A Study on the Levels of Selected Proangiogenic Proteins in Human Tissues and Plasma in Relation to Brain Glioma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
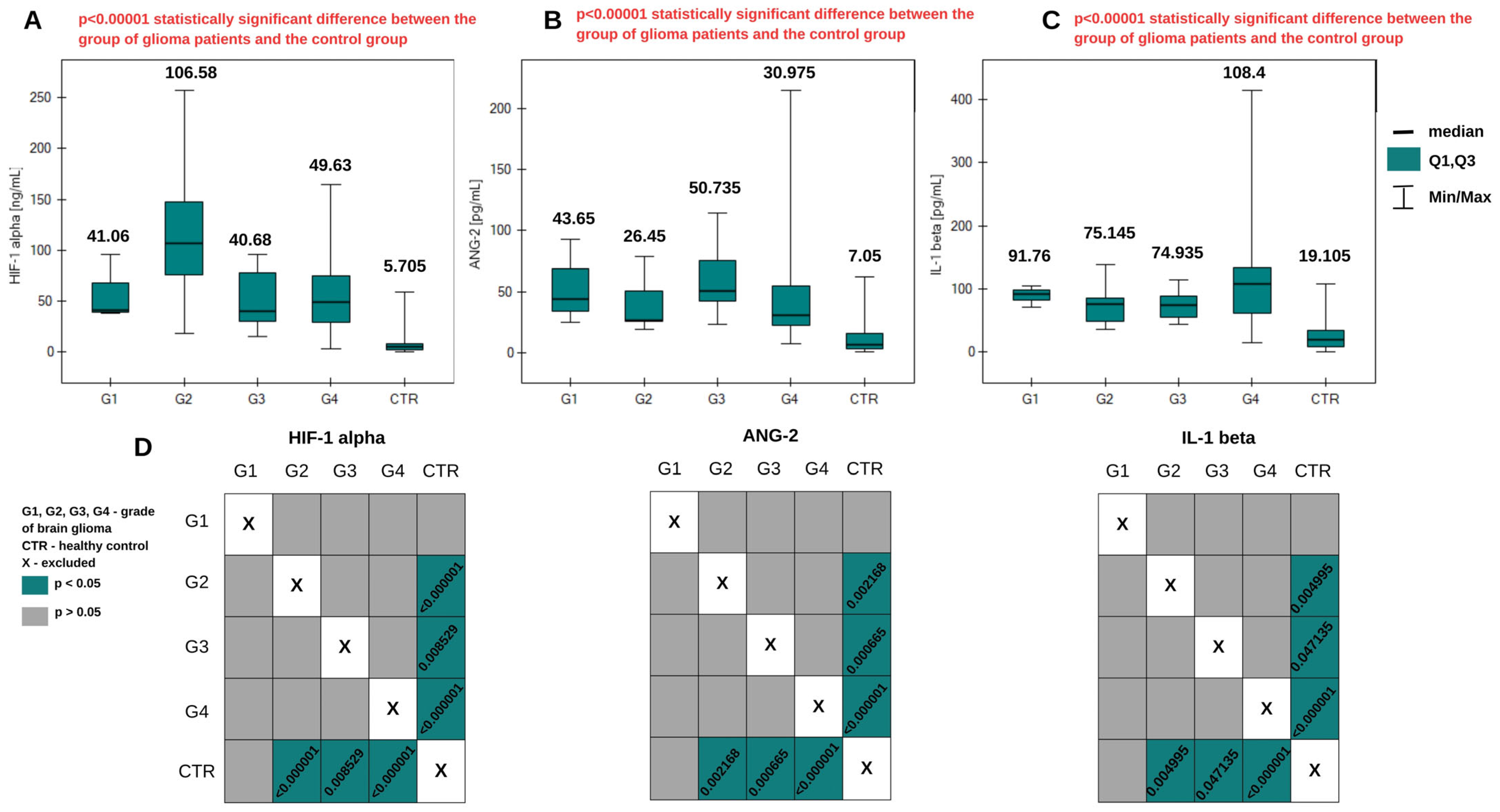
2.1. Angiogenic Compounds in the Blood Plasma of Glioma Patients
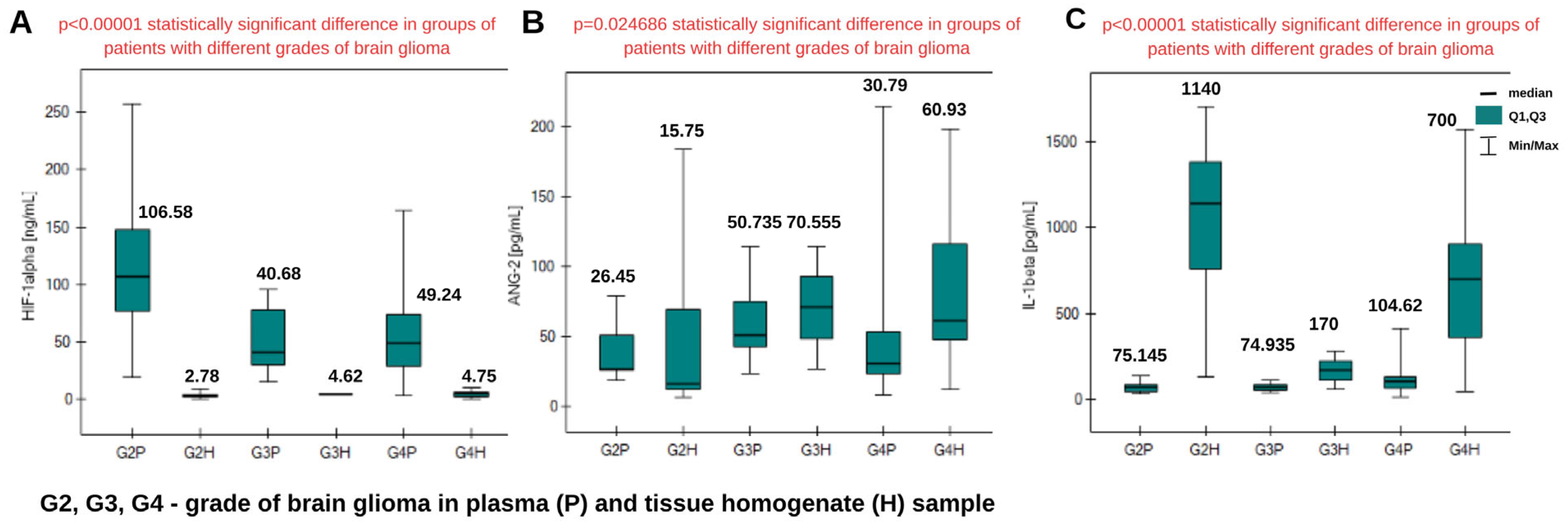
2.2. Determination of HIF-1α, ANG-2, and IL-1β in Tissue Homogenates from Patients with Brain Glioma
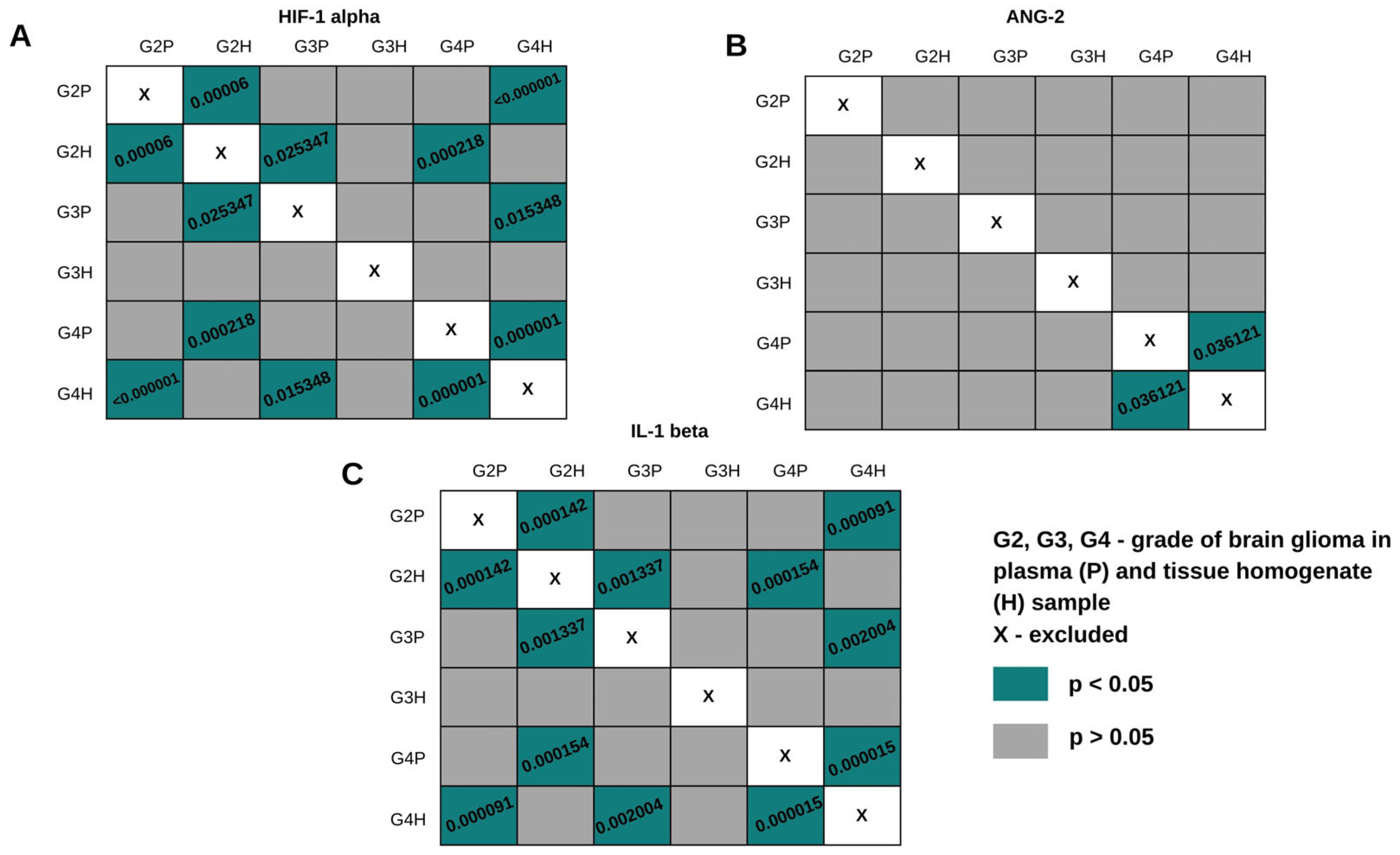
2.3. Comparison of HIF-1α, ANG-2, and IL-1β Levels in Plasma Samples and Tissue Homogenates
3. Discussion
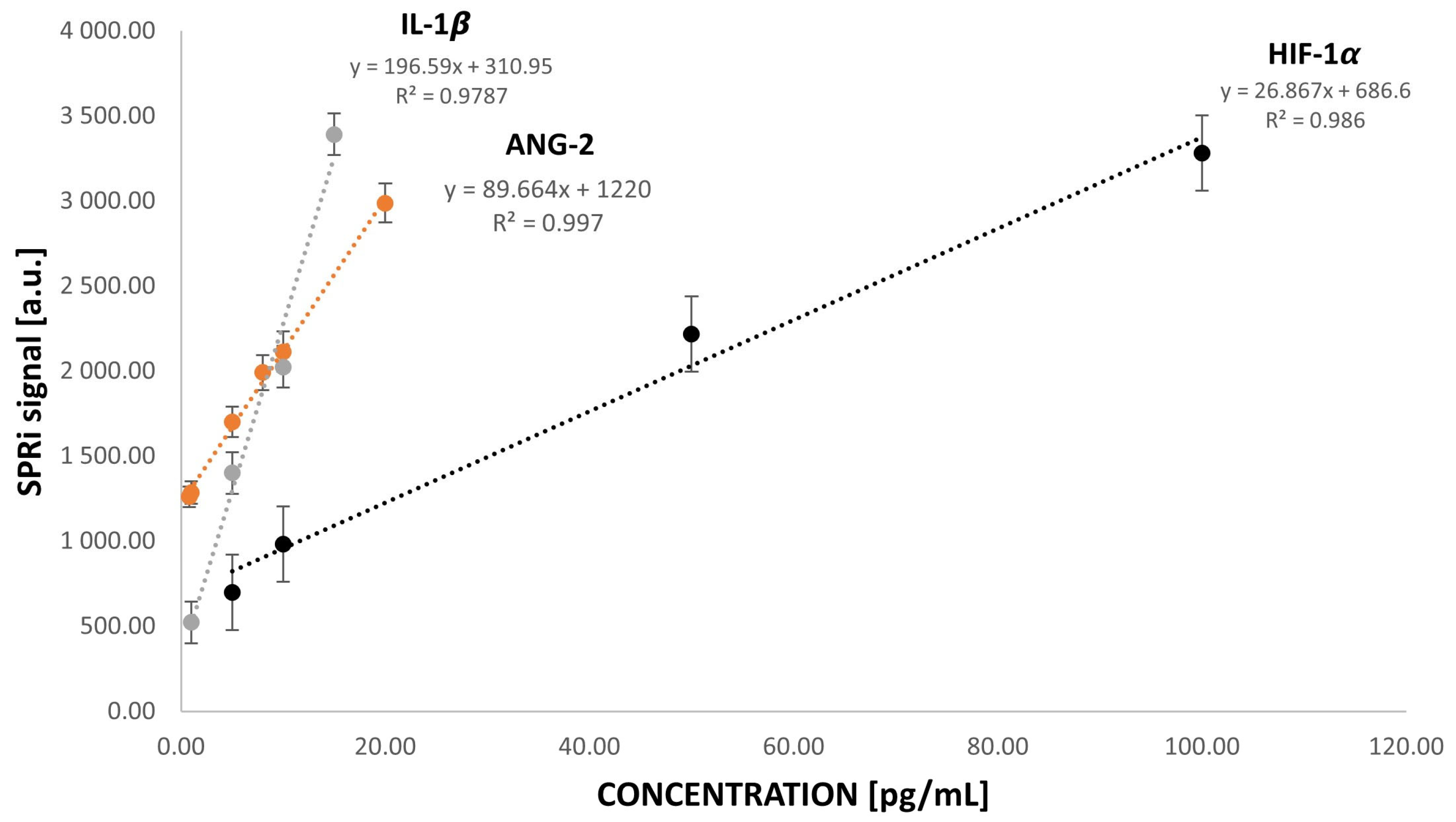
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Reagents and Materials
4.2. SPRi Device and Analysis
4.3. Biological Material
Homogenates and Plasma Sample Preparation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| Human Brain Glioma Plasma Samples | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIF-1alpha [ng/mL] | |||||
| Glioma grade/CTR | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | CTR |
| Median (Q2) | 41.06 | 106.58 | 40.60 | 49.63 | 5.705 |
| Lower quartile (Q1) | 39.44 | 76.437 | 30.295 | 29.79 | 2.73 |
| Upper quartile (Q3) | 68.295 | 147.59 | 77.825 | 74.6975 | 8.8675 |
| Minimum concentration value | 37.82 | 18.85 | 15.44 | 3.02 | 0.47 |
| Maximum concentration value | 95.53 | 257.17 | 95.53 | 164.3 | 59.06 |
| IQR | 28.855 | 71.153 | 47.53 | 44.9075 | 6.1375 |
| ANG-2 [pg/mL] | |||||
| Glioma grade/CTR | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | CTR |
| Median (Q2) | 43.65 | 26.45 | 50.735 | 30.975 | 7.05 |
| Lower quartile (Q1) | 34.405 | 25.3675 | 42.605 | 22.2675 | 3.69 |
| Upper quartile (Q3) | 68.44 | 50.9525 | 75.335 | 54.755 | 16.195 |
| Minimum concentration value | 25.16 | 18.78 | 22.93 | 7.73 | 0.91 |
| Maximum concentration value | 93.23 | 78.59 | 114.62 | 214.68 | 62.34 |
| IQR | 34.035 | 25.585 | 32.73 | 32.4875 | 12.505 |
| IL-1beta [pg/mL] | |||||
| Glioma grade/CTR | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | CTR |
| Median (Q2) | 91.76 | 75.145 | 74.935 | 108.4 | 19.105 |
| Lower quartile (Q1) | 81.515 | 47.9 | 54.5725 | 61.7175 | 9.04 |
| Upper quartile (Q3) | 97.89 | 85.4 | 88.9675 | 133.1075 | 33.4475 |
| Minimum concentration value | 71.27 | 35.28 | 43.54 | 14.28 | 0.38 |
| Maximum concentration value | 104.02 | 137.64 | 114.44 | 414.18 | 108.21 |
| IQR | 16.375 | 37.5 | 34.395 | 71.39 | 24.4075 |
Appendix A.2
