Conventional and Tropism-Modified High-Capacity Adenoviral Vectors Exhibit Similar Transduction Profiles in Human iPSC-Derived Retinal Organoids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
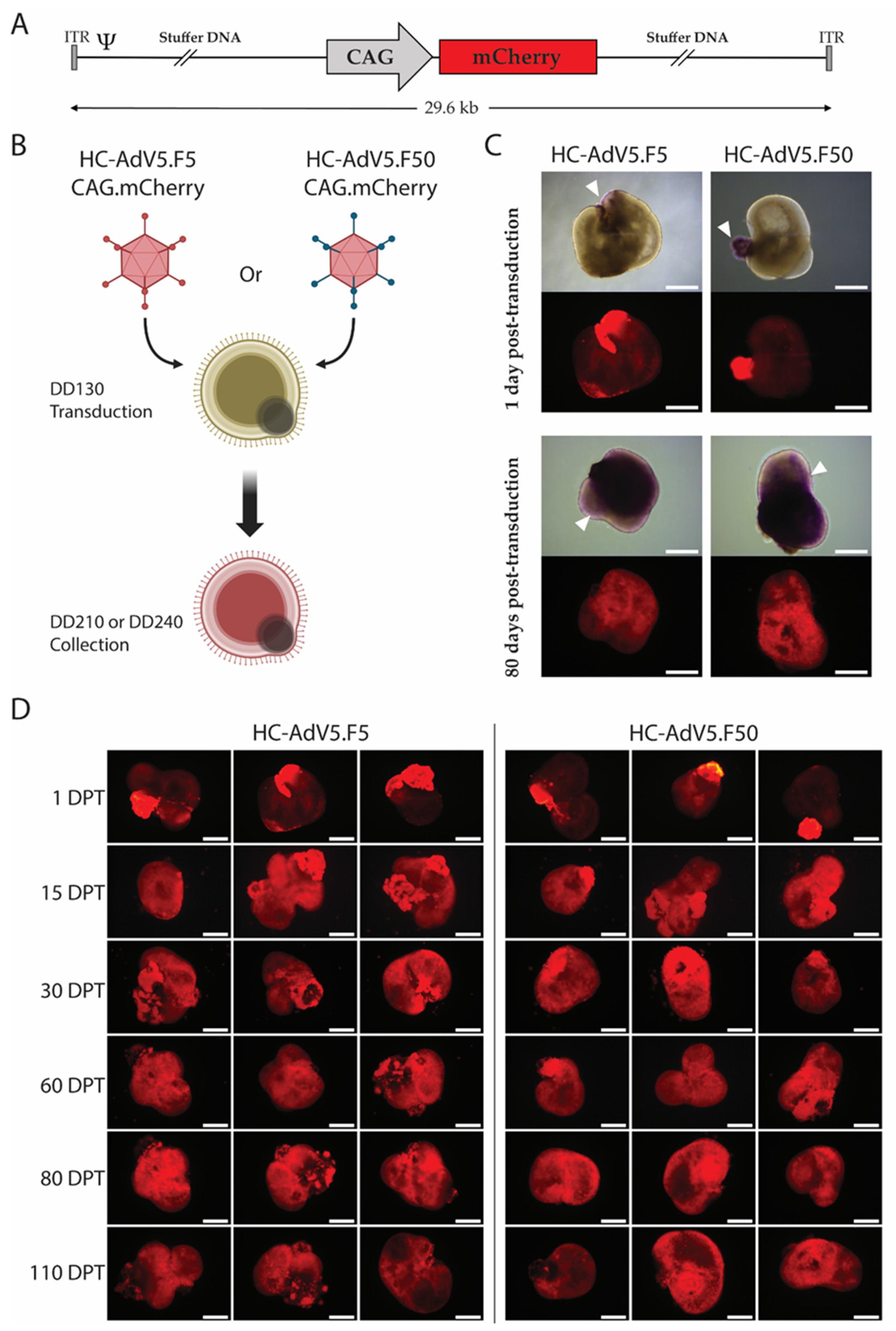
2.1. Adenoviral Vector Transduction of Retinal Organoids
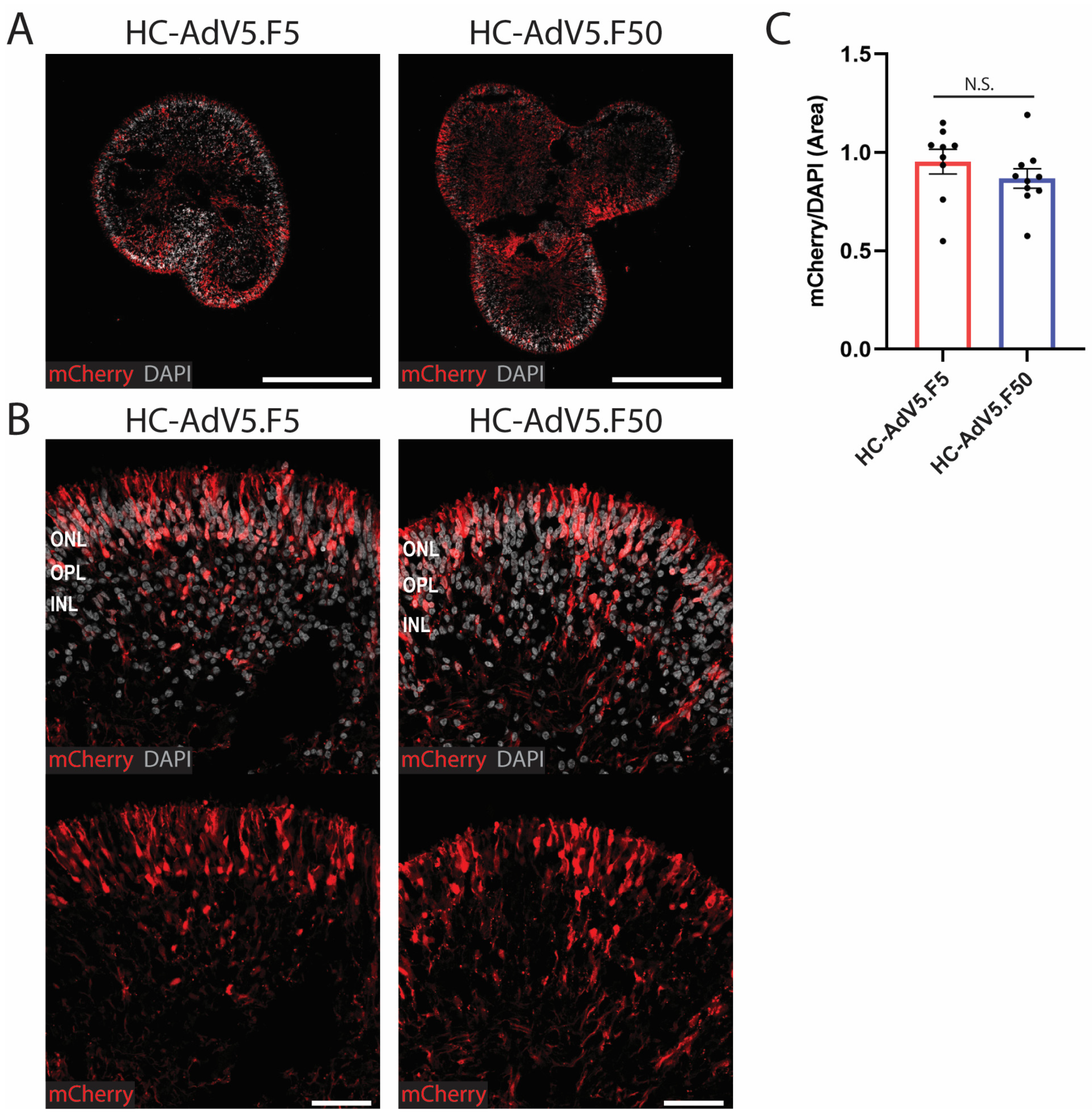
2.2. Transduction Efficiency of Adenoviral Vectors in Human Retinal Organoids
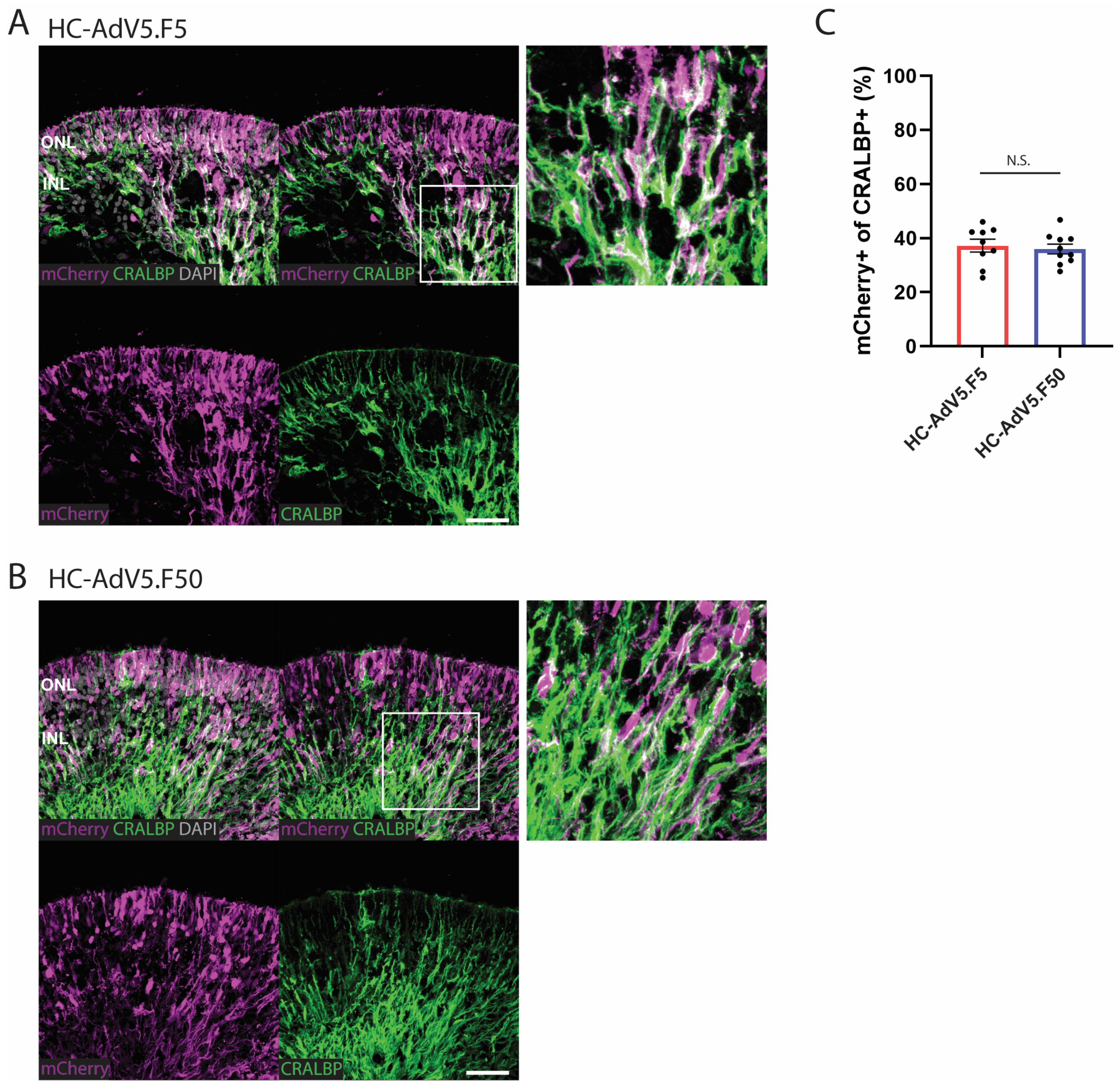
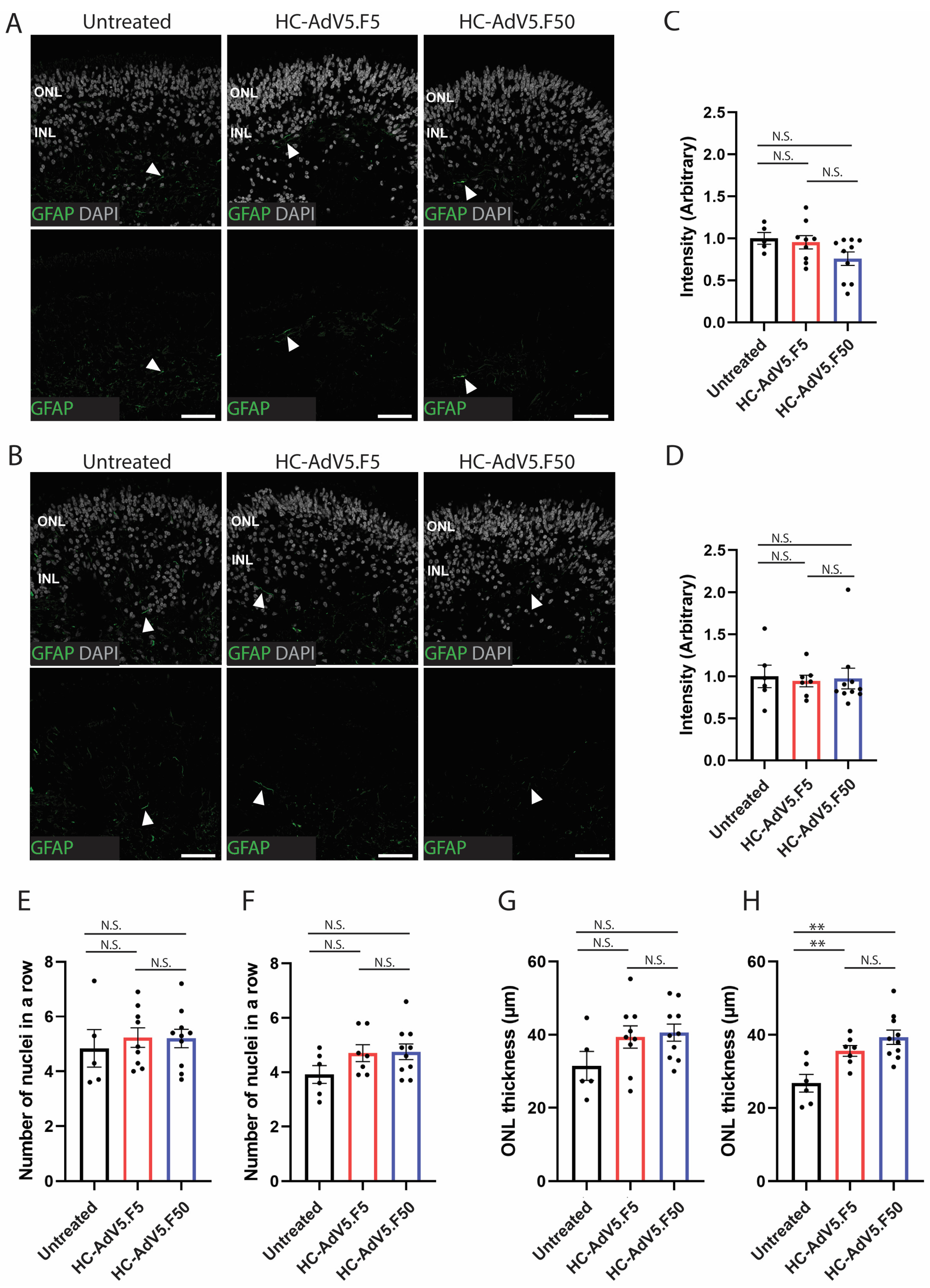
2.3. Adenoviral Vector Transduction of Müller Glial Cells
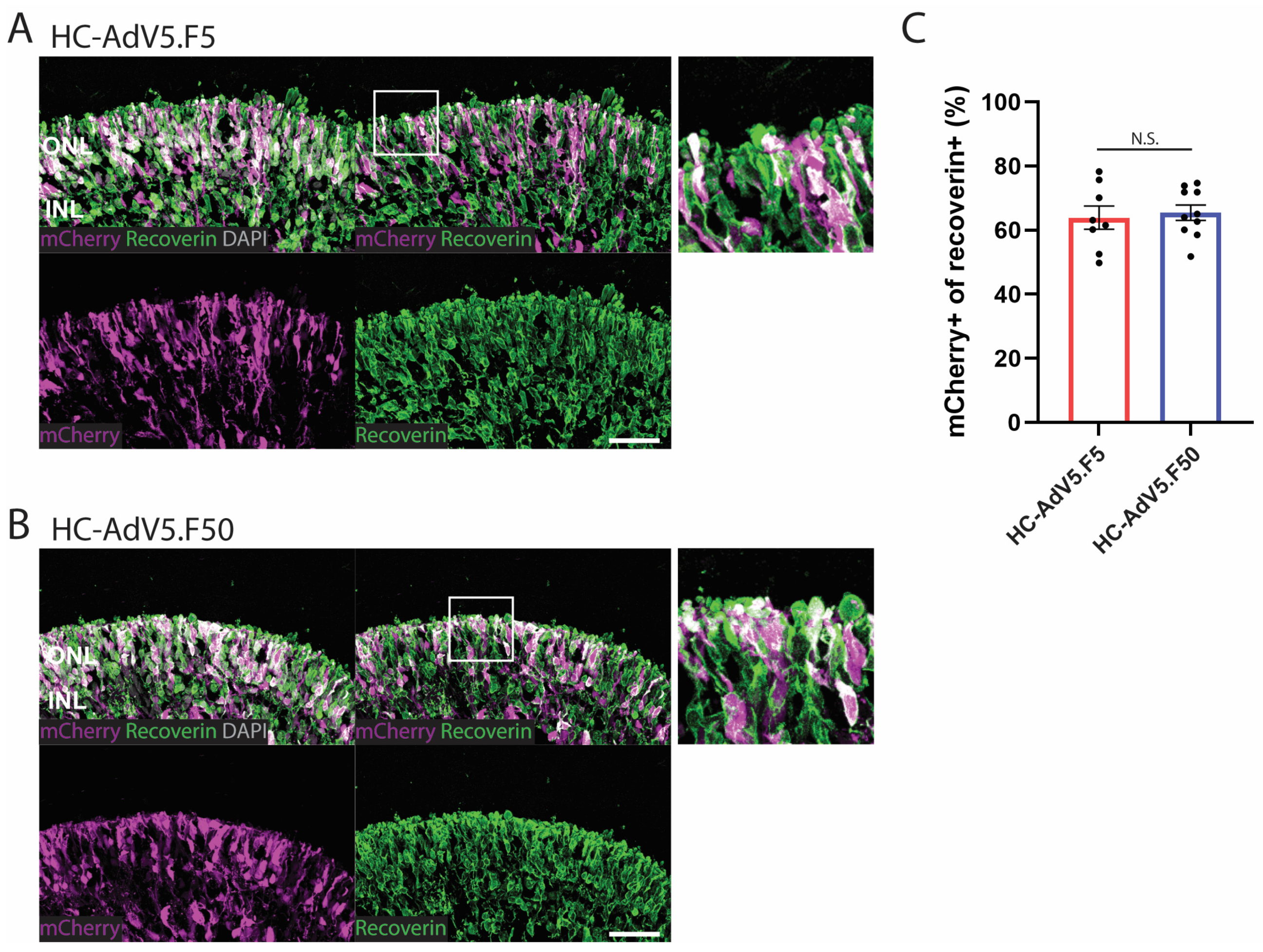
2.4. Adenoviral Vector Transduction of Photoreceptors
2.5. Increased ONL Thickness Following Adenoviral Vector Transduction
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. iPSC Culture
4.2. Retinal Organoid Differentiation
4.3. Production and Titration of Adenoviral Vectors
4.4. Adenoviral Vector Transduction of Human iPSC-Derived Retinal Organoids
4.5. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.6. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, P. Treatment to cure: Advancing AAV gene therapy manufacture. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, T.M.; Wijnholds, J. Recombinant Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors (rAAV)-Vector Elements in Ocular Gene Therapy Clinical Trials and Transgene Expression and Bioactivity Assays. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-H.; Gessler, D.J.; Zhan, W.; Gallagher, T.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus as a delivery vector for gene therapy of human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, A.; Wijnholds, J. Retinal Ciliopathies and Potential Gene Therapies: A Focus on Human iPSC-Derived Organoid Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, C.; Gonçalves, M.A.F.V.; Wijnholds, J. Novel Therapeutic Approaches for the Treatment of Retinal Degenerative Diseases: Focus on CRISPR/Cas-Based Gene Editing. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, M.A.F.V.; de Vries, A.A.F. Adenovirus: From foe to friend. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasca, F.; Brescia, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Janssen, J.M.; Szuhai, K.; Gonçalves, M.A.F.V. Large-scale genome editing based on high-capacity adenovectors and CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases rescues full-length dystrophin synthesis in DMD muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 7761–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brescia, M.; Janssen, J.M.; Liu, J.; Gonçalves, M.A.F.V. High-Capacity Adenoviral Vectors Permit Robust and Versatile Testing of DMD Gene Repair Tools and Strategies in Human Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricobaraza, A.; Gonzalez-Aparicio, M.; Mora-Jimenez, L.; Lumbreras, S.; Hernandez-Alcoceba, R. High-Capacity Adenoviral Vectors: Expanding the Scope of Gene Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, V.S.; Nemerow, G.R. Structures and organization of adenovirus cement proteins provide insights into the role of capsid maturation in virus entry and infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, L.H.; Bell, P.; Cearley, C.N.; Xiao, R.; Calcedo, R.; Wang, L.; Castle, M.J.; Maguire, A.C.; Grant, R.; Wolfe, J.H.; et al. Dosage thresholds for AAV2 and AAV8 photoreceptor gene therapy in monkey. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 88ra54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, A.; Marrocco, E.; Puppo, A.; Cesi, G.; Sommella, A.; Della Corte, M.; Rossi, S.; Giunti, M.; Craft, C.M.; Bacci, M.L.; et al. Combined rod and cone transduction by adeno-associated virus 2/8. Hum. Gene Ther. 2013, 24, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Gutierrez, C.; Xue, T.; Hampton, C.; Vergara, M.N.; Cao, L.