Abstract
Toxoplasmosis is a widely spread zoonosis worldwide, considered one of the most important parasitic infections that affect global public health, and usually, it is not correctly diagnosed. Serological tests for the diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection have limitations in differentiating acute from chronic infection, which is important to determine the appropriate clinical management and treatment, mainly in pregnant women and immunocompromised individuals infected by this parasite. The present study aimed to characterize immunogenic epitopes from T. gondii immunodominant antigens, as SAG1(SRS29B), SAG2A (SRS34A), GRA1, GRA2, GRA3, GRA5, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, BSR4, and CCp5A, by investigating if these parasite components might emerge as alternatives to improve the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. A detailed comparative in silico analysis was used for this purpose. Once the protein sequences were retrieved from the ToxoDB database, different parameters were calculated, including physicochemical characteristics, accessibility values, and antigenicity. Multiple sequence alignment, 3D structures modeling, and the validation of 3D structures were also performed among all 11 peptides. Considering the results from the combination of all parameters analyzed, it can be hypothesized that the linear epitopes from SAG1, GRA3, and BSR4 proteins were found to be stable and hydrophilic, with a significant antigenicity score, and accessibility on the protein surface. Also, these three selected peptides were able to detect anti-T. gondii antibodies in serum samples from pigs infected by tachyzoites, when compared with control serum samples, obtained from the same naïve animals and tested by ELISA, demonstrating remarkable difference in terms of reactivity. Taken together, as our study addresses a critical challenge in the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis, particularly in gestational and congenital infections, where false-positive and false-negative results often arise from the use of native or recombinant antigens of T. gondii, our findings highlight the potential of synthetic peptides derived from novel epitopes of this parasite as alternative tools for the development of more accurate immunodiagnostic assays for toxoplasmosis.
1. Introduction
Toxoplasmosis is a widely spread zoonosis worldwide, caused by the obligate intracellular parasite Toxoplasma gondii, a protozoan with the ability to infect a large number of warm-blooded animal species, including humans [1,2]. With approximately one-third of the world’s population chronically infected by different genotypes, and a prevalence that varies extensively depending on the geographic region, toxoplasmosis is one of the neglected parasitic infections requiring active health control [3,4,5,6]. In this regard, the development of effective diagnostic methods, as well as vaccines, is necessary to avoid the consequences of toxoplasmosis on global public health and the economy [7].
Usually, infection is asymptomatic in immunocompetent individuals, sometimes causing nonspecific clinical signs [8]. From the medical point of view, the recognition of the infection is relevant in pregnant women, where the risk of transmission of the parasite to the fetus is high, and the associated consequences can compromise the life of the fetus and infected mothers. The detection of the parasite is also important in immunosuppressed individuals, such as HIV, cancer, and transplant patients, where the reactivation of the disease can cause severe health problems, which depending on various factors can even lead to the death of these patients [9,10].
The diagnosis of T. gondii infection through sensitive and specific methods is a fundamental step in treating and managing patients with suspected toxoplasmosis. T. gondii is capable of inducing a potent immune response that generates persistent antibody titers; thus, the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis carried out by serological tests, with emphasis on the detection of specific IgA, IgM, and IgG antibodies, against antigens of the parasite is useful [11,12]. While humans can be infected by any of the three infectious stages (sporozoites, bradyzoites, and tachyzoites), most commercial tests use native antigens derived from T. gondii tachyzoites. Despite their high sensitivity and specificity, it has been shown that the use of these antigens has limitations associated with different production and purification methods, laborious procedures, and difficulties in standardizing which finally cause ambiguous results, avoiding the accurate diagnosis and effective therapeutic and preventive procedures [11,13]. Moreover, it has been described in the literature that these antigenic preparations lack the ability to differentiate the clinical phases of infection (acute and chronic) [14,15].
Due to the difficulties associated with using native T. gondii antigens, new diagnostic tools are being investigated. Recombinant antigens, chimeric antigens, and peptides derived from T. gondii proteins have been suggested by various studies, not only to improve the diagnosis of T. gondii infection but also to improve the ways to discriminate the different stages of toxoplasmosis [11,12,16,17,18]. The use of bioinformatics tools, for the characterization of these new antigenic peptides capable of selectively stimulating the B-cell response, has a relevant role in making it possible to understand the antigenic structure of pathogens and to design new diagnostic methods and vaccine applications for several diseases [19].
The life cycle of T. gondii is complex and the expression of its proteins changes during different stages of development, some of which have been recognized to activate the immune system, generating antibody titers that remain throughout the life of the host [20,21]. The surface antigens SAG1 and SAG2A of T. gondii are highly immunogenic proteins that are expressed primarily on tachyzoites [22,23]. SAG1 has been used in several serodiagnosis studies that have suggested the usefulness of this antigen in detecting IgG antibodies in chronically infected individuals [24,25]. SAG2A has been considered a potential marker for the diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis in humans [26].
Dense granule proteins (GRA) play an important role in the process of host-cell invasion. They have shown good antigenicity, expressed by both tachyzoites and bradyzoites, and they have been recognized as both acute and chronic phase markers [7,27,28,29]. The GRA 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, and 7 antigens have demonstrated utility in the detection of antibodies to T. gondii with high sensitivity in acute and chronic phases of toxoplasmosis [27,30,31,32,33].
The surface antigen BSR4 and matrix antigen 1 (MAG1) are bradyzoite-specific proteins involved in human B and T cell responses [34,35]. In an ELISA assay, BSR4 protein demonstrated specific immunoreactivity in sera from patients in the chronic phase and MAG1 detected antibodies in the acute stage more frequently than in the chronic stage of toxoplasmosis [34,36]. CCp5A is a polypeptide specifically expressed by T. gondii sporozoites and is considered a good molecular marker to differentiate infectious stages [18]. Thus, the identification of B-cell epitopes from T. gondii immunodominant proteins could be a determining factor in the diagnosis of T. gondii infection and differentiation of clinical stages, from the appropriate selection of epitopes of antigens expressed in different stages of the parasite [37].
In the present study, an in silico comparative analysis was performed to characterize B-cell epitopes from the sequence of immunodominant proteins using different bioinformatics tools, aiming to provide new alternatives to improve the diagnosis of T. gondii infection.
2. Results
2.1. B-Cell Epitope Prediction Design
Using reference scores equal to or greater than 0.5 in each prediction, as suggested in the BepiPred 2.0 method, it was possible to identify a total of 11 linear B-cell epitopes from the SAG1, SAG2A, GRA1, GRA2, GRA3, GRA5, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, BSR4, and CCp5A T. gondii immunodominant proteins, with amino acid sequences between 12 and 21 residues, arranged in the least polymorphic regions of the proteins and with the best scores, as shown in Figure 1. The numbers of predicted epitopes, their length, position, as well as the protein to which they belong, are shown in Table 1.
