Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Prediction of LRR-RLK Family Genes in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) in Response to Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Classification of LRR-RLK Family Types in Foxtail Millet Genome
2.2. Distribution of the LRR-RLK Family in Foxtail Millet
2.3. Transcriptome Analysis of the LRR-RLK Family in Foxtail Millet
2.4. Functional Predictions for LRR-RLKs in Foxtail Millet Related to Stress Responses
3. Discussion
3.1. LRR-RLKs’ Function in Plant Immunity
3.2. LRR-RLKs’ Function in Drought Stress
3.3. LRR-RLKs’ Function in Salt Stress
3.4. LRR-RLKs’ Function in Temperature Stress
3.5. LRR-RLKs’ Function in Oxidation Stress
3.6. Perspectives
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Acquisition of LRR-RLK Family Sequences in Foxtail Millet
4.2. The Classification of LRR-RLK Family Sequences in Foxtail Millet
4.3. Analysis of LRR-RLK Family Structure in Foxtail Millet
4.4. Transcriptome Analysis of LRR-RLK Family in Foxtail Millet
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gish, L.A.; Clark, S.E. The RLK/Pelle family of kinases. Plant J. 2011, 66, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Agusti, J.; Lichtenberger, R.; Schwarz, M.; Nehlin, L.; Greb, T. Characterization of transcriptome remodeling during cambium formation identifies MOL1 and RUL1 as opposing regulators of secondary growth. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001312. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Gomez, L.; Boller, T. FLS2: An LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schoof, H.; Lenhard, M.; Haecker, A.; Mayer, K.F.; Jürgens, G.; Laux, T. The stem cell population of Arabidopsis shoot meristems in maintained by a regulatory loop between the CLAVATA and WUSCHEL genes. Cell 2000, 100, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, C.; Russinova, E.; Hecht, V.; Baaijens, E.; de Vries, S. The Arabidopsis thaliana SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASES1 and 2 control male sporogenesis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 3337–3349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zipfel, C.; Kunze, G.; Chinchilla, D.; Caniard, A.; Jones, J.D.G.; Boller, T.; Felix, G. Felix G Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell 2006, 125, 749–760. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, A.J.; Wood, A.J.; Lightfoot, D.A. Plant receptor-like serine threonine kinases: Roles in signaling and plant defense. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 507–517. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.A.; Lopes, K.V.G.; Apfata, J.A.C.; Fontes, E.P.B. NSP-interacting kinase, NIK: A transducer of plant defence signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3839–3845. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrichsen, D.M.; Joazeiro, C.A.P.; Li, J.; Hunter, T.; Chory, J. Chory J Brassinosteroid-insensitive-1 is a ubiquitously expressed leucine-rich repeat receptor serine/threonine kinase. Plant Physiol. 2000, 123, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Q.; Lamb, C.; Ronald, P.; Chory, J. Perception of brassinosteroids by the extracellular domain of the receptor kinase BRI1. Science 2000, 288, 2360–2363. [Google Scholar]
