Deficits of Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropsychological Architecture Correlate with Specific Exosomal mRNA Expression: Evidence of a Continuum?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Subjects
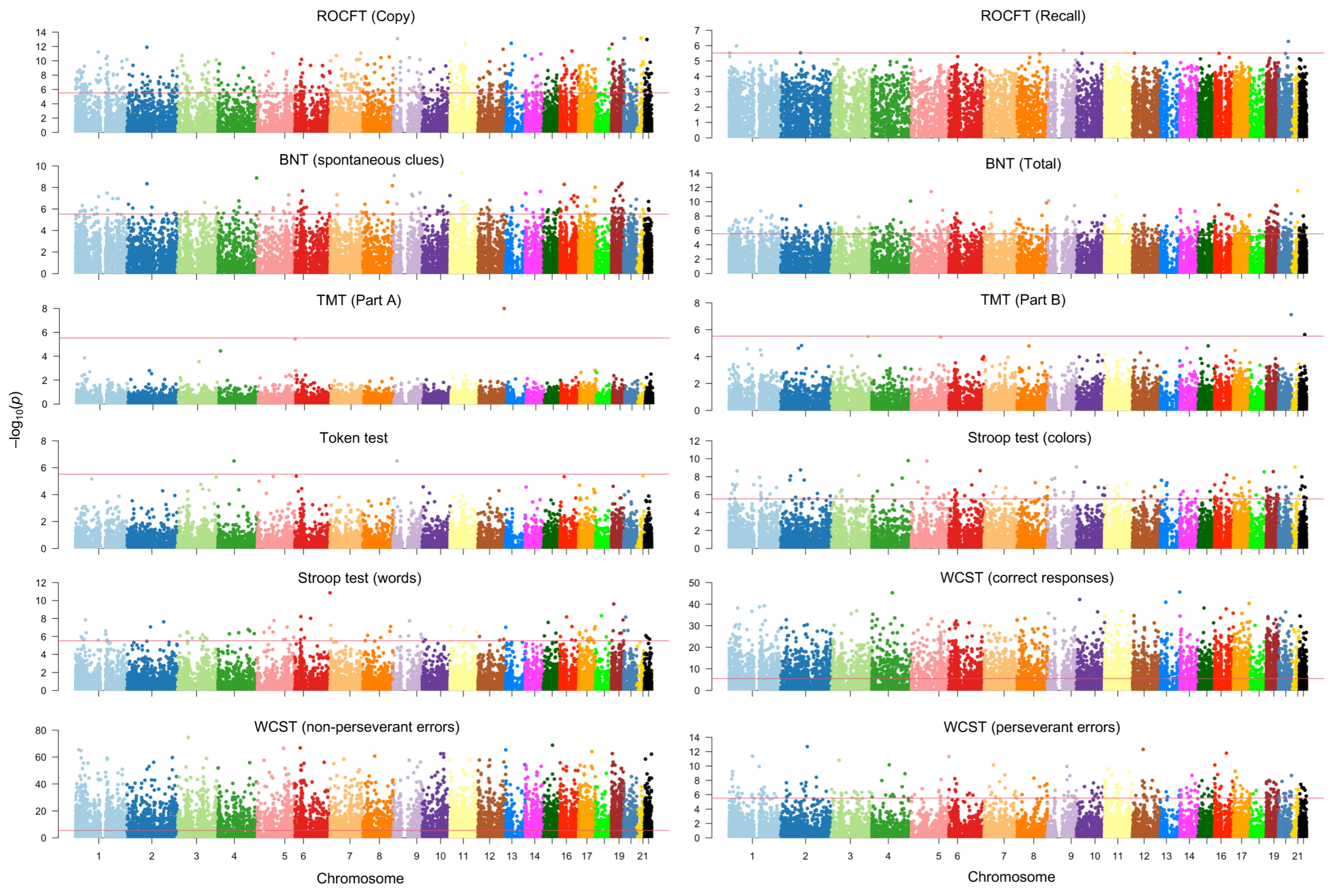
2.2. mRNA Signatures Contributing to Neuropsychological Manifestations of AD
2.3. PPS of mRNA Signatures Across Neuropsychological Tests
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Neuropsychological Assessment
4.3. RNA Isolation and Extraction
4.4. mRNA Microarray Study
4.5. mRNA Signatures Linked to Neuropsychological Manifestations of AD
4.6. Predictive Power of mRNAs in AD
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ADAOO | Alzheimer’s Disease Age of Onset |
| AVMR | Auditory–Verbal Memory Recognition |
| Aβ | Amyloid-beta |
| BNT | Boston Naming Test |
| circRNA | Circular RNA |
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| FAST | Functional Assessment Screening Tool |
| GLM | Generalized Linear Model |
| lncRNA | Long Non-Coding RNA |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| MoCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| PPS | Predictive Power Score |
| ROCFT | Rey–Osterrieth Complex Figure Test |
| TMT | Trail Making Test |
| WCST | Wisconsin Card Sorting Test |
References
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, E.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Vollset, S.E.; Fukutaki, K.; Chalek, J.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdoli, A.; Abualhasan, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Akram, T.T.; et al. Estimation of the Global Prevalence of Dementia in 2019 and Forecasted Prevalence in 2050: An Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera-Heredia, M.I.; Morales, L.C.; Vidal, O.M.; Barceló, E.; Silvera-Redondo, C.; Vélez, J.I.; Garavito-Galofre, P. Exosomes: Potential Disease Biomarkers and New Therapeutic Targets. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, W.; Zhu, H.; Ge, W.; Ma, C. Long RNA Profiles of Human Brain Extracellular Vesicles Provide New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobeiri, P.; Alilou, S.; Jaberinezhad, M.; Zare, F.; Karimi, N.; Maleki, S.; Teixeira, A.L.; Perry, G.; Rezaei, N. Circulating Long Non-Coding RNAs as Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease (AD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxtater, K.; Tripathi, M.; Khan, M. Recent Advances on the Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 2253–2254. [Google Scholar]
- Mosquera-Heredia, M.I.; Vidal, O.M.; Morales, L.C.; Silvera-Redondo, C.; Barceló, E.; Allegri, R.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; Vélez, J.I.; Garavito-Galofre, P. Long Non-Coding RNAs and Alzheimer’s Disease: Towards Personalized Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolívar, D.A.; Mosquera-Heredia, M.I.; Vidal, O.M.; Barceló, E.; Allegri, R.; Morales, L.C.; Silvera-Redondo, C.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; Garavito-Galofre, P.; Vélez, J.I. Exosomal MRNA Signatures as Predictive Biomarkers for Risk and Age of Onset in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Mizuno, K.; Tiwari, S.S.; Proitsi, P.; Gomez Perez-Nievas, B.; Glennon, E.; Martinez-Nunez, R.T.; Giese, K.P. Alzheimer’s Diseasx10-Related Dysregulation of MRNA Translation Causes Key Pathological Features with Ageing. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işık, M.; Beydemir, Ş. AChE MRNA Expression as a Possible Novel Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease and Alzheimer’s Disease, and Its Association with Oxidative Stress. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 128, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubauskienė, E.; Vilys, L.; Pečiulienė, I.; Kanopka, A. The Role of Hypoxia on Alzheimer’s Diseasx10-Related APP and Tau MRNA Formation. Gene 2021, 766, 145146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phu Pham, L.H.; Chang, C.-F.; Tuchez, K.; Chen, Y. Assess Alzheimer’s Disease via Plasma Extracellular Vesiclx10-Derived MRNA. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor Eddin, A.; Hamsho, K.; Adi, G.; Al-Rimawi, M.; Alfuwais, M.; Abdul Rab, S.; Alkattan, K.; Yaqinuddin, A. Cerebrospinal Fluid MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1210191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riscado, M.; Baptista, B.; Sousa, F. New RNA-Based Breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis and Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zou, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Yang, C.; Ma, L. Plasma Long Non-Coding RNAs ASMTL-AS1, AP001363.1, AC005730.3 and AL133415.1 as a Potential Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurol Res. 2023, 45, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhenaky, A.; Alhazmi, S.; Alamri, S.H.; Alkhatabi, H.A.; Alharthi, A.; Alsaleem, M.A.; Abdelnour, S.A.; Hassan, S.M. Exosomal MicroRNAs in Alzheimer’s Disease: Unveiling Their Role and Pioneering Tools for Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zheng, D.; Nao, J. Circulating Exosome MicroRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers of Dementia. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 580199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, I.; de Benedittis, S.; Quattrone, A.; Maisano, D.; Iaccino, E.; Quattrone, A. Exosomal MiRNAs as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yue, B.L.; Huang, Y.Z.; Lan, X.Y.; Liu, W.J.; Chen, H. Exosomal RNAs: Novel Potential Biomarkers for Diseases—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, Y.; Yamazaki, K.; Ozaki, Y.; Sao, T.; Yoshida, T.; Mori, T.; Mori, Y.; Ochi, S.; Iga, J.I.; Ueno, S.I. INPP5D MRNA Expression and Cognitive Decline in Japanese Alzheimer’s Disease Subjects. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 58, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.J.; Ng, A.S.L.; Vipin, A.; Lim, J.K.W.; Chander, R.J.; Ji, F.; Qiu, Y.; Ting, S.K.S.; Hameed, S.; Lee, T.S.; et al. Higher Peripheral TREM2 MRNA Levels Relate to Cognitive Deficits and Hippocampal Atrophy in Alzheimer’s Disease and Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 58, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sao, T.; Yoshino, Y.; Yamazaki, K.; Ozaki, Y.; Mori, Y.; Ochi, S.; Yoshida, T.; Mori, T.; Iga, J.I.; Ueno, S.I. MEF2C MRNA Expression and Cognitive Function in Japanese Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 72, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktar, A.; Lam, S.; Altay, O.; Li, X.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, C.; Arif, M.; Turkez, H.; Uhlén, M.; Shoaie, S.; et al. Revealing the Molecular Mechanisms of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Network Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhaye, S.; Jarjat, M.; Boulksibat, A.; Sanchez, C.; Tempio, A.; Turtoi, A.; Giorgi, M.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Baj, G.; Rovere, C.; et al. Defects in AMPAR Trafficking and Microglia Activation Underlie Socio-Cognitive Deficits Associated to Decreased Expression of Phosphodiesterase 2 a. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 191, 106393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. Role of PDE2A in Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Available online: https://reporter.nih.gov/project-details/10832468 (accessed on 9 April 2025).
- Kubota, S.; Doi, H.; Koyano, S.; Tanaka, K.; Komiya, H.; Katsumoto, A.; Ikeda, S.; Hashiguchi, S.; Nakamura, H.; Fukai, R.; et al. SGTA Associates with Intracellular Aggregates in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Brain 2021, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benarroch, R.; Austin, J.M.; Ahmed, F.; Isaacson, R.L. The Roles of Cytosolic Quality Control Proteins, SGTA and the BAG6 Complex, in Disease. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2019, 114, 265–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, L.K.; Day, T.K.; Butler, M.S.; Laven-Law, G.; Jindal, S.; Hickey, T.E.; Scher, H.I.; Butler, L.M.; Tilley, W.D. Small Glutaminx10-Rich Tetratricopeptide Repeat-Containing Protein Alpha (SGTA) Ablation Limits Offspring Viability and Growth in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathys, H.; Davila-Velderrain, J.; Peng, Z.; Gao, F.; Mohammadi, S.; Young, J.Z.; Menon, M.; He, L.; Abdurrob, F.; Jiang, X.; et al. Singlx10-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2019, 570, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Xiang, Y.; Ye, F. Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients with Different Lifespan: A Bioinformatics Study Focusing on the Disease Heterogeneity. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1072184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramopoulos, D.; Szymanski, M.; Wang, R.; Bassett, S. Gene Expression Reveals Overlap between Normal Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease Genes. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 2319.e27–2319.e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Pilozzi, A.; Huang, X. Network Medicine Approach for Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease Gene Expression Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetschoreck, F. RIP Correlation. Introducing the Predictive Power Score. Available online: https://medium.com/data-science/rip-correlation-introducing-the-predictive-power-score-3d90808b9598 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- van der Laken, P. Ppsr: Predictive Power Score. In CRAN: Contributed Packages; 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Arzouni, N.; Matloff, W.; Zhao, L.; Ning, K.; Toga, A.W. Identification of Dysregulated Genes for Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease Using Gene Expression Data in Brain. J. Alzheimers Dis. Park. 2020, 10, 498. [Google Scholar]
- Kocinaj, A.; Chaudhury, T.; Uddin, M.S.; Junaid, R.R.; Ramsden, D.B.; Hondhamuni, G.; Klamt, F.; Parsons, L.; Parsons, R.B. High Expression of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase in Patients with Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canchi, S.; Raao, B.; Masliah, D.; Rosenthal, S.B.; Sasik, R.; Fisch, K.M.; De Jager, P.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Rissman, R.A. Integrating Gene and Protein Expression Reveals Perturbed Functional Networks in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 1103–1116.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, M.M.; Al-Karawi, K.A.; Semary, H.E. Deep Learning-Based Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Microarray Gene Expression Data. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Lee, H. Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Blood Gene Expression Data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gawady, A.; Makhlouf, M.A.; Tawfik, B.S.; Nassar, H. Machine Learning Framework for the Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Gene Expression Data Based on Efficient Gene Selection. Symmetry 2022, 14, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Plass, M. RNA Dynamics in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2021, 26, 5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Weng, L. Identification and Validation of Aging-Related Genes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 905722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashendorf, L.; Jefferson, A.L.; O’Connor, M.K.; Chaisson, C.; Green, R.C.; Stern, R.A. Trail Making Test Errors in Normal Aging, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Dementia. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2008, 23, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, N.J.; Lohse, A.; Haas, R.; Reiche, S.; Sedlaczek, L.; Brandl, E.J.; Riemer, T.G. Trail Making Test Error Analysis in Subjective Cognitive Decline, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Alzheimer’s Dementia with and without Depression. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2023, 38, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferris, J.; Greeley, B.; Yeganeh, N.M.; Rinat, S.; Ramirez, J.; Black, S.; Boyd, L. Exploring Biomarkers of Processing Speed and Executive Function: The Role of the Anterior Thalamic Radiations. Neuroimage Clin. 2022, 36, 103174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, P.; Feng, R.; Jiang, N.; Chen, X.; Song, H.; Chen, Z. Cell Adhesion Molecules Contribute to Alzheimer’s Disease: Multiple Pathway Analyses of Two Genome-Wide Association Studies. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.J.; Wong, B.Y.X.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Sreejith, S.; Chia, S.Y.; Kandiah, N.; Ng, A.S.L.; Zeng, L. Altered Cerebrospinal Fluid Exosomal MicroRNA Levels in Young-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2021, 5, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeever, P.M.; Schneider, R.; Taghdiri, F.; Weichert, A.; Multani, N.; Brown, R.A.; Boxer, A.L.; Karydas, A.; Miller, B.; Robertson, J.; et al. MicroRNA Expression Levels Are Altered in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Young-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8826–8841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.S.; Lv, W.; Hu, X.Y. Altered MicroRNA Profiles in Cerebrospinal Fluid Exosome in Parkinson Disease and Alzheimer Disease. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37043–37053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos-Burgos, M.; Muenke, M. Genetics of Population Isolates. Clin. Genet. 2002, 61, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda-Falla, D.; Vélez, J.I.; Acosta-Baena, N.; Baena, A.; Moreno, S.; Krasemann, S.; Lopera, F.; Mastronardi, C.A.; Arcos-Burgos, M. Genetic Modifiers of Cognitive Decline in PSEN1 E280A Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, J.I.; Chandrasekharappa, S.C.; Henao, E.; Martinez, A.F.; Harper, U.; Jones, M.; Solomon, B.D.; Lopez, L.; Garcia, G.; Aguirre-Acevedo, D.C.; et al. Pooling/Bootstrap-Based GWAS (PbGWAS) Identifies New Loci Modifying the Age of Onset in PSEN1 p.Glu280Ala Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, J.I.; Lopera, F.; Sepulveda-Falla, D.; Patel, H.R.; Johar, A.S.; Chuah, A.; Tobon, C.; Rivera, D.; Villegas, A.; Cai, Y.; et al. APOE*E2 Allele Delays Age of Onset in PSEN1 E280A Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Baena, N.; Sepulveda-Falla, D.; Lopera-Gómez, C.M.; Jaramillo-Elorza, M.C.; Moreno, S.; Aguirrx10-Acevedo, D.C.; Saldarriaga, A.; Lopera, F. Prx10-Dementia Clinical Stages in Presenilin 1 E280A Familial Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool For Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folstein, M.F.; Robins, L.N.; Helzer, J.E. The Mini-Mental State Examination. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1983, 40, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; ISBN 0-89042-575-2. [Google Scholar]
- Allegri, R.F.; Villavicencio, A.F.; Taragano, F.E.; Rymberg, S.; Mangone, C.A.; Baumann, D. Spanish Boston Naming Test Norms. Clin. Neuropsychol. 1997, 11, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.L.; Fulbright, R.L. Construct and Concurrent Validity of the Spanish Adaptation of the Boston Naming Test. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 2015, 22, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterrieth, P.A. The Test of Copying a Complex Figure: A Contribution to the Study of Perception and Memory. Arch. Psychol. 1944, 30, 206–356. [Google Scholar]
- Bean, J. Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test, Rey AVLT. In Encyclopedia of Clinical Neuropsychology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 2174–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Reitan, R.M. The Relation of the Trail Making Test to Organic Brain Damage. J. Consult. Psychol. 1955, 19, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitan, R.M. Validity of the Trail Making Test as an Indicator of Organic Brain Damage. Percept. Mot. Skills 1958, 8, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A. Symbol Digit Modalities Test. Clin. Neuropsychol. 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, C.J. Stroop Color and Word Test. Stoelting Company 1978.
- De Renzi, E.; Vignolo, L.A. The Token Test: A Sensitive Test to Detect Receptive Disturbances in Aphasics. Brain 1962, 85, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, A.L. Visuospatial Judgment: A Clinical Test. Arch. Neurol. 1978, 35, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aprahamian, I.; Martinelli, J.E.; Neri, A.L.; Yassuda, M.S. The Clock Drawing Test A Review of Its Accuracy in Screening for Dementia. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2009, 3, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, D.A.; Berg, E. A Behavioral Analysis of Degree of Reinforcement and Ease of Shifting to New Responses in a Weigl-Type Card-Sorting Problem. J. Exp. Psychol. 1948, 38, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, T.L.; Yesavage, J.A.; Lum, O.; Heersema, P.H.; Adey, M.; Rose, T.L. Screening Tests for Geriatric Depression. Clin. Gerontol. 1982, 1, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisberg, B.; Ferris, S.H.; De Leon, M.J.; Crook, T. The Global Deterioration Scale for Assessment of Primary Degenerative Dementia. Am. J. Psychiatry 1982, 139, 1136–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, F.I.; Barthel, D.W. Functional Evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md. State Med. J. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, J. The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: Development and Applications. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2020, 33, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naj, A.C.; Jun, G.; Reitz, C.; Kunkle, B.W.; Perry, W.; Park, Y.S.; Beecham, G.W.; Rajbhandary, R.A.; Hamilton-Nelson, K.L.; Wang, L.-S.; et al. Effects of Multiple Genetic Loci on Age at Onset in Latx10-Onset Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.; Brkanac, Z.; Wijsman, E.M. Family-based Genome Scan for Age at Onset of Latx10-onset Alzheimer’s Disease in Whole Exome Sequencing Data. Genes. Brain Behav. 2015, 14, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Bühlmann, P. Missforest-Non-Parametric Missing Value Imputation for Mixed-Type Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stekhoven, D.J. missForest: Nonparametric Missing Value Imputation Using Random Forest; R Package Version 1.4; p. 2022.
