Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Patients with Hashimoto’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
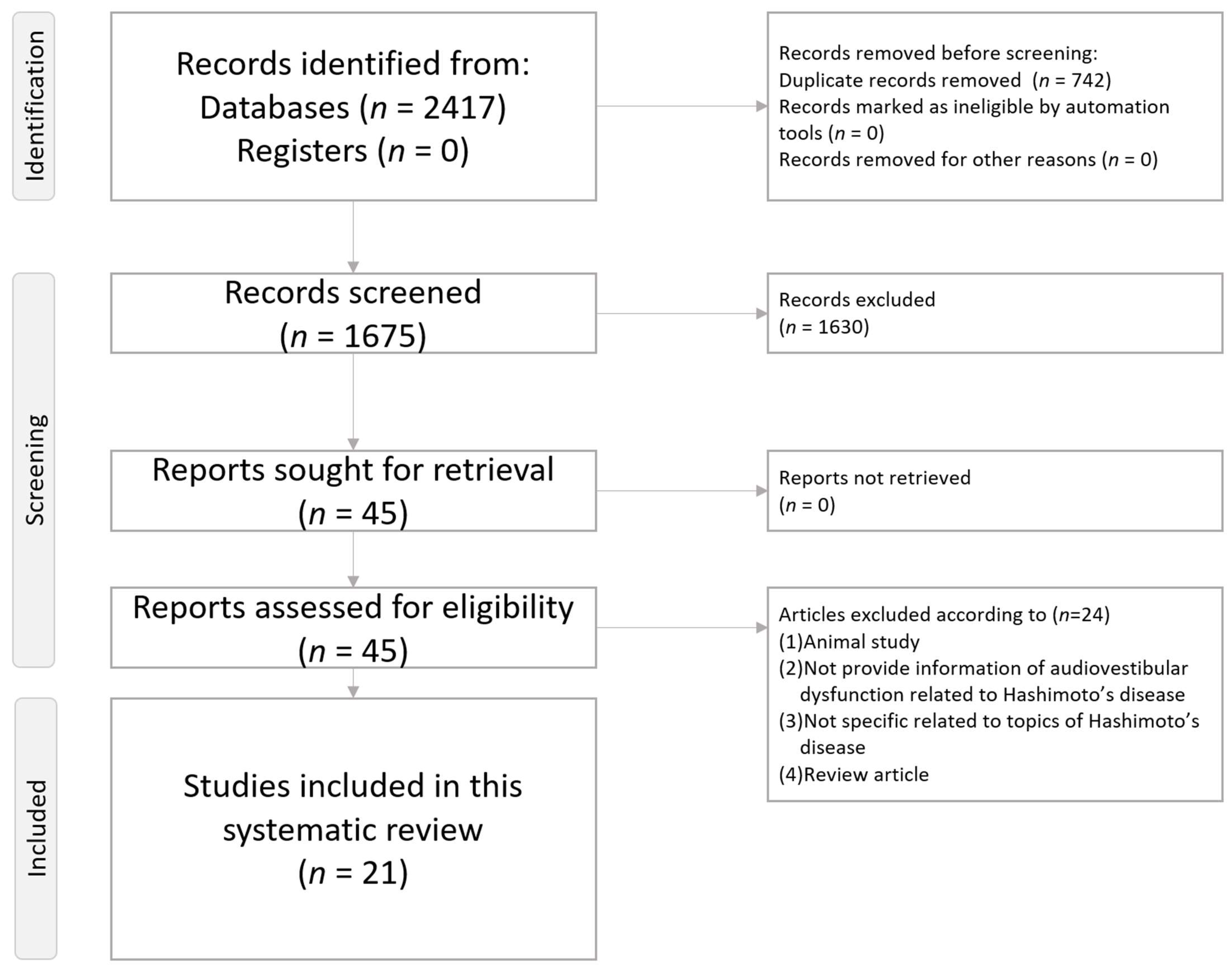
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Article Screening Process
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Article Quality Grading
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Vestibular System Involvement
3.1.1. Characteristics of Vestibular System Involvement
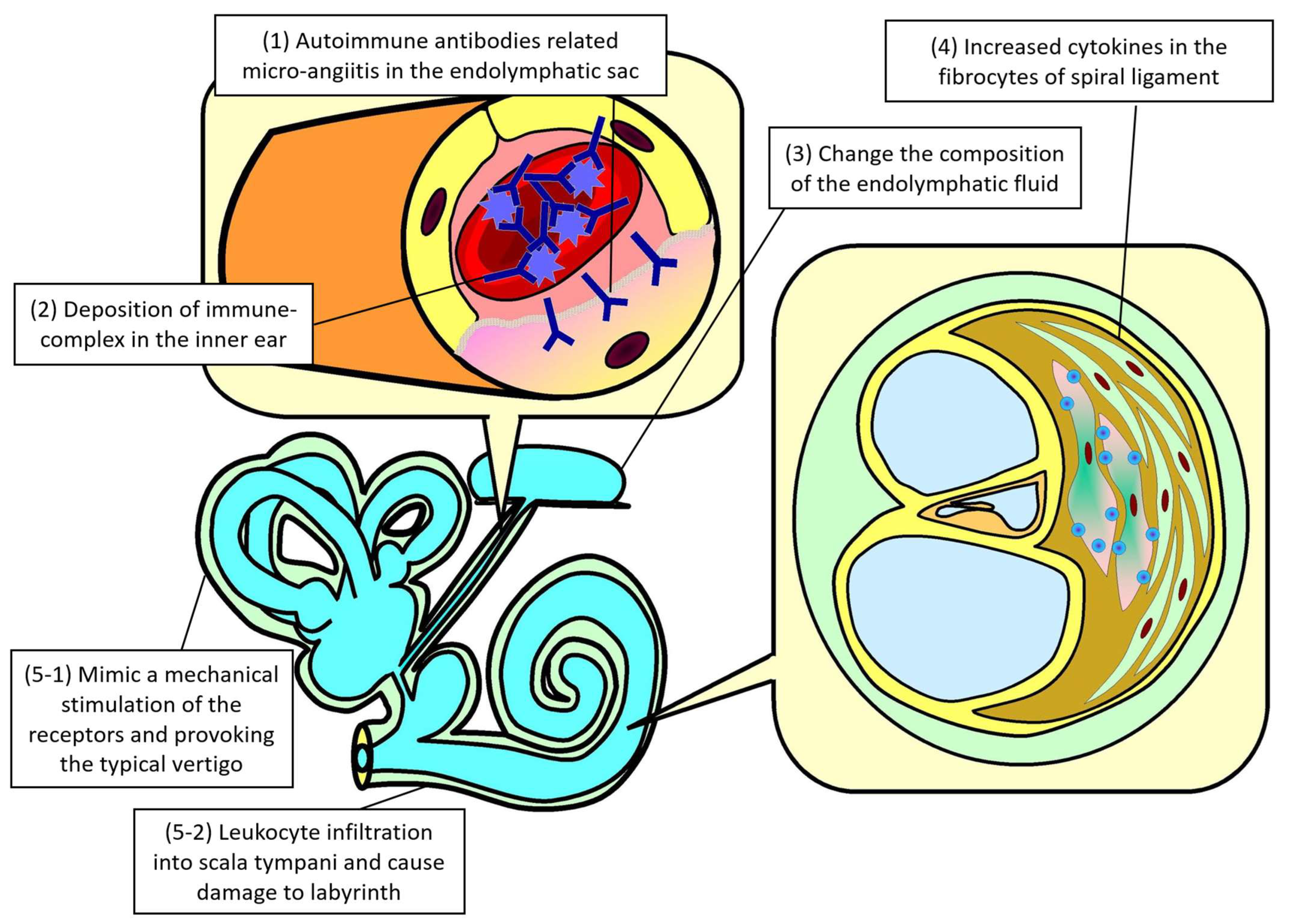
3.1.2. Pathophysiology of Vestibular System Involvement
3.1.3. Examination of Vestibular System Involvement
3.2. Auditory System Involvement
3.2.1. Characteristics of Auditory System Involvement
3.2.2. Physiopathology of Auditory System Involvement
3.2.3. Examination of Auditory System Involvement
3.3. Treatment of Hashimoto’s Disease-Related Audiovestibular Dysfunction
3.3.1. Temporary Protocol of Steroid Treatment to Manage Hashimoto’s Disease-Associated Audiovestibular Dysfunction
3.3.2. Recommendations About Referral to Otorhinolaryngological Examination
4. Conclusions
Limitation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanderpump, M.P. The epidemiology of thyroid disease. Br. Med. Bull. 2011, 99, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, T. Immune system of the inner ear as a novel therapeutic target for sensorineural hearing loss. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.S.; Tseng, P.T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.S.; Tseng, P.T. Audiological Features in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.Y.; Tseng, P.T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction Related to Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovo, R.; Aimoni, C.; Martini, A. Immune-mediated inner ear disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2006, 126, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Valiente, A.; Alvarez-Montero, O.; Gorriz-Gil, C.; Garcia-Berrocal, J.R. l-Thyroxine does not prevent immunemediated sensorineural hearing loss in autoimmune thyroid diseases. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 70, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Yue, C. The association between thyroid disease and hearing loss: A meta-analysis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2024, 144, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, F.; Fallahi, P.; Elia, G.; Gonnella, D.; Paparo, S.R.; Giusti, C.; Churilov, L.P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Antonelli, A. Hashimotos' thyroiditis: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinic and therapy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 33, 101367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, G.; Corsello, S.M.; Milite, M.T.; Zanni, M.; Ciardullo, A.V.; Donato, C.D.; Pontecorvi, A. Association between benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and autoimmune chronic thyroiditis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 70, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Montero, O.L.; Rodriguez Valiente, A.; Gorriz Gil, C.; Garcia Berrocal, J.R. Audiological evaluation (128-20,000Hz) in women with autoimmune thyroiditis: The role of antibodies vs. l-thyroxine deficiency. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 74, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, K.T.; Dias, N.H.; Mazeto, G.M.; Carvalho, L.R.; Lapate, R.L.; Martins, R.H. Audiologic evaluation in patients with acquired hypothyroidism. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 76, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topaloglu, O.; Sahin, B. Hearing Impairment and Audiological Alterations in Euthyroid Hashimoto's Thyroiditis. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2022, 84, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, H.; Nishizato, C.; Shimazu, T.; Watanabe, H.; Mizukami, T.; Kosuge, H.; Ozasa, S.; Nomura, K.; Kimura, S.; Takahashi, Y. Hashimoto's encephalopathy presenting with vertigo and muscle weakness in a male pediatric patient. No To Hattatsu 2016, 48, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Modugno, G.C.; Pirodda, A.; Ferri, G.G.; Montana, T.; Rasciti, L.; Ceroni, A.R. A relationship between autoimmune thyroiditis and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Med. Hypotheses 2000, 54, 614–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskiewicz-Orczyk, K.; Kos-Kudla, B.; Lisowska, G. The function of the vestibular organ in Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Endokrynol. Pol. 2022, 73, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricarico, L.; Di Cesare, T.; Galli, J.; Fetoni, A.R.; Paludetti, G.; Picciotti, P.M. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Is hypothyroidism a risk factor for recurrence? Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2022, 42, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, B.; Upreti, S. Autoimmune inner ear disease secondary to Hashimoto's thyroiditis: A case report. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2018, 8, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 12 June 2024).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, G.; Guidetti, G.; Corsello, S.M.; Di Donato, C.; Pontecorvi, A. The association between benign paroxysmal positional vertigo and autoimmune chronic thyroiditis is not related to thyroid status. Thyroid 2010, 20, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, A.; Maihoub, S.; Tamas, L.; Szirmai, A. A possible objective test to detect benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. The role of the caloric and video-head impulse tests in the diagnosis. J. Otol. 2022, 17, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskiewicz-Orczyk, K.A.; Lisowska, G.; Kajdaniuk, D.; Wojtulek, M. Can Hashimoto's thyroiditis cause vertigo? [Czy choroba Hashimoto moze byc przyczyna zawrotow glowy?]. Endokrynol. Pol. 2020, 70, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.M.; Paiva, D.F.F.; Corona, A.P.; Lessa, M.M. Association between Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo and Thyroid Diseases: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 28, e530–e536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskiewicz-Orczyk, K.; Vlaykov, A.; Lisowska, G.; Strzelczyk, J.; Kos-Kudla, B. Does Thyroid Hormone Metabolism Correlate with the Objective Assessment of the Vestibular Organ in Patients with Vertigo? J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D. Low vitamin D status is associated with hypothyroid Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Hormones 2016, 15, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.L.; Wang, P.Y.; Hsu, H.Y. Reversible electroencephalographic and single photon emission computed tomography abnormalities in Hashimoto's encephalopathy. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2005, 68, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Chang, T.C. Hashimoto's encephalopathy: Report of three cases. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferracci, F.; Moretto, G.; Candeago, R.M.; Cimini, N.; Conte, F.; Gentile, M.; Papa, N.; Carnevale, A. Antithyroid antibodies in the CSF: Their role in the pathogenesis of Hashimoto's encephalopathy. Neurology 2003, 60, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churilov, L.P.; Sobolevskaia, P.A.; Stroev, Y.I. Thyroid gland and brain: Enigma of Hashimoto’s encephalopathy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 33, 101364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.M.; Zhuang, S.M.; Xiao, Z.W.; Luo, J.Q.; Long, Z.; Lan, L.C.; Zhang, H.Q.; Zhang, G.P. Autoimmune thyroiditis in patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarella, G.; Tognini, S.; Nacci, A.; Sieli, R.; Costante, G.; Petrolo, C.; Mancini, V.; Guzzi, P.H.; Pasqualetti, G.; Cassandro, E.; et al. Vestibular disorders in euthyroid patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis: Role of thyroid autoimmunity. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 81, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymen, G.; Gunay, G.; Cirik, A.A.; Surmeli, R.; Surmeli, M. Vestibular Dysfunction in Euthyroid Children with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2024, 20, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maihoub, S.; Mavrogeni, P.; Molnar, V.; Molnar, A. Tinnitus and Its Comorbidities: A Comprehensive Analysis of Their Relationships. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.; Tsou, Y.A.; Wang, T.C.; Chang, W.D.; Lin, C.L.; Tyler, R.S. Hypothyroidism and related comorbidities on the risks of developing tinnitus. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduc, A.; Isik, S.; Allusoglu, S.; Iriz, A.; Dogan, B.A.; Gocer, C.; Tuna, M.M.; Berker, D.; Guler, S. Evaluation of hearing functions in patients with euthyroid Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Endocrine 2015, 50, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunes, A.; Karakus, M.F.; Telli, T.A.; Gunes, N.A.; Mutlu, M. The effect of thyroid autoantibody positivity on the functions of internal ear. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 3853–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S.; Billings, P.; Harris, J.P.; Firestein, G.S.; Keithley, E.M. Innate immunity contributes to cochlear adaptive immune responses. Audiol. Neurootol. 2005, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Hara, T.; Akama, T.; Yoshihara, A.; Sue, M.; Tanigawa, K.; Wu, H.; Ishido, Y.; Takeshita, F.; et al. Demonstration of innate immune responses in the thyroid gland: Potential to sense danger and a possible trigger for autoimmune reactions. Thyroid 2013, 23, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Camacho, R.; Garcia-Berrocal, J.R.; Trinidad, A.; Gonzalez-Garcia, J.A.; Verdaguer, J.M.; Ibanez, A.; Rodriguez, A.; Sanz, R. Central role of supporting cells in cochlear homeostasis and pathology. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 67, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabet Diramerian, L.; Ejaz, S. Pendred Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Sogi, C.; Shima, H.; Adachi, M.; Honkura, Y.; Kikuchi, A.; Kanno, J. Hearing loss with two pathogenic SLC26A4 variants and positive thyroid autoantibody: A case report. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2024, 33, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Aftab, M.; Jain, S.; Kumar, D. Audiological Evaluation in Hypothyroid Patients and Effect of Thyroxine Replacement Therapy. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 71, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Chang, I.J.; Hsu, C.M.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Tsai, M.S.; Chang, G.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Huang, E.I.; Lin, M.H.; et al. Association between Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Preexisting Thyroid Diseases: A Nationwide Case-Control Study in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Berrocal, J.R.; Ramirez-Camacho, R.; Trinidad, A.; Zurita, M.; de la Fuente, R.; Lobo, D. Controversies and criticisms on designs for experimental autoimmune labyrinthitis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2004, 113, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawron, W.; Pospiech, L.; Noczynska, A.; Orendorz-Fraczkowska, K. Electrophysiological tests of the hearing organ in Hashimoto's disease. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 17, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.X.; Lu, Q.H.; Guo, Z.K. Multiple intracranial lesions as the unusual imaging features of Hashimoto's encephalopathy: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e10814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossowski, A.; Moniuszko, M.; Dabrowska, M.; Sawicka, B.; Rusak, M.; Jeznach, M.; Wojtowicz, J.; Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, A.; Bossowska, A. Lower proportions of CD4+CD25(high) and CD4+FoxP3, but not CD4+CD25+CD127(low) FoxP3+ T cell levels in children with autoimmune thyroid diseases. Autoimmunity 2013, 46, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Berrocal, J.R.; Vargas, J.A.; Ramirez-Camacho, R.A.; Gonzalez, F.M.; Gea-Banacloche, J.C.; Vergara, J.; Durantez, A. Deficiency of naive T cells in patients with sudden deafness. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1997, 123, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrocal, J.R.; Ramirez-Camacho, R. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: Supporting the immunologic theory. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2002, 111, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Tsai Do, B.S.; Schwartz, S.R.; Bontempo, L.J.; Faucett, E.A.; Finestone, S.A.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Kelley, D.M.; Kmucha, S.T.; Moonis, G.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2019, 161, S1–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, A.; Maihoub, S.; Tamas, L.; Szirmai, A. Effectiveness of intratympanic dexamethasone for the treatment of vertigo attacks in patients with Meniere's disease compared with betahistine pharmacotherapy. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 300060520985647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, A.; Maihoub, S.; Tamas, L.; Szirmai, A. Intratympanically administered steroid for progressive sensorineural hearing loss in Meniere's disease. Acta Otolaryngol. 2019, 139, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatlipinar, A.; Kartal, I.; Keskin, S.; Kulbay, H.; Gozu, H.; Gokceer, T. The Effect of Hormone Replacement Treatment on Hearing Function in Hypothyroid Patients. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 75, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Xu, K.; Xie, L.