- Bojar, D.; Martinez, J.; Santiago, J.; Rybin, V.; Bayliss, R.; Hothorn, M. Crystal structures of the phosphorylated BRI1 kinase domain and implications for brassinosteroid signal initiation. Plant J. 2014, 78, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gou, X.; Yuan, T.; Lin, H.; Asami, T.; Yoshida, S.; Russell, S.D.; Li, J. BAK1 and BKK1 regulate Brassinosteroid-dependent growth and Brassinosteroid Independent cell-death pathways. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Shiu, S.H.; Karlowski, W.M.; Pan, R.; Tzeng, Y.H.; Mayer, K.F.; Li, W.H. Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soltabayeva, A.; Dauletova, N.; Serik, S.; Sandybek, M.; Omondi, J.O.; Kurmanbayeva, A.; Srivastava, S. Receptor-like Kinases (LRR-RLKs) in Response of Plants to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Plants. 2022, 11, 2660. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, L.J. Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase genes in soybean. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Tirnaz, S.; Bayer, P.E.; Inturrisi, F.; Zhang, F.; Yang, H.; Dolatabadian, A.; Neik, T.X.; Severn-Ellis, A.; Patel, D.A.; Ibrahim, M.I.; et al. Resistance Gene Analogs in the Brassicaceae: Identification, Characterization, Distribution, and Evolution. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 909–922. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Song, Y. Identification and expression analysis of the LRR-RLK gene family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) Heinz 1706. Genome 2015, 58, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Brutnell, T.P. Setaria viridis and Setaria italica, model genetic systems for the Panicoid grasses. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3031. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.; Huang, X.; Zhi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, W.; Chai, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, K.; Lu, H.; et al. A haplotype map of genomic variations and genome-wide association studies of agronomic traits in foxtail millet (Setaria italica). Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 957–961. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Lu, Z.; Xie, K.; Tang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhi, H.; et al. A complete reference genome assembly for foxtail millet and Setaria-db, a comprehensive database for Setaria. Mol. Plant. 2024, 17, 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Asekova, S.; Oh, E.; Kulkarni, K.P.; Siddique, M.I.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, J.-D.; Kim, M.; Oh, K.-W.; Ha, T.-J.; et al. An Integrated Approach of QTL Mapping and Genome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies Candidate Genes for Phytophthora Blight Resistance in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 604709. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Wang, C.; Niu, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Q.; Feng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yuan, X.; Yu, H.; et al. Detecting novel loci underlying rice blast resistance by integrating a genome-wide association study and RNA sequencing. Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; He, M.; Zhou, X.; Yang, C.; Yuan, C.; Wang, J.; Chern, M.; Yin, J.; et al. The durably resistant rice cultivar Digu activates defense gene expression before the full maturation of Magnaporthe oryzae appressorium. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 354–368. [Google Scholar]