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, P.K.; Smyth, G.K. Generalized Linear Models with Examples in R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bonferroni, C.E. Teoria Statistica Delle Classi e Calcolo Delle Probabilità. Pubbl. Del R Ist. Super. Di Sci. Econ. E Commer. di Firenze 1936, 8, 3–62. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, J.I.; Correa, J.C.; Arcos-Burgos, M. A New Method for Detecting Significant P-Values with Applications to Genetic Data. Rev. Colomb. Estad. 2014, 37, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.P. Multiple Hypothesis Testing. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 1995, 46, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Cases | Controls | W a | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | ||||
| Age (years) | 77.5 (8.5) | 82.1 (8.6) | 900 | <0.001 |
| MMSE | 13.9 (9.5) | 25.2 (5.6) | 855 | <0.001 |
| MoCA | 5.5 (5.3) | 25.9 (2.9) | 224 | <0.001 |
| FAST | 4.5 (3.2) | 2.5 (0.6) | 19 | <0.001 |
| Boston Naming Test | ||||
| Spontaneous clues | 14.1 (11.6) | 37.5 (13.9) | 200.5 | <0.001 |
| Semantic clues | 0.7 (1.2) | 1.3 (1.4) | 138.5 | 0.248 |
| Total score | 14.8 (12.1) | 38.7 (14.2) | 201.5 | <0.001 |
| Verbal Fluency | ||||
| Letter “a” | 3.4 (2.8) | 11.2 (3.7) | 212.5 | <0.001 |
| Letter “c” | 4.5 (3.8) | 8.7 (4) | 177 | 0.008 |
| Phonological fluency | ||||
| Letter ”a” | 2.6 (3.4) | 8.6 (4.8) | 191 | 0.001 |
| Letter “s” | 2.8 (2.8) | 8.3 (5.3) | 179 | 0.006 |
| Letter “f” | 3.6 (3.8) | 8.2 (5.8) | 163.5 | 0.035 |
| Trail Making Test | ||||
| Part A | 115.5 (79.8) | 109 (77) | 101 | 0.648 |
| Part B | 145.4 (130.8) | 233 (105) | 157.5 | 0.063 |
| Token test | 14.1 (10) | 26.2 (10.8) | 187 | 0.002 |
| Lawton and Brody test | 1.7 (1.4) | 0.3 (0.8) | 175.5 | 0.003 |
| ROCFT | ||||
| Copy | 5.6 (9.2) | 24.7 (13.5) | 193 | <0.001 |
| Recall | 1.3 (2.4) | 6.3 (5.6) | 181 | 0.004 |
| AVMR, “Yes” | 6.7 (6.4) | 11.7 (4.1) | 169.5 | 0.018 |
| AVMR, “No” | 7.3 (6.2) | 11.9 (5.2) | 163 | 0.033 |
| Stroop test | ||||
| Words | 33.2 (17.3) | 60.1 (32.4) | 178 | 0.007 |
| Colours | 20.3 (13) | 39.4 (22.2) | 170 | 0.018 |
| Wisconsin Card Sorting Test | ||||
| Categories | 0.7 (0.9) | 2.6 (2.2) | 170 | 0.015 |
| NPE | 25.8 (24.1) | 20.5 (29.9) | 89 | 0.339 |
| Perseverant errors | 26.1 (19.2) | 18.9 (12.9) | 87.5 | 0.309 |
| Correct responses | 25.1 (23.8) | 42.8 (40.1) | 137 | 0.319 |
| Test | Transcript | Chr | Position a | Gene | p | pBonferroni | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROCFT | |||||||
| Copy | ENST00000382830 | 21 | 31,962,424 | KRTAP22-2 | 0.567 (0.076) | 6.74 × 10−14 | 1.12 × 10−9 |
| ENST00000361033 | 20 | 2,796,948 | TMEM239 | −1.384 (0.185) | 7.41 × 10−14 | 1.23 × 10−9 | |
| ENST00000380210 | 9 | 21,349,834 | IFNA6 | 0.396 (0.053) | 8.14 × 10−14 | 1.35 × 10−9 | |
| ENST00000216037 | 22 | 29,190,543 | XBP1 | 0.475 (0.064) | 1.06 × 10−13 | 1.76 × 10−9 | |
| ENST00000398576 | 13 | 46,700,055 | LCP1 | −0.268 (0.037) | 3.64 × 10−13 | 6.04 × 10−9 | |
| ENST00000221566 | 19 | 2,754,712 | SGTA | −0.992 (0.137) | 4.74 × 10−13 | 7.86 × 10−9 | |
| ENST00000334456 | 11 | 72,287,185 | PDE2A | 0.387 (0.054) | 5.11 × 10−13 | 8.48 × 10−9 | |
| ENST00000295201 | 2 | 95,537,188 | TEKT4 | 1.205 (0.17) | 1.29 × 10−12 | 2.14 × 10−8 | |
| ENST00000360242 | 18 | 66,465,317 | CCDC102B | −0.639 (0.091) | 2.00 × 10−12 | 3.31 × 10−8 | |
| ENST00000544413 | 12 | 121,416,552 | HNF1A | −1.399 (0.2) | 2.45 × 10−12 | 4.06 × 10−8 | |
| Recall | HBMT00000891055 | 20 | 47,127,407 | CATG00000053459.1 | −0.845 (0.169) | 5.33 × 10−7 | 8.84 × 10−3 |
| ENST00000339480 | 1 | 35,225,342 | GJB4 | −0.852 (0.174) | 1.03 × 10−6 | 1.70 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000545128 | 9 | 78,505,560 | PCSK5 | −0.972 (0.205) | 2.08 × 10−6 | 3.45 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000398093 | 11 | 102,980,304 | DYNC2H1 | 1.23 (0.261) | 2.46 × 10−6 | 4.08 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000295201 | 2 | 95,537,188 | TEKT4 | 1.375 (0.294) | 2.95 × 10−6 | 4.89 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000378567 | 1 | 1,981,909 | PRKCZ | −1.004 (0.215) | 2.95 × 10−6 | 4.90 × 10−2 | |
| BNT | |||||||
| Spontaneous Clues | ENST00000216487 | 14 | 92,980,118 | RIN3 | 0.453 (0.081) | 2.39 × 10−8 | 3.97 × 10−4 |
| ENCT00000457686 | 9 | 90,652,380 | CATG00000108922.1 | 0.554 (0.101) | 4.36 × 10−8 | 7.22 × 10−4 | |
