Repeated Valproic Acid Administration Fundamentally Ameliorated Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Dose–Response Effects and Temporal Changes on CDDP-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats Following Single Administration of VPA
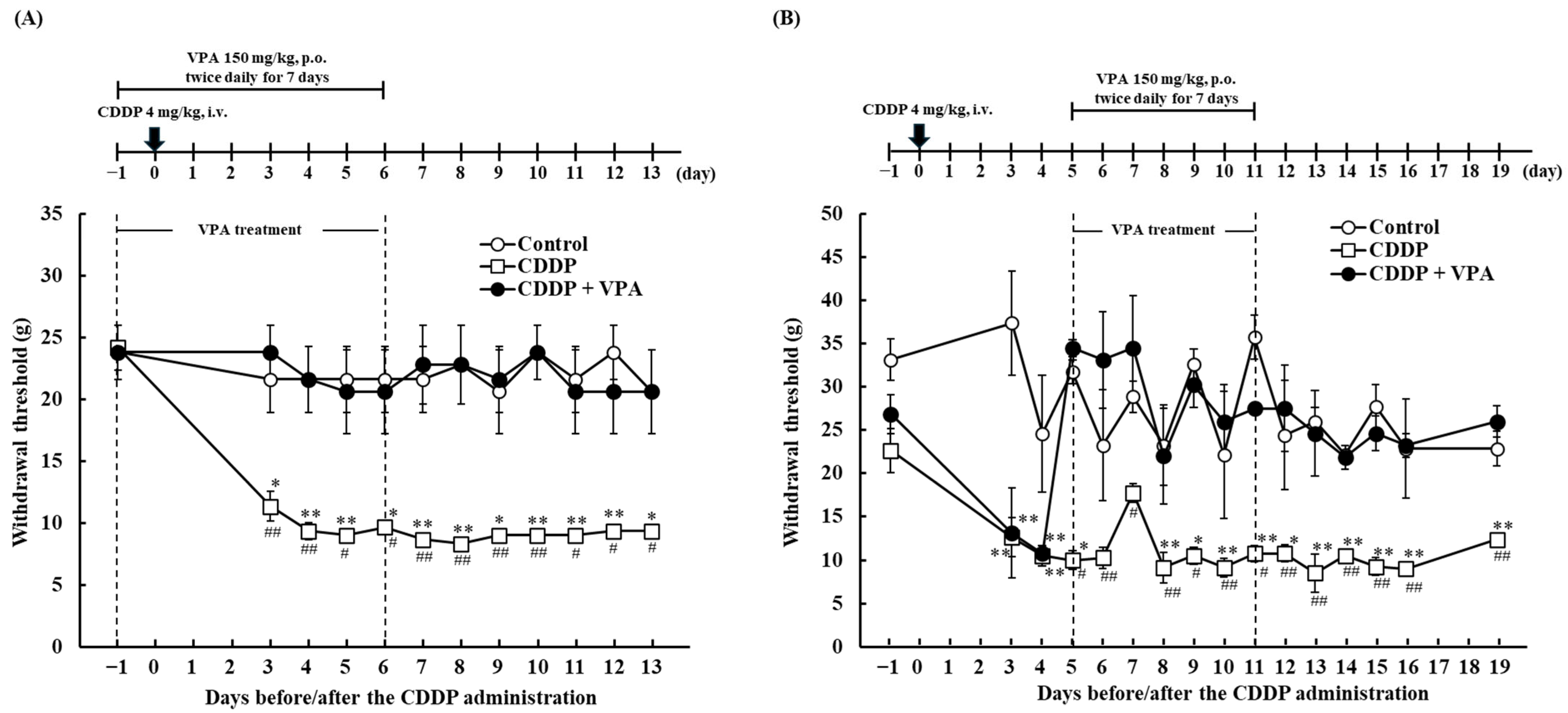
2.2. Effect of Repeated VPA Administration on CDDP-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats
2.3. Time Profiles of Serum VPA Concentrations Following Single and Repeated VPA Administration in Rats
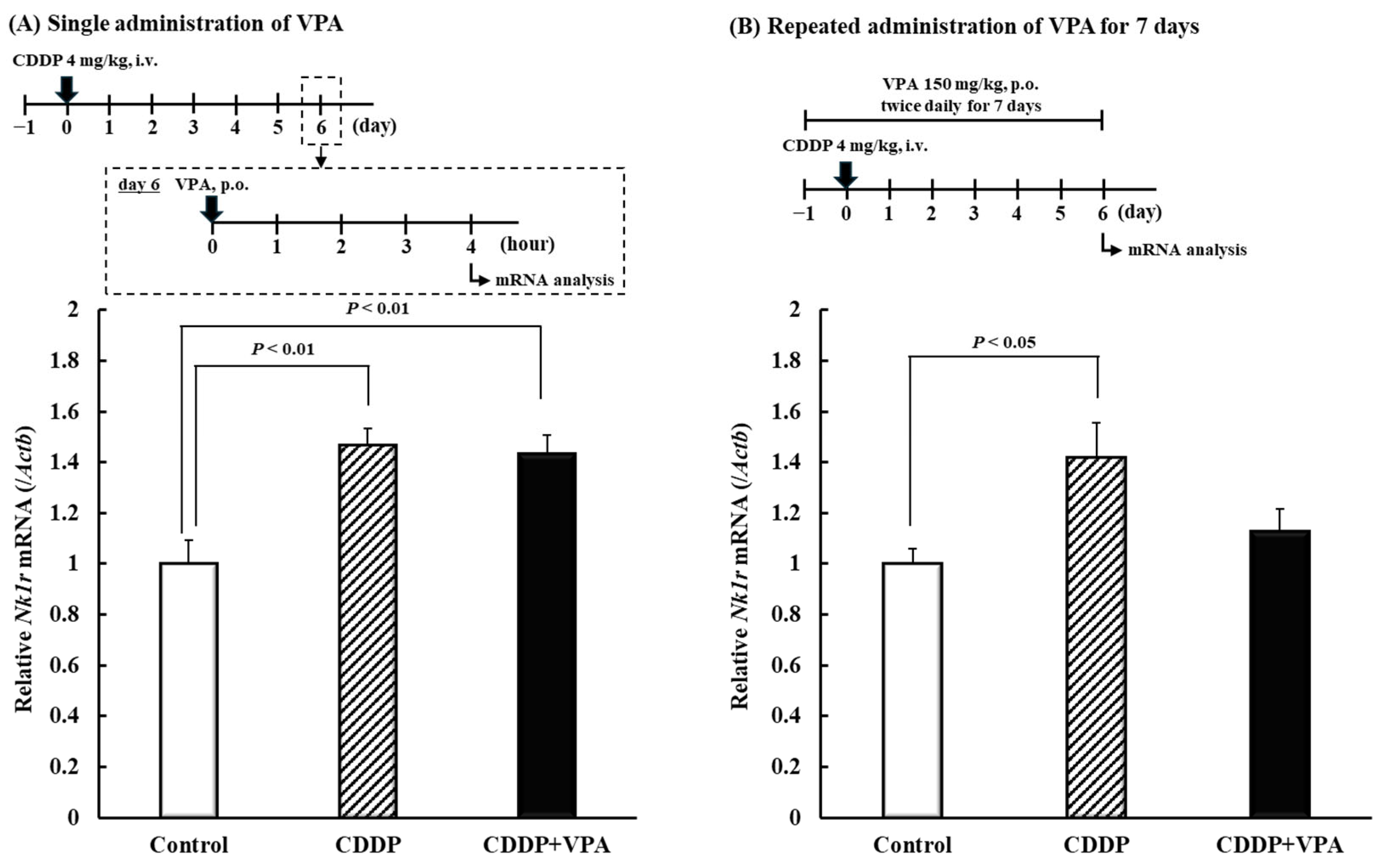
2.4. Effects of Single and Repeated VPA Administration on Nk1r mRNA in Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn of Rats
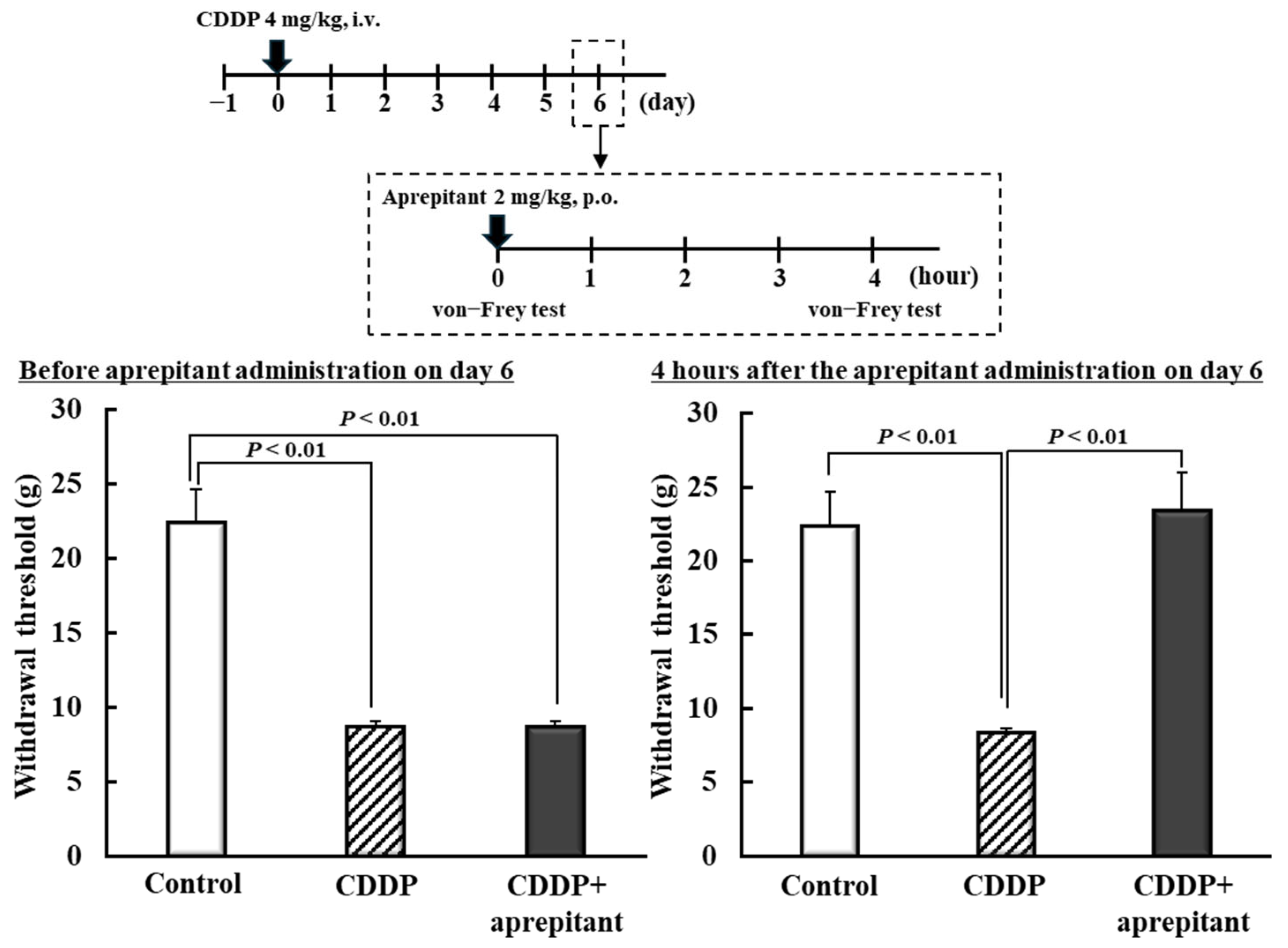
2.5. Effect of NK1R Antagonist on CDDP-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats
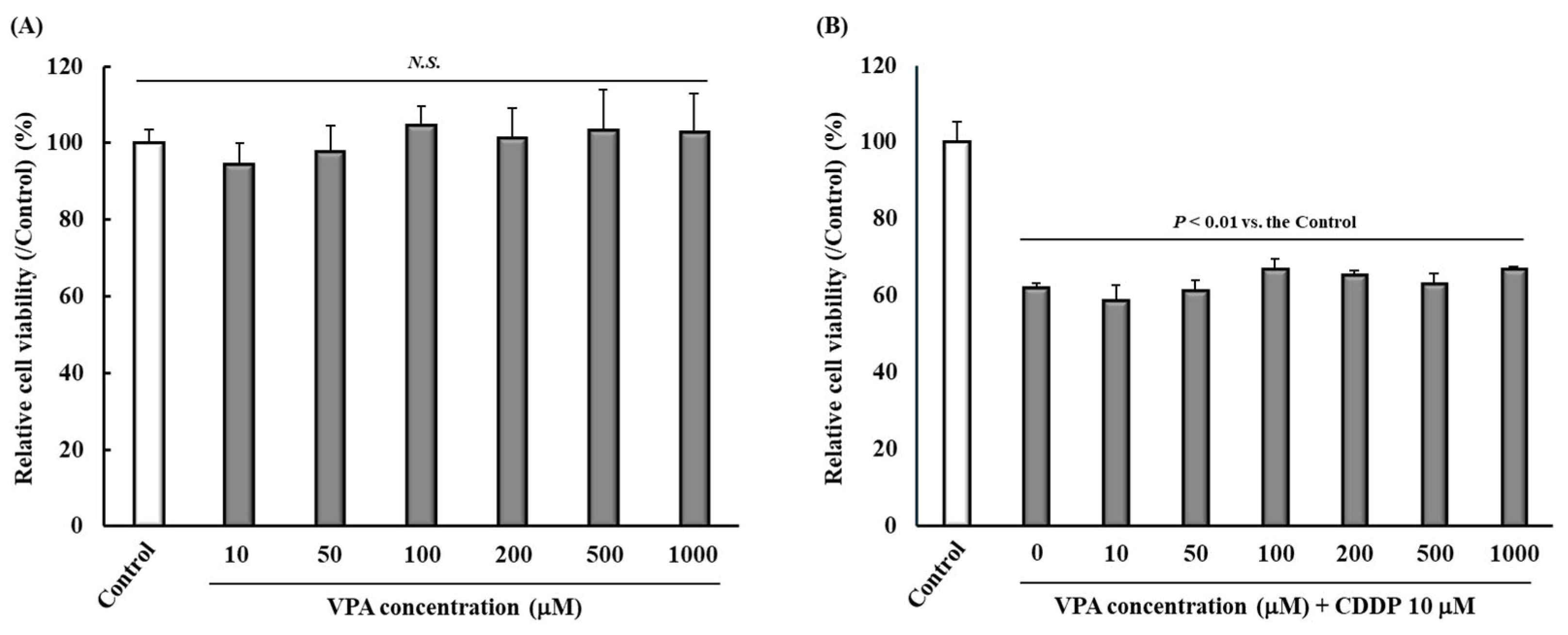
2.6. Effect of VPA Administration on Tumor Cell Viability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Cell Culture and Drugs
4.3. Experiment I: Dose–Response Effects and Temporal Changes on CDDP-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats Following Single VPA Administration
4.4. Experiment II: Effects of Repeated VPA Administration on CDDP-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats
4.5. Experiment III: Time Profiles of Serum Concentration After Single and Repeated VPA Administration in Rats
4.6. Experiment IV: Effects of Single and Repeated VPA Administration on Nk1r mRNA Expression in Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn and Effect of NK1R Antagonist on CDDP-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats
4.7. Experiment V: Effect of VPA on Tumor Cell Viability
4.8. Von Frey Test
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDDP | Cis-diamminedichloro-platinum |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| NK1R | Neurokinin 1 receptor |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| TDM | Therapeutic drug monitoring |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| VPA | Valproic acid |
References
- Kenmotsu, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Misumi, T.; Yoh, K.; Saito, H.; Sugawara, S.; Yamazaki, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Sugio, K.; Seto, T.; et al. Five-Year Overall Survival Analysis of the JIPANG Study: Pemetrexed or Vinorelbine Plus Cisplatin for Resected Stage II-IIIA Nonsquamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5242–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Mesia, R.; Rivera, F.; Remenar, E.; Kawecki, A.; Rottey, S.; Erfan, J.; Zabolotnyy, D.; Kienzer, H.