Evidence for a Putative Regulatory System Consisting of an ECF σE-Type Factor, LIC_12757, and a FecR-like σ Factor Regulator, LIC_12756, in the Pathogenic Spirochaetes Leptospira interrogans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
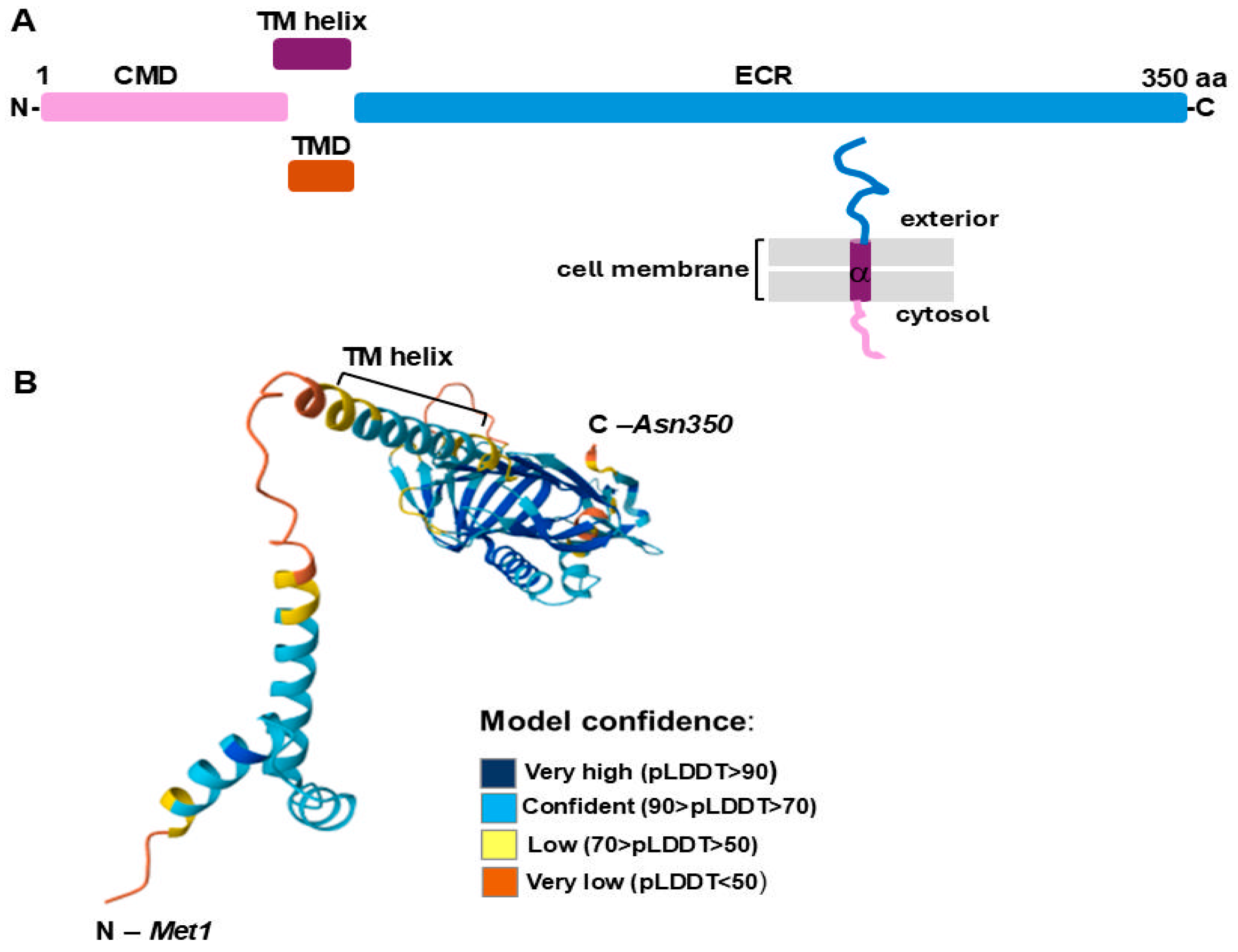
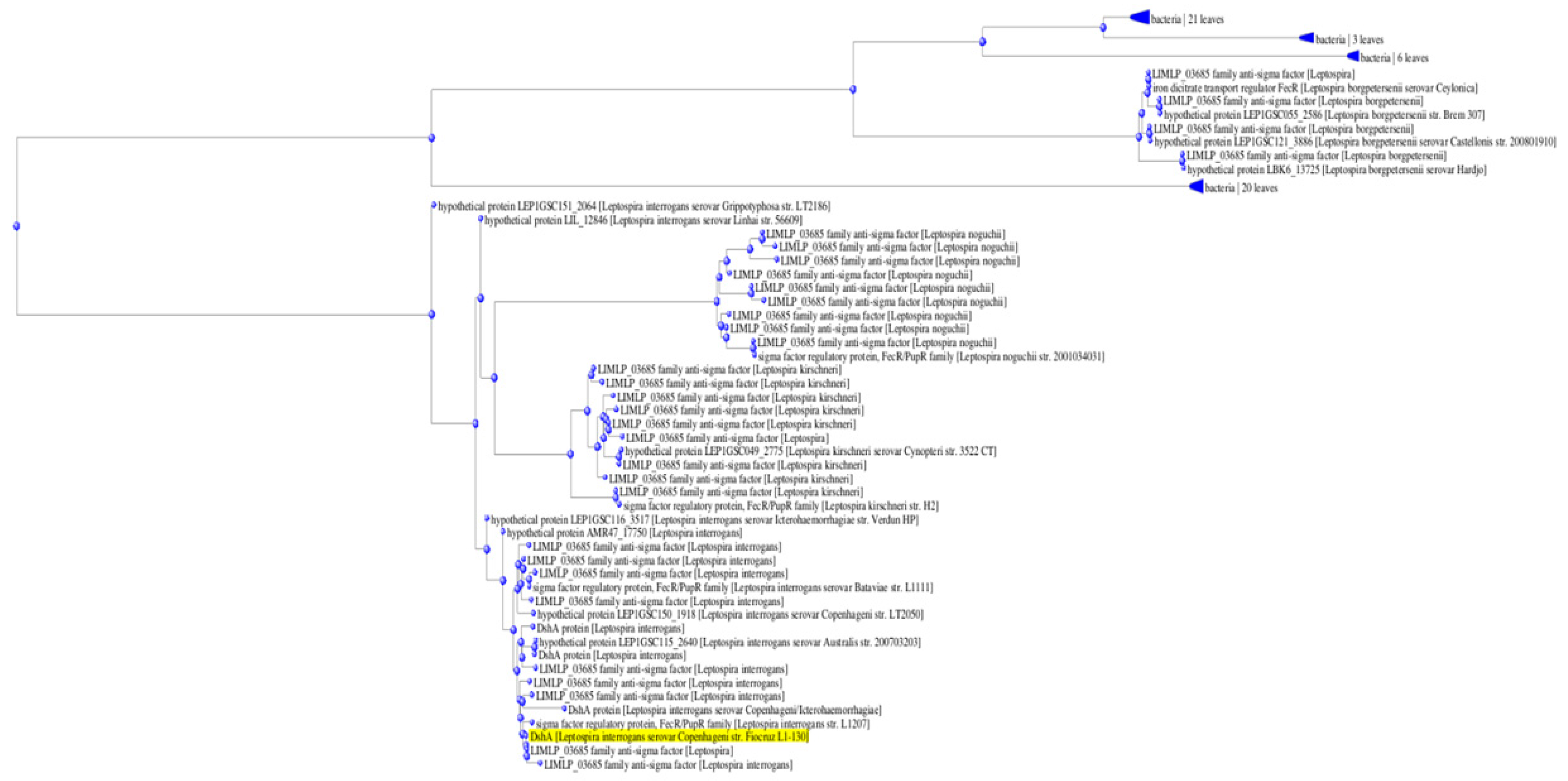
2.1. Analysis of LIC_12756 Amino Acid Sequence
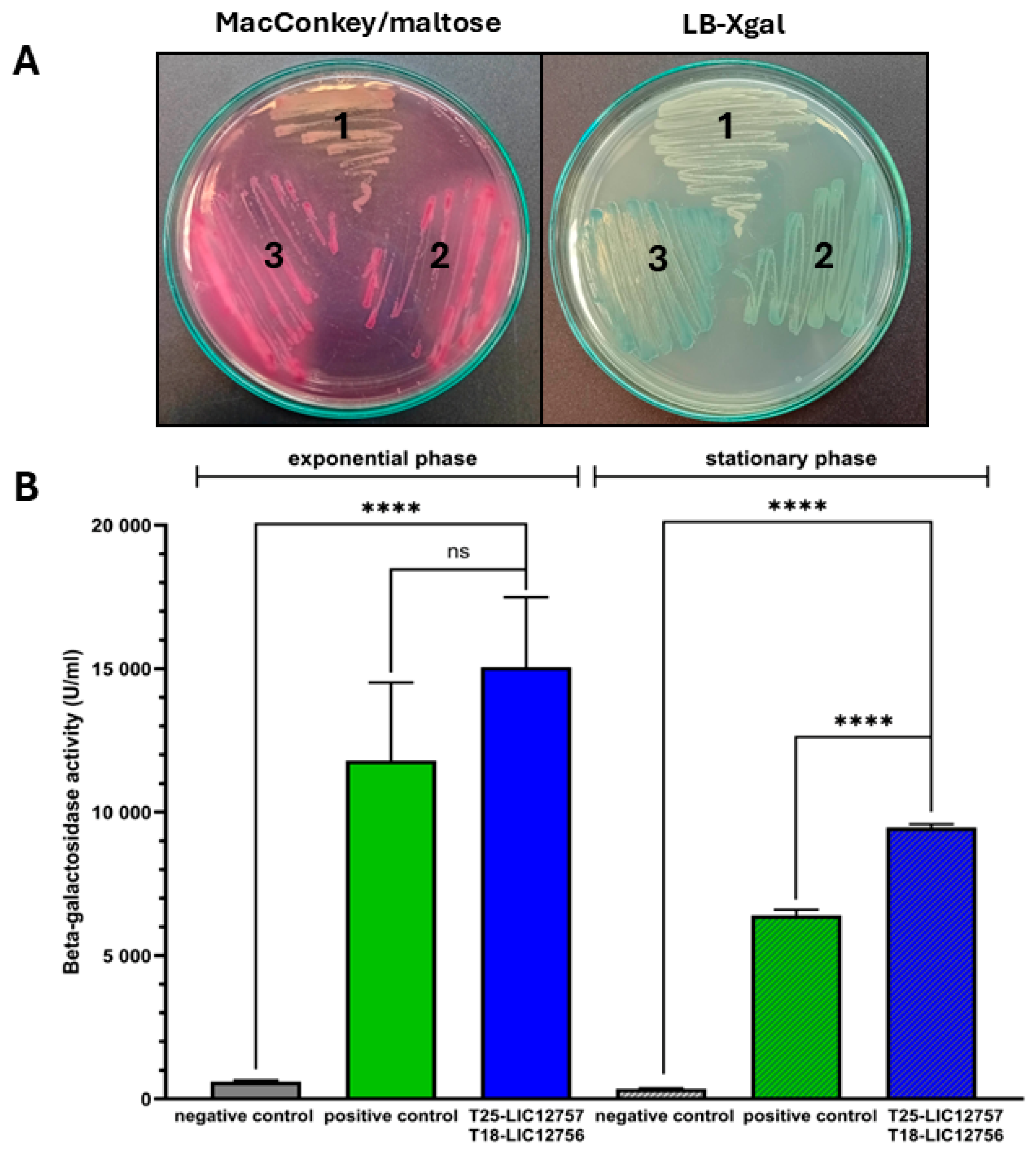
2.2. Detection of LIC_12757 and LIC_12756 Interactions—In Vivo BACTH Assay
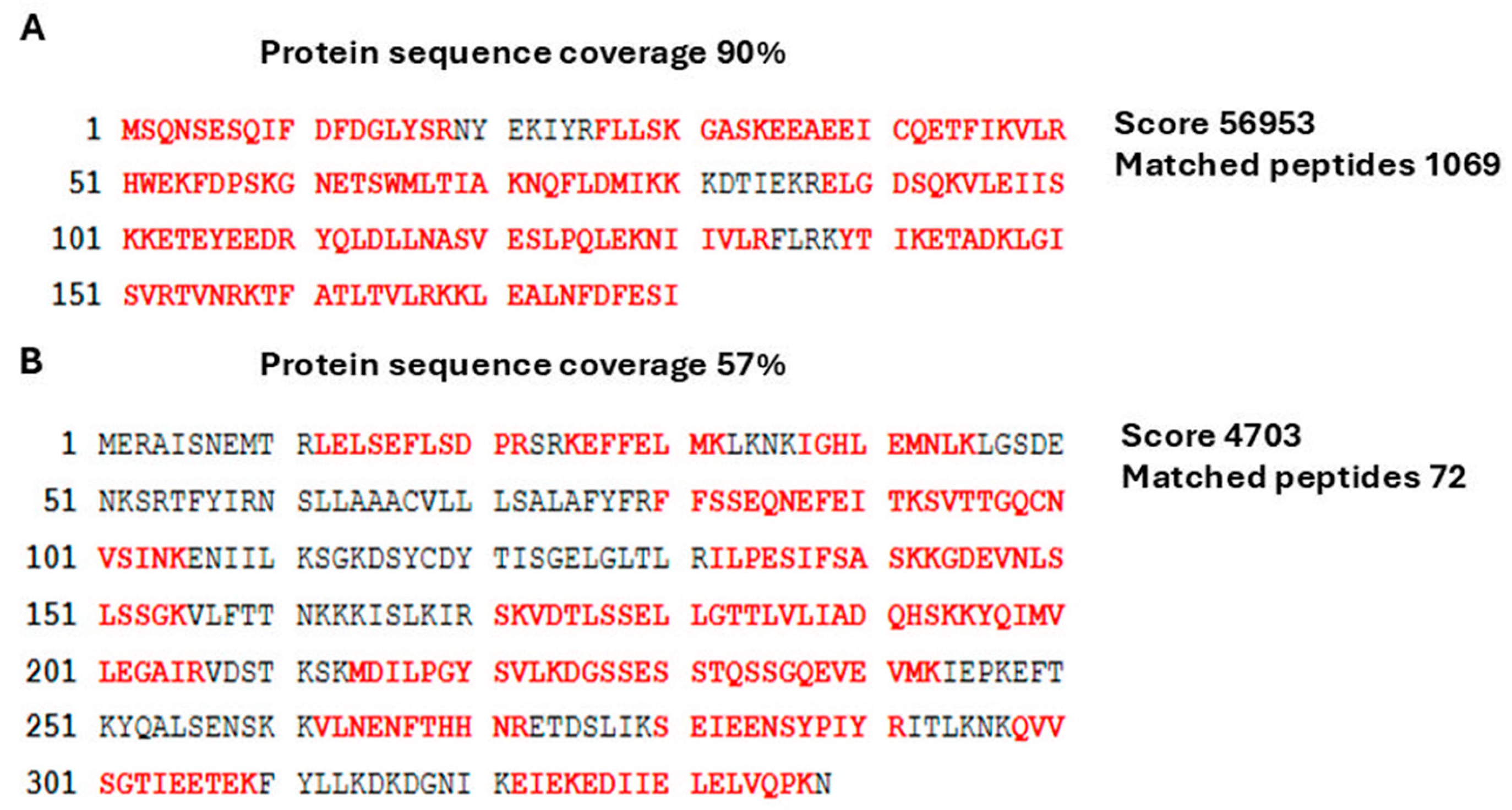
2.3. Detection of LIC_12757 and LIC_12756 Interactions—Study of LIC_12757–LIC_12756 Interactions In Vitro
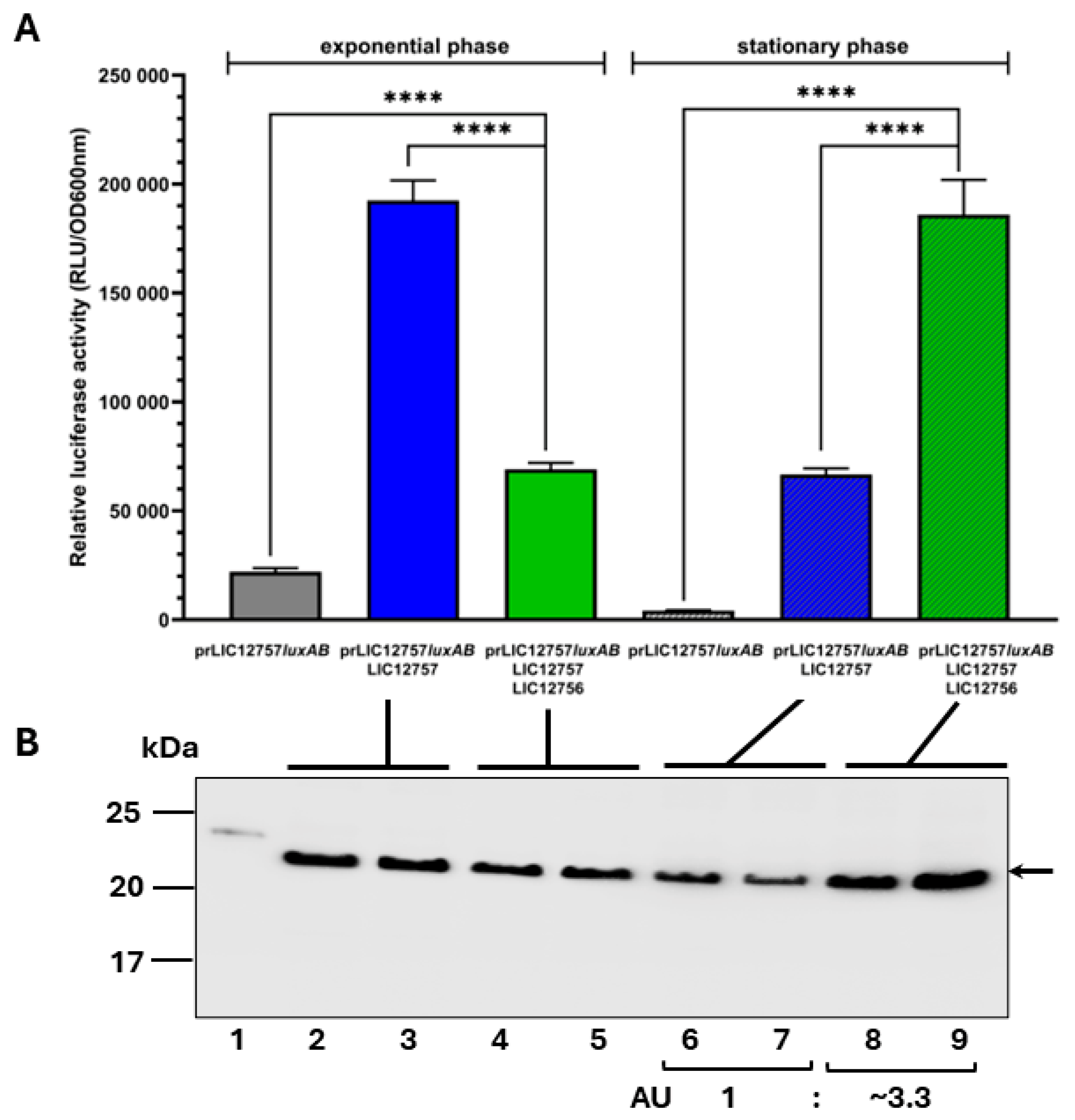
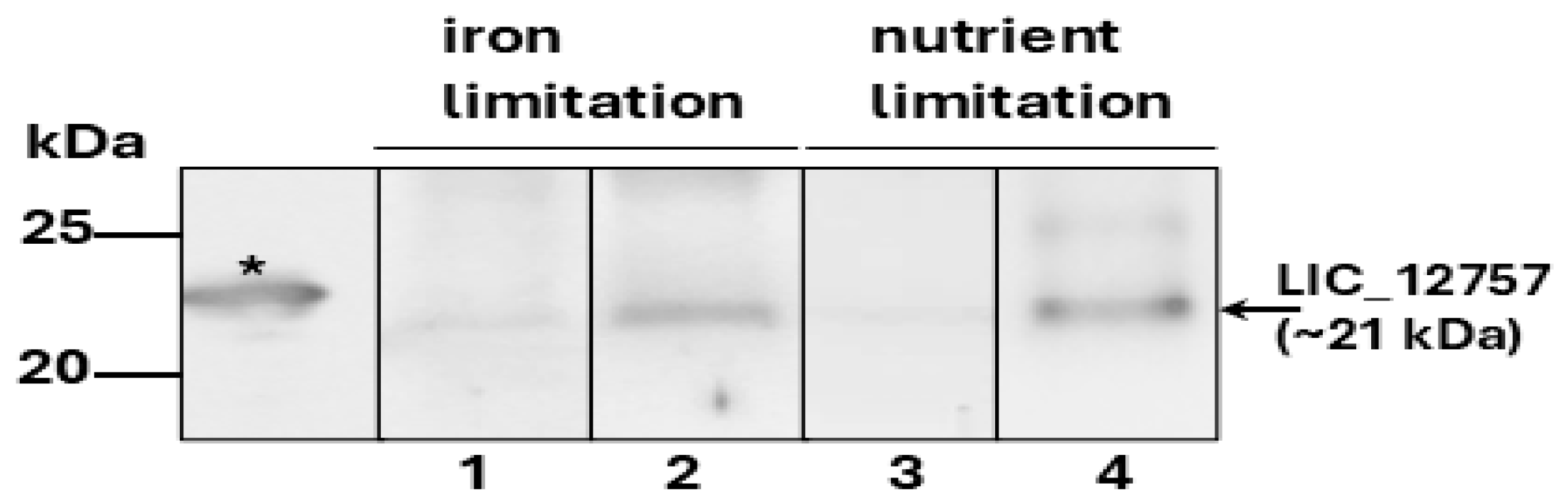
2.4. Effect of LIC_12756 on LIC_12757 Activity
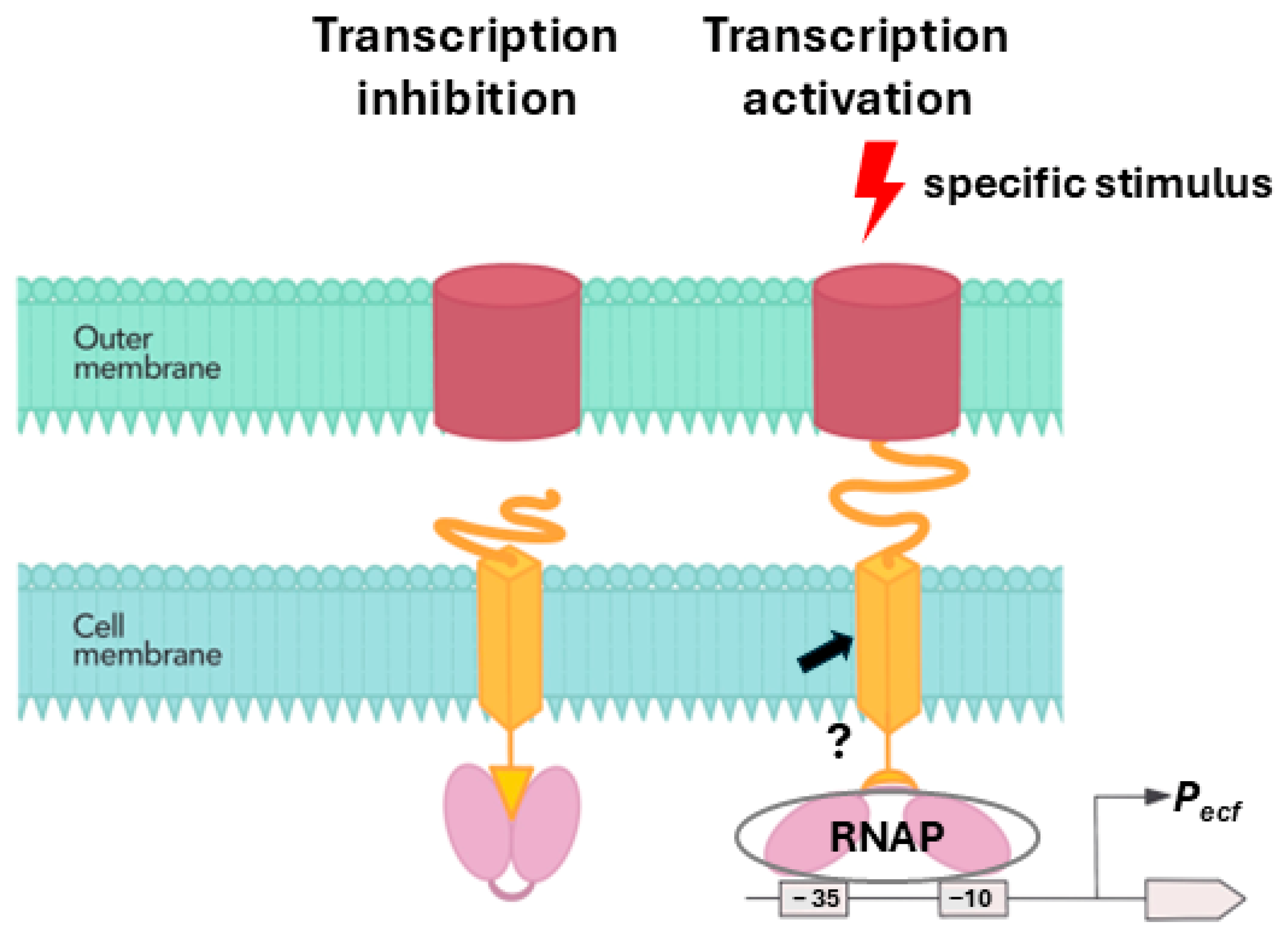
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Growth Media, Plasmids, and Genomic DNA
4.2. LIC_12756 Sequence Analyses—Bioinformatic Tools and Analyses
4.3. Plasmid Construction and DNA Manipulations
4.4. Detection of LIC_12757–LIC_12756 Interactions
4.4.1. BACTH Assay—Screening and β-Galactosidase Activity Assays
4.4.2. Affinity Pull-Down Assay and MS Analysis
4.5. In Vivo LIC_12757 Promoter Activity Assay
4.6. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDM | N-terminal cytoplasmic domain |
| CL | cell lysate |
| ECF | extracytoplasmic function |
| ECR | C-terminal non-cytoplasmic domain |
| RNAP | RNA polymerase core enzyme |
| TM helix | transmembrane helical domain |
References
- Bierue, E.; Thibeaux, R.; Girault, D.; Soupé-Gilbert, M.E.; Goarant, C.A. A systematic review of Leptospira in water and soil environments. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Bulcha, M.R.; Bune, W.M. Leptospirosis and one health perspective. Am. J. Public Health Res. 2021, 9, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Torgerson, P.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Stein, C.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Ko, A.I. Global morbidity and mortality of leptospirosis: A systematic review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.G.; Nola, L.; O’Grady, L.; More, S.J.; Doherty, L.M. Seroprevalence of Leptospira Hardjo in the irish suckler cattle population. Ir. Vet. J. 2012, 65, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arent, Z.; Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S. Seroprevalence study of leptospirosis in horses in northern Poland. Vet. Rec. 2013, 172, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Dong, H.