Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Against Chronic Hypobaric Hypoxia-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Inhibiting CaMKII Activation in a Mouse Model Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
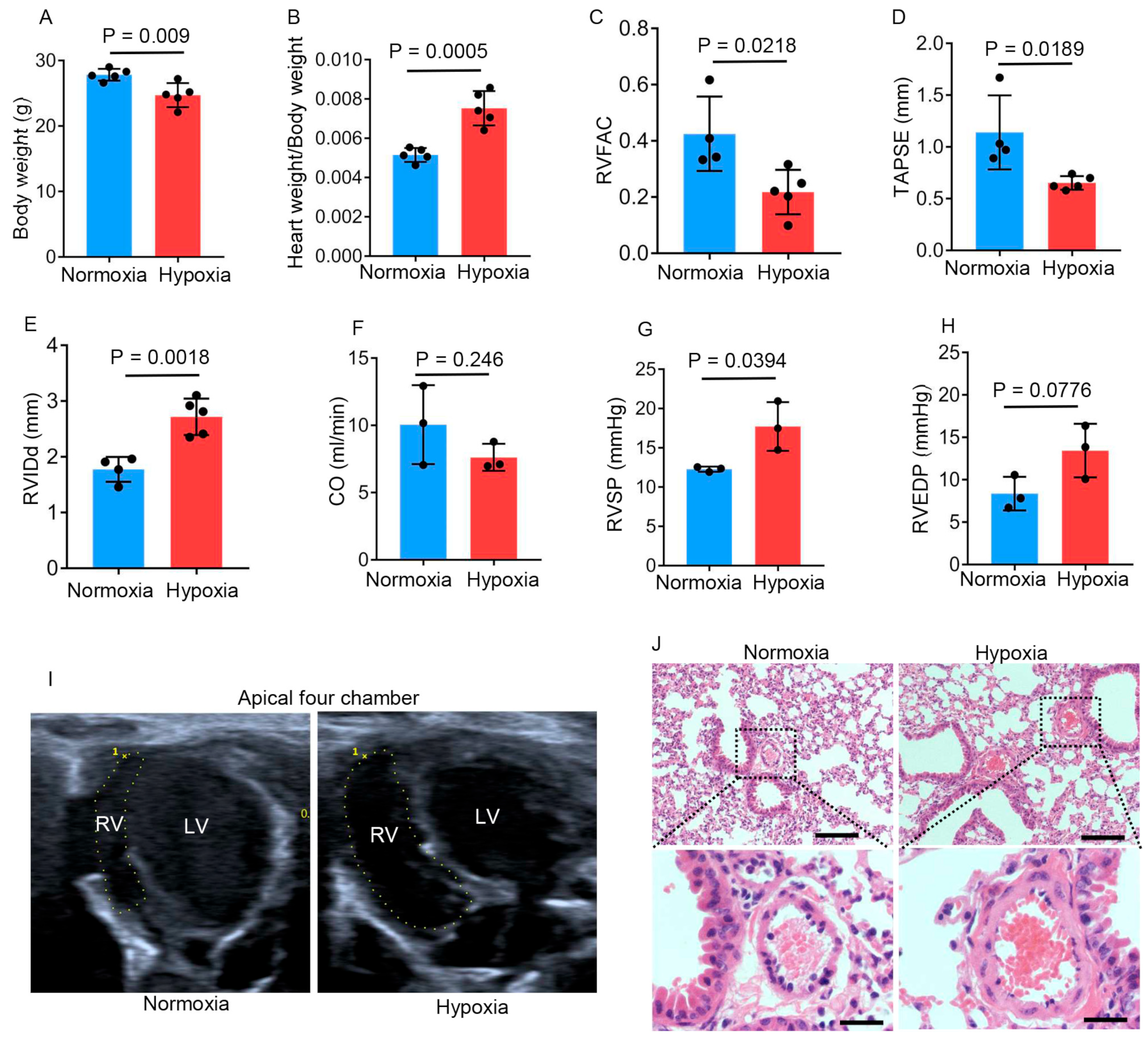
2.1. Chronic Hypobaric Hypoxia Impairs Right Ventricular Function
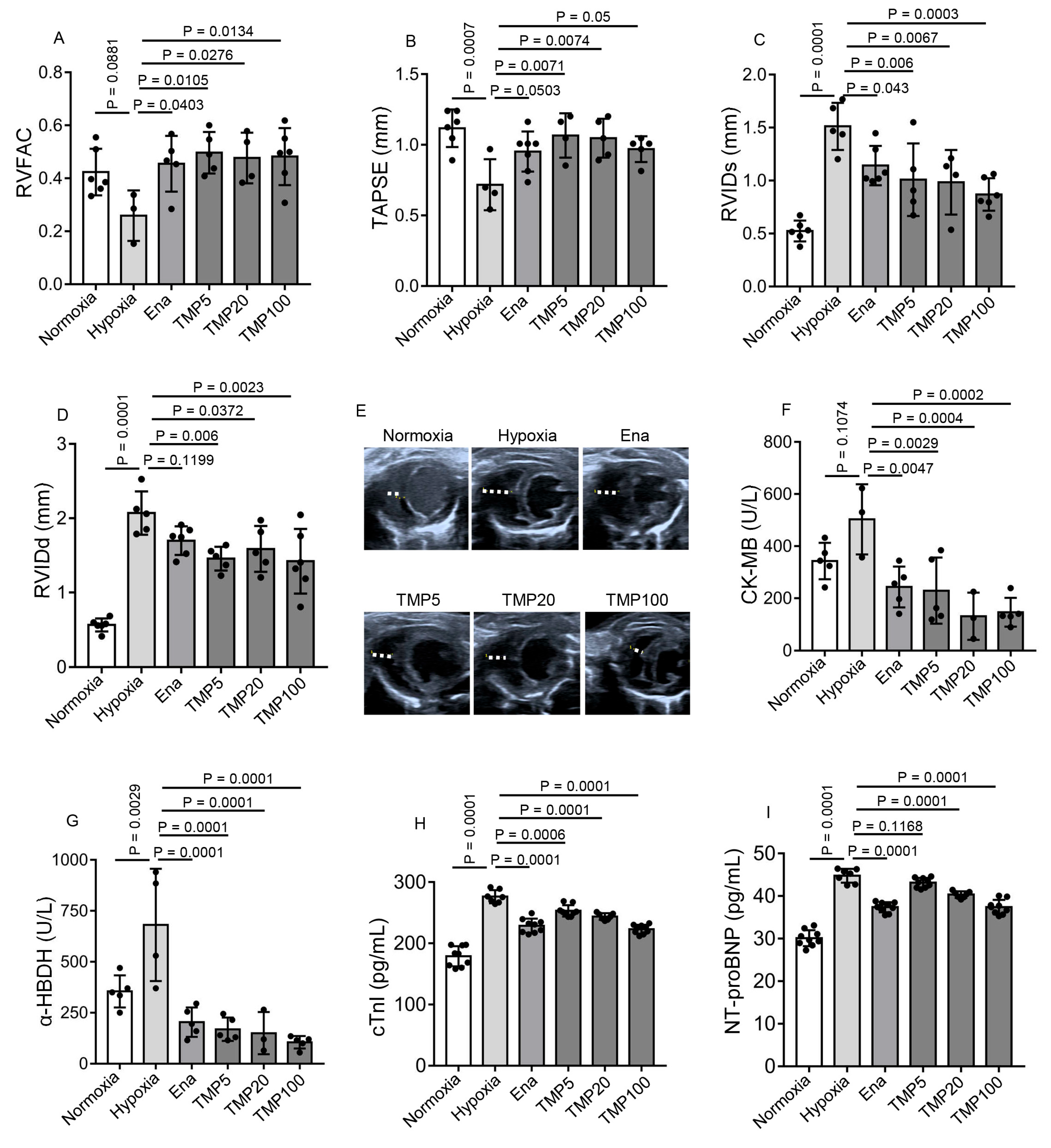
2.2. TMP Improves Cardiac Function and Alleviates Myocardial Injury in Hypobaric Hypoxic Mice
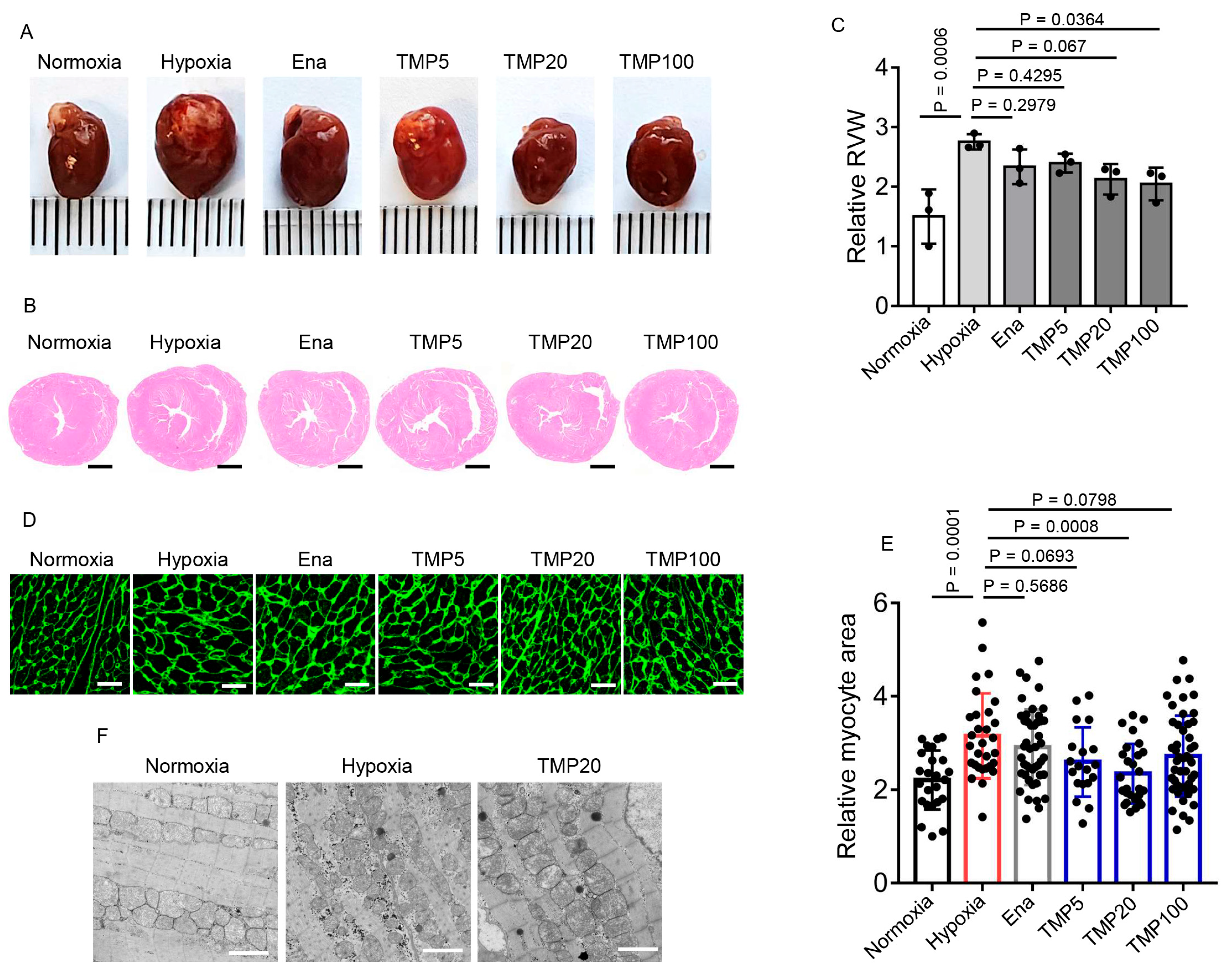
2.3. TMP Alleviates Hypobaric Hypoxia-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy
2.4. TMP Enhances Myocardial Contraction
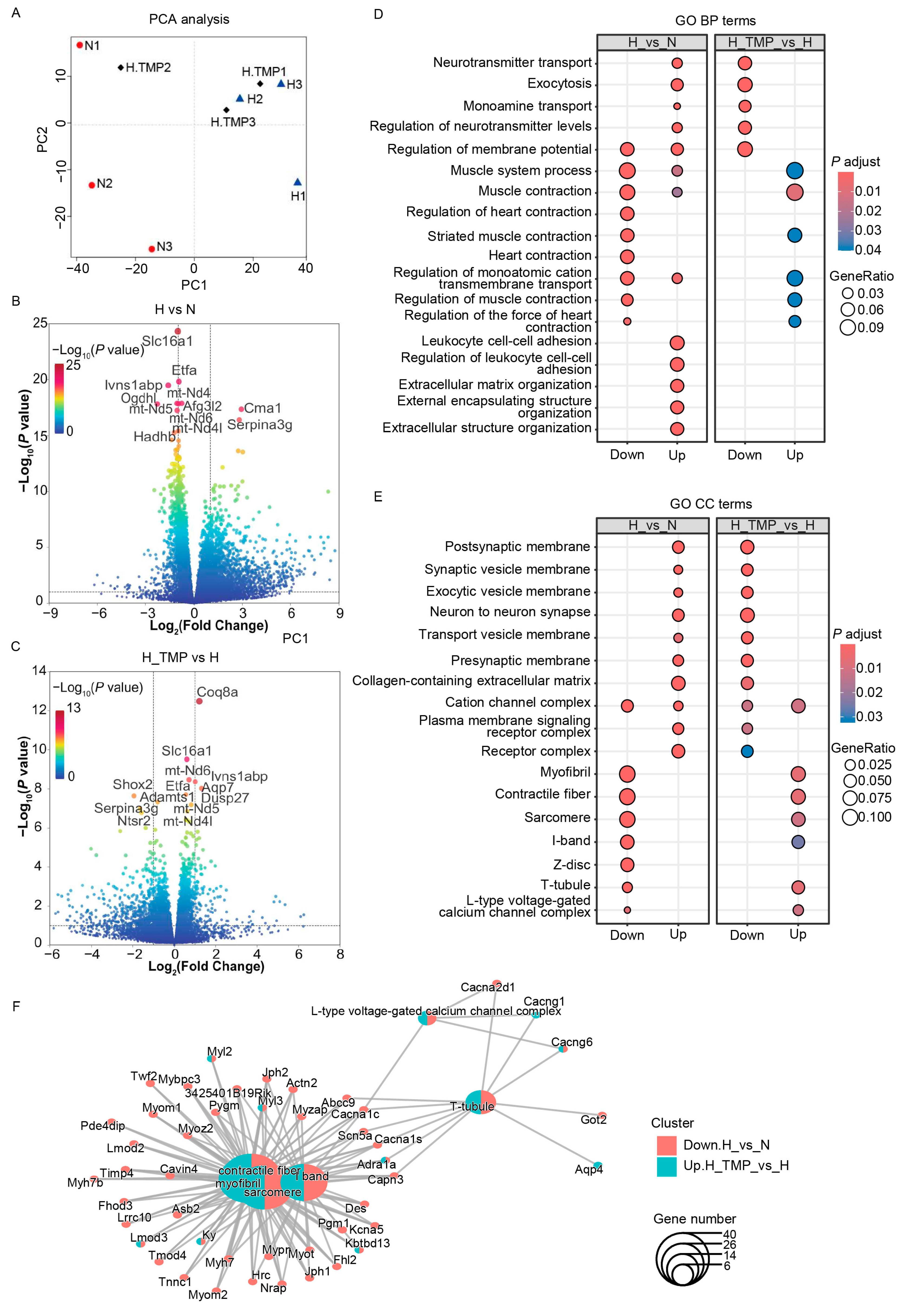
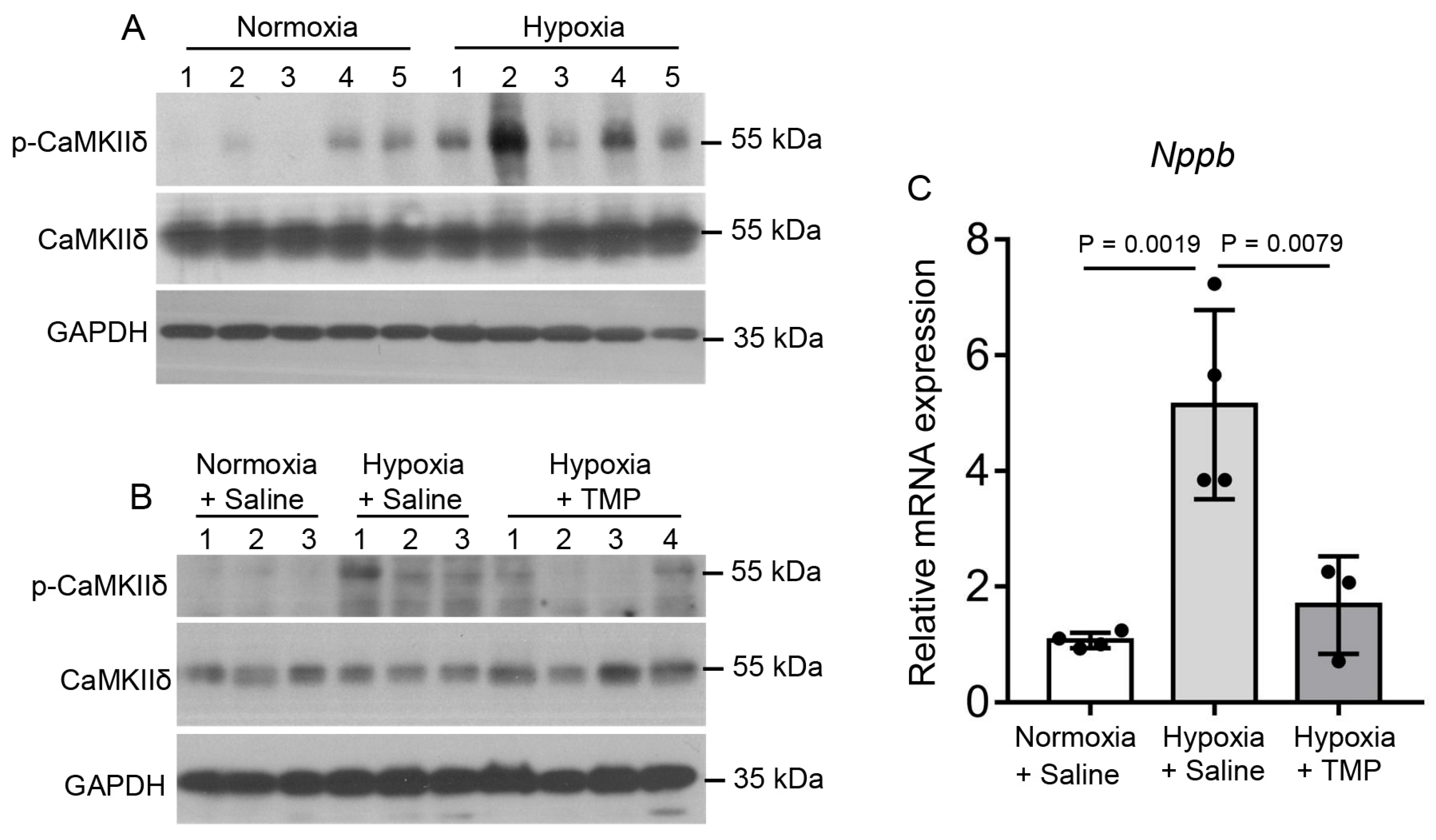
2.5. TMP Inhibits Hypobaric Hypoxia-Induced CaMKII Activation in Mouse Heart
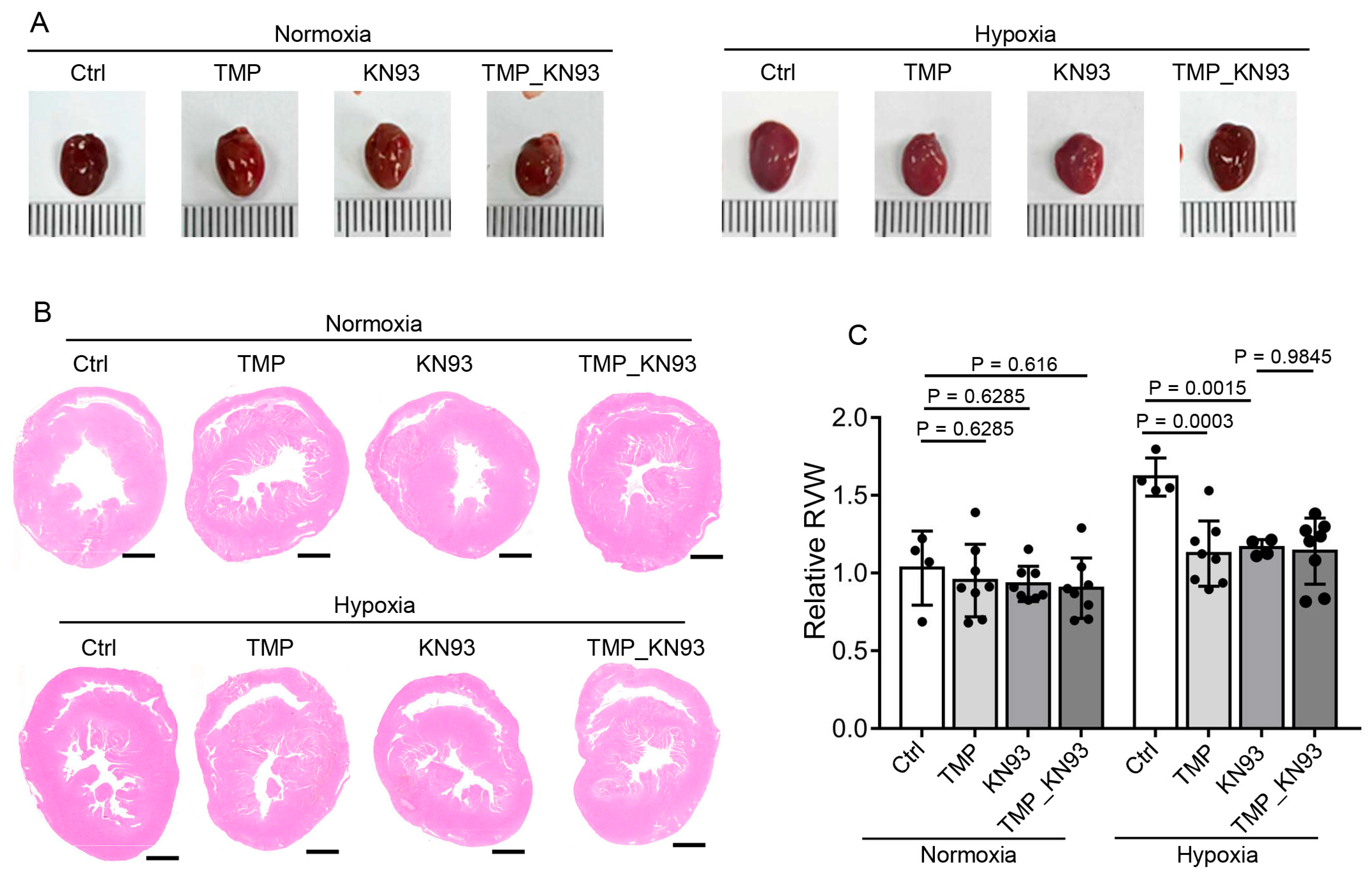
2.6. TMP Improves Cardiac Function Through Inhibiting CaMKII Activation in Hypobaric Hypoxic Mice
2.7. TMP Alleviates Cardiac Hypertrophy Through Inhibiting CaMKII Activation in Hypobaric Hypoxic Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Echocardiography
4.3. Hemodynamic Measurements
4.4. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
4.5. Measurement of Myocardial Injury Markers
4.6. Histology
4.7. Wheat Germ Agglutinin (WGA) Analyses
4.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.9. Western Blots
4.10. Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davies, S.W.; Wedzicha, J.A. Hypoxia and the heart. Br. Heart J. 1993, 69, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fukuda, T.; Maegawa, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Komatsu, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Nagai, R.; Kawahara, T. Effects of acute hypoxia at moderate altitude on stroke volume and cardiac output during exercise. Int. Heart J. 2010, 51, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Richalet, J.P.; Hermand, E.; Lhuissier, F.J. Cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology at high altitude. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2024, 21, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, C.J.; Montgomery, H.E.; Murray, A.J.; Cochlin, L.E.; Codreanu, I.; Hopwood, N.; Johnson, A.W.; Rider, O.J.; Levett, D.Z.; Tyler, D.J.; et al. Cardiac response to hypobaric hypoxia: Persistent changes in cardiac mass, function, and energy metabolism after a trek to Mt. Everest Base Camp. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, E.; Brito, J.; El Alam, S.; Siques, P. Oxidative Stress, Kinase Activity and Inflammatory Implications in Right Ventricular Hypertrophy and Heart Failure under Hypobaric Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, D.A.; Frise, M.C.; Bakker-Dyos, J.; Boos, C.; Dorrington, K.L.; Woods, D.; Mellor, A.; Robbins, P.A. Iron bioavailability and cardiopulmonary function during ascent to very high altitude. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 1902285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huez, S.; Faoro, V.; Guenard, H.; Martinot, J.B.; Naeije, R. Echocardiographic and tissue Doppler imaging of cardiac adaptation to high altitude in native highlanders versus acclimatized lowlanders. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 103, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alam, S.; Pena, E.; Aguilera, D.; Siques, P.; Brito, J. Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension and Edema Induced by Hypobaric Hypoxia Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostadal, B.; Kolar, F. Cardiac adaptation to chronic high-altitude hypoxia: Beneficial and adverse effects. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2007, 158, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, J.; Siques, P.; Leon-Velarde, F.; De La Cruz, J.J.; Lopez, V.; Herruzo, R. Chronic intermittent hypoxia at high altitude exposure for over 12 years: Assessment of hematological, cardiovascular, and renal effects. High. Alt. Med. Biol. 2007, 8, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, S.J.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.X.; Qin, X.H. Ligustrazine Attenuates Hyperhomocysteinemia-induced Alzheimer-like Pathologies in Rats. Curr. Med. Sci. 2021, 41, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Xu, D.Q.; Yue, S.