction |
| Raf | Ras-activated factor; it is a kinase that phosphorylates and activates MEK |
| Ras | Retrovirus-associated sequences of Monomeric G protein; it is a G protein, involved in the MAPK activation pathway by growth factors and mitogens |
| Src | Steroid receptor coactivator |
| SSC | Sodium citrate solution |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| STAT5 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 |
| TBS | Trizma saline buffer |
References
- Tyson, J.E.; Friesen, H.G. Factors influencing the secretion of human prolactin and growth hormone in menstrual and gestational women. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1973, 116, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, G.L.; Suh, H.K.; Frantz, A.G. Prolactin release during nursing and breast stimulation in postpartum and nonpostpartum subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1974, 38, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanoye-Carlo, A.; Morales, T.; Ramos, E.; Mendoza-Rodríguez, A.; Cerbón, M. Neuroprotective effects of lactation against kainic acid treatment in the dorsal hippocampus of the rat. Horm. Behav. 2008, 53, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, V.; Cantú, D.; Ramos, E.; Vanoye-Carlo, A.; Cerbón, M.; Morales, T. Lactation is a natural model of hippocampus neuroprotection against excitotoxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 461, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathipati, P.; Gorba, T.; Scheepens, A.; Goffin, V.; Sun, Y.; Fraser, M. Growth hormone and prolactin regulate human neural stem cell regenerative activity. Neuroscience 2011, 190, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, T.; Lorenson, M.; Walker, A.; Ramos, E. Both prolactin (prl) and a molecular mimic of phosphorylated prl, s179d-prl, protect the hippocampus of female rats against excitotoxicity. Neuroscience 2014, 258, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Flores-Soto, E.; García de la Cadena, S.; Coronado-Mares, I.; Gomez-Verjan, J.C.; Ferreira, D.G.; Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Lopes, L.V.; Massieu, L.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin-induced neuroprotection against glutamate excitotoxicity is mediated by the reduction of [Ca2+]i overload and NF-κB activation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thébault, S. Potential mechanisms behind the antioxidant actions of prolactin in the retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 160, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostou, I.; Muñoz-Mayorga, D.; Morales, T. Prolactin neuroprotective action against excitotoxic insult in the hippocampus of male mice. Peptides 2021, 135, 170425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holubová, M.; Hrubá, L.; Popelová, A.; Bencze, M.; Pražienková, V.; Gengler, S.; Kratochvílová, H.; Haluzík, M.; Železná, B.; Kuneš, J.; et al. Liraglutide and a lipidized analog of prolactin-releasing peptide show neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of β-amyloid pathology. Neuropharmacology 2019, 144, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeeth, D.M.; Kourouzidou, I.; Duarte, R.R.R.; Powell, T.R.; Thuret, S. Prolactin, estradiol and testosterone differentially impact human hippocampal neurogenesis in an in vitro model. Neuroscience 2021, 454, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, V.; Young, J.; Chanson, P.; Binart, N. New insights in prolactin: Pathological implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goffin, V.; Martial, J.A.; Summers, N.L. Use of a model to understand prolactin and growth hormone specificities. Protein Eng. 1995, 8, 1215–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bole-Feysot, C.; Goffin, V.; Edery, M.; Binart, N.; Kelly, P.A. Prolactin (prl) and its receptor: Actions, signal transduction pathways and phenotypes observed in prl receptor knockout mice. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 225–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugge, K.; Papaleo, E.; Haxholm, G.W.; Hopper, J.T.S.; Robinson, C.V.; Olsen, J.G.; Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Kragelund, B.B. A combined computational and structural model of the full-length human prolactin receptor. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretero-Hernández, M.; Catalano-Iniesta, L.; Blanco, E.J.; García-Barrado, M.J.; Carretero, J. Highlights regarding prolactin in the dentate gyrus and hippocampus. Vitam. Horm. 2022, 118, 479–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, J.A.; Sawyer, B.D. Identification of prolactin in cerebrospinal fluid. Exp. Brain Res. 1974, 21, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shingo, T.; Gregg, C.; Enwere, E.; Fujikawa, H.; Hassam, R.; Geary, C.; Cross, J.C.; Weiss, S. Pregnancy-stimulated neurogenesis in the adult female forebrain mediated by prolactin. Science 2003, 299, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogami, H.; Hoshino, R.; Ogasawara, K.; Miyamoto, S.; Hisano, S. Region-specific expression and hormonal regulation of the first exon variants of rat prolactin receptor mrna in rat brain and anterior pituitary gland. J. Neuroendocr. 2007, 19, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Limón-Morales, O.; Rivero-Segura, N.A.; Camacho-Arroyo, I.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin function and putative expression in the brain. Endocrine 2017, 57, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Pérez, A.; Limón-Morales, O.; Rojas-Castañeda, J.C.; Cerbón, M.; Picazo, O. Prolactin prevents the kainic acid-induced neuronal loss in the rat hippocampus by inducing prolactin receptor and putatively increasing the vglut1 overexpression. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 694, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Briguglio, J.J.; Romani, S.; Magee, J.C. Mechanisms of memory-supporting neuronal dynamics in hippocampal area CA3. Cell 2024, 187, 6804–6819.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, R.J.; Posner, B.I.; Kopriwa, B.M.; Brawer, J.R. Prolactin binding sites in the rat brain. Science 1978, 201, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posner, B.I.; van Houten, M.; Patel, B.; Walsh, R.J. Characterization of lactogen binding sites in choroid plexus. Exp. Brain Res. 1983, 49, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crumeyrolle-Arias, M.; Latouche, J.; Jammes, H.; Djiane, J.; Kelly, P.A.; Reymond, M.J.; Haour, F. Prolactin receptors in the rat hypothalamus: Autoradiographic localization and characterization. Neuroendocrinology 1993, 57, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, X.J.; Grattan, D.R. Distribution of prolactin receptor immunoreactivity in the brain of estrogen-treated, ovariectomized rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 394, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, X.J.; Grattan, D.R. Increased prolactin receptor immunoreactivity in the hypothalamus of lactating rats. J. Neuroendocr. 1999, 11, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roky, R.; Paut-Pagano, L.; Goffin, V.; Kitahama, K.; Valatx, J.-L.; Kelly, P.A.; Jouvet, M. Distribution of prolactin receptors in the rat forebrain: Immunohistochemical study. Neuroendocrinology 1996, 63, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakowska, J.C.; Morrell, J.I. Atlas of the neurons that express mrna for the long form of the prolactin receptor in the forebrain of the female rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 386, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakowska, J.C.; Morrell, J.I. The distribution of mrna for the short form of the prolactin receptor in the forebrain of the female rat. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 116, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, S.; Wise, P.M. Prolactin receptor mrna localization in the hypothalamus by in situ hybridization. J. Neuroendocr. 1994, 6, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.S.; Kokay, I.C.; Herbison, A.E.; Grattan, D.R. Distribution of prolactin-responsive neurons in the mouse forebrain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2010, 518, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokay, I.C.; Wyatt, A.; Phillipps, H.R.; Aoki, M.; Ectors, F.; Boehm, U.; Grattan, D.R. Analysis of prolactin receptor expression in the murine brain using a novel prolactin receptor reporter mouse. J. Neuroendocr. 2018, 30, e12634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Vergara-Castañeda, E.; Rivero-Segura, N.; Cerbón, M. Sex differences in prolactin and its receptor expression in pituitary, hypothalamus, and hippocampus of the rat. Rev. Mex. Endocrinol. Metab. Nutr. 2015, 2, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Vergara-Castañeda, E.; Grattan, D.R.; Pasantes-Morales, H.; Pérez-Domínguez, M.; Cabrera-Reyes, E.A.; Morales, T.; Cerbón, M. Prolactin mediates neuroprotection against excitotoxicity in primary cell cultures of hippocampal neurons via its receptor. Brain Res. 2016, 1636, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, T.; Minoura, H.; Toyoda, N.; Sakaguchi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Sudo, S.; Nakashima, K. Pup contact induces the expression of long form prolactin receptor mrna in the brain of female rats: Effects of ovariectomy and hypophysectomy on receptor gene expression. J. Endocrinol. 