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Hu, W.; Sun, A.; Troxell, B.; Yang, X.F.; Yan, J. Transcriptional responses of Leptospira interrogans to host innate immunity: Significant changes in metabolism, oxygen tolerance, and outer membrane. PLoS Negl. Trop. 2010, 4, e857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.; Bulach, D.M.; Powell, D.R.; Haake, D.A.; Matsunaga, J.; Paustian, M.L.; Zuerner, R.L.; Adler, B. Effects of temperature on gene expression patterns in Leptospira interrogans serowar Lai as assessed by whole-genome microarrays. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 5848–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.; Murray, G.L.; Khoo, C.A.; Haake, D.A.; Zuerner, R.L.; Adler, B. Transcriptional response of Leptospira interrogans to iron limitation and characterization of a PerR homolog. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 4850–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.H.; Sheng, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Shi, Y.Z.; He, P.; Hu, B.Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.G.; Zhao, G.P.; Guo, X.K. Genome-wide transcriptional analysis of temperature shift in L. interrogans serovar Lai strain 56601. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, J.; Lo, M.; Bulach, D.M.; Zuerner, R.L.; Adler, B.; Haake, D.A. Response of Leptospira interrogans to physiologic osmolarity: Relevance in signaling the environment-to-host transition. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patarakul, K.; Lo, M.; Adler, B. Global transcriptomic response of Leptospira interrogans serovar Copenhageni upon exposure to serum. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caimano, M.J.; Sivasankaran, S.K.; Allard, A.; Hurley, D.; Hokamp, K.; Grassmann, A.A.; Hinton, J.C.; Nally, J.E. A model system for studying the transcriptomic and physiological changes associated with mammalian host-adaptation by Leptospira interrogans serovar Copenhageni. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nally, J.E.; Grassmann, A.A.; Planchon, S.; Sergeant, K.; Renaut, J.; Seshu, J.; McBride, A.J.; Caimano, M.J. Pathogenic leptospires modulate protein expression and post-translational modifications in response to mammalian host signals. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, C.A.; Chan, C.; Dombrowski, A.; Gruber, T.; Sharp, M.; Tupy, J.; Young, B. The functional and regulatory roles of sigma factors in transcription. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1998, 63, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, R.R.; Anthony, L. How sigma docks to RNA polymerase and what sigma does. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2001, 4, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouts, D.E.; Matthias, M.A.; Adhikarla, H.; Adler, B.; Amorim-Santos, L.; Berg, D.E.; Bulach, D.; Buschiazzo, A.; Chang, Y.F.; Galloway, R.L.; et al. What makes a bacterial species pathogenic?: Comparative genomic analysis of the genus Leptospira. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, A.; Fernandes, L.G.; Hugon, P.; Pappas, C.J.; Sismeiro, O.; Coppée, J.-Y.; Becavin, C.; Malabat, C.; Eshghi, A.; Zhang, J.J.; et al. Genome-wide transcriptional start site mapping and sRNA identification in the pathogen Leptospira interrogans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, C.; Groot Kormelink, T.; Hagemeijer, Y.; Overmars, L.; Sluijter, V.; Moezelaar, R.; Sjezen, R.J. Comparative analyses imply that the enigmatic sigma factor 54 is a central controller of the bacterial exterior. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmann, J.D. The extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2002, 46, 47–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganelli, R.; Fattorini, L.; Tan, D.; Iona, E.; Orefici, G.; Altavilla, G.; Cusatelli, P.; Smith, I. The extracytoplasmic function sigma factor σE is essentials for Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence in mice. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 3038–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierczak, M.J.; Wiedmann, M.; Boor, K.J. Alternative sigma factors and their roles in bacterial virulence. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karls, R.; Guarner, J.; McMurray, D.N.; Birkness, K.A.; Quin, F.D. Examination of Mycobacterium tuberculosis sigma factor mutants using low-dose aerozol infection of guinea pigs suggest a role for SigC in pathogenesis. Microbiology 2006, 152, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMeechan, A.; Roberts, M.; Cogan, T.A.; Jørgensen, F.; Stevenson, A.; Lewis, C.; Rowley, G.; Humphrey, T.J. Role of the alternative sigma factors σE and σS in survival