Enhancing Nutraceutical Efficacy: The Role of M.A.T.R.I.S. Technology in Modulating Intestinal Release of Lipoic Acid and L-Carnitine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
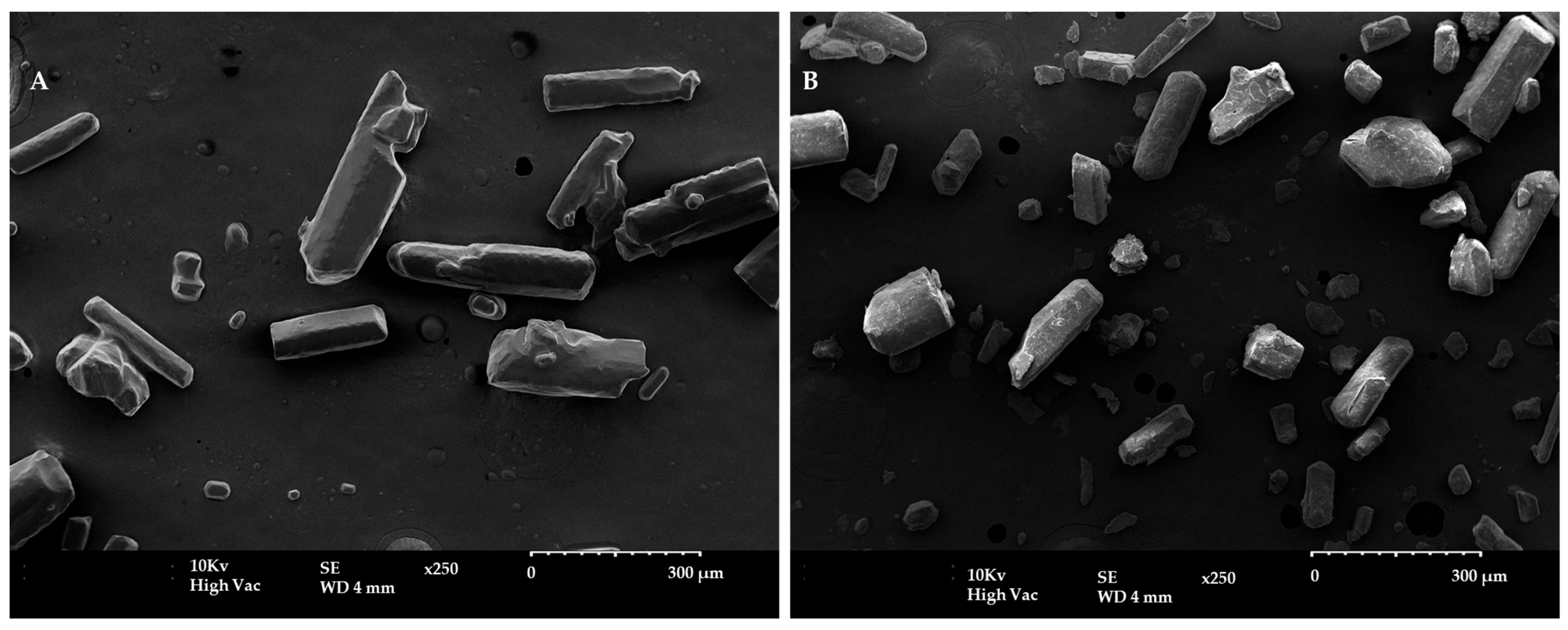
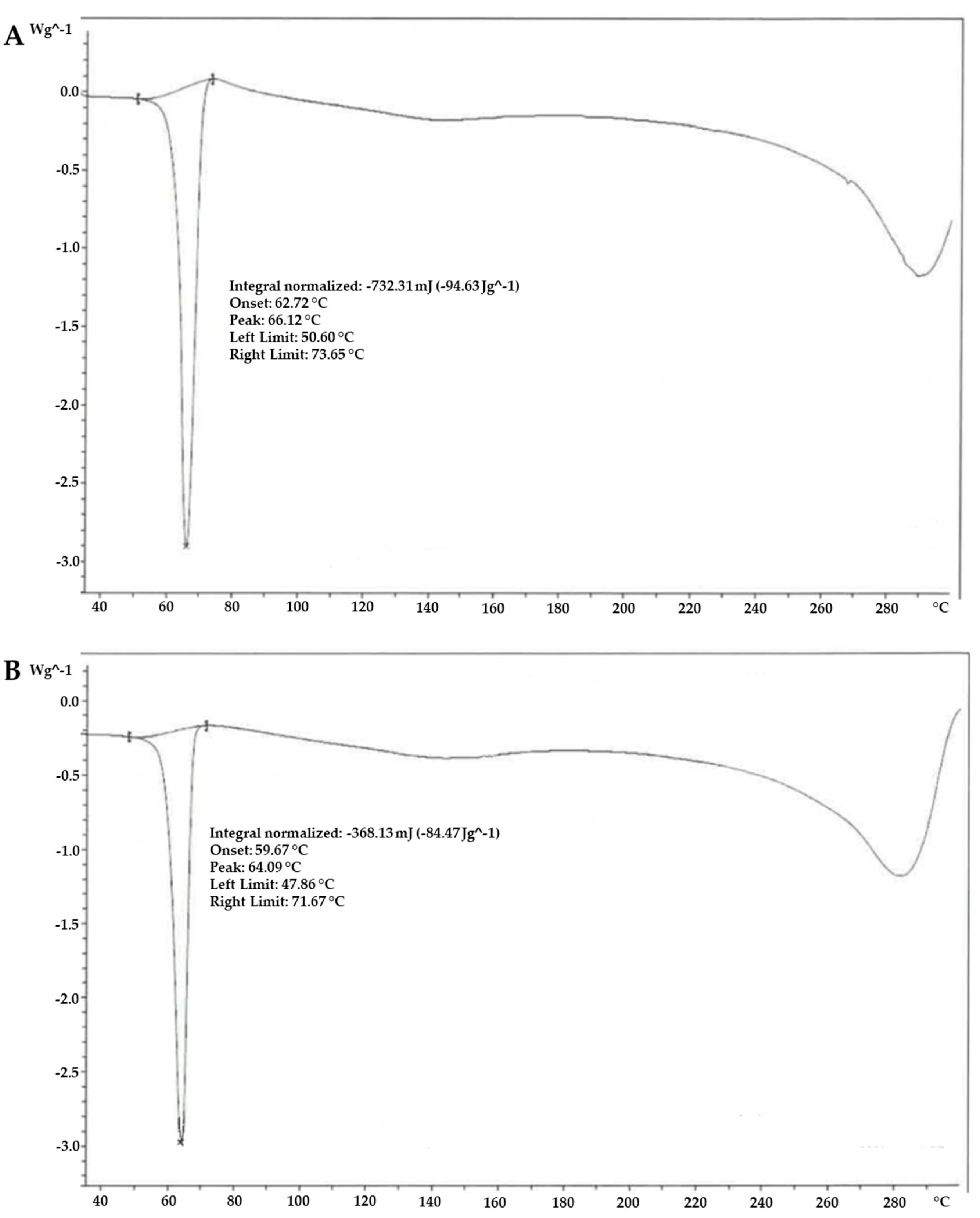
2.1. Chemical and Morphological Characterisation of α-Lipoic Acid Two Forms
