Characterization of Novel and Known Activators of Cannabinoid Receptor Subtype 2 Reveals Mixed Pharmacology That Differentiates Mycophenolate Mofetil and GW-842,166X from MDA7
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
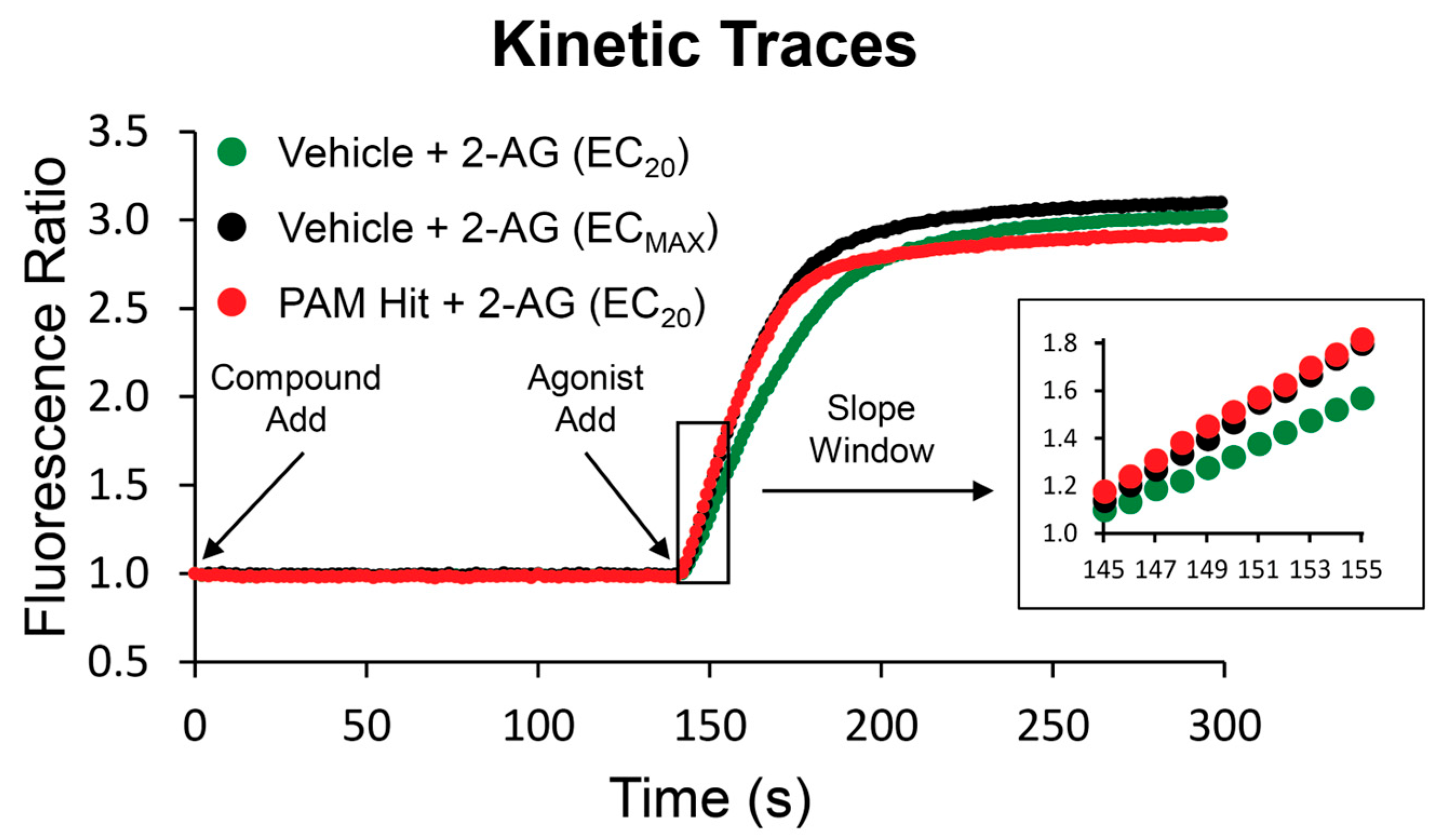
2.1. Identification of Novel Modulators of the CB2 Receptor
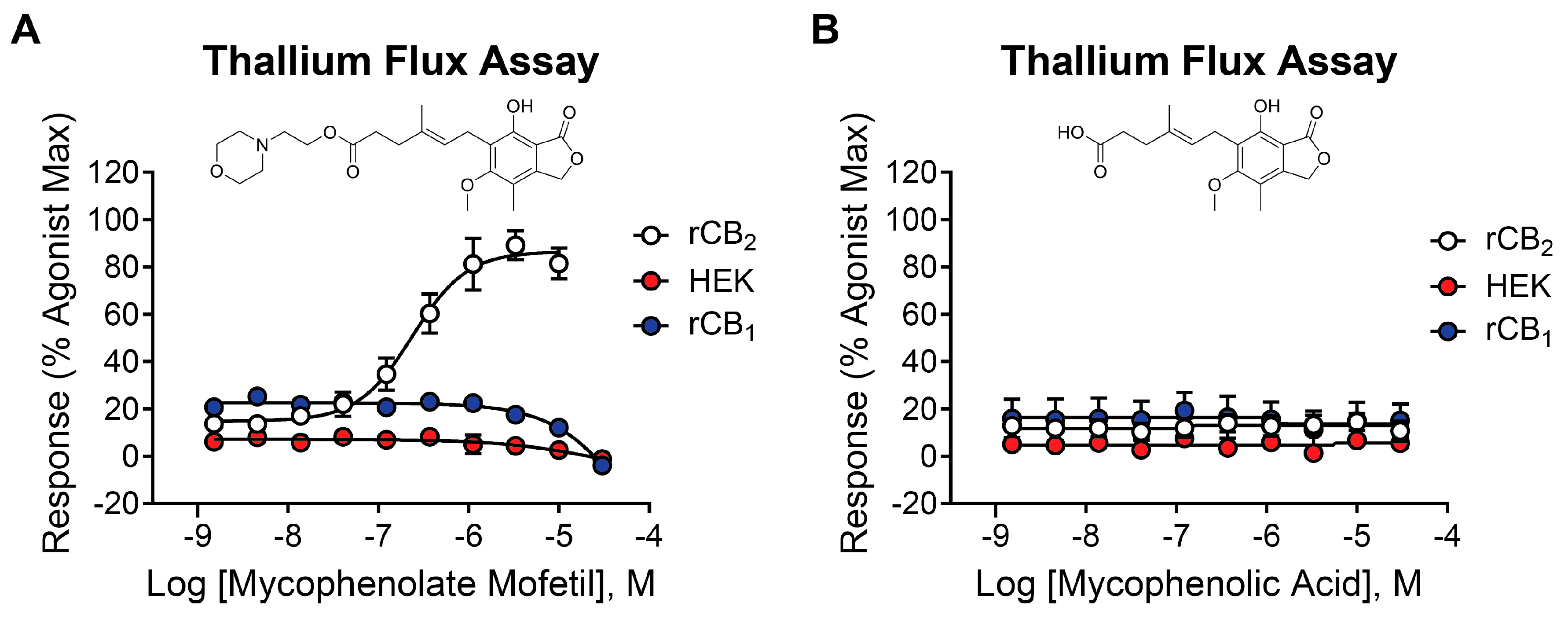
2.2. Mycophenolate Mofetil Is a Potent and Selective Activator of rCB2
2.3. Mycophenolic Acid Is Inactive at CB Receptors
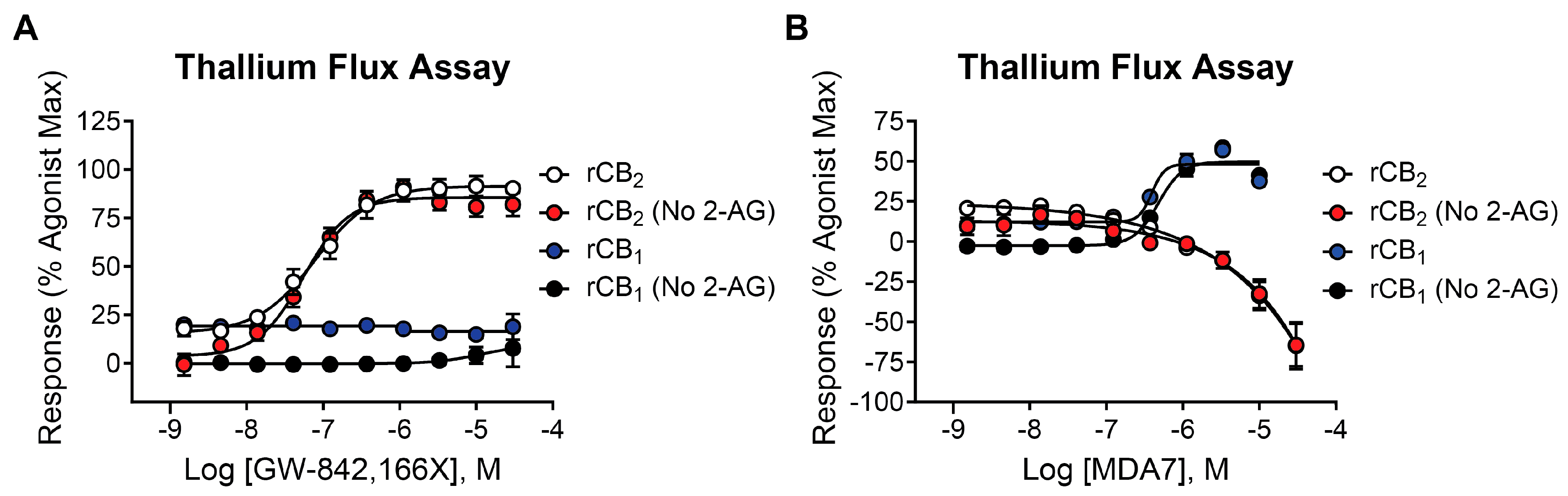
2.4. Mycophenolate Mofetil Has Similar Activity in the Presence and Absence of 2-AG in Thallium Flux Assays
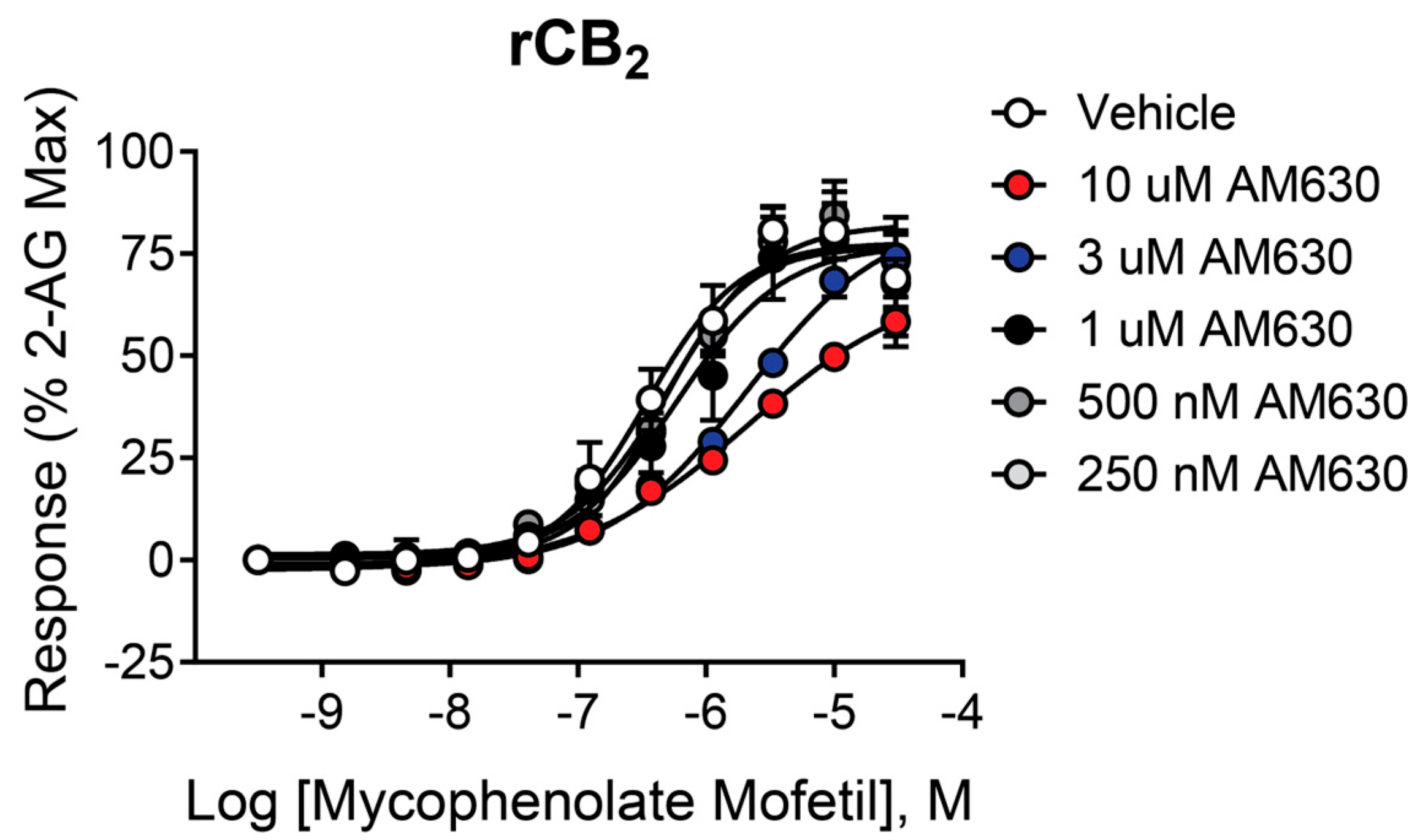
2.5. The Antagonist/Inverse Agonist AM630 Shifts the Mycophenolate Mofetil Concentration–Response Curve (CRC) to the Right Without Significantly Decreasing the Maximal Response
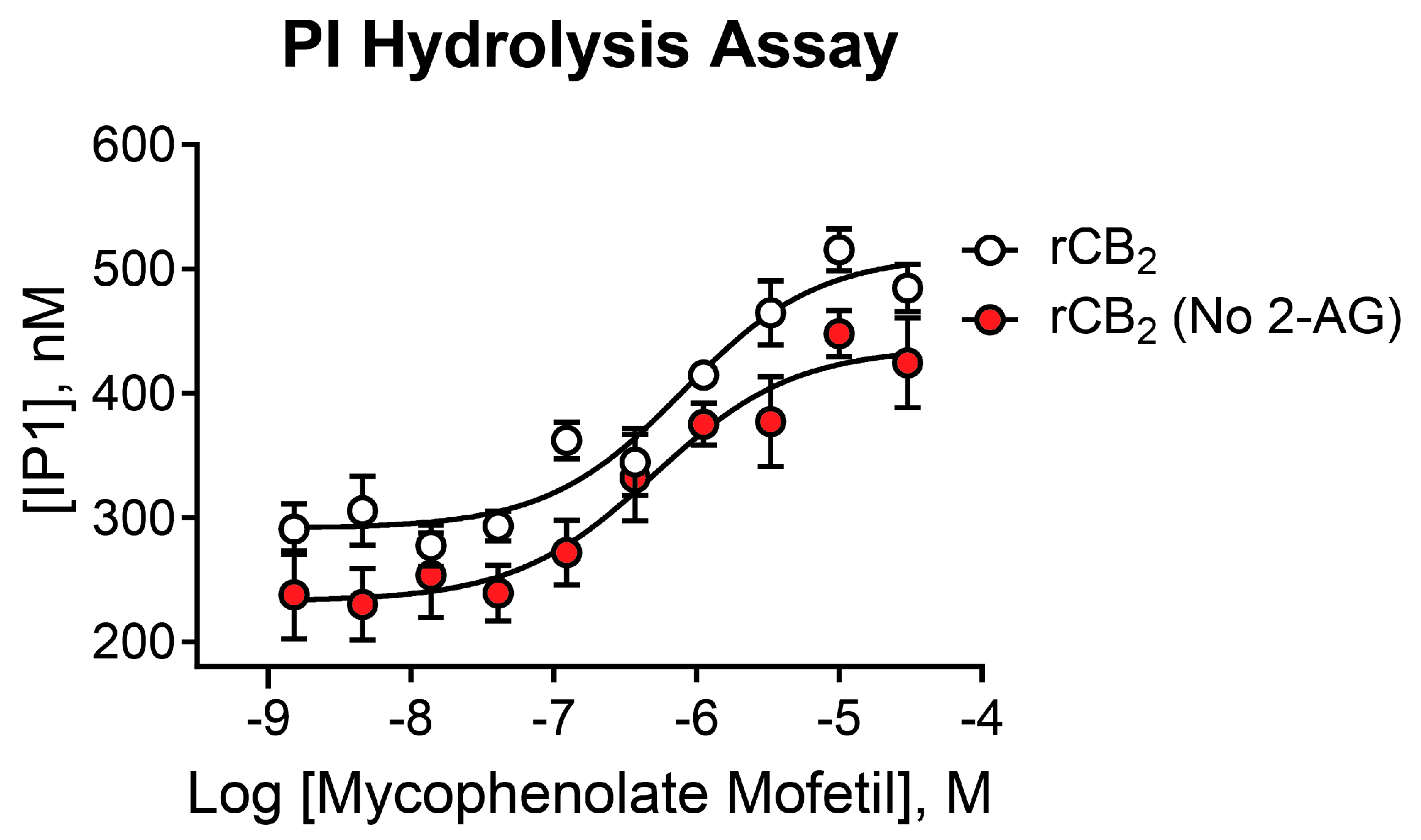
2.6. Mycophenolate Mofetil Is Active in Phosphoinositide Hydrolysis Assays and Demonstrates Similar Activity in the Presence and Absence of 2-AG
2.7. The CB2 Receptor Agonist GW-842,166X Exhibits a Similar Functional Activity Profile Compared to Mycophenolate Mofetil
2.8. In Contrast to Mycophenolate Mofetil and GW-842,166X, the CB2 Receptor Agonist MDA7 Exhibits Inverse Agonist Activity at rCB2 in Thallium Flux Assays
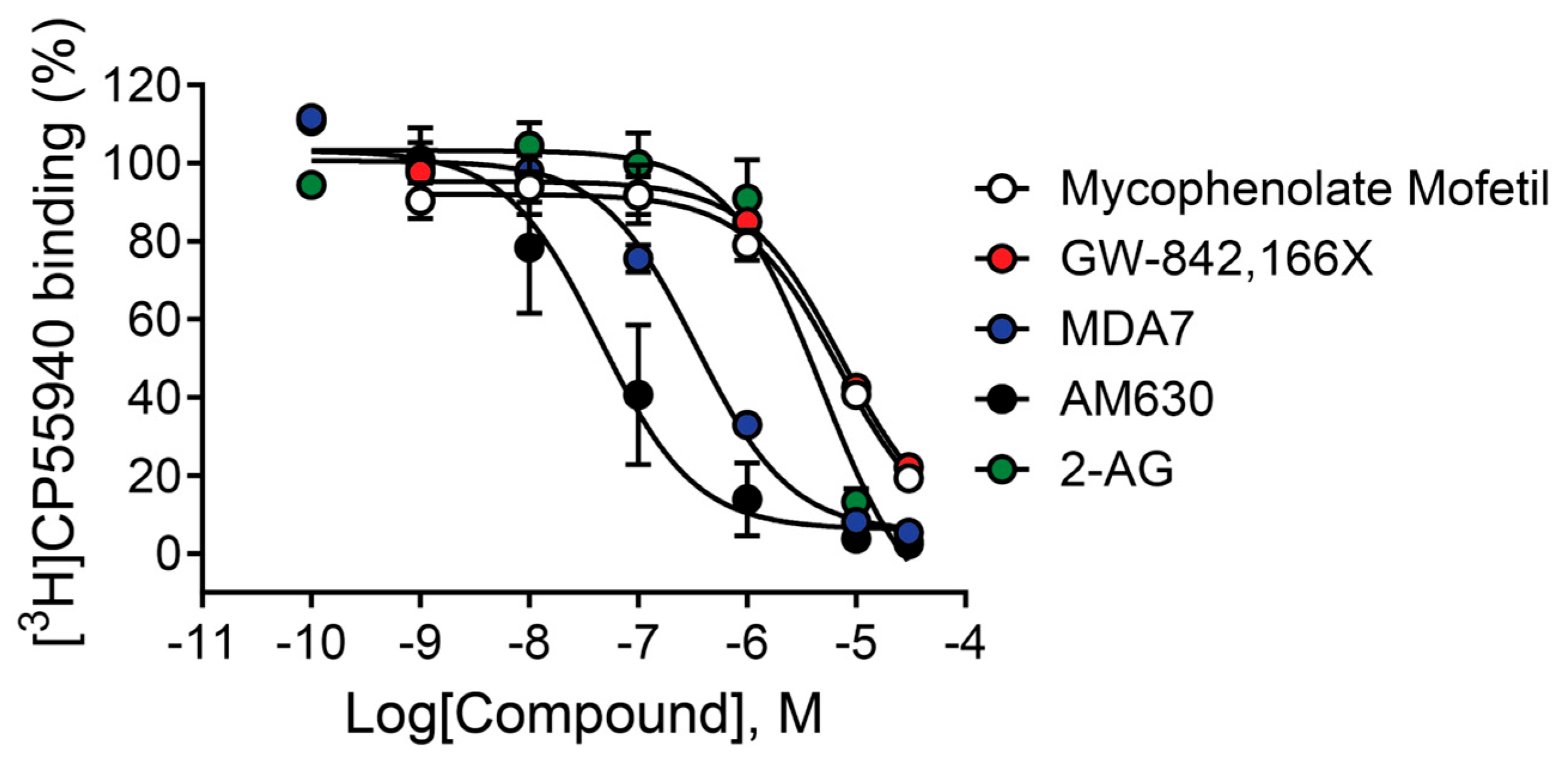
2.9. Mycophenolate Mofetil and Other CB2 Modulators Differentially Bind to the Site Occupied by [3H]CP55,940
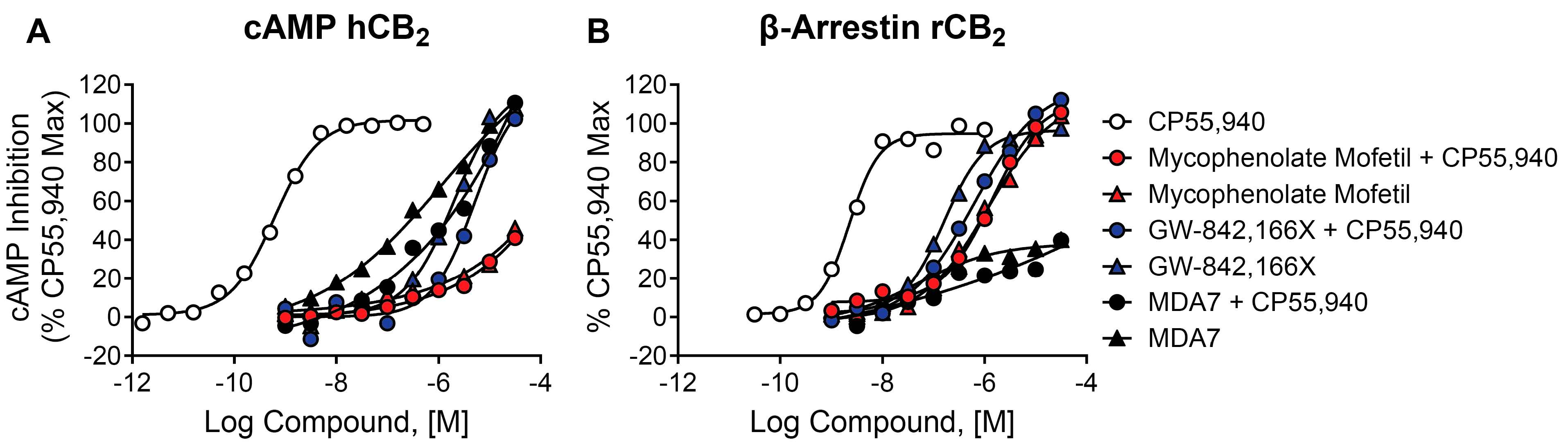
2.10. Mycophenolate Mofetil, GW-842,166X, and MDA7 Behave as Agonists in cAMP and β-Arrestin Assays
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Thallium Flux Assay
4.4. PI Hydrolysis Assay
4.5. Radioligand Binding Assays
4.6. cAMP Assays
4.7. β-Arrestin Assays
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-AG | 2-Arachidonylglycerol |
| AM630 | 6-Iodo-2-methyl-1-[2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl]-1H-indol-3-yl](4-methoxyphenyl)methanone |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CB1 | Cannabinoid receptor subtype 1 |
| CB2 | Cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 |
| CP55,940 | 2-[(1R,2R,5R)-5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxypropyl)cyclohexyl]-5-(2-methyloctan-2-yl)phenol |
| CRC | Concentration response curve |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Media |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EC20 | 20% maximal effective concentration |
| EC21a | N-(5-bromo-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-4-methyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)cycloheptanecarboxamide |
| F12 | Ham’s F-12 Nutrient Mixture |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| GIRK | G protein-regulated inwardly rectifying potassium channel |
| GW-842,166X | 2-(2,4-dichloroanilino)-N-(oxan-4-ylmethyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)pyrimidine-5-carboxamide |
| HBSS | Hank’s balanced salt solution |
| HEK | Human embryonic kidney |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid |
| IP1 | Inositol monophosphate |