1996, 149, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustine, R.A.; Kokay, I.C.; Andrews, Z.B.; Ladyman, S.R.; Grattan, D.R. Quantitation of prolactin receptor mrna in the maternal rat brain during pregnancy and lactation. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 31, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.E.; Kanyicska, B.; Lerant, A.; Nagy, G. Prolactin: Structure, function, and regulation of secretion. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1523–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torner, L.; Karg, S.; Blume, A.; Kandasamy, M.; Kuhn, H.G.; Winkler, J.; Aigner, L.; Neumann, I.D. Prolactin prevents chronic stress-induced decrease of adult hippocampal neurogenesis and promotes neuronal fate. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Moura, A.C.; Lazzari, V.M.; Becker, R.O.; Gil, M.S.; Ruthschilling, C.A.; Agnes, G.; Almeida, S.; da Veiga, A.B.; Lucion, A.B.; Giovenardi, M. Gene expression in the cns of lactating rats with different patterns of maternal behavior. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 99, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emanuele, N.V.; Jurgens, J.K.; Halloran, M.M.; Tentler, J.J.; Lawrence, A.M.; Kelley, M.R. The rat prolactin gene is expressed in brain tissue: Detection of normal and alternatively spliced prolactin messenger rna. Mol. Endocrinol. 1992, 6, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möderscheim, T.A.; Gorba, T.; Pathipati, P.; Kokay, I.C.; Grattan, D.R.; Williams, C.E.; Scheepens, A. Prolactin is involved in glial responses following a focal injury to the juvenile rat brain. Neuroscience 2007, 145, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.H.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.Y.; Guo, K.M. Reducing prlr expression and jak2 activity results in an increase in bdnf expression and inhibits the apoptosis of ca3 hippocampal neurons in a chronic mild stress model of depression. Brain Res. 2019, 1725, 146472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, S.; Martínez-Moreno, C.G.; Luna, M.; Arámburo, C. Autocrine/paracrine roles of extrapituitary growth hormone and prolactin in health and disease: An overview. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 220, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Hassan, S.A.; Zhao, P.; Tsai-Morris, C.H.; Dufau, M.L. Impact of subdomain d1 of the short form s1b of the human prolactin receptor on its inhibitory action on the function of the long form of the receptor induced by prolactin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 2272–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejadilla, D.; Cerbón, M.; Morales, T. Prolactin reduces the damaging effects of excitotoxicity in the dorsal hippocampus of the female rat independently of ovarian hormones. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquifino, A.I.; Cano, P.; Jimenez, V.; Reyes Toso, C.F.; Cardinali, D.P. Changes of prolactin regulatory mechanisms in aging: 24-h rhythms of serum prolactin and median eminence and adenohypophysial concentration of dopamine, serotonin, (γ-aminobutyric acid, taurine and somatostatin in young and aged rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2004, 39, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goya, R.G.; Castro, M.G.; Meites, J. Differential effect of aging on serum levels of prolactin and α-melanotropin in rats. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1991, 196, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraris, J.; Bernichtein, S.; Pisera, D.; Goffin, V. Use of prolactin receptor antagonist to better understand prolactin regulation of pituitary homeostasis. Neuroendocrinology 2013, 98, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, C.M.; Grattan, D.R. Prolactin, neurogenesis, and maternal behaviors. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, M.J.; Henry, M.A.; Akopian, A.N. Prolactin receptor in regulation of neuronal excitability and channels. Channels 2014, 8, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Mendoza, J.; Morales, T. Post-treatment with prolactin protects hippocampal ca1 neurons of the ovariectomized female rat against kainic acid-induced neurodegeneration. Neuroscience 2016, 328, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, C.M.; Kokay, I.C.; Grattan, D.R. Male pheromones initiate prolactin-induced neurogenesis and advance maternal behavior in female mice. Horm. Behav. 2008, 53, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.; Couillard-Despres, S.; Lehner, B.; Brockhoff, G.; Rivera, F.J.; Blume, A.; Neumann, I.; Aigner, L. Prolactin induces mapk signaling in neural progenitors without alleviating glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of in vitro neurogenesis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 24, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, T.L.; Vukovic, J.; Koudijs, M.M.; Blackmore, D.G.; Mackay, E.W.; Sykes, A.M.; Overall, R.W.; Hamlin, A.S.; Bartlett, P.F. Prolactin stimulates precursor cells in the adult mouse hippocampus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkley, P.R.; Bobrovskaya, L.; Graham, M.E.; von Nagy-Felsobuki, E.I.; Dickson, P.W. Tyrosine hydroxylase phosphorylation: Regulation and consequences. J. Neurochem. 2004, 91, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T. The spectrum of prolactin action in teleosts. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1986, 205, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hodson, D.J.; Henderson, H.L.; Townsend, J.; Tortonese, D.J. Photoperiodic modulation of the suppressive actions of prolactin and dopamine on the pituitary gonadotropin responses to gonadotropin-releasing hormone in sheep. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVito, W.J.; Connors, J.M.; Hedge, G.A. Immunoreactive prolactin in the rat hypothalamus: In vitro release and subcellular localization. Neuroendocrinology 1987, 46, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devito, W.J.; Stone, S.; Avakian, C. Prolactin stimulation of protein kinase c activity in the rat hypothalamus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 176, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVito, W.J.; Okulicz, W.C.; Stone, S.; Avakian, C. Prolactin-stimulated mitogenesis of cultured astrocytes. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 2549–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Moratalla, A.; Martín, E.D. Prolactin enhances hippocampal synaptic plasticity in female mice of reproductive age. Hippocampus 2021, 31, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Jo, W.H.; Hoang, N.H.M.; Yu, B.P.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, M.S. 1,2-Diacetylbenzene impaired hippocampal memory by activating proinflammatory cytokines and upregulating the prolactin pathway: An in vivo and in vitro study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 108, 108901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Happel, J. If-Grad: Fluorescent Image Gradient Converter (v0.1.2) Free Computer Software. Available online: https://github.com/chaotix1992/IF-Grad (accessed on 17 November 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carretero-Hernández, M.; Herráez, E.; Hernández-González, D.; Díez-Castro, D.; Catalano-Iniesta, L.; García-Barrado, J.; Blanco, E.J.; Carretero, J. Lifetime Variations of Prolactin Receptor Isoforms mRNA in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat—Effects of Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115023
Carretero-Hernández M, Herráez E, Hernández-González D, Díez-Castro D, Catalano-Iniesta L, García-Barrado J, Blanco EJ, Carretero J. Lifetime Variations of Prolactin Receptor Isoforms mRNA in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat—Effects of Aging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115023
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarretero-Hernández, Marta, Elisa Herráez, David Hernández-González, David Díez-Castro, Leonardo Catalano-Iniesta, Josefa García-Barrado, Enrique J. Blanco, and José Carretero. 2025. "Lifetime Variations of Prolactin Receptor Isoforms mRNA in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat—Effects of Aging" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115023
APA StyleCarretero-Hernández, M., Herráez, E., Hernández-González, D., Díez-Castro, D., Catalano-Iniesta, L., García-Barrado, J., Blanco, E. J., & Carretero, J. (2025). Lifetime Variations of Prolactin Receptor Isoforms mRNA in the Hippocampus and Dentate Gyrus of the Rat—Effects of Aging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115023