-H.; Peters, A.; Park, T.S.; Zambidis, E.T.; Meyer, J.S.; et al. Generation of three-dimensional retinal tissue with functional photoreceptors from human iPSCs. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlin, K.J.; Maruotti, J.A.; Sripathi, S.R.; Ball, J.; Angueyra, J.M.; Kim, C.; Grebe, R.; Li, W.; Jones, B.W.; Zack, D.J. Photoreceptor Outer Segment-like Structures in Long-Term 3D Retinas from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.A.; Holkers, M.; Cudré-Mauroux, C.; van Nierop, G.P.; Knaän-Shanzer, S.; van der Velde, I.; Valerio, D.; de Vries, A.A. Transduction of myogenic cells by retargeted dual high-capacity hybrid viral vectors: Robust dystrophin synthesis in duchenne muscular dystrophy muscle cells. Mol. Ther. 2006, 13, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggar, A.; Shayakhmetov, D.M.; Lieber, A. CD46 is a cellular receptor for group B adenoviruses. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1408–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.K.; Rolling, F.; Baker, E.; Rakoczy, P.E. Kinetics of efficient recombinant adeno-associated virus transduction in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2001, 267, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevany, B.M.; Palczewski, K. Phagocytosis of retinal rod and cone photoreceptors. Physiology 2010, 25, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, A.M.; Russell, S.; Wellman, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Yu, Z.-F.; Tillman, A.; Wittes, J.; Pappas, J.; Elci, O.; Marshall, K.A.; et al. Efficacy, Safety, and Durability of Voretigene Neparvovec-rzyl in RPE65 Mutation–Associated Inherited Retinal Dystrophy: Results of Phase 1 and 3 Trials. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Punzo, C. Update on Viral Gene Therapy Clinical Trials for Retinal Diseases. Hum. Gene Ther. 2022, 33, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasca, F.; Wang, Q.; Gonçalves, M.A. Adenoviral Vectors Meet Gene Editing: A Rising Partnership for the Genomic Engineering of Human Stem Cells and Their Progeny. Cells 2020, 9, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.C.; Burnight, E.R.; Ulferts, M.J.; Worthington, K.S.; Russell, S.R.; Sohn, E.H.; Mullins, R.F.; Stone, E.M.; Tucker, B.A.; Wiley, L.A. Helper-Dependent Adenovirus Transduces the Human and Rat Retina but Elicits an Inflammatory Reaction When Delivered Subretinally in Rats. Hum. Gene Ther. 2019, 30, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.; Cao, H.; Wu, J.; Duan, R.; Hu, J. Highly efficient retinal gene delivery with helper-dependent adenoviral vectors. Genes Dis. 2014, 1, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puppo, A.; Cesi, G.; Marrocco, E.; Piccolo, P.; Jacca, S.; Shayakhmetov, D.M.; Parks, R.J.; Davidson, B.L.; Colloca, S.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; et al. Retinal transduction profiles by high-capacity viral vectors. Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, M.P.; Cerullo, V.; Lee, B. Immune response to helper dependent adenoviral mediated liver gene therapy: Challenges and prospects. Curr. Gene Ther. 2007, 7, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruve, D.A.; Cotter, M.J.; Zaiss, A.K.; White, L.R.; Liu, Q.; Chan, T.; Clark, S.A.; Ross, P.J.; Meulenbroek, R.A.; Maelandsmo, G.M.; et al. Helper-dependent adenovirus vectors Elicit intact innate but attenuated adaptive host immune responses in vivo. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5966–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayakhmetov, D.M.; Papayannopoulou, T.; Stamatoyannopoulos, G.; Lieber, A. Efficient gene transfer into human CD34 + cells by a retargeted adenovirus vector. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2567–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaän-Shanzer, S.; Van Der Velde, I.; Havenga, M.J.; Lemckert, A.A.; De Vries, A.A.; Valerio, D. Highly efficient targeted transduction of undifferentiated human hematopoietic cells by adenoviral vectors displaying fiber knobs of subgroup B. Hum. Gene Ther. 2001, 12, 1989–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knaän-Shanzer, S.; van de Watering, M.J.; van der Velde, I.; Gonçalves, M.A.; Valerio, D.; de Vries, A.A. Endowing human adenovirus serotype 5 vectors with fiber domains of species B greatly enhances gene transfer into human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell. 2005, 23, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, N.; Lu, X.; Andriessen, C.A.; Moustakas, I.; Buck, T.M.; Freund, C.; Arendzen, C.H.; Böhringer, S.; Boon, C.J.; Mei, H.; et al. AAV-mediated gene augmentation therapy of CRB1 patient-derived retinal organoids restores the histological and transcriptional retinal phenotype. Stem Cell Rep. 2023, 18, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnis, J.F.; Stepanik, P.L.; Jariangprasert, S.; Lerious, V. Functional significance of recoverin localization in multiple retina cell types. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 50, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, A.; Iandiev, I.; Pannicke, T.; Wurm, A.; Hollborn, M.; Wiedemann, P.; Osborne, N.N.; Reichenbach, A. Cellular signaling and factors involved in Müller cell gliosis: Neuroprotective and detrimental effects. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2009, 28, 423–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemiakina, I.; Ermakova, G.; Cranfill, P.; Baird, M.; Evans, R.; Souslova, E.; Staroverov, D.; Gorokhovatsky, A.; Putintseva, E.; Gorodnicheva, T.; et al. A monomeric red fluorescent protein with low cytotoxicity. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-González, L.; Velasco, S.; Campillo, I.; Rodrigo, R. Retinal Inflammation, Cell Death and Inherited Retinal Dystrophies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerullo, V.; Diaconu, I.; Romano, V.; Hirvinen, M.; Ugolini, M.; Escutenaire, S.; Holm, S.-L.; Kipar, A.; Kanerva, A.; Hemminki, A. An oncolytic adenovirus enhanced for toll-like receptor 9 stimulation increases antitumor immune responses and tumor clearance. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Shamsuddin, N. Retinal muller glia initiate innate response to infectious stimuli via toll-like receptor signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coroadinha, A.S. Host Cell Restriction Factors Blocking Efficient Vector Transduction: Challenges in Lentiviral and Adeno-Associated Vector Based Gene Therapies. Cells 2023, 12, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, W. Innate Immune Response to Viral Vectors in Gene Therapy. Viruses 2023, 15, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissier, L.P.; Hoek, R.M.; Vos, R.M.; Aartsen, W.M.; Klimczak, R.R.; A Hoyng, S.; Flannery, J.G.; Wijnholds, J. Specific tools for targeting and expression in Müller glial cells. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014, 1, 14009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Janssen, J.M.; Tasca, F.; Mei, H.; Gonçalves, M.A.F.V. Broadening the reach and investigating the potential of prime editors through fully viral gene-deleted adenoviral vector delivery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 