| MDA7 | 1-[(3-benzyl-3-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-6-yl)carbonyl]piperidine |
| mGlu1 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 1 |
| M4 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtype 4 |
| PAM | Positive allosteric modulator |
| PI | Phosphoinositide |
| RLU | Relative light units |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
References
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Torregrosa, A.B.; Navarrete, F.; Navarro, D.; Manzanares, J. A comprehensive review of the multifaceted role of cannabinoid receptor type 2 in neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 213, 107657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C.; Barth, F.; Bonner, T.I.; Cabral, G.; Casellas, P.; Devane, W.A.; Felder, C.C.; Herkenham, M.; Mackie, K.; Martin, B.R.; et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 161–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgohary, R.; Salama, A.; Omara, E.A. Protective Effects of Cannabis sativa on chemotherapy-induced nausea in a rat: Involvement of CB1 receptors. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 37, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.N.; Haney, M.; Hillard, C.J.; Karhson, D.S.; Vecchiarelli, H.A. The endocannabinoid system as a putative target for the development of novel drugs for the treatment of psychiatric illnesses. Psychol. Med. 2023, 53, 7006–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, J.; Varga, B.; Ledent, C.; Freund, T.F. CB1 cannabinoid receptors mediate anxiolytic effects: Convergent genetic and pharmacological evidence with CB1-specific agents. Behav. Pharmacol. 2004, 15, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, J.M.; Diaz, L.E.; Galve-Roperh, I.; Bustos, R.H.; Leon, M.X.; Beltran, S.; Dodd, S. The endocannabinoid system as a therapeutic target in neuropathic pain: A review. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2024, 28, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sickle, M.D.; Duncan, M.; Kingsley, P.J.; Mouihate, A.; Urbani, P.; Mackie, K.; Stella, N.; Makriyannis, A.; Piomelli, D.; Davison, J.S.; et al. Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science 2005, 310, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.P.; Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Liu, Q.R.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Brusco, A.; Uhl, G.R. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: Immunohistochemical localization in rat brain. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gong, J.P.; Patel, S.; Perchuk, A.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Mora, Z.; Tagliaferro, P.; Gardner, E.; et al. Discovery of the presence and functional expression of cannabinoid CB2 receptors in brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1074, 514–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Pérez-Ortiz, J.M.; Gutiérrez-Adán, A.; Manzanares, J. Depression-resistant endophenotype in mice overexpressing cannabinoid CB(2) receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Manzanares, J. Overexpression of CB2 cannabinoid receptors decreased vulnerability to anxiety and impaired anxiolytic action of alprazolam in mice. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Sejal, P.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Tagliaferro, P.; Hope, B.; Leonard, C.M.; Uhl, G.R.; Brusco, A.; et al. Methods to study the behavioral effects and expression of CB2 cannabinoid receptor and its gene transcripts in the chronic mild stress model of depression. In Marijuana and Cannabinoid Research: Methods in Molecular Medicine™; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 123, pp. 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, H.; Iwasaki, S.; Teasenfitz, L.; Higuchi, S.; Horiuchi, Y.; Saito, T.; Arinami, T.; Onaivi, E.S. Involvement of cannabinoid CB2 receptor in alcohol preference in mice and alcoholism in humans. Pharmacogenomics J. 2007, 7, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.J.; Wilson, J.M.; Remke, D.H.; Mahmood, M.S.; Uddin, M.J.; Wess, J.; Patel, S.; Marnett, L.J.; Niswender, C.M.; Jones, C.K.; et al. Antipsychotic-like Effects of M4 Positive Allosteric Modulators Are Mediated by CB2 Receptor-Dependent Inhibition of Dopamine Release. Neuron 2016, 91, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohn, S.E.; Foster, D.J.; Covey, D.P.; Moehle, M.S.; Galbraith, J.; Garcia-Barrantes, P.M.; Cho, H.P.; Bubser, M.; Blobaum, A.L.; Joffe, M.E.; et al. Activation of the mGlu1 metabotropic glutamate receptor has antipsychotic-like effects and is required for efficacy of M4 muscarinic receptor allosteric modulators. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 2786–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giblin, G.M.; O’Shaughnessy, C.T.; Naylor, A.; Mitchell, W.L.; Eatherton, A.J.; Slingsby, B.P.; Rawlings, D.A.; Goldsmith, P.; Brown, A.J.; Haslam, C.P.; et al. Discovery of 2-[(2,4-dichlorophenyl)amino]-N-[(tetrahydro- 2H-pyran-4-yl)methyl]-4-(trifluoromethyl)- 5-pyrimidinecarboxamide, a selective CB2 receptor agonist for the treatment of inflammatory pain. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2597–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostenfeld, T.; Price, J.; Albanese, M.; Bullman, J.; Guillard, F.; Meyer, I.; Leeson, R.; Costantin, C.; Ziviani, L.; Nocini, P.F.; et al. A randomized, controlled study to investigate the analgesic efficacy of single doses of the cannabinoid receptor-2 agonist GW842166, ibuprofen or placebo in patients with acute pain following third molar tooth extraction. Clin. J. Pain 2011, 27, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attala, M.N.; Brown, D.L. Neuroprotective CB2 Receptor Agonists. WIPO Patent WO2014011949A2, 16 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Attala, M.N.; Diaz, P. Heterocycle Modulators of Cannabinoid Receptors. U.S. Patent US9339486B2, 17 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Naguib, M.; Diaz, P.; Xu, J.J.; Astruc-Diaz, F.; Craig, S.; Vivas-Mejia, P.; Brown, D.L. MDA7: A novel selective agonist for CB2 receptors that prevents allodynia in rat neuropathic pain models. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootten, D.; Christopoulos, A.; Sexton, P.M. Emerging paradigms in GPCR allostery: Implications for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsley, C.W.; Emmitte, K.A.; Hopkins, C.R.; Bridges, T.M.; Gregory, K.J.; Niswender, C.M.; Conn, P.J. Practical Strategies and Concepts in GPCR Allosteric Modulator Discovery: Recent Advances with Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 6707–6741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, F.; Meini, S.; Bertini, S.; Digiacomo, M.; Macchia, M.; Manera, C. Allosteric modulators targeting cannabinoid cb1 and cb2 receptors: Implications for drug discovery. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 2019–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, F.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Lucarini, E.; Bertini, S.; Cappelli, E.; Digiacomo, M.; Stevenson, L.A.; Macchia, M.; Tuccinardi, T.; Ghelardini, C.; et al. Identification of the First Synthetic Allosteric Modulator of the CB2 Receptors and Evidence of Its Efficacy for Neuropathic Pain Relief. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, L.; Gado, F.; Manera, C.; Escayg, A. Allosteric modulation of the cannabinoid 2 receptor confers seizure resistance in mice. Neuropharmacology 2021, 188, 108448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, A.; Han, X.; Quitalig, M.; Wu, J.; Christov, P.P.; Jeon, K.; Jana, S.; Kim, K.; Engers, D.W.; Lindsley, C.W.; et al. The cannabinoid CB2 receptor positive allosteric modulator EC21a exhibits complicated pharmacology in vitro. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2024, 44, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, Z.; Delre, P.; Iliadis, S.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Contino, M.; Howell, L.A.; McCormick, P.J. Identification of a Cannabinoid Receptor 2 Allosteric Site Using Computational Modeling and Pharmacological Analysis. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2025, 8, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, A.C.; Eugui, E.M. Immunosuppressive and other anti-rheumatic activities of mycophenolate mofetil. Agents Actions Suppl. 1993, 44, 165–188. [Google Scholar]
- Eugui, E.M.; Allison, A.C. Immunosuppressive activity of mycophenolate mofetil. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 685, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, M.L.; Pirofski, L. Mycophenolate mofetil: Effects on cellular immune subsets, infectious complications, and antimicrobial activity. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2009, 11, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niswender, C.M.; Johnson, K.A.; Luo, Q.; Ayala, J.E.; Kim, C.; Conn, P.J.; Weaver, C.D. A novel assay of Gi/o-linked G protein-coupled receptor coupling to potassium channels provides new insights into the pharmacology of the group III metabotropic glutamate receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.S.; Secchi, R.L.; Sung, E.; Lemaire, M.; Bonhaus, D.W.; Hedley, L.R.; Lowe, D.A. Effects of cannabinoid receptor ligands on psychosis-relevant behavior models in the rat. Psychopharmacology 2003, 165, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobira, P.H.; LaMar, J.; Marques, J.; Sartim, A.; Silveira, K.; Santos, L.; Wegener, G.; Guimaraes, F.S.; Mackie, K.; Lu, H.C.; et al. CB1 Receptor Silencing Attenuates Ketamine-Induced Hyperlocomotion Without Compromising Its Antidepressant-Like Effects. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2023, 8, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, L.M.; Abood, M.E. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling and Biased Signaling. Molecules 2021, 26, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, A.C.; Eugui, E.M. Immunosuppressive and other effects of mycophenolic acid and an ester prodrug, mycophenolate mofetil. Immunol. Rev. 1993, 136, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, A.C.; Kowalski, W.J.; Muller, C.D.; Eugui, E.M. Mechanisms of action of mycophenolic acid. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 696, 63–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertwee, R.; Griffin, G.; Fernando, S.; Li, X.; Hill, A.; Makriyannis, A. AM630, a competitive cannabinoid receptor antagonist. Life Sci. 1995, 56, 1949–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosohata, K.; Quock, R.M.; Hosohata, Y.; Burkey, T.H.; Makriyannis, A.; Consroe, P.; Roeske, W.R.; Yamamura, H.I. AM630 is a competitive cannabinoid receptor antagonist in the guinea pig brain. Life Sci. 1997, 61, PL115–PL118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosohata, Y.; Quock, R.M.; Hosohata, K.; Makriyannis, A.; Consroe, P.; Roeske, W.R.; Yamamura, H.I. AM630 antagonism of cannabinoid-stimulated [35S]GTP gamma S binding in the mouse brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 321, R1–R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.A.; Brockie, H.C.; Stevenson, L.A.; Murphy, V.L.; Templeton, F.; Makriyannis, A.; Pertwee, R.G. Agonist-inverse agonist characterization at CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors of L759633, L759656, and AM630. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 126, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; Reyes-Resina, I.; Rivas-Santisteban, R.; Sánchez de Medina, V.; Morales, P.; Casano, S.; Ferreiro-Vera, C.; Lillo, A.; Aguinaga, D.; Jagerovic, N.; et al. Cannabidiol skews biased agonism at cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors with smaller effect in CB1-CB2 heteroreceptor complexes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 157, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Baillie, G.L.; Phillips, A.M.; Razdan, R.K.; Ross, R.A.; Pertwee, R.G. Cannabidiol displays unexpectedly high potency as an antagonist of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, F.; Ferrisi, R.; Polini, B.; Mohamed, K.A.; Ricardi, C.; Lucarini, E.; Carpi, S.; Domenichini, F.; Stevenson, L.A.; Rapposelli, S.