| Glioma Grade | G2 | G3 | G4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIF-1α [ng/mL] | |||
| Median (Q2) | 2.78 | 4.62 | 4.75 |
| Lower quartile (Q1) | 2.34 | 4.165 | 1.88 |
| Upper quartile (Q3) | 4.55 | 5.075 | 6.46 |
| Minimum concentration value | 0.16 | 3.71 | 0.27 |
| Maximum concentration value | 9.59 | 5.53 | 9.72 |
| IQR | 2.21 | 0.91 | 4.58 |
| ANG-2 [pg/mL] | |||
| Median (Q2) | 15.75 | 70.56 | 60.93 |
| Lower quartile (Q1) | 12.31 | 48.59 | 47.7 |
| Upper quartile (Q3) | 68.93 | 92.52 | 116.29 |
| Minimum concentration value | 6.28 | 26.62 | 12.25 |
| Maximum concentration value | 183.91 | 114.49 | 198.55 |
| IQR | 56.62 | 43.93 | 68.59 |
| IL-1β [ng/mL] | |||
| Median (Q2) | 1.14 | 0.17 | 0.7 |
| Lower quartile (Q1) | 0.76 | 0.115 | 0.36 |
| Upper quartile (Q3) | 1.38 | 0.225 | 0.9 |
| Minimum concentration value | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| Maximum concentration value | 1.41 | 0.28 | 1.57 |
| IQR | 0.62 | 0.11 | 0.54 |
Appendix A.3
References
- Kan, L.K.; Drummond, K.; Hunn, M.; Williams, D.; O’Brien, T.J.; Monif, M. Potential biomarkers and challenges in glioma diagnosis, therapy and prognosis. BMJ Neurol. Open 2020, 2, e000069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakis, D.; Perdikakis, M.; Gargalionis, A.N.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Gliomas. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahir, B.K.; Engelhard, H.H.; Lakka, S.S. Tumor Development and Angiogenesis in Adult Brain Tumor: Glioblastoma. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 2461–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; LeBrun, D.G.; Yang, J.; Zhu, V.F.; Li, M. Deregulated signaling pathways in glioblastoma multiforme: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Cancer Investig. 2012, 30, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, H.; Ma, Y.; Becker, T.M.; Roberts, T.L.; de Souza, P.; Powter, B. Molecular Biomarkers in Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services; National Institutes of Health; National Cancer Institute; USA.gov. Oligodendroglioma and Other IDH-Mutated Tumors: Diagnosis and Treatment. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/rare-brain-spine-tumor/tumors/oligodendroglioma (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Panek, P.; Jezela-Stanek, A. Genetyczne i molekularne podłoża rozwoju glejaka. Postępy Biochem. 