11986–12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapani, I.; Tornabene, P.; Auricchio, A. Large gene delivery to the retina with AAV vectors: Are we there yet? Gene Ther. 2020, 28, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedmayr, L.M.; Hinrichsmeyer, K.S.; Thalhammer, S.B.; Mittas, D.M.; Karguth, N.; Otify, D.Y.; Böhm, S.; Weber, V.J.; Bartoschek, M.D.; Splith, V.; et al. mRNA trans-splicing dual AAV vectors for (epi)genome editing and gene therapy. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindley, S.R.; Subbaiah, K.C.V.; Priyanka, F.; Poosala, P.; Ma, Y.; Jalinous, L.; West, J.A.; Richardson, W.A.; Thomas, T.N.; Anderson, D.M. Ribozyme-activated mRNA trans-ligation enables large gene delivery to treat muscular dystrophies. Science 2024, 386, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.; Rhee, K.-D.; Staudt, R.J.; Thompson, J.M.; Hsu, Y.; Hassan, S.; Drack, A.V.; Seo, S. Delivering large genes using adeno-associated virus and the CRE-lox DNA recombination system. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2024, 33, 2094–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, P.M.; Buck, T.M.; Mulder, A.A.; Ohonin, C.; Alves, C.H.; Vos, R.M.; Bialecka, M.; van Herwaarden, T.; van Dijk, E.H.; Talib, M.; et al. Human iPSC-Derived Retinas Recapitulate the Fetal CRB1 CRB2 Complex Formation and Demonstrate that Photoreceptors and Müller Glia Are Targets of AAV5. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 906–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.M.; Liu, J.; Skokan, J.; Gonçalves, M.A.F.V.; de Vries, A.A.F. Development of an AdEasy-based system to produce first- and second-generation adenoviral vectors with tropism for CAR- or CD46-positive cells. J. Gene Med. 2013, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Capelletti, S.; Liu, J.; Janssen, J.M.; Gonçalves, M.A.F.V. Selection-free precise gene