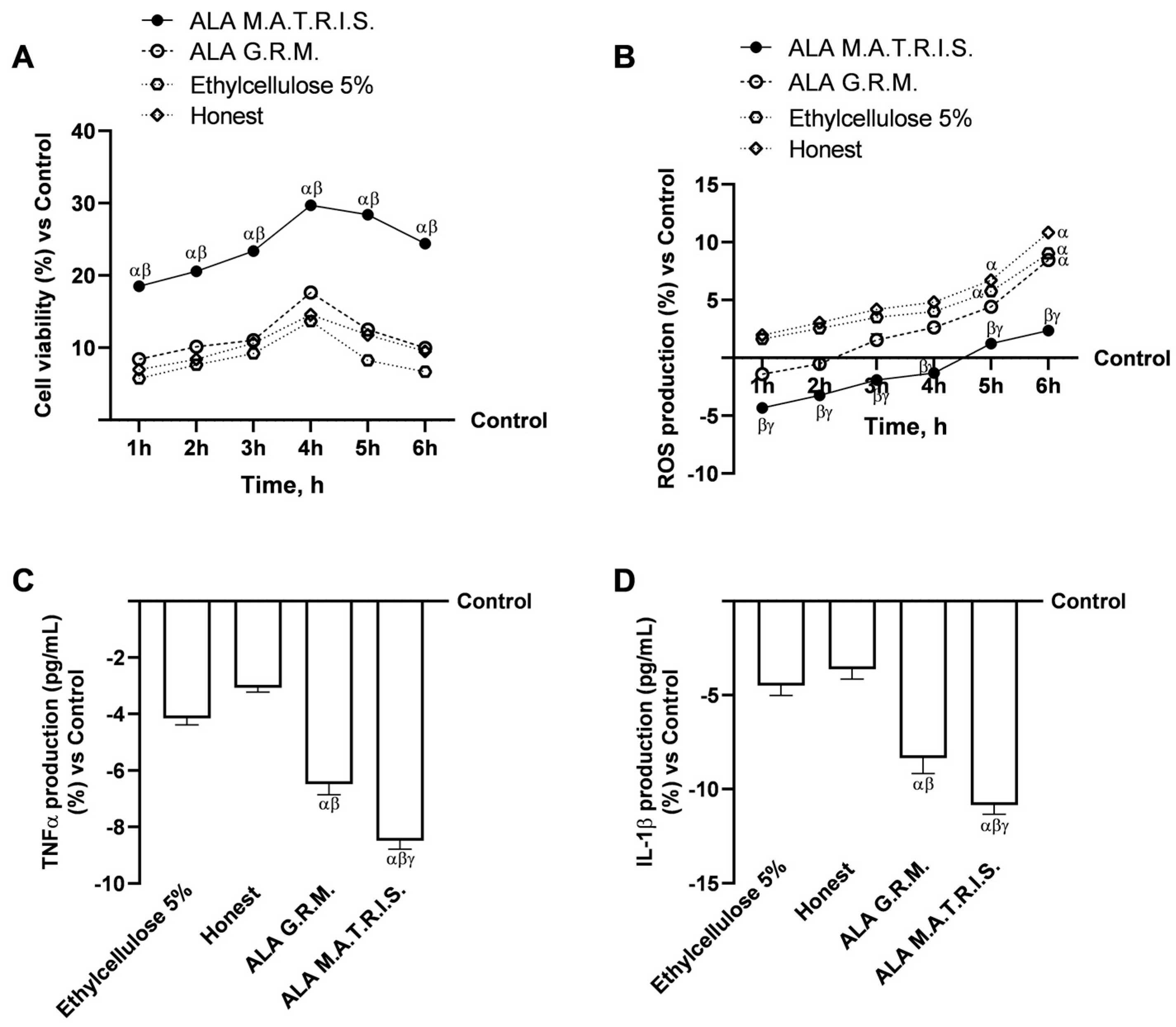
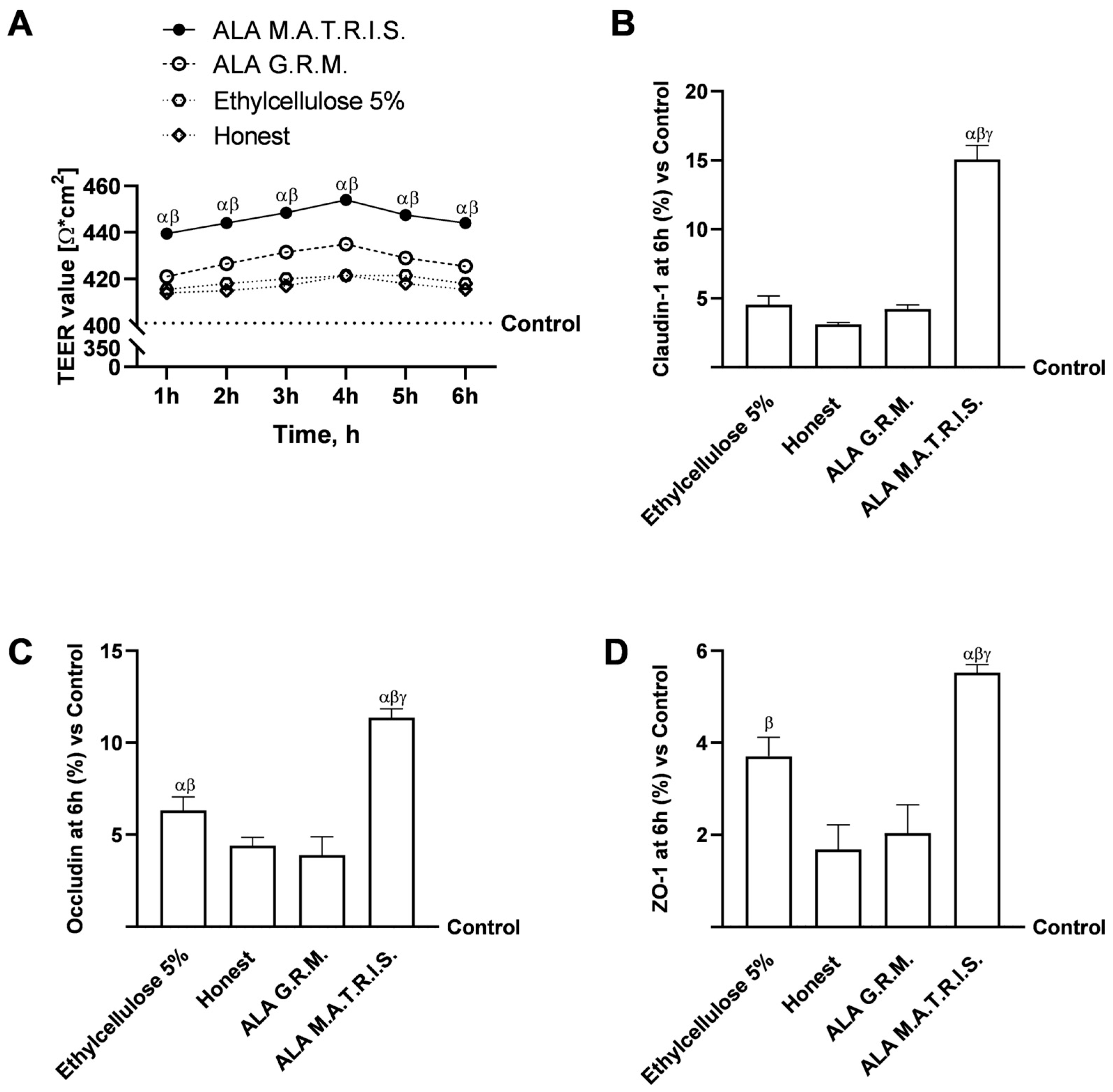
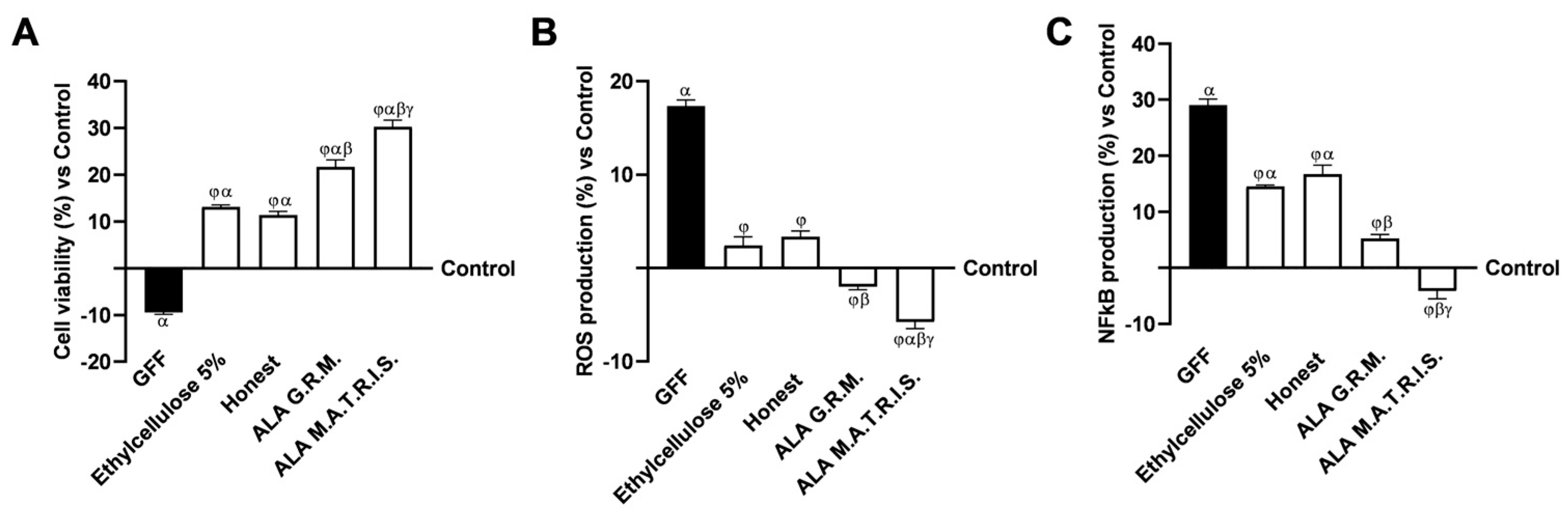
2.2. Intestinal Health Analysis After ALA Treatment