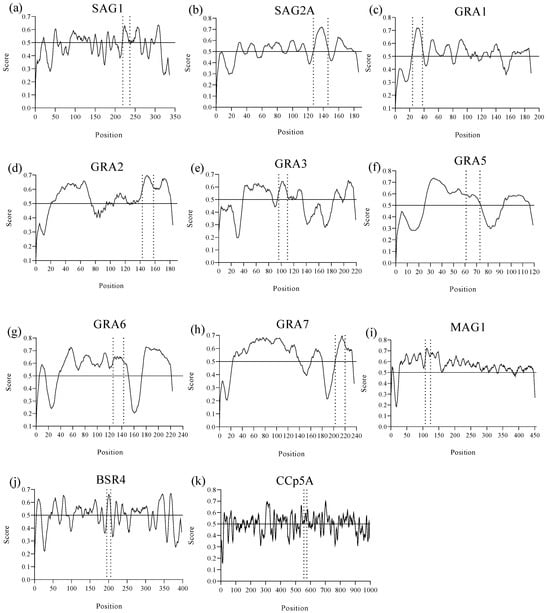
Figure 1.
Epitope prediction from T. gondii immunodominant proteins by BepiPred Linear Epitope Prediction version 2.0 from the Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource (IEDB) (https://www.iedb.org/, accessed on 3 April 2025) to identify the presence of linear B-cell epitopes. The figure demonstrates the predicted peptides delimited by the dashed lines that showed the best scores (≥0.5) arranged in the least polymorphic regions of the following T. gondii proteins: (a) SAG1, (b) SAG2A, (c) GRA1, (d) GRA2, (e) GRA3, (f) GRA5, (g) GRA6, (h) GRA7, (i) MAG1, (j) BSR4, (k) CCp5A.

Table 1.
The predicted peptides from T. gondii immunodominant proteins by Bepipred Linear Epitope Prediction version 2.0, characterized by their length and position in each protein.
2.2. Homology and Phylogenetic Relationship
To verify that the predicted peptides were conserved among the T. gondii strains of interest, multiplex sequence alignment was performed. The results of alignment and phylogenetic tree construction are shown in Figure 2.
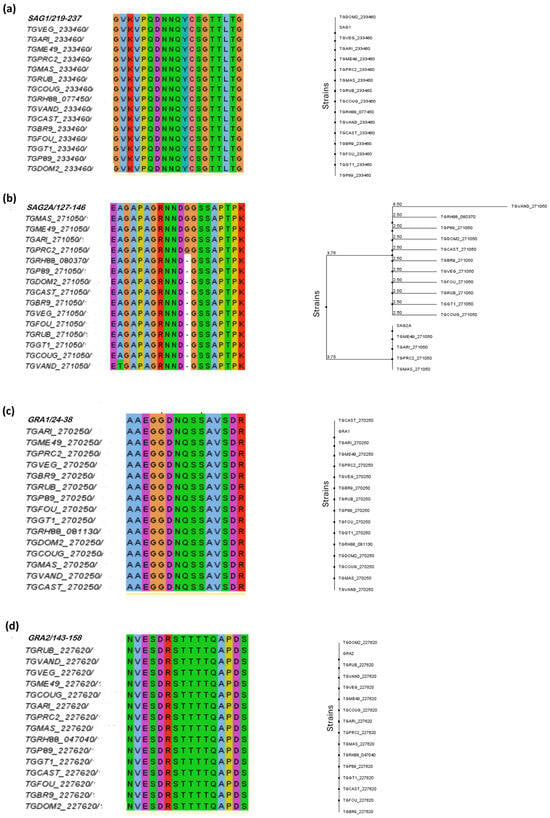
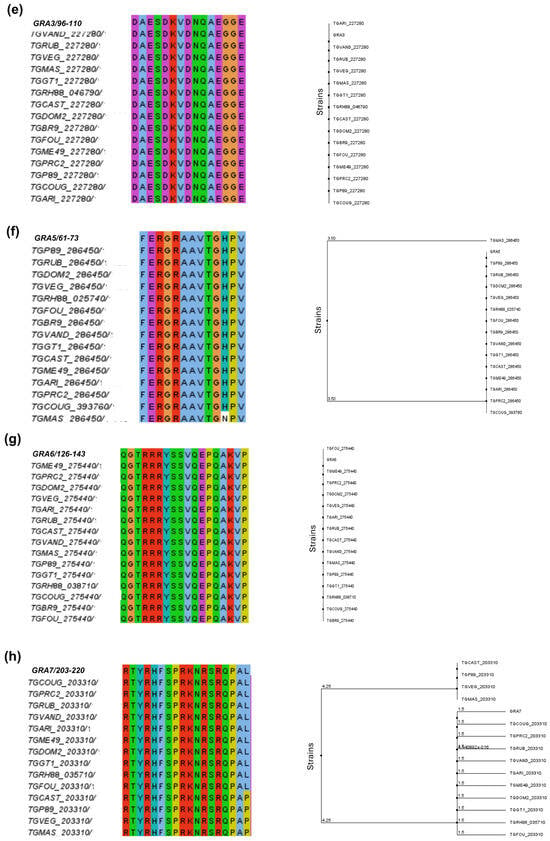
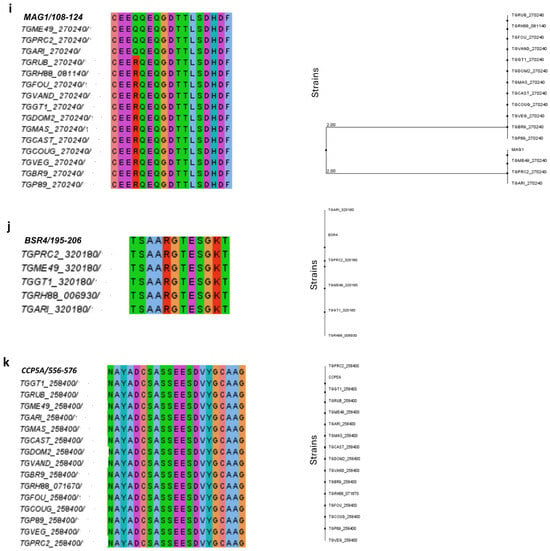
Figure 2.
A phylogenetic analysis of predicted epitopes from T. gondii immunodominant proteins. The figure shows the multiple sequence alignment for each predicted epitope and the respective phylogenetic trees designed in Jalview version 2 platform. The different colors in the alignment refer to the polarity of the amino acids in the sequences of the peptides. Note that the alignment of most peptides was possible in 15 T. gondii strains, except for the BSR4 peptide, where alignment was possible with only 5 strains. The phylogenetic alignment and phylogenetic trees are shown in the following order: (a) SAG1, (b) SAG2A, (c) GRA1, (d) GRA2, (e) GRA3, (f) GRA5, (g) GRA6, (h) GRA7, (i) MAG1, (j) BSR4, (k) CCp5A.
According to the alignment, it was possible to observe that the predicted peptides for SAG1, GRA1, GRA2, GRA3, GRA6, and CCp5A proteins showed the highest degree of conservation and identity in the different T. gondii strains, such as types I, II, and III of epidemiological importance.