repair using high-capacity adenovector delivery of advanced prime editing systems rescues dystrophin synthesis in DMD muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 2740–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallaux, F.J.; Bout, A.; van der Velde, I.; van den Wollenberg, D.J.; Hehir, K.M.; Keegan, J.; Auger, C.; Cramer, S.J.; van Ormondt, H.; van der Eb, A.J.; et al. New helper cells and matched early region 1-deleted adenovirus vectors prevent generation of replication-competent adenoviruses. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McDonald, A.; Gallego, C.; Andriessen, C.; Orlová, M.; Gonçalves, M.A.F.V.; Wijnholds, J. Conventional and Tropism-Modified High-Capacity Adenoviral Vectors Exhibit Similar Transduction Profiles in Human iPSC-Derived Retinal Organoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010055
McDonald A, Gallego C, Andriessen C, Orlová M, Gonçalves MAFV, Wijnholds J. Conventional and Tropism-Modified High-Capacity Adenoviral Vectors Exhibit Similar Transduction Profiles in Human iPSC-Derived Retinal Organoids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010055
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcDonald, Andrew, Carmen Gallego, Charlotte Andriessen, Michaela Orlová, Manuel A. F. V. Gonçalves, and Jan Wijnholds. 2025. "Conventional and Tropism-Modified High-Capacity Adenoviral Vectors Exhibit Similar Transduction Profiles in Human iPSC-Derived Retinal Organoids" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010055
APA StyleMcDonald, A., Gallego, C., Andriessen, C., Orlová, M., Gonçalves, M. A. F. V., & Wijnholds, J. (2025). Conventional and Tropism-Modified High-Capacity Adenoviral Vectors Exhibit Similar Transduction Profiles in Human iPSC-Derived Retinal Organoids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010055