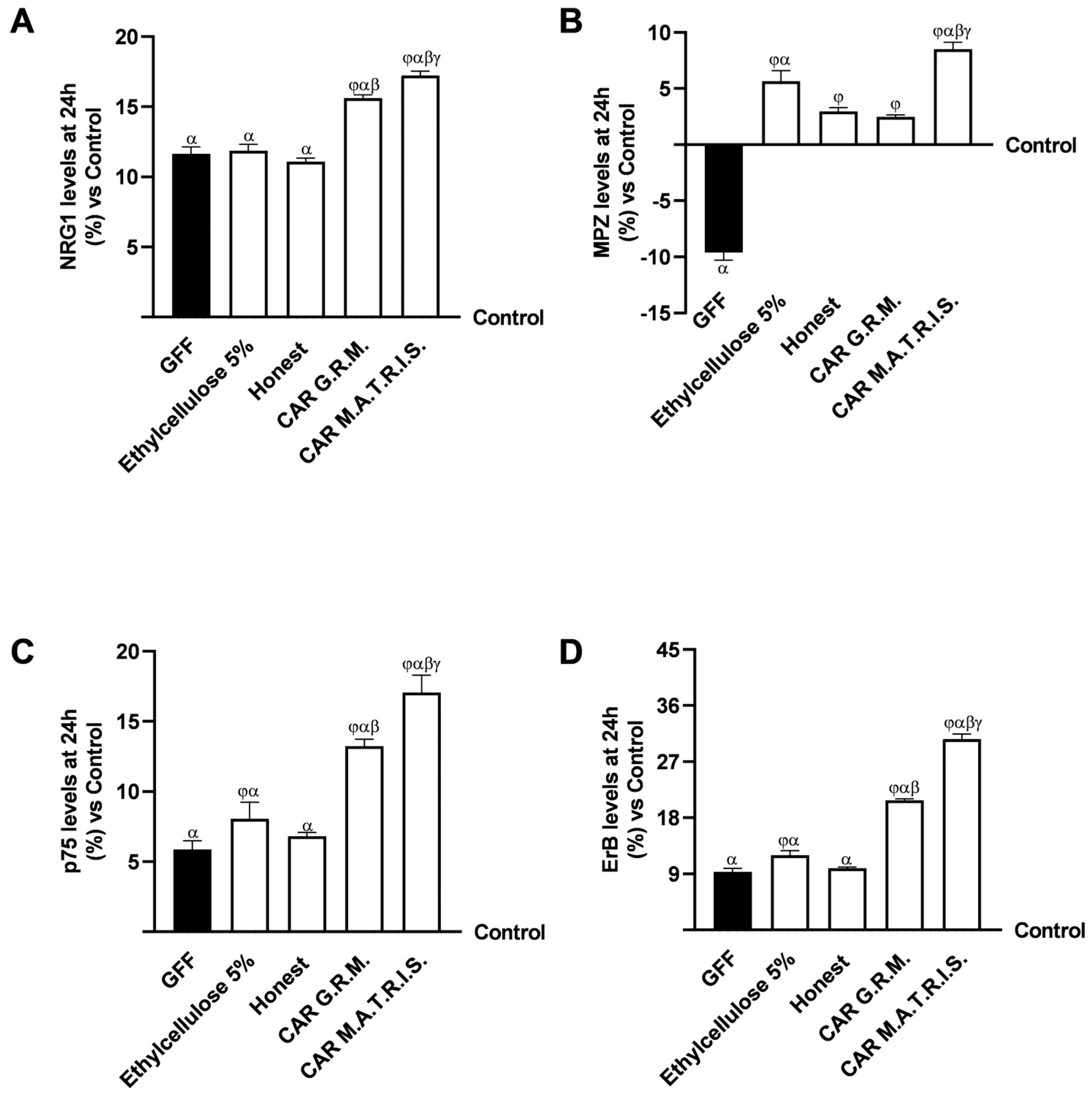
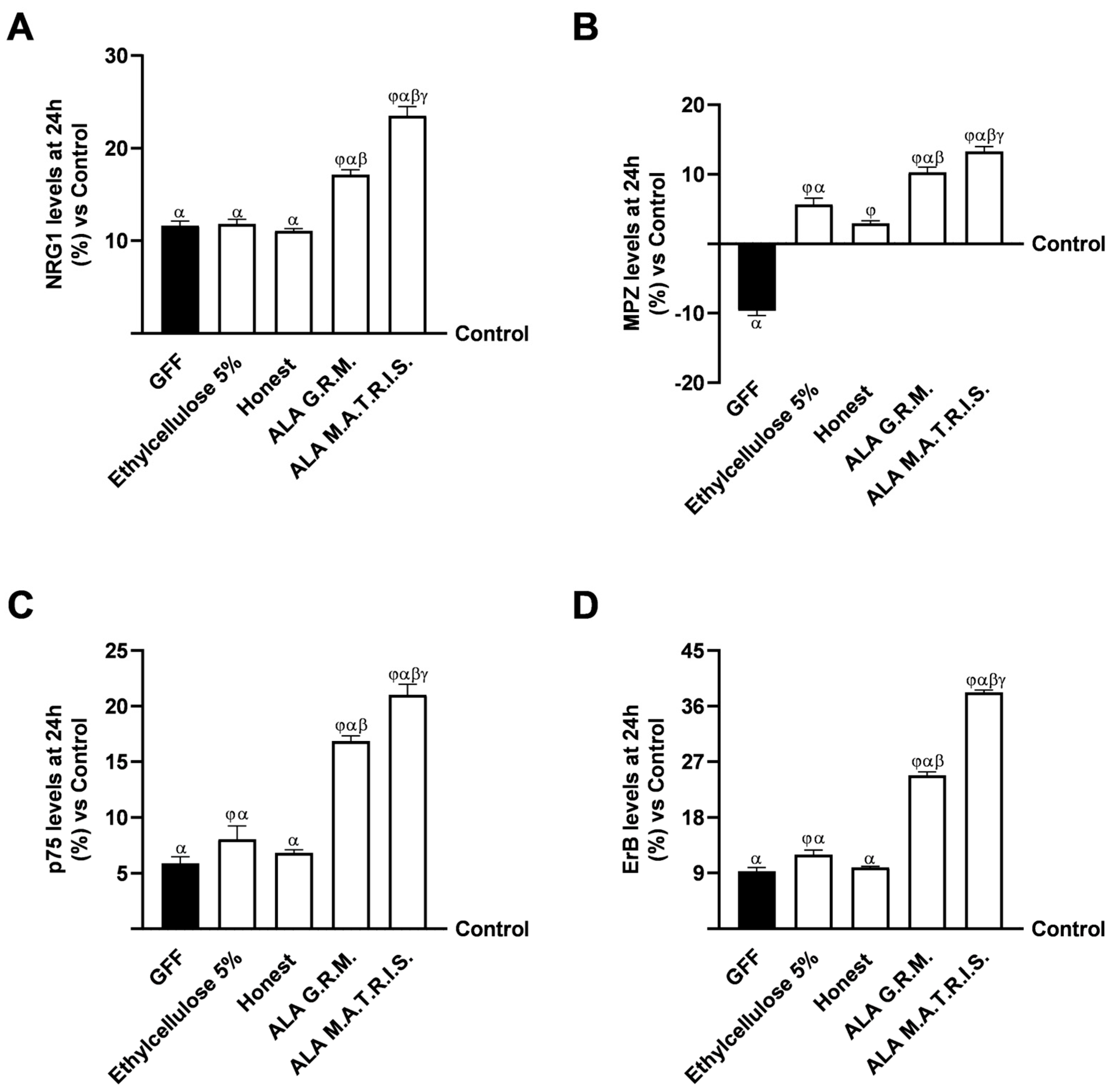
2.3. Effects of ALA G.R.M. And ALA M.A.T.R.I.S. on 3D EngNT Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Agents Preparation
4.2. SEM Analysis
4.3. X-Ray Diffraction
- 2θ range: 3–40 degrees;
- Step: 0.02 degrees 2θ;
- Scanning time: 1 s;
- Intensity, voltage: 15 mA, 40 kV.