of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium during starvation, refrigeration and osmotic shock. Microbiology 2007, 15, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Asman, J.R.; Quesada, J.M.; Jim, K.K.; Ocampo-Sosa, A.; Civantos, C.; Bitter, W.; Llamas, M.A. The extracytoplasmic function sigma factor σVrel is active during infection and contributes to phosphate starvation-induced virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visca, P.; Leoni, L.; Wilson, M.J.; Lamont, I.L. Iron transport and regulation, cell signaling and genomics: Lessons from Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paget, M.S. Bacterial sigma factors and anti-sigma factors: Structure, function and distribution. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1245–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S. Sigma factors of RNA polymerase in the pathogenic spirochaete Leptospira interrogans, the causative agent of leptospirosis. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiefel, A.; Mahren, S.; Ochs, M.; Schindler, P.T.; Enz, S.; Braun, V. Control of the ferric citrate transport system of Escherichia coli: Mutations in region 2.1 of the FecI extracytoplasmic-function sigma factor suppress mutations in the FecR transmembrane regulatory protein. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascher, T. Past, present, and future of extracytoplasmic function σ factors: Distribution and regulatory diversity of the third pillar of bacterial signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 77, 625–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Niinae, T.; Tsumagari, K.; Imami, K.; Ishihama, Y.; Hizukuri, Y.; Akiyama, Y. The Escherichia coli S2P intramembrane protease RseP regulates ferric citrate uptake by cleaving the sigma factor regulator FecR. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S.; Kędzierska, B.; Potrykus, K. LIC_12757 from the pathogenic spirochaetes Leptospira interrogans encodes an autoregulated ECF σE-type factor. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 293, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.H.; von Heijne, G. Transmembrane helices before, during, and after insertion. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005, 15, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Fjgurnov, M. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively expanding the structural coverage of protein-sequence space with high-accuracy models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, K.; Sasaki, H.; Hamada, N.; Sharma, A. An extracytoplasmic function sigma/anti-sigma factor system, regulates β-glucanase expression in Tannerella forsythia in response to Fusobacterium nucleatum sensing. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.E.; Buchanan, S.K. Signaling mechanisms for activation of extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 1930–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler Leman, J.; Szczerbiak, P.; Renfrew, P.D.; Gligorijevic, V.; Berenberg, D.; Vatanen, T.; Taylor, B.C.; Chandler, C.; Janssen, S.; Pataki, A.; et al. Sequence-structure-function relationships in the microbial protein universe. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimova, G.; Pidoux, J.; Ullmann, A.; Ladant, D. A bacterial two-hybrid system based on a reconstituted signal transduction pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 5752–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.G.; Goldammer, M.; Gauliard, E.; Ladant, D.; Ouellette, S.P. A bacterial adenylate cyclase-based two-hybrid system compatible with gateway cloning. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1794, 5–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletnev, P.; Osterman, I.; Sergiev, P.; Bogdanov, A.; Dontsova, O. Survival guide: Escherichia coli in the stationary phase. Acta Naturae 2015, 7, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.L.; Ko, A.I.; Martins, E.A.; Monteiro-Vitorello, C.B.; Ho, P.L.; Haake, D.A.; Verjovski-Almeida, S.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Marques, M.D.; Oliveira, M.C.; et al. Comparative genomics of two Leptospira interrogans reveals novel insights into physiology and pathogenesis. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaultney, R.A.; Vincent, A.T.; Lorioux, C.; Coppée, J.Y.; Sismeiro, O.; Varet, H.; Legendre, R.; Cockram, C.A.; Veyrier, F.J.; Picardeau, M. 4-methylcytosine DNA modification is critical for global epigenetic regulation and virulence in the human pathogen Leptospira interrogans. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 12102–12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, H.S.; Mehta, S.; Cárdenas, W.B.; Stewart-Ibarra, A.M.; Finkelstein, J.L. Micronutrients and leptospirosis: A review of the current evidence. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S.; Potrykus, K.; Arent, Z.; Krajewska, J. Identification of σE-dependent promoter upstream of clpB from the pathogenic spirochaete Leptospira interrogans by applying an E. coli two-plasmid system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, J.; Modrak-Wójcik, A.; Arent, Z.; Więckowski, D.; Zolkiewski, M.; Bzowska, A.; Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S. Characterization of the molecular chaperone ClpB from the pathogenic spirochaete Leptospira interrogans. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S.; Zolkiewski, M. Hsp100 molecular chaperone ClpB and its role in virulence of bacterial pathogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourdault, K.; Cerqueira, G.M.; Wunder, E.A., Jr.; Picardeau, M. Inactivation of clpB in the pathogen Leptospira interrogans reduces virulence and resistance to stress conditions. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3711–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Lata, K.S.; Sharma, P.; Bhairappanavar, S.B.; Soni, S.; Das, J. Inferring pathogen-host interactions between Leptospira interrogans and Homo sapiens using network theory. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvel, H.; Bommezzadri, S.; Zidane, N.; Boursaux-Eude, C.; Creno, S.; Magnier, A.; Rouy, Z.; Médigue, C.; Girons, I.S.; Bouchier, C.; et al. Comparative and functional genomic analyses of iron transport and regulation in Leptospira spp. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7893–7904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, J.; Arent, Z.; Zolkiewski, M.; Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S. Immunoreactivity of the AAA+ chaperone ClpB from Leptospira interrogans with sera from Leptospira-infected animals. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.L.; Verjovski-Almeida, S.; Van Sluys, M.A.; Monteiro-Vitorello, C.B.; Camargo, L.E.; Digiampietri, L.A.; Harstkeerl, R.A.; Ho, P.L.; Marques, M.D.; Oliveira, M.C.; et al. Genome features of Leptospira interrogans serovar Copenhageni. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2004, 37, 459–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Blum, M.; Chuguransky, S.; Grego, T.; Pinto, B.L.; Salazar, G.A.; Bileschi, M.L.