- Man, J.; Gallagher, J.P.; Bartlett, M. Structural evolution drives diversification of the large LRR-RLK gene family. New Phytol. 2020, 226, 1492–1505. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Feng, B.; Zhou, J.M.; Tang, D. Plant immune signaling: Advancing on two frontiers. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 2–24. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Chen, L.L.; Kim, H.S.; Pi, L.Y.; Holsten, T.; Gardner, J.; Wang, B.; Zhai, W.X.; Zhu, L.H.; et al. A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 1995, 270, 1804–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, Z.; Gómez-Gómez, L.; Boller, T.; Felix, G. Sensitivity of different ecotypes and mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana toward the bacterial elicitor flagellin correlates with the presence of receptor-binding sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45669–45676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kunze, G.; Zipfel, C.; Robatzek, S.; Niehaus, K.; Boller, T.; Felix, G. The N terminus of bacterial elongation factor Tu elicits innate immunity in Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 3496–3507. [Google Scholar]
- Miya, A.; Albert, P.; Shinya, T.; Desaki, Y.; Ichimura, K.; Shirasu, K.; Narusaka, Y.; Kawakami, N.; Kaku, H.; Shibuya, N. CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19613–19618. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, X.-C.; Neece, D.; Ramonell, K.M.; Clough, S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Stacey, M.G.; Stacey, G. A LysM receptor-like kinase plays a critical role in chitin signaling and fungal resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 471–481. [Google Scholar]
- Petutschnig, E.K.; Jones, A.M.; Serazetdinova, L.; Lipka, U.; Lipka, V. The lysin motif receptor-like kinase (LysM-RLK) CERK1 is a major chitin-binding protein in Arabidopsis thaliana and subject to chitin-induced phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28902–28911. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Li, L.; Yin, Y. Recent advances in the regulation of brassinosteroid signaling and biosynthesis pathways. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Song, C.; Hu, Y.; Han, Z.; She, J.; Fan, F.; Wang, J.; Jin, C.; Chang, J.; et al. Chitin-Induced Dimerization Activates a Plant Immune Receptor. Science 2012, 336, 1160–1164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaku, H.; Nishizawa, Y.; Ishii-Minami, N.; Akimoto-Tomiyama, C.; Dohmae, N.; Takio, K.; Minami, E.; Shibuya, N. Plant cells recognize chitin fragments for defense signaling through a plasma membrane receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11086–11091. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, T.; Nakano, T.; Takamizawa, D.; Desaki, Y.; Ishii-Minami, N.; Nishizawa, Y.; Minami, E.; Okada, K.; Yamane, H.; Kaku, H.; et al. Two LysM receptor molecules, CEBiP and OsCERK1, cooperatively regulate chitin elicitor signaling in rice. Plant J. 2010, 64, 204–214. [Google Scholar]
- Shinya, T.; Motoyama, N.; Ikeda, A.; Wada, M.; Kamiya, K.; Hayafune, M.; Kaku, H.; Shibuya, N. Functional characterization of CEBiP and CERK1 homologs in arabidopsis and rice reveals the presence of different chitin receptor systems in plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 1696–1706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willmann, R.; Lajunen, H.M.; Erbs, G.; Newman, M.-A.; Kolb, D.; Tsuda, K.; Katagiri, F.; Fliegmann, J.; Bono, J.-J.; Cullimore, J.V.; et al. Arabidopsis lysin-motif proteins LYM1 LYM3 CERK1 mediate bacterial peptidoglycan sensing and immunity to bacterial infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19824–19829. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Li, J.-F.; Ao, Y.; Qu, J.; Li, Z.