Regarding the SAG2A peptide, it was possible to observe that most residues were highly conserved, with good alignment quality and consensus among amino acids; however, it is known that the SAG2A protein is highly polymorphic. Only the addition of glycine (G) residue was present in strains ME49, MAS, ARI, and PRC2, with a consensus of 31%. It was not present in type I and type III strains. The substitution of the amino acid alanine (A) for threonine (T) at position 128 was observed in T. gondii strain VAND (Figure 2b).
For GRA5, most residues were conserved, and a conservative substitution of histidine (H) by an asparagine (N) was observed at position 71 in the T. gondii MAS strain (Figure 2f). After analyzing the GRA7 peptide, was noticed a substitution of leucine (L) by a proline (P) in the strains CAST, P89, VEG, and MAS (Figure 2h)
The sequence alignment of MAG1 resulted in a high percentage of identity and similarity, but the strains ME49, GARI, and PRC2 showed a non-conservative substitution of the amino acid arginine (R) by glutamine (Q) at position 111 (Figure 2i). The BSR4 peptide was totally conserved only in the 5 strains for which the protein has been described, among them the RH and ME49 strains (Figure 2j).
2.3. General Characteristics of Peptides: Physicochemical Properties, Accessibility, and Antigenicity
The physicochemical parameters calculated using Expasy’s ProtParam tool are shown in Table 2. The server results showed that all peptides had a molecular weight above 1000 kDa. For most peptides, the isoelectric point values were less than 7 and were considered to be acidic. In this case, the predicted peptides would be more stable at acidic pH, except for peptides GRA5, GRA6, GRA7, and BSR4, which would be more stable at basic pH.

Table 2.
Physicochemical properties of the selected peptides calculated by Expasy’s ProtParam online server.
Defined as the relative volume occupied by aliphatic side chains (alanine, valine, isoleucine, and leucine), the aliphatic index provides an estimate of the thermal stability of a protein. The aliphatic index of the peptides ranged from 16.67 to 60.00; the higher the aliphatic index, the higher the probability that the peptides are more stable over a wide temperature range. The predicted peptides showed an acceptable aliphatic index, with the GRA5 peptide having the highest index, and were thus considered to be thermostable.
The instability index estimates the stability of the protein in a test tube. A protein with an instability index lower than 40 is considered stable, while a value higher than 40 predicts that the protein may be unstable. SAG1, GRA3, GRA5, and BSR4 peptides were more stable when compared to the SAG2A, GRA1, GRA2, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, and CCp5A peptides.
Regarding the hydropathicity index (GRAVY), the calculated values for the peptides were between −1.713 and −0.281. Negative values indicate better interaction with water, and greater solubility, that is, more hydrophilic peptides, while positive GRAVY values indicate greater hydrophobicity.
Using the Emini method, the solvent accessibility of epitopes was evaluated. It was observed that when the amino acid residues had a score equal to or greater than the 1.0 threshold, the probability of this peptide being found on the protein surface increased (Figure 3). In this sense, peptides from SAG1, GRA2, GRA3, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, and BSR4 were found in more accessible regions within the protein structures, whereas SAG2A, GRA1, GRA5, and CCp5A peptides were less exposed with only a few solvent-accessible residues, making it difficult for them to interact with water molecules.
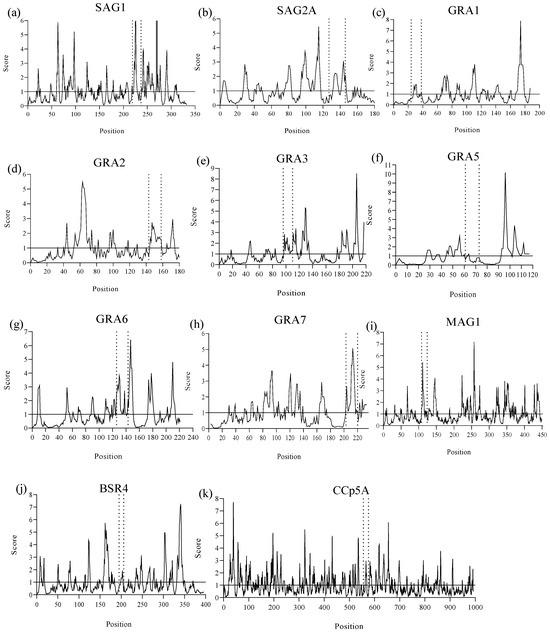
Figure 3.
An analysis of surface accessibility of the predicted epitopes using Emini surface accessibility prediction tool of Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource (IEDB) (https://www.iedb.org/, accessed on 3 April 2025). The image shows the predicted peptides delimited by the dashed lines and their amino acid residues that hold the default threshold value of 1.0, indicating the probability of these residues being found on the surface of their respective T. gondii proteins: (a) SAG1, (b) SAG2A, (c) GRA1, (d) GRA2, (e) GRA3, (f) GRA5, (g) GRA6, (h) GRA7, (i) MAG1, (j) BSR4, (k) CCp5A.
Using the VaxiJen 2.0 server, the antigenic potential of each predicted linear B-cell epitope was analyzed. The results showed that the epitopes had antigenicity values ranging from 0.3953 to 1.4757, with those that demonstrated values above the threshold of 0.5 being considered antigenic epitopes. All selected peptides were considered as probable antigens, except for the GRA6 peptide that showed the lowest score according to the server. Table 3 demonstrates the antigenicity values for each epitope.

Table 3.
Predicted linear B-cell epitopes and their antigenicity value obtained from the VaxiJen 2.0 server.
2.4. Three-Dimensional Modeling of Proteins and Validation
The three-dimensional structures of 10 T. gondii proteins were not yet available in PDB format. Therefore, the 3D structures for the proteins SAG2A, GRA1, GRA2, GRA3, GRA5, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, BSR4, and CCp5A were modeled using the Robetta server. The 3D structure for SAG1 was not modeled because it was available in PDB format.
In terms of stereochemical quality, the predicted models were analyzed using the Ramachandran plot. The results of the Ramachandran plots are presented in Table S1 and Figure S1, showing the phi–psi torsion angles for all residues in the 3D structure of proteins. Generally, it is expected to have at least 90% of the residues in the most allowed regions of phi–psi values. All the models constructed presented more than 90% of their amino acid residues between the most allowed and additional allowed regions. Although the proteins SAG2A, GRA2, GRA3, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, and CCp5A presented amino acid residues between the non-allowed zones, the combination of the Ramachandran and G-factor data suggests an overall good quality of the models.
The results of the ERRAT and PROVE tools are shown in Table 4. The overall quality factor of the modeled proteins resulted in values of 89.4467–100, suggesting models with adequate resolutions. The PROVE values were between 0.8 and 4.2%.

Table 4.
ERRAT and PROVE analyses of three-dimensional modeled structures from whole molecules and peptides.
2.5. Three-Dimensional Modeling of Peptides and Validation
All 11 linear B-cell epitopes predicted were modeled using the Pep fold server. From the amino acid sequence, the site predicts a consistent peptide structure on a large scale, providing a total of 5 models for each of the epitopes, the best of which were selected. The generated 3D models are shown in Figure 4.