2023, 69, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bock, K.; Cauwenberghs, S.; Carmeliet, P. Vessel abnormalization: Another hallmark of cancer? Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2011, 21, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemann, D.W.; Chaplin, D.J.; Horsman, M.R. Realizing the Potential of Vascular Targeted Therapy: The Rationale for Combining Vascular Disrupting Agents and Anti-Angiogenic Agents to Treat Cancer. Cancer Investig. 2017, 35, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Lu, M.; Hu, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1: Regulatory mechanisms and drug therapy in myocardial infarction. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 963, 176277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriely, G.; Wheeler, M.A.; Takenaka, M.C.; Quintana, F.J. Role of AHR and HIF-1α in Glioblastoma Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Park, K.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Sheen, S.S.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, H.N.; Oh, Y.J.; Hwang, S.C. Serum angiopoietin-2 as a clinical marker for lung cancer. Chest 2007, 132, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiani, E.; Christofori, G. Angiopoietins in angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2013, 328, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Depping, R.; Jelkmann, W. Interleukin-1β promotes hypoxia-induced apoptosis of glioblastoma cells by inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediated adrenomedullin production. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmi, Y.; Dotan, S.; Rider, P.; Kaplanov, I.; White, M.R.; Baron, R.; Voronov, E. The Role of IL-1 in the Early Tumor Cell-Induced Angiogenic Response. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3500–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ren, Z.-H.; Zhao, W.-M.; Yan, X.; Zhu, A.-S.; Qiu, F.-Q.; Zhang, K.-K. Research advances on surface plasmon resonance biosensors. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 564–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaru, A.; Bala, C.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Biosensors in Pharmaceutical Analysis. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2015, 45, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.W. A suspected case of the electrical resonance of minute metal particles for light-waves. A new type of absorption. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. 1902, 18, 1478. [Google Scholar]