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, D.; Qi, K.; et al. Lysin motif-containing proteins LYP4 and LYP6 play dual roles in peptidoglycan and chitin perception in rice innate immunity. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 3406–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzatto, C.; Machado, J.P.B.; Lopes, K.V.G.; Nascimento, K.J.T.; Pereira, W.A.; Brustolini, O.J.B.; Reis, P.A.B.; Calil, I.P.; Deguchi, M.; Sachetto-Martins, G.; et al. NIK1-mediated translation suppression functions as a plant antiviral immunity mechanism. Nature 2015, 520, 679–682. [Google Scholar]
- Liebrand, T.W.H.; van den Berg, G.C.M.; Zhang, Z.; Smit, P.; Cordewener, J.H.G.; America, A.H.P.; Sklenar, J.; Jones, A.M.E.; Tameling, W.I.L.; Robatzek, S.; et al. Receptor-like kinase SOBIR1/EVR interacts with receptor-like proteins in plant immunity against fungal infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebrand, T.W.H.; van den Burg, H.A.; Joosten, M.H.A.J. Two for all: Receptor-associated kinases SOBIR1 and BAK1. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, D.; Shan, L.; He, P.; de Vries, S.; Kemmerling, B. One for all: The receptor-associated kinase BAK1. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Hwang, H.; Hong, J.-W.; Lee, Y.-N.; Ahn, I.P.; Yoon, I.S.; Yoo, S.-D.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, B.-G. A rice orthologue of the ABA receptor, OsPYL/RCAR5, is a positive regulator of the ABA signal transduction pathway in seed germination and early seedling growth. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, F.; Suzuki, T.; Osakabe, Y.; Betsuyaku, S.; Kondo, Y.; Dohmae, N.; Fukuda, H.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. A small peptide modulates stomatal control via abscisic acid in long-distance signalling. Nature 2018, 556, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masle, J.; Gilmore, S.R.; Farquhar, G.D. The ERECTA gene regulates plant transpiration efficiency in Arabidopsis. Nature 2005, 436, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P.X.; Xu, P.; Yu, G.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xiong, Y.; Xiang, C.B. AtEDT1/HDG11 regulates stomatal density and water-use efficiency via ERECTA and E2Fa. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Gao, Z.; Xiao, G.; Huang, R.; Zhang, H. Leucine-Rich Repeat Receptor-Like Kinase FON1 Regulates Drought Stress and Seed Germination by Activating the Expression of ABA-Responsive Genes in Rice. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Sheng, P.; Tan, J.; Chen, X.; Lu, G.; Ma, W.; Heng, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Plasma membrane receptor-like kinase leaf panicle 2 acts downstream of the DROUGHT AND SALT TOLERANCE transcription factor to regulate drought sensitivdity in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.W.; Yang, S.H.; Shin, K.H.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, S.H. The AtLRK10L1.2, Arabidopsis ortholog of wheat LRK10, is involved in ABA-mediated signaling and drought resistance. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.-Q.; Liu, Y.-F.; Liu, P.; Lei, G.; He, S.-J.; Ma, B.; Zhang, W.-K.; Zhang, J.-S.; Chen, S.-Y. Receptor-like kinase OsSIK1 improves drought and salt stress tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) plants. Plant J. 2010, 62, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-J.; Wuriyanghan, H.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Duan, K.-X.; Chen, H.-W.; Li, Q.-T.; Lu, X.; He, S.-J.; Ma, B.; Zhang, W.