4.4. Thermal Analysis—Differential Scanning Calorimetry
4.5. FT-IR/ATR Spectroscopy
4.6. Cell Culture
4.7. Experimental Protocol
4.8. Cell Viability
4.9. ROS Production and Measurement
4.10. Intestinal Barrier In Vitro Model
4.11. TJs Analysis
4.12. TNF-α ELISA Assay
4.13. Interleukin-1β ELISA Assay
4.14. Area Under the Curve (AUC) Evaluation
4.15. D EngNT In Vitro Model
4.16. NFkB ELISA Assay
4.17. p75 ELISA Assay
4.18. MPZ ELISA Assay
4.19. NRG1 ELISA Assay
4.20. Estrogen Receptor β ELISA Assay
4.21. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALA | α-lipoic acid |
| AUC | plasma concentration-time curve |
| CAR | Acetyl-L-carnitine |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry test |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| Erb | beta receptor |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FT-IR/ATR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy /attenuated total reflection |
| GGF | Glial Growth Factor |
| G.R.M. | Granular Raw Material |
| IL-1β | interleukin 1β |
| M.A.T.R.I.S. | Multiform Administration Timed Release Ingredients System |
| MPZ | myelin protein-zero |
| NFkB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NRG1 | Neuregulin 1 |
| Papp | apparent permeability coefficient |
| ROS | radical oxygen species |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| TEER | transepithelial electrical resistance |
| TNFα | tumour necrosis factor-α |
| TJs | tight junctions |
Appendix A


References
- Zhang, A.; Jung, K.; Li, A.; Liu, J.; Boyer, C. Recent advances in stimuli-responsive polymer systems for remotely controlled drug release. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 99, 101164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadpour, E.; Jafari, S.M. Importance of release and bioavailability studies for nanoencapsulated food ingredients. In Release and Bioavailability of Nanoencapsulated Food Ingredients; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 5, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boostani, S.; Jafari, S.M. Controlled release of nanoencapsulated food ingredients. In Release and Bioavailability of Nanoencapsulated Food Ingredients; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 5, pp. 27–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Nanoparticle-and Microparticle-Based Delivery Systems: Encapsulation, Protection and Release of Active Compounds; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hillery, A.; Park, K. Drug Delivery: Fundamentals and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Adepu, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems: Current Status and Future Directions. Molecules 2021, 26, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nokhodchi, A.; Raja, S.; Patel, P.; Asare-Addo, K. The role of oral controlled release matrix tablets in drug delivery systems. BioImpacts 2012, 2, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasotti, G.; Spalla, A.; De Zanet, E. International Products and Services IPS SRL. Polyvalent Polymeric Matrix for Modified Release Solid Oral Preparations and Method of Preparation Thereof. US Patent US9333170B2, 10 May 2016. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/74/9e/0b/1a026f74f200b9/US9333170.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- Gorąca, A.; Huk-Kolega, H.; Piechota, A.; Kleniewska, P.; Ciejka, E.; Skibska, B. Lipoic acid—Biological activity and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, J.A.; Feichtinger, R.G.; Tort, F.; Ribes, A.; Sperl, W. Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2014, 37, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Yasuno, R.; Wada, H. Do mammalian cells synthesize lipoic acid?: Identification of a mouse cDNA encoding a lipoic acid synthase located in mitochondria. FEBS 2001, 498, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehnpfennig, B.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Carlson, D.A.; Quick, M. Interaction of α-lipoic acid with the human Na+/multivitamin transporter (hSMVT). J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 290, 16372–16382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.J.; Butler, J.A.; Bemer, B.; Dixon, B.; Johnson, S.; Garrard, M.; Sudakin, D.L.; Christensen, J.M.; Pereira, C.; Hagen, T.M. Age and gender dependent bioavailability of R-and R, S-α-lipoic acid: A pilot study. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosallaei, N.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, A.; Sarraf Shirazi, S.; Behmadi, J.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. A comprehensive review on alpha-lipoic acid delivery by nanoparticles. BioImpacts 2024, 14, 30136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Nazhand, A.; Souto, S.B.; Silva, A.M.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B.; Santini, A. The Nutraceutical Value of Carnitine and Its Use in Dietary Supplements. Molecules 2020, 25, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Maldonado, A.; Pastoriza, S.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á. Assessing the antioxidant and metabolic effect of an alpha-lipoic acid and acetyl-L-carnitine nutraceutical. Curr. Res. Food. Sci. 2021, 4, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhasaniah, A.H. l-carnitine: Nutrition, pathology, and health benefits. Saudi. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 30, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignini, F.; Nasuti, C.; Gioventu, G.; Napolioni, P.D.; Martino, P.D. Human Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetic Profile of Different Formulations Delivering Alpha Lipoic Acid. J. Clin. Cell Immun. 2012, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Amenta, F.; Traini, E.; Tomassoni, D.; Mignini, F. Pharmacokinetics of different formulations of tioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid in healthy volunteers. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2008, 30, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine 500, mg. Available online: https://www.protocolforlife.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/P0076-Acetyl-L-Carnitine-500-mg.pdf (accessed on 19 February 2025).