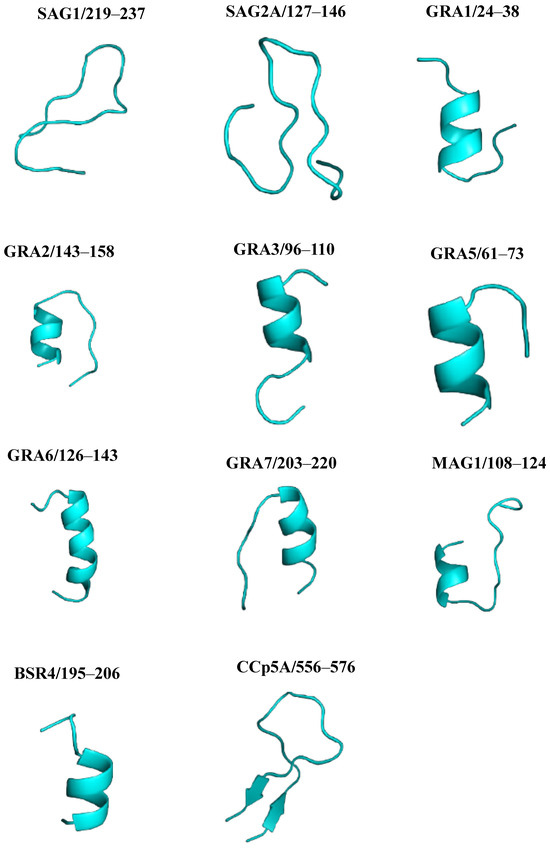
Figure 4.
T. gondii peptide structure prediction and analysis using the Pep Fold server (https://bioserv.rpbs.univ-paris-diderot.fr/services/PEP-FOLD/, accessed on 3 April 2025). The figure shows the best three-dimensional structures (blue) of peptides derived from T. gondii immunodominant proteins.
After analyzing the Ramachandran plot and G-factors, amino acid residues were arranged in both the most optimal and additional permitted regions of the diagram. These parameters suggest that the 3D structure of the peptides is adequate, stable, and of good stereochemical quality (Table S2) (Figure S2).
The overall quality factor of all modeled peptides was 100, indicating that the models predicted here exhibit good high resolution. The z-score for most peptides demonstrates lower atomic values. The ERRAT and PROVE analyses of peptide three-dimensional modeled structures are shown in Table 4.
2.6. PYMOL Alignment
To compare the predicted structures and visualize the arrangement of peptides in the proteins, a structural alignment was performed. Initially, the PYMOL server performs the sequence alignment and then the structure alignment, calculating the RMSD. Figure 5 shows the graphical representation of the structural alignment made in the PYMOL program. It can be seen that the peptides showed differences in structural conformation and accessibility on the surface protein. The secondary structure analysis suggested that peptides from SAG1, and SAG2A, presented a more distended disposition forming random coils, while peptides GRA1, GRA2, GRA3, GRA5, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, BSR4, and CCp5A adopted folding conformations, forming an α-helix and, in the case of CCp5A, forming a β-hairpin in their respective proteins.
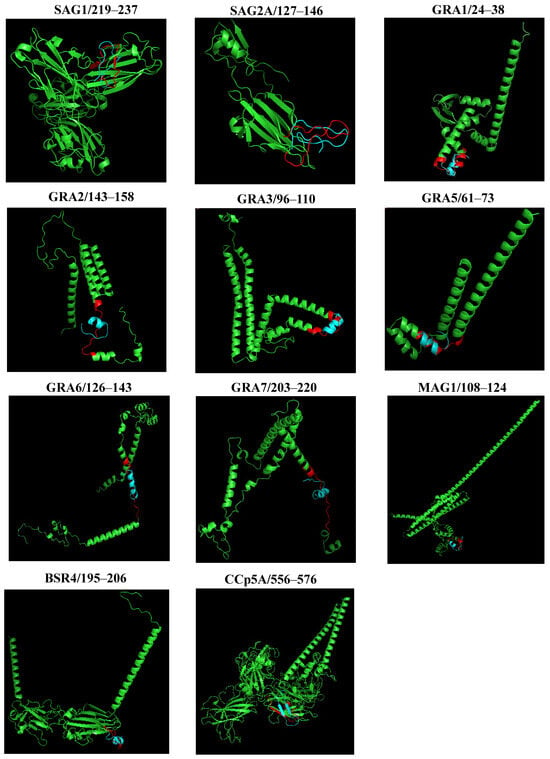
Figure 5.
A structural representation of the alignment of the 3D structures of proteins and peptides obtained through PYMOL. The colors were used to indicate the 3D structure of the T. gondii proteins (green), the peptide region (red), and the 3D structures of the aligned peptides (blue) by PYMOL.
2.7. Biological Activity of the Selected Peptides
As shown in Figure 6, ELISA carried out with SAG1, BSR4 and GRA3 peptides was able to detect anti-T. gondii antibodies in serum samples from pigs infected by tachyzoites. When compared with control serum samples, obtained from the same animals before infection (naïve), samples from infected animals tested by ELISA using the three selected peptides demonstrated remarkable difference in terms of reactivity. When the ELISA peptides were compared with the reference test (STAg ELISA) to obtain the co-positivity (sensitivity) and co-negativity (specificity) scores, the results demonstrated 100% agreement for both immunoassays.
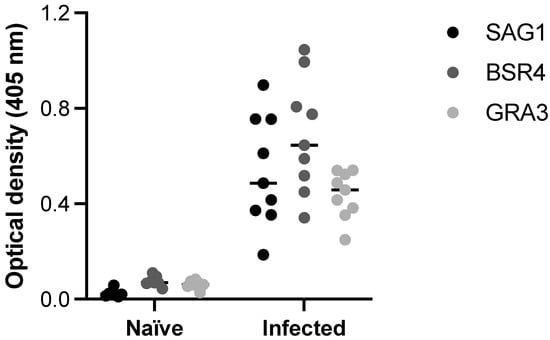
Figure 6.
ELISA with SAG1, BSR4, and GRA3 peptides as antigenic preparations. The detection of anti-T. gondii antibodies in serum samples from pigs infected by tachyzoites, compared with control serum samples (naïve), obtained from the same animals before infection. The reactivity using the three selected peptides was determined by optical densities at 405 nm.
3. Discussion
The sensitivity and specificity of immunodiagnostic assays for toxoplasmosis depend on the antigens used [37]. New alternative immunoassays have been proposed in the literature to replace the use of native T. gondii antigens, aiming to solve the limitations related to production cost and standardization of those antigenic preparations and making possible to obtain significant improvements in the detection of phase of infection by this parasite [11].