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, S.; Sun, Y. The Dual Roles of Triiodothyronine in Regulating the Morphology of Hair Cells and Supporting Cells during Critical Periods of Mouse Cochlear Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chen, S.; Sun, Y. Connexin Mutations and Hereditary Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, V.; Shukla, G.K.; Bhatia, N. Hearing profile in hypothyroidism. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2002, 54, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, D.R.; Garcia-Berrocal, J.R.; Ramirez-Camacho, R. New prospects in the diagnosis and treatment of immune-mediated inner ear disease. World J. Methodol. 2014, 4, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giribet Fernandez-Pacheco, A.; Tomas Perez, M.A.; Almela Rojo, M.T.; Garcia-Purrinos Garcia, F.J. Relationship between vestibular syndrome and autoimmune thyroiditis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 69, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Zeng, B.S.; Wu, C.N.; Stubbs, B.; Carvalho, A.F.; Brunoni, A.R.; Su, K.P.; Tu, Y.K.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, T.Y.; et al. Association of Central Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Interventions With Efficacy and Safety in Tinnitus Management: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2020, 146, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Zeng, B.Y.; Lui, C.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Tseng, P.T. Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine associated tinnitus and treatment with transcranial magnetic stimulation. QJM 2022, 115, 623–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Jialal, I. Hashimoto Thyroiditis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, H.J.; Kwak, S.G.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, J.Y. A Nationwide, Population-based Cohort Study on Potential Autoimmune Association of Meniere Disease to Atopy and Vitiligo. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.Y.; Hahm, J.R.; Jung, T.S.; Lee, G.W.; Kim, D.R.; Park, M.H. A 20-year-old woman with Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Evans' syndrome. Yonsei Med. J. 2006, 47, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resende de Paiva, C.; Gronhoj, C.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; von Buchwald, C. Association between Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Thyroid Cancer in 64,628 Patients. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akay, B.N.; Bozkir, M.; Anadolu, Y.; Gullu, S. Epidemiology of vitiligo, associated autoimmune diseases and audiological abnormalities: Ankara study of 80 patients in Turkey. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 24, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.T.; Yu, J.T.; Tsao, T.Y.; Tseng, Y.H. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of thyroid and adrenal glands with primary adrenal insufficiency. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2024, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, U.L.; Hamza, H.M.; Malik, M.M.; Awan, A.A. Association of latent autoimmune diabetes of adults with type 3 polyglandular autoimmune syndrome-a diagnostic challenge. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2024, 74, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Shastri, M.; Patel, N.S.; Dobariya, R. Unravelling a Triad: A Rare Case of Takayasu Arteritis, Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis, and Psoriasis in a Young Female with Heart Failure. Cureus 2024, 16, e61153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Song, Y.S.; Wee, J.H.; Min, C.; Yoo, D.M.; Kim, S.Y. Analyses of the Relation between BPPV and Thyroid Diseases: A Nested Case-Control Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarella, G.; Russo, D.; Monzani, F.; Petrolo, C.; Fattori, B.; Pasqualetti, G.; Cassandro, E.; Costante, G. Hashimoto Thyroiditis and Vestibular Dysfunction. Endocr. Pract. 2017, 23, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renda, L.; Parlak, M.; Selcuk, O.T.; Renda, R.; Eyigor, H.; Yilmaz, M.D.; Osma, U.; Filiz, S. Do antithyroid antibodies affect hearing outcomes in patients with pediatric euthyroid Hashimoto’s thyroiditis? Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 79, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Vestibular System Involvement | Auditory System Involvement |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Feature | Sometimes associated with Hashimoto’s encephalopathy, especially in pediatric subjects. | Unilateral or bilateral sensorineural hearing loss. Predominantly sudden onset sensorineural hearing loss. |
| Hypothyroidism | Not necessarily associated with the presence of hypothyroidism. | Sometimes associated with hypothyroidism in a reciprocal relationship. |
| Clinical Examination | Mainly resulted from canalithiasis and cupulolithiasis, among which the posterior semicircular canals were the most often affected parts. Recording of cortical dysfunction evidence plus the existence of positive anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody. Traditional videonystagmography, oculomotor test, caloric response test, video head impulse test, and cervical vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials, could help in distinguishing central-origin or peripheral-origin vertigo | Hearing impairment in all frequencies. More profound between 9–16 kHz and 20 kHz in young age patients. Sensorineural hearing loss may have a positive correlation with anti-thyroid antibody levels. Ordinary frequency ranges of pure-tone audiometry are not recommended. Abnormal findings in brain auditory-evoked potential. Tympanic peak pressure and air conduction thresholds were significantly positively correlated with the anti-TPO antibody titers |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-J.; Hsu, C.-W.; Chen, T.-Y.; Liang, C.-S.; Chen, Y.-W.; Zeng, B.-Y.; Tseng, P.-T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Patients with Hashimoto’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104703
Chen J-J, Hsu C-W, Chen T-Y, Liang C-S, Chen Y-W, Zeng B-Y, Tseng P-T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Patients with Hashimoto’s Disease: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104703
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiann-Jy, Chih-Wei Hsu, Tien-Yu Chen, Chih-Sung Liang, Yen-Wen Chen, Bing-Yan Zeng, and Ping-Tao Tseng. 2025. "Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Patients with Hashimoto’s Disease: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104703
APA StyleChen, J.-J., Hsu, C.-W., Chen, T.-Y., Liang, C.-S., Chen, Y.-W., Zeng, B.-Y., & Tseng, P.-T. (2025). Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Patients with Hashimoto’s Disease: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104703