| ENCT00000061513 | 10 | 134,202,355 | CATG00000001242.1 | −0.44 (0.081) | 5.67 × 10−8 | 9.40 × 10−4 | |
| ENST00000219070 | 16 | 55,512,883 | MMP2 | −0.445 (0.084) | 1.15 × 10−7 | 1.91 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000228958 | 2 | 119,913,597 | CATG00000044356.1 | −0.788 (0.159) | 6.86 × 10−7 | 1.14 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000234347 | 19 | 840,960 | PRTN3 | −0.443 (0.09) | 8.98 × 10−7 | 1.49 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000210313 | 9 | 123,578,331 | PSMD5 | −0.243 (0.05) | 9.45 × 10−7 | 1.57 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000216756 | 14 | 102,814,619 | CINP | 0.264 (0.054) | 1.13 × 10−6 | 1.87 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000242819 | 13 | 52,436,117 | CCDC70 | −0.498 (0.103) | 1.36 × 10−6 | 2.25 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000004531 | 8 | 17,396,286 | SLC7A2 | −0.366 (0.077) | 2.07 × 10−6 | 3.43 × 10−2 | |
| Total | ENCT00000061513 | 10 | 134,202,355 | CATG00000001242.1 | −0.458 (0.08) | 9.05 × 10−9 | 1.50 × 10−4 |
| ENCT00000457686 | 9 | 90,652,380 | CATG00000108922.1 | 0.552 (0.099) | 2.81 × 10−8 | 4.66 × 10−4 | |
| ENST00000004531 | 8 | 17,396,286 | SLC7A2 | −0.396 (0.076) | 1.57 × 10−7 | 2.60 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000228958 | 2 | 119,913,597 | CATG00000044356.1 | −0.808 (0.155) | 1.89 × 10−7 | 3.14 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000380453 | 6 | 168,062,372 | CATG00000086946.1 | 0.377 (0.075) | 4.66 × 10−7 | 7.73 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000200728 | 19 | 3,630,183 | CATG00000038258.1 | 0.264 (0.055) | 1.35 × 10−6 | 2.25 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000029805 | 1 | 109,072,893 | CATG00000070137.1 | 0.256 (0.054) | 1.78 × 10−6 | 2.96 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000447643 | 9 | 88,474,187 | CATG00000105979.1 | −0.342 (0.073) | 2.41 × 10−6 | 4.00 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000424376 | 8 | 41,121,640 | CATG00000098647.1 | 0.351 (0.075) | 2.47 × 10−6 | 4.10 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000370852 | 6 | 29,601,041 | CATG00000083443.1 | 0.261 (0.056) | 2.78 × 10−6 | 4.61 × 10−2 | |
| TMT | |||||||
| Part A | ENST00000228506 | 12 | 121,124,672 | MLEC | −43.181 (5.064) | 1.00 × 10−8 | 1.66 × 10−4 |
| Part B | MICT00000221720 | 20 | 60,942,556 | CATG00000053936.1 | −86.275 (11.342) | 7.61 × 10−8 | 1.26 × 10−3 |
| ENST00000263246 | 22 | 43,265,777 | PACSIN2 | −69.407 (11.271) | 2.31 × 10−6 | 3.83 × 10−2 | |
| Token test | MICT00000383608 | Y | 18,943,870 | CATG00000114908.1 | −0.71 (0.134) | 1.15 × 10−7 | 1.91 × 10−3 |
| ENST00000296043 | 4 | 77,356,253 | SHROOM3 | −0.663 (0.13) | 3.16 × 10−7 | 5.24 × 10−3 | |
| ENST00000380534 | 9 | 18,927,656 | SAXO1 | 0.728 (0.142) | 3.16 × 10−7 | 5.24 × 10−3 | |
| Stroop test | |||||||
| Colours | ENCT00000309252 | 3 | 134,030,483 | CATG00000066161.1 | −0.565 (0.098) | 7.53 × 10−9 | 1.25 × 10−4 |
| ENST00000216037 | 22 | 29,190,543 | XBP1 | 0.251 (0.044) | 1.06 × 10−8 | 1.76 × 10−4 | |
| ENST00000174618 | 17 | 2,287,354 | MNT | 0.225 (0.04) | 1.44 × 10−8 | 2.39 × 10−4 | |
| ENST00000215743 | 22 | 24,115,006 | MMP11 | 0.439 (0.085) | 2.61 × 10−7 | 4.34 × 10−3 | |
| ENST00000221566 | 19 | 2,754,712 | SGTA | −0.456 (0.09) | 4.03 × 10−7 | 6.68 × 10−3 | |
| ENST00000223369 | 7 | 44,240,648 | YKT6 | −0.349 (0.07) | 6.00 × 10−7 | 9.95 × 10−3 | |
| ENST00000216133 | 22 | 39,526,777 | CBX7 | 0.293 (0.062) | 2.17 × 10−6 | 3.60 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000231228 | 5 | 158,741,791 | IL12B | −0.22 (0.047) | 2.32 × 10−6 | 3.85 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000193672 | 18 | 60,987,564 | CATG00000036339.1 | −0.328 (0.07) | 2.59 × 10−6 | 4.29 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000431277 | 8 | 144,959,539 | CATG00000101329.1 | −0.381 (0.082) | 2.98 × 10−6 | 4.94 × 10−2 | |
| Words | ENST00000171111 | 19 | 10,596,796 | KEAP1 | 0.271 (0.043) | 2.40 × 10−10 | 3.98 × 10−6 |
| ENST00000201647 | 19 | 55,587,269 | EPS8L1 | −0.369 (0.065) | 1.46 × 10−8 | 2.43 × 10−4 | |
| ENST00000250160 | 8 | 134,203,282 | WISP1 | −0.252 (0.047) | 7.78 × 10−8 | 1.29 × 10−3 | |
| ENST00000251453 | 19 | 39,923,847 | RPS16 | 0.334 (0.066) | 4.46 × 10−7 | 7.39 × 10−3 | |