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Colwell, L.; et al. InterPro in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D418–D427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Guenther, I.; Zolkiewski, M.; Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S. Cooperation between two ClpB isoforms enhances the recovery of the recombinant β-galactosidase from inclusion bodies. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H. Experiments in Molecular Genetics; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S.; Arent, Z. Immunoreactivity of a putative ECF σ factor, LIC_10559, from Leptospira interrogans with sera from Leptospira-infected animals. Pathogens 2023, 12, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| E. coli Strain/Plasmid | Genotype | Reference/Source |
|---|---|---|
| DH5α | supE44, hsdR1, recA1, endA1, gyrA1, gyrA96, thi-1, relA1 | laboratory stock |
| DHM1 | F−, cya-854, recA1, endA1, gyrA96 (Nalr), thi1, hsdR17, spoT1, rfbD1, glnV44(AS) | Euromedex (France) |
| MG1655 | F−, lambda- ilvG-, rfb-50, rph-1 | laboratory stock |
| XL1-Blue | recA1, endA1, gyrA96, thi-1 hsdR17, supE44, relA1, lac [F’proAB lacIq Z∆M15Tn10 (Tetr)] | laboratory stock |
| pJET1.2/blunt | PCR cloning vector carrying an ampicillin resistance gene | ThermoFisher Scientific, Poznań, Poland |
| pKT25 | pSU40 derivative that encodes the T25 fragment (corresponding to the first 224 amino acid residues of bacterial cyclase adenylate, CyaA), the production of which is controlled by a lac promoter; this plasmid contains a kanamycin resistance selectable marker | Euromedex (France) |
| pUT18C | pUC19 derivative that encodes the T18 fragment (corresponding to the amino acid residues 225 to 399 of CyaA), the production of which is controlled by a lac promoter; this plasmid contains an ampicillin resistance selectable marker | Euromedex (France) |
| pKT25-zip | pKT25 derivative encoding a fusion protein in which the leucine zipper of GCN4 is fused with the T25 fragment of CyaA; it is used together with pUT18C-zip as a positive control for complementation assay (BACTH assay) | Euromedex (France) |
| pUT18C-zip | pUT18C derivative encoding a fusion protein in which the leucine zipper GCN4 is fused with the T18 fragment of CyaA; used in complementation assay (BACTH assay) | Euromedex (France) |
| pAC-LIC12757 | pAC7 derivative containing the L. interrogans LIC_12757 gene under the control of a pBAD promoter and a chloramphenicol resistance gene; used for luciferase activity assay | Kędzierska-Mieszkowska et al., 2019 [44] |