-K.; et al. An S-Domain Receptor-Like Kinase, OsSIK2, Confers Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Delays Dark-Induced Leaf Senescence in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 1752–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Rehman, A.U.; Wang, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, Z.; Song, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, S.; Gong, Z. Arabidopsis U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase PUB11 negatively regulates drought tolerance by degrading the receptor-like protein kinases LRR1 and KIN7. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 494–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Zhu, C. The role of receptor-like protein kinases (RLKs) in abiotic stress response in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, N.; Pandey, P.; Srivastava, V.K.; Tuteja, N. Pea lectin receptor-like kinase functions in salinity adaptation without yield penalty, by alleviating osmotic and ionic stresses and upregulating stress-responsive genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 88, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Li, S.; Wang, K.; Tian, H.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Q.; Du, C. A leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase, OsSTLK, modulates salt tolerance in rice. Plant Sci. 2020, 296, 110465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.L.; Zhang, L.Q.; Ai, L.F.; Han, Y.F.; Sun, D.Y.; Zhang, S.W.; Sun, Y. The Receptor-Like Kinase SIT1 Mediates Salt Sensitivity by Activating MAPK3/6 and Regulating Ethylene Homeostasis in Rice. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2538–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaminami, K.; Okamoto, M.; Higuchi-Takeuchi, M.; Yoshizumi, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Fukao, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Ohashi, C.; Tanaka, M.; Matsui, M.; et al. AtPep3 is a hormone-like peptide that plays a role in the salinity stress tolerance of plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5810–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Kita, D.; Peaucelle, A.; Cartwright, H.N.; Doan, V.; Duan, Q.; Liu, M.-C.; Maman, J.; Steinhorst, L.; Schmitz-Thom, I.; et al. The FERONIA Receptor Kinase Maintains Cell-Wall Integrity during Salt Stress through Ca2+ Signaling. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zayed, O.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, P.; Hsu, C.-C.; Zhang, L.; Tao, W.A.; Lozano-Duran, R.; Zhu, J.-K. Leucine-rich repeat extensin proteins regulate plant salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 13123–13128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, F.; Liu, Y.; Du, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Lan, W.; Rodriguez, P.L.; Liu, X.; et al. FERONIA interacts with ABI2-type phosphatases to facilitate signaling cross-talk between abscisic acid and RALF peptide in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5519–E5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, T.S.; Figueiredo, D.D.; Cordeiro, A.M.; Almeida, D.M.; Lourenço, T.; Abreu, I.A.; Sebastián, A.; Fernandes, L.; Contreras-Moreira, B.; Oliveira, M.M.; et al. OsRMC, a negative regulator of salt stress response in rice, is regulated by two AP2/ERF transcription factors. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerbler, S.M.; Wigge, P.A. Temperature Sensing in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2023, 74, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Shad Ali, G.; Yang, L.; Du, L.; Reddy, A.S.N.; Poovaiah, B.W. A calcium/calmodulin-regulated member of the receptor-like kinase family confers cold tolerance in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7119–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Ding, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Gong, Z.; Yang, S. Plasma Membrane CRPK1-Mediated Phosphorylation of 14-3-3 Proteins Induces Their Nuclear Import to Fine-Tune CBF Signaling during Cold Response. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 117–128.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Shi, H.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, H.; Yang, S.; Zheng, W.; et al. Natural variation in CTB4a enhances rice adaptation to cold habitats. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.G.; Hwang, S.-G.; Park, Y.C.; Park, H.M.; Kim, D.S.; Park, D.H.; Jang, C.S. Molecular characterization of the cold- and heat-induced Arabidopsis PXL1 gene and its potential role in transduction pathways under temperature fluctuations. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 176, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, K.; Gao, P.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Wu, Z. GsLRPK, a novel cold-activated leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase from Glycine soja, is a positive regulator to cold stress tolerance. Plant Sci. 2014, 215, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhong, X.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B.; Li, Q.; Chen, G.; Mao, B.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Overexpression of receptor-like kinase ERECTA improves thermotolerance in rice and tomato. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.S.; Shen, J.B.; Shan, J.X.; Qi, P.; Shi, M.; Zhu, M.Z.; Huang, X.H.; Feng, Q.; et al. A two-locus interaction causes interspecific hybrid weakness in rice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Han, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Song, M.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Fu, R.; Luo, Z.; Hu, J.; Liang, W.; et al. Two rice receptor-like kinases maintain male fertility under changing temperatures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12327–12332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Chi, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xie, L.; Huang, F.; Wan, D.; Ni, J.; Yuan, F.; Wu, X.; et al. Hydrogen peroxide sensor HPCA1 is an LRR receptor kinase in Arabidopsis. Nature 2020, 578, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, D.; Wang, C.; He, J.; Liao, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gong, Z. A plasma membrane receptor kinase, GHR1, mediates abscisic acid- and hydrogen peroxide-regulated stomatal movement in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2546–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrzaczek, M.; Vainonen, J.P.; Stael, S.; Tsiatsiani, L.; Help-Rinta-Rahko, H.; Gauthier, A.; Kaufholdt, D.; Bollhoner, B.; Lamminmaki, A.; Staes, A.; et al. GRIM REAPER peptide binds to receptor kinase PRK5 to trigger cell death in Arabidopsis. Embo J. 2015, 34, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yan, J.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, X.; Peng, J. Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)—An Updated Review. Rice 2020, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Q.; Liu, S.Y.; Shuai, Z. Molecular and pathogenic characterization of newXanthomonas oryzaepv.oryzaestrains from the coastline region of Fangchenggang city in China. World J. Microb. Biot. 2013, 29, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Aluko, O.O.