| ENST00000225698 | 17 | 5,336,097 | C1QBP | −0.223 (0.045) | 6.24 × 10−7 | 1.03 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000309252 | 3 | 134,030,483 | CATG00000066161.1 | −0.371 (0.077) | 1.28 × 10−6 | 2.12 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000230588 | 6 | 46,761,127 | MEP1A | −0.238 (0.049) | 1.43 × 10−6 | 2.37 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000225567 | 17 | 45,000,486 | GOSR2 | −0.345 (0.072) | 1.82 × 10−6 | 3.03 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000216254 | 22 | 41,865,129 | ACO2 | 0.267 (0.056) | 1.96 × 10−6 | 3.25 × 10−2 | |
| WCST | |||||||
| Correct responses | ENCT00000012768 | 1 | 156,638,559 | CATG00000020670.1 | 0.736 (0.085) | 4.37 × 10−18 | 7.25 × 10−14 |
| ENCT00000000389 | 1 | 1,874,595 | CATG00000071025.1 | −0.679 (0.08) | 2.46 × 10-17 | 4.09 × 10−13 | |
| ENCT00000004417 | 1 | 38,891,158 | CATG00000115972.1 | 0.19 (0.023) | 4.03 × 10−16 | 6.68 × 10−12 | |
| ENCT00000000232 | 1 | 1,138,890 | CATG00000019495.1 | −0.566 (0.082) | 4.07 × 10−12 | 6.75 × 10−8 | |
| ENCT00000000644 | 1 | 4,077,807 | CATG00000116876.1 | −0.654 (0.095) | 6.99 × 10−12 | 1.16 × 10−7 | |
| ENCT00000002816 | 1 | 25,046,862 | CATG00000062929.1 | −0.389 (0.061) | 1.34 × 10−10 | 2.22 × 10−6 | |
| ENCT00000001323 | 1 | 10,960,567 | CATG00000015125.1 | 0.479 (0.078) | 6.95 × 10−10 | 1.15 × 10−5 | |
| ENCT00000003570 | 1 | 30,996,263 | CATG00000087839.1 | 0.31 (0.051) | 1.32 × 10−9 | 2.19 × 10−5 | |
| ENCT00000002257 | 1 | 19,234,224 | CATG00000038794.1 | 0.513 (0.092) | 2.23 × 10−8 | 3.70 × 10−4 | |
| ENCT00000004031 | 1 | 35,331,806 | CATG00000107162.1 | −0.287 (0.059) | 1.02 × 10−6 | 1.69 × 10−2 | |
| NPE | ENCT00000000276 | 1 | 1,284,939 | CATG00000033020.1 | −1.178 (0.137) | 1.08 × 10−17 | 1.80 × 10−13 |
| ENCT00000020781 | 1 | 1,964,944 | CATG00000043697.1 | −0.899 (0.109) | 1.47 × 10−16 | 2.43 × 10−12 | |
| ENCT00000005948 | 1 | 53,558,713 | CATG00000001175.1 | 0.614 (0.083) | 1.37 × 10−13 | 2.28 × 10−9 | |
| ENCT00000020405 | 1 | 984,575 | CATG00000042982.1 | −0.479 (0.068) | 2.20 × 10−12 | 3.64 × 10−8 | |
| ENCT00000004031 | 1 | 35,331,806 | CATG00000107162.1 | −0.426 (0.069) | 6.99 × 10−10 | 1.16 × 10−5 | |
| ENCT00000000644 | 1 | 4,077,807 | CATG00000116876.1 | −0.55 (0.102) | 7.09 × 10−8 | 1.18 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000020445 | 1 | 1,087,776 | CATG00000043113.1 | 0.752 (0.14) | 7.36 × 10−8 | 1.22 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000002816 | 1 | 25,046,862 | CATG00000062929.1 | −0.374 (0.07) | 9.87 × 10−8 | 1.64 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000018210 | 1 | 225,841,146 | CATG00000037190.1 | 0.258 (0.051) | 3.41 × 10−7 | 5.65 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000029656 | 1 | 104,998,991 | CATG00000069026.1 | −0.543 (0.115) | 2.43 × 10−6 | 4.03 × 10−2 | |
| Perseverant errors | ENCT00000228958 | 2 | 119,913,597 | CATG00000044356.1 | −0.731 (0.135) | 6.09 × 10−8 | 1.01 × 10−3 |
| ENCT00000045141 | 10 | 38,027,225 | CATG00000112585.1 | 0.453 (0.084) | 7.49 × 10−8 | 1.24 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000272151 | 21 | 46,270,031 | CATG00000056264.1 | −0.37 (0.071) | 1.83 × 10−7 | 3.03 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000263490 | 20 | 61,077,116 | CATG00000053945.1 | 0.626 (0.124) | 4.77 × 10−7 | 7.91 × 10−3 | |
| ENCT00000474207 | X | 2,742,248 | CATG00000112964.1 | −0.361 (0.073) | 6.42 × 10−7 | 1.07 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000431277 | 8 | 144,959,539 | CATG00000101329.1 | 0.422 (0.088) | 1.47 × 10−6 | 2.44 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000113077 | 13 | 55,351,449 | CATG00000014934.1 | 0.49 (0.103) | 1.92 × 10−6 | 3.18 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000055682 | X | 73,952,691 | NEXMIF | −0.323 (0.068) | 2.28 × 10−6 | 3.78 × 10−2 | |
| ENST00000013807 | 19 | 45,916,692 | ERCC1 | −0.383 (0.081) | 2.30 × 10−6 | 3.81 × 10−2 | |
| ENCT00000202697 | 19 | 17,008,342 | CATG00000038771.1 | 0.393 (0.083) | 2.43 × 10−6 | 4.02 × 10−2 |
| Variable | Transcript | Chr | Position | Gene | PPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVMR | |||||
| No | ENST00000295268 | 4 | 98,480,027 | STPG2 | 0.295 |
| ENST00000474844 | 1 | 46,805,849 | NSUN4 | 0.295 | |
| ENST00000274773 | 5 | 180,620,924 | TRIM7 | 0.293 | |
| ENST00000623276 | 6 | 28,234,931 | ZSCAN26 | 0.289 | |
| ENST00000317907 | 2 | 32,853,129 | TTC27 | 0.273 | |
| Yes | ENST00000307395 | 3 | 128,779,610 | GP9 | 0.347 |