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Tang, Y.P. Neuroprotection by tetramethylpyrazine and its synthesized analogues for central nervous system diseases: A review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Zuo, P.F.; Sheng, Z.L.; Wang, X.; Ding, J.D.; Ma, G.S. Tetramethylprazine attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through modulation of autophagy. Life Sci. 2019, 239, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.F.; Shi, C.G.; Sun, M.Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.X.; Wang, H.F.; Xu, Z.Q.; Chen, D.M. Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates atherosclerosis development and protects endothelial cells from ox-LDL. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2013, 27, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Liu, R.P.; Ding, M.N.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, J.Z.; Xue, X.Y.; Gu, Y.Q.; Ma, B.N.; Cai, Y.J.; Li, S.; et al. Tetramethylpyrazine prevents liver fibrotic injury in mice by targeting hepatocyte-derived and mitochondrial DNA-enriched extracellular vesicles. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2026–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.H.; Kuo, W.W.; Jiang, A.Z.; Pai, P.; Lin, J.Y.; Chen, W.K.; Day, C.H.; Shen, C.Y.; Padma, V.V.; Huang, C.Y. Tetramethylpyrazine Ameliorated Hypoxia-Induced Myocardial Cell Apoptosis via HIF-1alpha/JNK/p38 and IGFBP3/BNIP3 Inhibition to Upregulate PI3K/Akt Survival Signaling. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhong, F.M.; Yao, Y.; Deng, S.Q.; Xu, H.Q.; Lu, J.F.; Ruan, M.; Shen, X.C. Synergistic protection of tetramethylpyrazine phosphate and borneol on brain microvascular endothelium cells injured by hypoxia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 2168–2180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoelz, A.; Nairn, A.C.; Kuriyan, J. Crystal structure of a tetradecameric assembly of the association domain of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, P.D.; Purohit, A.; Hund, T.J.; Anderson, M.E. Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: Linking heart failure and arrhythmias. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 1661–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Zhang, T.; Pereira, L.; Means, C.K.; Cheng, H.; Gu, Y.; Dalton, N.D.; Peterson, K.L.; Chen, J.; Bers, D.; et al. Requirement for Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II in the transition from pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy to heart failure in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Maier, L.S.; Dalton, N.D.; Miyamoto, S.; Ross, J., Jr.; Bers, D.M.; Brown, J.H. The deltaC isoform of CaMKII is activated in cardiac hypertrophy and induces dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, F.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Shang, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. CaMKII is a RIP3 substrate mediating ischemia- and oxidative stress-induced myocardial necroptosis. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joiner, M.L.; Koval, O.M.; Li, J.; He, B.J.; Allamargot, C.; Gao, Z.; Luczak, E.D.; Hall, D.D.; Fink, B.D.; Chen, B.; et al. CaMKII determines mitochondrial stress responses in heart. Nature 2012, 491, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.J.; Joiner, M.L.; Singh, M.V.; Luczak, E.D.; Swaminathan, P.D.; Koval, O.M.; Kutschke, W.; Allamargot, C.; Yang, J.; Guan, X.; et al. Oxidation of CaMKII determines the cardiotoxic effects of aldosterone. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Khoo, M.S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Grueter, C.E.; Ni, G.; Price, E.E., Jr.; Thiel, W.; Guatimosim, S.; Song, L.S.; et al. Calmodulin kinase II inhibition protects against structural heart disease. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oort, R.J.; McCauley, M.D.; Dixit, S.S.; Pereira, L.; Yang, Y.; Respress, J.L.; Wang, Q.; De Almeida, A.C.; Skapura, D.G.; Anderson, M.E.; et al. Ryanodine receptor phosphorylation by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II promotes life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias in mice with heart failure. Circulation 2010, 122, 2669–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesubi, O.O.; Anderson, M.E. Atrial remodelling in atrial fibrillation: CaMKII as a nodal proarrhythmic signal. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 109, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sossalla, S.; Fluschnik, N.; Schotola, H.; Ort, K.R.; Neef, S.; Schulte, T.; Wittkopper, K.; Renner, A.; Schmitto, J.D.; Gummert, J.; et al. Inhibition of elevated Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II improves contractility in human failing myocardium. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, M.S.; Li, J.; Singh, M.V.; Yang, Y.; Kannankeril, P.; Wu, Y.; Grueter, C.E.; Guan, X.; Oddis, C.V.; Zhang, R.; et al. Death, cardiac dysfunction, and arrhythmias are increased by calmodulin kinase II in calcineurin cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2006, 114, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backs, J.; Backs, T.; Neef, S.; Kreusser, M.M.; Lehmann, L.H.; Patrick, D.M.; Grueter, C.E.; Qi, X.; Richardson, J.A.; Hill, J.A.; et al. The delta isoform of CaM kinase II is required for pathological cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling after pressure overload. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2342–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes Gaido, O.E.; Nkashama, L.J.; Schole, K.L.; Wang, Q.; Umapathi, P.; Mesubi, O.O.; Konstantinidis, K.; Luczak, E.D.; Anderson, M.E. CaMKII as a Therapeutic Target in Cardiovascular Disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Anderson, M.E. CaMKII is a nodal signal for multiple programmed cell death pathways in heart. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2017, 103, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczak, E.D.; Wu, Y.; Granger, J.M.; Joiner, M.A.; Wilson, N.R.; Gupta, A.; Umapathi, P.; Murphy, K.R.; Reyes Gaido, O.E.; Sabet, A.; et al. Mitochondrial CaMKII causes adverse metabolic reprogramming and dilated cardiomyopathy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenma, T.; Mitsuyama, H.; Watanabe, M.; Kakutani, N.; Otsuka, Y.; Mizukami, K.; Kamada, R.; Takahashi, M.; Takada, S.; Sabe, H.; et al. Small-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel activation deteriorates hypoxic ventricular arrhythmias via CaMKII in cardiac hypertrophy. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H262–H272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Hao, J.; Zeng, M.; Song, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, P.; Luo, A.; Cao, Z.; Belardinelli, L.; Ma, J. Modulation of late sodium current by Ca(2+) -calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, protein kinase C and Ca(2+) during hypoxia in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Exp. Physiol. 2017, 102, 818–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelouch, V.; Kolar, F.; Ost’adal, B.; Milerova, M.; Cihak, R.; Widimsky, J. Regression of chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension, right ventricular hypertrophy, and fibrosis: Effect of enalapril. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 1997, 11, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.S.; Lin, F.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, Y.K.; Higa, S.; Chen, S.A.; Chen, Y.J. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Activation Reduces Pulmonary Vein Arrhythmogenesis and Regulates Calcium Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Huang, D.D.; Li, D.G.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.M.; Yuan, C.L.; Huang, H.H. Tetramethylpyrazine exerts a protective effect against injury from acute myocardial ischemia by regulating the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathway. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wu, G.; Tang, S. The effects of tetramethylpyrazine on the incidence of arrhythmias and the release of PGI2 and TXA2 in the ischemic rat heart. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Shao, H.T.; Ge, W.P.; Liu, N.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C.M.; Qin, C.; Zhang, L.F. Ginsenoside-Rb1 and tetramethylpyrazine phosphate act synergistically to prevent dilated cardiomyopathy in cTnTR141W transgenic mice. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2012, 59, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, K.; Tan, X.; Wu, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhou, F.; Zhu, L. Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Retinal Capillary Endothelial Cells (TR-iBRB2) against IL-1beta-Induced Nitrative/Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21775–21790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Xu, S.; Yao, K. Tetramethylpyrazine: A review on its mechanisms and functions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 113005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sng, K.S.; Shu, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Yao, M.; Cui, X.J. Effects of tetramethylpyrazine treatment in a rat model of spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 945, 175524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, R.S.; Reeves, J.T. Adrenergic contribution during acclimatization to high altitude: Perspectives from Pikes Peak. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2003, 31, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghi, S.; Furmanik, M.; Jaminon, A.; Veltrop, R.; Rapp, N.; Wichapong, K.; Bidar, E.; Buschini, A.; Schurgers, L.J. Calcium Signalling in Heart and Vessels: Role of Calmodulin and Downstream Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.K.; Shan, J.J.; Chiu, K.W. Tetramethylpyrazine, a calcium antagonist. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.C.; Lai, T.Y.; Huang, W.C.; Yang, T.; Liu, I.M.; Wong, K.L.; Chan, P.; Cheng, J.T. Tetramethylpyrazine as potassium channel opener to lower calcium influx into cultured aortic smooth muscle cells. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 557–558. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, P.; Luo, A.; Zhang, S.; Kong, L.; Qian, C. The effect of ligustrazine on L-type calcium current, calcium transient and contractility in rabbit ventricular myocytes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 144, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picca, A.; Mankowski, R.T.; Burman, J.L.; Donisi, L.; Kim, J.S.; Marzetti, E.; Leeuwenburgh, C. Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms as molecular targets in cardiac ageing. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouette-Gaulain, K.; Malgat, M.; Rocher, C.; Savineau, J.P.; Marthan, R.; Mazat, J.P.; Sztark, F. Time course of differential mitochondrial energy metabolism adaptation to chronic hypoxia in right and left ventricles. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 66, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mallet, R.T.; Burtscher, J.; Pialoux, V.; Pasha, Q.; Ahmad, Y.; Millet, G.P.; Burtscher, M. Molecular Mechanisms of High-Altitude Acclimatization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luczak, E.D.; Anderson, M.E. CaMKII oxidative activation and the pathogenesis of cardiac disease. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2014, 73, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, J.; Habbout, K.; Shimauchi, T.; Wu, W.H.; Breuils-Bonnet, S.; Tremblay, E.; Martineau, S.; Nadeau, V.; Gagnon, K.; Mazoyer, F.; et al. Identification of Long Noncoding RNA H19 as a New Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Right Ventricular Failure in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circulation 2020, 142, 1464–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Deng, H.; Lan, X.; Shen, P.; Bai, Z.; Huangfu, C.; Wang, N.; Xiao, C.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Against Chronic Hypobaric Hypoxia-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Inhibiting CaMKII Activation in a Mouse Model Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010054
Zhang P, Deng H, Lan X, Shen P, Bai Z, Huangfu C, Wang N, Xiao C, Gao Y, Sun Y, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Against Chronic Hypobaric Hypoxia-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Inhibiting CaMKII Activation in a Mouse Model Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Pengfei, Huifang Deng, Xiong Lan, Pan Shen, Zhijie Bai, Chaoji Huangfu, Ningning Wang, Chengrong Xiao, Yehui Gao, Yue Sun, and et al. 2025. "Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Against Chronic Hypobaric Hypoxia-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Inhibiting CaMKII Activation in a Mouse Model Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010054
APA StyleZhang, P., Deng, H., Lan, X., Shen, P., Bai, Z., Huangfu, C., Wang, N., Xiao, C., Gao, Y., Sun, Y., Li, J., Guo, J., Zhou, W., & Gao, Y. (2025). Tetramethylpyrazine Protects Against Chronic Hypobaric Hypoxia-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Inhibiting CaMKII Activation in a Mouse Model Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26010054