- El Barky, A.R.; Hussein, S.A.; Mohamed, T.M. The potent antioxidant alpha lipoic acid. J. Plant Chem. Ecophysiol. 2017, 2, 1016. [Google Scholar]
- Maglione, E.; Marrese, C.; Migliaro, E.; Marcuccio, F.; Panico, C.; Salvati, C.; Citro, G.; Quercio, M.; Roncagliolo, F.; Torello, C.; et al. Increasing bioavailability of (R)-alpha-lipoic acid to boost antioxidant activity in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Acta Bio-Medica Atenei Parmensis 2015, 86, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, G.C.; McKenna, M.C. L-carnitine and acetyl-L-carnitine roles and neuroprotection in developing brain. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 1661–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Superti, F.; Russo, R. Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Biological Mechanisms and Health Benefits. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska, M.; Starek, M. Analytical approaches to determination of carnitine in biological materials, foods and dietary supplements. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brufani, M.; Figliola, R. (R)-α-lipoic acid oral liquid formulation: Pharmacokinetic parameters and therapeutic efficacy. Acta Bio-Medica Atenei Parmensis 2014, 85, 108–115. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, B.; Berkay Yılmaz, Y.; Antika, G.; Boyunegmez Tumer, T.; Fawzi Mahomoodally, M.; Lobine, D.; Akram, M.; Riaz, M.; Capanoglu, E.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Insights on the Use of α-Lipoic Acid for Therapeutic Purposes. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, A.M.; Fornasini, G. Pharmacokinetics of L-carnitine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2003, 42, 941–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassanego, G.; Rodrigues, P.; De Freitas Bauermann, L.; Trevisan, G. Evaluation of the analgesic effect of a-lipoic acid in treating pain disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochette, L.; Ghibu, S.; Richard, C.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Direct and indirect antioxidant properties of alpha-lipoic acid and therapeutic potential. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, G.; Di Lionardo, A.; Galosi, E.; Truini, A.; Cruccu, G. Acetyl-L-carnitine in painful peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Sergi, G.; Stubbs, B.; Bourdel-Marchasson, I.; Tessier, D.; Sieber, C.; Strandberg, T.; Gillain, S.; Barbagallo, M.; Crepaldi, G.; et al. Effect of acetyl-l-carnitine in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2017, 8, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerboom, A.; Dion, V.; Chariot, A.; Franzen, R. Molecular mechanisms involved in schwann cell plasticity. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Dobrowsky, R.T. Differential expression of neuregulin-1 isoforms and downregulation of erbin are associated with Erb B2 receptor activation in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jiang, W.; Wang, C.; Xie, J.; Liang, X.; Sun, Y.; Gong, L.; Liu, W.; Qu, L. Jinmaitong, a traditional Chinese compound prescription, ameliorates the streptozocin-induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy rats by increasing sciatic nerve IGF-1 and IGF-1R expression. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Sun, Y.; Liang, X.C.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, W. Jinmaitong ameliorates diabetes-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, C.; Morsanuto, V.; Ghirlanda, S.; Ruga, S.; Notte, F.; Gaetano, L.; Uberti, F. Role of combined lipoic acid and vitamin D3 on astrocytes as a way to prevent brain ageing by induced oxidative stress and iron accumulation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2843121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, H.S.; Makong Ekpan, F. The use of Scanning Electron Microscopy SEM for Medical Application: A Mini Review. Eurasian J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 4, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadayanti, F. Application of SEM: Review. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Engenearing Rev. 2020, 1, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Klang, V.; Valenta, C.; Matsko, N.B. Electron Microscopy of Pharmaceutical System. Micron 2013, 44, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lea, T. Caco-2 cell line. In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- DiMarco, R.L.; Hunt, D.R.; Dewi, R.E.; Heilshorn, S.C. Improvement of paracellular transport in the Caco-2 drug screening model using protein-engineered substrates. Biomaterials 2017, 129, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galla, R.; Grisenti, P.; Farghali, M.; Saccuman, L.; Ferraboschi, P.; Uberti, F. Ovotransferrin Supplementation Improves the Iron Absorption: An In Vitro Gastro-Intestinal Model. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsanuto, V.; Galla, R.