| ENST00000299608 | 18 | 66,340,925 | TMX3 | 0.331 | |
| ENST00000609883 | X | 71,347,574 | RTL5 | 0.329 | |
| ENST00000343053 | 9 | 140,149,625 | NELFB | 0.322 | |
| ENST00000409299 | 20 | 32,290,560 | PXMP4 | 0.316 | |
| BNT | |||||
| Spontaneous clues | ENST00000274773 | 5 | 180,620,924 | TRIM7 | 0.391 |
| ENST00000361900 | 15 | 75,287,939 | SCAMP5 | 0.298 | |
| ENST00000375581 | 13 | 113,760,121 | F7 | 0.287 | |
| ENST00000368751 | 1 | 153,065,611 | SPRR2E | 0.274 | |
| ENST00000524140 | 19 | 16,830,791 | NWD1 | 0.264 | |
| Semantic clues | ENST00000517870 | 1 | 53,099,016 | SHISAL2A | 0.374 |
| ENST00000622339 | 1 | 104,159,433 | AMY2A | 0.361 | |
| ENST00000330233 | 14 | 105,952,654 | CRIP1 | 0.336 | |
| ENST00000254691 | 5 | 40,841,286 | CARD6 | 0.320 | |
| ENST00000409790 | 16 | 11,038,345 | CLEC16A | 0.311 | |
| Total | ENST00000274773 | 5 | 180,620,924 | TRIM7 | 0.386 |
| ENST00000361900 | 15 | 75,287,939 | SCAMP5 | 0.304 | |
| ENST00000375581 | 13 | 113,760,121 | F7 | 0.292 | |
| ENST00000262426 | 16 | 86,544,133 | FOXF1 | 0.275 | |
| ENST00000323853 | 2 | 96,940,074 | SNRNP200 | 0.267 | |
| FAST | ENST00000378165 | 10 | 15,149,865 | NMT2 | 0.271 |
| ENST00000311550 | 15 | 26,788,693 | GABRB3 | 0.227 | |
| ENST00000611257 | 17 | 34,493,061 | TBC1D3B | 0.209 | |
| ENST00000643399 | 10 | 71,038,252 | HK1 | 0.167 | |
| ENST00000290158 | 17 | 45,727,204 | KPNB1 | 0.160 | |
| Lawton and Brody | ENST00000216442 | 14 | 67,804,788 | ATP6V1D | 0.306 |
| ENST00000297770 | 8 | 68,334,307 | CPA6 | 0.308 | |
| ENST00000318225 | 3 | 126,268,516 | C3orf22 | 0.315 | |
| ENST00000250056 | 17 | 6,347,761 | PIMREG | 0.341 | |
| ENST00000299367 | 6 | 31,895,254 | C2 | 0.430 | |
| MMSE | ENST00000528494 | 11 | 46,639,150 | ATG13 | 0.221 |
| ENST00000304385 | 4 | 153,539,784 | TMEM154 | 0.232 | |
| ENST00000394152 | 7 | 99,214,571 | ZSCAN25 | 0.240 | |
| ENST00000262426 | 16 | 86,544,133 | FOXF1 | 0.247 | |
| ENST00000274773 | 5 | 180,620,924 | TRIM7 | 0.292 | |
| MoCA | ENST00000311550 | 15 | 26,788,693 | GABRB3 | 0.647 |
| ENST00000343289 | 10 | 104,847,775 | NT5C2 | 0.439 | |
| ENST00000340116 | 18 | 6739 | ENOSF1 | 0.428 | |
| ENST00000331581 | 11 | 115,047,015 | CADM1 | 0.425 | |
| FTMT26400003890 | 16 | 67,267,859 | FHOD1 | 0.423 | |
| Phonological fluency | |||||
| Letter “a” | ENST00000355790 | 10 | 72,058,729 | LRRC20 | 0.255 |
| ENST00000611257 | 17 | 34,493,061 | TBC1D3B | 0.235 | |
| ENST00000382258 | 13 | 24,153,499 | TNFRSF19 | 0.224 | |
| ENST00000379731 | 9 | 33,110,635 | B4GALT1 | 0.224 | |
| ENST00000374510 | 9 | 113,065,867 | TXNDC8 | 0.222 | |
| Letter “f” | ENST00000355790 | 10 | 72,058,729 | LRRC20 | 0.297 |
| ENST00000296043 | 4 | 77,356,253 | SHROOM3 | 0.277 | |
| ENST00000259883 | 6 | 28,249,349 | PGBD1 | 0.242 | |
| ENST00000340913 | 12 | 54,674,539 | HNRNPA1 | 0.231 | |
| HBMT00001348771 | 7 | 140,772,165 | TMEM178B | 0.228 | |
| Letter “s” | ENST00000284268 | 5 | 14,704,909 | ANKH | 0.224 |
| ENST00000598357 | 19 | 45,842,445 | L47234.1 | 0.215 | |
| ENST00000222990 | 7 | 2,291,405 | SNX8 | 0.211 | |
| ENST00000355790 | 10 | 72,058,729 | LRRC20 | 0.206 | |
| ENST00000305366 | 3 | 149,086,809 | TM4SF1 | 0.206 | |
| ROCFT | |||||
| Copy | ENCT00000073979 | 11 | 1,403,334 | BRSK2 | 0.336 |
| ENST00000274773 | 5 | 180,620,924 | TRIM7 | 0.327 | |
| ENST00000310248 | 12 | 48,595,866 | OR10AD1 | 0.300 | |
| ENST00000418703 | 12 | 110,220,890 | TRPV4 | 0.298 | |
| ENST00000300433 | 17 | 48,348,767 | TMEM92 | 0.293 | |
| Recall | ENST00000334571 | 14 | 74,416,996 | COQ6 | 0.330 |
| ENST00000578812 | 17 | 8,282,463 | RPL26 | 0.316 | |
| ENST00000310248 | 12 | 48,595,866 | OR10AD1 | 0.301 | |
| ENST00000358607 | 19 | 18,699,535 | REX1BD | 0.288 | |
| ENST00000382723 | 4 | 4,861,393 | MSX1 | 0.285 | |
| Stroop test | |||||
| Colors | ENST00000278483 | 11 | 86,013,265 | HIKESHI | 0.323 |
| ENST00000335852 | 1 | 156,213,112 | PAQR6 | 0.264 | |
| ENST00000283928 | 7 | 27,870,192 | JAZF1 | 0.237 | |
| MICT00000155430 | 17 | 76,171,134 | TK1 | 0.230 | |
| ENST00000300093 | 16 | 23,690,143 | PLK1 | 0.215 | |
| Words | MICT00000155430 | 17 | 76,171,134 | TK1 | 0.249 |
| ENST00000278483 | 11 | 86,013,265 | HIKESHI | 0.217 | |
| ENST00000540200 | 17 | 26,674,203 | POLDIP2 | 0.205 | |
| ENST00000378981 | X | 30,261,847 | MAGEB1 | 0.204 | |
| HBMT00000611233 | 17 | 75,249,896 | CATG00000032482.1 | 0.194 | |
| TMT | |||||