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G. MG2C: A user-friendly online tool for drawing genetic maps. Mol. Hortic. 2021, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.T.; Kong, Y.Z.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.H.; Gong, D.P.; Lv, J.; Liu, G. Mapgene2chrom, a tool to draw gene physical map based on perl and svg languages. Hereditas 2015, 37, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
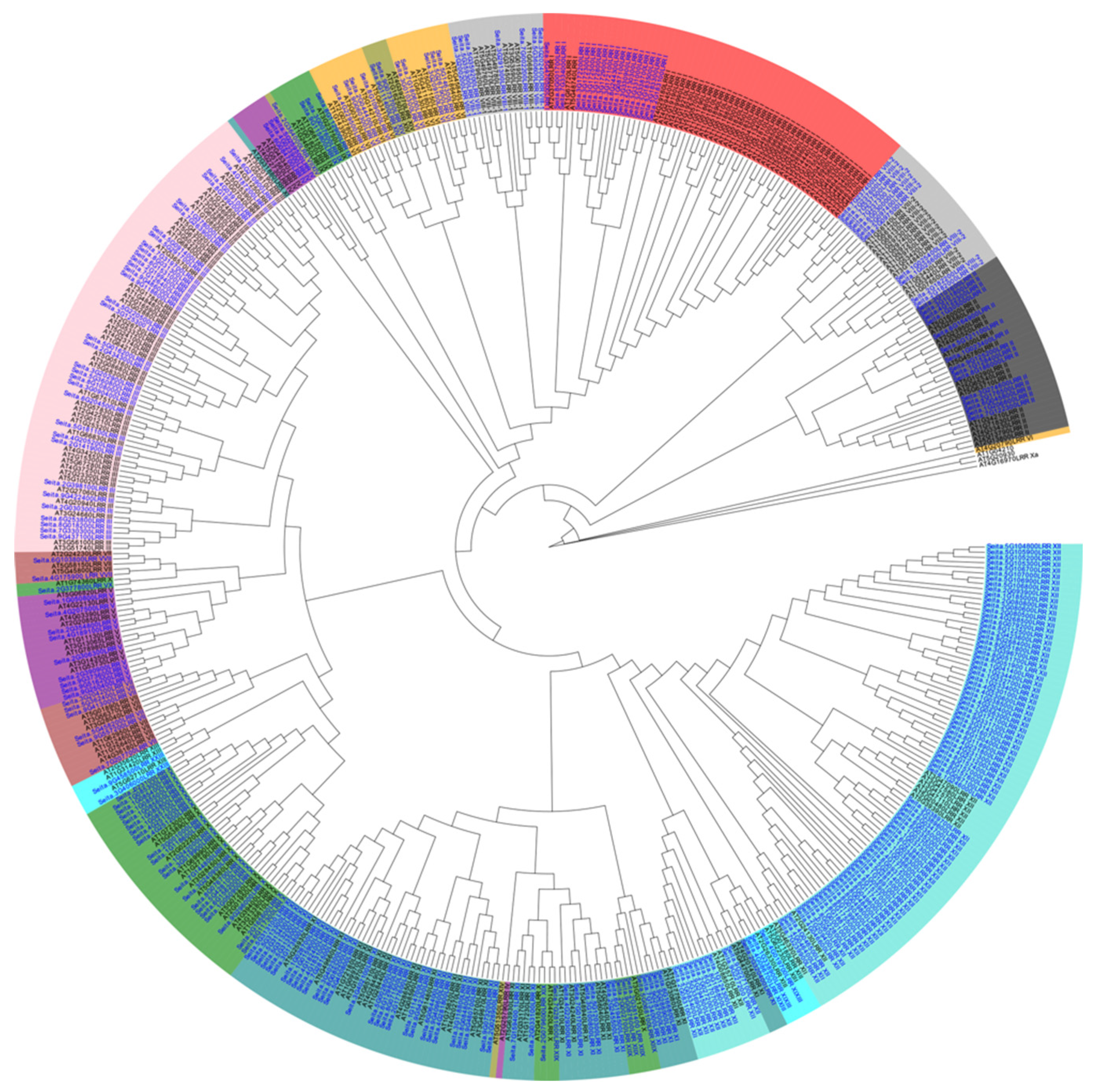
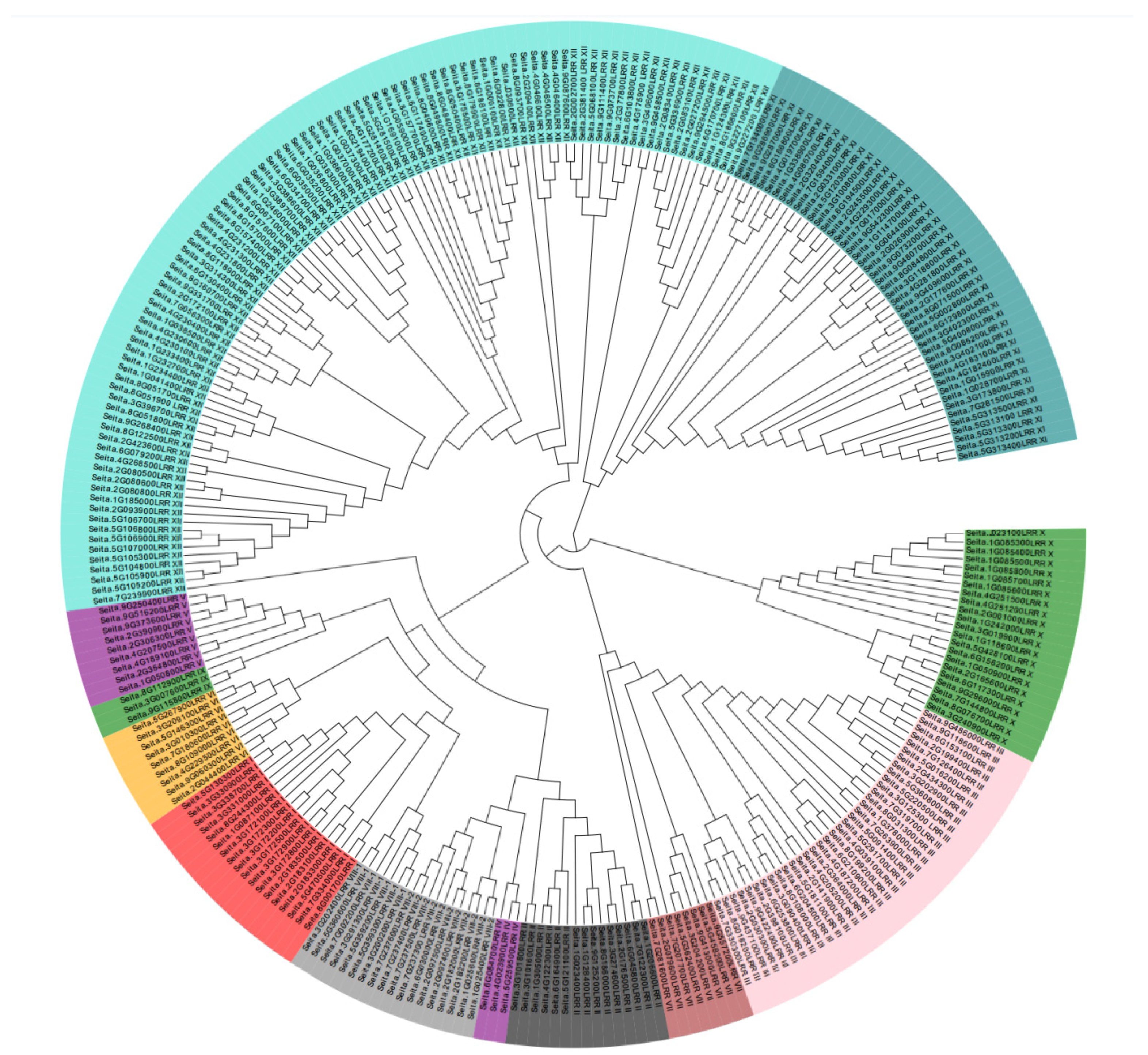
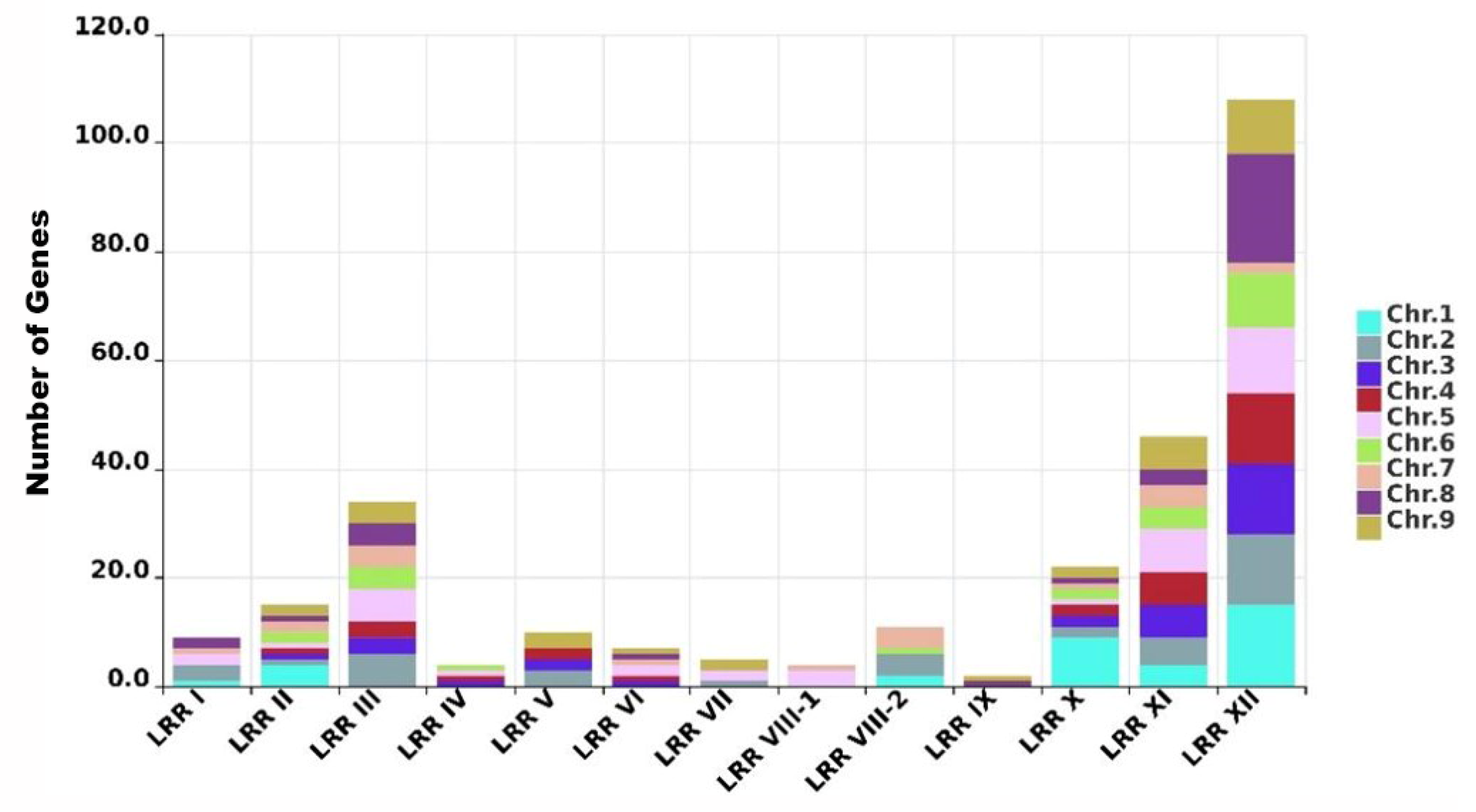

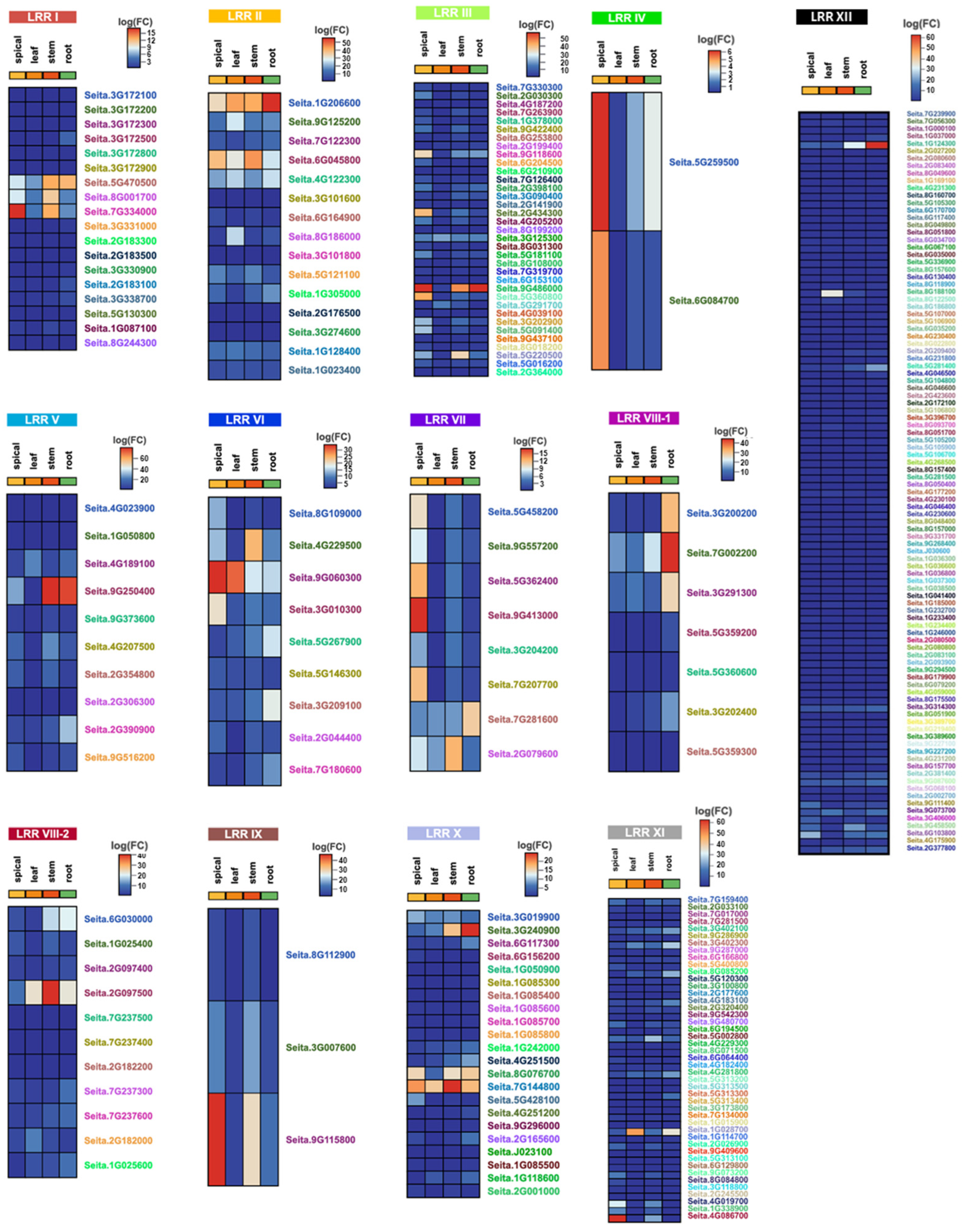
| Chr. | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | VIII | IX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of LRR-RLK genes | 37 | 39 | 34 | 29 | 38 | 24 | 21 | 33 | 28 |
| Number of LRR-RLK genes in the gene cluster | 19 | 21 | 21 | 17 | 22 | 9 | 9 | 13 | 8 |
| Concentration of LRR-RLK genes in the gene cluster (%) | 51.35 | 53.85 | 61.76 | 58.62 | 57.89 | 37.50 | 42.86 | 39.39 | 28.57 |
| Concentration of LRR-RLK genes on the chromosome (%) | 13.07 | 13.78 | 12.01 | 10.25 | 13.43 | 8.48 | 7.42 | 11.66 | 9.89 |
| Gene ID. | Gene Name | Plant Origin | Function | Homologous Genes in Setaria italica |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Os04g0226800 | Xa21 | Oryza sativa | Bacterial recognition and immune response | Seita.7G056300/Seita.7G056900 |
| At5g46330 | FLS2 | Arabidopsis thaliana | PAMP recognition, initiation of immune response (recognizes bacterial flagellin) | Seita.1G161700 Seita.1G169100/Seita.6G071500/Seita.7G239900 |
| At5g20480 | EFR | Arabidopsis thaliana | PAMP recognition, immune response (recognizes bacterial EF-Tu) | Seita.1G227300 Seita.1G233300/Seita.1G233400/Seita.1G234400/Seita.2G016400/Seita.3G354900/Seita.3G389600/Seita.5G106400/Seita.5G107200/Seita.6G117500/Seita.8G051700/Seita.8G157300/Seita.8G157400 |
| At3g21630 | CERK1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Chitin recognition and fungal immunity response | Seita.2G269700/Seita.5G280500/Seita.6G227400 |
| Os03g0133400 | CEBIP(RLP) | Oryza sativa | Chitin oligosaccharide recognition | Seita.9G550700 |
| AT1G21880 | LYM1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Peptidoglycan perception | Seita.1G333700/Seita.2G226100/Seita.4G084200/Seita.9G011000 |
| AT1G77630 | LYM3 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Peptidoglycan perception | Seita.1G333700 |
| Os09g27890 | LYP4 | Oryza sativa | Dual recognition of chitin and peptidoglycan | Seita.2G226100/Seita.5G280500 |
| Os06g10660 | LYP6 | Oryza sativa | Dual recognition of chitin and peptidoglycan | Seita.4G084200 |
| AT5G16000 | NIK1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Antiviral defense signaling | Seita.1G305000/Seita.4G122300/Seita.4G122500 |
| At4g33430 | BAK1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | BR signaling, PAMP-triggered immunity, regulation of cell death | Seita.6G045800/Seita.1G206600/Seita.7G122300/Seita.4G122300 |
| At2g31880 | SOBIR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Involved in immune response, forms complexes with other receptors to perceive PAMPs | Seita.1G207200 Seita.2G076800/Seita.4G126700/Seita.4G126800 |
| EU041719 | LecRLK | Pisum sativum | Pathogen recognition | Seita.9G240100 |
| AT5G16590 | LRR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Defense response regulation | Seita.7G126400/Seita.9G118600/Seita.3G202900/Seita.3G202900 |