-R.; Cupissol, D.; et al. Platinum-Based Chemotherapy plus Cetuximab in Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.K.; Bundy, B.; Wenzel, L.; Huang, H.Q.; Baergen, R.; Lele, S.; Copeland, L.J.; Walker, J.L.; Burger, R.A. Intraperitoneal Cisplatin and Paclitaxel in Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J.; Gómez, P.; Greil, R.; Braga, S.; Climent, M.A.; Wardley, A.M.; Kaufman, B.; Stemmer, S.M.; Pego, A.; Chan, A.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of the Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Monoclonal Antibody Cetuximab with Cisplatin versus Cisplatin Alone in Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2586–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avan, A.; Postma, T.J.; Ceresa, C.; Avan, A.; Cavaletti, G.; Giovannetti, E.; Peters, G.J. Platinum-Induced Neurotoxicity and Preventive Strategies: Past, Present, and Future. Oncologist 2015, 20, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Screnci, D.; McKeage, M.J. Platinum Neurotoxicity: Clinical Profiles, Experimental Models and Neuroprotective Approaches. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1999, 77, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jones, D.; Palmer, J.L.; Forman, A.; Dakhil, S.R.; Velasco, M.R.; Weiss, M.; Gilman, P.; Mills, G.M.; Noga, S.J.; et al. Oral Alpha-Lipoic Acid to Prevent Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, O.; Hernández-Pedro, N.; Fernández-González-Aragón, M.C.; Saavedra-Pérez, D.; Campos-Parra, A.D.; Ríos-Trejo, M.A.; Cerón-Lizárraga, T.; Martínez-Barrera, L.; Pineda, B.; Ordóñez, G.; et al. Retinoic Acid Reduces Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathy in an Animal Model and Patients with Lung Cancer. Neurology 2011, 77, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L.; Nan, G.; Kim, H.Y.; Cha, M.; Lee, B.H. Modulation of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy by JZL195 through Glia and the Endocannabinoid System. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 180, 117515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.C.; Blanton, H.; Dancel, C.L.; Castro-Piedras, I.; Rorabaugh, B.R.; Morgan, D.J.; Guindon, J. Chronic Administration of Cannabinoid Agonists ACEA (CB1), AM1241 (CB2), and CP55940 (Mixed CB1/CB2) Induce Sex-Specific Differences in Tolerance and Sex Hormone Changes in a Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2024, 391, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddiek, H.; Hanna, M.; Hamoud, A.E.M.; Elbaset, M.A.; Akabawy, A.M.A.; Kotb, M.Z.; Khalifa, M.M. Deferiprone Ameliorates Cisplatin Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity via Ferritinophagy Adjustment. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWhinney, S.R.; Goldberg, R.M.; McLeod, H.L. Platinum Neurotoxicity Pharmacogenetics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaletti, G.; Marzorati, L.; Bogliun, G.; Colombo, N.; Marzola, M.; Pittelli, M.R.; Tredici, G. Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity Is Dependent on TotaI-Dose Intensity and Single-Dose Intensity. Cancer 1992, 69, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunberg, S.M.; Sonka, S.; Stevenson, L.L.; Muggia, F.M. Progressive Paresthesias after Cessation of Therapy with Very High-Dose Cisplatin. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1989, 25, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottschade, L.A.; Sloan, J.A.; Mazurczak, M.A.; Johnson, D.B.; Murphy, B.P.; Rowland, K.M.; Smith, D.A.A.; Berg, A.R.; Stella, P.J.; Loprinzi, C.L. The Use of Vitamin E for the Prevention of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Results of a Randomized Phase III Clinical Trial. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 19, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.D.; Flynn, P.J.; Sloan, J.A.; Wong, G.Y.; Novotny, P.; Johnson, D.B.; Gross, H.M.; Renno, S.I.; Nashawaty, M.; Loprinzi, C.L. Efficacy of Lamotrigine in the Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Phase 3 Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial, N01C3. Cancer 2008, 112, 2802–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C. Adjunctive Treatment for Pediatric Focal Epilepsy: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2025, 81, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, T.; Ikuta, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Sakuma, K.; Okuya, M.; Nomura, I.; Hatano, M.; Iwata, N. Pharmacological Treatment for Bipolar Mania: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trials. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, M.A.; Sandoe, C.H. Migraine Management in Medically Complex Patients: A Narrative Review. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2024, 24, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, Y.; Araki, K.; Omotuyi, O.I.; Mukae, T.; Ueda, H. HDAC Inhibitors Restore C-Fibre Sensitivity in Experimental Neuropathic Pain Model. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 170, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherbiny, N.M.; Ahmed, E.; Kader, G.A.; Abdel-mottaleb, Y.; ElSayed, M.H.; Youssef, A.M.; Zaitone, S.A. Inhibitory Effect of Valproate Sodium on Pain Behavior in Diabetic Mice Involves Suppression of Spinal Histone Deacetylase 1 and Inflammatory Mediators. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 70, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyanwu, E.; Harding, G.F.A. The Involvement of Taurine in the Action Mechanism of Sodium Valproate (VPA) in the Treatment of Epilspey. Acta Physiol. Pharmacol. Ther. Latinoam. 1993, 43, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, A.; Guo, X.; Noro, T.; Harada, C.; Tanaka, K.; Namekata, K.; Harada, T. Valproic Acid Prevents Retinal Degeneration in a Murine Model of Normal Tension Glaucoma. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 588, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Niu, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z. Valproic Acid Attenuates Inflammation of Optic Nerve and Apoptosis of Retinal Ganglion Cells in a Rat Model of Optic Neuritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzreyan, V.A.; Rodkin, S.V.; Pitinova, M.A.; Uzdensky, A.B. HDAC1 Expression, Histone Deacetylation, and Protective Role of Sodium Valproate in the Rat Dorsal Root Ganglia After Sciatic Nerve Transection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biso, L.; Carli, M.; Kolachalam, S.; Monticelli, G.; Calabrò, P.F.; di Paolo, A.; Giorgi, F.S.; Bocci, G.; Scarselli, M. A 5-Year Study of Antiseizure Medications (ASMs) Monitoring in Patients with Neuropsychiatric Disorders in an Italian Clinical Center. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, R. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for the Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders: Clinical Use and Cost Effectiveness. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1995, 29, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ha, N.T.; Li, J.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Q.; Cai, L.; Li, W.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; Cheng, T.; et al. Tachykinin Signaling in the Right Parabrachial Nucleus Mediates Early-Phase Neuropathic Pain Development. Neuron 2025, 113, 605–619.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Chen, S.P.; Gao, Y.H.; Zhang, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Rong, P.J.; Liu, J.L. Electroacupuncture Relieves Hyperalgesia by Regulating Neuronal-Glial Interaction and Glutamate Transporters of Spinal Dorsal Horns in Rats with Acute Incisional Neck Pain. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 885107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoMonaco, M.; Milone, M.; Batocchi, A.P.; Padua, L.; Restuccia, D.; Tonali, P. Cisplatin Neuropathy: Clinical Course and Neurophysiological Findings. J. Neurol. 1992, 239, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, D.; West, P.J.; Smith, M.D.; Yagen, B.; Bialer, M.; Devor, M.; White, H.S.; Brennan, K.C. Sec-Butylpropylacetamide (SPD), a New Amide Derivative of Valproic Acid for the Treatment of Neuropathic and Inflammatory Pain. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Menendez, V.; Gilardini, A.; Bossi, M.; Canta, A.; Oggioni, N.; Carozzi, V.; Tremolizzo, L.; Cavaletti, G. Valproate Protective Effects on Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Menendez, V.; Tremolizzo, L.; Cavaletti, G. Targeting Cancer and Neuropathy with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Two Birds with One Stone? Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meka, S.T.; Bojja, S.L.; Kumar, G.; Birangal, S.R.; Rao, C.M. Novel HDAC inhibitors provide neuroprotection in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model of rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 959, 176067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furugen, A.; Kanno, Y.; Ohyama, N.; Kurosawa, Y.; Jinno, N.; Narumi, K.; Iseki, K.; Kobayashi, M. Effects of valproate, an HDAC inhibitor, on the expression of folate carriers and folate metabolism-related genes in the placenta of rats. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 40, 100409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, Y.; Okazaki, F.; Horikawa, K.; Zhang, J.; Sasaki, H.; To, H. Influence of Dosing Times on Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Rats. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, G.; Erb, S.J.; Lunzer, M.M.; Luong, N.; Akgün, E.; Portoghese, P.S.; Olson, J.K.; Simone, D.A. The Bivalent Ligand MCC22 Potently Attenuates Hyperalgesia in a Mouse Model of Cisplatin-Evoked Neuropathic Pain without Tolerance or Reward. Neuropharmacology 2019, 158, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, W.Q.; Hu, X.M.; Du, L.X.; Mi, W.L.; Chu, Y.X.; Wu, G.C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Mao-Ying, Q.L. Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells 2 (TREM2) Dependent Microglial Activation Promotes Cisplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 68, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.R.; Nackley, A.; Huh, Y.; Terrando, N.; Maixner, W. Neuroinflammation and Central Sensitization in Chronic and Widespread Pain. Anesthesiology 2018, 129, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, A.; Schug, S.A. Pathophysiology of Pain: A Practical Primer. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 8S–14S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, K.; Treffurth, Y.; Hamke, M.; Akundi, R.S.; Von Kleinsorgen, M.; Fiebich, B.L. Valproic Acid Inhibits Substance P-Induced Activation of Protein Kinase C Epsilon and Expression of the Substance P Receptor. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, P.; Szilvássy, Z.; Peitl, B.; Szilvássy, J.; Helyes, Z.; Szolcsányi, J.; Németh, J. Changes in Tracheo-Bronchial Sensory Neuropeptide Receptor Gene Expression Pattern in Rats with Cisplatin-Induced Sensory Neuropathy. Neuropeptides 2006, 40, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacky Ariffin, M.; Yun Ng, S.; Nadia, H.; Koh, D.; Loh, N.; Michiko, N.; Khanna, S. Neurokinin1—Cholinergic Receptor Mechanisms in the Medial Septum-Dorsal Hippocampus Axis Mediates Experimental Neuropathic Pain. Neurobiol. Pain. 2024, 16, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochster, H.S.; Grothey, A.; Childs, B.H. Use of Calcium and Magnesium Salts to Reduce Oxaliplatin-Related Neurotoxicity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4028–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laengle, J.; Kabiljo, J.; Hunter, L.; Homola, J.; Prodinger, S.; Egger, G.; Bergmann, M. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Valproic Acid and Vorinostat Enhance Trastuzumab-Mediated Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Phagocytosis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevi, L.; Pollanen, N.; Penna, F.; Caretti, G. Targeting Epigenetic Regulators with HDAC and BET Inhibitors to Modulate Muscle Wasting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; He, C.; An, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fu, W.; Wang, M.; Shan, Z.; Xie, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. The Role of Short Chain Fatty Acids in Inflammation and Body Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamnejad, M.R.; Medzikovic, L.; Dehghanitafti, A.; Rahman, B.; Vadgama, A.; Eghbali, M. Role of Gut Microbial Metabolites in Ischemic and Non-Ischemic Heart Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, K.-H.; Hull, R.; Morton, D.; Pfister, R.; Rabemampianina, Y.; Smith, D.; Vidal, J.