| Part A | ENST00000302823 | 2 | 204,732,509 | CTLA4 | 0.250 |
| ENST00000428112 | 1 | 47,024,371 | MKNK1 | 0.238 | |
| MICT00000156619 | 17 | 79,759,048 | GCGR | 0.219 | |
| ENST00000291700 | 21 | 48,018,875 | S100B | 0.216 | |
| ENST00000354905 | 3 | 190,146,444 | TMEM207 | 0.215 | |
| Part B | ENST00000304385 | 4 | 153,539,784 | TMEM154 | 0.421 |
| ENST00000274773 | 5 | 180,620,924 | TRIM7 | 0.414 | |
| ENST00000241051 | 11 | 33,037,410 | DEPDC7 | 0.302 | |
| ENST00000498273 | 1 | 62,660,503 | L1TD1 | 0.283 | |
| ENST00000398399 | 3 | 86,987,119 | VGLL3 | 0.273 | |
| Token test | ENST00000274773 | 5 | 180,620,924 | TRIM7 | 0.254 |
| ENST00000304385 | 4 | 153,539,784 | TMEM154 | 0.215 | |
| ENST00000278483 | 11 | 86,013,265 | HIKESHI | 0.212 | |
| ENST00000375581 | 13 | 113,760,121 | F7 | 0.208 | |
| ENST00000301838 | 11 | 70,049,269 | FADD | 0.202 | |
| Verbal Fluency | |||||
| Letter “a” | ENST00000375581 | 13 | 113,760,121 | F7 | 0.298 |
| ENST00000379052 | 6 | 17,281,577 | RBM24 | 0.272 | |
| ENST00000397095 | 7 | 1,094,921 | GPR146 | 0.271 | |
| ENST00000311550 | 15 | 26,788,693 | GABRB3 | 0.262 | |
| ENST00000427500 | 1 | 155,204,350 | GBA | 0.262 | |
| Letter “c” | ENST00000274773 | 5 | 180,620,924 | TRIM7 | 0.286 |
| ENST00000375259 | 9 | 99,082,992 | SLC35D2 | 0.226 | |
| ENST00000367175 | 1 | 204,586,298 | LRRN2 | 0.220 | |
| ENST00000611870 | 16 | 76,311,176 | CNTNAP4 | 0.215 | |
| ENST00000457091 | 7 | 6,537,405 | GRID2IP | 0.205 | |
| WCST | |||||
| Categories | ENST00000256495 | 3 | 5,020,801 | BHLHE40 | 0.316 |
| HBMT00000611233 | 17 | 75,249,896 | CATG00000032482.1 | 0.285 | |
| ENST00000379731 | 9 | 33,110,635 | B4GALT1 | 0.264 | |
| ENST00000230640 | 5 | 54,603,588 | MTREX | 0.254 | |
| ENST00000404371 | 2 | 10,923,519 | PDIA6 | 0.245 | |
| Correct responses | ENST00000230640 | 5 | 54,603,588 | MTREX | 0.291 |
| ENST00000281961 | 2 | 39,893,059 | TMEM178A | 0.281 | |
| ENST00000243253 | 3 | 127,771,212 | SEC61A1 | 0.268 | |
| ENST00000453960 | X | 153,295,685 | MECP2 | 0.267 | |
| ENST00000608842 | 22 | 18,893,866 | DGCR6 | 0.266 | |
| NPE | ENST00000260723 | 10 | 124,030,821 | BTBD16 | 0.252 |
| ENST00000360428 | 18 | 28,569,974 | DSC3 | 0.249 | |
| ENST00000267436 | 14 | 50,709,152 | L2HGDH | 0.245 | |
| ENST00000345080 | 6 | 105,404,923 | LIN28B | 0.241 | |
| ENST00000292907 | 19 | 36,641,824 | COX7A1 | 0.237 | |
| Perseverant errors | ENST00000255465 | 13 | 37,006,495 | CCNA1 | 0.291 |
| ENST00000541135 | 11 | 61,197,528 | AP003108.2 | 0.239 | |
| ENST00000375460 | 1 | 17,575,593 | PADI3 | 0.238 | |
| ENST00000305632 | 7 | 72,981,863 | TBL2 | 0.234 | |
| ENST00000427926 | 22 | 19,166,986 | CLTCL1 | 0.222 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barceló, E.; Mosquera-Heredia, M.I.; Vidal, O.M.; Bolívar, D.A.; Allegri, R.; Morales, L.C.; Silvera-Redondo, C.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; Garavito-Galofre, P.; Vélez, J.I. Deficits of Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropsychological Architecture Correlate with Specific Exosomal mRNA Expression: Evidence of a Continuum? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104897
Barceló E, Mosquera-Heredia MI, Vidal OM, Bolívar DA, Allegri R, Morales LC, Silvera-Redondo C, Arcos-Burgos M, Garavito-Galofre P, Vélez JI. Deficits of Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropsychological Architecture Correlate with Specific Exosomal mRNA Expression: Evidence of a Continuum? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104897
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarceló, Ernesto, María I. Mosquera-Heredia, Oscar M. Vidal, Daniel A. Bolívar, Ricardo Allegri, Luis C. Morales, Carlos Silvera-Redondo, Mauricio Arcos-Burgos, Pilar Garavito-Galofre, and Jorge I. Vélez. 2025. "Deficits of Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropsychological Architecture Correlate with Specific Exosomal mRNA Expression: Evidence of a Continuum?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104897
APA StyleBarceló, E., Mosquera-Heredia, M. I., Vidal, O. M., Bolívar, D. A., Allegri, R., Morales, L. C., Silvera-Redondo, C., Arcos-Burgos, M., Garavito-Galofre, P., & Vélez, J. I. (2025). Deficits of Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropsychological Architecture Correlate with Specific Exosomal mRNA Expression: Evidence of a Continuum? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104897