Advances in methodologies to identify epitopes by combining computational methods and mathematical algorithms using an extensive biological database have contributed to the development of bioinformatics. This novel tool makes it possible to analyze the structure of antibodies, B cells, and T cells, evaluate intermolecular interactions, characterize and model immunogenic epitopes, and design new vaccines and diagnostic methods [38]. Synthetic peptides predicted using bioinformatics tools offer distinct advantages such as shorter production time and cost when compared to lysed T. gondii antigens, accurate knowledge of antigen composition with a high degree of purity, and ease of method standardization [16,39]. Using a set of bioinformatics web servers, a group of 11 peptides from the antigenic components of T. gondii was assessed, as follows: SAG1, SAG2A, GRA1, GRA2, GRA3, GRA5, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, BSR4, and CCp5A, which are expressed in the different infectious stages of the parasite, as sporozoites, tachyzoites, and bradyzoites, as previously characterized [7,18,22,23,27,28,29,35].
When the whole data were analyzed and compared, peptides predicted from SAG1, GRA3, and BSR4 proteins, in particular, showed superior physicochemical, accessibility, and antigenic properties. The theoretical isoelectric point for these peptides was 5.83, 3.71, and 8.41, respectively. The isoelectric point indicates the pH at which a protein has zero net charges. At this pH there is a decrease in repulsive interactions and, therefore, the interaction between the molecules is improved; thus, even the proteins are more stable [40]. In that sense, the stability and solubility of these peptides is maintained between acidic and basic pH. The calculated isoelectric point will be useful for determining the solutions and buffer system needed to establish conditions for the standardization and development of new designed immunoassays. In terms of aliphatic index and instability index values, the peptides were stable and moderately thermotolerant, with high hydrophilicity due to negative GRAVY values, which is one of the important characteristics of antigenic epitopes that allow for the understanding the protein folding, predicting the secondary structure and interaction sites [7,41].
The peptides from the SAG1, GRA3, and BSR4 proteins presented significant antigenicity values of 1.1163, 1.2841, 1.4757, respectively. In addition, the multiple sequence alignment demonstrated that the peptides selected from SAG1, GRA3, and BSR4 proteins showed a high degree of conservation and identity in different T. gondii strains, such as the epidemiologically important type I, II, and III strains [42]. Also, a BLASTp search using these specified epitope sequences was performed against protozoan parasite databases, revealing that all of them are highly conserved within T. gondii strains and do not have homologs in other protozoan parasites, including Neospora caninum, Plasmodium sp., Leishmania sp., Trypanosoma sp., among others. This suggests that the chosen epitopes are appropriate, which is advantageous for developing species-specific diagnostic tools. It is also necessary to consider that, although a BLASTp search is useful for demonstrating specificity, the occurrence of cross-reactions cannot be excluded.
Approximately 30% of the human population is infected by various widely distributed genotypes of T. gondii, with clonal lineages type I, II, and III being the most important [6]. In addition to the classical clonal lineages, further genetic diversity of T. gondii associated with other divergent lineages, called atypical strains, has been described [42]. The classical clonal lineages represent a large majority of isolates in North America and Europe, with the type II lineage being the most predominant in these continents and the rest of the world. In South America, T. gondii strains show great genetic variability, with unique polymorphisms [42]. The identification of significantly antigenic epitopes that are also conserved among the different strains of T. gondii could aid the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis by increasing case detection independently of the infecting strain.
The prediction of the 3D models and the validation of the structure by Ramachandran plot analysis revealed that these peptides had more than 90% of their residues in energetically favorable regions of the diagram. In addition, the overall quality factor and PROVE of all modeled peptides mean that the quality of the modeling has been satisfactory. Thus, most of the amino acid residues for these peptides were found exposed on the surface of the proteins, adopting distinct structural conformations, which facilitate their interaction with molecules of the immune system. Secondary structures are of great importance for the epitopes, as the α-helices and β-turns have high-energy hydrogen bonds that maintain the structural conformation of the protein and therefore strengthen interactions with antibodies [43].
Numerous bioinformatics tools have been useful in the identification of immunogenic epitopes of various T. gondii antigens that may have better potential to ensure an accurate diagnosis [44]. SAG1 is known to be one of the most immunogenic T. gondii antigens and is considered a promising molecule for the development of diagnostic methods and vaccines by eliciting a strong immunodominant response [45]. In this sense, the reactivity of SAG1-derived epitopes has been tested with different clinical forms of toxoplasmosis in some studies, suggesting the potential for detecting infected individuals [46]. GRA3 has been used in association with the most immunoreactive regions of other T. gondii proteins, demonstrating a relevant performance in serodiagnosis [27].
BSR4 protein has demonstrated immunogenicity and protein-specific immunoreactivity in sera from patients in the chronic phase in ELISA assay; however, the diagnostic utility of peptides derived from this protein for the serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis has not been described, so it would be interesting to further investigate its potential for detecting T. gondii infection [34].
The characterization and use of new immunodominant epitopes from these proteins would allow us to formulate strategies to improve the diagnosis of T. gondii infection. Studies suggest the use of chimeric antigens for ELISA, based on multiplex antigenic epitopes expressed at different stages of the parasite, which should be recognized by antibodies against individual antigens and increase the sensitivity and specificity of diagnostic tests for toxoplasmosis. [47]. Using an in silico approach, Beghetto et al. (2006) [27] designed a multi-epitope with sequences of six immunodominant T. gondii proteins, among which SAG1 and GRA3 were present. The study indicated the significant diagnostic performance of the chimeric antigen in detecting acquired infection in adults and in infants born to mothers with a primary T. gondii infection. Holec-Gąsior et al. (2012) [48], using peptides of MIC1, MAG1, and SAG1 bound in a chimera, obtained significant results when compared to the multi-epitope with just MIC1 and MAG1 sequences, suggesting the immunogenicity of SAG1. The use of individual recombinant or chimeric formulations has shown the potential to differentiate T. gondii-infected individuals from uninfected individuals, as well as the stage of infection [11,12,49,50].
The use of chimerical antigens in the diagnosis of infections offers a high density of immunoreactive epitopes of various antigens that increase the chances of detection of antibodies in serum samples and, therefore, improve the performance of the immunoassay [51]. The in silico analysis performed here, therefore, suggests that the peptides from SAG1, GRA3, and BSR4 protein could be used individually or together in new immunodiagnostic assays to validate their potential in detecting specific anti-T. gondii antibodies.
Overall, this study highlights the physicochemical properties, accessibility, and antigenicity of three synthetic peptides, selected based on the prediction and analysis of linear B-cell epitopes from the protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of the study, as peptide selection was based solely on the highest-scoring candidates identified through bioinformatic tools, out of a total of eleven predicted peptides. Future research should include an experimental evaluation of the remaining eight epitopes, and extend beyond those derived from SAG1, BSR4, and GRA3. In this context, additional ELISA assays should be conducted using all characterized epitopes, with performance compared to that of the STAg-based ELISA.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Prediction and Analysis of Linear B-Cell Epitopes
To analyze the presence of linear B-cell epitopes in T. gondii immunodominant antigens, complete amino acid sequences of the proteins SAG1, SAG2A, GRA1, GRA2, GRA3, GRA5, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, BSR4, and CCp5A were obtained in FASTA format from the ToxoDB database (https://toxodb.org/toxo/app, accessed on 3 April 2025). The sequences of each protein were thoroughly analyzed using bioinformatics tools for immunological epitope prediction, available online in the Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource (IEDB) software (https://www.iedb.org/, accessed on 3 April 2025). The prediction of linear epitopes was made based on data obtained from the BepiPred Linear Epitope Prediction version 2.0 method (BepiPred-2.0: Sequential B-Cell Epitope Predictor), using reference scores equal to or greater than 0.5. Using the Random Forest Regression algorithm, the BepiPred-2.0 server is able to predict linear B-cell epitopes from the 3D structure of the protein. BepiPred-2.0 represents a method with improved predictive power compared to other methods available online, which predicts that residues with values above the threshold (predetermined value 0.5) are part of a B-cell epitope [52].