| At1g73080 | PEPR1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | DAMP recognition, immune response (recognizes plant endogenous peptides) | Seita.6G166800 Seita.6G167000/Seita.9G287000 |
| Gene ID. | Gene Name | Plant Origin | Function | Homologous Genes in Setaria italica |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT2G26330 | ERECTA | Arabidopsis thaliana | Organ development and patterning regulation | Seita.1G084800/Seita.1G338900/Seita.4G086700/Seita.5G281200 |
| AT3G23130 | FON1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Floral meristem regulation | Seita.1G000900 |
| AT2G38530 | LP2 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Development and defense response | Seita.7G301200/Seita.7G301100/Seita.8G013600/Seita.5G363000/Seita.8G013500/Seita.7G300900/Seita.3G204700 |
| AT1G18390 | LRK10L1.2 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Stress response signaling | Seita.3G157100/Seita.3G157200/Seita.5G093200/Seita.5G093300/Seita.5G093600/Seita.5G093700/Seita.5G093900/Seita.5G094200/Seita.5G095000/Seita.5G095300/Seita.5G277200/Seita.5G277400 |
| Os05g0461600 | SIK1 | Oryza sativa | Abiotic stress response | Seita.3G215600 |
| Os07g0186200 | SIK2 | Oryza sativa | Abiotic stress response | Seita.3G040300/Seita.3G040400/Seita.3G040500/Seita.3G060400/Seita.3G060600 |
| AT3G02880 | KIN7 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Kinase signaling pathway | Seita.9G118600/Seita.7G126400/Seita.7G126400/Seita.5G360800 |
| Os06g0130100 | SLK1 | Oryza sativa | Salt stress response | Seita.4G019700 |
| Os05g0305900 | STLK | Oryza sativa | Salt tolerance signaling | Seita.3G291300 |
| Os02g0640500 | SIT1 | Oryza sativa | Salt stress tolerance | Seita.1G249800 |
| AT3G51550 | FER | Arabidopsis thaliana | Growth and stress response regulation | Seita.3G288700/Seita.3G289000/Seita.7G215600/Seita.8G153000/Seita.9G381900/Seita.9G382300/Seita.9G382400/Seita.9G382500/Seita.9G382700/Seita.9G414400 |
| BAF16049.1 | RMC | Oryza sativa | Root growth regulation | Seita.9G250400/Seita.9G516200/Seita.2G390900 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Kang, X.; Song, M.; Dong, X.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, G.; Diao, X.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Prediction of LRR-RLK Family Genes in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) in Response to Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104576
Li Z, Kang X, Song M, Dong X, Ma J, Yu J, Li X, Zheng Y, Sun G, Diao X, et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Prediction of LRR-RLK Family Genes in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) in Response to Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104576
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhijiang, Xinmiao Kang, Miaomiao Song, Xiaojie Dong, Jinfeng Ma, Jinhai Yu, Xiangyu Li, Yalu Zheng, Guangquan Sun, Xianmin Diao, and et al. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Prediction of LRR-RLK Family Genes in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) in Response to Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104576
APA StyleLi, Z., Kang, X., Song, M., Dong, X., Ma, J., Yu, J., Li, X., Zheng, Y., Sun, G., Diao, X., & Liu, X. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Prediction of LRR-RLK Family Genes in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) in Response to Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4576. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104576