- Wijaya, E.; Lenaerts, C.; Maricot, S.; Hastanin, J.; Habraken, S.; Vilcot, J.-P.; Boukherroub, R.; Szunerits, S. Surface Plasmon Resonance Based Biosensors: From the Development of Different SPR Structures to Novel Surface Functionalization Strategies. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2011, 15, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schasfoort, R.B.M. Handbook of Surface Plasmon Resonance, 2nd ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Y. Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors: A Review of Molecular Imaging with High Spatial Resolution. Biosensors 2024, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, S.; Scuffi, C.; Mascini, M.; Minunni, M. Surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRi)-based sensing: A new approach in signal sampling and management. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1380–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, E.M.; Correa, J.; Riguera, R.; Fernandez-Megia, E. Real-time evaluation of binding mechanisms in multivalent interactions: A surface plasmon resonance kinetic approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5966–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weremijewicz, A.; Matuszczak, E.; Sankiewicz, A.; Tylicka, M.; Komarowska, M.; Tokarzewicz, A.; Debek, W.; Gorodkiewicz, E.; Hermanowicz, A. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and its correlation with basal membrane components laminin-5 and collagen type IV in paediatric burn patients measured with Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging (SPRI) biosensors. Burns 2018, 44, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toliczenko-Bernatowicz, D.; Matuszczak, E.; Tylicka, M.; Szymańska, B.; Komarowska, M.; Gorodkiewicz, E.; Debek, W.; Hermanowicz, A. Overexpression of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 1 (UCHL1) in boys with cryptorchidism. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldak, L.; Leśniewska, A.; Zelazowska-Rutkowska, B.; Latoch, E.; Lukaszewski, Z.; Krawczuk-Rybak, M.; Gorodkiewicz, E. An Array SPRi Biosensor for Simultaneous VEGF-A and FGF-2 Determination in Biological Samples. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, M.C.; Aghi, M.K. Biology of angiogenesis and invasion in glioma. Neurotherapeutics 2009, 6, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reszec, J.; Rutkowski, R.; Chyczewski, L. The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in primary brain tumors. Int. J. Neurosci. 2013, 123, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, Y.; Machein, M.R.; Plate, K.H. The Role of Angiopoietins During Angiogenesis in Gliomas. Brain Pathol. 2006, 15, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarassishin, L.; Casper, D.; Lee, S.C. Aberrant Expression of Interleukin-1β and Inflammasome Activation in Human Malignant Gliomas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N.; Dawande, P.; Shukla, S.; Acharya, S. Effect of lifestyle and dietary factors in the development of brain tumors. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 5200–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, K.; Watad, A.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Lichtbroun, M.; Amital, H.; Shoenfeld, Y. Physical activity and autoimmune diseases: Get moving and manage the disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.L.; Ragel, B.T.; Whang, K. Inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) decreases vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion and tumor growth in malignant gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2006, 78, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, C.; Malfettone, A.; Ranieri, G.; Danza, K.; Simone, G.; Paradiso, A.; Mangia, A. VEGF, HIF-1α expression and MVD as an angiogenic network in familial breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, Z.; Oldak, L.; Guszcz, T.; Hermanowicz, A.; Gorodkiewicz, E. SPRi Biosensor for Simultaneous Determination of HIF-1α, Angiopoietin-2, and Interleukin-1β in Blood Plasma. Sensors 2024, 24, 5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Pairs of Proteins | Correlation Strength [r] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| HIF-1α–ANG-2 | 0.31 low positive correlation | p < 0.05 |
| HIF-1α–IL-1β | 0.02 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| ANG-2–IL-1β | −0.06 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| HIF-1α | ANG-2 | IL-1β | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyzed Variable | Correlation Strength [r] | p-Value | Correlation Strength [r] | p-Value | Correlation Strength [r] | p-Value |