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity of New CB2 Receptor Ligands: From Orthosteric and Allosteric Modulators to Dualsteric/Bitopic Ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 9918–9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrisi, R.; Polini, B.; Ricardi, C.; Gado, F.; Mohamed, K.A.; Baron, G.; Faiella, S.; Poli, G.; Rapposelli, S.; Saccomanni, G.; et al. New Insights into Bitopic Orthosteric/Allosteric Ligands of Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.R.; Tu, J.X.; Qiao, A.Q.; Chen, L.J. GW842166X Alleviates Osteoarthritis by Repressing LPS-mediated Chondrocyte Catabolism in Mice. Curr. Med. Sci. 2022, 42, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Chen, B.; Friedman, V.; Mu, L.; Kelly, T.J.; Ruiz-Pérez, G.; Zhao, L.; Bai, X.; Hillard, C.J.; et al. CB2 Agonist GW842166x Protected against 6-OHDA-Induced Anxiogenic- and Depressive-Related Behaviors in Mice. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naikoo, R.A.; Painuli, R.; Akhter, Z.; Singh, P.P. Cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) modulators: A patent review (2016–2024). Bioorganic Chem. 2024, 153, 107775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, P.; Phatak, S.S.; Xu, J.; Fronczek, F.R.; Astruc-Diaz, F.; Thompson, C.M.; Cavasotto, C.N.; Naguib, M. 2,3-Dihydro-1-benzofuran derivatives as a series of potent selective cannabinoid receptor 2 agonists: Design, synthesis, and binding mode prediction through ligand-steered modeling. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1615–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.J.; Diaz, P.; Bie, B.; Astruc-Diaz, F.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Brown, D.L.; Naguib, M. Spinal gene expression profiling and pathways analysis of a CB2 agonist (MDA7)-targeted prevention of paclitaxel-induced neuropathy. Neuroscience 2014, 260, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hocevar, M.; Bie, B.; Foss, J.F.; Naguib, M. Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptor System Modulates Paclitaxel-Induced Microglial Dysregulation and Central Sensitization in Rats. J. Pain 2019, 20, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bie, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.J.; Brown, D.L.; Naguib, M. Activation of the CB2 receptor system reverses amyloid-induced memory deficiency. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hocevar, M.; Foss, J.F.; Bie, B.; Naguib, M. Activation of CB2 receptor system restores cognitive capacity and hippocampal Sox2 expression in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 811, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Xie, M.; Bie, B.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Foss, J.F.; Yang, B.; Rosenquist, R.W.; Naguib, M. Activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 attenuates mechanical allodynia and neuroinflammatory responses in a chronic post-ischemic pain model of complex regional pain syndrome type I in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2016, 44, 3046–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuth, D.G.; Molleman, A. Cannabinoid signalling. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soethoudt, M.; Grether, U.; Fingerle, J.; Grim, T.W.; Fezza, F.; de Petrocellis, L.; Ullmer, C.; Rothenhäusler, B.; Perret, C.; van Gils, N.; et al. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor ligand profiling reveals biased signalling and off-target activity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E. CB1 and CB2 Receptor Pharmacology. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, V.; Guzzo, T.; Topai, A.; Gambacorta, N.; Ciriaco, F.; Nicolotti, O.; Maccarrone, M. Recent Advances on Type-2 Cannabinoid (CB2) Receptor Agonists and their Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 1420–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legare, C.A.; Raup-Konsavage, W.M.; Vrana, K.E. Therapeutic Potential of Cannabis, Cannabidiol, and Cannabinoid-Based Pharmaceuticals. Pharmacology 2022, 107, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagzoog, A.; Brandt, A.L.; Black, T.; Kim, E.D.; Burkart, R.; Patel, M.; Jin, Z.; Nikolaeva, M.; Laprairie, R.B. Assessment of select synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist bias and selectivity between the type 1 and type 2 cannabinoid receptor. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Sukagawa, A.; Nakane, S.; Shinoda, A.; Itoh, K.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol: A possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand in brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 215, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yang, B.; Hou, G.; Xie, X.Q.; Feng, Z. Targeting the endocannabinoid system: Structural determinants and molecular mechanism of allosteric modulation. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh Tabrizi, M.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Potential Therapeutic Benefits of Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Agonists. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 519–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, T. Recent development of CB2 selective and peripheral CB1/CB2 cannabinoid receptor ligands. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, H.; Kibret, B.G.; Horiuchi, Y.; Onaivi, E.S. Potential Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors in Neuropsychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 828895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kibret, B.G.; Ishiguro, H.; Horiuchi, Y.; Onaivi, E.S. New Insights and Potential Therapeutic Targeting of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors in CNS Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legge, S.E.; Jones, H.J.; Kendall, K.M.; Pardiñas, A.F.; Menzies, G.; Bracher-Smith, M.; Escott-Price, V.; Rees, E.; Davis, K.A.S.; Hotopf, M.; et al. Association of Genetic Liability to Psychotic Experiences With Neuropsychotic Disorders and Traits. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, H.; Horiuchi, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Koga, M.; Imai, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Morikawa, M.; Inada, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Brain cannabinoid CB2 receptor in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Xu, J.J.; Diaz, P.; Brown, D.L.; Cogdell, D.; Bie, B.; Hu, J.; Craig, S.; Hittelman, W.N. Prevention of paclitaxel-induced neuropathy through activation of the central cannabinoid type 2 receptor system. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 114, 1104–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compound | rCB2 GIRK | rCB1 GIRK | HEK GIRK | rCB2 Binding | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (+) 2-AG pEC50 ± SEM % Max ± SEM | (−) 2-AG pEC50 ± SEM % Max ± SEM | (+) 2-AG pEC50 ± SEM % Max ± SEM | (−) 2-AG pEC50 ± SEM % Max ± SEM | (+) ACh pEC50 ± SEM % Max ± SEM | Binding Affinity pKi ± SEM % Max ± SEM | |
Mycophenolate mofetil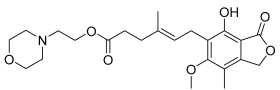 | 6.64 ± 0.06 74 ± 2% | 6.81 ± 0.12 71 ± 5% | <5.0 −5.5 ± 1.1% | <5.0 −15 ± 3% | Inactive | Incomplete pEC50 < 5.0 20 ± 1 |
Mycophenolic acid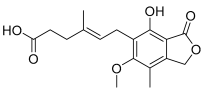 | Inactive | ND | Inactive | ND | Inactive | ND |
GW-842,166X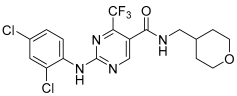 | 7.13 ± 0.08 82 ± 4% | 7.26 ± 0.05 89 ± 5% | Inactive | Inactive | ND | Incomplete pEC50 < 5.0 22 ± 2 |
MDA7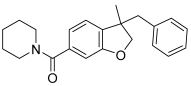 | <5.0 −65 ± 15% | <5.0 −64 ± 13% | 6.40 ± 0.02 48 ± 2 | 6.32 ± 0.03 50 ± 2 | ND | 6.60 ± 0.05 5.3 ± 1.7 |
| Compound | hCB2 cAMP | rCB2 β-Arrestin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (+) CP55,940 pEC50 % Max | (−) CP55,940 pEC50 % Max | (+) CP55,940 pEC50 % Max | (−) CP55,940 pEC50 % Max | |
| Mycophenolate mofetil | <5.0 41 | <5.0 46 | 5.87 113 | 5.94 114 |
| GW-842,166X | 5.29 119 | 5.69 120 | 6.20 120 | 6.79 97 |
| MDA7 | <5.0 111 | <5.0 108 | <5.0 40 | 7.32 38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez, A.L.; Qi, A.; Han, A.; Kling, H.E.; Quitalig, M.C.; Bender, A.M.; Barbaro, L.; Whomble, D.; Lindsley, C.W.; Niswender, C.M. Characterization of Novel and Known Activators of Cannabinoid Receptor Subtype 2 Reveals Mixed Pharmacology That Differentiates Mycophenolate Mofetil and GW-842,166X from MDA7. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104956
Rodriguez AL, Qi A, Han A, Kling HE, Quitalig MC, Bender AM, Barbaro L, Whomble D, Lindsley CW, Niswender CM. Characterization of Novel and Known Activators of Cannabinoid Receptor Subtype 2 Reveals Mixed Pharmacology That Differentiates Mycophenolate Mofetil and GW-842,166X from MDA7. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104956
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez, Alice L., Aidong Qi, Allie Han, Haley E. Kling, Marc C. Quitalig, Aaron M. Bender, Lisa Barbaro, David Whomble, Craig W. Lindsley, and Colleen M. Niswender. 2025. "Characterization of Novel and Known Activators of Cannabinoid Receptor Subtype 2 Reveals Mixed Pharmacology That Differentiates Mycophenolate Mofetil and GW-842,166X from MDA7" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104956
APA StyleRodriguez, A. L., Qi, A., Han, A., Kling, H. E., Quitalig, M. C., Bender, A. M., Barbaro, L., Whomble, D., Lindsley, C. W., & Niswender, C. M. (2025). Characterization of Novel and Known Activators of Cannabinoid Receptor Subtype 2 Reveals Mixed Pharmacology That Differentiates Mycophenolate Mofetil and GW-842,166X from MDA7. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104956