4.2. Sequence Alignment and Estimation of Phylogenetic Trees
The multiple sequence alignment of T. gondii immunodominant proteins was carried out on the MUSCLE website (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/muscle/, accessed on 3 April 2025). The obtained information was used to analyze and evaluate the homology and conservation of the chosen peptides among T. gondii strains, and to estimate phylogenetic trees using the Jalview version 2 platform (https://www.jalview.org/, accessed on 3 April 2025) [53].
4.3. Prediction of Physicochemical Properties, Accessibility, and Antigenicity
To estimate the physicochemical properties of the selected epitopes, the web tool ProtParam (ExPASy) was used (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/, accessed on 3 April 2025), which calculated the main parameters of the sequences such as molecular weight (MW), theoretical isoelectric point (pI), aliphatic index, instability index, and average hydropathicity (GRAVY). From this analysis, it was possible to characterize the peptides.
The solvent accessibility of the selected peptides was determined using the Emini surface accessibility prediction tool [54] available on the IEDB website. The Emini method calculates the probability of amino acids being exposed on the surface of a given protein when the score is greater than the set threshold value (greater than or equal to 1).
Antigenicity forecasting of peptides was carried out through the free web server VaxiJen v2.0 (http://www.ddg-pharmfac.net/vaxijen/VaxiJen/VaxiJen.html, accessed on 3 April 2025). The prediction of antigenicity through the VaxiJen v2.0 website is based on the physicochemical characteristics of the proteins of a given organism (parasites, bacteria, fungi, viruses) and the transformation of the sequences into uniform vectors of the main amino acid properties using the automatic cross-covariance (ACC) system [55].
4.4. Prediction of the Three-Dimensional (3D) Model of the T. gondii Proteins
The construction of the three-dimensional structure of SAG1, SAG2A, GRA1, GRA2, GRA3, GRA5, GRA6, GRA7, MAG1, BSR4, and CCp5A proteins was performed in the Robetta server (https://robetta.bakerlab.org/, accessed on 3 April 2025). Robetta is a free online service that analyzes and predicts protein structure using the methods of comparative modeling or de novo structure prediction. Through an automated interface, sequences sent to the server are analyzed in putative domains and a protein model is predicted in the presence or absence of sequence homology with proteins of known structure. The server produces PDB extension files that enabled an analysis of the generated structures in Discovery Studio and PYMOL [56].
4.5. Prediction of the Three-Dimensional (3D) Model of the T. gondii Peptides
Using the Pep Fold website (https://bioserv.rpbs.univ-paris-diderot.fr/services/PEP-FOLD/, accessed on 3 April 2025) the 11 predicted peptides were modeled. For the 3D modeling of peptides of up to 52 amino acid residues, Pep Fold uses the structural alphabet (SA) concept derived from the hidden Markov model and ensembles the predicted fragments using an algorithm and modified version of the coarse-grained force field (OPEP) [57].
4.6. Validation of the 3D Modeling of Proteins and Peptides
In the next step, the quality of 3D models obtained using Robetta and Pep Fold software was checked by Ramachandran plot analysis of PDB SUM website (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl?pdbcode=index.html, accessed on 3 April 2025), ERRAT and PROVE tools of SAVES 6.0 server, also were used (https://saves.mbi.ucla.edu/, accessed on 3 April 2025).
With the Ramachandran diagram, it is possible to detect phi–psi torsion angles for all amino acid residues in a structure, allowing for an analysis of which residues lie outside the energetically favorable regions and thus verifying the conformational or stereochemical stability of the protein [58]. ERRAT validates the structure of a protein based on the interaction and distribution of the different types of atoms, which can be distinguished using a quadratic error function. Generally, good high-resolution structures produce values around 95% or higher, and lower resolutions the overall quality factor is around 91% [59]. PROVE evaluates the quality of protein structures by comparing the deviations of the atomic volumes (Z-scores) with the standard values of highly resolved and refined proteins, since better-resolved models present a lower Z-score [60].
4.7. Three-Dimensional Structure Alignment of Proteins and Peptides
Once modeled and validated, the 3D structures of the proteins and their respective predicted peptides were aligned using PYMOL version 3.0 software (https://pymol.org/2/, accessed on 3 April 2025). PYMOL is a tool that allowed for the visualization of the 3D models as well as analysis of the arrangement of the peptides calculating the Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) and their accessibility on the protein surface.
4.8. Serum Samples from Uninfected and Experimentally Infected Pigs
Serum samples were obtained from experimentally infected pigs, as previously described [61]. Briefly, nine 6- to 8-week-old mixed-breed pigs, seronegative for T. gondii, were lodged in separate stables, and received an intramuscular infection with 7 × 107 tachyzoites of the RH strain. The control group was constituted by the serum samples from the same animals prior to the infection. Serum was collected weekly after the infection, and we chose samples obtained between 14 and 28 days after the inoculation to test the antigenicity of the selected peptides. All samples were checked for seroconversion by using T. gondii native soluble antigen [STAg] ELISA. This experimental protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee for Experimental Utilization of Animals from the State University of Londrina (CEUA 17/09).
4.9. ELISA to Evaluate the Biological Activity of the Selected Peptides
For ELISA using synthetic peptides, previous optimization of the reaction was established through block titration of the selected peptides, blocking buffers, serum samples, and conjugated antibodies. High-binding 96-well plates (Corning, New York City, NY, USA) were sensitized with 2 µg/well of each peptide in sodium carbonate buffer (pH 9.6) and incubated overnight, at 37 °C. The wells were washed 4 times with 100 µL of PBS-Tween 20 and blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in PBS, for 1 h at 37 °C. The serum samples were diluted at 1:100 in PBS in 2.5% BSA and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C. After 4 washes, anti-pig IgG peroxidase (Bio-Rad, Santo Amaro, Brazil) was used as the secondary antibody, at 1:2000 dilution in 2.5% BSA in PBS. Again, the plates were incubated 1 h at 37 °C, and after a new washing cycle, the reaction was revealed with 2.2′-azino-bis-3-ethyl-benzothiazoline sulfonic acid peroxidase substrate (ABTS, Thermo, São Paulo, Brazil) and the optical densities were read at 405 nm (M2e, Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA). The results of ELISA peptide were compared as a percentage of co-positivity (sensitivity) and co-negativity (specificity) in relation to the results obtained by the reference test, STAg ELISA.