| Age | −0.41 moderate negative correlation | p < 0.05 | −0.007 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.23 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Karnofsky Performance Scale | 0.23 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.016 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.201 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Physical activity in the patient’s life | 0.15 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.003 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.28 low negative correlation | p < 0.05 |
| Vegetables and fruits in the diet | 0.06 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.02 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.06 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Meat in the diet | 0.02 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.09 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.09 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Pack-years | −0.13 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.11 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.14 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Size of the tumor | 0.03 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.05 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.12 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Marked Protein | Direction of the Diagnostic Variable | AUC | Sensitivity [%] | Specificity [%] | PPV [%] | NPV [%] | Cut-Off Point | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIF-1α | stimulant | 0.95 | 84.91 | 95.83 | 95.74 | 85.19 | 25.06 ng/mL | p < 0.01 |
| ANG-2 | stimulant | 0.89 | 88.68 | 85.42 | 87.04 | 87.23 | 17.78 pg/mL | p < 0.01 |
| IL-1β | stimulant | 0.92 | 94.34 | 77.08 | 81.97 | 92.50 | 35.28 pg/mL | p < 0.01 |
| HIF-1α | ANG-2 | IL-1β | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analyzed Variable | Correlation Strength [r] | p-Value | Correlation Strength [r] | p-Value | Correlation Strength [r] | p-Value |
| Age | 0.03 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.09 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.37 low negative correlation | p < 0.05 |