| prLIC12757luxAB | pGB2 derivative containing the V. harveyi luxAB genes and a promoter region of the L. interrogans LIC_12757 gene (used for luciferase activity assay) | Kędzierska-Mieszkowska et al., 2024 [31] |
| pKT25-LIC12757 | pKT25 derivative encoding a fusion protein T25-LIC_12757 (BACTH assay) | this study |
| pTU18C-LIC12756 | pUT18C derivative encoding a fusion protein T18-LIC_12756 (BACTH assay) | this study |
| Oligonucleotide | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| pF12757PstI | CTGCAGGGATGGCCAAAATTCCGAAAG | cloning of LIC_12757 into pJET1.2/blunt → pKT25 |
| prev12757KpnI | GGTACCCGTATACTCTCAAAGTCGAAATTC | cloning of LIC_12757 into pJET1.2/blunt → pKT25 |
| pF12756PstI | CTGCAGGATGGAACCTAATTCAGATTC | cloning of LIC_12756 into pJET1.2/blunt → pUT18C |
| prev12756KpnI | GGTACCCGGTTCTTTGGTTGAACAAGTTC | cloning of LIC_12756 into pJET1.2/blunt → pUT18C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kędzierska-Mieszkowska, S.; Kędzierska, B.; Pardyak, L.; Arent, Z. Evidence for a Putative Regulatory System Consisting of an ECF σE-Type Factor, LIC_12757, and a FecR-like σ Factor Regulator, LIC_12756, in the Pathogenic Spirochaetes Leptospira interrogans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114994
Kędzierska-Mieszkowska S, Kędzierska B, Pardyak L, Arent Z. Evidence for a Putative Regulatory System Consisting of an ECF σE-Type Factor, LIC_12757, and a FecR-like σ Factor Regulator, LIC_12756, in the Pathogenic Spirochaetes Leptospira interrogans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):4994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114994
Chicago/Turabian StyleKędzierska-Mieszkowska, Sabina, Barbara Kędzierska, Laura Pardyak, and Zbigniew Arent. 2025. "Evidence for a Putative Regulatory System Consisting of an ECF σE-Type Factor, LIC_12757, and a FecR-like σ Factor Regulator, LIC_12756, in the Pathogenic Spirochaetes Leptospira interrogans" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 4994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114994
APA StyleKędzierska-Mieszkowska, S., Kędzierska, B., Pardyak, L., & Arent, Z. (2025). Evidence for a Putative Regulatory System Consisting of an ECF σE-Type Factor, LIC_12757, and a FecR-like σ Factor Regulator, LIC_12756, in the Pathogenic Spirochaetes Leptospira interrogans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 4994. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114994