-M.; Van De Vorstenbosch, C. European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries A, European Centre for the Validation of Alternative M. A good practice guide to the administration of substances and removal of blood, including routes and volumes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2001, 21, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, P.; Rajani Kumar, V.; Satyanarayana, V.; Krishna, D.R. HPLC Determination of Valproic Acid in Human Serum. Pharmazie 2003, 58, 378–380. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, Y.; Niwa, K.; Okazaki, F.; To, H. Time Dependent Cisplatin Dosing Differences on Hypoalgesia Focusing on Oxidative Stress. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 942, 175519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, Y.; Takase, M.; Tsuji, Y.; To, H. Pregabalin Reduces Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 134, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Time After a Single VPA Administration | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 h | 0.5 h | 1 h | 2 h | 4 h | 6 h | 8 h | 12 h | 14 h | 16 h | 24 h |
| 77.09 ± 6.01 | 65.62 ± 5.77 | 38.20 ± 5.94 | 10.28 ± 1.47 | 18.81 ± 2.05 | 20.07 ± 1.99 | 13.51 ± 0.95 | 8.62 ± 1.49 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Time After Repeated VPA Administration | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 h | 0.5 h | 1 h | 2 h | 4 h | 6 h | 8 h | 12 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
| 75.98 ± 12.36 | 56.99 ± 7.06 | 20.32 ± 3.39 | 9.36 ± 2.21 | 17.37 ± 2.67 | 19.00 ± 2.65 | 15.27 ± 2.27 | 16.59 ± 0.68 | 6.56 ± 2.30 | 1.78 ± 1.75 | N.D. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seto, Y.; Ohara, Y.; Tachi, M.; Tomonari, M.; Inoue, D.; Okazaki, F.; Tsuji, Y.; To, H. Repeated Valproic Acid Administration Fundamentally Ameliorated Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114977
Seto Y, Ohara Y, Tachi M, Tomonari M, Inoue D, Okazaki F, Tsuji Y, To H. Repeated Valproic Acid Administration Fundamentally Ameliorated Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114977
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeto, Yoshihiro, Yuki Ohara, Manami Tachi, Mari Tomonari, Daisuke Inoue, Fumiyasu Okazaki, Yasuhiro Tsuji, and Hideto To. 2025. "Repeated Valproic Acid Administration Fundamentally Ameliorated Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114977
APA StyleSeto, Y., Ohara, Y., Tachi, M., Tomonari, M., Inoue, D., Okazaki, F., Tsuji, Y., & To, H. (2025). Repeated Valproic Acid Administration Fundamentally Ameliorated Cisplatin-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114977