| Karnofsky Performance Scale | 0.27 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.24 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.29 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Physical activity in the patient’s life | −0.39 low negative correlation | p < 0.05 | −0.002 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.13 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Vegetables and fruits in the diet | −0.10 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.10 no correlation | p > 0.05 | 0.19 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Meat in the diet | −0.02 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.11 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.30 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Pack-years | −0.19 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.09 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.14 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Size of the tumor | 0.72 high positive correlation | p < 0.05 | 0.05 no correlation | p > 0.05 | −0.12 no correlation | p > 0.05 |
| Biomarker | Type of Biological Material | Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| HIF-1α | Plasma | 10-fold |
| Tissue homogenate | 100-fold | |
| ANG-2 | Plasma | 2-fold |
| Tissue homogenate | 10-fold | |
| IL-1β | Plasma | 10-fold |
| Tissue homogenate | 100-fold |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zielinska, Z.; Giełażyn, J.; Dzieciol-Anikiej, Z.; Dzieciol, J.; Mrozek, P.; Reszec-Gielazyn, J.; Gorodkiewicz, E. A Study on the Levels of Selected Proangiogenic Proteins in Human Tissues and Plasma in Relation to Brain Glioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104802
Zielinska Z, Giełażyn J, Dzieciol-Anikiej Z, Dzieciol J, Mrozek P, Reszec-Gielazyn J, Gorodkiewicz E. A Study on the Levels of Selected Proangiogenic Proteins in Human Tissues and Plasma in Relation to Brain Glioma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104802
Chicago/Turabian StyleZielinska, Zuzanna, Julia Giełażyn, Zofia Dzieciol-Anikiej, Janusz Dzieciol, Piotr Mrozek, Joanna Reszec-Gielazyn, and Ewa Gorodkiewicz. 2025. "A Study on the Levels of Selected Proangiogenic Proteins in Human Tissues and Plasma in Relation to Brain Glioma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104802
APA StyleZielinska, Z., Giełażyn, J., Dzieciol-Anikiej, Z., Dzieciol, J., Mrozek, P., Reszec-Gielazyn, J., & Gorodkiewicz, E. (2025). A Study on the Levels of Selected Proangiogenic Proteins in Human Tissues and Plasma in Relation to Brain Glioma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4802. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104802