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. A New Palmitoylethanolamide Form Combined with Antioxidant Molecules to Improve Its Effectivess on Neuronal Aging. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, M.L.D.; Laranjeira, S.; Evans, R.E.; Shipley, R.J.; Healy, J.; Phillips, J.B. Developing an In Vitro Model to Screen Drugs for Nerve Regeneration. Anatom Rec. 2018, 301, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, P.; Lim, W.K. Optimisation of a PC12 cell-based in vitro stroke model for screening neuroprotective agents. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Ahn, J.; Jeong, H.E.; Youn, I.; Hu, D.; Chung, S. A three-dimensional in vitro model of the peripheral nervous system. NPG Asia Mater. 2021, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Xu, H.; Guo, R.; Lu, T.; Li, X. Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 alleviates bupivacaine-induced neurotoxicity by regulating the miR-421/zinc finger protein564 (ZNF564) axis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 5231–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uberti, F.; Trotta, F.; Pagliaro, P.; Bisericaru, D.M.; Cavalli, R.; Ferrari, S.; Penna, C.; Matencio, A. Developing New Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges Complexes to Improve Vitamin D Absorption in an In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christides, T.; Wray, D.; McBride, R.; Fairweather, R.; Sharp, P. Iron bioavailability from commercially available iron supplements. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanzaga, M.; Bollati, C.; Ranaldi, G.; Sucato, S.; Fustinoni, S.; Roda, G.; Lammi, C. Bioavailability Assessment of an Iron Formulation Using Differentiated Human Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. Foods 2023, 12, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulè, S.; Rosso, G.; Botta, M.; Brovero, A.; Ferrari, S.; Galla, R.; Molinari, C.; Uberti, F. Design of Mixed Medicinal Plants, Rich in Polyphenols, Vitamins B, and Palmitoylethanolamide-Based Supplement to Help Reduce Nerve Pain: A Preclinical Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Morsanuto, V.; Ghirlanda, S.; Molinari, C. Iron Absorption from Three Commercially Available Supplements in Gastrointestinal Cell Lines. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uberti, F.; Ruga, S.; Farghali, M.; Galla, R.; Molinari, C. A Combination of α-Lipoic Acid (ALA) and Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) Blocks Endotoxin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Cytokine Storm: A Possible Intervention for COVID-19. J. Diet. Suppl. 2023, 20, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.A.; Heeba, G.H.; Elwy, H.M.; Murali, C.; El-Awady, R.; Amin, A. Molecular characterization of the grape seeds extract’s effect against chemically induced liver cancer: In vivo and in vitro analyses. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomellini, E.; Lagadec, C.; Polakowska, R.; Le Bourhis, X. Role of p75 neurotrophin receptor in stem cell biology: More than just a marker. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2467–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruga, S.; Galla, R.; Ferrari, S.; Invernizzi, M.; Uberti, F. Novel Approach to the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain Using a Combination with Palmitoylethanolamide and Equisetum arvense L. in an In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzemieniec, J.; Litwa, E.; Wnuk, A.; Lason, W.; Krzeptowski, W.; Kajta, M. Selective Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Modulator 3,3′-Diindolylmethane Impairs AhR and ARNT Signaling and Protects Mouse Neuronal Cells Against Hypoxia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5591–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galla, R.; Ferrari, S.; Mulè, S.; Nebuloni, M.; Calvi, M.; Botta, M.; Uberti, F. Enhancing Nutraceutical Efficacy: The Role of M.A.T.R.I.S. Technology in Modulating Intestinal Release of Lipoic Acid and L-Carnitine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104866
Galla R, Ferrari S, Mulè S, Nebuloni M, Calvi M, Botta M, Uberti F. Enhancing Nutraceutical Efficacy: The Role of M.A.T.R.I.S. Technology in Modulating Intestinal Release of Lipoic Acid and L-Carnitine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104866
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalla, Rebecca, Sara Ferrari, Simone Mulè, Marino Nebuloni, Marco Calvi, Mattia Botta, and Francesca Uberti. 2025. "Enhancing Nutraceutical Efficacy: The Role of M.A.T.R.I.S. Technology in Modulating Intestinal Release of Lipoic Acid and L-Carnitine" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104866
APA StyleGalla, R., Ferrari, S., Mulè, S., Nebuloni, M., Calvi, M., Botta, M., & Uberti, F. (2025). Enhancing Nutraceutical Efficacy: The Role of M.A.T.R.I.S. Technology in Modulating Intestinal Release of Lipoic Acid and L-Carnitine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4866. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104866