5. Conclusions
The current limitations of the antigens used in the immunodiagnosis of T. gondii infection suggest the necessity to develop new antigenic preparations, aiming to increase the accuracy of toxoplasmosis, particularly to characterize the phase of infection. Bioinformatic methods allow for the identification of immunodominant regions of a particular antigen in less time and cost. Through in silico analysis, 3 out of 11 peptides were selected from the parasite, SAG1, BSR4, and GRA3. These selected components were found to be stable, hydrophilic, and protein-surface accessible, with an antigenic role, suggesting their potential use for toxoplasmosis diagnosis as a single or multiepitope tool to design new immunodiagnostic assays.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26104689/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.N.-J., J.L.G., R.T.F., T.W.P.M., and J.R.M.; methodology, A.d.V.B.B., T.L.S., D.K.d.F.O., J.L.G., R.T.F., and T.W.P.M.; formal analysis, A.d.V.B.B., T.L.S., D.K.d.F.O., N.N.-J., J.L.G., R.T.F., and T.W.P.M.; data curation, J.R.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.d.V.B.B. and D.K.d.F.O.; writing—review and editing, T.W.P.M., and J.R.M.; project administration, T.W.P.M., and J.R.M.; funding acquisition, J.R.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by Brazilian research agencies (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais-FAPEMIG, Grant # RED-00198-23 and #APQ-01313-14; Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico-CNPq, Grant # 312201/2021-4 and # 445569/2020-4; Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior-CAPES, Grant # AUXPE-02450/09-7).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study was approved by the by the Ethical Committee for Experimental Utilization of Animals from the State University of Londrina (Protocol # CEUA 17/09).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ana Cláudia Arantes Marquez Pajuaba for her technical assistance. The authors also acknowledge the use of ChatGPT (OpenAI, May 2025 version, https://chat.openai.com, accessed on 8 May 2025) to assist in the language editing of the final paragraph of the manuscript. All content generated was critically reviewed and approved by the authors to ensure accuracy and integrity.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest concerning the results of this study.
References
- Macêdo, A.G., Jr.; Cunha, J.P., Jr.; Cardoso., T.H.S.; Silva, M.V.; Santiago, F.M.; Silva, J.S.; Pirovani, C.P.; Silva, D.A.O.; Mineo, J.R.; Mineo, T.W.P. SAG2A protein from Toxoplasma gondii interacts with both innate and adaptive immune compartments of infected hosts. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Harari, R.R.; Connolly, M.P. High burden and low awareness of toxoplasmosis in the United States. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.; Teixeira, C.; Gomes, P.; Borges, M. Promising drug targets and compounds with anti-Toxoplasma gondii activity. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Outbreaks of clinical toxoplasmosis in humans: Five decades of personal experience, perspectives and lessons learned. Parasit. Vectors 2021, 14, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Cai, J.P. Identifying novel B cell epitopes within Toxoplasma gondii GRA6. Korean J. Parasitol. 2016, 54, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis—An overview. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 1991, 22, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Luft, B.J.; Remington, J.S. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in AIDS. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 15, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambroise-Thomas, P. Parasitic diseases and immunodeficiencies. Parasitology 2001, 122, S65–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasz Ferra, B.; Holec-Gąsior, L.; Gatkowska, J.; Dziadek, B.; Dzitko, K.; Grąźlewska, W.; Lautenbach, D. The first study on the usefulness of recombinant tetravalent chimeric proteins containing fragments of SAG2, GRA1, ROP1 and AMA1 antigens in the detection of specific anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in mouse and human sera. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217866. Available online: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0217866 (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Ybañez, R.H.D.; Ybañez, A.P.; Nishikawa, Y. Review on the current trends of toxoplasmosis serodiagnosis in humans. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudan, V.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Shanker, D. Recent trends in the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Clin. Rev. Opin. 2013, 5, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat, J.B.; Hidalgo, H.F.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Pelloux, H. Human toxoplasmosis: Which biological diagnostic tests are best suited to which clinical situations? Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roiko, M.S.; LaFavers, K.; Leland, D.; Arrizabalaga, G. Toxoplasma gondii-positive human sera recognize intracellular tachyzoites and bradyzoites with diverse patterns of immunoreactivity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2018, 48, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, S.S.; Paiva, C.F.; Carvalho, F.R.; Barros, H.L.S.; Silva, T.L.; Barros, P.S.C.; Pajuaba, A.C.A.M.; Barros, G.B.; Dietze, R.; Mineo, T.W.P.; et al. A peptide originated from Toxoplasma gondii microneme 8 displaying serological evidence to differentiate recent from chronic human infection. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 84, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lu, H.; Jia, B.; Chang, Z.; Peng, S.; Yin, J.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, N. A comparative study of Toxoplasma gondii seroprevalence in three healthy Chinese populations detected using native and recombinant antigens. Parasit. Vectors 2013, 6, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, S.S.; Gebrim, L.C.; Carvalho, F.R.; Barros, H.S.; Barros, P.C.; Pajuaba, A.C.A.M.; Messina, V.; Possenti, A.; Cherchi, S.; Reiche, E.M.V.; et al. CCp5A protein from Toxoplasma gondii as a serological marker of oocyst-driven infections in humans and domestic animals. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.S. Immunoinformatics approach for the identification and characterization of T cell and B cell epitopes towards the peptide-based vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arranz-Solís, D.; Cordeiro, C.; Young, L.H.; Dardé, M.L.; Commodaro, A.G.; Grigg, M.E.; Saeij, J.P.J. Serotyping of Toxoplasma gondii infection using peptide membrane arrays. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.T.; Grigg, M.E.; Uyetake, L.; Parmley, S.; Boothroyd, J.C. Serotyping of Toxoplasma gondii infections in humans using synthetic peptides. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekutis, C.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; Grigg, M.E.; Camps, M.; Boothroyd, J.C. Surface antigens of Toxoplasma gondii: Variations on a theme. Inter. J. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomavo, S.; Schwarz, R.T.; Dubremetz, J.F. Evidence for glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchoring of Toxoplasma gondii major surface antigens. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1989, 9, 4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalallou, N.; Bandepour, M.; Khazan, H.; Haghighi, A.; Abdollahi, S.; Kazemi, B. Recombinant SAG1 antigen to detect Toxoplasma gondii specific Immunoglobulin G in human sera by ELISA test. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2010, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bel-Ochi, N.C.; Bouratbine, A.; Mousli, M. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay using recombinant SAG1 antigen to detect Toxoplasma gondii-specific Immunoglobulin G antibodies in human sera and saliva. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béla, S.R.; Silva, D.A.O.; Cunha-Júnior, J.P.; Pirovani, C.P.; Chaves-Borges, F.A.; Carvalho, F.R.; Oliveira, T.C.; Mineo, J.R. Use of SAG2A recombinant Toxoplasma gondii surface antigen as a diagnostic marker for human acute toxoplasmosis: Analysis of titers and avidity of IgG and IgG1 antibodies. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 62, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghetto, E.; Spadoni, A.; Bruno, L.; Buffolano, W.; Gargano, N. Chimeric antigens of Toxoplasma gondii: Toward standardization of toxoplasmosis serodiagnosis using recombinant products. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.G.; Vilariño, M.J. Semiquantitative dot blot with the GRA8 antigen to differentiate the stages of toxoplasmosis infection. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 149, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotresha, D.; Poonam, D.; Hafiznur, Y.M.; Saadatnia, G.; Nurulhasanah, O.; Sabariah, O.; Tan, S.Y.; Zahidah, A.K.I.; Rahmah, N. Recombinant proteins from new constructs of SAG1 and GRA7 sequences and their usefulness to detect acute toxoplasmosis. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 29, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Pietkiewicz, H.; Hiszczyńska-Sawicka, E.; Kur, J.; Petersen, E.; Nielsen, H.V.; Stankiewicz, M.; Andrzejewska, I.; Myjak, P. Usefulness of Toxoplasma gondii-specific recombinant antigens in serodiagnosis of human toxoplasmosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1779–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec-Ga, L.; Kur, J.; Hiszczyńska-Sawicka, E. GRA2 and ROP1 recombinant antigens as potential markers for detection of Toxoplasma gondii-specific Immunoglobulin G in humans with acute toxoplasmosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holec-Ga, L.; Kur, J. Toxoplasma gondii: Recombinant GRA5 antigen for detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 124, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyasi, H.; Babaie, J.; Fricker-Hidalgo, H.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.P.; Zare, M.; Sadeghiani, G.; Assmar, M.; Pelloux, H.; Golkar, M. Use of Dense Granule Antigen GRA6 in an Immunoglobulin G avidity test to exclude acute Toxoplasma gondii infection during pregnancy. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing-Zhi, C.; Guo, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.-L.; Shen, J.-L.; Jiao, Y.-M.; Fang, Q.; Sun, X. Recombinant expression and immunologic identification of bradyzoite-specific antigen BSR4 of Toxoplasma gondii. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2012, 30, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Di Cristina, M.; Del Porto, P.; Buffolano, W.; Beghetto, E.; Spadoni, A.; Guglietta, S.; Piccolella, E.; Felici, F.; Gargano, N. The Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoite antigens BAG1 and MAG1 induce early humoral and cell-mediated immune responses upon human infection. Microbes Infect. 2004, 6, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holec, L.; Hiszczyńska-Sawicka, E.; Ga, A.; Brillowska-Da, A.; Kur, J. Use of MAG1 recombinant dntigen for Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ybañez, R.H.; Nishikawa, Y. Comparative performance of recombinant GRA6, GRA7, and GRA14 for the serodetection of T. gondii infection and analysis of IgG subclasses in human sera from the Philippines. Pathogens 2022, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potocnakova, L.; Bhide, M.; Pulzova, L.B. An introduction to B-cell epitope mapping and in silico epitope prediction. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 1, 6760830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Trincado, J.L.; Gomez-Perosanz, M.; Reche, P.A. Fundamentals and methods for T- and B-cell epitope prediction. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 1, 2680160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy Server, In 2-D Proteome Analysis Protocols; Link, A.J., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; He, S.; Zhao, G.; Chen, L.; Shi, N.; Zhou, H.; Cong, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, X.-Q. Toxoplasma gondii: Bioinformatics analysis, cloning and expression of a novel protein TgIMP1. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 132, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardé, M.L. Toxoplasma gondii, “new” genotypes and virulence. Parasite 2008, 15, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaddel, M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Tabandeh, M.R. Bioinformatics analysis of single and multi-hybrid epitopes of GRA-1, GRA-4, GRA-6 and GRA-7 proteins to improve DNA vaccine design against Toxoplasma gondii. J. Parasit. Dis. 2018, 42, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi-Mamaghani, A.; Seyyed-Tabaei, S.J.; Ranjbar, M.M.; Haghighi, A.; Spotin, A.; Rezaee, H. Designing diagnostic kit for Toxoplasma gondii based on GRA7, SAG1, and ROP1 antigens: An in silico strategy. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 2269–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, J.L.; Perelman, D.; Kasper, L.H.; Ware, P.L.; Boothroyd, J.C. Molecular analysis of the gene encoding the major surface antigen of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Immunol. 1988, 141, 3584–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, N.; de-la-Torre, A.; Siachoque, H.; Patarroyo, M.A.; Gomez-Marin, J.E. Toxoplasma gondii: P30 peptides recognition pattern in human toxoplasmosis. Exp. Parasitol. 2009, 123, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holec-Gąsior, L.; Ferra, B.; Grąźlewska, W. Toxoplasma gondii tetravalent chimeric proteins as novel antigens for detection of specific Immunoglobulin G in sera of small ruminants. Animals 2019, 9, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec-Ga, L.; Ferra, B.; Drapała, D. MIC1-MAG1-SAG1 chimeric protein, a most effective antigen for detection of human toxoplasmosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1977–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.-F.; Jiang, M.; Qu, L.-L.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Gong, L.-L.; Gong, R.-J.; Si, J. Toxoplasma gondii: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on a recombinant multi-epitope peptide for distinguishing recent from past infection in human sera. Exp. Parasitol. 2013, 133, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holec-Ga, L. Toxoplasma gondii recombinant antigens as tools for serodiagnosis of human toxoplasmosis: Current status of studies. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, M.Q.; Galdino, A.S.; Santos, J.C.D.; Soares, M.V.; de Nóbrega, Y.C.; Alvares, A.C.M.; de Freitas, S.M.; Torres, F.A.G.; Felipe, M.S.S. A recombinant multiepitope protein for hepatitis B diagnosis. BioMed Res. Inter. 2013, 1, 148317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, M.C.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M.; Marcatili, P. BepiPred-2.0: Improving sequence-based B-cell epitope prediction using conformational epitopes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W24–W29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version—A multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emini, E.A.; Hughes, J.V.; Perlow, D.S.; Boger, J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J. Virol. 1985, 55, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: A server for prediction of protective antigens, tumor antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.E.; Chivian, D.; Baker, D. Protein structure prediction and analysis using the Robetta server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W526–W531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Maupetit, J.; Derreumaux, P.; Tufféry, P. Improved PEP-FOLD approach for peptide and miniprotein structure prediction. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 4745–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, A.L.; MacArthur, M.W.; Hutchinson, E.G.; Thornton, J.M. Stereochemical quality of protein structure coordinates. Proteins 1992, 12, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colovos, C.; Yeates, T.O. Verification of protein structures: Patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, J.; Richelle, J.; Wodak, S.J. Deviations from standard atomic volumes as a quality measure for protein crystal structures. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 264, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.L.; Gennari, S.M.; Navarro, I.T.; Machado, R.Z.; Sinhorini, I.L.; Freire, R.L.; Marana, E.R.M.; Tsutsui, V.; Contente, A.P.A.; Begale, L.P. Partial protection against tissue cysts formation in pigs vaccinated with crude rhoptry proteins of Toxoplasma gondii. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 129, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).